无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 521-528.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220627 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20220627
所属专题: 【能源环境】污染物催化去除(202506); 【信息功能】MAX、MXene及其他二维材料(202506)
收稿日期:2022-10-25
修回日期:2022-12-02
出版日期:2023-01-11
网络出版日期:2023-01-11
通讯作者:
李晓燕, 副教授. E-mail: lixiaoyan@usst.edu.cn;作者简介:王世怡(1996-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: wsysues051115114@163.com
WANG Shiyi1,2( ), FENG Aihu2, LI Xiaoyan1(
), FENG Aihu2, LI Xiaoyan1( ), YU Yun2(
), YU Yun2( )
)
Received:2022-10-25
Revised:2022-12-02
Published:2023-01-11
Online:2023-01-11
Contact:
LI Xiaoyan, associate professor. E-mail: lixiaoyan@usst.edu.cn;About author:WANG Shiyi (1996-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: wsysues051115114@163.com
摘要:
Ti3C2Tx MXene材料具有二维层状结构及丰富的表面官能团, 是一种非常有潜力的重金属离子吸附材料, 但其层间距较小, 且在水溶液中的稳定性较差。本工作探索了Ti3C2Tx的改性策略, 提高其化学稳定性与离子吸附容量, 利用一步水热方法制备出不同Fe3O4掺杂量的Fe3O4-Ti3C2Tx(FeMX)复合吸附剂材料。研究结果表明:FeMX吸附剂对Pb(II)的理论饱和吸附量可达到210.54 mg/g。研究进一步揭示了FeMX材料对Pb(II)离子的吸附机理, Fe3O4纳米颗粒均匀分散、插层在Ti3C2Tx纳米片层间, 有效增加了Ti3C2Tx纳米片的比表面积与层间距, 提高了对Pb(II)的去除能力。本研究可为发展优异重金属离子吸附特性的MXene基复合材料提供基础数据。
中图分类号:
王世怡, 冯爱虎, 李晓燕, 于云. Fe3O4负载Ti3C2Tx对Pb(II)的吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 521-528.
WANG Shiyi, FENG Aihu, LI Xiaoyan, YU Yun. Pb (II) Adsorption Process of Fe3O4 Supported Ti3C2Tx[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 521-528.
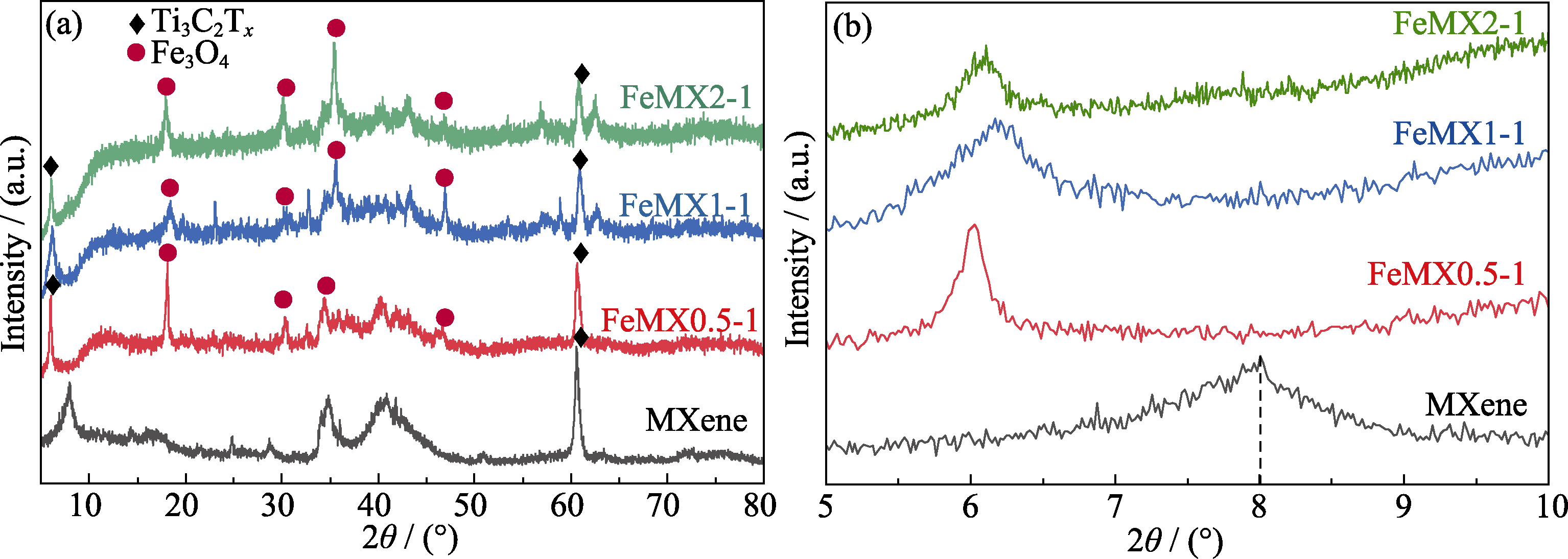
图1 Ti3C2Tx MXene、FeMX0.5-1、FeMX1-1、FeMX2-1样品的XRD图谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of Ti3C2Tx MXene, FeMX0.5-1, FeMX1-1 and FeMX2-1 samples (b) Enlarged XRD patterns of (002) crystalline

图2 (a)Fe3O4掺杂Ti3C2Tx MXene示意图; Ti3AlC2(b)、Ti3C2Tx(c)和FeMX1-1(d)样品SEM照片; (e)FeMX1-1样品不同元素分布情况
Fig. 2 (a) Diagram of Ti3C2Tx MXene doped with Fe3O4; SEM images of (b)Ti3AlC2, (c)Ti3C2Tx and (d) FeMX1-1 sample; (e)Elements distributions of FeMX1-1 sample Colorful figures are available on website
