无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 337-347.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240431 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240431
所属专题: 【生物材料】骨骼与齿类组织修复(202506)
• 综述 • 下一篇
田睿智1,2( ), 兰正义1, 殷杰1,2, 郝南京3, 陈航榕1,2, 马明1,2(
), 兰正义1, 殷杰1,2, 郝南京3, 陈航榕1,2, 马明1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-12
修回日期:2024-11-05
出版日期:2025-04-20
网络出版日期:2024-11-25
通讯作者:
马 明, 研究员. E-mail: mma@mail.sic.ac.cn作者简介:田睿智(2001-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: tianruizhi23@mails.ucas.ac.cn
基金资助:
TIAN Ruizhi1,2( ), LAN Zhengyi1, YIN Jie1,2, HAO Nanjing3, CHEN Hangrong1,2, MA Ming1,2(
), LAN Zhengyi1, YIN Jie1,2, HAO Nanjing3, CHEN Hangrong1,2, MA Ming1,2( )
)
Received:2024-10-12
Revised:2024-11-05
Published:2025-04-20
Online:2024-11-25
Contact:
MA Ming, professor. E-mail: mma@mail.sic.ac.cnAbout author:TIAN Ruizhi (2001-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: tianruizhi23@mails.ucas.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
无机纳米颗粒在生物医学领域展现出广阔的应用和发展前景, 其生物医学功能和理化性质受到颗粒尺寸和形貌的显著影响。但对于传统的间歇式合成方法, 无机纳米颗粒批次间的高度可重复性合成仍存在较大挑战。相比之下, 微流控技术为无机纳米颗粒的高度可控性和可重复性合成提供了一种先进方法。同时, 微流控技术能够实现快速传质和传热, 并且具有反应体积小、能耗低等优势, 使其成为纳米无机生物材料合成的理想途径。本文对微流控技术在纳米无机生物材料制备领域中的研究和应用进展进行了综述。首先概述了微流控装置中的流体特征和混合机制; 接着进一步介绍了5种经典的微流控装置的微通道结构特征和相应的流体混合特点, 并系统总结了不同类型微流控装置在无机纳米颗粒合成和表面改性中的应用; 最后简要描述了微流控技术在纳米无机生物材料的合成和应用中所面临的挑战以及未来发展的潜在机遇。
中图分类号:
田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347.
TIAN Ruizhi, LAN Zhengyi, YIN Jie, HAO Nanjing, CHEN Hangrong, MA Ming. Microfluidic Technology Based Synthesis of Inorganic Nano-biomaterials: Principles and Progress[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 337-347.
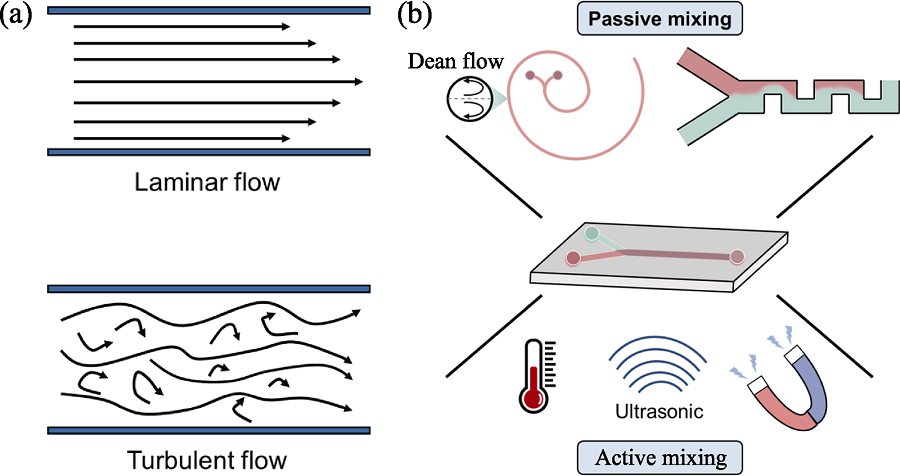
图1 微流控装置中的流体状态及流体混合策略
Fig. 1 Flow patterns and fluid mixing strategies in microfluidic devices (a) Diagram of laminar flow and turbulent flow in a microchannel; (b) Schematic diagram of active and passive mixing strategies in microfluidic device
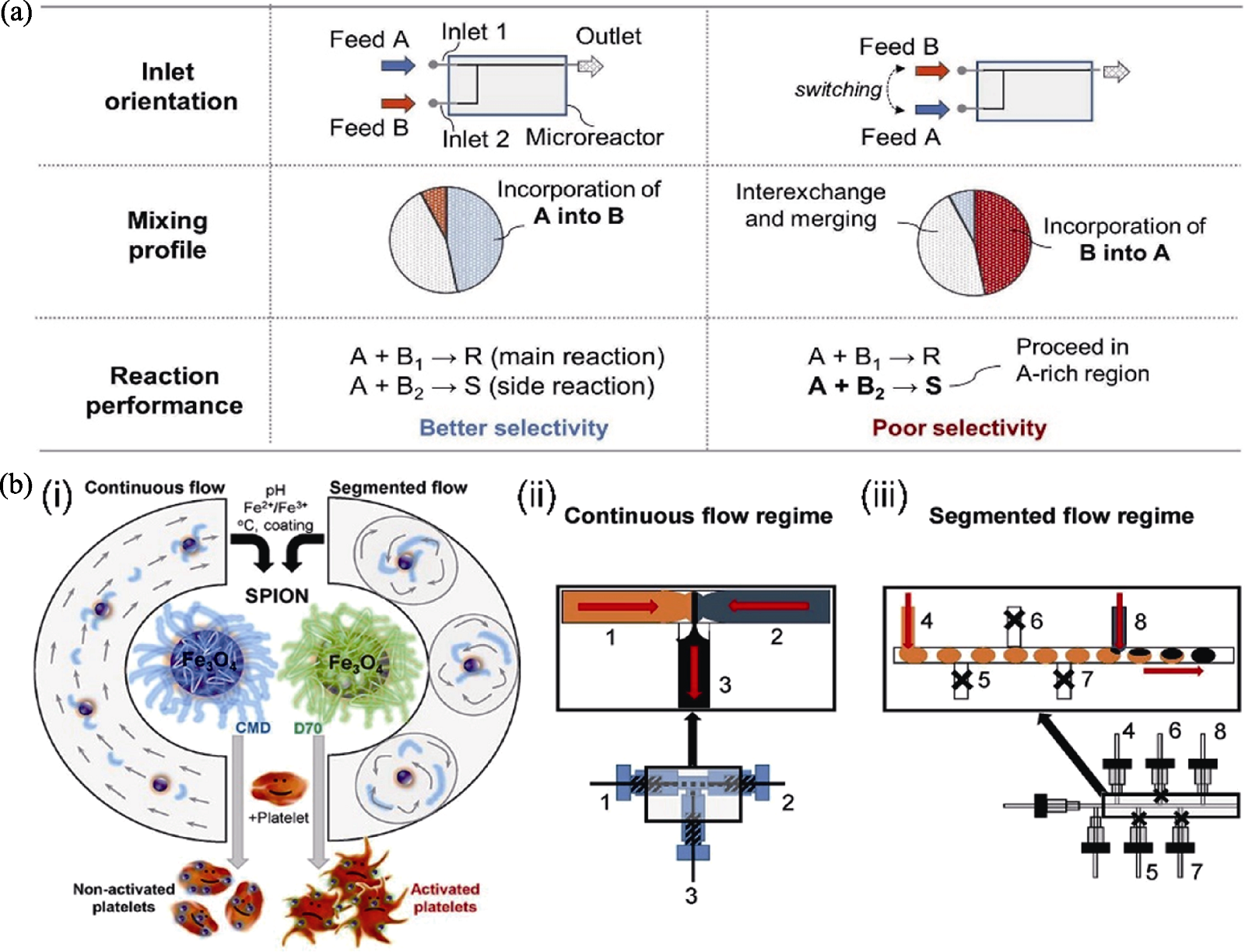
图2 T形微流控装置中的流体混合及其在无机纳米生物材料制备中的应用[25,35]
