无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 569-576.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220548 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20220548
吴爽( ), 苟燕子(
), 苟燕子( ), 王永寿, 宋曲之, 张庆雨, 王应德(
), 王永寿, 宋曲之, 张庆雨, 王应德( )
)
收稿日期:2022-09-19
修回日期:2022-11-10
出版日期:2022-11-16
网络出版日期:2022-11-16
通讯作者:
苟燕子, 副研究员. E-mail: y.gou2012@hotmail.com;作者简介:吴 爽(1996-), 女, 博士研究生. E-mail: alanwu37@163.com
基金资助:
WU Shuang( ), GOU Yanzi(
), GOU Yanzi( ), WANG Yongshou, SONG Quzhi, ZHANG Qingyu, WANG Yingde(
), WANG Yongshou, SONG Quzhi, ZHANG Qingyu, WANG Yingde( )
)
Received:2022-09-19
Revised:2022-11-10
Published:2022-11-16
Online:2022-11-16
Contact:
GOU Yanzi, associate professor. E-mail: y.gou2012@hotmail.com;About author:WU Shuang(1996-), female, PhD candidate. E-mail: alanwu37@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
高结晶近化学计量比SA型SiC纤维以其优异的耐温性, 在新一代航空发动机和高超声速飞行器等领域得到广泛应用。对比国产第二代SiC纤维(F-II), 本工作研究了第三代SA型SiC纤维(F-III)高温热处理前后的微观结构演变和拉伸强度及断裂行为。结果表明, F-III纤维主要由β-SiC晶粒(~200 nm)和少量游离碳组成, F-II纤维则由β-SiC晶粒(~5 nm)、游离碳和SiCxOy无定形相组成。与F-II纤维相比, F-III纤维具有更大的晶粒尺寸与孔隙, 室温下的拉伸强度较低。但经1800 ℃热处理后, F-III纤维结构和强度基本保持不变, 而F-II纤维由于发生了SiCxOy相的分解和晶粒长大, 强度明显降低。SA型SiC纤维的耐高温性能优异, 可归因于纤维组成结构上的高结晶、大晶粒和低碳氧含量。
中图分类号:
吴爽, 苟燕子, 王永寿, 宋曲之, 张庆雨, 王应德. 高温热处理对国产KD-SA型SiC纤维组成结构与力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 569-576.