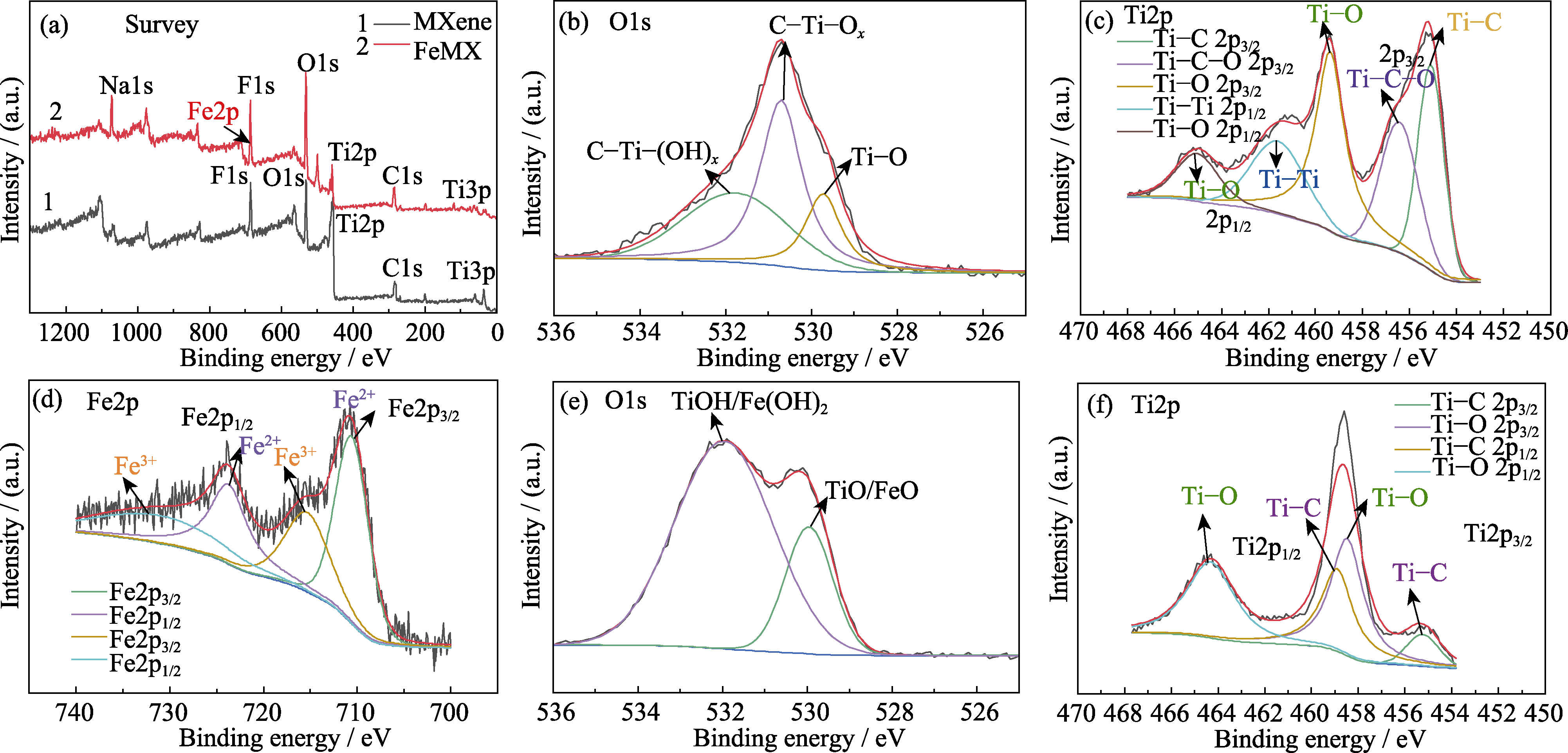
图4 (a)MXene和FeMX样品的XPS全谱; MXene材料的(b)O1s和(c)Ti2p图谱; FeMX复合材料的(d)Fe2p, (e)O1s和(f)Ti2p图谱
Fig. 4 (a) XPS spectra of FeMX before and after doping; (b) O1s and (c) Ti2p spectra of MXene materials; (d) Fe2p, (e) O1s and (f) Ti2p spectra of FeMX composite
| Temperature | Langmiur | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | Qm/(mg·g-1) | R2 | KF | n | R2 | |
| 30 ℃ | 0.05 | 110.54 | 0.8327 | 32.80 | 0.20 | 0.9881 |
| 40 ℃ | 0.21 | 126.04 | 0.8854 | 76.09 | 0.12 | 0.9435 |
| 50 ℃ | 0.29 | 120.24 | 0.9190 | 62.61 | 0.09 | 0.9934 |
表S1 不同温度下FeMX1-1对Pb(II)的吸附的Langmuir和Freundlich等温吸附模型的拟合参数
Table 1 Fitting parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich isothermal adsorption models for Pb (II) adsorption by FeMX1-1 at different temperatures
| Temperature | Langmiur | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | Qm/(mg·g-1) | R2 | KF | n | R2 | |
| 30 ℃ | 0.05 | 110.54 | 0.8327 | 32.80 | 0.20 | 0.9881 |
| 40 ℃ | 0.21 | 126.04 | 0.8854 | 76.09 | 0.12 | 0.9435 |
| 50 ℃ | 0.29 | 120.24 | 0.9190 | 62.61 | 0.09 | 0.9934 |
| Absorbance | Langmiur | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | Qm/(mg·g-1) | R2 | KF | n | R2 | |
| MXene | 0.0177 | 110.23 | 0.86006 | 15.8026 | 0.30 | 0.9106 |
| FeMX0.5-1 | 0.1652 | 149.63 | 0.99028 | 67.9776 | 0.14 | 0.90833 |
| FeMX1-1 | 0.2781 | 126.04 | 0.88536 | 76.0907 | 0.09 | 0.94345 |
| FeMX2-1 | 0.0139 | 210.54 | 0.97478 | 22.1793 | 0.36 | 0.91117 |
表S2 不同掺杂比例FeMX对Pb(II)的吸附的Langmuir和Freundlich等温吸附模型的拟合参数
Table S2 Fitting parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich isothermal adsorption models for Pb (II) adsorption by FeMX with different doping ratios
| Absorbance | Langmiur | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | Qm/(mg·g-1) | R2 | KF | n | R2 | |
| MXene | 0.0177 | 110.23 | 0.86006 | 15.8026 | 0.30 | 0.9106 |
| FeMX0.5-1 | 0.1652 | 149.63 | 0.99028 | 67.9776 | 0.14 | 0.90833 |
| FeMX1-1 | 0.2781 | 126.04 | 0.88536 | 76.0907 | 0.09 | 0.94345 |