Fig. 2 Fluid mixing in T-shaped microfluidic device and its application in synthesis of inorganic nano-biomaterials[25,35] (a) Influence of inlet orientation on the mixing profile and reaction selectivity[25]; (b) Schematic diagrams of SPION synthesis and labeling of human platelets (i), continuous flow (ii), and segmented flow (iii) used in the synthesis of SPION[35]
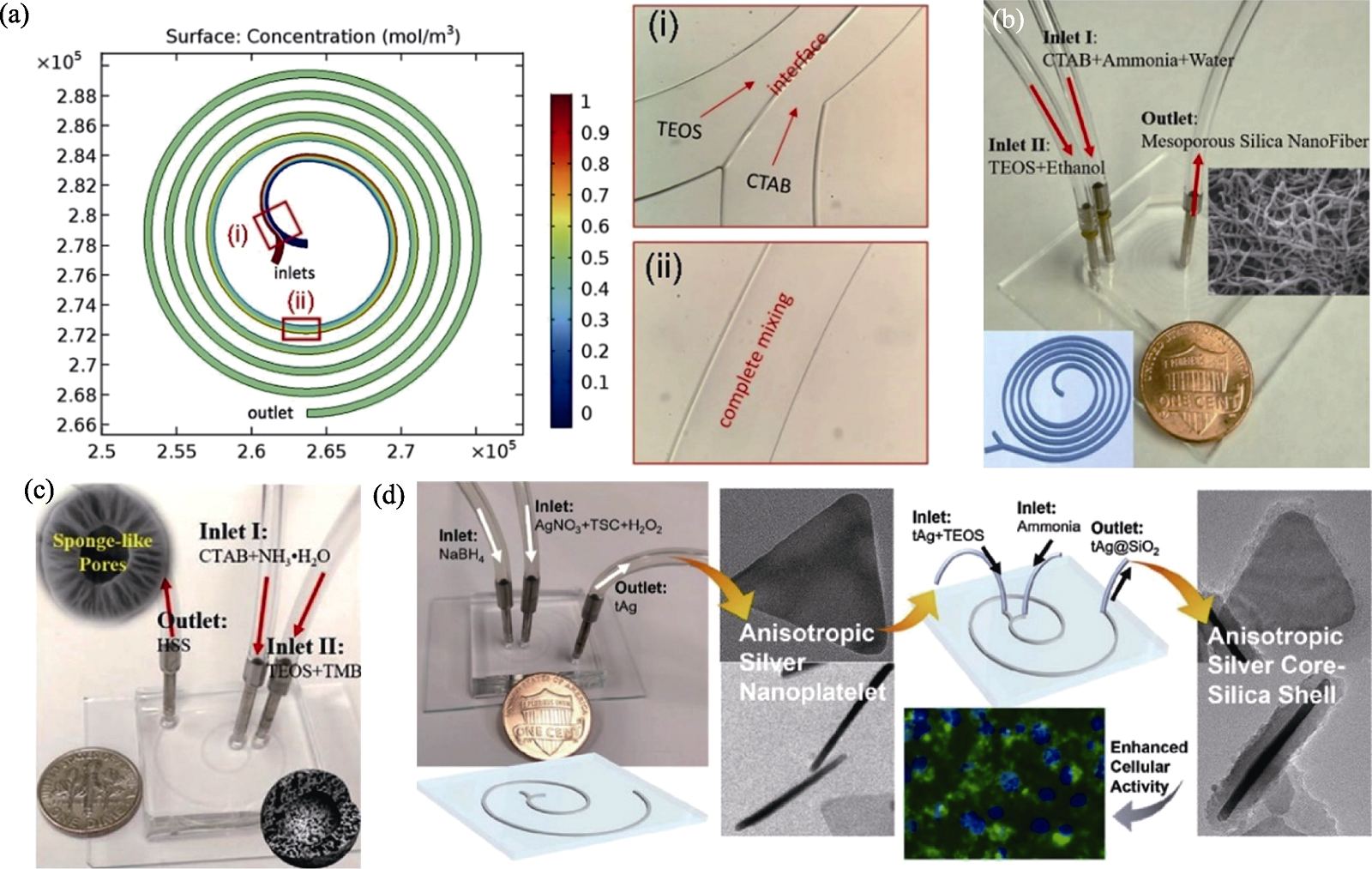
图3 平面螺旋微流控装置在无机纳米生物材料制备中的应用[42⇓⇓-45]
Fig. 3 Application of planar spiral microfluidic devices in the preparation of inorganic nano-biomaterials[42⇓⇓-45] (a) Simulatied and experimental results of mixing in spiral microchannel utilized in the microfluidic synthesis of smHSS[42]; (b) Spiral microreactor used for the preparation of MSNF[43]; (c) Spiral microreactor with three arcs and generation of spherical hollow SiO2 with hierarchical sponge-like porous structure[44]; (d) Schematic diagram showing the synthesis of triangular core-shell tAg@SiO2 with spiral microreactor[45]
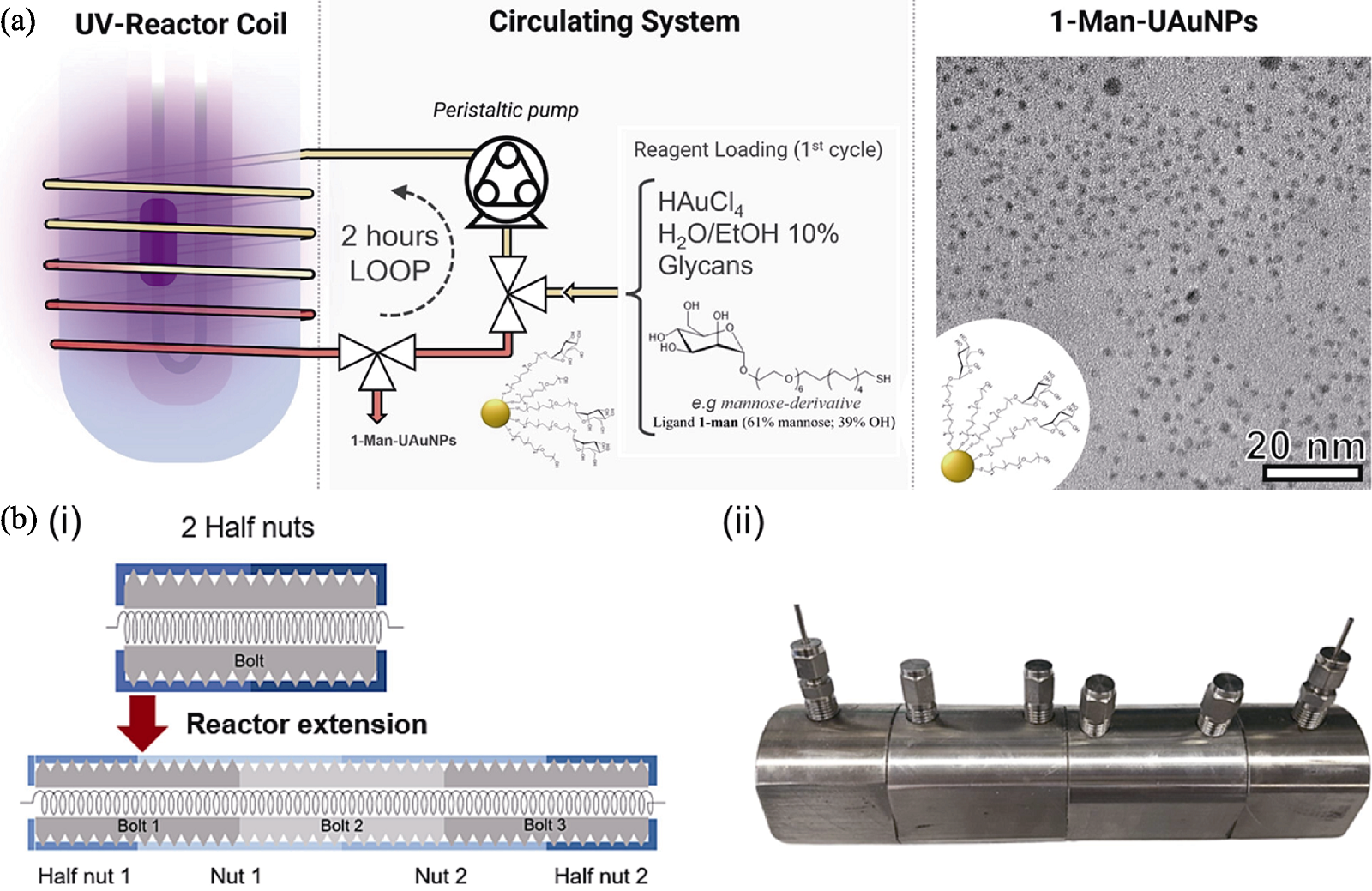
图4 立体螺旋微流控装置在无机纳米生物材料制备中的应用[48-49]
Fig. 4 Application of three-dimensional helical microfluidic devices in the preparation of inorganic nano-biomaterials[48-49] (a) Schematic diagram for the synthesis of 1-Man-UAuNPs (left) and their TEM image (right)[48]; (b) Schematic diagram (i) and photograph (ii) of the bolt-nut microfluidic device made of stainless steel[49]
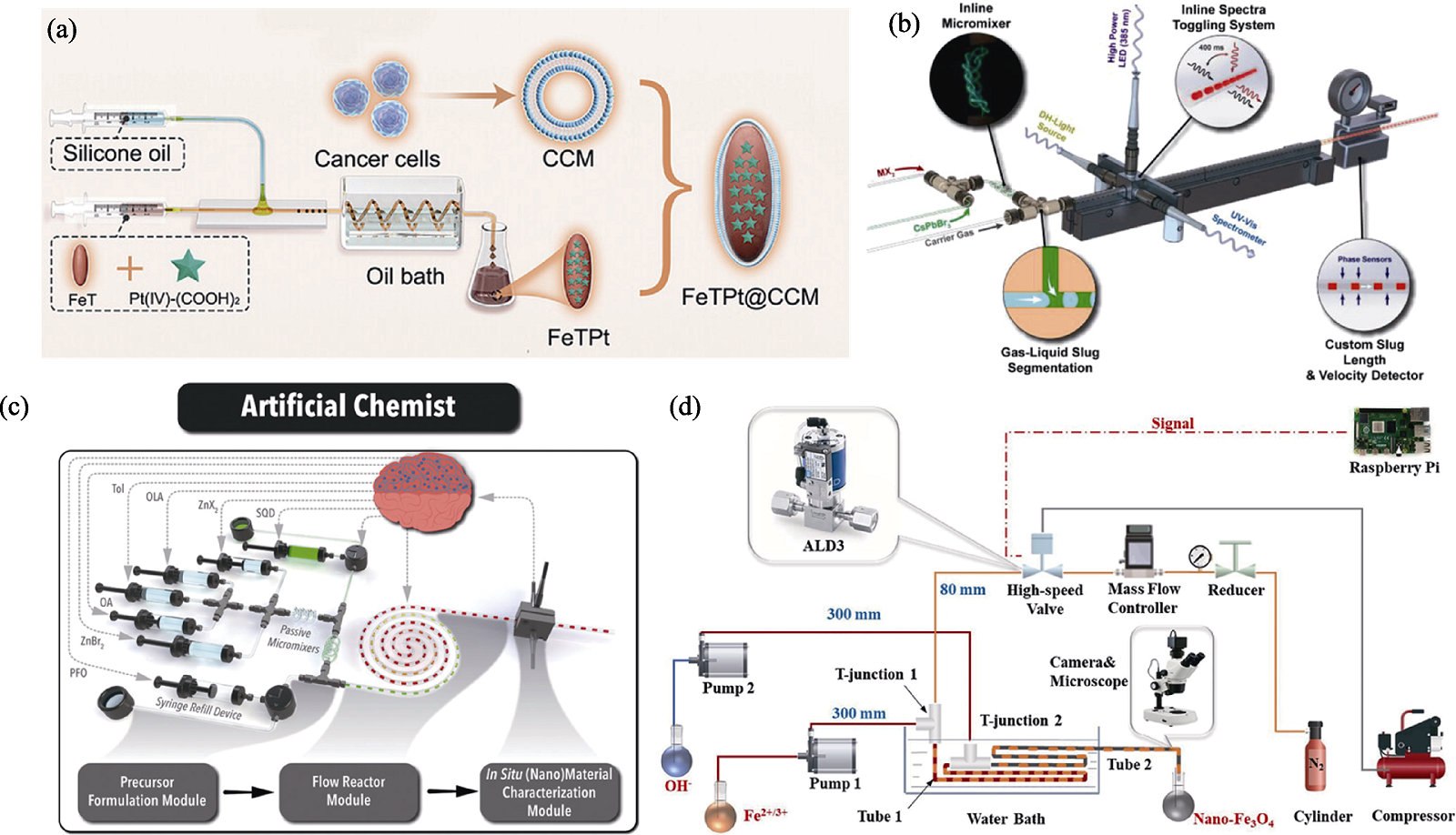
图5 分段流微流控系统在无机纳米生物材料制备中的应用[61,66⇓ -68]
Fig. 5 Application of segmented flow microfluidic systems in the preparation of inorganic nano-biomaterials[61,66⇓ -68] (a) Schematic diagram showing the segmented flow microfluidic preparation of FeTPt, and the generation of FeTPt@CCM via CCM coating[61]; (b) Schematic illustration of the modular automated microfluidic platform based on gas-liquid segmented flow[66]; (c) Schematic of the self-driving “Artificial Chemist” for autonomous synthetic path discovery and optimization of colloidal quantum dots[67]; (d) Schematic of the gas-liquid segmented flow based microfluidic device for high-throughput and continuous synthesis of nano-Fe3O4[68]
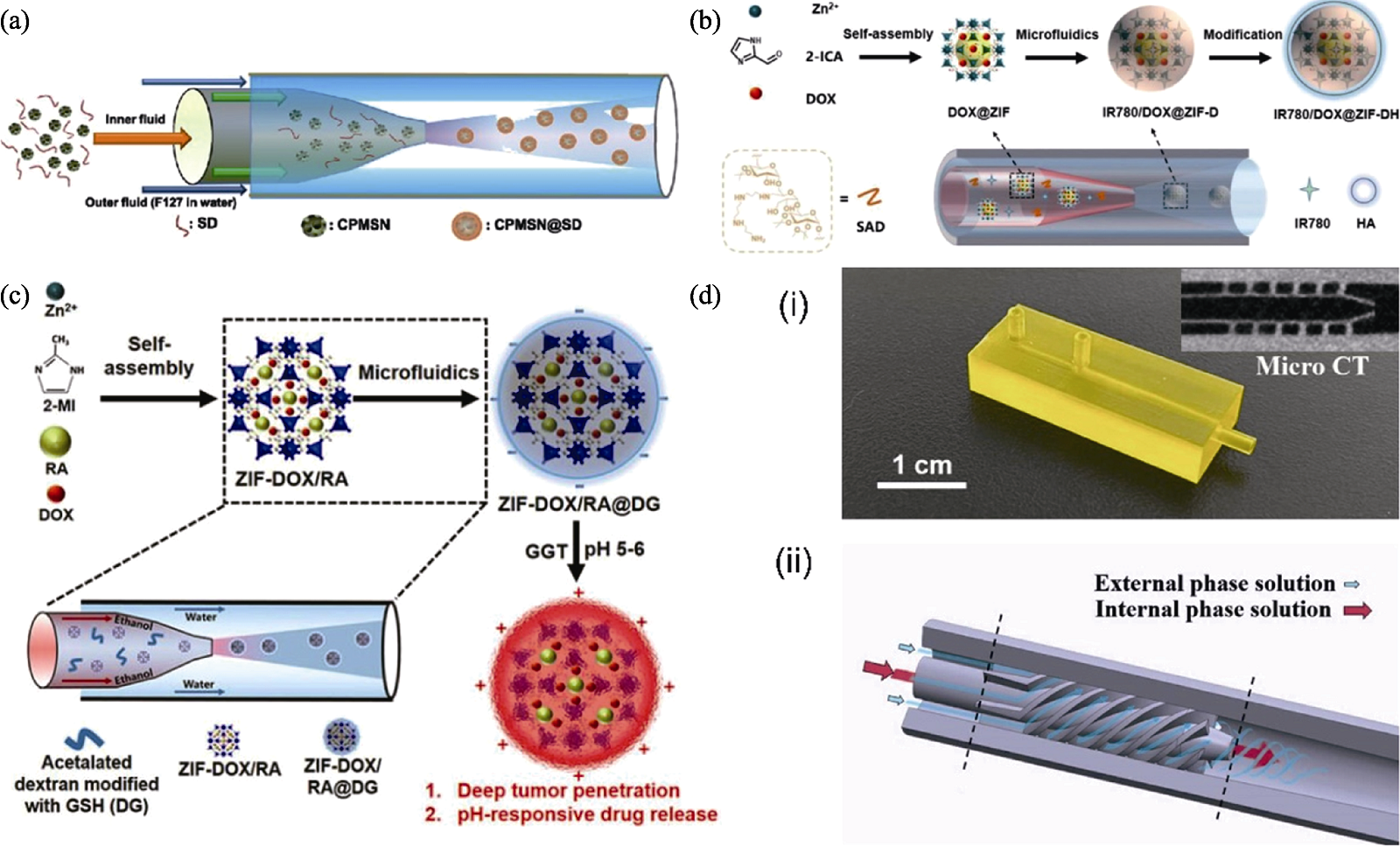
图6 聚焦流微流控装置在无机纳米生物材料制备和表面改性中的应用[24,74⇓ -76]
