无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (8): 860-870.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240508 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240508
肖晓琳1,2( ), 王玉祥1,2, 谷佩洋1,2, 朱圳荣1,2, 孙勇1,2(
), 王玉祥1,2, 谷佩洋1,2, 朱圳荣1,2, 孙勇1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-04
修回日期:2025-01-09
出版日期:2025-08-20
网络出版日期:2025-01-24
通讯作者:
孙 勇, 研究员. E-mail: sunyong8702@scu.edu.cn作者简介:肖晓琳(2001-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: xiaolin203232@163.com
基金资助:
XIAO Xiaolin1,2( ), WANG Yuxiang1,2, GU Peiyang1,2, ZHU Zhenrong1,2, SUN Yong1,2(
), WANG Yuxiang1,2, GU Peiyang1,2, ZHU Zhenrong1,2, SUN Yong1,2( )
)
Received:2024-12-04
Revised:2025-01-09
Published:2025-08-20
Online:2025-01-24
Contact:
SUN Yong, professor. E-mail: sunyong8702@scu.edu.cnAbout author:XIAO Xiaolin (2001-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: xiaolin203232@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
二维无机材料作为一类具有单原子层或多原子层的无机超薄纳米片, 呈现出高比表面积、高导电性和/或高光热转换效率等特点。这些独特的理化特性赋予其促凝血、抗菌、抗炎和抗氧化等生物效应。近年来, 鉴于降解和代谢问题, 该类材料被应用于调控病损皮肤组织, 如全层皮肤缺损、烧烫伤及糖尿病创面等, 展现出加速伤口愈合、减轻感染及改善炎症微环境的显著效果。本文围绕二维无机材料的特有结构和生物效应, 系统性阐述了其在伤口愈合中的应用及相关作用机制, 并展望了二维无机材料在皮肤修复领域面临的挑战和前景。
中图分类号:
肖晓琳, 王玉祥, 谷佩洋, 朱圳荣, 孙勇. 二维无机材料调控病损皮肤组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 860-870.
XIAO Xiaolin, WANG Yuxiang, GU Peiyang, ZHU Zhenrong, SUN Yong. Advances in Regulation of Damaged Skin Regeneration by Two-dimensional Inorganic Materials[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 860-870.
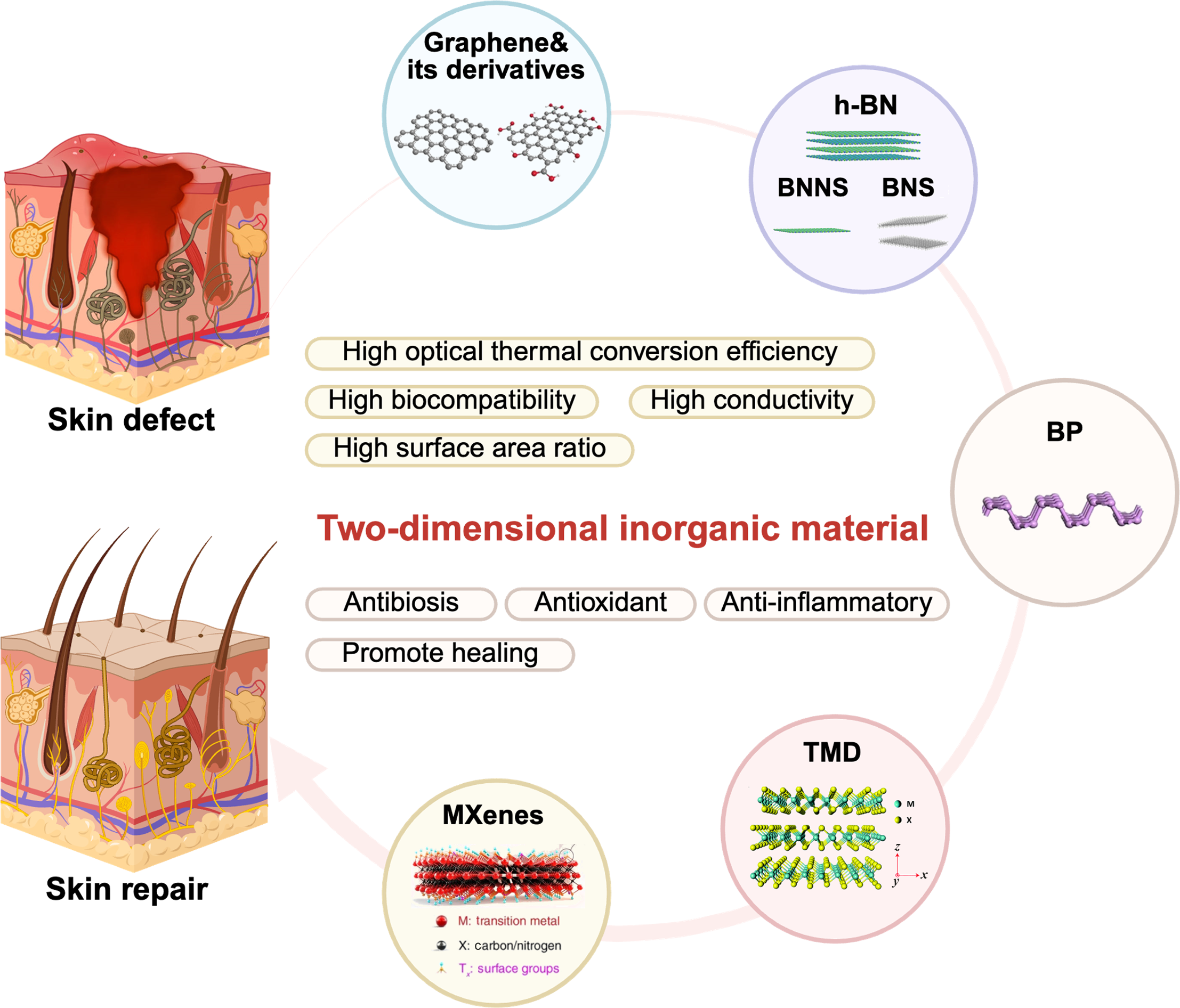
图1 二维无机材料调控病损皮肤再生[34-37]
Fig. 1 2D inorganic materials regulating regeneration of damaged skin[34-37] BP: Black phosphorus; h-BN: Hexagonal boron nitride; BNNS: Boron nitride nanosheet; BNS: Boron nanosheet; TMD: Transition-metal disulfide. Created with BioRender.com. Colorful figure is available on website
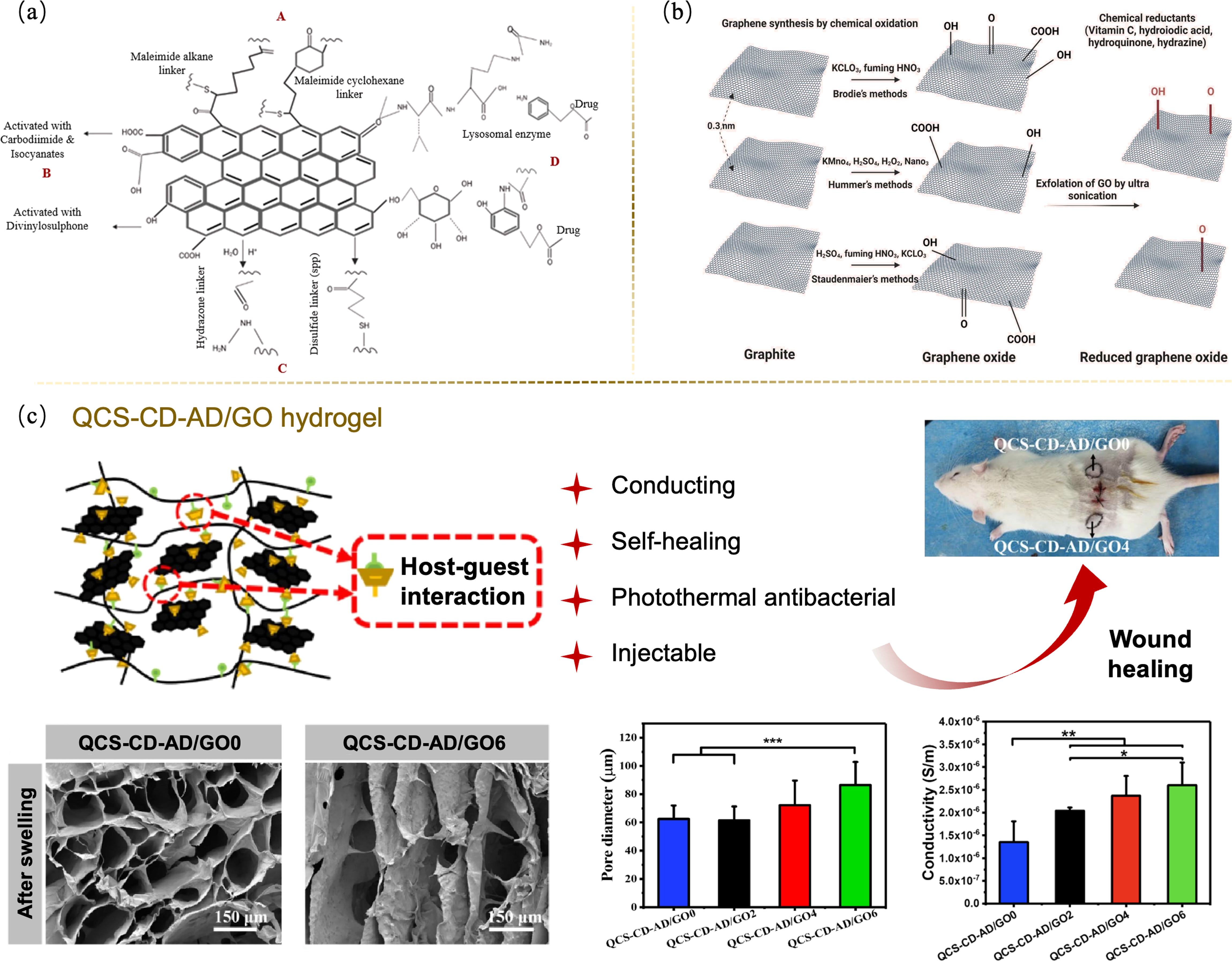
图2 石墨烯及其衍生物调控病损皮肤修复[39,41]
Fig. 2 Regulations of graphene and its derivatives for the repair of damaged skin[39,41] (a) Structure of functionalized graphene[39]; (b) Conversion of graphene to GO/rGO[39]; (c) QCS-CD-AD/GO supramolecular hydrogel promoting bioelectrical signal transmission to repair full-thickness skin defects[41]. QCS-CD-AD: Quaternized chitosan-β-cyclodextrin-adamantane. Colorful figures are available on website
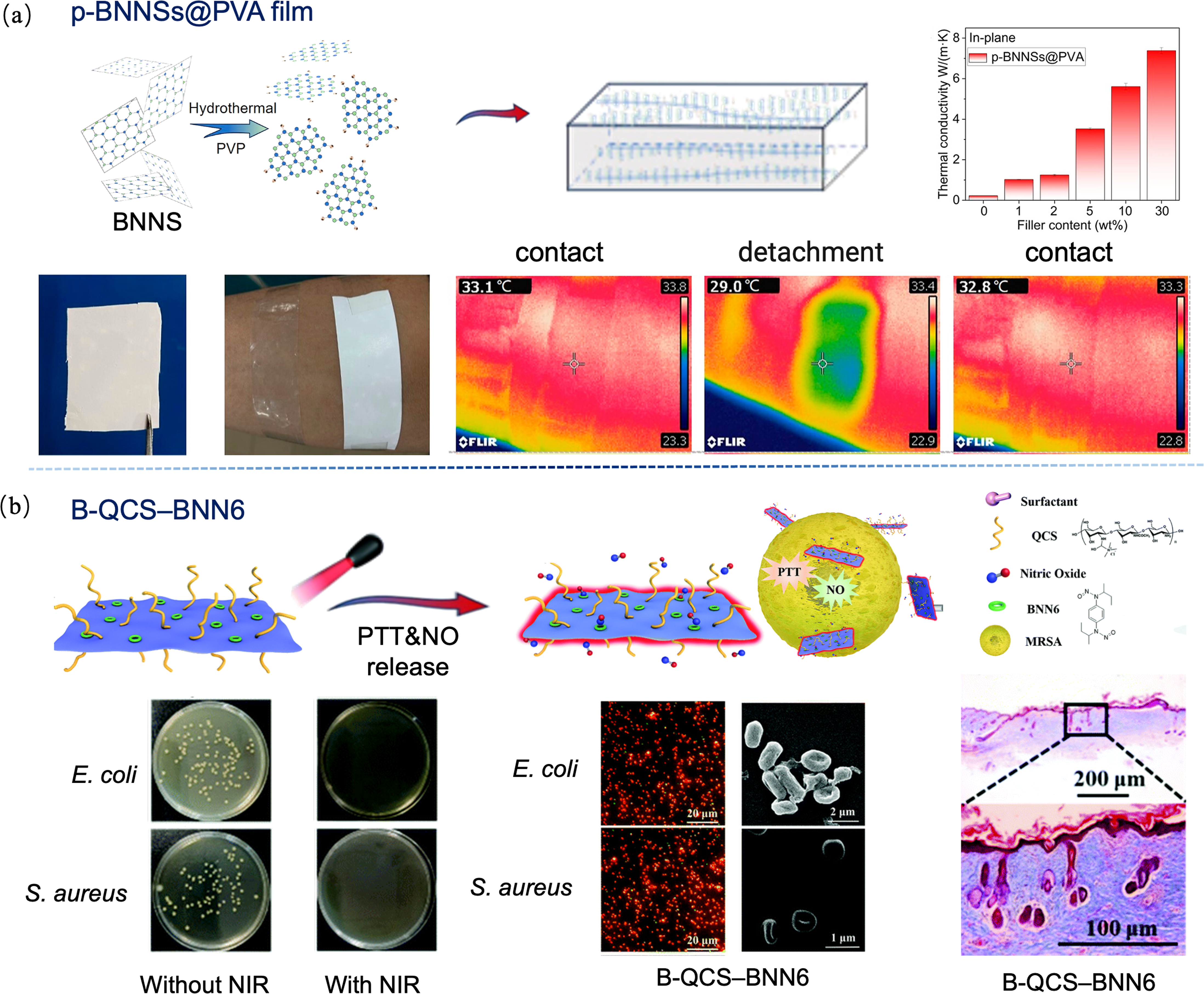
图3 硼基二维材料调控病损皮肤修复[47-48]
Fig. 3 Regulations of boron-based 2D materials for the repair of damaged skin[47-48] (a) p-BNNSs@PVA film with high thermal conductivity promoting heat dissipation of skin wounds[47]; (b) B-QCS-BNN6 transfering NO to achieve efficient antibacterial effect[48]. BNNSs: Boron nitride nanosheets; QCS: Quaternized chitosan. Colorful figures are available on website
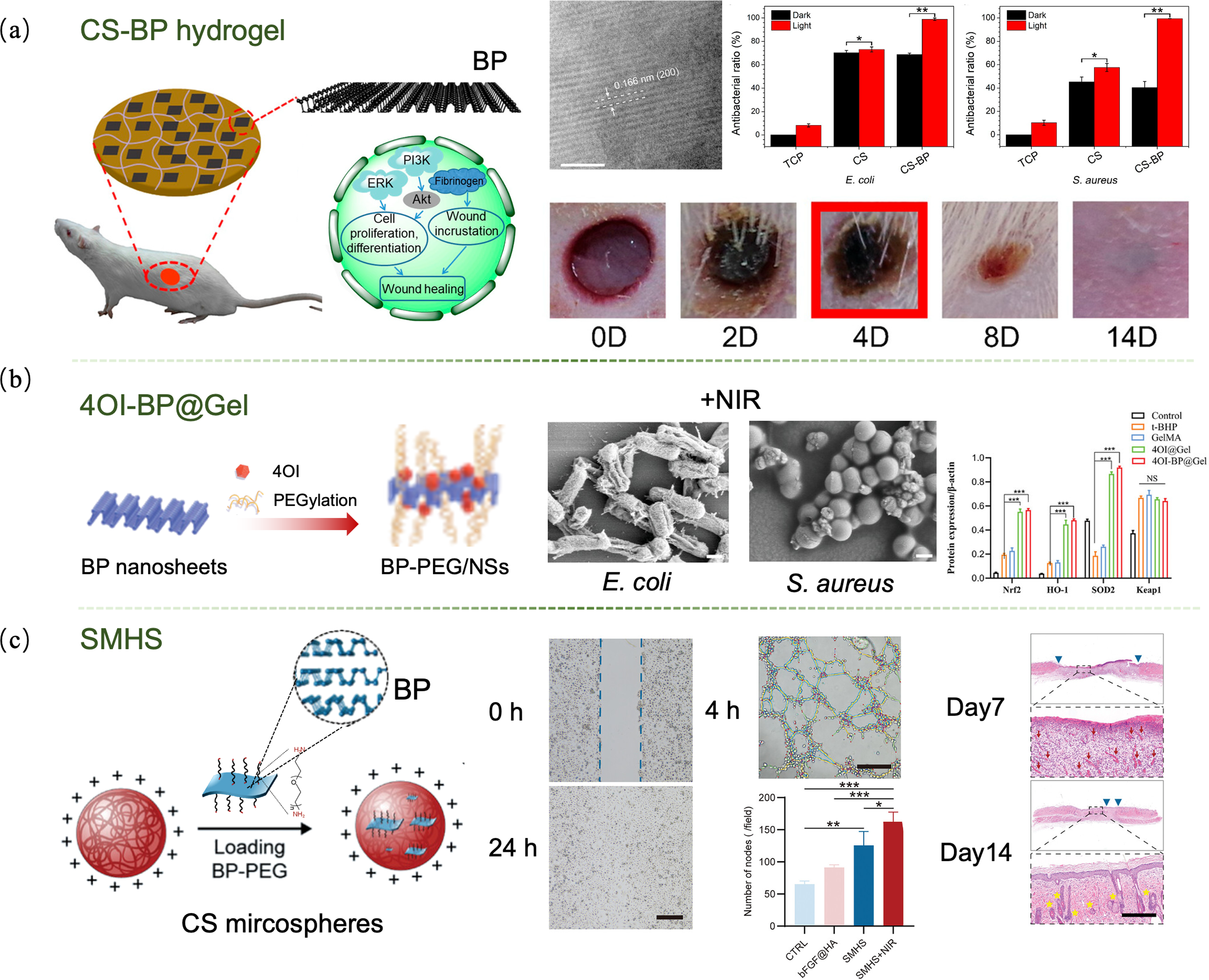
图4 黑磷纳米片调控病损皮肤修复[52,56 -57]
