无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 215-224.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230510 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20230510
所属专题: 【信息功能】MAX、MXene及其他二维材料(202506); 【能源环境】太阳能电池(202506)
收稿日期:2023-11-02
修回日期:2023-12-15
出版日期:2023-12-25
网络出版日期:2023-12-25
通讯作者:
汪德高, 研究员. E-mail: wangdegao@nimte.ac.cn作者简介:费 玲(1995-), 女, 硕士. E-mail: feiling@nimte.ac.cn
基金资助:
FEI Ling1,2( ), LEI Lei1,2, WANG Degao1,2,3(
), LEI Lei1,2, WANG Degao1,2,3( )
)
Received:2023-11-02
Revised:2023-12-15
Published:2023-12-25
Online:2023-12-25
Contact:
WANG Degao, professor. E-mail: wangdegao@nimte.ac.cnAbout author:FEI Ling (1995-), female, Master. E-mail: feiling@nimte.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
太阳能作为自然界中丰富的可持续清洁能源, 可以在解决当前能源短缺问题的同时有效减少因过度消耗化石燃料造成的环境污染问题。近年来, 第三代新型薄膜太阳能电池, 如染料敏化太阳能电池(DSSCs)和钙钛矿太阳能电池(PSCs)等, 凭借其原料丰富、制造成本低廉和光电性能良好等优点而受到广泛关注。然而, 新型薄膜太阳能电池器件的电荷传输性能和运行稳定性与正式商用的要求仍有一定差距。二维MXene材料具有比表面积高、表面官能团丰富、导电性优良、功函数可调和亲水性等优点, 已成为能源转换领域的研究热点。鉴于此, 本文在综述二维MXene材料的结构、光学和电学特性的基础上, 阐述了近些年二维MXene材料应用于新型薄膜太阳能电池的研究进展, 并重点探讨了二维MXene材料增强太阳能电池光电性能的机制。二维MXene材料可通过作为钙钛矿太阳能电池中钙钛矿层和电荷传输层的添加剂、修饰染料敏化太阳能电池的光电阳极和制备电极, 来调整能带对齐、降低功函数、拓宽吸光范围和形成“柱撑效应”, 有效改善器件的光吸收效率、载流子迁移率和电荷提取能力, 从而提升器件的光电性能和稳定性。最后, 结合目前的研究进展, 对二维MXene材料在新型薄膜太阳能电池技术中的发展前景及面临的挑战提出了建议。
中图分类号:
费玲, 雷蕾, 汪德高. 二维MXene材料在新型薄膜太阳能电池技术中的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 215-224.