Fig. 6 Application of flow-focusing microfluidic devices in the preparation and surface modification of inorganic nano-biomaterials[24,74⇓ -76] (a) Schematic illustration of the synthesis of CPMSN@SD using a flow-focusing microfluidic device[74]; (b) Schematic illustration of the microfluidic synthesis of IR780/DOX@ZIF-DH[75]; (c) Schematic illustration of the synthesis of pH/enzyme dual-environment responsive ZIF-DOX/RA@DG[76]; (d) Physical picture of the HBSCF device and micro CT image of the fluid mixing area (i), along with the enlarged cross-sectional view of the core hybrid structure within the HBSCF device (ii)[24]
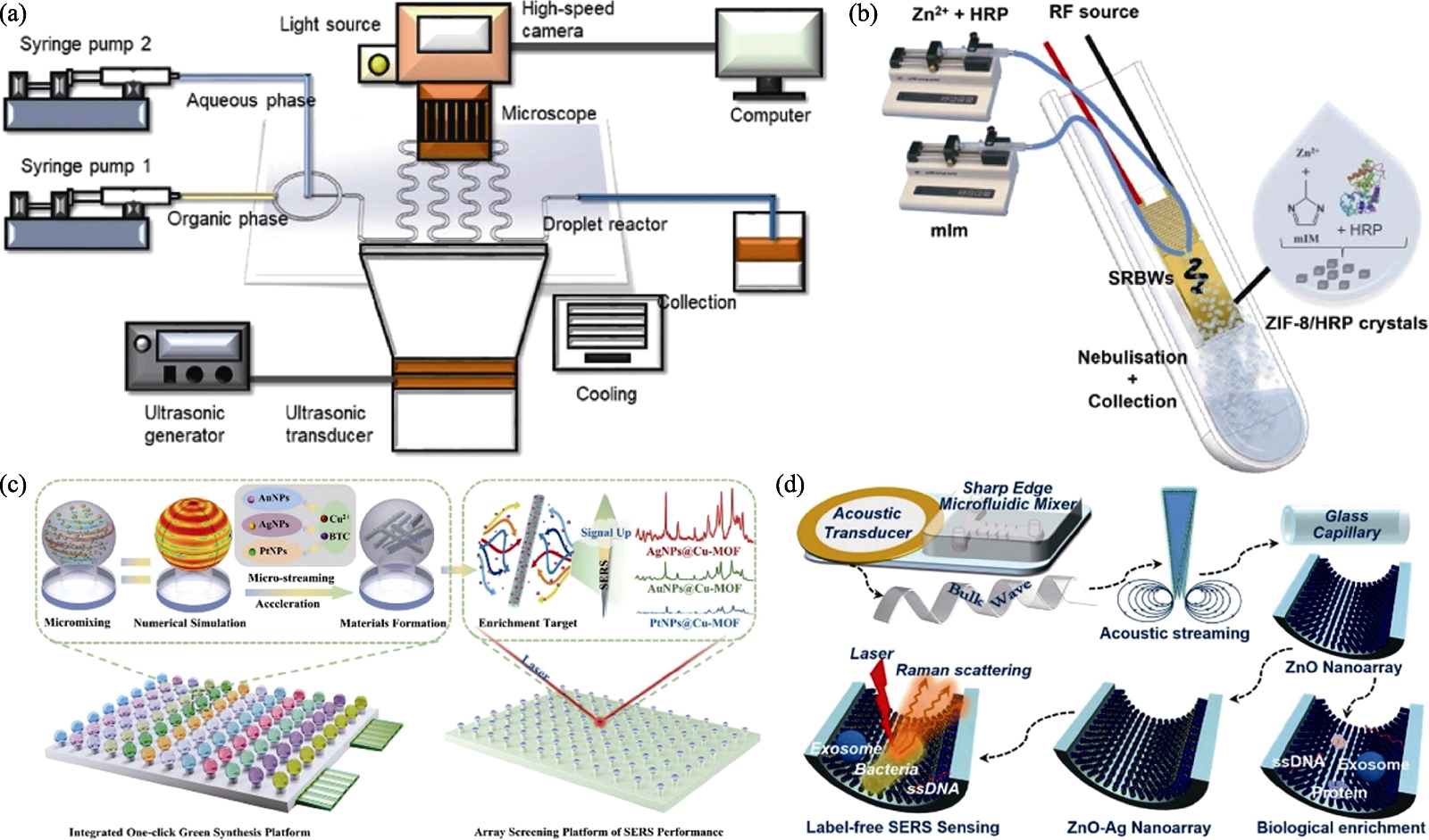
图7 超声增强的微流控装置在无机纳米生物材料制备和表面改性中的应用[84⇓⇓-87]
Fig. 7 Application of ultrasound-enhanced microfluidic devices in the preparation and surface modification of inorganic nano-biomaterials[84⇓⇓-87] (a) Schematic diagram of ultrasound-enhanced microdroplet reaction system for the synthesis of Ag2S quantum dots[84]; (b) Schematic illustration of the microfluidic device employed for the simultaneous synthesis of ZIF-8 and encapsulation of HRP[85]; (c) Schematic illustration of the one-click green and integrated platform incorporating ultrasound-enhanced droplet arrays synthesis system and high-throughput screening system via Raman performance [86]; (d) Schematic diagram showing the construction of ZnO-Ag nanoarray inside of confined capillary microchannel as multifunctional biological enrichment and sensing platform[87]
| [1] | CONG Y, BAIMANOV D, ZHOU Y, et al. Penetration and translocation of functional inorganic nanomaterials into biological barriers. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2022, 191: 114615. |
| [2] | FENG Z, XIANG X, HUANG J, et al. Intelligent sonocatalytic nanoagents for energy conversion-based therapies. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(45):2302579. |
| [3] | WANG J, FAN X, HAN X, et al. Ultrasmall inorganic mesoporous nanoparticles: preparation, functionalization, and application. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(28):2312374. |
| [4] | SONG Z, SHAFIQ M, TIAN R, et al. Microfluidic production of inorganic nanoparticles//LAMPROU D A, WEAVER E. Microfluidics in pharmaceutical sciences: formulation, drug delivery, screening, and diagnostics. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2024: 133. |
