无机材料学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 1-7.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190560 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20190560
所属专题: MAX相和MXene材料; 二维材料; 副主编黄庆研究员专辑; 优秀作者论文集锦; 2019~2020年度优秀作者作品欣赏:功能材料; MXene材料专辑(2020~2021); 【虚拟专辑】层状MAX,MXene及其他二维材料
收稿日期:2019-11-01
修回日期:2019-11-13
出版日期:2020-01-20
网络出版日期:2019-12-04
作者简介:李 勉(1989-),男,博士. E-mail:limian@nimte.ac.cn
基金资助:Received:2019-11-01
Revised:2019-11-13
Published:2020-01-20
Online:2019-12-04
About author:LI Mian(1989-), male, PhD. E-mail:limian@nimte.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
近年来, 三元层状碳氮化合物(MAX相)及其衍生二维纳米材料MXene受到了科学界的广泛关注。MAX相的晶体结构由Mn+1Xn结构单元与A元素单原子面交替堆垛排列而成, 兼具金属和陶瓷的诸多优点, 在高温结构材料、摩擦磨损器件、核能结构材料等领域有较大的应用潜力。MAX相的A层原子被刻蚀之后获得成分为Mn+1XnTx(Tx为表面基团)的二维纳米材料, 即MXene, 具有丰富的成分组合以及可调谐的物理化学性质, 在储能器件、电磁屏蔽、电子器件等领域表现出良好的应用前景。本文简要介绍近年来国内外MAX相和MXene材料领域在成分与结构、合成方法、性能与应用研究等方面的研究动态, 据此展望未来几年该类新颖材料的发展方向。
中图分类号:
李勉, 黄庆. 三元层状碳氮化合物(MAX相)及其衍生二维纳米材料(MXene)研究趋势与展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(1): 1-7.
LI Mian, HUANG Qing. Recent Progress and Prospects of Ternary Layered Carbides/Nitrides MAX Phases and Their Derived Two-dimensional Nanolaminates MXenes[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 1-7.
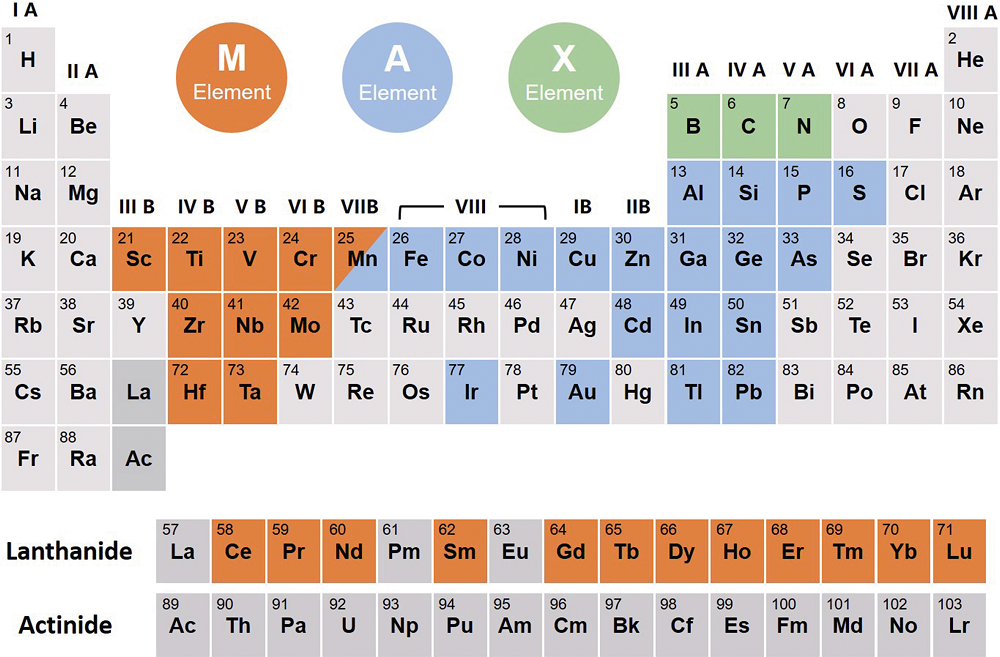
图1 目前已合成MAX相的组元分布, 其中M位元素(赤橙色)已经拓展到镧系稀土, A位(天青色)添加了含未满d电子的副族元素, X位(草绿色)则增加了硼元素
Fig. 1 Element distribution of the MAX phases known to date. The M-site elements (orange color) have been extended to lanthanides, A-site elements (blue color) have been extended to subgroup element with unsaturated d-orbitals, and boron has been added into X-site elements (green color)
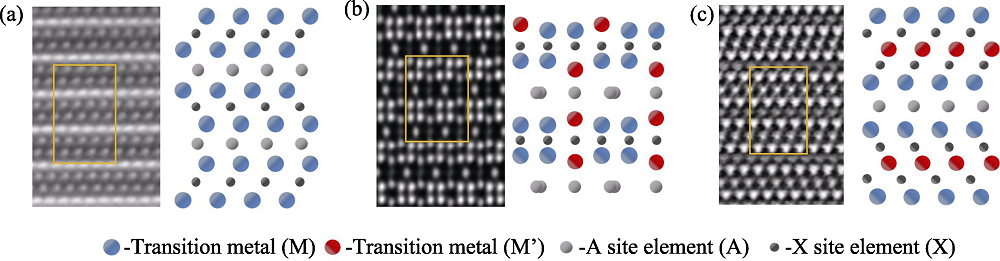
图2 高分辨扫描透射电镜照片显示MAX(a)、i-MAX(b)和(c)o-MAX的原子排布[8,16-17]
Fig. 2 HR-STEM images showing the atomic positions of MAX phase (a), i-MAX phase (b), and o-MAX phase (c)[8,16-17]
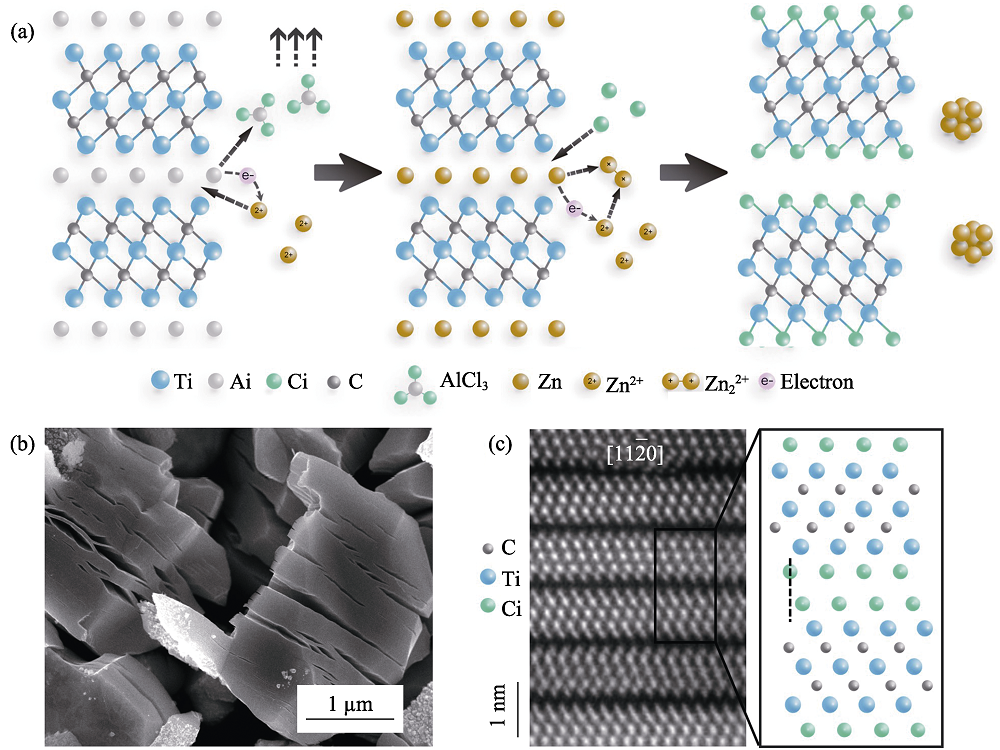
图3 氯化锌熔盐刻蚀MAX相制备MXene过程示意图(a), 扫描电镜照片显示Ti3C2Cl2 MXene的微观形貌(b)和高分辨扫描透射电镜照片显示Ti3C2Cl2 MXene的原子排布(c)[8]
Fig. 3 A schematic diagram showing the process of producing MXene by using ZnCl2 to etch MAX phase (a), scanning electron microscopy(SEM) image showing the microstructure of Ti3C2Cl2 MXene (b), and HR-STEM image showing the atomic positions of Ti3C2Cl2 MXene (c)[8]
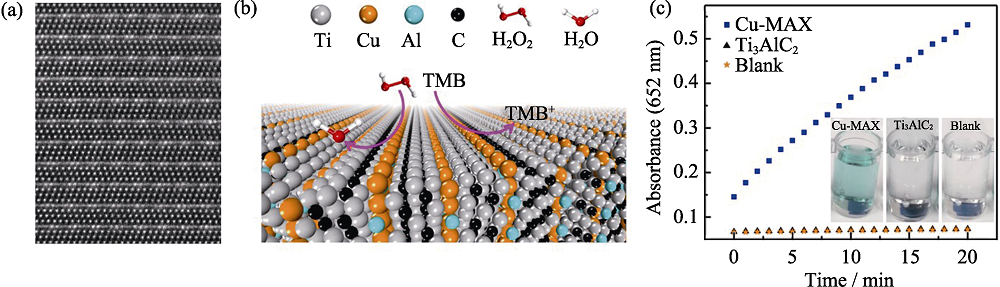
图4 高分辨扫描透射电镜照片显示Ti3(AlxCu1-x)C2的原子排布(a)、Ti3(AlxCu1-x)C2探测过氧化氢机理示意图(b)和Ti3(AlxCu1-x)C2与Ti3AlC2探测过氧化氢性能对比(c)[9]
Fig. 4 HR-STEM image showing the atomic positions of Ti3(AlxCu1-x)C2 (a), a schematic diagram showing the H2O2 detecting mechanism of Ti3(AlxCu1-x)C2 (b), and comparison of the H2O2 detecting ability between Ti3(AlxCu1-x)C2 and Ti3AlC2 (c)[9]
| [1] |