FEI Ling, LEI Lei, WANG Degao. Progress of Two-dimensional MXene in New-type Thin-film Solar Cells[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(2): 215-224.
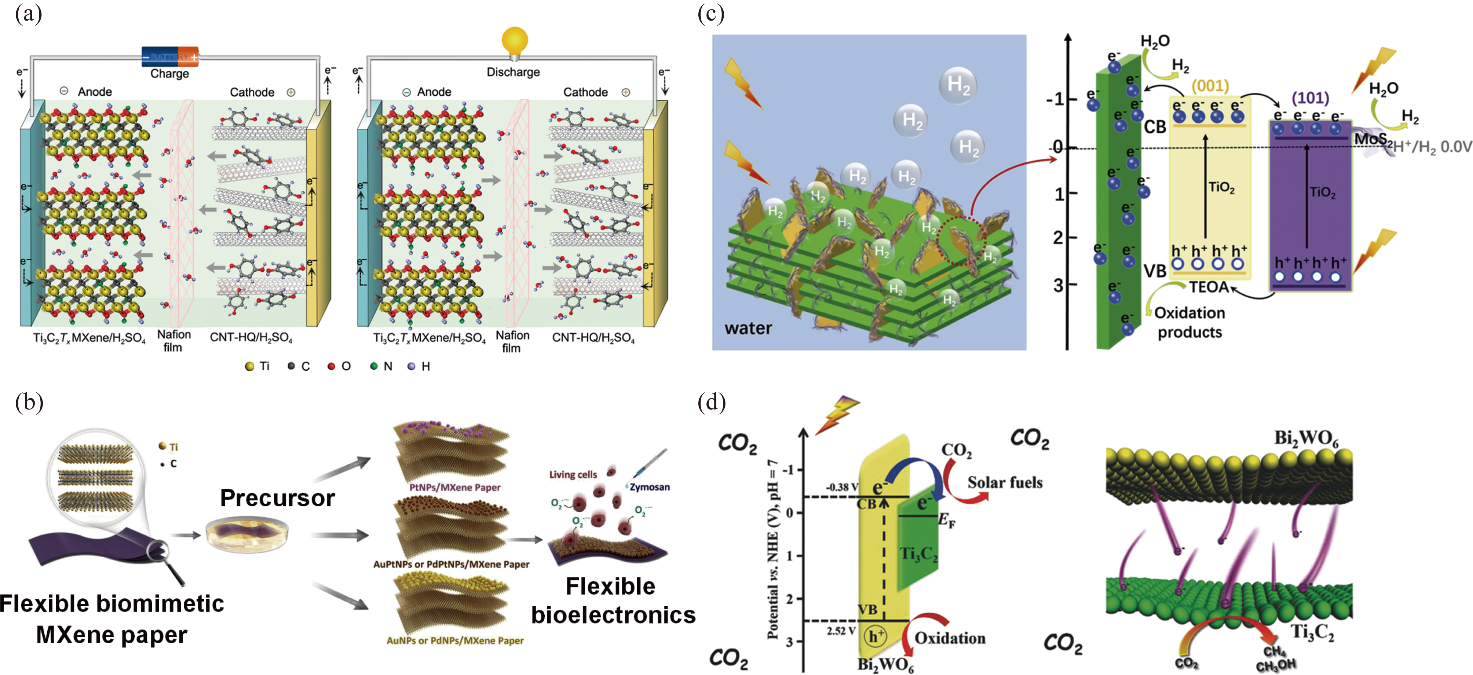
图1 二维MXene基纳米材料的应用[13,15,18-19]
Fig. 1 Application of 2D MXene-based nanomaterials[13,15,18-19] (a) Ti3C2Tx//CNT-HQ hybrid supercapacitors[13]; (b) Schematic diagram of flexible biomimetic Ti3C2 MXene-based platform for extracellular superoxide biosensing[15]; (c) Schematic photocatalytic water splitting mechanism for Ti3C2@TiO2@MoS2 composites[18]; (d) Schematic photocatalytic CO2 reduction for 2D/2D heterojunction of ultrathin Ti3C2/Bi2WO6 nanosheets[19]
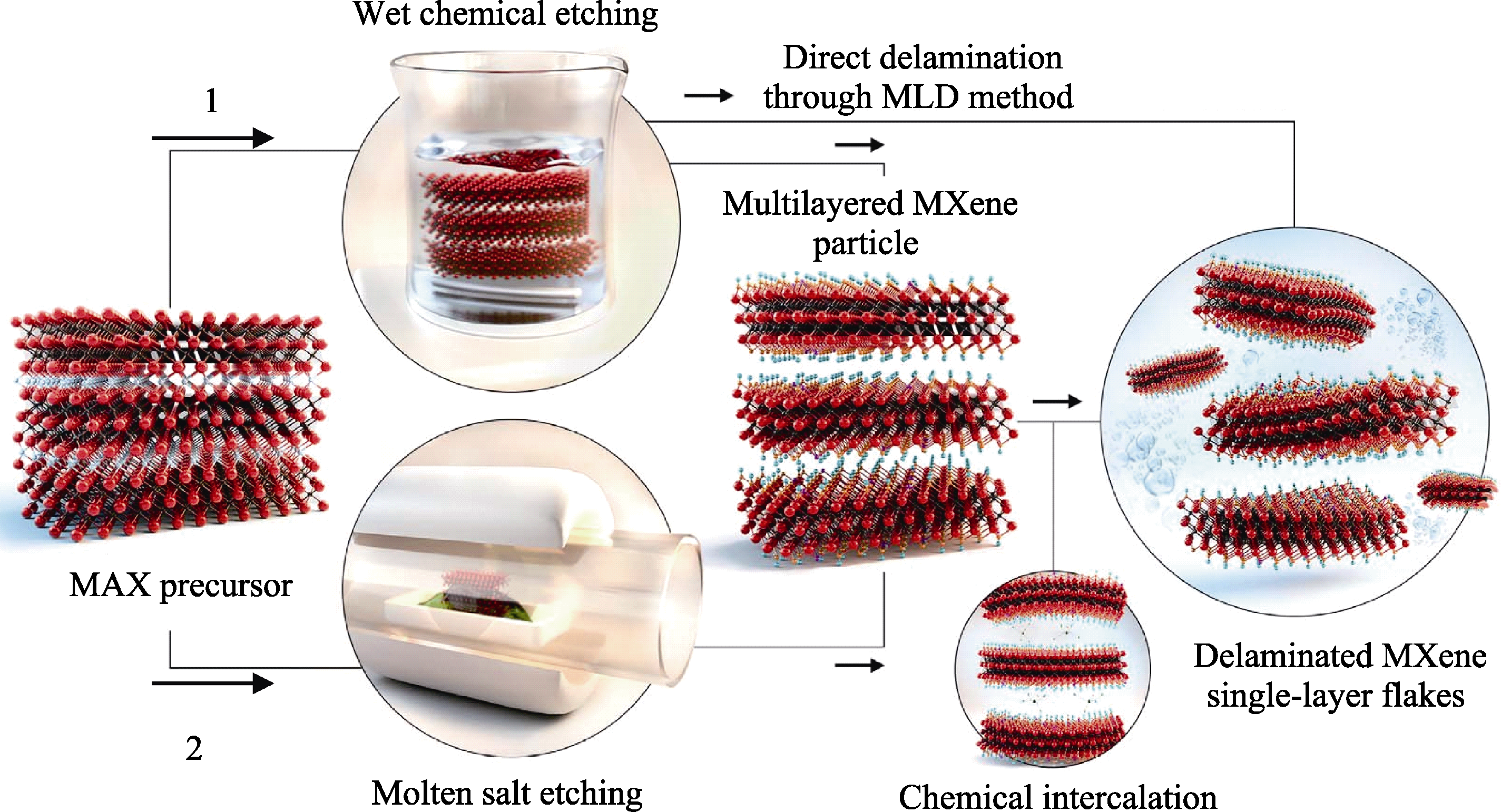
图2 MAX相选择性蚀刻A原子层制备MXene[24]
Fig. 2 Schematic illustration of two approaches to produce MXene by removal of A layers from MAX phases and related layered compounds[24] (1) MAX phase selectively etched in fluoride ion-containing acids; (2) MAX phase selectively etched in molten salts
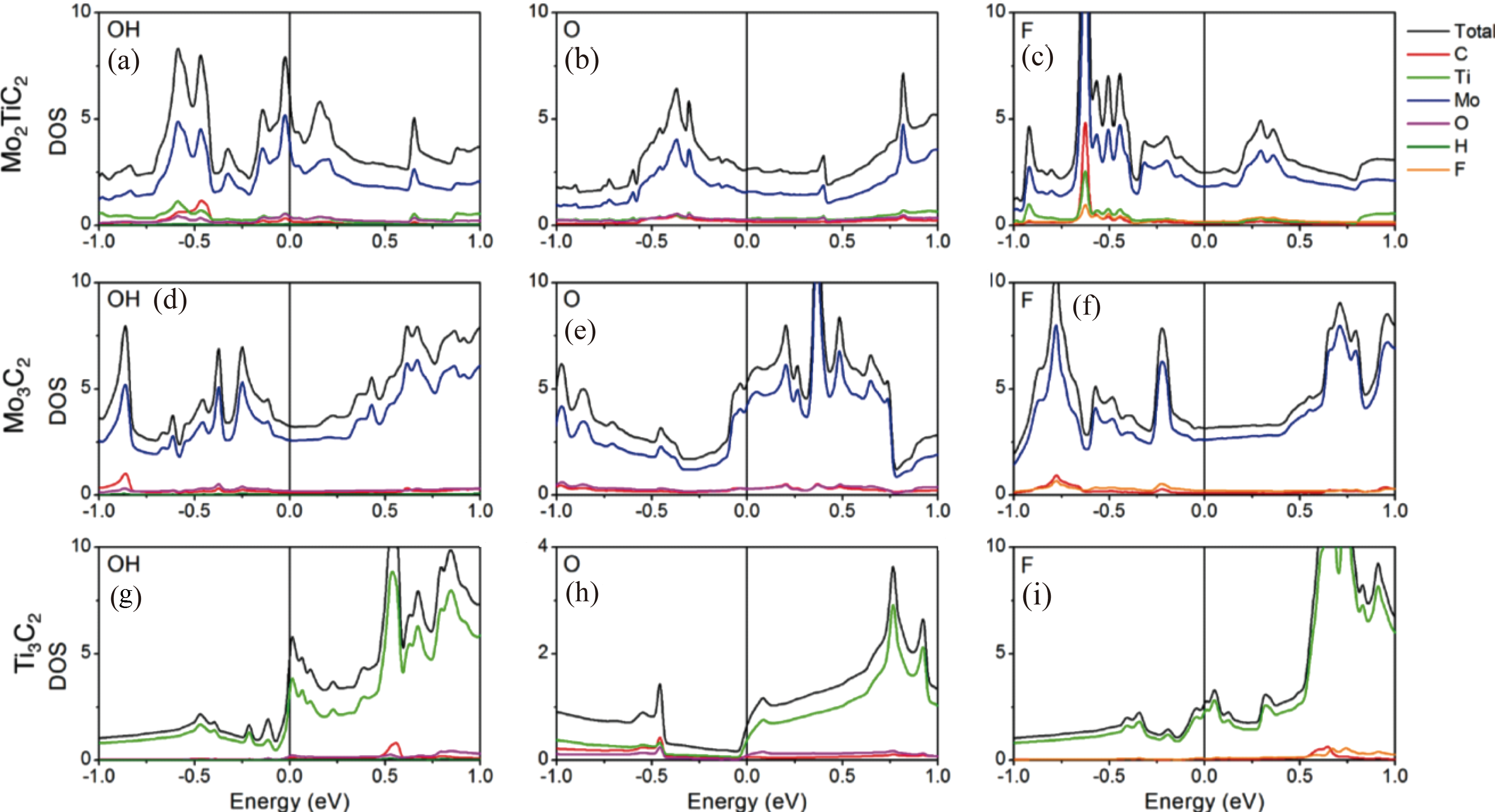
图4 Mo2TiC2, Mo3C和Ti3C MXene的电子结构[43]
Fig. 4 Electronic structures of Mo2TiC2, Mo3C and Ti3C MXene[43] (a-i) Total and projected densities of states for OH-, O-, and F-terminated Mo2TiC2 (a-c), Mo3C2 (d-f), and Ti3C2 (g-i) MXenes
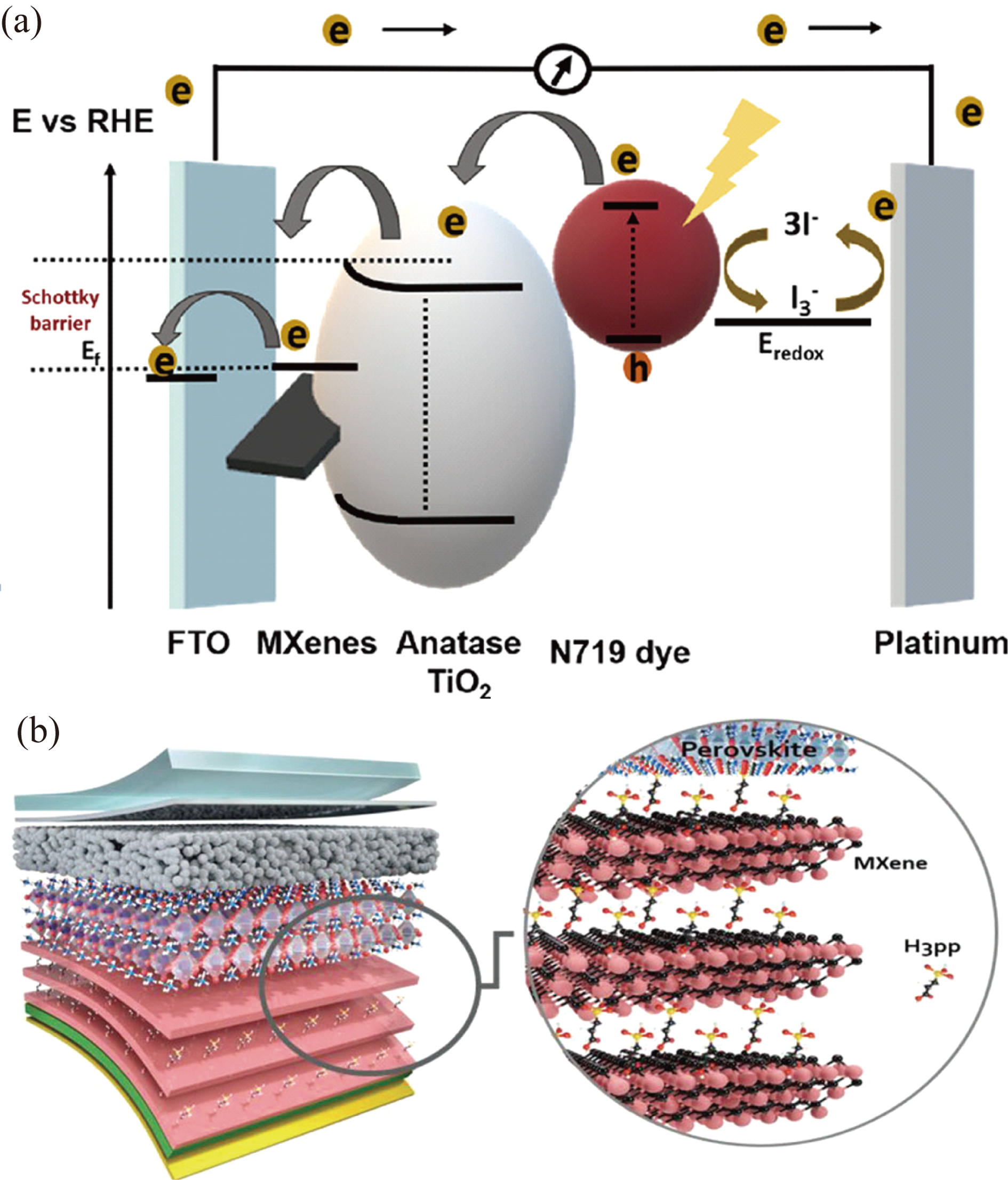
图6 新型薄膜太阳能电池结构[16-17]
Fig. 6 Structures of novel thin-film solar cells[16-17] (a) Schematic representation of a DSSC used the MXene[16]; (b) Schematic representation of a PSC used the MXene[17]