| [5] | XU M, QI Y, LIU G, et al. Size-dependent in vivo transport of nanoparticles: implications for delivery, targeting, and clearance. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(21):20825. |
| [6] |
KAMAT V, DEY P, BODAS D, et al. Active microfluidic reactor-assisted controlled synthesis of nanoparticles and related potential biomedical applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2023, 11(25):5650.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | RAN J, WANG X, LIU Y, et al. Microreactor-based micro/ nanomaterials: fabrication, advances, and outlook. Materials Horizons, 2023, 10(7):2343. |
| [8] | MARK D, HAEBERLE S, ROTH G, et al. Microfluidic lab-on-a- chip platforms: requirements, characteristics and applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 2010, 39(3):1153. |
| [9] | ILLATH K, KAR S, GUPTA P, et al. Microfluidic nanomaterials: from synthesis to biomedical applications. Biomaterials, 2022, 280: 121247. |
| [10] |
ZHANG L, CHEN Q, MA Y, et al. Microfluidic methods for fabrication and engineering of nanoparticle drug delivery systems. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2020, 3(1):107.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | FABOZZI A, SALA F D, GENNARO M, et al. Design of functional nanoparticles by microfluidic platforms as advanced drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. Lab on a Chip, 2023, 23(5):1389. |
| [12] | LIU Z, FONTANA F, PYTHON A, et al. Microfluidics for production of particles: mechanism, methodology, and applications. Small, 2020, 16(9):1904673. |
| [13] | ZHANG Q, KUANG G, WANG L, et al. Tailoring drug delivery systems by microfluidics for tumor therapy. Materials Today, 2024, 73: 151. |
| [14] |
TOMEH M A, ZHAO X. Recent advances in microfluidics for the preparation of drug and gene delivery systems. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 2020, 17(12):4421.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | CONVERY N, GADEGAARD N. 30 years of microfluidics. Micro and Nano Engineering, 2019, 2: 76. |
| [16] | FERNANDES P. Basic principles of microfluidics//LAMPROU D A, WEAVER E. Microfluidics in pharmaceutical sciences: formulation, drug delivery, screening, and diagnostics. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2024: 1. |