Fig. 4 Regulations of black phosphorus nanosheets for the repair of damaged skin[52,56 -57] (a) CS-BP hydrogel enhancing fibrinogen expression to accelerate wound scab formation[52]; (b) 4OI-BP@Gel with high antibacterial effect promoting diabetic wound healing[56]; (c) SMHS promoting wound healing in diabetic rats[57]. CS: Chitosan; BP: Black phosphorus; 4OI: 4-octyl itaconate; SMHS: Self-assembled microsphere hydrogel scaffold. Colorful figures are available on website

图5 TMD调控病损皮肤修复[37,64,66]
Fig. 5 Regulations of TMD for the repair of damaged skin[37,64,66] (a) Structure of TMD[37]; (b) 2H-WS2 nanosheets for treating deep burn wounds[37]; (c) PCNPs@NIR-gel accelerating full-thickness skin healing in diabetic mice[64]; (d) MoS2@CSH repairing skin wounds of various shapes and sizes[66]. TMD: Transition-metal disulfide; PCNPs: Polydeoxyribonucleotide nano-vectors particles; CSH: Chitosan hydrogel. Colorful figures are available on website
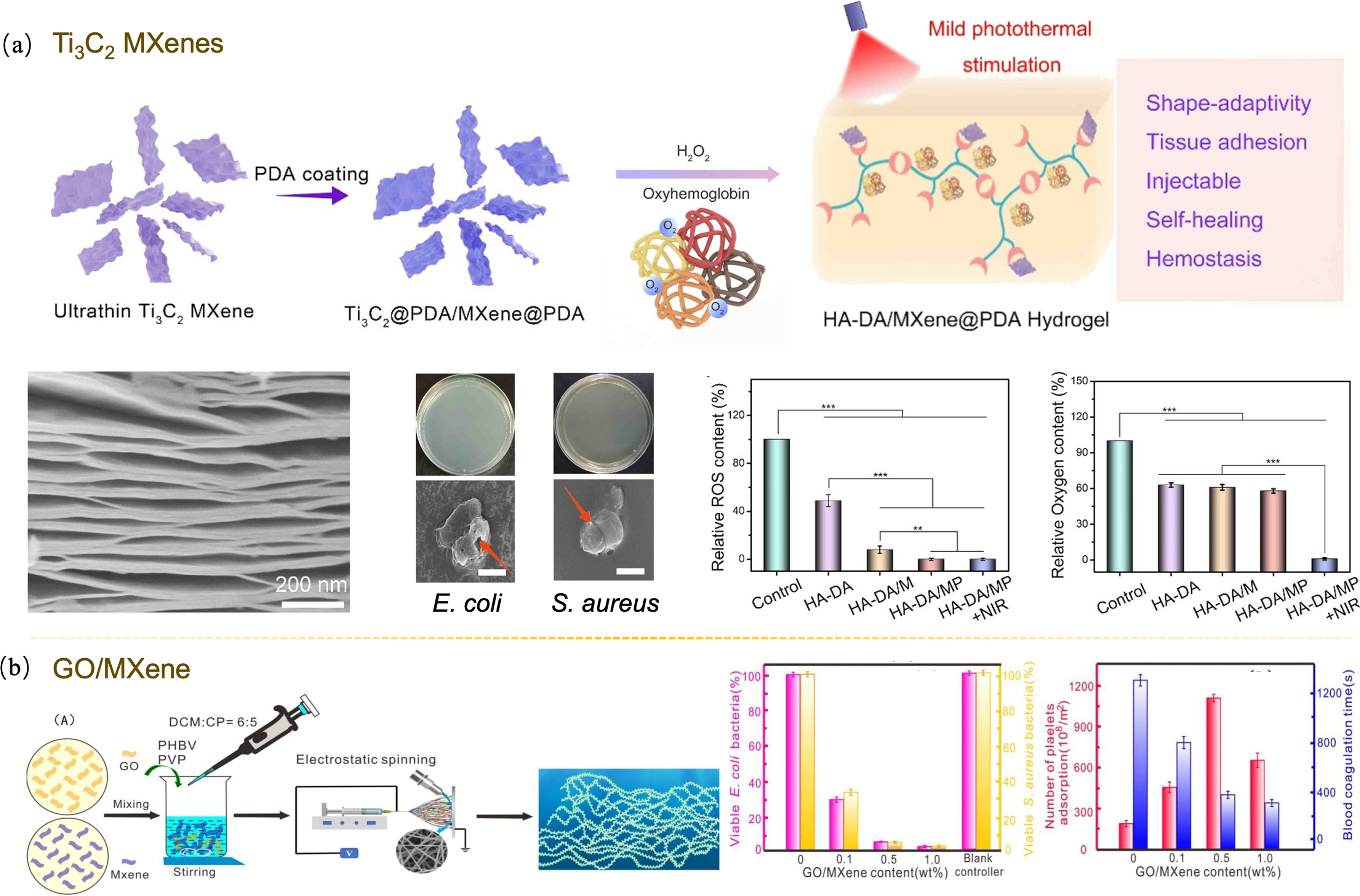
图6 MXenes调控病损皮肤修复[69,71]
Fig. 6 Regulations of MXenes for the repair of damaged skin[69,71] (a) Ti3C2 MXenes nanosheet accelerating wound healing in diabetes[69]; (b) GO/MXene laminate with excellent hemostatic properties[71]. Colorful figures are available on website
| Material | Characteristic | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphene/GO/rGO | QCS-CD-AD/GO supramolecular hydrogel | rGO-CD: 0.6% (in mass) Swelling ratio: 129% Conductivity: 0.07-0.11 S/m Wound closure rate: 98.3% | [ |
| Boron-based 2D materials | p-BNNSs@PVA thin film | p-BNNSs: 30% (in mass) Thermal conductivity: 7.38 W/(m·K) | [ |
| B-QCS-BNN6 | Bacterial inactivation rate: >99.9% (under NIR irradiation) | [ | |
| BP nanosheets | CS-BP hydrogel | E. coli inactivation rate: 98.90% S. aureus inactivation rate: 99.51% | [ |
| 4OI-BP@Gel | Bacterial inactivation rate: >90% ROS clearance rate: 51.9% Wound healing rate: 99.64% (under NIR irradiation) | [ | |
| SMHS | Degradation product: PO43-/HPO42- | [ | |
| TMD | WS2 nanosheet | Cell viability of 2H-WS2: 100% Cell viability of 1H-WS2: 60.4% (150 μg/mL, 48 h) | [ |
| PCNPs@NIR-gel | Swelling ratio: 169% Bacterial inactivation rate: >99.9% (under NIR irradiation) | [ | |
| MoS2@CSH | Bacterial inactivation rate: ~100% (under NIR irradiation) | [ | |
| MXenes | Ti3C2 MXenes nanosheet | DPPH clearance: 80% (2 mg) Wound closure rate: 98.8% | [ |
| GO/MXene laminate | GO/MXene: 0.5% (in mass) Coagulation time: 379 s | [ | |
表1 二维无机材料在促进病损皮肤修复中的特性
Table 1 Characterization of various 2D inorganic materials in promoting the repair of diseased skin
| Material | Characteristic | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphene/GO/rGO | QCS-CD-AD/GO supramolecular hydrogel | rGO-CD: 0.6% (in mass) Swelling ratio: 129% Conductivity: 0.07-0.11 S/m Wound closure rate: 98.3% | [ |
| Boron-based 2D materials | p-BNNSs@PVA thin film | p-BNNSs: 30% (in mass) Thermal conductivity: 7.38 W/(m·K) | [ |
| B-QCS-BNN6 | Bacterial inactivation rate: >99.9% (under NIR irradiation) | [ | |
| BP nanosheets | CS-BP hydrogel | E. coli inactivation rate: 98.90% S. aureus inactivation rate: 99.51% | [ |