NOWOTNY V H . Strukturchemie einiger verbindungen der übergangsmetalle mit den elementen C, Si, Ge, Sn. Prog. Solid State Chem., 1971,5:27-70.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
JEITSCHKO W, NOWOTNY V H, BENESOVSKY F . Die H-phasen: Ti2CdC, Ti2GaC, Ti2GaN, Ti2InN, Zr2InN und Nb2GaC. Monatshefte für Chemie, 1964,95(1):178-179.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BARSOUM M W, EI-RAGHY T . Synthesis and characterization of a remarkable ceramic: Ti3SiC2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1996,79(7):1953-1956.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
BARSOUM M W . The MN+1AXN phases a new class of solids; thermodynamically stable nanolaminates. Prog. Solid State Chem., 2000,28:201-281.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] |
SOKOL M, NATU V, KOTA S ,et al. On the chemical diversity of the MAX phases. Trends Chem., 2019,1(2):210-223.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] |
TAO Q, LU J, DAHLQVIST M , et al. Atomically layered and ordered rare-earth i-MAX phases: a new class of magnetic quaternary compounds . Chem. Mater., 2019,31(7):2476-2485.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
FASHANDI H, DAHLQVIST M, LU J , et al. Synthesis of Ti3AuC2, Ti3Au2C2and Ti3IrC2 by noble metal substitution reaction in Ti3SiC2 for high-temperature-stable Ohmic contacts to SiC. Nat. Mater., 2017,16(8):814-818.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] |
LI M, LU J, LUO K , et al. Element replacement approach by reaction with Lewis acidic molten salts to synthesize nanolaminated MAX phases and MXenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019,141(11):4730-4737.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] |
LI Y, LI M, LU J , et al. Single-atom-thick active layers realized in nanolaminated Ti3( AlxCu1-x)C2 and its artificial enzyme behavior. ACS Nano, 2019,13(8):9198-9205.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] |
WANG J, YE T N, GONG Y , et al. Discovery of hexagonal ternary phase Ti2InB2 and its evolution to layered boride TiB. Nat. Commun., 2019,10(1):2284.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] |
PHATAK N A, SAXENA S K, FEI Y , et al. Synthesis of a new MAX compound (Cr0.5V0.5)2GeC and its compressive behavior up to 49 GPa. J. Alloys Compd., 2009,475(1/2):629-634.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
GANGULY A, ZHEN T, BARSOUM M W . Synthesis and mechanical properties of Ti3GeC2 and Ti3(SixGe1-x)C2 (x=0.5, 0.75) solid solutions . J. Alloys Compd., 2004,376(1/2):287-295.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MANOUN B, SAXENA S K . Synthesis and compressibility of Ti3(Al, Sn0.2)C2 and Ti3Al(C0.5, N0.5)2. J. Appl. Phys., 2007,101(11):113523.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