WU Shuang, GOU Yanzi, WANG Yongshou, SONG Quzhi, ZHANG Qingyu, WANG Yingde. Effect of Heat Treatment on Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Domestic KD-SA SiC Fibers[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 569-576.
| Parameter | F-II | F-II-1800 ℃ | F-III | F-III-1800 ℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/Si | 1.34 | 1.42 | 1.08 | 1.08 |
| Al content/ (%, in mass) | / | / | <1.00 | <1.00 |
| O content/ (%, in mass) | 0.98 | 0.53 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
| Diameter/μm | 12.0 | 11.9 | 9.9 | 9.9 |
| Density/ (g·cm-3) | 2.72 | 2.66 | 3.08 | 3.09 |
| Tensile strength/ GPa | 2.7 | 0.9 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Elastic modulus/GPa | 260 | 207 | 372 | 366 |
表1 热处理前后SiC纤维的组成和基本性能
Table 1 Composition and general properties of SiC fibers before and after heat treatment
| Parameter | F-II | F-II-1800 ℃ | F-III | F-III-1800 ℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/Si | 1.34 | 1.42 | 1.08 | 1.08 |
| Al content/ (%, in mass) | / | / | <1.00 | <1.00 |
| O content/ (%, in mass) | 0.98 | 0.53 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
| Diameter/μm | 12.0 | 11.9 | 9.9 | 9.9 |
| Density/ (g·cm-3) | 2.72 | 2.66 | 3.08 | 3.09 |
