无机材料学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (4): 423-430.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190195 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20190195
所属专题: 2020年能源材料论文精选(三) :太阳能电池、热电材料及其他
收稿日期:2019-05-05
修回日期:2019-07-26
出版日期:2020-04-20
网络出版日期:2019-09-04
作者简介:朱泽阳(1992-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 15210220045@fudan.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHU Zeyang,WEI Jishi,HUANG Jianhang,DONG Xiangyang,ZHANG Peng,XIONG Huanming( )
)
Received:2019-05-05
Revised:2019-07-26
Published:2020-04-20
Online:2019-09-04
Supported by:摘要:
作为绿色、高功率密度的二次电池, 镍锌电池的应用往往受限于负极材料性能的不足。本工作以乌洛托品(HMT)为模板剂, 通过溶胶-凝胶法合成与热退火处理制备了高性能ZnO纳米棒。透射电子显微镜(TEM)、X射线衍射(XRD)和红外光谱(FT-IR)数据分别揭示了ZnO纳米棒的微观形貌、晶型结构和表面官能团。X射线光电子能谱(XPS)和电子顺磁共振(EPR)结果表明ZnO纳米棒中存在表层碳和晶格空位。Tafel曲线和电化学阻抗等测试表明: 与ZnO商品相比, ZnO纳米棒电极的腐蚀电流和电荷转移电阻分别降低了40%和62%。进一步研究发现, ZnO纳米棒构筑的镍锌电池具有更好的循环性能, 在1 A·g-1下循环100圈后, ZnO纳米棒的容量保持率为92%, 显著优于市售的ZnO粉末(32%)。
中图分类号:
朱泽阳,魏济时,黄健航,董向阳,张鹏,熊焕明. 晶格空位ZnO纳米棒的制备及其在镍锌电池中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(4): 423-430.
ZHU Zeyang,WEI Jishi,HUANG Jianhang,DONG Xiangyang,ZHANG Peng,XIONG Huanming. Preparation of ZnO Nanorods with Lattice Vacancies and Their Application in Ni-Zn Battery[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 423-430.
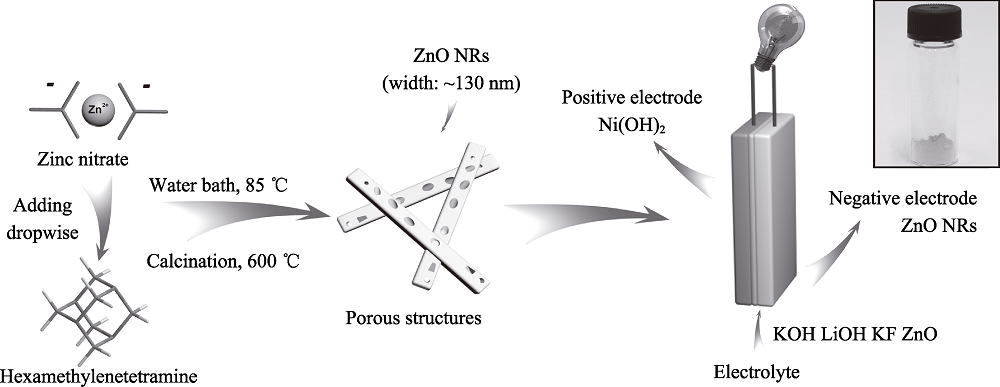
图1 ZnO纳米棒的制备以及电池组成示意图, 插图为ZnO纳米棒粉末照片
Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of the preparation of ZnO NRs and the Ni-Zn battery with inset showing the photograph of ZnO NRs
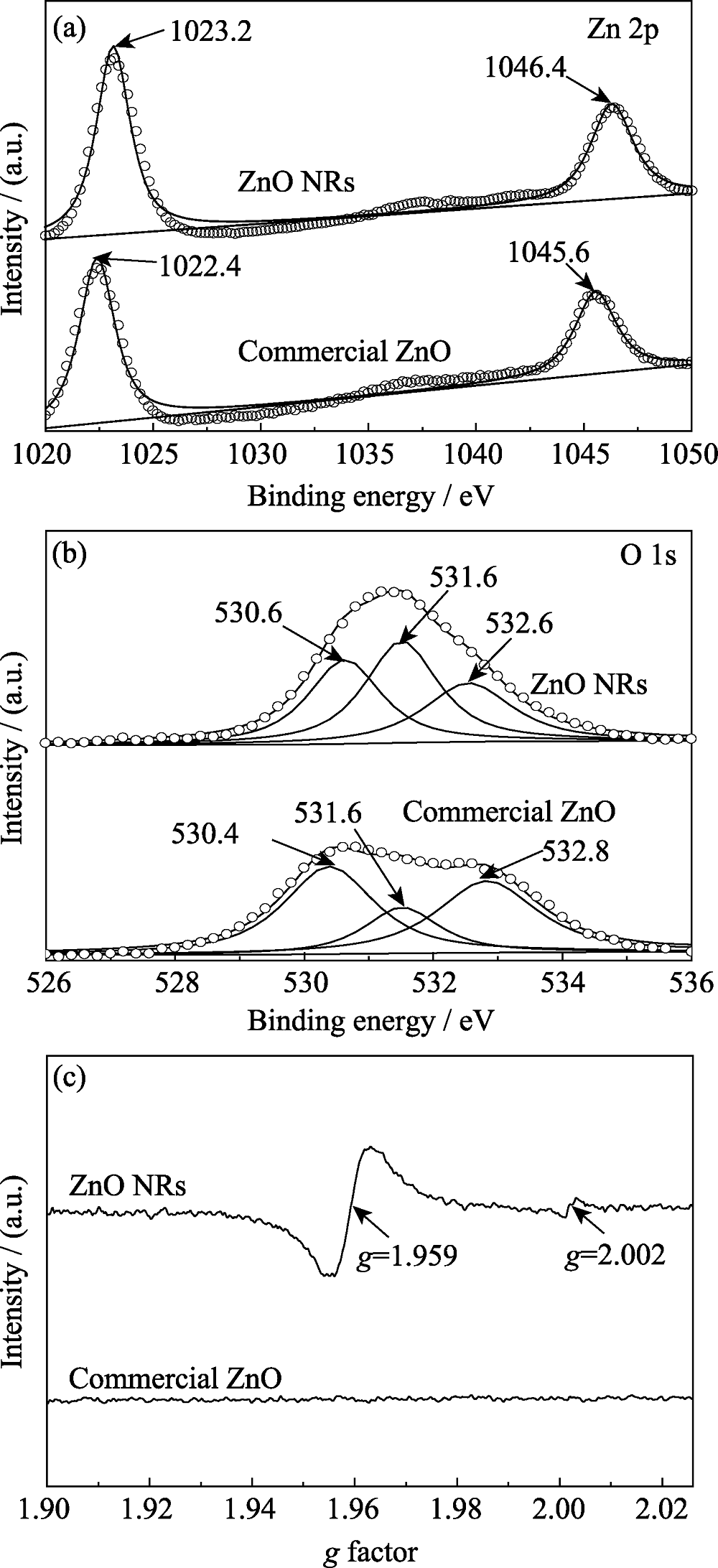
图5 ZnO商品和ZnO纳米棒的XPS高分辨谱((a) Zn 2p, (b) O 1s); (c) ZnO商品和ZnO纳米棒的电子顺磁共振谱
