无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (8): 911-920.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250014 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250014
收稿日期:2025-01-09
修回日期:2025-02-19
出版日期:2025-08-20
网络出版日期:2025-03-25
通讯作者:
徐 合, 教授. E-mail: xuhe@shnu.edu.cn;作者简介:王宇彤(2001-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 1000566516@smail.shnu.edu.cn
基金资助:
WANG Yutong1( ), CHANG Jiang2, XU He1(
), CHANG Jiang2, XU He1( ), WU Chengtie2(
), WU Chengtie2( )
)
Received:2025-01-09
Revised:2025-02-19
Published:2025-08-20
Online:2025-03-25
Contact:
XU He, professor. E-mail: xuhe@shnu.edu.cn;About author:WANG Yutong (2001-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 1000566516@smail.shnu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
大面积皮肤创伤是全球公共卫生最具挑战性的问题之一, 其修复与治疗给医疗保健系统造成了巨大的经济负担, 亟需开发能够促进创面皮肤组织再生的高效伤口敷料。近年来, 硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃因具备促进血管再生、刺激细胞胶原蛋白沉积以及抗感染等多重优势, 在创面修复领域得到了广泛的关注与应用。本文简要概述了硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃在皮肤再生过程中的作用机制, 介绍了硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃材料和一些新技术的结合方法及其在创面修复领域的相关应用, 最后总结了硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃的优势与局限性, 为硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃材料在创面修复领域的临床应用提供参考。
中图分类号:
王宇彤, 常江, 徐合, 吴成铁. 硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃促创面修复的研究进展:作用、机制和应用方式[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 911-920.
WANG Yutong, CHANG Jiang, XU He, WU Chengtie. Advances in Silicate Bioceramic/Bioglass for Wound Healing: Effects, Mechanisms and Application Ways[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 911-920.
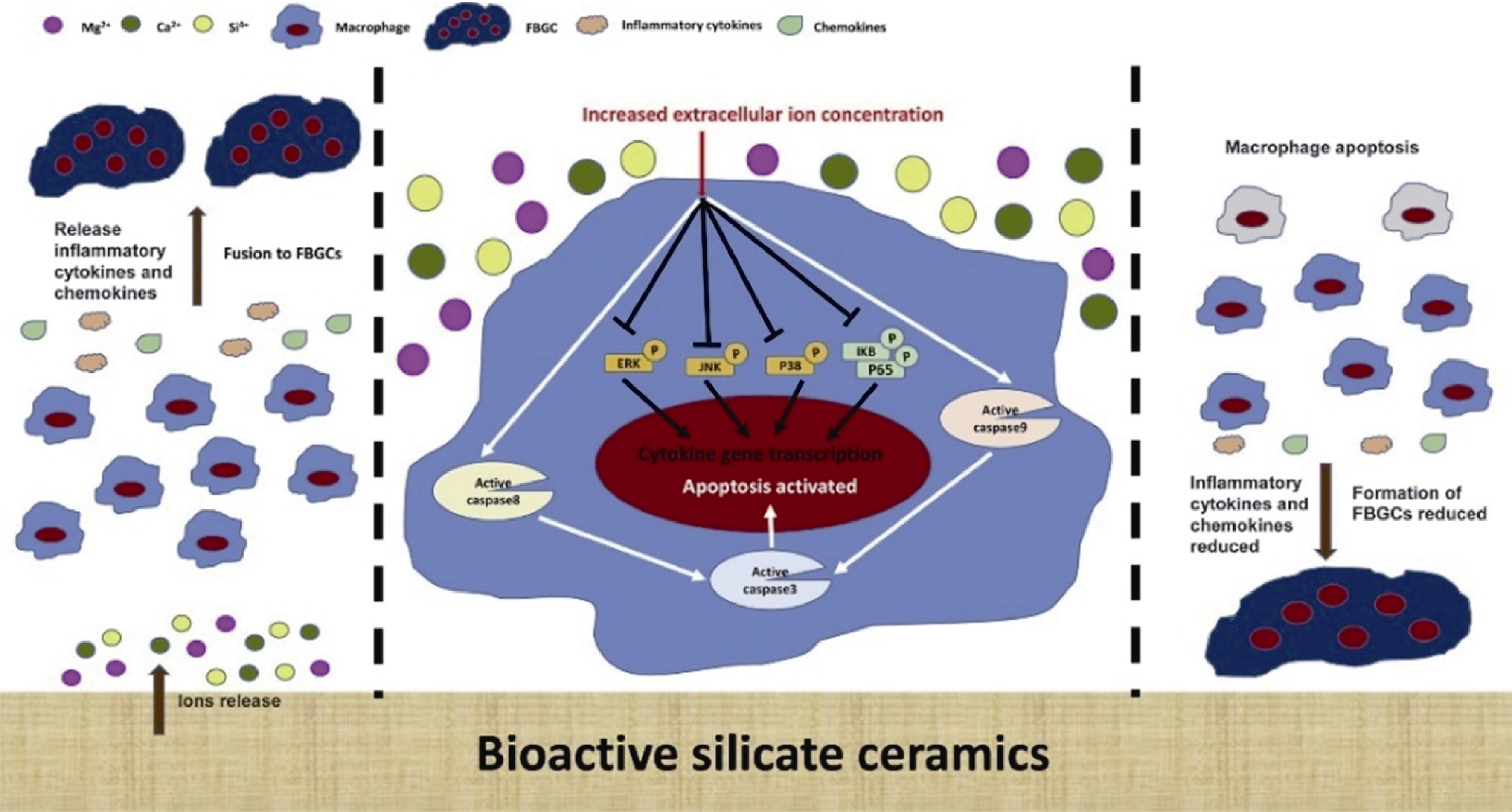
图2 生物活性硅酸盐陶瓷调控巨噬细胞炎症反应的机制示意图[27]
Fig. 2 Schematic illustration of the probable regulatory mechanism to macrophage inflammation responses by bioactive silicate ceramics[27] (Reprinted with permission; Copyright (2018) Elsevier Ltd.)