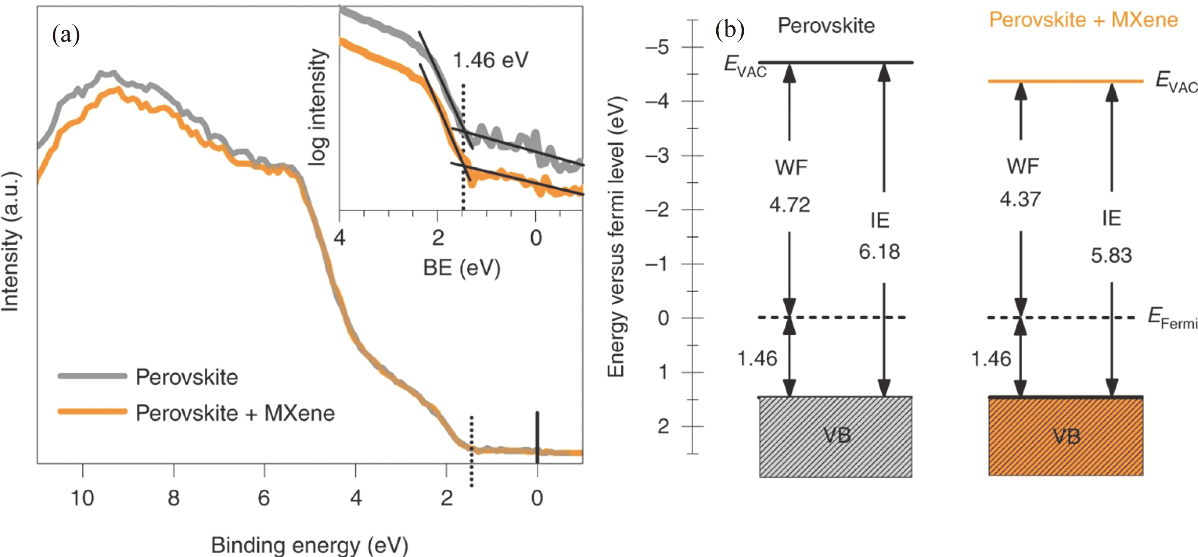
图7 原始PSC和掺杂MXene的PSC的UPS谱图和费米能级[42]
Fig. 7 UPS curves and energy versus Fermi level of pristine and MXene-doped perovskite films[42] (a) UPS spectra in the valence band (VB) region; (b) Energy scheme for undoped and MXene-doped perovskite with respect to the EFermi. IE: Ionization energy; EVAC: Vacuum level; BE: Binding energy
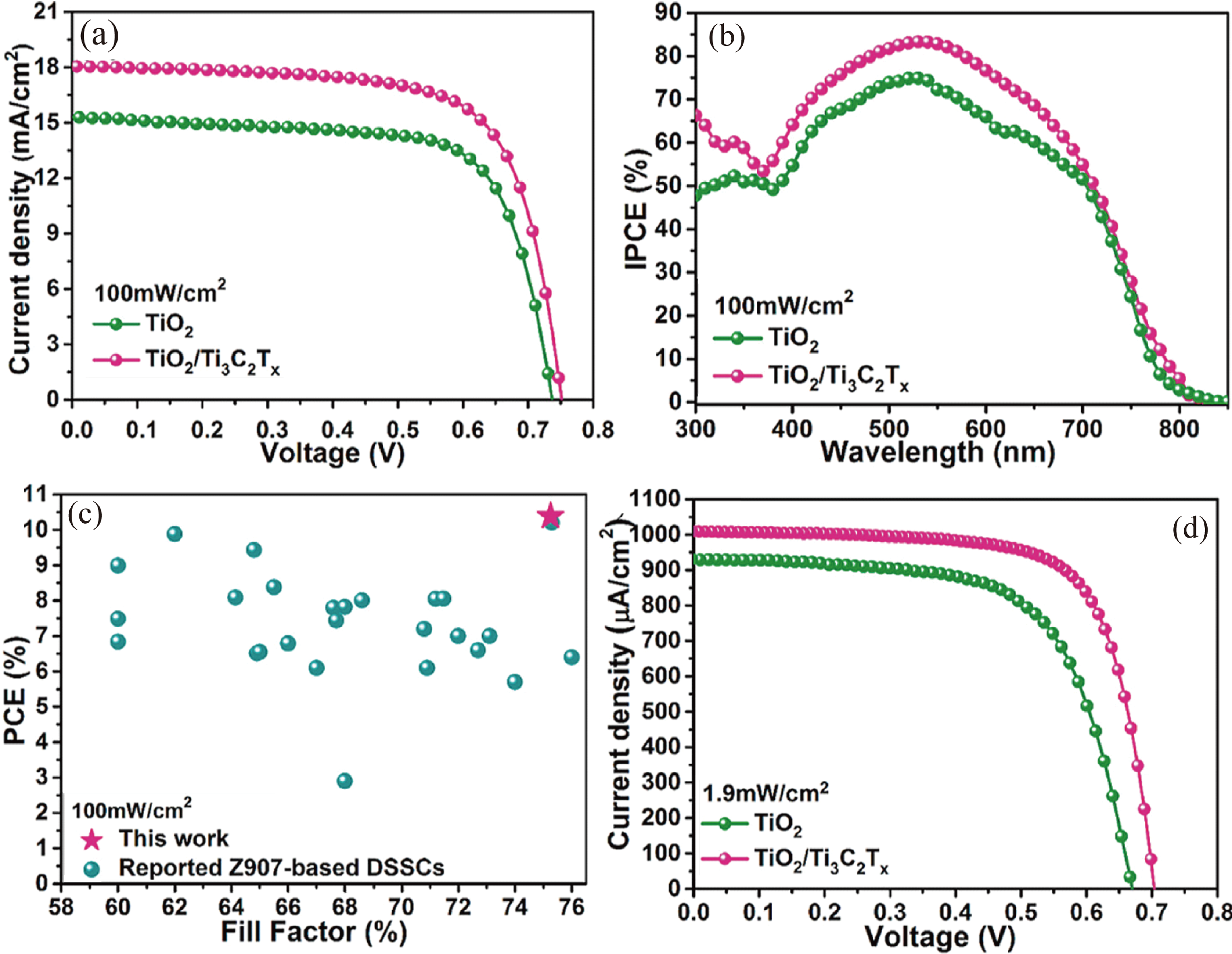
图8 TiO2/Ti3C2Tx光阳极性能[52]
Fig. 8 Photovoltaic performance of TiO2/Ti3C2Tx photoanode[52] (a, b) J-V curves (a) and IPCE curves (b) of champion DSSCs based on the TiO2 photoanode or TiO2/Ti3C2Tx photoanode under 100 mW/cm2; (c) Plots of PCE against FF of reported Z907-based DSSCs; (d) J-V curves of champion DSSCs based on the TiO2 photoanode or TiO2/Ti3C2Tx photoanode under dim light with an intensity of ∼1.9 mW/cm2 (6000 lux)
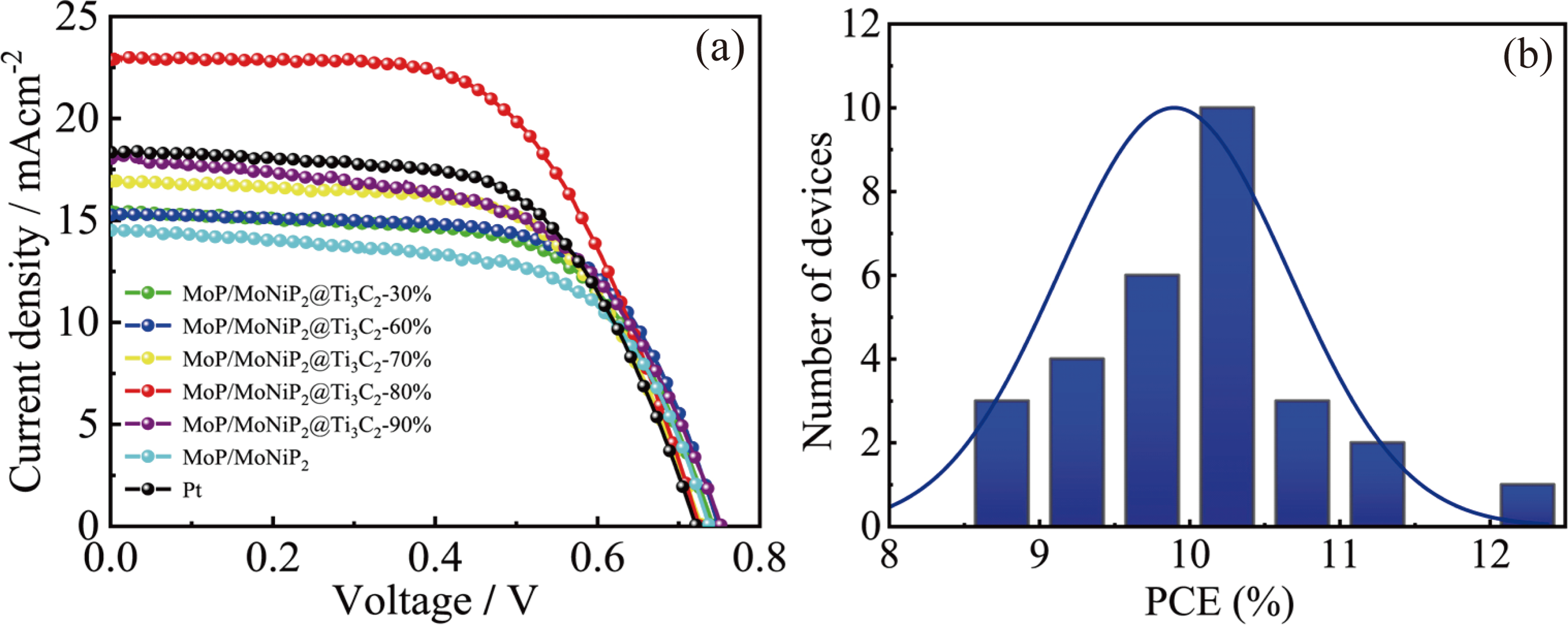
图9 MoP/MoNiP2@Ti3C2、MoP/MoNiP2和Pt对电极的光电性能比较[57]
Fig. 9 Photoelectric properties of MoP/MoNiP2@Ti3C2, MoP/MoNiP2 and Pt counter electrodes[57] (a) Photocurrent density-voltage curves of DSSCs with various CEs; (b) Distribution of PCEs of the DSSCs assembled with the MoP/MoNiP2@Ti3C2-80% CE; CE: counter electrode; PCE: power conversion efficiency
| [1] |