Fig. 5 HRXPS spectra of (a) Zn 2p and (b) O 1s for commercial ZnO and ZnO NRs, and (c) EPR spectra of commercial ZnO and ZnO NRs
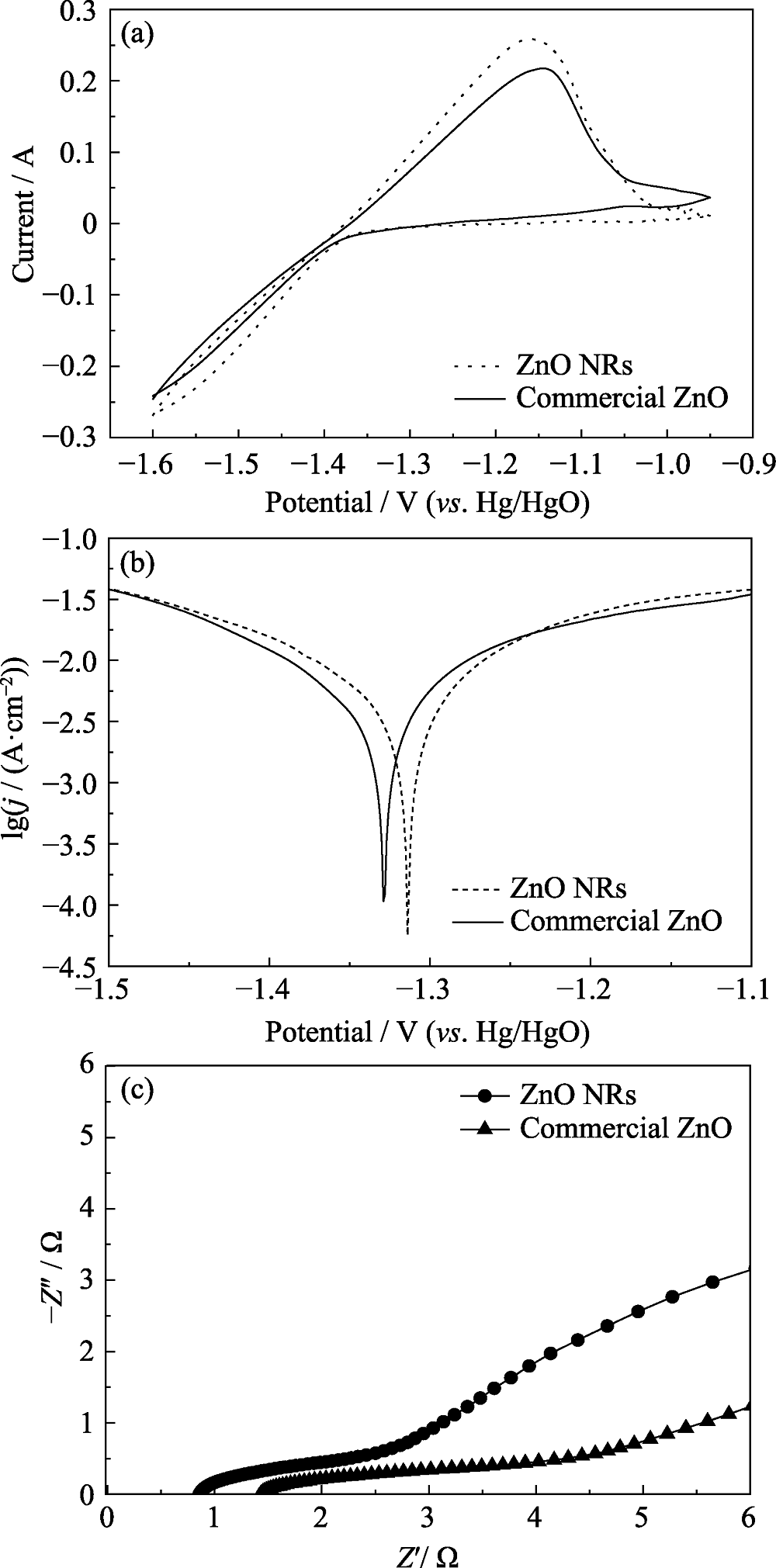
图6 ZnO商品和ZnO纳米棒电极的电化学性能
Fig. 6 Electrochemical performances of commercial ZnO and ZnO NRs electrodes (a) CV curves at a scan rate of 10 mV·s-1; (b) Tafel plots; (c) Nyquist plots
| Electrode | Tafel plots | EIS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecorr/V (vs. Hg/HgO) | Icorr/(mA·cm-2) | RS/Ω | RCT/Ω | |
| Commercial ZnO | -1.327 | 5.01×10-3 | 1.4 | 7.9 |
| ZnO NRs | -1.311 | 3.01×10-3 | 0.9 | 3.0 |
表1 ZnO商品和ZnO纳米棒的Tafel曲线和电化学阻抗参数
Table 1 Parameters of Tafel plots and EIS for commercial ZnO and ZnO NRs
| Electrode | Tafel plots | EIS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecorr/V (vs. Hg/HgO) | Icorr/(mA·cm-2) | RS/Ω | RCT/Ω | |
| Commercial ZnO | -1.327 | 5.01×10-3 | 1.4 | 7.9 |
| ZnO NRs | -1.311 | 3.01×10-3 | 0.9 | 3.0 |
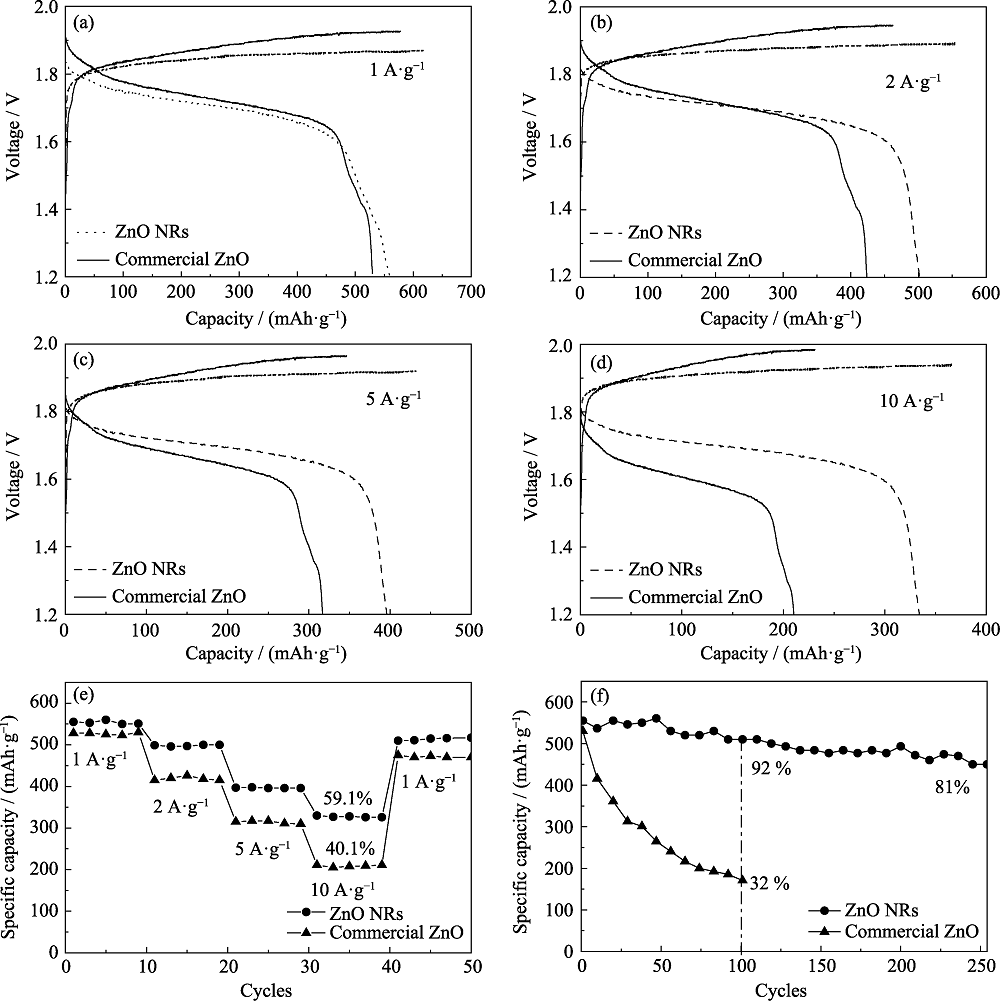
图7 以ZnO商品或ZnO纳米棒为负极、氢氧化镍为正极的镍锌电池的电化学性能
Fig. 7 Electrochemical performances of the Ni(OH)2//commercial ZnO and Ni(OH)2//ZnO NRs (a-d) Charge-discharge curves at different current densities; (e) Rate capabilities; (f) Cycling performances
| Sample | Current density | Capacity retention/% |
|---|---|---|
| ZnO@Bi/C[ | 1C-5C | ~52.5 |
| ZnO@RGO[ | 1C-5C | ~58.3 |
| SnO2@ZnO[ | 1C-8C | ~24.0 |
| ZnO-N2@C[ | 1C-10C | ~56.4 |
| This work | 1.5C-15C | ~59.1 |
表2 不同氧化锌负极材料的倍率性能
Table 2 Rate performances of different ZnO negative materials
| Sample | Current density | Capacity retention/% |
|---|---|---|
| ZnO@Bi/C[ | 1C-5C | ~52.5 |
| ZnO@RGO[ | 1C-5C | ~58.3 |
