|
|
Recent Progress on Preparation of 3C-SiC Single Crystal
XU Jintao, GAO Pan, HE Weiyi, JIANG Shengnan, PAN Xiuhong, TANG Meibo, CHEN Kun, LIU Xuechao
2026 Vol. 41 (1): 1–11
 Abstract
Abstract(
192 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(2861KB)(
380
)
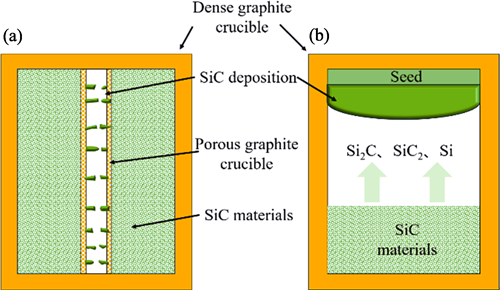
Silicon carbide (SiC), as a representative wide bandgap semiconductor material, has increasingly demonstrated its significance in high-power, high-frequency and high-temperature electronic device applications. In recent years, SiC semiconductors have become primary material for power devices in electric drive modules and charging modules of new energy vehicles. Compared to Si-based insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs), a kind of minority carrier device, SiC materials enable high-voltage resistance through majority carrier devices (such as Schottky barrier diodes and metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs)) with high-frequency device structures, which conversely allows SiC to simultaneously achieve key characteristics of low on-resistance and high frequency. It is easy to deduce that, SiC will also play an indispensable role in emerging fields such as electric aircrafts, electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) vehicles for low-altitude transportation, augmented reality (AR), photovoltaic inverters, and rail transportation. Among various SiC polytypes, 3C-SiC stands out due to its unique cubic crystal structure, higher thermal conductivity (500 W/(m·K)) and channel mobility (approximately 300 cm2/(V·s)), showcasing significant application potential and research value. This paper provides an overview of the crystal structure, fundamental physical properties, application advantages, and major growth methods of 3C-SiC, including chemical vapor deposition (CVD), continuous-feed physical vapor transport (CF-PVT), sublimation epitaxy (SE), and top-seeded solution growth (TSSG). Research progress and the latest achievements in 3C-SiC crystal growth using above techniques are reviewed, focusing on the thermodynamic characteristics and growth mechanisms of vapor-phase and liquid-phase methods. The microscopic processes of crystal growth are analyzed and summarized, and the future development directions and application prospects for 3C-SiC crystals are discussed.
|
|
|
Graphene Oxide-based Adsorbents for Pb(II) Removing in Water: Progresses on Synthesis, Performance and Mechanism
FAN Yuzhu, WANG Yuan, WANG Linyan, XIANG Meiling, YAN Yuting, LI Benhui, LI Min, WEN Zhidong, WANG Haichao, CHEN Yongfu, QIU Huidong, ZHAO Bo, ZHOU Chengyu
2026 Vol. 41 (1): 12–26
 Abstract
Abstract(
197 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(2284KB)(
2544
)
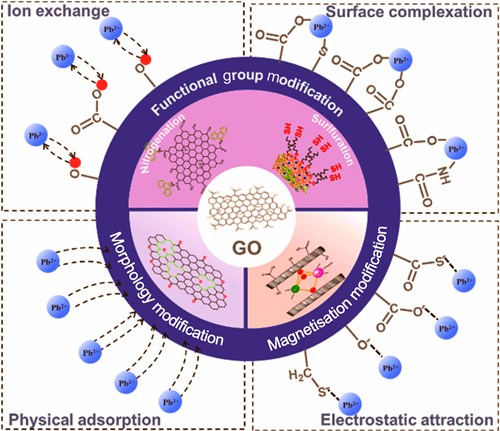
Pb(II) pollution in water constitutes a serious form of heavy metal pollution that endangers both ecological environment and human health. As an effective sewage treatment technology, adsorption has been considered an economic and common method because of its low cost, environmental friendliness and easy operation. Graphene oxide (GO), an innovative material with superior properties, has garnered extensive research as an ideal adsorbent. Nonetheless, GO still faces many challenges in practical applications due to its limited surface functional groups, suboptimal adsorption selectivity and poor regenerative properties. Current main research focuses on developing various modification strategies to enhance the adsorption performance of GO. In this paper, modification methods of GO and their adsorption mechanisms are reviewed. Firstly, three strategies for improving Pb(II) adsorption properties of GO-based materials are introduced, including N/S functionalization, morphological alteration and magnetization. Their adsorption properties covering adsorption capacity, adsorption selectivity, regeneration, and other performance metrics of GO-based adsorbents are evaluated. Subsequently, the adsorption mechanisms of Pb(II) by GO-based adsorbents such as physical adsorption, electrostatic attraction, ion exchange, and surface complexation are summarized to develop highly efficient GO-modified materials. Finally, the future development of GO-based materials for Pb(II) adsorption is prospected. This review provides novel insights for rational design of emerging GO-based adsorbents and serves as a reference foundation for research and application of GO-modified materials in Pb(II) treatment.