| [17] | KLEIN A K, DIETZEL A. A primer on microfluidics: from basic principles to microfabrication//BAHNEMANN J, GRÜNBERGER A. Microfluidics in biotechnology. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2022: 17. |
| [18] | MARTINS J P, TORRIERI G, SANTOS H A. The importance of microfluidics for the preparation of nanoparticles as advanced drug delivery systems. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery, 2018, 15(5):469. |
| [19] | MARTINS J P, SANTOS H A. Microfluidics as a tool for the synthesis of advanced drug delivery systems//LAMPROU D. Nano- and microfabrication techniques in drug delivery: recent developments and future prospects. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2023: 321. |
| [20] |
LIU Y, SUN L, ZHANG H, et al. Microfluidics for drug development: from synthesis to evaluation. Chemical Reviews, 2021, 121(13):7468.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
MA Q, CAO J, GAO Y, et al. Microfluidic-mediated nano-drug delivery systems: from fundamentals to fabrication for advanced therapeutic applications. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(29):15512.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | LIU Y, YANG G, HUI Y, et al. Microfluidic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Small, 2022, 18(36):2106580. |
| [23] |
ZHANG H, YANG J, SUN R, et al. Microfluidics for nano-drug delivery systems: from fundamentals to industrialization. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2023, 13(8):3277.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | WANG H, LAN Z, TIAN R, et al. Combined helical-blade- strengthened co-flow focusing and high-throughput screening for the synthesis of highly homogeneous nanoliposomes. Nano Today, 2024, 56: 102301. |
| [25] | ASANO S, MAKI T, INOUE S, et al. Incorporative mixing in microreactors: influence on reactions and importance of inlet designation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 451: 138942. |
| [26] | FAN J, LI S, WU Z, et al. Diffusion and mixing in microfluidic devices//Microfluidics for pharmaceutical applications. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2019: 79. |