| SnO2@ZnO[ | 1C-8C | ~24.0 |
| ZnO-N2@C[ | 1C-10C | ~56.4 |
| This work | 1.5C-15C | ~59.1 |
| Sample | Capacity retention |
|---|---|
| Spherical ZnO[ | 0.2C, 100 cycles, ~64% |
| ZnO/PPy16.8%[ | 1C, 100 cycles, ~74% |
| 12wt% TPP-modified ZnO[ | 1C, 50 cycles, ~89% |
| This work | 1.5C, 100 cycles, ~92% |
表3 不同氧化锌负极材料的循环性能
Table 3 Cycling performances of different ZnO negative materials
| Sample | Capacity retention |
|---|---|
| Spherical ZnO[ | 0.2C, 100 cycles, ~64% |
| ZnO/PPy16.8%[ | 1C, 100 cycles, ~74% |
| 12wt% TPP-modified ZnO[ | 1C, 50 cycles, ~89% |
| This work | 1.5C, 100 cycles, ~92% |
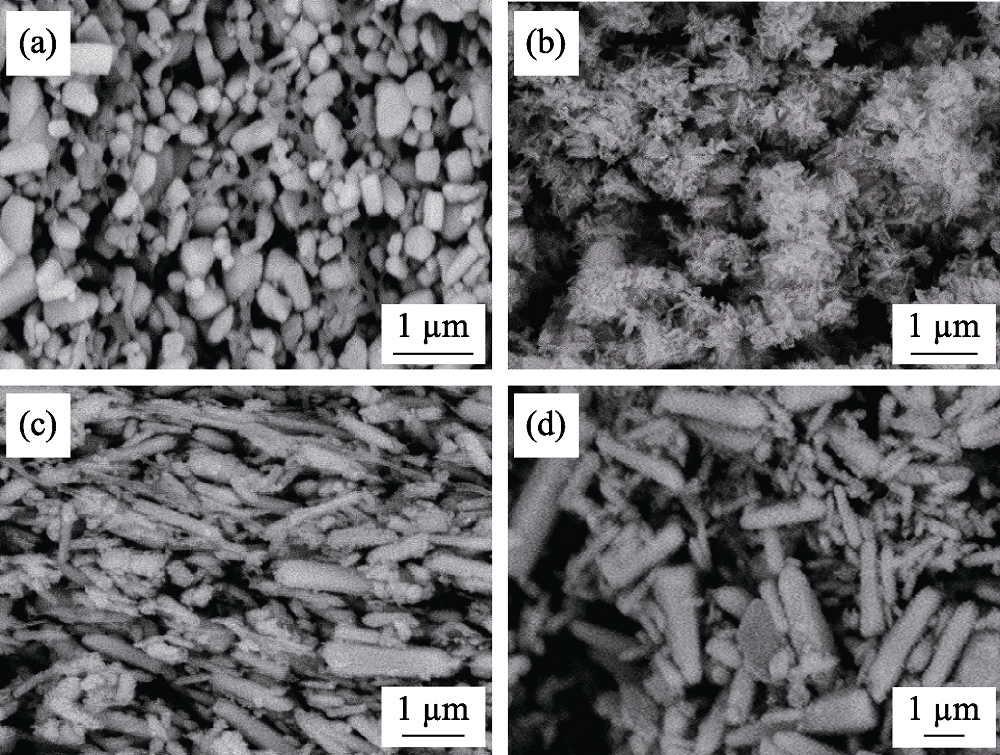
图8 在5 A·g-1电流密度下, (a, b)ZnO商品和(c, d)ZnO纳米棒100圈循环(a, c)前(b, d)后的扫描电镜照片
Fig. 8 SEM images of (a, b) commercial ZnO and (c, d) ZnO NRs (a, c) before and (b, d) after 100 cycles at 5 A·g-1
| [1] | CHEN L N, YAN M Y, MEI Z W , et al. Research progress and prospect of aqueous zinc ion battery. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017,32(3):225-234. |
| [2] | WEI X J, LI Y B, GAO S Y . Biomass-derived interconnected carbon nanoring electrochemical capacitors with high performance in both strongly acidic and alkaline electrolytes. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017,5(1):181-188. |
| [3] | WEI X J, ZOU H L, GAO S Y . Chemical crosslinking engineered nitrogen-doped carbon aerogels from polyaniline-boric acid- polyvinyl alcohol gels for high-performance electrochemical capacitors. Carbon, 2017,123:471-480. |
| [4] | WEI X J, WEI J S, LI Y B , et al. Robust hierarchically interconnected porous carbons derived from discarded Rhus typhina fruits for ultrahigh capacitive performance supercapacitors. Journal of Power Sources, 2019,414:13-23. |