|
|
|
Synergistic Mechanism of Gd3+ and Yb3+ on Crystallization Behavior of CMAS Corrosion Products
ZHANG Guangheng, SHI Jinyu, SHEN Hongyu, ZHANG Jie, WANG Jingyang
2026 Vol. 41 (1): 27–36
 Abstract
Abstract(
183 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(19899KB)(
239
)
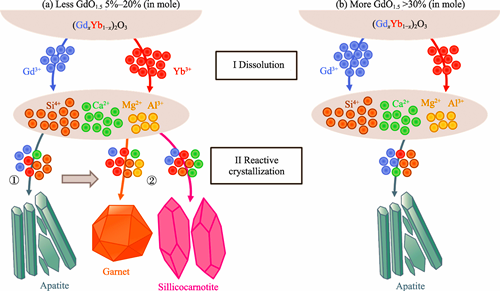
As the operating temperature of aero-engine rises, degradation of thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) and environmental barrier coatings (EBCs) on hot-section components affected mainly by infiltration of calcium-magnesium-alumina-silicate (CaO-MgO-AlO1.5-SiO2, CMAS) has garnered increasing attention. Rare earth constituents play an essential role in forming corrosion products and subsequent melt penetration when conventional TBCs and EBCs are attacked by CMAS deposits. This study focused on preparation of a series of gadolinium-ytterbium oxides ((GdxYb1-x)2O3, x=0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.20, 0.30, 0.50 and 1.00), with particular emphasis on the roles of ytterbium and gadolinium. Their reaction with CMAS deposits was systematically investigated at 1300 ℃ to explore the synergistic mechanism associated with these two rare earth elements. The results indicate that gadolinium cations can efficiently induce the crystallization of products with apatite structure which have a low melt consumption. Conversely, ytterbium cations can induce the formation of products with garnet and silicocarnotite structure which have sluggish kinetics. Furthermore, partitioning of gadolinium and ytterbium ions within corrosion products, along with variation of residual CMAS melt composition, was further analyzed. It is proposed that these two rare earth ions exhibit a synergistic effect within a certain composition range (5%-20% (in mole) of gadolinium content). The optimized ratio of gadolinium and ytterbium within coatings is anticipated to promote apatite crystallization, prevent melt penetration, and modify the sluggish crystallization kinetics of garnet and silicocarnotite, thereby significantly improving the melt consumption. This investigation on synergistic effect of gadolinium and ytterbium cations provides a theoretical support for the anti-CMAS-corrosion composition modification of TBCs/EBCs.