TAO Q, DAHLQVIST M, LU J , et al. Two-dimensional Mo1.33C MXene with divacancy ordering prepared from parent 3D laminate with in-plane chemical ordering. Nat. Commun., 2017,8:14949.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] |
LIU Z, WU E, WANG J , et al. Crystal structure and formation mechanism of (Cr2/3Ti1/3)3AlC2 MAX phase. Acta Mater., 2014,73:186-193.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ANASORI B, XIE Y, BEIDAGHI M , et al. Two-dimensional, ordered, double transition metals carbides (MXenes). ACS Nano, 2015,9(10):9507-9516.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
LU J, THORE A, MESHKIAN R , et al. Theoretical and experimental exploration of a novel in-plane chemically ordered (Cr2/3M1/3)2AlC i-MAX phase with M = Sc and Y. Cryst. Growth Des., 2017,17(11):5704-5711.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
NAGUIB M, KURTOGLU M, PRESSER V , et al. Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Adv. Mater., 2011,23(37):4248-4253.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
TANG Q, ZHOU Z, SHEN P . Are MXenes promising anode materials for Li ion batteries? Computational studies on electronic properties and Li storage capability of Ti3C2 and Ti3C2X2 (X=F, OH) monolayer. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012,134(40):16909-16916.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
SHAHZAD F, ALHABEB M, HATTER C B , et al. Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes) . Science, 2016,353(6304):1137-1140.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] |
GHIDIU M, LUKATSKAYA M R, ZHAO M Q , et al. Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide ‘clay’ with high volumetric capacitance. Nature, 2014,516(7529):78-81.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
NAGUIB M, MASHTALIR O, CARLE J , et al. Two-dimensional transition metal carbides. ACS Nano, 2012,6(2):1322-1331.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] |
NAGUIB M, MOCHALIN V N, BARSOUM M W , et al. 25th anniversary article: MXenes: a new family of two-dimensional materials. Adv. Mater., 2014,26(7):992-1005.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
MESHKIAN R, DAHLQVIST M, LU J , et al. W-based atomic laminates and their 2D derivative W1.33C MXene with vacancy ordering. Adv. Mater., 2018,30(21):1-8.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] |
LU J, PERSSON I, LIND H , et al. Tin+1Cn MXenes with fully saturated and thermally stable Cl terminations. Nanoscale Adv., 2019,1(9):3680-3685.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
