无机材料学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (3): 306-312.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200364 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20200364
武志红1( ), 邓悦1, 蒙真真1, 张国丽1, 张路平1,2, 王宇斌3
), 邓悦1, 蒙真真1, 张国丽1, 张路平1,2, 王宇斌3
收稿日期:2020-07-01
修回日期:2020-08-01
出版日期:2021-03-20
网络出版日期:2020-09-09
作者简介:武志红(1974-), 男, 博士, 副教授. E-mail: zhihong@xauat.edu.cn
基金资助:
WU Zhihong1( ), DENG Yue1, MENG Zhenzhen1, ZHANG Guoli1, ZHANG Luping1,2, WANG Yubin3
), DENG Yue1, MENG Zhenzhen1, ZHANG Guoli1, ZHANG Luping1,2, WANG Yubin3
Received:2020-07-01
Revised:2020-08-01
Published:2021-03-20
Online:2020-09-09
About author:WU Zhihong(1974-), male, PhD, associate professor. E-mail: zhihong@xauat.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
以葡萄糖、Si粉、碳纤维为原料, 采用化学镀结合高温烧结两步法制备了具有SiC阵列改性涂层的新型SiC/Cf复合材料。采用不同手段表征SiC/Cf复合材料的相组成、微观结构和吸波特性。结果表明: 碳纤维表面包覆大量结合紧密、垂直表面向外生长的SiC阵列, 且阵列分布均匀, 高度约为1.4 μm。当SiC/Cf复合材料厚度在1~2 mm范围内时, 随厚度增加, 最小反射损耗(RLmin)由高频向低频移动; 当厚度为1.8 mm时, 在8.31 GHz下的RLmin为-40.653 dB, 有效吸收带宽为1.11 GHz(RL < -10 dB); 当厚度为1.5 mm时, 有效吸收带宽可达2.42 GHz, 且厚度为1.3~1.8 mm时, RLmin均小于-20 dB。SiC阵列改性碳纤维新型SiC/Cf复合材料有望成为一种轻质高效的电磁波吸收材料。
中图分类号:
武志红, 邓悦, 蒙真真, 张国丽, 张路平, 王宇斌. 含SiC阵列改性涂层的新型SiC/Cf复合材料吸波性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 306-312.
WU Zhihong, DENG Yue, MENG Zhenzhen, ZHANG Guoli, ZHANG Luping, WANG Yubin. Microwave Absorbing Properties of Novel SiC/Cf Composites Containing SiC Array Modified Coating[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 306-312.
| Composition | NaH2PO2/ ( mol·L-1) | C6H5Na3O7·2H2O/ ( mol·L-1) | NiSO4/ ( mol·L-1) | NH4Cl/ ( mol·L-1) | H2O/mL | Temperature/℃ | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process conditions | 0.38 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 1.87 | 200 | (90±2) | 8-9 |
表1 镀液基本成分和工艺条件
Table 1 Basic composition and process conditions of plating solution
| Composition | NaH2PO2/ ( mol·L-1) | C6H5Na3O7·2H2O/ ( mol·L-1) | NiSO4/ ( mol·L-1) | NH4Cl/ ( mol·L-1) | H2O/mL | Temperature/℃ | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process conditions | 0.38 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 1.87 | 200 | (90±2) | 8-9 |