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of Ytterbium Aluminosilicate Glass and SiC Modified h-BN-based Composites
ZHANG Yongheng, CHEN Jixin
2026 Vol. 41 (1): 37–44
 Abstract
Abstract(
132 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(2629KB)(
143
)
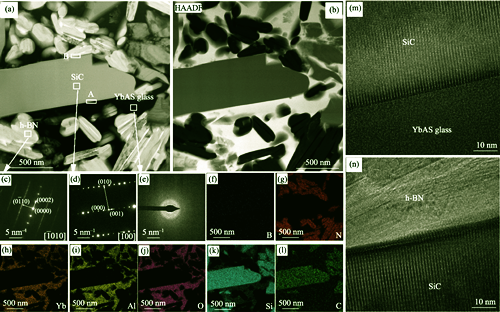
Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) ceramics are significant in industrial applications, however, their special layered structure, combined with low strength and hardness, limits their application. In this study, ytterbium aluminum silicate (YbAS) glass and hard SiC particles were simultaneously introduced as reinforcing phases, and a series of h-BN/YbAS/SiC composites were prepared by in-situ reaction hot pressing sintering techniques. With the volume fraction of YbAS glass fixed at 30%, the effect of SiC content on the properties of the composites was studied. The results demonstrate that the synergistic effect of YbAS glass and SiC can effectively enhance the strength and toughness of h-BN-based composites. This composite exhibits optimal mechanical performance when the SiC volume fraction reaches 30%, yielding flexural strength, compressive strength, fracture toughness, Vickers hardness, and elastic modulus values of (462±5) MPa, (1465±58) MPa, (5.5±0.3) MPa·m1/2, (4.7±0.3) GPa, and 140 GPa, respectively. The strengthening mechanism is identified as when the SiC content reaches a certain proportion, it plays a supporting role, effectively bearing external loads to enhance the composites. Moreover, SiC can effectively suppress the growth of h-BN grains during the sintering process, contributing to fine-grained strengthening. The composites also have good high-temperature mechanical properties and relatively low thermal conductivity, with the thermal expansion coefficient being related to structure of h-BN and transition temperature of YbAS glass. This study provides an effective approach for the strengthening and toughening of h-BN ceramic materials.
|
|
|
High-temperature Oxidation Mechanism and Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties of Fe2AlB2
MA Xinchao, ZHI Qing, LI Wei, CHEN Mao, WANG Hailong, ZHANG Rui, ZHANG Fan, FAN Bingbing
2026 Vol. 41 (1): 45–54
 Abstract
Abstract(
489 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(4269KB)(
96
)
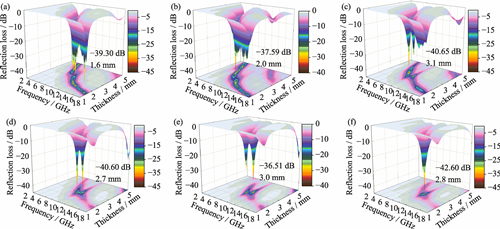
Traditional wave-absorbing materials often exhibit performance limitations at high temperatures, which makes it difficult to meet performance demands in extreme high-temperature environments. Fe2AlB2 has garnered significant attention in the field of high-temperature wave absorption due to its nano-layered structure and exceptional high-temperature stability. This study synthesized Fe2AlB2 powder through a wet ball milling process followed by sintering in an argon atmosphere. Investigation was conducted to elucidate the oxidation mechanisms and to assess the evolution of its wave-absorbing properties at elevated temperatures. Additionally, electromagnetic simulation software was utilized to model the radar cross-section associated with its absorption process under 7 GHz microwave irradiation. The results indicate that the onset oxidation temperature of Fe2AlB2 is 671 ℃. As the oxidation temperature increases, a dense Al2O3 protective film forms on its surface, significantly enhancing its oxidation resistance. Beyond 1000 ℃, this Al2O3 film fractures, leading to transformation of the primary phases into Fe2O3, Al4B2O9 and amorphous B2O3. Within the oxidation temperature range of 300-800 ℃, the wave absorption performance of the sample progressively improves with increasing oxidation temperature, exhibiting particularly outstanding dielectric loss capabilities around 10 GHz. At an oxidation temperature of 900 ℃, the sample achieves a reflection loss of -42.60 dB at a frequency of 11.28 GHz, with corresponding a thickness of 2.8 mm. The Al2O3 film significantly enhances dielectric loss efficiency by inducing interfacial polarization loss at the "oxide film-matrix" interface. This study elucidates that oxidation mechanisms of Fe2AlB2 at varying temperatures and examines consequent impacts on wave-absorbing properties, thereby providing a theoretical foundation for its application in high-temperature wave-absorbing environments.