| 4OI-BP@Gel | Bacterial inactivation rate: >90% ROS clearance rate: 51.9% Wound healing rate: 99.64% (under NIR irradiation) | [ | |
| SMHS | Degradation product: PO43-/HPO42- | [ | |
| TMD | WS2 nanosheet | Cell viability of 2H-WS2: 100% Cell viability of 1H-WS2: 60.4% (150 μg/mL, 48 h) | [ |
| PCNPs@NIR-gel | Swelling ratio: 169% Bacterial inactivation rate: >99.9% (under NIR irradiation) | [ | |
| MoS2@CSH | Bacterial inactivation rate: ~100% (under NIR irradiation) | [ | |
| MXenes | Ti3C2 MXenes nanosheet | DPPH clearance: 80% (2 mg) Wound closure rate: 98.8% | [ |
| GO/MXene laminate | GO/MXene: 0.5% (in mass) Coagulation time: 379 s | [ | |
| Material | Type of skin defect | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| QCS-CD-AD/GO supramolecular hydrogel | Full-thickness wounds | Bacterial cell membrane damage Modulation of immune cells Reduction: IL-6 Up-regulation: VEGF | [ |
| p-BNNSs@PVA thin film | High-temperature environment | Out-of-plane thermal conductivity (TC): 7.38 W/(m·K) The higher TC, the faster heat dissipation | [ |
| B-QCS-BNN6 | MRSA infection | Bacterial cell membrane damage Controlled release of NO | [ |
| CS-BP hydrogel | Bacterial infection | Producing 1O2 Promoting formation of the fibrinogen Activation: PI3K, Akt, ERK1/2 | [ |
| 4OI-BP@Gel | Diabetic ulcers | High PTT (photothermal therapy) and PDT (photodynamics therapy) efficacy Up-regulation: Nrf2, HO-1 Activation: KEAP1-Nrf2 | [ |
| SMHS | Diabetic ulcers | Enhancing M2 activation Bacterial cell membrane damage Promoting collagen deposition | [ |
| WS2 nanosheet | Deep burn | Up-regulation: CAT, GPx, antimicrobial peptides Reduction: TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-8, IL-6 Reduction: caspase-8, caspase-3, PARP | [ |
| PCNPs@NIR-gel | Diabetic total skin defects | Bacterial cell membrane damage Up-regulation: VEGF, α-SMA Reduction: TGF-β, MPO Enhancing M2 activation Promoting collagen deposition Activation: PI3K-Akt, cAMP | [ |
| MoS2@CSH | Irregular wounds | Increase: CD31 Up-regulation: TNF-α | [ |
| Ti3C2 MXenes nanosheet | Diabetic ulcers | Enhancing M2 activation Scavenging ABTS•+ Increase: IL-10, CD31 Up-regulation: TNF-α, HIF-1α, VEGF, α-SMA | [ |
| GO/MXene laminate | Skin hemostasis | Presence of hydroxyl groups and terminal oxygen Free radical polymerization of ester bonds | [ |
表2 二维无机材料修复各类病损皮肤的作用机制
Table 2 Mechanisms of 2D inorganic materials for the repair of various types of diseased skin
| Material | Type of skin defect | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| QCS-CD-AD/GO supramolecular hydrogel | Full-thickness wounds | Bacterial cell membrane damage Modulation of immune cells Reduction: IL-6 Up-regulation: VEGF | [ |
| p-BNNSs@PVA thin film | High-temperature environment | Out-of-plane thermal conductivity (TC): 7.38 W/(m·K) The higher TC, the faster heat dissipation | [ |
| B-QCS-BNN6 | MRSA infection | Bacterial cell membrane damage Controlled release of NO | [ |