SUN Z Q, CHEN X Q, HE Y C, et al. Toward efficiency limits of crystalline silicon solar cells: recent progress in high-efficiency silicon heterojunction solar cells. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(23): 2200015.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
MATSUI T, SAI H, BIDIVILLE A, et al. Progress and limitations of thin-film silicon solar cells. Solar Energy, 2018, 170: 486.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
PARK J S, KIM S, XIE Z J, et al. Point defect engineering in thin-film solar cells. Nature Reviews Materials, 2018, 3: 194.
DOI |
| [4] |
LI F Z, JEN A K Y. Interface engineering in solution-processed thin- film solar cells. Accounts of Materials Research, 2022, 3(3): 272.
DOI URL |
| [5] | PRAJAPAT K, DHONDE M, SAHU K, et al. The evolution of organic materials for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Journal of Photochemistry & Photobiology, C: Photochemistry Reviews, 2023, 55: 100586. |
| [6] |
MA F, ZHAO Y, QU Z H, et al. Developments of highly efficient perovskite solar cells. Accounts of Materials Research, 2023, 4(8): 716.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
SOFER Z, WANG X Z, YU M H. MXene chemistry and applications. Small Methods, 2023, 7(8): 2300778.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
WANG G Y, PARK J M, KANG T, et al. Anion storage of MXene. Small Methods, 2023, 7(8): 2201440.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHU Y Y, Ma J X, DAS P, et al. High-voltage MXene-based supercapacitors: present status and future perspectives. Small Methods, 2023, 7: 2201609.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