| Tensile strength/ GPa | 2.7 | 0.9 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Elastic modulus/GPa | 260 | 207 | 372 | 366 |
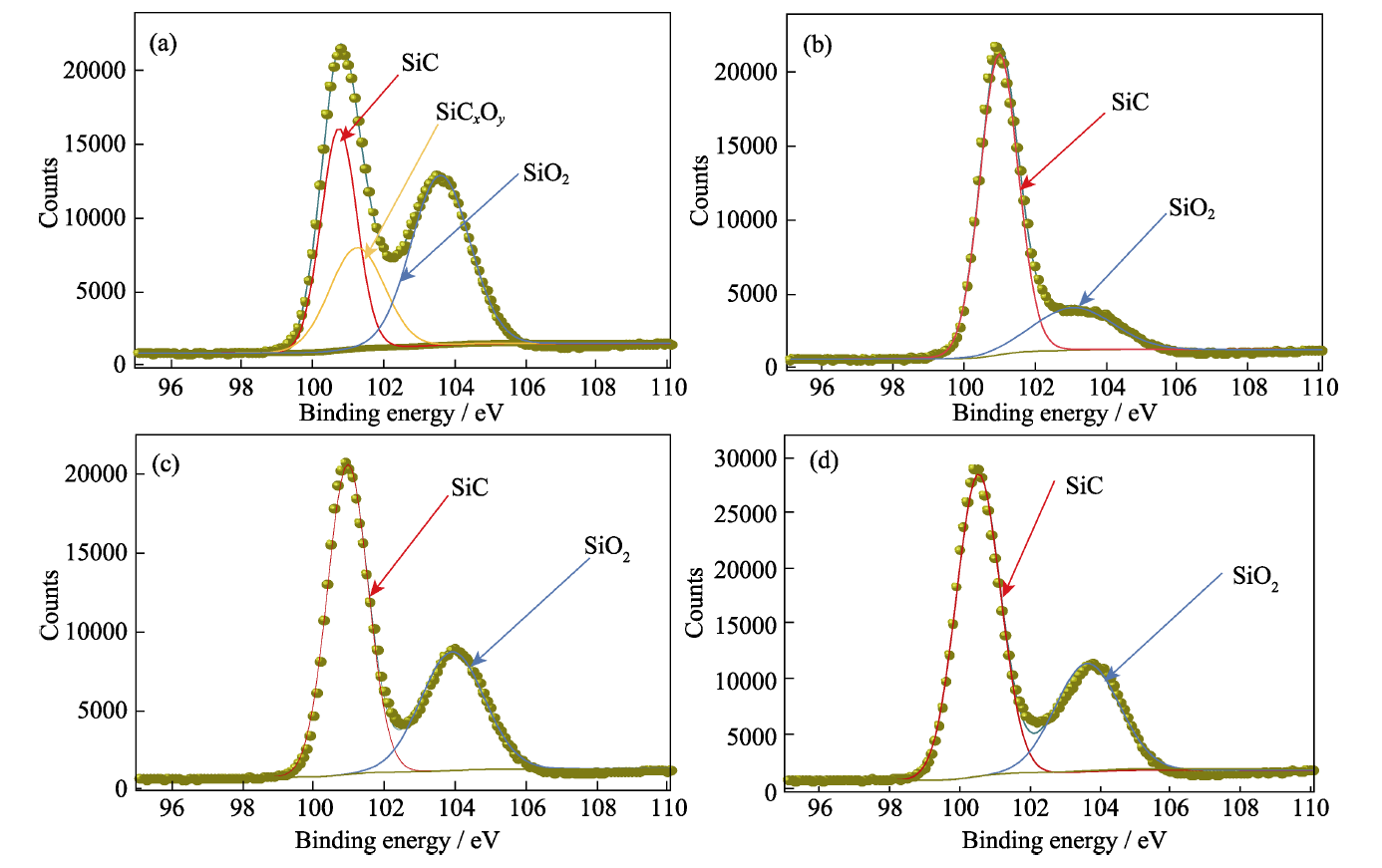
图1 (a)F-II, (b)F-II-1800 ℃、(c)F-III 和(d)F-III-1800 ℃ 纤维的Si2p的XPS图谱
Fig. 1 Si2p XPS spectra of (a) F-II, (b) F-II-1800 ℃, (c)F-III, and (d)F-III-1800 ℃ fibers
| Sample | D Band | G Band | ID/IG | La/nm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position/cm-1 | FWHM | Position/cm-1 | FWHM | |||
| F-II | 1356.3 | 112.5 | 1599.8 | 122.7 | 1.39 | 13.8 |
| F-II-1800 ℃ | 1351.3 | 59.9 | 1586.8 | 63.2 | 1.09 | 17.6 |
| F-III | 1352.9 | 79.9 | 1590.1 | 89.0 | 1.12 | 17.2 |
| F-III-1800 ℃ | 1354.3 | 64.9 | 1593.0 | 72.8 | 1.18 | 16.3 |
表2 纤维中自由碳的拉曼峰信息
Table 2 Raman characteristics of free carbon phase of the fibers
| Sample | D Band | G Band | ID/IG | La/nm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position/cm-1 | FWHM | Position/cm-1 | FWHM | |||
| F-II | 1356.3 | 112.5 | 1599.8 | 122.7 | 1.39 | 13.8 |
| F-II-1800 ℃ | 1351.3 | 59.9 | 1586.8 | 63.2 | 1.09 | 17.6 |
| F-III | 1352.9 | 79.9 | 1590.1 | 89.0 | 1.12 | 17.2 |
| F-III-1800 ℃ | 1354.3 | 64.9 | 1593.0 | 72.8 | 1.18 | 16.3 |
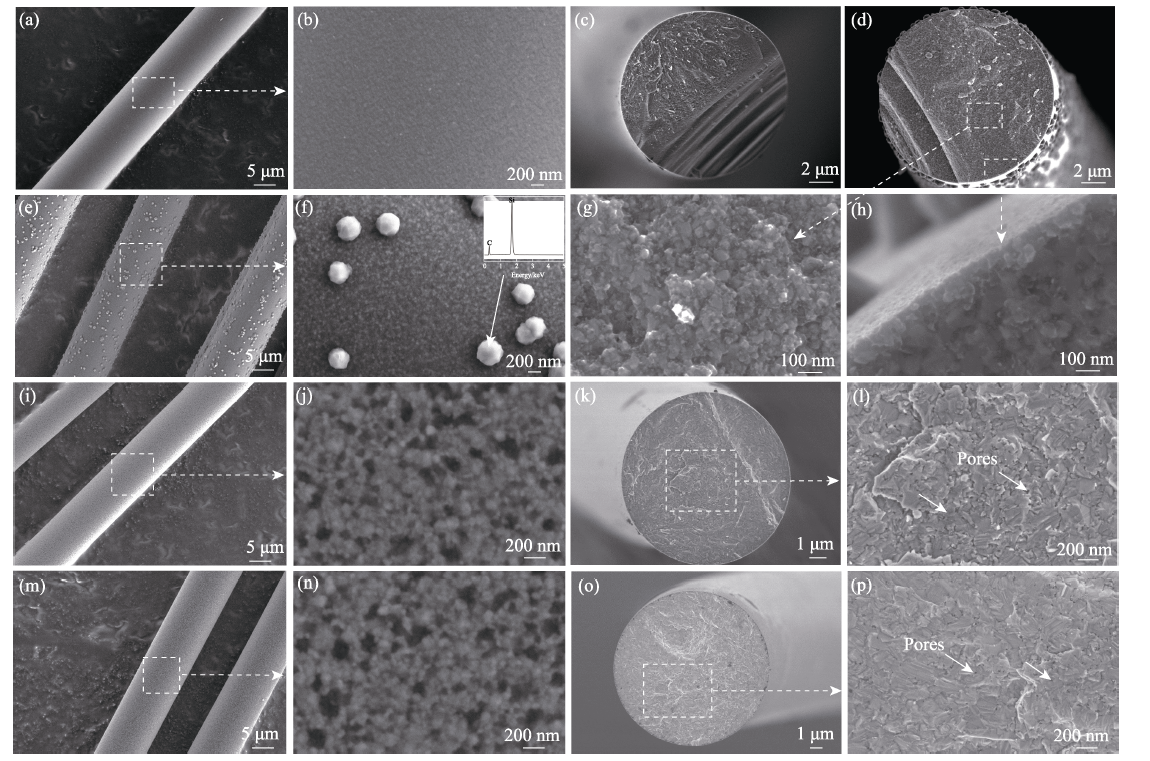
图3 (a~c)F-II, (d~h)F-II-1800 ℃, (i~l)F-III, and (m~p)F-III-1800 ℃纤维的SEM形貌照片