| CS-BP hydrogel | Bacterial infection | Producing 1O2 Promoting formation of the fibrinogen Activation: PI3K, Akt, ERK1/2 | [ |
| 4OI-BP@Gel | Diabetic ulcers | High PTT (photothermal therapy) and PDT (photodynamics therapy) efficacy Up-regulation: Nrf2, HO-1 Activation: KEAP1-Nrf2 | [ |
| SMHS | Diabetic ulcers | Enhancing M2 activation Bacterial cell membrane damage Promoting collagen deposition | [ |
| WS2 nanosheet | Deep burn | Up-regulation: CAT, GPx, antimicrobial peptides Reduction: TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-8, IL-6 Reduction: caspase-8, caspase-3, PARP | [ |
| PCNPs@NIR-gel | Diabetic total skin defects | Bacterial cell membrane damage Up-regulation: VEGF, α-SMA Reduction: TGF-β, MPO Enhancing M2 activation Promoting collagen deposition Activation: PI3K-Akt, cAMP | [ |
| MoS2@CSH | Irregular wounds | Increase: CD31 Up-regulation: TNF-α | [ |
| Ti3C2 MXenes nanosheet | Diabetic ulcers | Enhancing M2 activation Scavenging ABTS•+ Increase: IL-10, CD31 Up-regulation: TNF-α, HIF-1α, VEGF, α-SMA | [ |
| GO/MXene laminate | Skin hemostasis | Presence of hydroxyl groups and terminal oxygen Free radical polymerization of ester bonds | [ |
| [1] |
WU A J, ZHU M, ZHU Y F. Copper-incorporated calcium silicate nanorods composite hydrogels for tumor therapy and skin wound healing. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1203.
DOI |
| [2] |
ZHANG H, HAN K Y, DONG L L, et al. Preparation and characterization of β-tricalcium phosphate/nano clay composite scaffolds via digital light processing printing. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1116.
DOI |
| [3] |
SHI J X, ZHAI D, ZHU M, et al. Preparation and characterization of bioactive glass-manganese dioxide composite scaffolds. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 427.
DOI |
| [4] |
杜琳, 薛健民, 郇志广, 等. 含钼的硅酸盐生物陶瓷释放的化学离子对肌腱-骨相关的多细胞调控. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1334.
DOI |
| [5] |
BAO F, CHANG J. Calcium silicate nanowires based composite electrospun scaffolds: preparation, ion release and cytocompatibility. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1199.
DOI |
| [6] | ZHU Y, ZHANG X, CHANG G, et al. Bioactive glass in tissue regeneration: unveiling recent advances in regenerative strategies and applications. Advanced Materials, 2024, 37(2): 2312964. |
| [7] |
WU R, ZHANG M H, JIN C Y, et al. Photothermal core-shell TiN@borosilicate bioglass nanoparticles: degradation and mineralization. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 708.
DOI |
| [8] | WU C T, CHANG J. Silicate bioceramics for bone tissue regeneration. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(1): 29. |
| [9] |
GUO Y, XU K, WU C, et al. Surface chemical-modification for engineering the intrinsic physical properties of inorganic two-dimensional nanomaterials. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(3): 637.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | YANG B, CHEN Y, SHI J. Material chemistry of two-dimensional inorganic nanosheets in cancer theranostics. Chem, 2018, 4(6): 1284. |