ZHU Y Y, WANG S, MA J X, et al. Recent status and future perspectives of 2D MXene for micro-supercapacitors and micro-batteries. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 51: 500.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GUO Y, DU Z G, CAO Z J, et al. MXene derivatives for energy storage and conversions. Small Methods, 2023, 7(8): 2201559.
DOI URL |
| [12] | WANG X, LI H, LI H, et al. 2D/2D 1T-MoS2/Ti3C2 MXene heterostructure with excellent supercapacitor performance. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(15): 1910302. |
| [13] |
HU M M, CUI C, SHI C, et al. High-energy-density hydrogen- ion-rocking-chair-hybrid supercapacitors based on Ti3C2Tx MXene and carbon nanotubes mediated by redox active molecule. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(6): 6899.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MOSTAFAVI E, IRAVANI S. MXene-graphene composites: a perspective on biomedical potentials. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 14: 130.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
YAO Y, LAN L Y, LIU X X, et al. Spontaneous growth and regulation of noble metal nanoparticles on flexible biomimetic MXene paper for bioelectronics. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2019, 148(15): 111799.
DOI URL |
| [16] | LEMOS H G, RONCHI R M, PORTUGAL G R, et al. Efficient Ti3C2Tx MXene/TiO2 hybrid photoanodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Appliedl Energy Materials, 2022, 5(12): 15928. |
| [17] |
KARIMIPOUR M, PARAMBIL A P, TANKO K T, et al. Functionalized MXene/halide perovskite heterojunctions for perovskite solar cells stable under real outdoor conditions. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(44): 2301959.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LI Y J, YIN Z H, JI G R, et al. 2D/2D/2D heterojunction of Ti3C2 MXene/MoS2 nanosheets/TiO2 nanosheets with exposed (001) facets toward enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production activity. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 246: 12.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
CAO S W, SHEN B J, TONG T, et al. 2D/2D heterojunction of ultrathin MXene/Bi2WO6 nanosheets for improved photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(21): 1800136.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WANG H, PENG R, D. HOOD Z, et al. Titania composites with 2D transition metal carbides as photocatalysts for hydrogen production under visible-light irradiation. ChemSusChem, 2016, 9(12): 1490.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
YIN L J, LI Y T, YAO X C, et al. MXene for solar cells. Nano-Micro Letters, 2021, 13: 78.