PERSSON I, GHAZALY A E, TAO Q , et al. Tailoring structure, composition, and energy storage properties of MXenes from selective etching of in-plane, chemically ordered MAX phases. Small, 2018,14(17):1-7.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] |
SCHULTZ T, FREY N C, HANTANASIRISAKUL K , et al. Surface termination dependent work function and electronic properties of Ti3C2Tx MXene. Chem. Mater., 2019,31(17):6590-6597.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
EKLUND P, BECKERS M, JANSSON U , et al. The Mn+1AXn phases: materials science and thin-film processing. Thin Solid Films, 2010,518(8):1851-1878.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] |
SHU R, GE F, MENG F , et al. One-step synthesis of polycrystalline V2AlC thin films on amorphous substrates by magnetron co-sputtering. Vacuum, 2017,146:106-110.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
DING H, LI Y, LU J , et al. Synthesis of MAX phases Nb2CuC and Ti2( Al0.1Cu0.9)N by A-site replacement reaction in molten salts. Mater. Res. Lett., 2019,7(12):510-516.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
ANASORI B, LUKATSKAYA M R, GOGOTSI Y . 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for energy storage. Nat. Rev. Mater., 2017,2(2):16098.
DOI URL PMID |
| [32] |
NG V M H, HUANG H, ZHOU K , et al. Recent progress in layered transition metal carbides and/or nitrides (MXenes) and their composites: synthesis and applications. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017,5(7):3039-3068.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] | LI Y, SHAO H, LIN Z , et al. A general Lewis acidic etching route for preparing MXenes with enhanced electrochemical performance in non-aqueous electrolyte. arXiv:1909. 13236. |
| [34] |
BARSOUM M W, EL-RAGHY T OGBUJI L U J T . Oxidation of Ti3SiC2 in air. J. Electrochem. Soc., 1997,144(7):2508-2516.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
FENG Z, KE P, HUANG Q , et al. The scaling behavior and mechanism of Ti2AlC MAX phase coatings in air and pure water vapor. Surf. Coatings Technol., 2015,272:380-386.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
HAJAS D E, BABEN M T, HALLSTEDT B , et al. Oxidation of Cr2AlC coatings in the temperature range of 1230 to 1410 ℃. Surf. Coatings Technol., 2011,206(4):591-598.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
HUANG Q, HAN H, LIU R , et al. Saturation of ion irradiation effects in MAX phase Cr2AlC. Acta Mater., 2016,110:1-7.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
YANG T, WANG C, TAYLOR C A , et al. The structural transitions of Ti3AlC2 induced by ion irradiation. Acta Mater., 2014,65:351-359.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
WANG C, YANG T, TRACY C L , et al. Disorder in Mn+1AXn phases at the atomic scale. Nat. Commun., 2019,10(1):1-9.