| [11] | TAN A Y S, LO N W, CHENG F, et al. 2D carbon materials based photoelectrochemical biosensors for detection of cancer antigens. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2023, 219: 114811. |
| [12] | SAKTHIVEL R, KEERTHI M, CHUNG R J, et al. Heterostructures of 2D materials and their applications in biosensing. Progress in Materials Science, 2023, 132: 101024. |
| [13] |
BAI Z, ZHAO L, BAI Y, et al. Research progress on MXenes: preparation, property and application in tumor theranostics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 361.
DOI |
| [14] | LIU S, PAN X, LIU H. Two-dimensional nanomaterials for photothermal therapy. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(15): 5890. |
| [15] |
WANG X, MA B, XUE J, et al. Defective black nano-titania thermogels for cutaneous tumor-induced therapy and healing. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(3): 2138.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | PENG G, FADEEL B. Understanding the bidirectional interactions between two-dimensional materials, microorganisms, and the immune system. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2022, 188: 114422. |
| [17] | CHANG T H, LI K, YANG H, et al. Multifunctionality and mechanical actuation of 2D materials for skin-mimicking capabilities. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(47): 1802418. |
| [18] | KIM J, LEE Y, KANG M, et al. 2D Materials for skin-mountable electronic devices. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(47): 2005858. |
| [19] |
KIM H S, SUN X, LEE J H, et al. Advanced drug delivery systems and artificial skin grafts for skin wound healing. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2019, 146: 209.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
OLSSON M, JÄRBRINK K, DIVAKAR U, et al. The humanistic and economic burden of chronic wounds: a systematic review. Wound Repair and Regeneration, 2019, 27(1): 114.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | PEÑA O A, MARTIN P. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of skin wound healing. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2024, 25(8): 599. |
| [22] |
XUE M, ZHAO R, LIN H, et al. Delivery systems of current biologicals for the treatment of chronic cutaneous wounds and severe burns. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2018, 129: 219.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | TU C, LU H, ZHOU T, et al. Promoting the healing of infected diabetic wound by an anti-bacterial and nano-enzyme-containing hydrogel with inflammation-suppressing, ROS-scavenging, oxygen and nitric oxide-generating properties. Biomaterials, 2022, 286: 121597. |
| [24] | WANG G, YANG F, ZHOU W, et al. The initiation of oxidative stress and therapeutic strategies in wound healing. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2023, 157: 114004. |
| [25] | PEREIRA R F, BARRIAS C C, GRANJA P L, et al. Advanced biofabrication strategies for skin regeneration and repair. Nanomedicine, 2013, 8(4): 603. |