| FeMX2-1 | 0.0139 | 210.54 | 0.97478 | 22.1793 | 0.36 | 0.91117 |
| Absorbance | Pseudo first-order reaction | Pseudo second-order reaction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/min-1 | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R2 | k2/(g·(mg·min) -1) | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R2 | |
| MXene | 2.0966 | 104.22 | 0.98786 | 0.4378 | 108.85 | 0.99402 |
| FeMX0.5-1 | 0.6308 | 173.65 | 0.95009 | 0.0039 | 201.10 | 0.98103 |
| FeMX1-1 | 0.7447 | 148.66 | 0.90406 | 0.0053 | 171.57 | 0.95077 |
| FeMX2-1 | 1.1093 | 184.59 | 0.97027 | 0.0076 | 204.46 | 0.99135 |
表S3 不同掺杂比例FeMX复合材料对Pb(II)的吸附的拟一阶和拟二阶动力学吸附模型的拟合参数
Table S3 Fitting parameters of pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic adsorption models for Pb (II) adsorption by FeMX composites with different doping ratios
| Absorbance | Pseudo first-order reaction | Pseudo second-order reaction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/min-1 | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R2 | k2/(g·(mg·min) -1) | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R2 | |
| MXene | 2.0966 | 104.22 | 0.98786 | 0.4378 | 108.85 | 0.99402 |
| FeMX0.5-1 | 0.6308 | 173.65 | 0.95009 | 0.0039 | 201.10 | 0.98103 |
| FeMX1-1 | 0.7447 | 148.66 | 0.90406 | 0.0053 | 171.57 | 0.95077 |
| FeMX2-1 | 1.1093 | 184.59 | 0.97027 | 0.0076 | 204.46 | 0.99135 |

图7 (a)FeMX1-1样品吸附Pb(II)前后XPS全谱; FeMX1-1样品吸附Pb(II)后的(b)Pb4f和(c)O1s图谱; (d)FeMX1-1样品吸附Pb(II)前后的Na1s图谱
Fig. 7 (a) XPS spectra of FeMX before and after Pb (II) adsorption ; (b) Pb4f and (c) O1s spectra of FeMX1-1 sample after Pb(II) adsorption; (d)Na1s spectra of FeMX1-1 sample before and after Pb(II) adsorption Colorful figures are available on website
| Absorbance | Condition | Adsorption property/ (mg·g-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolite A based on blast furnace slag | Shake for 60 min at room temperature, C0=50 mg/L | 39.37 | [S1] |
| MXene (Ti3C2Tx) | T=293 K, pH 6, C0=2 mg/L, 2 min contact time | ~90 | [S2] |