DOI |
| [22] |
AFTAB S, LQBAL M Z, HUSSAIN S, et al. 2D MXene interface engineering for organic solar cells. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2023, 11: 13189.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
BATI A S R, BATMUNKH M, SHAPTER J G. Emerging 2D layered materials for perovskite solar cells. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(13): 1902253.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
VAHIDMOHAMMADI A, ROSEN J, GOGOTSL Y. The world of two-dimensional carbides and nitrides (MXenes). Science, 2021, 372(6547): eabf1581.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WEI Y, ZHANG P, A. SOOMRO R, et al. Advances in the synthesis of 2D MXenes. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(39): 2103148.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ZHU Q Z, LI J P, SIMON P, et al. Two-dimensional MXenes for electrochemical capacitor applications: progress, challenges and perspectives. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 35: 630.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
FU L, XIA W. MAX Phases as nanolaminate materials: chemical composition, microstructure, synthesis, properties, and applications. Advanced Engineering Material, 2021, 23(4): 2001191.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
HAEMERS J, GUSMAO R, SOFER Z. Synthesis protocols of the most common layered carbide and nitride MAX phases. Small Methods, 2020, 4(3): 1900780.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
ANASORI B, NAGUIB M, EDITORS G. Two-dimensional MXenes. MRS Bulletin, 2023, 48: 238.
DOI |
| [30] |
BJORK J, ROSEN J. Functionalizing MXenes by tailoring surface terminations in different chemical environments. Chemistry of Materials, 2021, 33(23): 9108.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
XIE X Q, ZHANG N. Positioning MXenes in the photocatalysis landscape: competitiveness, challenges, and future perspectives. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(36): 2002528.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
XU D X, LI Z D, LI L S, et al. Insights into the photothermal conversion of 2D MXene nanomaterials: synthesis, mechanism, and applications. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(47): 2000712.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
LING Z, E.REN C, ZHAO M Q, et al. Flexible and conductive MXene films and nanocomposites with high capacitance. PNAS, 2014, 111(47): 16676.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
ZHANG C F, ANASORI B, SER-ASCASO A, et al. Transparent, flexible, and conductive 2D titanium carbide (MXene) films with high volumetric capacitance. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(36): 1702678.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
BERDIYOROV G R. Optical properties of functionalized Ti3C2T2 (T=F, O, OH) MXene: first-principles calculations. AIP Advances, 2016, 6: 055105.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
LASHGAI H, ABOLHASSANI M R, BOOCHANI A, et al. Electronic and optical properties of 2D graphene-like compounds titanium carbides and nitrides: DFT calculations. Solid State Communications, 2014, 195: 61.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
BAI Y L, ZHOU K, SRIKANTH N, et al. Dependence of elastic and optical properties on surface terminated groups in two dimensional MXene monolayers: a first-principles study. RSC Advances, 2016, 6: 35731.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
JIANG X T, V KUKLIN A, BAEV A, et al. Two-dimensional MXenes: from morphological to optical, electric, and magnetic properties and applications. Physics Reports, 2020, 848: 1.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
ZHANG H J, YANG G, ZUO X Q, et al. Computational studies on the structural, electronic and optical properties of graphene-like MXenes (M2CT2, M = Ti, Zr, Hf; T = O, F, OH) and their potential applications as visible-light driven photocatalysts. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4: 12913.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
GUO T Z, ZHOU D, GAO M, et al. Large-area smooth conductive films enabled by scalable slot-die coating of Ti3C2Tx MXene aqueous inks. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(15): 2213183.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
WANG G, MA L J, LEI B X, et al. Enhanced electron transport through two-dimensional Ti3C2 in dye-sensitized solar cells. Rare Metals, 2022, 41: 3078.
DOI |
| [42] |
AGRESTI A, PAZNIAK A, PESCETELLI S, et al. Titanium- carbide MXenes for work function and interface engineering in perovskite solar cells. Nature Materials, 2019, 18: 1228.
DOI |
| [43] |
ANASORI B, XIE Y, BEIDAGHI M, et al. Two-dimensional, ordered, double transition metals carbides (MXenes). ACS Nano, 2015, 9(10): 9507.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
ZHA X H, LUO K, LI Q W, et al. Role of the surface effect on the structural, electronic and mechanical properties of the carbide MXenes. Europhysics Letters, 2015, 111(2): 26007.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
PENG J H, CHEN X Z, ONG W J, et al. Surface and heterointerface engineering of 2D MXenes and their nanocomposites: Insights into electro- and photocatalysis. Chem, 2019, 5: 18.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
LIU Y Y, XIAO H, GODDARD W A. Schottky-barrier-free contacts with two-dimensional semiconductors by surface-engineered MXenes. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(49): 15853.
PMID |
| [47] |
YANG L, LI P, MA J G, et al. MXenes for perovskite solar cells: Progress and prospects. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023, 81: 443.
DOI |
| [48] |
WANG K, SHI Y T, LI B, et al. Amorphous inorganic electron- selective layers for efficient perovskite solar cells: feasible strategy towards room-temperature fabrication. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(9): 1891.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
ZHAO YU, ZHANG X, HAN X F, et al. Tuning the reactivity of PbI2 film via monolayer Ti3C2Tx MXene for two-step-processed CH3NH3PbI3 solar cells. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 417: 127912.
DOI URL |
| [50] | D HANDOKO A, N STEINMANN S, WEI F X, et al. Theory- guided materials design: two-dimensional MXenes in electro- and photocatalysis. Nanoscale Norizons, 2019, 4: 1014. |
| [51] |
KUMAR S, KUMAR S, RAI R N. Recent development in two-dimensional material-based advanced photoanodes for high- performance dye-sensitized solar cells. Solar Energy, 2023, 249: 606.