|
|
|
Fabrication and Thermoelectric Performance of Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12 Thin Films via Magnetron Sputtering for Flexible Thermoelectric and Sensing Applications
GE Yeming, TANG Zhe, LIU Miao, LOU Size, LIU Zhenguo, ZHOU Yan, WAN Shun, ZONG Peng'an
2026 Vol. 41 (1): 55–62
 Abstract
Abstract(
172 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(3347KB)(
175
)
Skutterudite-based CoSb3 materials have attracted significant attention in thermoelectric applications due to their environmental friendliness, thermal stability and excellent thermoelectric properties. While considerable progress has been made in the development of n-type skutterudite thermoelectric thin films, research on high-performance p-type filled skutterudite flexible thin films remains limited, particularly in the context of flexible device integration. In this work, p-type Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12 thin films were deposited on glass substrates via radio frequency magnetron sputtering, and influence of sputtering power (100-120 W) on the film composition, microstructure, and thermoelectric properties was systematically investigated. The results reveal that increasing the sputtering power leads to a gradual decrease in the Ce/Fe atomic ratio and a corresponding increase in the hole concentration, which enhances the electrical conductivity (σ) but reduces the Seebeck coefficient (S). The film deposited at 110 W exhibits the highest thermoelectric performance, achieving a power factor (PF) of 76.7 μW·m-1∙K-2 at room temperature and 103.5 μW·m-1∙K-2 at 500 K. Building upon these findings, flexible Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12 films were further fabricated on polyimide (PI) substrates with substrate heating applied during deposition to improve interfacial adhesion. A flexible thin-film thermoelectric generator was successfully integrated, and its potential application in temperature sensing was evaluated. The device demonstrates excellent mechanical flexibility and reliable thermal sensing performance, highlighting its promise for use in flexible thermoelectric sensor technologies.

|
|
|
Enhanced Thermoelectric Properties of Two-dimensional Planar Copper Polyphthalocyanine by Dispersing Single-walled Carbon Nanotubes
HU Yuchen, XU Zishuo, HU Yuejuan, CHEN Lidong, YAO Qin
2026 Vol. 41 (1): 63–69
 Abstract
Abstract(
160 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(4584KB)(
68
)
Two-dimensional planar metal polyphthalocyanine is considered a kind of promising organic thermoelectric material due to its unique molecular structure and high carrier mobility, but its low carrier concentration and low electrical conductivity impede improvement of thermoelectric performance. In this work, copper polyphthalocyanine/single-walled carbon nanotubes (CuPPc/SWCNTs) composites were prepared by in-situ polymerization and mechanical ball-milling, respectively. As compared with ball-milled sample (BM-CuPPc/SWCNTs), in-situ polymerized sample (IS-CuPPc/SWCNTs) presents strong π-π conjugation between CuPPc and SWCNTs, which can effectively reduce the interfacial resistance between CuPPc and SWCNTs. Therefore, IS-CuPPc/SWCNTs shows higher electrical conductivity than BM-CuPPc/SWCNTs at high SWCNTs concentration. With 80% (in mass) SWCNTs, the electrical conductivity of IS-CuPPc/SWCNTs reaches 1.31×104 S·m-1, 30% higher than that of BM-CuPPc/SWCNTs, and six orders of magnitude higher than that of pure CuPPc. Meanwhile, the maximum thermoelectric power factor of IS-CuPPc/SWCNTs reaches 18.24 μW·m-1·K-2, which is higher than that of BM-CuPPc/SWCNTs and surpasses that of pure CuPPc by six orders of magnitude. This study provides an effective way to enhance the thermoelectric properties of metallic polyphthalocyanine.

|
|
|
Ag Doping Modulating Cathode Acidic Sites to Enhance Chromium Resistance for Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
GAO Yuan, WEI Bo, JIN Fangjun, LÜ Zhe, LING Yihan
2026 Vol. 41 (1): 70–78
 Abstract
Abstract(
149 )
 HTML
HTML(
0)
 PDF
PDF(3888KB)(
39
)
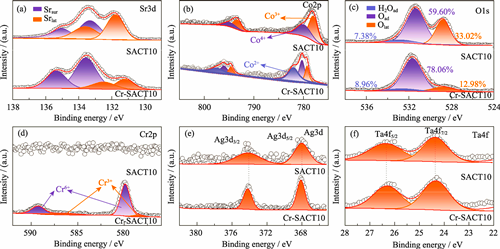
Cr poisoning is an important factor restricting the practical application of solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) cathodes. In particular, the alkaline earth-rich perovskite oxide cathodes are prone to cation segregation and impurity poisoning at high temperatures, which can significantly reduce the cathode performance. To improve the Cr resistance of the cathode, the acid site of SrCo0.9Ta0.1O3-δ (SCT) was regulated by Ag doping, whose conductivity, catalytic activity, surface morphology, and composition were then systematically investigated. The results show that Ag doping enhances the conductivity of the material, and the doped material exhibits higher oxygen surface exchange coefficient, which is conducive to improving its cathodic catalytic activity. At 700 ℃, polarization resistance (Rp) of Sr0.9Ag0.1Co0.9Ta0.1O3-δ (SACT10) cathode is 0.0176 Ω·cm2, significantly lower than that of SCT cathode (0.0366 Ω·cm2). In addition, due to the Ag doping strategy, the average valence state of Co in SACT10 material increases, which further increases the relative acidity and improves the Cr resistance. After operating in Cr-containing atmosphere for 22 h, Rp of SACT10 cathode is 0.205 Ω·cm2, significantly lower than that of SCT cathode (0.964 Ω·cm2), and fewer inert secondary phases are observed on the surface of SACT10 cathode after testing. All above results confirm that Ag doping can effectively increase acid sites, improve activity and enhance Cr resistance. SACT10 obtained in this work is expected to be a promising medium temperature SOFC cathode material.