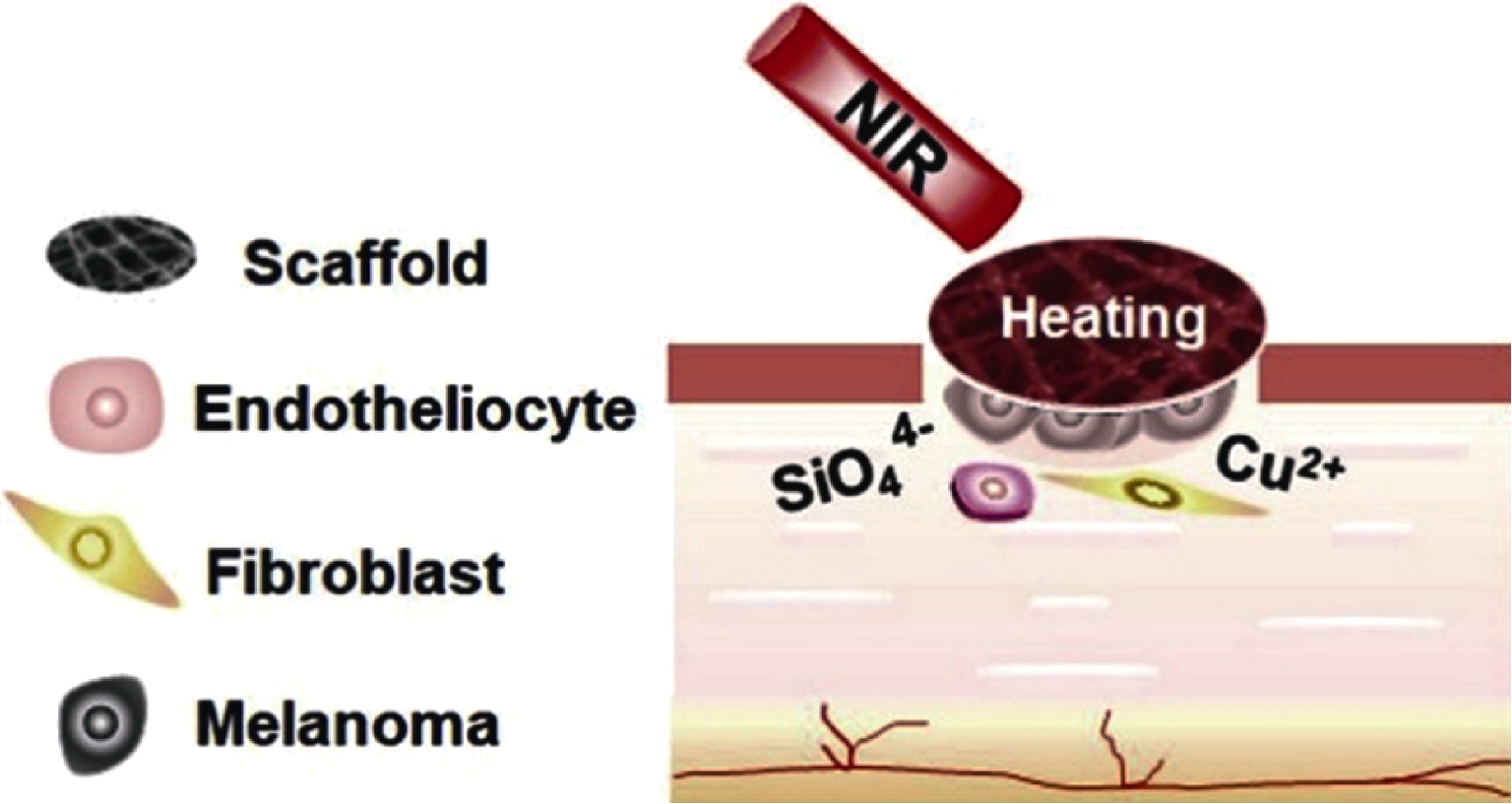
图3 表面修饰CaCuSi4O10的纤维支架用于早期的光热疗法和后期的皮肤组织重建[39]
Fig. 3 Fiber scaffolds with surface modification of CaCuSi4O10 for early photothermal therapy and subsequent skin tissue reconstruction[39] (Reprinted with permission; Copyright (2019) Elsevier Ltd.)