| [27] | BAYAREH M, ASHANI M N, USEFIAN A. Active and passive micromixers: a comprehensive review. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2020, 147: 107771. |
| [28] | WANG X, LIU Z, WANG B, et al. An overview on state-of-art of micromixer designs, characteristics and applications. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2023, 1279: 341685. |
| [29] | CORTES-QUIROZ C A, AZARBADEGAN A, ZANGENEH M. Effect of channel aspect ratio of 3-D T-mixer on flow patterns and convective mixing for a wide range of Reynolds number. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2017, 239: 1153. |
| [30] | MARIOTTI A, ANTOGNOLI M, GALLETTI C, et al. A study on the effect of flow unsteadiness on the yield of a chemical reaction in a T micro-reactor. Micromachines, 2021, 12(3):242. |
| [31] | AGARWAL T, WANG L. Numerical analysis of vortex T micromixer with diffuser plates and obstacles. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 2022, 28: 101156. |
| [32] | MATSUNAGA T, NISHINO K. Swirl-inducing inlet for passive micromixers. RSC Advances, 2013, 4(2):824. |
| [33] | ZHAO S, HU R, NIE Y, et al. Intensification of mixing efficiency and reduction of pressure drop in a millimeter scale T-junction mixer optimized by an elliptical array hole structure. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2022, 178: 109034. |
| [34] | KURNIA J C, AHMADIHOSSEINI A, SASMITO A P. Flow behavior and mixing of single-phase laminar Newtonian miscible fluid in T-junction micromixer with twisted mixing channel - a numerical study. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2022, 181: 109171. |
| [35] | SCHEMBERG J, ABBASSI A E, LINDENBAUER A, et al. Synthesis of biocompatible superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION) under different microfluidic regimes. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(42):48011. |
| [36] | ZHAN T, SONG Y, YANG Q, et al. Structure and catalytic activity of hemoglobin assembled with layered double hydroxide nanosheets by coprecipitation using a T-shaped microreactor. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 306: 1143. |
| [37] |
NIVEDITA N, LIGRANI P, PAPAUTSKY I. Dean flow dynamics in low-aspect ratio spiral microchannels. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1):44072.