Fig. 3 SEM morphologies of (a-c) F-II, (d-h) F-II-1800 ℃, (i-l) F-III, and (m-p) F-III-1800 ℃ fibers
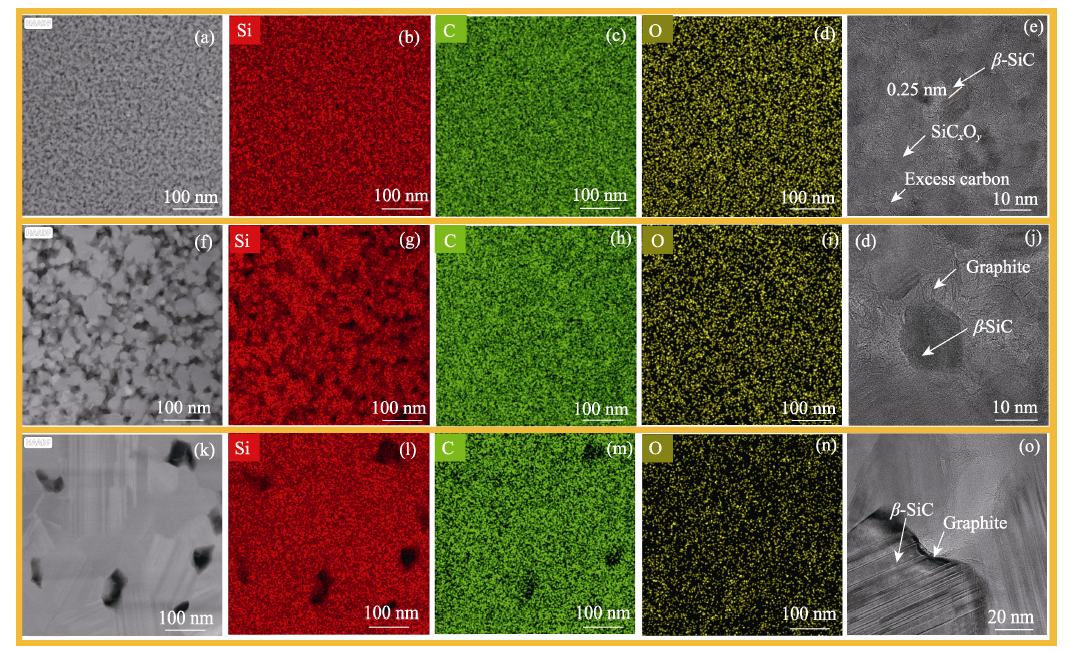
图4 (a~e) F-II、(f~j) F-II-1800 ℃和(k~o) F-III-1800 ℃纤维的TEM和HRTEM照片
Fig. 4 TEM and HRTEM images of (a-e) F-II fibers, (f-j)F-II-1800 ℃ fibers, and (k-o) F-III-1800 ℃ fibers
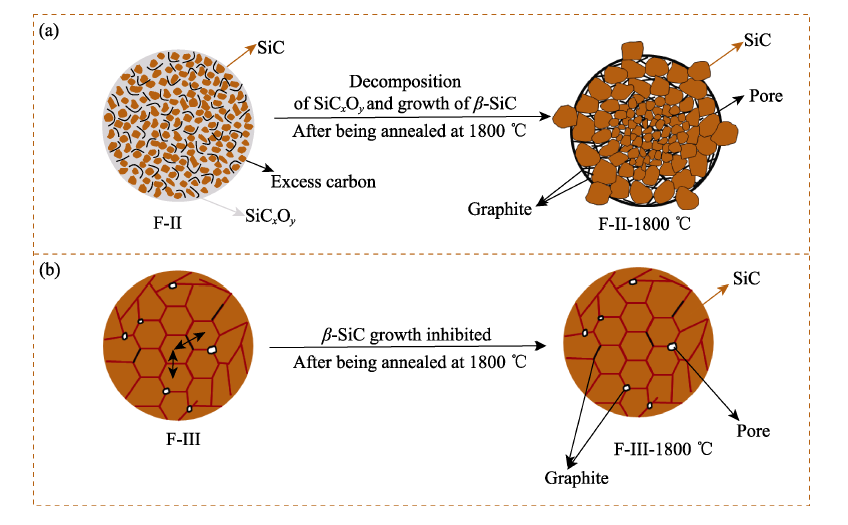
图6 (a)F-II-1800 ℃纤维皮芯结构示意图和(b)F-III纤维热稳定性的示意图
Fig. 6 Schematic diagram of (a) formation process of skin-core structure of F-II-1800 ℃and (b) thermal stability of F-III fibers
| [1] |
AN Q L, CHEN J, MING W W, et al. Machining of SiC ceramic matrix composites: a review. Chinese Journal of Aeronautic, 2021, 34(4): 540.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
YUAN Q, SONG Y C. Research and development of continuous SiC fibers and SiCf/SiC composities. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(11): 1157.
DOI |
| [3] |
WANG P, WANG Q L, ZHANG X Y, et al. Oxidation behavior of SiCf/SiC composites modified by layered-Y2Si2O7 in wet oxygen environment. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(8): 904.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LÜ X X, JIANG Z Y, ZHOU Y R, et al. Effect of BN/SiC multilayered interphases on mechanical properties of SiC Fibers and minicomposites by PIP. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1099.
DOI |
| [5] | 刘虎, 杨金华, 焦健. 航空发动机用连续SiCf/SiC复合材料制备工艺及应用前景. 航空制造技术, 2017, (16): 90. |
| [6] |
WANG P, LIU F Q, WANG H, et al. A review of third generation SiC fibers and SiCf/SiC composites. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2019, 35(12): 2743.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
BUNSELL A R, PIANT A. A review of the development of three generations of small diameter silicon carbide fibres. Journal of Materials Science, 2006, 41(3): 823.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
INCHIKAWA H. Polymer-derived ceramic fibers. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2016, 46(1): 335.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
SHA J J, HINOKI T, KOHYAMA A. Microstructural characterization and fracture properties of SiC-based fibers annealed at elevated temperatures. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42(13): 5046.
DOI URL |
| [10] | SHA J J, NOZAWA T, PARK J S, et al. Effect of heat treatment on the tensile strength and creep resistance of advanced SiC fibers. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2004, 329-333: 592. |
| [11] |
ISHIKAWA T, KOHTOKU Y, KUMAGAWA K, et al. High-strength alkali-resistant sintered SiC fibre stable to 2200 ℃. Nature, 1998, 391(6669): 773.