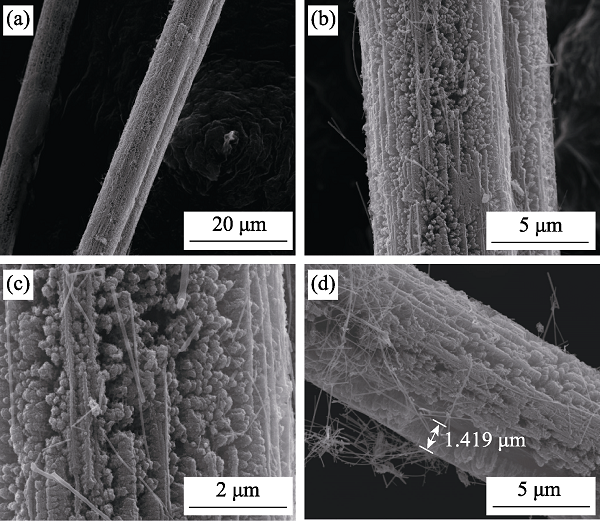
图2 SiC/Cf复合材料的SEM照片
Fig. 2 SEM images of SiC/Cf composite (a) SiC tightly wrapped on the Cf; (b) SiC uniformly distributed; (c) SiC orderly arranged and insulated; (d) A few SiC nanowires distributed
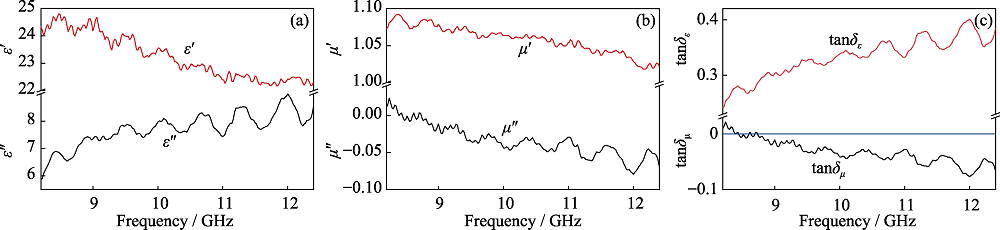
图3 SiC/Cf复合材料电磁参数
Fig. 3 Electromagnetic parameters of SiC/Cf composite (a) Real part (ε′) and imaginary part (ε″) of relative permittivity; (b) Real part (μ′) and imaginary part (μ″) of relative permeability; (c) Dielectric loss tangent (tanδε) and magnetic loss tangent (tanδμ)
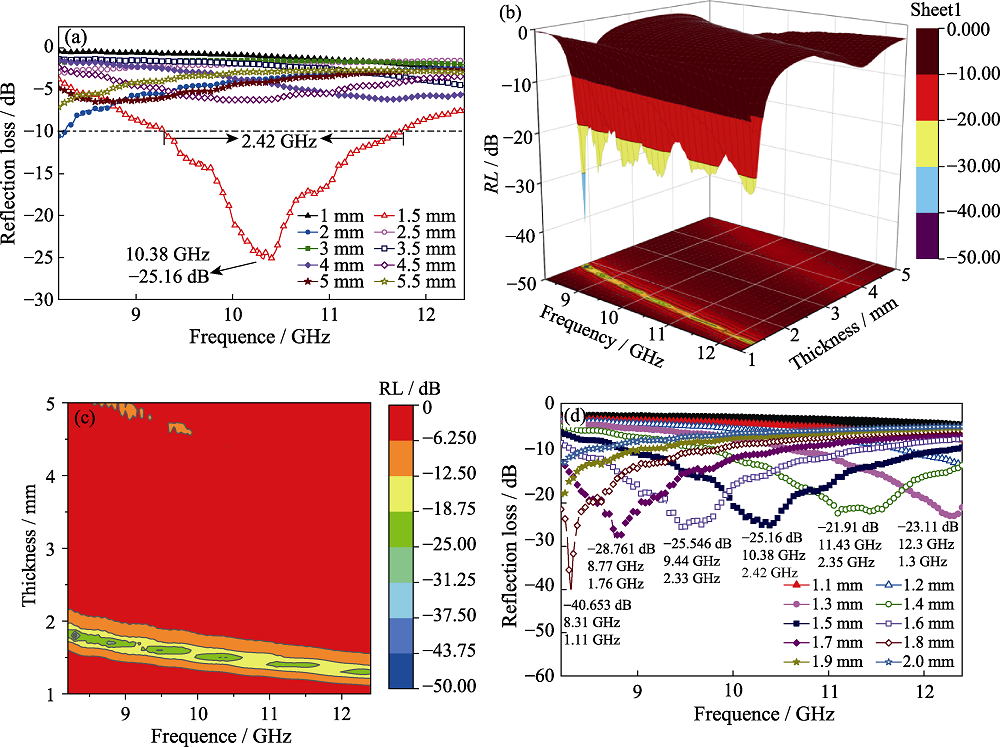
图5 SiC/Cf复合材料的RL图
Fig. 5 RL diagrams of SiC/Cf composite material RL value (a), 3D display RL value (b) and 3D RL value projection (c) with a thickness of 1-5.5 mm; RL value with thickness of 1.1-2.0 mm (d)
| Absorbent material | Thickness/mm | RLmin/dB | Frequency/GHz | Effective absorption bandwidth/GHz | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiCNW | 3.00 | -17.40 | 11.20 | 2.50 | [29] |
| SiCNW/Cf | 2.00 | -21.50 | 7.70 | 2.40 | [30] |
| SiCNW-Cf/LAS | 3.00 | -37.80 | 7.20 | <2.00 | [31] |
| ZnO/Cf | 4.35 | -33.00 | - | 5.10 | [32] |
| NiZn ferrite/BC | 2.00 | -11.00 | - | - | [33] |
| HPC/Fe3O4 | 5.50 | -20.10 | 11.76 | ~2.00 | [34] |
| SiC/Cf | 1.50 | -25.16 | 10.38 | 2.42 | This work |
| 1.80 | -40.66 | 8.31 | 1.11 | This work |
表2 SiC/Cf复合材料与其他同类不同结构材料的对比
Table 2 Comparison between SiC/Cf composite and other similar structural materials
| Absorbent material | Thickness/mm | RLmin/dB | Frequency/GHz | Effective absorption bandwidth/GHz | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiCNW | 3.00 | -17.40 | 11.20 | 2.50 | [29] |
| SiCNW/Cf | 2.00 | -21.50 | 7.70 | 2.40 | [30] |
| SiCNW-Cf/LAS | 3.00 | -37.80 | 7.20 | <2.00 | [31] |
| ZnO/Cf | 4.35 | -33.00 | - | 5.10 | [32] |
| NiZn ferrite/BC | 2.00 | -11.00 | - | - | [33] |
| HPC/Fe3O4 | 5.50 | -20.10 | 11.76 | ~2.00 | [34] |