DOI PMID |
| [38] | NGO I L, LAI T K, CHOI H J, et al. A study on mixing performance of dean flows through spiral micro-channel under various effects. Physics of Fluids, 2020, 32(2):022004. |
| [39] | CHEN H, ZHANG Y, HUANG L, et al. Microfluidic production of silica nanofluids for highly efficient two-phase cooling with micro pin-fins structure. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 465: 142799. |
| [40] |
HAO N, NIE Y, SHEN T, et al. Microfluidics-enabled rational design of immunomagnetic nanomaterials and their shape effect on liquid biopsy. Lab on a Chip, 2018, 18(14): 1997.
DOI PMID |
| [41] | YANG H, AKINOGLU E M, GUO L, et al. A PTFE helical capillary microreactor for the high throughput synthesis of monodisperse silica particles. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 401: 126063. |
| [42] | NIE Y, HAO N, ZHANG J X J. Ultrafast synthesis of multifunctional submicrometer hollow silica spheres in microfluidic spiral channels. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 12616. |
| [43] | HAO N, NIE Y, ZHANG J X J. Microfluidic flow synthesis of functional mesoporous silica nanofibers with tunable aspect ratios. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(2):1522. |
| [44] | HAO N, NIE Y, XU Z, et al. Microfluidic continuous flow synthesis of functional hollow spherical silica with hierarchical sponge-like large porous shell. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 366: 433. |
| [45] | HAO N, NIE Y, XU Z, et al. Ultrafast microfluidic synthesis of hierarchical triangular silver core-silica shell nanoplatelet toward enhanced cellular internalization. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 542: 370. |
| [46] | SINGH J, KOCKMANN N, NIGAM K D P. Novel three- dimensional microfluidic device for process intensification. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2014, 86: 78. |
| [47] | KOCKMANN N, ROBERGE D M. Transitional flow and related transport phenomena in curved microchannels. Heat Transfer Engineering, 2011, 32(7/8):595. |
| [48] | SCHMIDT P P, PAGANO K, LENARDI C, et al. Photo-induced microfluidic production of ultrasmall glyco gold nanoparticles. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(1):e202210140. |
| [49] | KIM H, KIM D H, KIM S H. Robust and versatile bolt-nut microreactors designed for controlled synthesis of quantum dots. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 474: 145761. |
| [50] | HU G, YANG L, LI Y, et al. Continuous and scalable fabrication of stable and biocompatible MOF@SiO2 nanoparticles for drug loading. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2018, 6(47):7936. |
| [51] | MAHIN J, TORRENTE-MURCIANO L. Continuous synthesis of monodisperse iron@iron oxide core@shell nanoparticles. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 396: 125299. |
| [52] | GAO Y, PINHO B, TORRENTE-MURCIANO L. Tailoring the size of silver nanoparticles by controlling mixing in microreactors. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 432: 134112. |
| [53] | WU K J, DE VARINE BOHAN G M, TORRENTE-MURCIANO L. Synthesis of narrow sized silver nanoparticles in the absence of capping ligands in helical microreactors. Reaction Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 2(2):116. |
| [54] | LUO X, SU P, ZHANG W, et al. Microfluidic devices in fabricating nano or micromaterials for biomedical applications. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2019, 4(12):1900488. |
| [55] | SONG H, CHEN D L, ISMAGILOV R F. Reactions in droplets in microfluidic channels. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2006, 45(44):7336. |
| [56] |
DING Y, HOWES P D, DEMELLO A J. Recent advances in droplet microfluidics. Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 92(1):132.
DOI PMID |
| [57] | KUMAR D V R, PRASAD B L V, KULKARNI A A. Segmented flow synthesis of Ag nanoparticles in spiral microreactor: role of continuous and dispersed phase. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 192: 357. |
| [58] | PENG Z, WANG G, MOGHTADERI B, et al. A review of microreactors based on slurry Taylor (segmented) flow. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 247: 117040. |
| [59] | FU Q, NIU W, YAN L, et al. A versatile microfluidic strategy using air-liquid segmented flow for continuous and efficient synthesis of metal-organic frameworks. Materials Letters, 2023, 343: 134344. |
| [60] | PASETA L, SEOANE B, JULVE D, et al. Accelerating the controlled synthesis of metal-organic frameworks by a microfluidic approach: a nanoliter continuous reactor. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(19):9405. |
| [61] | ZHANG Q, KUANG G, WANG H, et al. Multi-bioinspired MOF delivery systems from microfluidics for tumor multimodal therapy. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(33):2303818. |
| [62] | BAGI S, YUAN S, ROJAS-BUZO S, et al. A continuous flow chemistry approach for the ultrafast and low-cost synthesis of MOF-808. Green Chemistry, 2021, 23(24):9982. |
| [63] |
LIGNOS I, STAVRAKIS S, NEDELCU G, et al. Synthesis of cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals in a droplet-based microfluidic platform: fast parametric space mapping. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(3): 1869.