| Bead-supported MnFe2O4 nanoparticles | T=298 K, pH 5, C0= 20 mg/L, 2 h equilibrium time | 11.98 | [S3] |
| Polyhydroxyl-aluminum | T=298 K, shake for 270 min, C0=1500 mg/L, 150 min equilibrium time | 3.99 | [S4] |
| Peanut shell-based biochar | T=293 K, pH 5.5, C0=100 mg/L, 180 min contact time | 56.5 | [S5] |
| MnO2 modified magnetic graphitic carbon nitride composite | T=298 K, pH 6, C0=250 mg/L, shake for 270 min | 187.6 | [S6] |
| FeMX2-1 | T=313 K, pH 6, C0=500 mg/L, 3 h equilibrium time | 210.54 | This work |
表S4 现有吸附材料对Pb(II)的吸附性能与FeMX的对比
Table S4 Comparison of Pb(II) adsorption properties of existing adsorption materials and FeMX
| Absorbance | Condition | Adsorption property/ (mg·g-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolite A based on blast furnace slag | Shake for 60 min at room temperature, C0=50 mg/L | 39.37 | [S1] |
| MXene (Ti3C2Tx) | T=293 K, pH 6, C0=2 mg/L, 2 min contact time | ~90 | [S2] |
| Bead-supported MnFe2O4 nanoparticles | T=298 K, pH 5, C0= 20 mg/L, 2 h equilibrium time | 11.98 | [S3] |
| Polyhydroxyl-aluminum | T=298 K, shake for 270 min, C0=1500 mg/L, 150 min equilibrium time | 3.99 | [S4] |
| Peanut shell-based biochar | T=293 K, pH 5.5, C0=100 mg/L, 180 min contact time | 56.5 | [S5] |
| MnO2 modified magnetic graphitic carbon nitride composite | T=298 K, pH 6, C0=250 mg/L, shake for 270 min | 187.6 | [S6] |
| FeMX2-1 | T=313 K, pH 6, C0=500 mg/L, 3 h equilibrium time | 210.54 | This work |
| [1] |
FU L, YAN Z, ZHAO Q, et al. Novel 2D Nanosheets with potential applications in heavy metal purification: a review. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2018, 5(23): 1801094.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
WANG X, YANG S, SHI W, et al. Different interaction mechanisms of Eu (III) and (243) Am (III) with carbon nanotubes studied by batch, spectroscopy technique and theoretical calculation. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49(19): 11721.