| [5] | MA G Q, JIANG Z M, CHEN H C , et al. Research process on novel electrolyte of lithium-ion battery based on lithium salts. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018,33(7):699-710. |
| [6] | TAN Y, XUE B . Research progress on lithium titanate as anode material in lithium-ion battery. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018,33(5):475-482. |
| [7] | OUYANG Y, GUO Y P, LI D , et al. Single additive with dual functional- ions for stabilizing lithium anodes. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019,11(12):11360-11368. |
| [8] | LIU J P, GUAN C, ZHOU C , et al. A flexible quasi-solid-state nickel-zinc battery with high energy and power densities based on 3D electrode design. Advanced Materials, 2016,28(39):8732-8739. |
| [9] | HUANG J H, YANG Z H, YANG B , et al. Ultrasound assisted polymerization for synthesis of ZnO/polypyrrole composites for zinc/nickel rechargeable battery. Journal of Power Sources, 2014,271:143-151. |
| [10] | WEN R J, YANG Z H, FAN X M , et al. Electrochemical performances of ZnO with different morphology as anodic materials for Ni/Zn secondary batteries. Electrochimica Acta, 2012,83:376-382. |
| [11] | LI J, ZHAO T H, SHANGGUAN E B , et al. Enhancing the rate and cycling performance of spherical ZnO anode material for advanced zinc-nickel secondary batteries by combined in-situ doping and coating with carbon. Electrochimica Acta, 2017,236:180-189. |
| [12] | ZHAO Z J, YANG K, PENG K , et al. Synergistic effect of ZnO@Bi/C sphere for rechargeable Zn-Ni battery with high specific capacity. Journal of Power Sources, 2019,410:10-14. |