| SiC/Cf | 1.50 | -25.16 | 10.38 | 2.42 | This work |
| 1.80 | -40.66 | 8.31 | 1.11 | This work |
| [1] | YE X L, CHEN Z F, AI S F, et al. Novel three-dimensional SiC/ melamine-derived carbon foam-reinforced SiO2 aerogel composite with low dielectric loss and high impedance matching ratio. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019,7(2):2774-2783. |
| [2] | 赵灵智, 胡社军, 李伟善 , 等. 吸波材料的吸波原理及其研究进展. 现代防御技术, 2007(1):27-31. |
| [3] | LIANG X H, ZHANG X M, LIU W, et al. A simple hydrothermal process to grow MoS2 nanosheets with excellent dielectric loss and microwave absorption performance. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2016,4(28):6816-6821. |
| [4] | JIANG Y, CHEN Y, LIU Y J, et al. Lightweight spongy bone-like graphene@SiC aerogel composites for high-performance microwave absorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018,337:522-531. |
| [5] | QIU J, WU X Y, QIU T T. High electromagnetic wave absorbing performance of activated hollow carbon fibers decorated with CNTs and Ni nanoparticles. Ceramics International, 2016,42(4):5278-5285. |
| [6] | 武志红, 李妤婕, 张聪 , 等. 竹炭/SiC复合材料结构及其吸波性能. 硅酸盐学报, 2018,46(1):150-155. |
| [7] | 刘丹莉, 刘平安, 杨青松 , 等. 吸波材料的研究现状及其发展趋势. 材料导报, 2013(17):77-81. |
| [8] | LI W W, CHEN M J, ZENG Z H, et al. Broadband composite radar absorbing structures with resistive frequency selective surface: optimal design, manufacturing and characterization. Composites Science and Technology, 2017,145:10-14. |
| [9] | CHOI W, KIM C. Broadband microwave-absorbing honeycomb structure with novel design concept. Composites Part B-Engineering, 2015,83:14-20. |
| [10] | LI W C, LI C S, LIN L H, et al. All-dielectric radar absorbing array metamaterial based on silicon carbide/carbon foam material. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019 ( 781):883-891. |
| [11] |
YE W, SUN Q L, ZHANG G Y. Effect of heat treatment conditions on properties of carbon-fiber-based electromagnetic-wave-absorbing composites. Ceramics International, 2019,45(4):5093-5099.