| [26] |
ZHAO J, LI T, YUE Y, et al. Advancements in employing two-dimensional nanomaterials for enhancing skin wound healing: a review of current practice. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2024, 22(1): 520.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | TU Y, LV M, XIU P, et al. Destructive extraction of phospholipids from Escherichia coli membranes by graphene nanosheets. Nature Nanotechnology, 2013, 8(8): 594. |
| [28] | RASOOL K, HELAL M, ALI A, et al. Antibacterial activity of Ti3C2Tx MXene. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(3): 3674. |
| [29] |
AKHAVAN O, GHADERI E. Toxicity of graphene and graphene oxide nanowalls against bacteria. ACS Nano, 2010, 4(10): 5731.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | PULINGAM T, THONG K L, APPATURI J N, et al. Mechanistic actions and contributing factors affecting the antibacterial property and cytotoxicity of graphene oxide. Chemosphere, 2021, 281: 130739. |
| [31] | SONG W, WANG D, XIAO S, et al. NIR-II-amplify high-entropy MXene-based sonosensitizer as sonodynamic therapy promotes methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-infected wound healing. Materials & Design, 2024, 240: 112857. |
| [32] | SEIDI F, SHAMSABADI A A, FIROUZJAEI M D, et al. MXenes antibacterial properties and applications: a review and perspective. Small, 2023, 19(14): e2206716. |
| [33] | WANG T, SUN X, GUO X, et al. Ultraefficiently calming cytokine storm using Ti3C2Tx MXene. Small Methods, 2021, 5(5): 2001108. |
| [34] | CAI Q, LI L H, MATETI S, et al. Boron nitride nanosheets: thickness-related properties and applications. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(40): 2403669. |
| [35] | CHUNG J Y, YUAN Y, MISHRA T P, et al. Structure and exfoliation mechanism of two-dimensional boron nanosheets. Nature Communications, 2024, 15: 6122. |
| [36] | ALI S, RAZA A, AFZAL A M, et al. Recent advances in 2D-MXene based nanocomposites for optoelectronics. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2022, 9(31): 2200556. |
| [37] | SO Y, YIM D, SON W, et al. Deciphering the therapeutic mechanism of topical WS2nanosheets for the effective therapy of burn injuries. Applied Materials Today, 2022, 29: 101591. |
| [38] | BANERJEE A N. Graphene and its derivatives as biomedical materials: future prospects and challenges. Interface Focus, 2018, 8(3): 20170056. |
| [39] | SHARIATI A, HOSSEINI S M, CHEGINI Z, et al. Graphene- based materials for inhibition of wound infection and accelerating wound healing. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2023, 158: 114184. |
| [40] |
HUANG H, FENG W, CHEN Y. Two-dimensional biomaterials: material science, biological effect and biomedical engineering applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(20): 11381.
DOI PMID |