DOI URL |
| [3] | CAI Y, WU C, LIU Z, et al. Fabrication of a phosphorylated graphene oxide-chitosan composite for highly effective and selective capture of U(VI). Environmental Science: Nano, 2017, 4(9): 1876. |
| [4] |
LIU Y, LÜ H, LIU Y, et al. Progresses on electrospun metal- organic frameworks nanofibers and their wastewater treatment applications. Materials Today Chemistry, 2022, 25: 100974.
DOI URL |
| [5] | LIU J, WEN X, ZHAO S Q, et al. Synthesis of the Zeolite a based on blast furnace slag and adsorption of Pb2+ ions. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2019, 48(6): 1129. |
| [6] |
LIU X, VERMA G, CHEN Z, et al. Metal-organic framework nanocrystal-derived hollow porous materials: synthetic strategies and emerging applications. The Innovation, 2022, 3(5): 100281.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ZHANG Y, LIU H, GAO F, et al. Application of MOFs and COFs for photocatalysis in CO2 reduction, H2 generation, and environmental treatment. EnergyChem, 2022, 4(4): 100078.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CHEN X, ZHAO Y, LI L, et al. MXene/Polymer nanocomposites: preparation, properties, and applications. Polymer Reviews, 2020, 61(1): 80.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
IBRAHIM Y, KASSAB A, EID K, et al. Unveiling fabrication and environmental remediation of MXene-based nanoarchitectures in toxic metals removal from wastewater: strategy and mechanism. Nanomaterials, 2020, 10: 885.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
NAGUIB M, KURTOGLU M, PRESSER V, et al. Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(37): 4248.
DOI URL |
| [11] | IHSANULLAH I. MXenes (two-dimensional metal carbides) as emerging nanomaterials for water purification: progress, challenges and prospects. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 388: 124300. |
| [12] |
CHEN J, HUANG Q, HUANG H, et al. Recent progress and advances in the environmental applications of MXene related materials. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(6): 3574.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
GHIDIU M, LUKATSKAYA M R, ZHAO M Q, et al. Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide 'clay' with high volumetric capacitance. Nature, 2014, 516(4): 78.
DOI |
| [14] | SHI W, WANG H, WANG L, et al. Adsorption of Eu(III) on alkalized Ti3C2Tx MXene studied by batch experiment and mechanism investigation. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 35(1): 65. |
| [15] |
WANG L, TAO W, YUAN L, et al. Rational control of the interlayer space inside two-dimensional titanium carbides for highly efficient uranium removal and imprisonment. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(89): 12084.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
GóMEZ-PASTORA J, DOMINGUEZ S, BRINGAS E, et al. Review and perspectives on the use of magnetic nanophotocatalysts (MNPCs) in water treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 310: 407.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
JANG J, SHAHZAD A, WOO S H, et al. Magnetic Ti3C2Tx (MXene) for diclofenac degradation via the ultraviolet/chlorine advanced oxidation process. Environmental Research, 2020, 182: 108990.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
YANG X, LIU Y, HU S, et al. Construction of Fe3O4@MXene composite nanofiltration membrane for heavy metal ions removal from wastewater. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2020, 32(3): 1000.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SHAHZAD A, RASOOL K, MIRAN W, et al. Mercuric ion capturing by recoverable titanium carbide magnetic nanocomposite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 344: 811.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
CUI Y, LIU M, HUANG H, et al. A novel one-step strategy for preparation of Fe3O4-loaded Ti3C2 MXenes with high efficiency for removal organic dyes. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(8): 11593.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
CUI Y, ZHANG D, SHEN K, et al. Biomimetic anchoring of Fe3O4 onto Ti3C2 MXene for highly efficient removal of organic dyes by fenton reaction. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(5): 104369.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHANG Q, TENG J, ZOU G, et al. Efficient phosphate sequestration for water purification by unique sandwich-like MXene/ magnetic iron oxide nanocomposites. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(13): 7085.