| [13] | YANG H, YANG Z H, WEN X , et al. The in-situ growth of zinc-aluminum layered double hydroxides on graphene and its application as anode active materials for Zn-Ni secondary battery. Electrochimica Acta, 2017,252:507-515. |
| [14] | LAI S B, JAMESH M I, WU X C , et al. A promising energy storage system: rechargeable Ni-Zn battery. Rare Metals, 2017,36(5):381-396. |
| [15] | XIE Q S, LIU P F, ZENG D Q , et al. Dual electrostatic assembly of graphene encapsulated nanosheet-assembled ZnO-Mn-C hollow microspheres as a lithium ion battery anode. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018,28(19):1707433. |
| [16] | HUANG G Y, YANG Y, SUN H Y , et al. Defective ZnCo2O4 with Zn vacancies: synthesis, property and electrochemical application. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017,724:1149-1156. |
| [17] | SHEN X Y, MU D B, CHEN S , et al. Enhanced electrochemical performance of ZnO-loaded/porous carbon composite as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013,5(8):3118-3125. |
| [18] | KIM J, IM Y, PARK K S , et al. Improved cell performances in Ni/Zn redox batteries fabricated by ZnO materials with various morphologies synthesized using amine chelates. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2017,56:463-471. |
| [19] | WU P Y, PIKE J, ZHANG F , et al. Low-temperature synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2006,3(4):272-278. |
| [20] | NOEI H, QIU H S, WANG Y M , et al. The identification of hydroxyl groups on ZnO nanoparticles by infrared spectroscopy. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2008,10(47):7092-7097. |