DOI URL PMID |
| [40] |
TALLMAN D J, HOFFMA E N, CASPI E N , et al. eEffect of neutron irradiation on select MAX phases. Acta Mater., 2015,85:132-143.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
TALLMAN D J, HE L, GARCIA-DIAZ B L , et al. Effect of neutron irradiation on defect evolution in Ti3SiC2 and Ti2AlC. J. Nucl. Mater., 2016,468:194-206.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
RESTER M, NEIDHARDT J, EKLUND P , et al. Annealing studies of nanocomposite Ti-Si-C thin films with respect to phase stability and tribological performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006,429(1/2):90-95.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
WANG D, TIAN W, MA A , et al. Anisotropic properties of Ag/Ti3 AlC2 electrical contact materials prepared by equal channel angular pressing. J. Alloys Compd., 2019,784:431-438.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
ZHANG J, WANG J Y, ZHOU Y C . Structure stability of Ti3AlC2 in Cu and microstructure evolution of Cu-Ti3AlC2 composites. Acta Mater., 2007,55(13):4381-4390.
DOI URL |
| [45] | LI Y, LU J, LI M , et al. Multielemental single-atom-thick A layers in nanolaminated V2(Sn, A)C (A=Fe, Co, Ni, Mn) for tailoring magnetic properties. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United Sates of America, DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1916256117. |
| [46] |
XU J, ZHAO M Q, WANG Y , et al. Demonstration of Li-ion capacity of MAX phases. ACS Energy Lett., 2016,1(6):1094-1099.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
ZHAO S, DALL’AGNESE Y, CHU X , et al. Electrochemical interaction of Sn-containing MAX phase (Nb2SnC) with Li-ions. ACS Energy Lett., 2019,4:2452-2457.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
WANG K, DU H, WANG Z , et al. Novel MAX-phase Ti3AlC2 catalyst for improving the reversible hydrogen storage properties of MgH2. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2017,42(7):4244-4251.
DOI URL |
| [49] | LIU Q, DING H M, DU Q B ,et al. Hydrogen insertion in Ti2AlC and its influence on the crystal structure and bonds. J. Ceram. Sci. Technol., 2017,8(2):201-208. |
| [50] |
GOGOTSI Y, ANASORI B . The rise of MXenes. ACS Nano, 2019,13(8):8491-8494.
DOI URL PMID |
| [51] |
KIM H, WANG Z, ALSHAREEF H N . MXetronics: electronic and photonic applications of MXenes. Nano Energy, 2019,60:179-197.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
PERSSON P O Å, ROSEN J . Current state of the art on tailoring the MXene composition, structure, and surface chemistry. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.cossms.2019.100774.
DOI URL PMID |
| [53] |
YANG Q, WANG Y, LI X , et al. Recent progress of MXene-based nanomaterials in flexible energy storage and electronic devices. Energy Environ. Mater., 2018,1(4):183-195.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
NATU V, HART JL, SOKOL M , et al. Edge capping of 2D-MXene sheets with polyanionic salts to mitigate oxidation in aqueous colloidal suspensions. Angew. Chemie. Int. Ed., 2019,58(36):12655-12660.
DOI URL PMID |
| [55] |
ZHAO X, VASHISTH A, PREHN E , et al. Antioxidants unlock shelf-stable Ti3C2T (MXene) nanosheet dispersions. Matter., 2019,1(2):513-526.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [8] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [9] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [10] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [11] | 范晓波, 祖梅, 杨向飞, 宋策, 陈晨, 王子, 罗文华, 程海峰. 质子调控型电化学离子突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [12] | 海热古·吐逊, 郭乐, 丁嘉仪, 周嘉琪, 张学良, 努尔尼沙·阿力甫. 上转换荧光探针辅助的光学成像技术在肿瘤显影中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [13] | 孙树娟, 郑南南, 潘昊坤, 马猛, 陈俊, 黄秀兵. 单原子催化剂制备方法的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [14] | 陶桂龙, 支国伟, 罗添友, 欧阳佩东, 衣新燕, 李国强. 空腔型薄膜体声波滤波器的关键技术进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| [15] | 刘会来, 李志豪, 孔德峰, 陈星. 酞菁铁/MXene复合阴极的制备及电芬顿降解磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 61-69. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