| [41] | ZHANG B, HE J, SHI M, et al. Injectable self-healing supramolecular hydrogels with conductivity and photo-thermal antibacterial activity to enhance complete skin regeneration. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 400: 125994. |
| [42] | MARCO P, LAURA F, VERONICA L, et al. Differential cytotoxic effects of graphene and graphene oxide on skin keratinocytes. Chemical Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 40572. |
| [43] |
YANG K, LI Y, TAN X, et al. Behavior and toxicity of graphene and its functionalized derivatives in biological systems. Small, 2013, 9(9/10): 1492.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
SASIDHARAN A, PANCHAKARLA L S, SADANANDAN A R, et al. Hemocompatibility and macrophage response of pristine and functionalized graphene. Small, 2012, 8(8): 1251.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
LI Y, LIU Y, FU Y, et al. The triggering of apoptosis in macrophages by pristine graphene through the MAPK and TGF-beta signaling pathways. Biomaterials, 2012, 33(2): 402.
DOI PMID |
| [46] | WU N, YANG W, CHE S, et al. Green preparation of high-yield and large-size hydrophilic boron nitride nanosheets by tannic acid- assisted aqueous ball milling for thermal management. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2023, 164: 107266. |
| [47] | CHEN C, YU B, JIA H, et al. Efficient preparation of hydrophilic boron nitride nanosheets for human heat dissipation applications. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2024, 7(10): 11487. |
| [48] | LV J, QI Y, TIAN Y, et al. Functionalized boron nanosheets with near-infrared-triggered photothermal and nitric oxide release activities for efficient antibacterial treatment and wound healing promotion. Biomaterials Science, 2022, 10(14): 3747. |
| [49] |
PELEGRINO M T, WELLER R B, CHEN X, et al. Chitosan nanoparticles for nitric oxide delivery in human skin. MedChemComm, 2017, 8(4): 713.
DOI PMID |
| [50] |
CARPENTER A W, SCHOENFISCH M H. Nitric oxide release: part II. Therapeutic applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(10): 3742.
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
LIU Y, QIU Z, CARVALHO A, et al. Gate-tunable giant Stark effect in few-layer black phosphorus. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(3): 1970.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
MAO C, XIANG Y, LIU X, et al. Repeatable photodynamic therapy with triggered signaling pathways of fibroblast cell proliferation and differentiation to promote bacteria-accompanied wound healing. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(2): 1747.
DOI PMID |
| [53] |
GE J, LAN M, ZHOU B, et al. A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4596.
DOI PMID |
| [54] | WALIA S, BALENDHRAN S, AHMED T, et al. Ambient protection of gew-layer black phosphorus via sequestration of reactive oxygen species. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(27): 1700152. |
| [55] |
TONG L, LIAO Q, ZHAO Y, et al. Near-infrared light control of bone regeneration with biodegradable photothermal osteoimplant. Biomaterials, 2019, 193: 1.