| [21] | N’KONOU K, HARIS M, LARE Y , et al. Effect of barium doping on the physical properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles elaborated via sonochemical synthesis method. Pramana-Journal of Physics, 2016,87(1):4. |
| [22] | KIM J G, LEE S H, KIM Y , et al. Fabrication of free-standing ZnMn2O4 mesoscale tubular arrays for lithium-ion anodes with highly reversible lithium storage properties. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013,5(21):11321-11328. |
| [23] | LIU J P, LI Y Y, DING R M , et al. Carbon/ZnO nanorod array electrode with significantly improved lithium storage capability. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009,113(13):5336-5339. |
| [24] | KAMBLE A, SINHA B, CHUNG K , et al. Facile linker free growth of CdS nanoshell on 1-D ZnO: solar cell application. Electronic Materials Letters, 2015,11(2):171-179. |
| [25] | ZENG Y X, LAI Z Z, HAN Y , et al. Oxygen-vacancy and surface modulation of ultrathin nickel cobaltite nanosheets as a high-energy cathode for advanced Zn-ion batteries. Advanced Materials, 2018,30(33):1802396. |
| [26] | NANDI P, DAS D . Photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine-B dye by stable ZnO nanostructures with different calcination temperature induced defects. Applied Surface Science, 2019,465:546-556. |
| [27] | XIA T, WALLENMEYER P, ANDERSON A , et al. Hydrogenated black ZnO nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic performance. RSC Advances, 2014,4(78):41654-41658. |