DOI URL |
| [12] | ADEBAYO L L, SOLEIMANI H, YAHYA N, et al. Recent advances in the development of Fe3O4-BASED microwave absorbing materials. Ceramics International, 2020,46(2):1249-1268. |
| [13] | LIU Y, ZHANG Z Q, XIAO S T, et al. Preparation and properties of cobalt oxides coated carbon fibers as microwave-absorbing materials. Applied Surface Science, 2011,257(17):7678-7683. |
| [14] | SONG Z M, LIU X F, SUN X, et al. Alginate-templated synthesis of CoFe/carbon fiber composite and the effect of hierarchically porous structure on electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Carbon, 2019,151:36-45. |
| [15] | CHEN X G, YE Y, CHENG J P. Recent progress in electromagnetic wave absorbers, Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011,26(5):449-457. |
| [16] | 吕晓艳, 田玉平, 魏云 , 等. 镍/碳纳米纤维复合物的制备及其吸波性能. 化学研究, 2016,27(6):756-759. |
| [17] | WU R B, YANG Z H, FU M S, et al. In-situ growth of SiC nanowire arrays on carbon fibers and their microwave absorption properties. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2016,687:833-838. |
| [18] | ZHOU W, LONG L, XIAO P, et al. Silicon carbide nano-fibers in-situ grown on carbon fibers for enhanced microwave absorption properties. Ceramics International, 2017,43(7):5628-5634. |
| [19] | WU Z H, ZHENG H K, ZHANG G L, et al. Synthesis of diameter- fluctuating silicon carbide nanowires for excellent microwave absorption. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2020,244:122648. |
| [20] | FU M, ZHU Z, ZHOU Y, et al. Multifunctional pompon flower- like nickel ferrites as novel pseudocapacitive electrode materials and advanced absorbing materials. Ceramics International, 2020,46(1):850-856. |
| [21] | LIANG C Y, WANG Z J. Eggplant-derived SiC aerogels with high- performance electromagnetic wave absorption and thermal insulation properties. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019,373:598-605. |
| [22] | DUAN Y, LIU Z, JING H, et al. Novel microwave dielectric response of Ni/Co-doped manganese dioxides and their microwave absorbing properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012,22(35):18291-18299. |
| [23] | DONG S, ZHANG X H, HU P T, et al. Biomass-derived carbon and polypyrrole addition on SiC whiskers for enhancement of electromagnetic wave absorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019,359:882-893. |
| [24] | HU P, DONG S, LI X, et al. A low-cost strategy to synthesize MnO nanorods anchored on 3D biomass-derived carbon with superior microwave absorption properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019,7(30):9219-9228. |
| [25] | ZHANG X J, LI S, WANG S W, et al. Self-supported construction of three-dimensional MoS2 hierarchical nanospheres with tunable high-performance microwave absorption in broadband. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016,120(38):22019-22027. |
| [26] | LIANG H S, LIU J L, ZHANG Y, et al. Ultra-thin broccoli-like SCFs@TiO2 one-dimensional electromagnetic wave absorbing material. Composites Part B Engineering, 2019,178:107507. |
| [27] |
NING M Q, LU M M, LI J B, et al. Two-dimensional nanosheets of MoS2: a promising material with high dielectric properties and microwave absorption performance. Nanoscale, 2015,7(38):15734-15740.