DOI PMID |
| [56] | DING Q, SUN T, SU W, et al. Bioinspired multifunctional black phosphorus hydrogel with antibacterial and antioxidant properties: a stepwise countermeasure for diabetic skin wound healing. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2022, 11(12): 2102791. |
| [57] | LUO X, ZHANG L, LUO Y, et al. Charge-driven self-assembled microspheres hydrogel scaffolds for combined drug delivery and photothermal therapy of diabetic wounds. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(26): 2214036. |
| [58] | SHAO J, XIE H, HUANG H, et al. Biodegradable black phosphorus-based nanospheres for in vivo photothermal cancer therapy. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 12967. |
| [59] | WANG H, YANG X, SHAO W, et al. Ultrathin black phosphorus nanosheets for efficient singlet oxygen generation. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(35): 11376. |
| [60] |
LV R, ROBINSON J A, SCHAAK R E, et al. Transition metal dichalcogenides and beyond: synthesis, properties, and applications of single- and few-layer nanosheets. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2015, 48(1): 56.
DOI PMID |
| [61] | LIN Y C, DUMCENCO D O, HUANG Y S, et al. Atomic mechanism of the semiconducting-to-metallic phase transition in single-layered MoS2. Nature Nanotechnology, 2014, 9(5): 391. |
| [62] |
ZHANG H. Ultrathin two-dimensional nanomaterials. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(10): 9451.
DOI PMID |
| [63] |
SPLENDIANI A, SUN L, ZHANG Y, et al. Emerging photoluminescence in monolayer MoS2. Nano Letters, 2010, 10(4): 1271.
DOI PMID |
| [64] | SUN Y, LI Y, DING X, et al. An NIR-responsive hydrogel loaded with polydeoxyribonucleotide nano-vectors for enhanced chronic wound healing. Biomaterials, 2025, 314: 122789. |
| [65] | ZHAO Y, XU J, JIANG X. DNA cleavage by chemically exfoliated molybdenum disulfide nanosheets. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(6): 4037. |
| [66] | WANG P, WU J, XIAO X, et al. Engineering injectable coassembled hydrogel by photothermal driven chitosan-stabilized MoS2 nanosheets for infected wound healing. ACS Nano, 2024, 18(39): 26961. |
| [67] | LI L, CHENG Q. Recent advances in the high performance MXenes nanocomposites. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(2): 153. |
| [68] | BARSOUM M W. The MN+1AXN phases: a new class of solids: thermodynamically stable nanolaminates. Progress in Solid State Chemistry, 2000, 28(1): 201. |
| [69] | LI Y, FU R, DUAN Z, et al. Artificial nonenzymatic antioxidant MXene aanosheet-anchored injectable hydrogel as a mild photothermal-controlled oxygen release platform for diabetic wound healing. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(5): 7486. |
| [70] |
REN X, HUO M, WANG M, et al. Highly catalytic niobium carbide (MXene) promotes hematopoietic recovery after radiation by free radical scavenging. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(6): 6438.
DOI PMID |
| [71] | WU Y, ZHENG W, XIAO Y, et al. Multifunctional, robust, and porous PHBV-GO/MXene composite membranes with good hydrophilicity, antibacterial activity, and platelet adsorption performance. Polymers, 2021, 13(21): 3748. |
| [72] | LUO R, DAI J, ZHANG J, et al. Accelerated skin wound healing by electrical stimulation. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2021, 10(16): 2100557. |
| [73] | VERDES M, MACE K, MARGETTS L, et al. Status and challenges of electrical stimulation use in chronic wound healing. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2022, 75: 102710. |
| [74] | ZHENG H, WANG S, CHENG F, et al. Bioactive anti- inflammatory, antibacterial, conductive multifunctional scaffold based on MXene@CeO2nanocomposites for infection-impaired skin multimodal therapy. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 424: 130148. |
| [75] |
LI D, HU X, ZHANG S. Biodegradation of graphene-based nanomaterials in blood plasma affects their biocompatibility, drug delivery, targeted organs and antitumor ability. Biomaterials, 2019, 202: 12.
DOI PMID |
| [76] | HAO J, SONG G, LIU T, et al. In vivo long-term biodistribution, excretion, and toxicology of PEGylated transition-metal dichalcogenides MS2 (M = Mo, W, Ti) nanosheets. Advanced Science, 2017, 4(1): 1600160. |
| [77] |
MA B, MARTÍN C, KURAPATI R, et al. Degradation-by-design: how chemical functionalization enhances the biodegradability and safety of 2D materials. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(17): 6224.
DOI PMID |
| [78] | ZHANG S, ZHANG X, LEI L, et al. pH-dependent degradation of layered black phosphorus: essential role of hydroxide ions. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(2): 467. |
| [79] | PATON K R, VARRLA E, BACKES C, et al. Scalable production of large quantities of defect-free few-layer graphene by shear exfoliation in liquids. Nature Materials, 2014, 13(6): 62. |
| [80] | TANG L, TAN J, NONG H, et al. Chemical vapor deposition growth of two-dimensional compound materials: controllability, material quality, and growth mechanism. Accounts of Materials Research, 2021, 2(1): 36. |
| [81] | GAO Y, HONG Y L, YIN L C, et al. Ultrafast growth of high-quality monolayer WSe2 on Au. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(29): 1700990. |
| [1] | 余升阳, 苏海军, 姜浩, 余明辉, 姚佳彤, 杨培鑫. 激光增材制造超高温氧化物陶瓷孔隙缺陷形成及抑制研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [2] | 刘江平, 管鑫, 唐振杰, 朱文杰, 罗永明. 含氮挥发性有机化合物催化氧化的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [3] | 马景阁, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料用于毛囊和毛发再生的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [4] | 张洪健, 赵梓壹, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料调控神经细胞功能及神经化组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [5] | 艾敏慧, 雷波. 微纳米生物活性玻璃: 功能化设计与血管化皮肤再生[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [6] | 王宇彤, 常江, 徐合, 吴成铁. 硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃促创面修复的研究进展:作用、机制和应用方式[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [7] | 马文平, 韩雅卉, 吴成铁, 吕宏旭. 无机活性材料在类器官研究领域的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [8] | 罗晓民, 乔志龙, 刘颍, 杨晨, 常江. 无机生物活性材料调控心肌再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [9] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [10] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [11] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [12] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [13] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [14] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [15] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||