|
|
|
Construction and Performance of ZnFe2O4//rGH Aqueous Photo-assisted Charging Supercapacitor
WANG Yu, BASSANYIN Christopher, LIU Xin, WANG Yanxiang, LI Jiake
2026 Vol. 41 (1): 79–86
 Abstract
Abstract(
216 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(3102KB)(
341
)
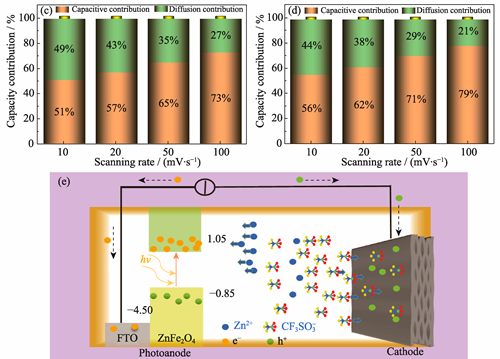
Synergistic innovation of solar energy collection and storage technology provides an important direction for constructing a new type of self-supply system, in which photo-assisted charging supercapacitor has become a research hotspot due to their unique photo-induced charge storage mechanism and fast charging/discharging characteristics with high power density and fast charging/discharging characteristics, which provides an efficient, environmentally friendly, and sustainable new strategy for energy harvesting and storage in wearable electronic devices and other related products. In this work, ZnFe2O4 was synthesized by hydrothermal method and employed as the supercapacitor photoanode, while reduced graphene oxide hydrogel (rGH), prepared using an improved Hummers method followed by hydrothermal treatment, served as the cathode, and Zn(CF3SO3)2 aqueous solution was used as the electrolyte to construct an aqueous photo-assisted charging supercapacitor. The results from the synthesized products, including phase composition, microscopic morphology, chemical structure, light absorption properties, and photoelectrochemical performance of the supercapacitor, show that under the photoelectrical synergistic charging conditions (a current density of 0.2 A·g-1 and a light intensity of 95 mW·cm-2), specific capacity of supercapacitor reaches 148 F·g-1, 17% higher than that under only electric charging conditions. The capacity retention rates of the device are 80% and 90% after 10000 cycles under only electric charging and photoelectric synergistic charging, respectively. Based on all above results, the constructed aqueous photo-assisted charging supercapacitor exhibits high specific capacity and excellent cycling stability, demonstrating promising potential for applications in wearable electronics and related fields.