| [28] | DENG S J, ZHANG Y, XIE D , et al. Oxygen vacancy modulated Ti2Nb10O29-x embedded onto porous bacterial cellulose carbon for highly efficient lithium ion storage. Nano Energy, 2019,58:355-364. |
| [29] | CARBONE M . Zn defective ZnCo2O4 nanorods as high capacity anode for lithium ion batteries. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2018,815:151-157. |
| [30] | YAN X Y, CHEN Z X, WANG Y , et al. In-situ growth of ZnO nanoplates on graphene for the application of high rate flexible quasi-solid-state Ni-Zn secondary battery. Journal of Power Sources, 2018,407:137-146. |
| [31] | SUN L S, YI Z, LIN J , et al. Fast and energy efficient synthesis of ZnO@RGO and its application in Ni-Zn secondary battery. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016,120(23):12337-12343. |
| [32] | GUO W C, TIAN Z L, YANG C , et al. ZIF-8 derived nano-SnO2@ZnO as anode for Zn/Ni secondary batteries. Electrochemistry Communications, 2017,82:159-162. |
| [33] | ZHAO T H, SHANGGUAN E B, LI Y , et al. Facile synthesis of high tap density ZnO microspheres as advanced anode material for alkaline nickel-zinc rechargeable batteries. Electrochimica Acta, 2015,182:173-182. |
| [34] | HUANG J H, YANG Z H, WANG T T . Evaluation of tetraphenylporphyrin modified ZnO as anode material for Ni-Zn rechargeable battery. Electrochimica Acta, 2014,123:278-284. |
| [1] | 万俊池, 杜路路, 张永上, 李琳, 刘建德, 张林森. Na4FexP4O12+x/C钠离子电池正极材料的结构演变及其电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 497-503. |
| [2] | 薛柯, 蔡长焜, 谢满意, 李舒婷, 安胜利. 固体氧化物燃料电池Pr1+xBa1-xFe2O5+δ阴极材料的制备及电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 363-371. |