DOI URL |
| [52] | HE S H, LAN Z, ZHANG B, et al. Holistically optimizing charge carrier dynamics enables high-performance dye-sensitized solar cells and photodetectors. ACS Applied Materials & Interface, 2022, 14(38): 43576. |
| [53] |
YANG L, HOU P F, WANG B N, et al. Performance improvement of dye-sensitized double perovskite solar cells by adding Ti3C2Tx MXene. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 446(2): 136963.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
DING S, YANG C Q, YUAN J, et al. An overview of the preparation and application of counter electrodes for DSSCs. RSC Advances, 2023, 13(18): 12309.
DOI PMID |
| [55] |
WEN S, HUANG J, LI T T, et al. Multiphase nanosheet-nanowire cerium oxide and nickel-cobalt phosphide for highly-efficient electrocatalytic overall water splitting. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 316: 121678.
DOI URL |
| [56] | WANG Z M, CHENG M, YU R B. Doping regulation in transition metal phosphides for hydrogen evolution catalysts. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2023, 43(11): 20220544. |
| [57] |
HE Y, YUE G, HUO J, et al. A dye-sensitized solar cells with an efficiency of 10.01% based on the MoP/MoNiP2@Ti3C2 composite counter electrode. Materials Today Sustainability, 2023, 22: 100329.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
ENYASHIN A N, IVANOVSKII A L. Two-dimensional titanium carbonitrides and their hydroxylated derivatives: structural, electronic properties and stability of MXenes Ti3C2-xNx(OH)2 from DFTB calculations. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2013, 207: 42.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
CHEN X Z, KONG Z Z, LI N, et al. Proposing the prospects of Ti3CN transition metal carbides (MXenes) as anodes of Li-ion batteries: a DFT study. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016, 18: 32937.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
LI Z R, WANG P L, LIANG Z H, et al. Bismuth nano-nest/Ti3CN quantum dot-based surface plasmon coupling electrochemiluminescence sensor for ascites miRNA-421 detection. Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 95(25): 9706.
DOI URL |
| [61] | YI D, WANG C, GAO L F, et al. Ti3CN MXene-based ultra- sensitive optical fiber salinity sensor. Optics Letters, 2022, 47(1): 1381. |
| [62] |
ZHANG W J, ZHENG Y B, MIAO Y P, et al. High-sensitivity optical fiber photothermal sensor for antibiotic detection with PDMS/Ti3CN MXene composite coating. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(3): 2220.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
GORDON K, ZHOU X D, FEI L. Carbonitride MXenes: an innovative catalyst support for sustainable hydrogen production. Chem Catalysis, 2023, 3(6): 100664.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
LI D Y, YANG C W, RAJENDRAN S, et al. Nanoflower-like Ti3CN@TiO2/CdS heterojunction photocatalyst for efficient photocatalytic water splitting. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(45): 19580.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
XU Y J, WANG F, LEI S, et al. In situ grown two-dimensional TiO2/Ti3CN MXene heterojunction rich in Ti3+ species for highly efficient photoelectrocatalytic CO2 reduction. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 452(3): 139392.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
MENG F N, GAO L G, YAN Y L, et al. Ultra-low-cost coal-based carbon electrodes with seamless interfacial contact for effective sandwich-structured perovskite solar cells. Carbon, 2019, 145: 290.
DOI URL |
| [67] | CAO J M, MENG F N, GAO L G, et al. Alternative electrodes for HTMs and noble-metal-free perovskite solar cells: 2D MXenes electrodes. RSC Advances, 2019, 59(9): 34152. |
| [1] | 陈曦, 袁媛, 谭业强, 刘昌胜. 无机非金属生物材料发展战略研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 449-456. |
| [2] | 倪晓萌, 许方贤, 刘静静, 张帅, 郭华飞, 袁宁一. 甲脒亚磺酸添加剂提升Sb2(S,Se)3薄膜质量及其光伏性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 372-378. |
| [3] | 刘会来, 李志豪, 孔德峰, 陈星. 酞菁铁/MXene复合阴极的制备及电芬顿降解磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 61-69. |
| [4] | 李世奇, 鲍群群, 胡萍, 施剑林. 基于乙二胺四乙酸插层锌铝双金属氢氧化物的晚期肿瘤抗转移免疫治疗研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 1044-1052. |
| [5] | 肖梓晨, 何世豪, 邱诚远, 邓攀, 张威, 戴维德仁, 缑炎卓, 李金华, 尤俊, 王贤保, 林俍佑. 钙钛矿太阳能电池纳米纤维改性电子传输层研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 828-834. |
| [6] | 张慧, 许志鹏, 朱从潭, 郭学益, 杨英. 大面积有机-无机杂化钙钛矿薄膜及其光伏应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 457-466. |
| [7] | 陈甜, 罗媛, 朱刘, 郭学益, 杨英. 有机-无机共添加增强柔性钙钛矿太阳能电池机械弯曲及环境稳定性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 477-484. |
| [8] | 于嫚, 高荣耀, 秦玉军, 艾希成. 上转换发光纳米材料对钙钛矿太阳能电池迟滞效应和离子迁移动力学的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 359-366. |
| [9] | 李雷, 程群峰. 高性能MXenes纳米复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 153-161. |
| [10] | 徐向明, Husam N ALSHAREEF. MXetronics—MXene电子学[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 171-178. |
| [11] | 李腊, 沈国震. 二维MXenes材料在柔性光电探测器中的应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 186-194. |
| [12] | 巴坤, 王建禄, 韩美康. MXene的红外特性及其应用研究展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 162-170. |
| [13] | 尹建宇, 刘逆霜, 高义华. MXene在压力传感中的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 179-185. |
| [14] | 刘艳艳, 谢曦, 刘增乾, 张哲峰. MAX相陶瓷增强金属基复合材料: 制备、性能与仿生设计[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 145-152. |
| [15] | 邓顺桂, 张传芳. 多功能MXene油墨:面向印刷能源及电子器件的新视角[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 195-203. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||