DOI URL PMID |
| [28] | ZHOU X F, JIA Z R, FENG A L, et al. Synthesis of fish skin- derived 3D carbon foams with broadened bandwidth and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Carbon, 2019,152:827-836. |
| [29] | WU R B, ZHOU K, YANG Z H, et al. Molten-salt-mediated synthesis of SiC nanowires for microwave absorption applications. CrystEngComm, 2013,15(3):570-576. |
| [30] | ZHANG W D, ZHANG X, WU H J, et al. Impact of morphology and dielectric property on the microwave absorbing performance of MoS2-based materials. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018,751:34-42. |
| [31] | XIA L, ZHANG X Y, YANG Y N, et al. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties of laminated SiCNW-Cf/lithium-aluminum- silicate (LAS) composites. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018,748:154-162. |
| [32] | WANG X X, YU M X, ZHANG W, et al. Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of graphene/nickel composite materials. Applied Physics A, 2015,118(3):1053-1058. |
| [33] | WU K H, TING T H, LIU C I, et al. Electromagnetic and microwave absorbing properties of Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4/bamboo charcoal core-shell nanocomposites. Composites Science and Technology, 2008,68(1):132-139. |
| [34] | LIU Z, LV Y X, FANG J Y, et al. A new method for an efficient porous carbon/Fe3O4 composite based electromagnetic wave absorber derived from a specially designed polyimide. Composites Part B-engineering, 2018,155:148-155. |
| [35] |
LIU L L, ZHANG S, YAN F, et al. Three-dimensional hierarchical MoS2 nanosheets/ultralong N-doped carbon nanotubes as high- performance electromagnetic wave absorbing material. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018,10(16):14108-14115.
DOI URL PMID |
| [36] | ZHAO H, CHENG Y, LV H, et al. Achieving sustainable ultralight electromagnetic absorber from flour by turning surface morphology of nanoporous carbon. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018,6(11):15850-15857. |
| [37] |
QIU X, WANG L X, ZHU H L, et al. Lightweight and efficient microwave absorbing materials based on walnut shell-derived nano-porous carbon. Nanoscale, 2017,9(22):7408-7418.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 周厚霖, 宋志庆, 田国, 高兴森. 生长条件对BiFeO3纳米岛内自组装铁电拓扑畴形成的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 667-674. |
| [2] | 陈义, 邱海鹏, 陈明伟, 徐昊, 崔恒. SiC/SiC复合材料基体硼改性方法及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [3] | 苟燕子, 康伟峰, 王堋人. 烧结条件对制备高结晶近化学计量比SiC纤维的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 405-414. |
| [4] | 穆爽, 马沁, 张禹, 沈旭, 杨金山, 董绍明. Yb2Si2O7改性SiC/SiC复合材料的氧化行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 323-328. |
| [5] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [6] | 高晨光, 孙晓亮, 陈君, 李达鑫, 陈庆庆, 贾德昌, 周玉. 基于湿法纺丝技术的SiBCN-rGO陶瓷纤维的组织结构、力学和吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [7] | 侯佳琪, 陈睿聪, 曾耀莹, 周磊, 张佳平, 付前刚. 气相渗硅法修复SiC涂层及其抗热震和烧蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 168-176. |
| [8] | 李伟, 许志明, 苟燕子, 尹森虎, 余艺平, 王松. SiC纤维烧结陶瓷的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 177-183. |
| [9] | 张立, 管皞阳, 郑琪宁, 洪智亮, 王佳璇, 邢宁, 李玫, 刘永胜, 张程煜. MI SiCf/SiC-SiYBC复合材料的蠕变性能及损伤机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 23-30. |
| [10] | 全文心, 余艺平, 方冰, 李伟, 王松. 管状C/SiC复合材料高温空气氧化行为与宏细观建模研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 920-928. |
| [11] | 谭敏, 陈小武, 杨金山, 张翔宇, 阚艳梅, 周海军, 薛玉冬, 董绍明. 流延成型结合反应熔渗制备ZrB2-SiC陶瓷及其微观结构与氧化行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 955-964. |
| [12] | 姜灵毅, 庞生洋, 杨超, 张悦, 胡成龙, 汤素芳. C/SiC-BN复合材料的制备及氧化行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 779-786. |
| [13] | 张育育, 吴轶城, 孙佳, 付前刚. 聚合物转化SiHfCN陶瓷的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 681-690. |
| [14] | 吴晓晨, 郑瑞晓, 李露, 马浩林, 赵培航, 马朝利. SiCf/SiC陶瓷基复合材料高温环境损伤原位监测研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 609-622. |
| [15] | 粟毅, 史扬帆, 贾成兰, 迟蓬涛, 高扬, 马青松, 陈思安. 浆料浸渍辅助PIP工艺制备C/HfC-SiC复合材料的微观结构及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 726-732. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||