|
|
|
Effect of CeO2 on Low-temperature Denitrification Performance of MnOx Catalysts and Its Mechanism
WU Boyu, ZHANG Shengen, ZHANG Shengyang, LIU Bo, ZHANG Bolin
2026 Vol. 41 (1): 87–95
 Abstract
Abstract(
150 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(1213KB)(
825
)
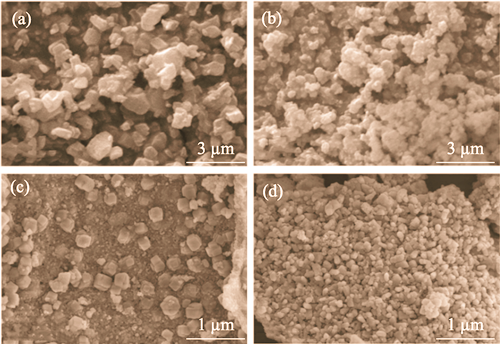
Nitrogen oxides (NOx), as main atmospheric pollutants in China, are usually removed through ammonia selective catalytic reduction (NH3-SCR) technology to achieve ultra-low emissions. Low-temperature NH3-SCR has gained much attention due to its low energy consumption and cost. However, MnOx-based catalysts generally suffer from insufficient stability and are susceptible to SO2 and H2O poisoning at 120 ℃. To improve the denitrification performance of MnOx-based catalysts under low temperature and lean flue gas conditions, CeO2/MnOx catalysts were prepared by precipitation-calcination decomposition method in this study. Influence of CeO2 modification on structure, surface properties and low-temperature NH3-SCR performance of catalyst was systematically studied. Combining first principles calculations, influence of CeO2 modification on catalytic mechanism for reducing activation energy of the reaction was revealed at microscopic level. The results showed that addition of CeO2 refined micro particle size of catalyst, reduced proportion of main crystalline phase MnO2, significantly increased concentration of weak acid sites in the catalyst, augmented proportion of Mn3+/Mn and Oα/O, and improved surface acidity and redox performance of the catalyst. The prepared Mn10Ce3 and Mn10Ce5 catalysts achieved a NO conversion rate of over 98%, maintaining stability even at 120 ℃. Addition of CeO2 dispersed the aggregated MnOx and reduced concentration of Mn4+ distribution, which to some extent hindered excessive oxidation of NH3 and NO by high valence Mn4+, thereby suppressing N2O formation and improving N2 selectivity of the catalyst. First principles calculations further confirmed that CeO2 modification reduced the activation energy of various intermediate states in reaction pathway, lowering the reaction temperature and improving the low-temperature NH3-SCR efficiency.
|
|
|
Electrocaloric Effect of Lead Magnesium Niobate-lead Titanate (PMN-PT) Ceramics
JIANG Niyu, SUN Haochen, LIN Mingmei, WANG Dingyuan, LIU Laijun
2026 Vol. 41 (1): 96–104
 Abstract
Abstract(
184 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(11635KB)(
289
)
Electrocaloric refrigeration technology has emerged as a research hotspot in solid-state cooling due to its advantages of high energy efficiency, miniaturization potential and environmental friendliness. However, achieving a large adiabatic temperature change (ΔT) and a wide operation temperature (Tspan) under low electric fields remains challenging. In this study, a new type of ceramics, (1-x)Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-xPbTiO3 (PMN-PT, x=0.08, 0.10, 0.12, 0.14) ferroelectric relaxor with different PT contents, was synthesized via a conventional solid-state reaction method. The influence of PT concentration on their electrocaloric performance was investigated. Results indicate that increasing PT content weakens their relaxor characteristics, reduces their dielectric frequency dispersion, and drives their relaxor ferroelectric behavior toward normal ferroelectric. Notably, the 0.88PMN-0.12PT ceramic exhibits outstanding electrocaloric properties under a low electric field of 50 kV/cm, achieving a maximum ΔT of 1.60 K, with ΔT exceeding 0.5 K across a broad temperature range of 30-180 ℃. Piezoresponse force microscopy (PFM) reveals its uniformly distributed long-range ferroelectric domain structure. The electrocaloric effect originates from entropy changes induced by transition of ferroelectric domains from an ordered to a disordered state during electric field unloading. By integrating dielectric, ferroelectric and domain structure analyses, the diffuse phase transition of relaxor ferroelectrics is correlated to their wide-temperature-range electrocaloric performance. This study provides theoretical guidance for designing lead-based electrocaloric materials compatible with low-field driving and wide temperature ranges, which has potential for applications in solid-state refrigeration devices.