| [3] | 陈正鹏, 金芳军, 李明飞, 董江波, 许仁辞, 徐韩昭, 熊凯, 饶睦敏, 陈创庭, 李晓伟, 凌意瀚. 双钙钛矿Sr2CoFeO5+δ阴极材料的制备及其中温固体氧化物燃料电池性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 337-344. |
| [4] | 胡梦菲, 黄丽萍, 李贺, 张国军, 吴厚政. 锂/钠离子电池硬碳负极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 32-44. |
| [5] | 王禹桐, 张非凡, 许乃才, 王春霞, 崔立山, 黄国勇. 水系锂离子电池负极材料LiTi2(PO4)3的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 481-492. |
| [6] | 王晶, 徐守冬, 卢中华, 赵壮壮, 陈良, 张鼎, 郭春丽. 钠离子电池中空结构CoSe2/C负极材料的制备及储钠性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1344-1350. |
| [7] | 李昆儒, 胡省辉, 张正富, 郭玉忠, 黄瑞安. 源于溪木贼的高性能锂离子电池三维多孔生物质硅/碳复合负极材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 929-935. |
| [8] | 刘芳芳, 传秀云, 杨扬, 李爱军. 氮/硫共掺杂对纤水镁石模板碳纳米管电化学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 711-717. |
| [9] | 张亚萍,雷宇轩,丁文明,于濂清,朱帅霏. 双铁电复合材料的制备及其光电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(9): 987-992. |
| [10] | 湛菁,徐昌藩,龙怡宇,李启厚. 聚丙烯酰胺凝胶法制备Bi2Mn4O10及其电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(7): 827-833. |
| [11] | 郑坤, 罗永春, 邓安强, 杨洋, 张海民. A2B7型La0.3Y0.7Ni3.4-xMnxAl0.1储氢合金微观结构和电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(5): 549-555. |
| [12] | 郑时有, 董飞, 庞越鹏, 韩盼, 杨俊和. 纳米金属氧化物基锂离子电池负极材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(12): 1295-1306. |
| [13] | 郭丝霖, 康帅, 陆文强. 一步法制备锗/MXene复合材料及其作为锂离子电池负极的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(1): 105-111. |
| [14] | 李学林, 朱建锋, 焦宇鸿, 黄家璇, 赵倩楠. 二氧化锰形貌对Ti3C2Tx@MnO2复合材料电化学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(1): 119-125. |
| [15] | 张亚萍, 丁文明, 朱海丰, 黄承兴, 于濂清, 王永强, 李哲, 徐飞. 电还原MoSe2修饰TiO2纳米管光电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(8): 797-802. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||