DOI |
| [12] |
HUGUST-GARCIA J, JANKOWIAK A, MIRO S, et al. Ion irradiation effects on third generation SiC fibers in elastic and inelastic energy loss regimes. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2014, 327: 93.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
GOU Y Z, JIAN K, WANG H, et al. Fabrication of nearly stoichiometric polycrystalline SiC fibers with excellent high- temperature stability up to 1900 ℃. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018, 101(5): 2050.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 王军, 宋永才, 王浩, 等. 先驱体转化法制备碳化硅纤维. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018: 199-250. |
| [15] |
CAO S Y, WANG J, WANG H. Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and tensile strength of KD-II SiC fibers. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2016, 673: 55.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
WANG P R, GOU Y Z, WANG H, et al. Revealing the formation mechanism of the skin-core structure in nearly stoichiometric polycrystalline SiC fibers. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(6): 2295.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHANG Y, WU C L, WANG Y D, et al. A detailed study of the microstructure and thermal stability of typical SiC fibers. Materials Characterization, 2018, 146: 91.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
USUKAWA R, ISHIKAWA T. Effect of Al contained in polymer- derived SiC crystals on creating stable crystal grain boundaries. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2021, 18(1): 6.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
WEIBULL W, STOCKHOLM, SWEDEN. A statistical distribution function of wide applicability. Journal of Applied Mechanics: Transactions of the ASME, 1951, 18(3): 293.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 姚荣迁, 唐学原, 王艳艳, 等. Hi-Nicalon SiC纤维高温热处理后的断裂机理研究. 金属热处理, 2007(8): 55. |
| [21] |
ISHIKAWA T, ODA H. Defect control of SiC polycrystalline fiber synthesized from poly-aluminocarbosilane. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(15): 3657.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
CAO S Y, WANG J, WANG H. Formation mechanism of large SiC grains on SiC fiber surfaces during heat treatment. CrystEngComm, 2016, 18(20): 3674.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 苟燕子, 康伟峰, 王堋人. 烧结条件对制备高结晶近化学计量比SiC纤维的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 405-414. |
| [2] | 穆浩洁, 张源江, 喻彬, 付秀梅, 周世斌, 李晓东. ZrO2掺杂Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 281-289. |
| [3] | 李伟, 许志明, 苟燕子, 尹森虎, 余艺平, 王松. SiC纤维烧结陶瓷的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 177-183. |
| [4] | 范武刚, 曹雄, 周响, 李玲, 赵冠楠, 张兆泉. 8YSZ陶瓷在模拟压水堆水环境中的耐腐蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 803-809. |
| [5] | 姜灵毅, 庞生洋, 杨超, 张悦, 胡成龙, 汤素芳. C/SiC-BN复合材料的制备及氧化行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 779-786. |
| [6] | 李广宇, 岳一凡, 王波, 张程煜, 索涛, 李玉龙. 2D-SiC/SiC复合材料的弹丸冲击损伤及冲击后拉伸性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 494-500. |
| [7] | 薛轶凡, 李玮洁, 张中伟, 庞旭, 刘愚. 碳纤维布表面PyC界面相微观结构及均匀性的工艺调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 399-408. |
| [8] | 苟燕子, 康伟峰, 张庆雨. 由聚钛碳硅烷制备高结晶近化学计量比SiC(Ti)纤维[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1377-1383. |
| [9] | 张硕, 付前刚, 张佩, 费杰, 李伟. C/C多孔体的高温热处理对C/C-SiC复合材料摩擦磨损行为的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 561-568. |
| [10] | 李建波, 田震, 蒋全伟, 于砺锋, 康慧君, 曹志强, 王同敏. 不同元素掺杂对CaTiO3微观结构及热电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1396-1404. |
| [11] | 吴东江, 赵紫渊, 于学鑫, 马广义, 由竹琳, 任冠辉, 牛方勇. Al2O3-TiCp复相陶瓷激光定向能量沉积直接增材制造[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1183-1192. |
| [12] | 吴西士, 朱云洲, 黄庆, 黄政仁. 树脂基多孔碳孔结构对Cf/SiC复合材料连接性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1275-1280. |
| [13] | 王袁杰, 裴学良, 李好义, 徐鑫, 何流, 黄政仁, 黄庆. 自由基引发活性聚碳硅烷交联及其在制备SiC纤维中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 967-973. |
| [14] | 朱勇, 顾军, 于涛, 何海佟, 姚睿. 铂钴合金纳米电催化剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 299-305. |
| [15] | 黄新友, 刘玉敏, 刘洋, 李晓英, 冯亚刚, 陈肖朴, 陈鹏辉, 刘欣, 谢腾飞, 李江. 醇水共沉淀法制备Yb:YAG透明陶瓷及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 217-224. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||