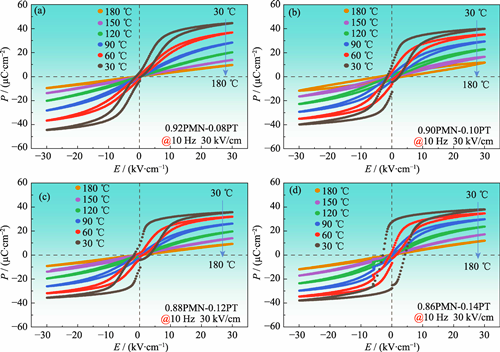
|
|
|
Femtosecond Laser Modulation on Luminescence Properties of CdS Quantum Dot Glasses
YUAN Zihao, XU Yinsheng, LI Xinkuo, TAN Dezhi
2026 Vol. 41 (1): 105–112
 Abstract
Abstract(
154 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(16271KB)(
55
)
CdS quantum dots have a quantum size effect, while photoluminescence wavelength can be regulated by manipulating their sizes, both of which show application potentials in many fields such as fabrication of micro-nano optical devices. With the development of ultrafast laser technology, femtosecond lasers have gradually been delved in the micro-nano manufacturing and optical property regulation of the optoelectronic materials. However, photoluminescence modulation of CdS quantum dots by the femtosecond lasers has never been achieved. This work aims at preparation and photoluminescence modulation of CdS quantum dots based on glass matrix by using femtosecond laser direct writing, and explores their applications in fields such as optical storage and information encryption. In the experiment, five groups of borosilicate glasses with different CdS contents were prepared via a melt quenching method, and the glass samples were finely polished for the subsequent femtosecond laser processing. Due to the local thermal accumulation effect generated by the femtosecond laser, CdS quantum dots can be directly written and precipitate inside the glass. Morphology, microstructure size and dispersion of CdS quantum dots precipitated inside the glass were analyzed by transmission electron microscopy. By changing the laser parameters to regulate size of the precipitated quantum dot spot, continuous regulation of the spot size of laser-induced processing within the range of 5.33-12.28 μm and modulation of the emission wavelength within the range of 540-610 nm were achieved. Finally, it was demonstrated that femtosecond lasers could direct write on the CdS quantum dots in fields such as information encryption and storage.
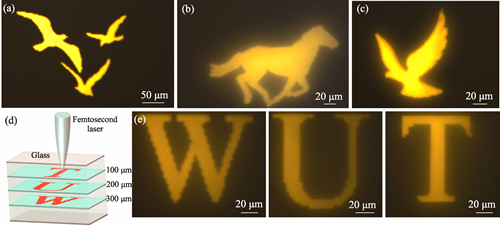
|
|
|
Sm:LuAG/Nd:LuAG Composite Laser Ceramics with Cladding Structure: Fabrication and Properties
HAN Weiwei, HUANG Dong, LI Tingsong, LI Jiang
2026 Vol. 41 (1): 113–118
 Abstract
Abstract(
140 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(2299KB)(
258
)
For high power lasers, the thermal effect imposes a limit on the power density dissipated inside the gain element, while it can be reduced by increasing the size of gain medium, which enhances heat dissipation. However, when aspect ratio of the gain medium increases, spontaneous fluorescence can be drastically amplified. Transverse propagation of spontaneous fluorescence induces amplified spontaneous emission, triggering detrimental parasitic oscillations. A promising solution involves applying cladding layers to the lateral surfaces of gain media to absorb stray radiation. For high repetition rate nanosecond high power solid-state lasers, it is essential to choose gain media with moderate saturation flux. Among these, Nd:LuAG transparent ceramics have shown significant potential due to their outstanding optical, mechanical, and thermodynamic properties. Additionally, Sm:LuAG transparent ceramics, with a high absorption coefficient at 1064 nm, excellent theoretical optical transmittance at 808 nm, and a refractive index similar to that of Nd:LuAG, have emerged as one of the best materials for cladding Nd:LuAG laser ceramics. Here, the 5% Sm:LuAG/1% Nd:LuAG (in atom) cladding laser ceramics (φ56.0 mm×4.8 mm) using commercial Lu2O3, α-Al2O3, Nd2O3 and Sm2O3 powders as raw materials were fabricated by vacuum pre-sintering at 1825 ℃ for 20 h and HIP post-treatment at 1750 ℃ for 3 h with TEOS and CaO as sintering additives. The in-line transmittance of the gain area is 81.5% at 1064 nm, while that of the cladding area is 78.6% at 808 nm.