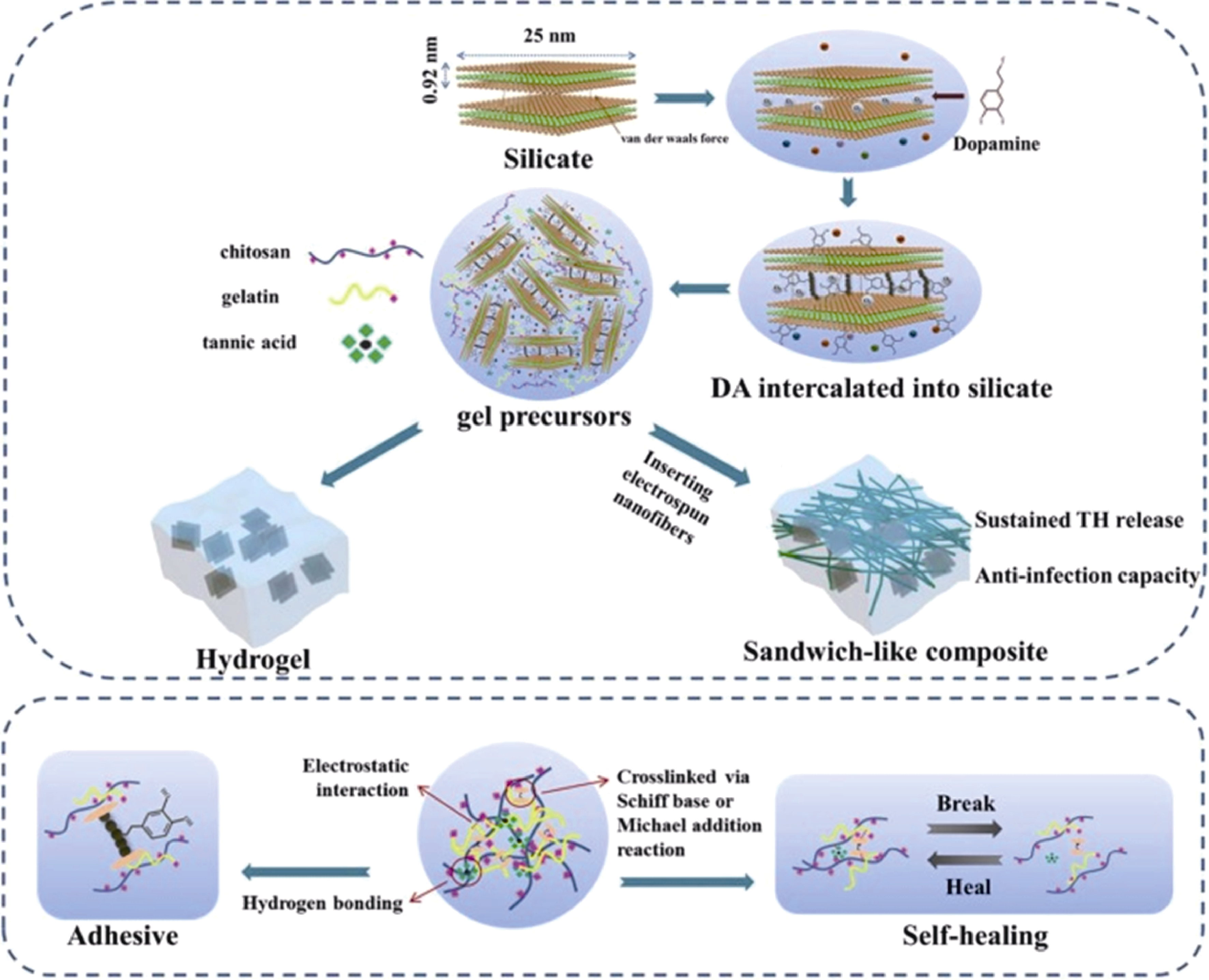
图4 多功能夹层状NF-HG的设计策略[62]
Fig. 4 Design strategy for fabrication of multifunctional sandwich-like NF-HG[62] DA: dopamine; TH: tetracycline hydrochloride; NF-HG: nanofibers/hydrogel (Reprinted with permission; Copyright (2020) Elsevier Ltd.)