DOI PMID |
| [64] | BATENI F, SADEGHI S, OROUJI N, et al. Smart dope: a self- driving fluidic lab for accelerated development of doped perovskite quantum dots. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024, 14(1):2302303. |
| [65] | VOLK A A, EPPS R W, YONEMOTO D, et al. Continuous biphasic chemical processes in a four-phase segmented flow reactor. Reaction Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 6(8):1367. |
| [66] | ABDEL-LATIF K, EPPS R W, KERR C B, et al. Facile room- temperature anion exchange reactions of inorganic perovskite quantum dots enabled by a modular microfluidic platform. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(23):1900712. |
| [67] | EPPS R W, BOWEN M S, VOLK A A, et al. Artificial chemist: an autonomous quantum dot synthesis bot. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(30):2001626. |
| [68] | JIANG X, LI S, SOTOWA K I, et al. High throughput continuous synthesis of size-controlled nanoFe3O4 in segmented flow. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 471: 144546. |
| [69] | SHEPHERD S J, ISSADORE D, MITCHELL M J. Microfluidic formulation of nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials, 2021, 274: 120826. |
| [70] | LE P T, AN S H, JEONG H H. Microfluidic Tesla mixer with 3D obstructions to exceptionally improve the curcumin encapsulation of PLGA nanoparticles. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 483: 149377. |
| [71] | TROFIMOV A D, IVANOVA A A, ZYUZIN M V, et al. Porous inorganic carriers based on silica, calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate for controlled/modulated drug delivery: fresh outlook and future perspectives. Pharmaceutics, 2018, 10(4):167. |
| [72] | SAYED E, HAJ-AHMAD R, RUPARELIA K, et al. Porous inorganic drug delivery systems—a review. AAPS PharmSciTech, 2017, 18(5):1507. |
| [73] | ZOU Y, HUANG B, CAO L, et al. Tailored mesoporous inorganic biomaterials: assembly, functionalization, and drug delivery engineering. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(2):2005215. |
| [74] | YAO M, SHI X, ZUO C, et al. Engineering of SPECT/photoacoustic imaging/antioxidative stress triple-function nanoprobe for advanced mesenchymal stem cell therapy of cerebral ischemia. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(34):37885. |
| [75] | SHEN J, MA M, ZHANG H, et al. Microfluidics-assisted surface trifunctionalization of a zeolitic imidazolate framework nanocarrier for targeted and controllable multitherapies of tumors. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(41):45838. |
| [76] | SHEN J, MA M, SHAFIQ M, et al. Microfluidics-assisted engineering of pH/enzyme dual-activatable ZIF@polymer nanosystem for co-delivery of proteins and chemotherapeutics with enhanced deep-tumor penetration. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(14):e202113703. |
| [77] | LIU Z, YANG M, YAO W, et al. Microfluidic ultrasonic cavitation enables versatile and scalable synthesis of monodisperse nanoparticles for biomedical application. Chemical Engineering Science, 2023, 280: 119052. |
| [78] | ZHAO S, YAO C, DONG Z, et al. Role of ultrasonic oscillation in chemical processes in microreactors: a mesoscale issue. Particuology, 2020, 48: 88. |
| [79] | ZHAO S, YAO C, LIU L, et al. Parametrical investigation of acoustic cavitation and extraction enhancement in ultrasonic microreactors. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450: 138185. |
| [80] | LIU Z, YANG M, DONG Z, et al. Cavitation behavior and mixing performance of antisolvent precipitation process in an ultrasonic micromixer. AIChE Journal, 2023, 69(7):e18080. |
| [81] | ZHAO S, YAO C, ZHANG Q, et al. Acoustic cavitation and ultrasound-assisted nitration process in ultrasonic microreactors: the effects of channel dimension, solvent properties and temperature. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 374: 68. |
| [82] | CHEN Z, PEI Z, ZHAO X, et al. Acoustic microreactors for chemical engineering. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 433: 133258. |
| [83] | LIU Z, YANG M, ZHAO Q, et al. Scale-up of antisolvent precipitation process with ultrasonic microreactors: cavitation patterns, mixing characteristics and application in nanoparticle manufacturing. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 475: 146040. |
| [84] | ZHANG Z, XU C, SONG S, et al. Ultrasonic enhancement of microdroplet-based interfacial reaction for improving the synthesis of Ag2S QDs. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2023, 95: 106411. |
| [85] | MASSAHUD E, AHMED H, AMBATTU L A, et al. Acoustomicrofluidic synthesis of ZIF-8/HRP metal-organic framework composites with enhanced enzymatic activity and stability. Materials Today Chemistry, 2023, 33: 101694. |
| [86] | FAN C, LUO Y, TIAN M, et al. Integrated microsystem toward high-throughput automated green synthesis and Raman enhancement performance screening of noble-metal@Cu-MOF. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(11):2211845. |
| [87] |
HAO N, LIU P, BACHMAN H, et al. Acoustofluidics-assisted engineering of multifunctional three-dimensional zinc oxide nanoarrays. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(5):6150.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 余升阳, 苏海军, 姜浩, 余明辉, 姚佳彤, 杨培鑫. 激光增材制造超高温氧化物陶瓷孔隙缺陷形成及抑制研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [2] | 刘江平, 管鑫, 唐振杰, 朱文杰, 罗永明. 含氮挥发性有机化合物催化氧化的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [3] | 肖晓琳, 王玉祥, 谷佩洋, 朱圳荣, 孙勇. 二维无机材料调控病损皮肤组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [4] | 马景阁, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料用于毛囊和毛发再生的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [5] | 张洪健, 赵梓壹, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料调控神经细胞功能及神经化组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [6] | 艾敏慧, 雷波. 微纳米生物活性玻璃: 功能化设计与血管化皮肤再生[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [7] | 王宇彤, 常江, 徐合, 吴成铁. 硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃促创面修复的研究进展:作用、机制和应用方式[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [8] | 马文平, 韩雅卉, 吴成铁, 吕宏旭. 无机活性材料在类器官研究领域的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [9] | 罗晓民, 乔志龙, 刘颍, 杨晨, 常江. 无机生物活性材料调控心肌再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [10] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [11] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [12] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [13] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [14] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [15] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||