|
|
|
Effect of Argon Atmosphere Heat Treatment on Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Evolution of Shicolon-II SiC Fibers
YUAN Wang, HU Jianbao, ZHOU Liang, KAN Yanmei, ZHANG Xiangyu, DONG Shaoming
2026 Vol. 41 (1): 119–128
 Abstract
Abstract(
137 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(5011KB)(
30
)
Silicon carbide fibers are considered ideal reinforcing materials for ceramic matrix composites due to their excellent mechanical properties and high-temperature performance. Different types of fibers necessitate individual investigation due to variations in their composition and fabrication processes. This study presents a comprehensive investigation into evolution of the mechanical properties, surface microstructure, and composition of Shicolon-II fibers subjected to argon heat treatment at temperatures ranging from 1300 ℃ to 1700 ℃. The Shicolon-II fibers are composed of small-sized β-SiC grains, SiCxOy amorphous phase, and a minor amount of graphite microcrystals. Following treatment in an argon atmosphere at 1300 ℃, the fibers maintain a monofilament tensile strength of 3.620 GPa, corresponding to a retention of 98.32%. This strength diminishes to 2.875 GPa, equating to a retention of 78.08%, after treatment at 1500 ℃. The reduction in mechanical properties of the fibers can be ascribed to the decomposition of the amorphous phase and the growth of β-SiC grains. Furthermore, creep resistance is an essential factor influencing the long-term performance of composite materials. After treatment at temperatures above 1400 ℃, the high-temperature creep resistance of the fibers is significantly enhanced due to growth of β-SiC grains. This study offers valuable theoretical insights into high-temperature applications of second-generation fibers, contributing to an enhanced understanding of their performance under extreme conditions.
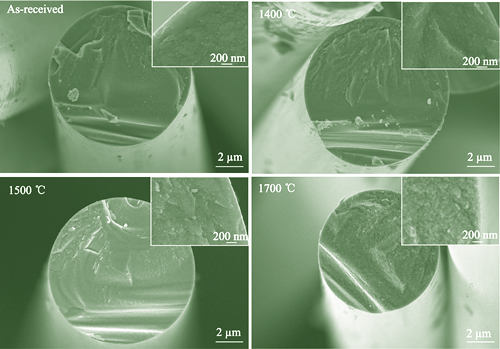
|
|
|
Achieving High Power Density in Paper-based Piezoelectric Nanogenerators through Dual-phase BCZT Doping Strategy
WANG Siting, SUN Zixiong, LIU Xinying, HAN Peiqiao, WANG Xiuli, ZHANG Sufeng
2026 Vol. 41 (1): 129–136
 Abstract
Abstract(
130 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(4695KB)(
238
)
Development of high performance, flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators (PENGs) is critical for advancing self-powered sensing and microelectronic applications. In this study, a hydrogen-bond substitute strategy was employed to fabricate a multi-layer PENG based on a cellulose/polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) blend film matrix, incorporating multi-phase BCZT (0.1BaZr0.2Ti0.8O3-0.9Ba0.7Ca0.3TiO3) ceramic fillers. Structural characterization via SEM and TEM revealed that an intricate hydrogen-bond network facilitated the uniform dispersion of ceramic fillers within the composite film’s sub-layers. In order to study the effect of filler distribution on piezoelectric performance, the single- and double-layer composite films with varying BCZT configurations were produced and evaluated. The results demonstrated that double-layer PENGs exhibit significantly enhanced electrical output compared to their single-layer counterparts, with the D-L3H7 configuration achieving an open circuit voltage (VOC) of 23.13 V and a short circuit current (ISC) of 8.32 μA. This enhancement is attributed to increased inter-layer interfaces, which effectively suppressed charge injection and migration, leading to improved charge density. Additionally, the presence of sharp tipped hexagonal tetragonal phase nanoparticles induced an electric field enhancement effect, further optimizing performance.
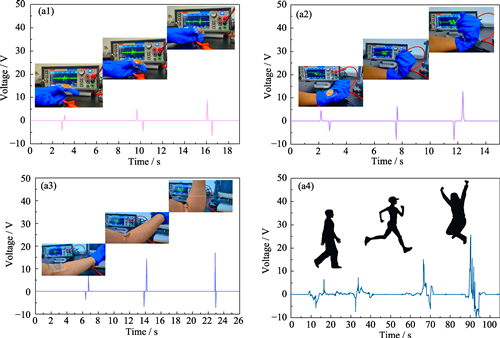
|
|