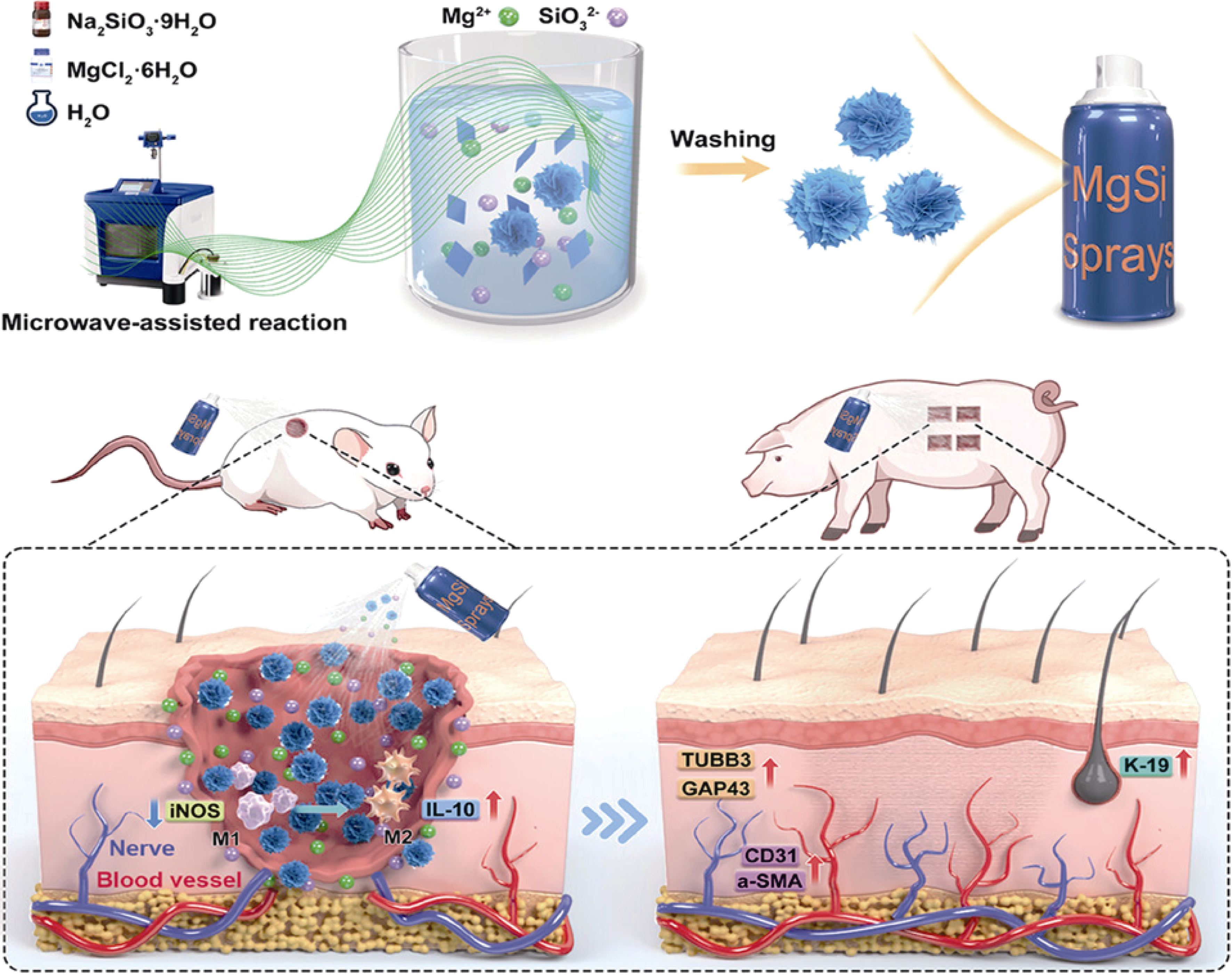
图5 镁硅酸盐喷雾剂的制备及其对烧伤创面修复和附属器官再生的作用机制[66]
Fig. 5 Preparation and mechanism of magnesium silicate sprays for burn-wound repair and appendage regeneration[66] TUBB3: Tubulin beta-3; GAP43: Growth-associated protein 43; α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin (Reprinted with permission; Copyright (2023) Elsevier Ltd.)