DOI URL |
| [23] | YU S, TANG H, ZHANG D, et al. MXenes as emerging nanomaterials in water purification and environmental remediation. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 811: 152280. |
| [24] | ZHANG P, XIANG M, LIU H, et al. Novel two-dimensional magnetic titanium carbide for Methylene Blue removal over a wide pH range: insight into removal performance and mechanism. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(27): 24027. |
| [25] |
DU Y, MA W, LIU P, et al. Magnetic CoFe2O4 nanoparticles supported on titanate nanotubes (CoFe2O4/TNTs) as a novel heterogeneous catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation and degradation of organic pollutants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 308: 58.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
JIN L, WANG J, WU F, et al. Tailoring MXene-based materials for sodium-ion storage: synthesis, mechanisms, and applications. Electrochemical Energy Reviews, 2020, 3(4): 766.
DOI |
| [27] |
YANG G, HU X, LIANG J, et al. Surface functionalization of MXene with chitosan through in-situ formation of polyimidazoles and its adsorption properties. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 419: 126220.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ZHANG C, PINILLA S, MCEVOY N, et al. Oxidation stability of colloidal two-dimensional titanium carbides (MXenes). Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29: 4848.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
YANG H, LU M, CHEN D, et al. Efficient and rapid removal of Pb2+ from water by magnetic Fe3O4@MnO2 core-shell nanoflower attached to carbon microtube: adsorption behavior and process study. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 563: 218.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
LI S S, JIANG M, JIANG T J, et al. Competitive adsorption behavior toward metal ions on nano-Fe/Mg/Ni ternary layered double hydroxide proved by XPS: evidence of selective and sensitive detection of Pb(II). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 338: 1.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
JUN B M, PARK C M, HEO J, et al. Adsorption of Ba2+ and Sr2+on Ti3C2Tx MXene in model fracking wastewater. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 256: 109940.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
LIU F, JIN Y, LIAO H, et al. Facile self-assembly synthesis of titanate/Fe3O4 nanocomposites for the efficient removal of Pb2+ from aqueous systems. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(3): 805.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 江宗玉, 黄红花, 清江, 王红宁, 姚超, 陈若愚. 铝离子掺杂MIL-101(Cr)的制备及其VOCs吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 747-753. |
| [2] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [3] | 刘会来, 李志豪, 孔德峰, 陈星. 酞菁铁/MXene复合阴极的制备及电芬顿降解磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 61-69. |
| [4] | 瞿牡静, 张淑兰, 朱梦梦, 丁浩杰, 段嘉欣, 代恒龙, 周国红, 李会利. CsPbBr3@MIL-53纳米复合荧光粉的合成、性能及其白光LEDs应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 1035-1043. |
| [5] | 潘建隆, 马官军, 宋乐美, 郇宇, 魏涛. 燃料还原法原位制备高稳定性/催化活性SOFC钴基钙钛矿阳极[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 911-919. |
| [6] | 苗鑫, 闫世强, 韦金豆, 吴超, 樊文浩, 陈少平. Te基热电器件反常界面层生长行为及界面稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 903-910. |
| [7] | 陈甜, 罗媛, 朱刘, 郭学益, 杨英. 有机-无机共添加增强柔性钙钛矿太阳能电池机械弯曲及环境稳定性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 477-484. |
| [8] | 杨博, 吕功煊, 马建泰. 镍铁氢氧化物-磷化钴复合电极电催化分解水研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 374-382. |
| [9] | 张宇晨, 陆知遥, 赫晓东, 宋广平, 朱春城, 郑永挺, 柏跃磊. 硫族MAX相硼化物的物相稳定性和性能预测[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 225-232. |
| [10] | 李雷, 程群峰. 高性能MXenes纳米复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 153-161. |
| [11] | 徐向明, Husam N ALSHAREEF. MXetronics—MXene电子学[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 171-178. |
| [12] | 李腊, 沈国震. 二维MXenes材料在柔性光电探测器中的应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 186-194. |
| [13] | 巴坤, 王建禄, 韩美康. MXene的红外特性及其应用研究展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 162-170. |
| [14] | 尹建宇, 刘逆霜, 高义华. MXene在压力传感中的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 179-185. |
| [15] | 邓顺桂, 张传芳. 多功能MXene油墨:面向印刷能源及电子器件的新视角[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 195-203. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||