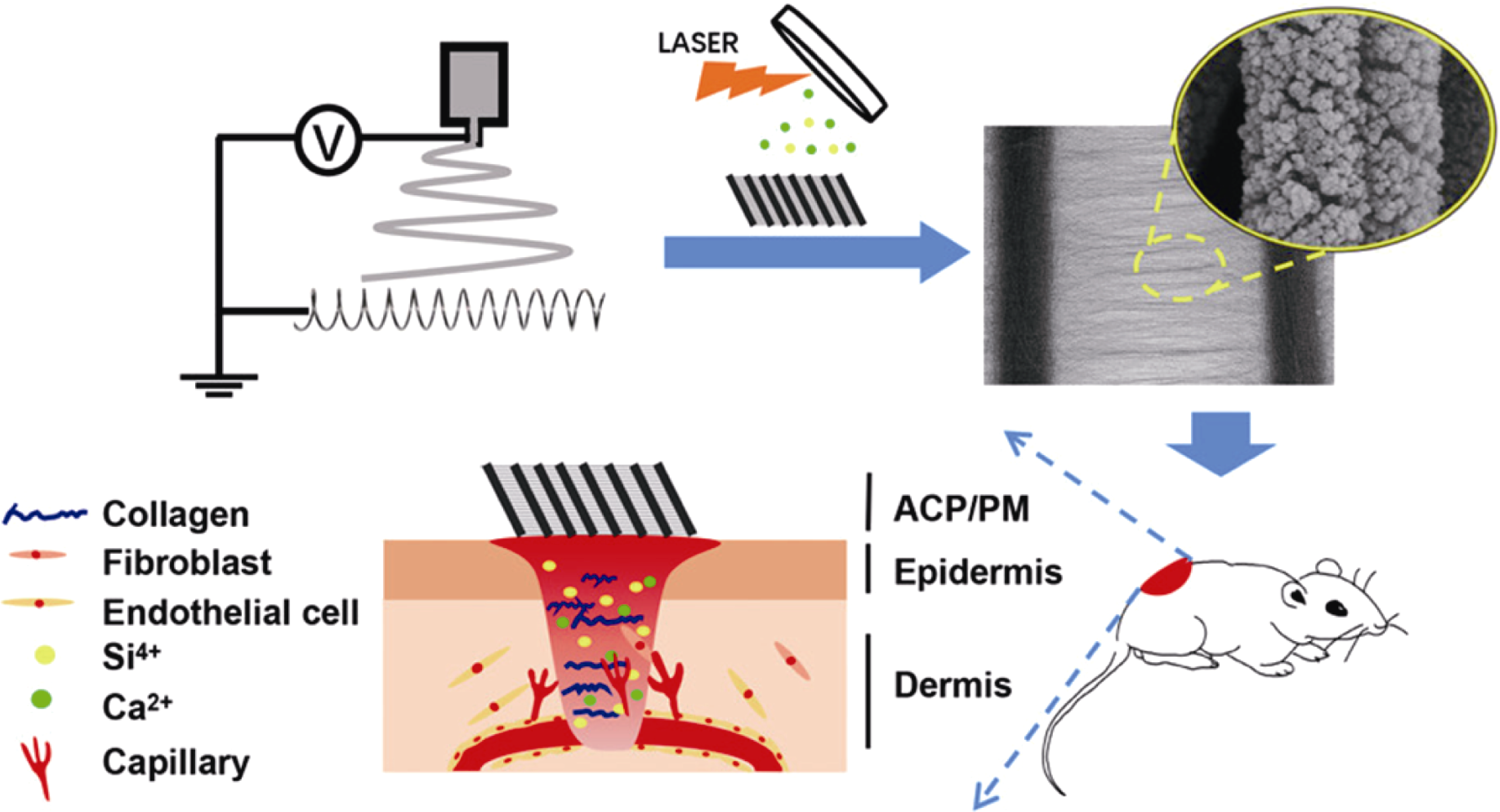
图6 硅酸盐复合静电纺丝支架示意图[69]
Fig. 6 Schematic illustration of silicate composite electrospun scaffolds[69] (Reprinted with permission; Copyright (2019) American Chemical Society)
| [1] | SANJARNIA P, PICCHIO M L, POLEGRE SOLIS A N, et al. Bringing innovative wound care polymer materials to the market: challenges, developments, and new trends. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2024, 207: 115217. |
| [2] | RAZIYEVA K, KIM Y, ZHARKINBEKOV Z, et al. Immunology of acute and chronic wound healing. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(5): 700. |
| [3] |
SEN C K. Human wounds and its burden: an updated compendium of estimates. Advances in Wound Care, 2019, 8(2): 39.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | WU M, GAO B B, WEI X B. Recent advances in Raman spectroscopy for skin diagnosis. Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences, 2023, 16(3): 2330003. |
| [5] |
SHANG F, LU Y H, GAO J, et al. Comparison of therapeutic effects between artificial dermis combined with autologous split-thickness skin grafting and autologous intermediate-thickness skin grafting alone in severely burned patients: a prospective randomised study. International Wound Journal, 2021, 18(1): 24.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | FAN C, XU Q, HAO R Q, et al. Multi-functional wound dressings based on silicate bioactive materials. Biomaterials, 2022, 287: 121652. |
| [7] | WANG L L, ZHAO R, LI J Y, et al. Pharmacological activation of cannabinoid 2 receptor attenuates inflammation, fibrogenesis, and promotes re-epithelialization during skin wound healing. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2016, 786: 128. |
| [8] |
YU Q Q, CHANG J, WU C T. Silicate bioceramics: from soft tissue regeneration to tumor therapy. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2019, 7(36): 5449.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
LI H Y, CHANG J. Stimulation of proangiogenesis by calcium silicate bioactive ceramic. Acta Biomaterialia, 2013, 9(2): 5379.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | LI H, CHANG J. Bioactive silicate materials stimulate angiogenesis in fibroblast and endothelial cell co-culture system through paracrine effect. Acta Biomaterialia, 2013, 9(6): 6981. |
| [11] |
ZHAI W Y, LU H X, CHEN L, et al. Silicate bioceramics induce angiogenesis during bone regeneration. Acta Biomaterialia, 2012, 8(1): 341.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | LI B M, HU W Z, MA K, et al. Are hair follicle stem cells promising candidates for wound healing. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 2019, 19(2): 119. |
| [13] | WU Y K, CHENG N C, CHENG C M. Biofilms in chronic wounds: pathogenesis and diagnosis. Trends in Biotechnology, 2019, 37(5): 505. |
| [14] |
LAXMINARAYAN R, SRIDHAR D, BLASER M, et al. Achieving global targets for antimicrobial resistance. Science, 2016, 353(6302): 874.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | HU S, CHANG J, LIU M Q, et al. Study on antibacterial effect of 45S5 Bioglass®. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 2009, 20: 281. |
| [16] | ZHANG E L, WANG X Y, CHEN M, et al. Effect of the existing form of Cu element on the mechanical properties, bio-corrosion and antibacterial properties of Ti-Cu alloys for biomedical application. Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications, 2016, 69: 1210. |
| [17] | REWAK-SOROCZYNSKA J, DOROTKIEWICZ-JACH A, DRULIS-KAWA Z, et al. Culture media composition influences the antibacterial effect of silver, cupric, and zinc ions against pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biomolecules, 2022, 12(7): 963. |
| [18] | RAUF A, YE J W, ZHANG S Q, et al. Copper(II)-based coordination polymer nanofibers as a highly effective antibacterial material with a synergistic mechanism. Dalton Transactions, 2019, 48(48): 17810. |
| [19] |
YANG T T, WANG D H, LIU X Y. Antibacterial activity of an NIR-induced Zn ion release film. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2020, 8(3): 406.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | KERAYECHIAN N, MARDANY A, BAHRAINI F, et al. Evaluation of the antibacterial effects of the various nanoparticles coated orthodontic brackets: a systematic review and meta-analysis br. Medicina Balear, 2023, 38(3): 107. |
| [21] |
LI J Y, ZHAI D, LV F, et al. Preparation of copper-containing bioactive glass/eggshell membrane nanocomposites for improving angiogenesis, antibacterial activity and wound healing. Acta Biomaterialia, 2016, 36: 254.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | LI Y H, HAN Y, WANG X Y, et al. Multifunctional hydrogels prepared by dual ion cross-linking for chronic wound healing. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(19): 16054. |
| [23] |
JOHNSON A P, SABU C, NIVITHA K P, et al. Bioinspired and biomimetic micro- and nanostructures in biomedicine. Journal of Controlled Release, 2022, 343: 724.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
WANG B, ZHAO J Y, LU W X, et al. The preparation of lactoferrin/magnesium silicate lithium injectable hydrogel and application in promoting wound healing. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2022, 220: 1501.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | GRANEY P L, BEN-SHAUL S, LANDAU S, et al. Macrophages of diverse phenotypes drive vascularization of engineered tissues. Science Advances, 2020, 6(18): eaay6391. |
| [26] | XU P, XING M, HUANG H Z, et al. Calcium silicate-human serum albumin composite hydrogel decreases random pattern skin flap necrosis by attenuating vascular endothelial cell apoptosis and inflammation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 423: 130285. |
| [27] |
HUANG Y, WU C T, ZHANG X L, et al. Regulation of immune response by bioactive ions released from silicate bioceramics for bone regeneration. Acta Biomaterialia, 2018, 66: 81.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | WANG H N, YU H Q, ZHOU X, et al. An overview of extracellular matrix-based bioinks for 3D bioprinting. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022, 10: 905438. |
| [29] | GARDEAZABAL L, IZETA A. Elastin and collagen fibres in cutaneous wound healing. Experimental Dermatology, 2024, 33(3): e15052. |
| [30] | CAO Z, WANG X Y, JIANG C Q, et al. Thermo-sensitive hydroxybutyl chitosan/diatom biosilica hydrogel with immune microenvironment regulatory for chronic wound healing. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 262: 130189. |
| [31] |
QUE Y M, ZHANG Z W B, ZHANG Y X, et al. Silicate ions as soluble form of bioactive ceramics alleviate aortic aneurysm and dissection. Bioactive Materials, 2023, 25: 716.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | REFFITT D M, OGSTON N, JUGDAOHSINGH R, et al. Orthosilicic acid stimulates collagen type 1 synthesis and osteoblastic differentiation in human osteoblast-like cells in vitro. Bone, 2003, 32(2): 127. |
| [33] |
LV F, WANG J, XU P, et al. A conducive bioceramic/polymer composite biomaterial for diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomaterialia, 2017, 60: 128.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | LIN F S, LEE J J, LEE A K X, et al. Calcium silicate-activated gelatin methacrylate hydrogel for accelerating human dermal fibroblast proliferation and differentiation. Polymers, 2021, 13(1): 70. |
| [35] |
NOSRATI H, KHOUY R A, NOSRATI A, et al. Nanocomposite scaffolds for accelerating chronic wound healing by enhancing angiogenesis. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2021, 19(1): 1.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
DASHNYAM K, JIN G Z, KIM J H, et al. Promoting angiogenesis with mesoporous microcarriers through a synergistic action of delivered silicon ion and VEGF. Biomaterials, 2017, 116: 145.
DOI PMID |
| [37] | YU J, XU Y Z, ZHANG Z W B, et al. Strontium zinc silicate bioceramic composite electrospun fiber membrane for hair follicle regeneration in burn wounds. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2023, 266: 110953. |
| [38] |
LIU Y Q, LI T, MA H S, et al. 3D-printed scaffolds with bioactive elements-induced photothermal effect for bone tumor therapy. Acta Biomaterialia, 2018, 73: 531.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
YU Q Q, HAN Y M, TIAN T, et al. Chinese sesame stick-inspired nano-fibrous scaffolds for tumor therapy and skin tissue reconstruction. Biomaterials, 2019, 194: 25.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | MEHRABI T, MESGAR A S, MOHAMMADI Z. Bioactive glasses: a promising therapeutic ion release strategy for enhancing wound healing. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2020, 6(10): 5399. |
| [41] | SHAO H J, WU X, DENG J J, et al. Application and progress of inorganic composites in haemostasis: a review. Journal of Materials Science, 2024, 59(17): 7169. |
| [42] | LIU C Y, CUI X, DU Y B, et al. Unusual surface coagulation activation patterns of crystalline and amorphous silicate-based biominerals. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2023, 12(20): 2300039. |
| [43] | ZHENG C Y, LIU J X, BAI Q, et al. Preparation and hemostatic mechanism of bioactive glass-based membrane-like structure camouflage composite particles. Materials & Design, 2022, 223: 111116. |
| [44] |
WANG Y D, LUO M, LI T, et al. Multi-layer-structured bioactive glass nanopowder for multistage-stimulated hemostasis and wound repair. Bioactive Materials, 2023, 25: 319.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
GUO B L, DONG R N, LIANG Y P, et al. Haemostatic materials for wound healing applications. Nature Reviews Chemistry, 2021, 5(11): 773.
DOI PMID |
| [46] | MATAI I, KAUR G, SEYEDSALEHI A, et al. Progress in 3D bioprinting technology for tissue/organ regenerative engineering. Biomaterials, 2020, 226: 119536. |
| [47] | YAN W C, DAVOODI P, VIJAYAVENKATARAMAN S, et al. 3D bioprinting of skin tissue: from pre-processing to final product evaluation. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2018, 132: 270. |
| [48] | MA J G, QIN C, WU J F, et al. 3D printing of strontium silicate microcylinder-containing multicellular biomaterial inks for vascularized skin regeneration. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2021, 10(16): 2100523. |
| [49] | ZHOU F F, HONG Y, LIANG R J, et al. Rapid printing of bio-inspired 3D tissue constructs for skin regeneration. Biomaterials, 2020, 258: 120287. |
| [50] |
MA H S, FENG C, CHANG J, et al. 3D-printed bioceramic scaffolds: from bone tissue engineering to tumor therapy. Acta Biomaterialia, 2018, 79: 37.
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
MA J G, QIN C, WU J F, et al. 3D multicellular micropatterning biomaterials for hair regeneration and vascularization. Materials Horizons, 2023, 10(9): 3773.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
XU H, LV F, ZHANG Y L, et al. Hierarchically micro-patterned nanofibrous scaffolds with a nanosized bio-glass surface for accelerating wound healing. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(44): 18446.
DOI PMID |
| [53] | ZHANG J P, ZENG Z, CHEN Y X, et al. 3D-printed GelMA/CaSiO3 composite hydrogel scaffold for vascularized adipose tissue restoration. Regenerative Biomaterials, 2023, 10: rbad049. |
| [54] | ZHOU Y L, GAO L, PENG J L, et al. Bioglass activated albumin hydrogels for wound healing. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2018, 7(16): 1800144. |
| [55] |
MA W P, ZHENG Y, YANG G Z, et al. A bioactive calcium silicate nanowire-containing hydrogel for organoid formation and functionalization. Materials Horizons, 2024, 11(12): 2957.
DOI PMID |
| [56] | TEHRANY P M, RAHMANIAN P, REZAEE A, et al. Multifunctional and theranostic hydrogels for wound healing acceleration: an emphasis on diabetic-related chronic wounds. Environmental Research, 2023, 238: 117087. |
| [57] | BAI Q, TENG L, ZHANG X L, et al. Multifunctional single-component polypeptide hydrogels: the gelation mechanism, superior biocompatibility, high performance hemostasis, and scarless wound healing. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2022, 11(6): 2101809. |
| [58] |
ZENG Q Y, HAN Y, LI H Y, et al. Design of a thermosensitive bioglass/agarose-alginate composite hydrogel for chronic wound healing. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2015, 3(45): 8856.
DOI PMID |
| [59] | HAN Y, LI Y H, ZENG Q Y, et al. Injectable bioactive akermanite/alginate composite hydrogels for in situ skin tissue engineering. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2017, 5(18): 3315. |
| [60] |
MA H S, ZHOU Q, CHANG J, et al. Grape seed-inspired smart hydrogel scaffolds for melanoma therapy and wound healing. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(4): 4302.
DOI PMID |
| [61] | ZARACA F, VACCARILI M, ZACCAGNA G, et al. Can a standardised ventilation mechanical test for quantitative intraoperative air leak grading reduce the length of hospital stay after video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery lobectomy. Journal of Visualized Surgery, 2017, 3(12): 179. |
| [62] | CHEN Y J, QIU Y Y, WANG Q Q, et al. Mussel-inspired sandwich-like nanofibers/hydrogel composite with super adhesive, sustained drug release and anti-infection capacity. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 399: 125668. |
| [63] | PLEGUEZUELOS-BELTRÁN P, GÁLVEZ-MARTÍN P, NIETO- GARCÍA D, et al. Advances in spray products for skin regeneration. Bioactive Materials, 2022, 16: 187. |
| [64] | MA W P, MA H S, QIU P F, et al. Sprayable β-FeSi2 composite hydrogel for portable skin tumor treatment and wound healing. Biomaterials, 2021, 279: 121225. |
| [65] |
DONG X, CHANG J, LI H Y. Bioglass promotes wound healing through modulating the paracrine effects between macrophages and repairing cells. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2017, 5(26): 5240.
DOI PMID |
| [66] | XU S X, ZHANG Y T, DAI B Y, et al. Green-prepared magnesium silicate sprays enhance the repair of burn-skin wound and appendages regeneration in rats and minipigs. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(9): 2307439. |
| [67] | JOHN J V, MCCARTHY A, KARAN A, et al. Electrospun nanofibers for wound management. Chemnanomat, 2022, 8(7): e202100349. |
| [68] |
BAO F, CHANG J. Calcium silicate nanowires based composite electrospun scaffolds: preparation, ion release and cytocompatibility. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1199.
DOI |
| [69] |
JIANG Y Q, HAN Y M, WANG J, et al. Space-oriented nanofibrous scaffold with silicon-doped amorphous calcium phosphate nanocoating for diabetic wound healing. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2019, 2(2): 787.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 余升阳, 苏海军, 姜浩, 余明辉, 姚佳彤, 杨培鑫. 激光增材制造超高温氧化物陶瓷孔隙缺陷形成及抑制研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [2] | 刘江平, 管鑫, 唐振杰, 朱文杰, 罗永明. 含氮挥发性有机化合物催化氧化的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [3] | 肖晓琳, 王玉祥, 谷佩洋, 朱圳荣, 孙勇. 二维无机材料调控病损皮肤组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [4] | 马景阁, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料用于毛囊和毛发再生的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [5] | 张洪健, 赵梓壹, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料调控神经细胞功能及神经化组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [6] | 艾敏慧, 雷波. 微纳米生物活性玻璃: 功能化设计与血管化皮肤再生[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [7] | 马文平, 韩雅卉, 吴成铁, 吕宏旭. 无机活性材料在类器官研究领域的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [8] | 罗晓民, 乔志龙, 刘颍, 杨晨, 常江. 无机生物活性材料调控心肌再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [9] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [10] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [11] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [12] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [13] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [14] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [15] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||