
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 105-112.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250121
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
YUAN Zihao1,2( ), XU Yinsheng1(
), XU Yinsheng1( ), LI Xinkuo2,3, TAN Dezhi2,3(
), LI Xinkuo2,3, TAN Dezhi2,3( )
)
Received:2025-03-24
Revised:2025-04-27
Published:2026-01-20
Online:2025-06-05
Contact:
XU Yinsheng, professor. E-mail: xuyinsheng@whut.edu.cn;About author:YUAN Zihao (2001-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: yuanzihao19@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
YUAN Zihao, XU Yinsheng, LI Xinkuo, TAN Dezhi. Femtosecond Laser Modulation on Luminescence Properties of CdS Quantum Dot Glasses[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 105-112.
| Sample | SiO2/(%, in mole) | B2O3/(%, in mole) | Na2O/(%, in mole) | ZnO/(%, in mole) | CdS/(%, in mole) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC0.3 | 40 | 28 | 22 | 10 | 0.3 |
| SC0.5 | 40 | 28 | 22 | 10 | 0.5 |
| SC0.7 | 40 | 28 | 22 | 10 | 0.7 |
| SC1.0 | 40 | 28 | 22 | 10 | 1.0 |
| SC1.5 | 40 | 28 | 22 | 10 | 1.5 |
Table 1 Compositions of the borosilicate glass with different CdS contents
| Sample | SiO2/(%, in mole) | B2O3/(%, in mole) | Na2O/(%, in mole) | ZnO/(%, in mole) | CdS/(%, in mole) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC0.3 | 40 | 28 | 22 | 10 | 0.3 |
| SC0.5 | 40 | 28 | 22 | 10 | 0.5 |
| SC0.7 | 40 | 28 | 22 | 10 | 0.7 |
| SC1.0 | 40 | 28 | 22 | 10 | 1.0 |
| SC1.5 | 40 | 28 | 22 | 10 | 1.5 |
| Classification | Repetition rate | Pulse width | Irradiation time/s | Pulse energy/μJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 200 kHz | 1 ps | 2~10 | 0.8-3.0 |
| II | 200 kHz | 230 fs~3 ps | 6 | 0.8-3.0 |
| III | 100 kHz-1 MHz | 1 ps | 6 | 0.5-2.0 |
Table 2 Laser processing parameters
| Classification | Repetition rate | Pulse width | Irradiation time/s | Pulse energy/μJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 200 kHz | 1 ps | 2~10 | 0.8-3.0 |
| II | 200 kHz | 230 fs~3 ps | 6 | 0.8-3.0 |
| III | 100 kHz-1 MHz | 1 ps | 6 | 0.5-2.0 |
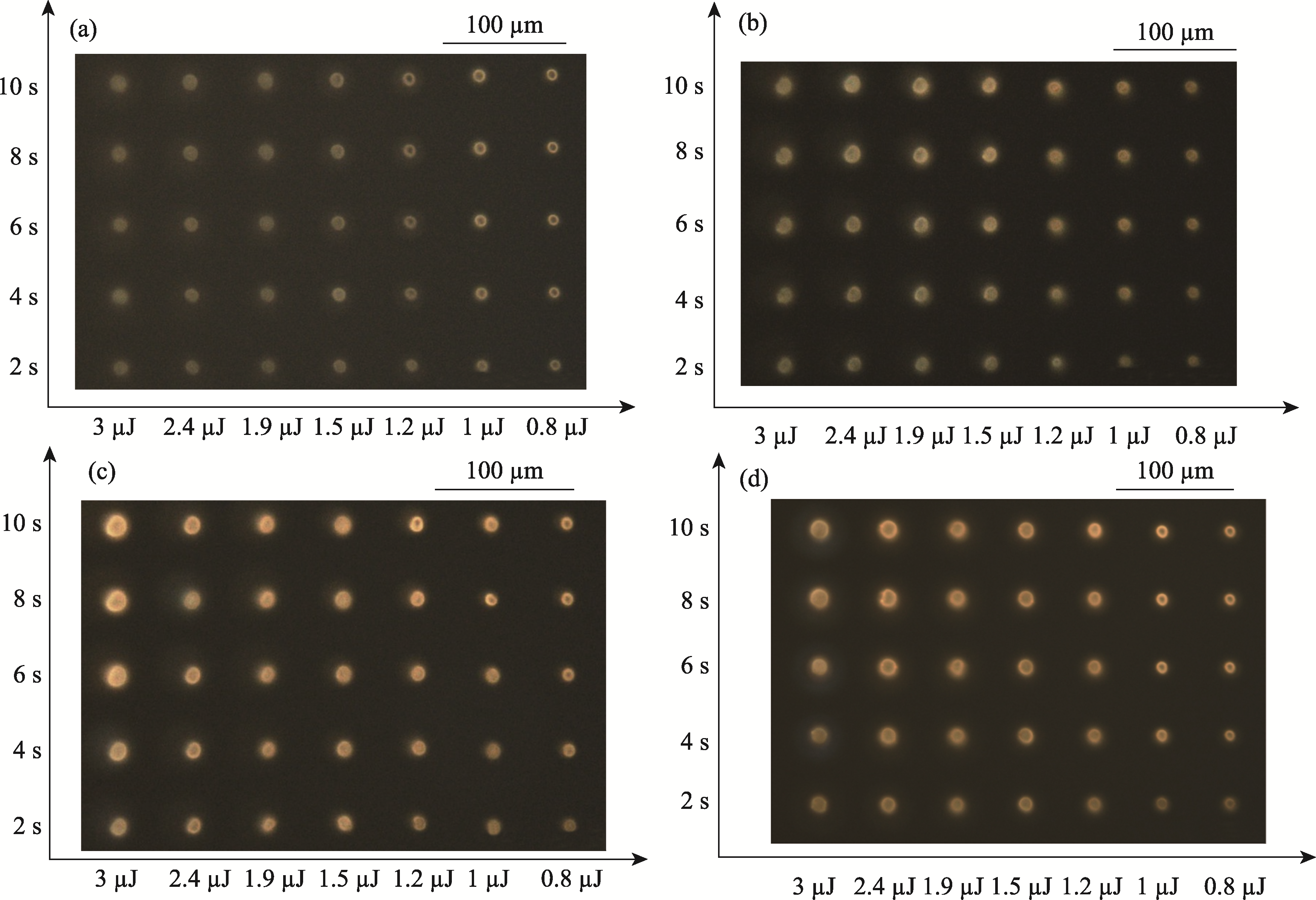
Fig. 1 Fluorescence micrograph of femtosecond laser direct writing of CdS quantum dots under different irradiation time and pulse energy (a) SC0.3 sample; (b) SC0.5 sample; (c) SC1.0 sample; (d) SC1.5 sample
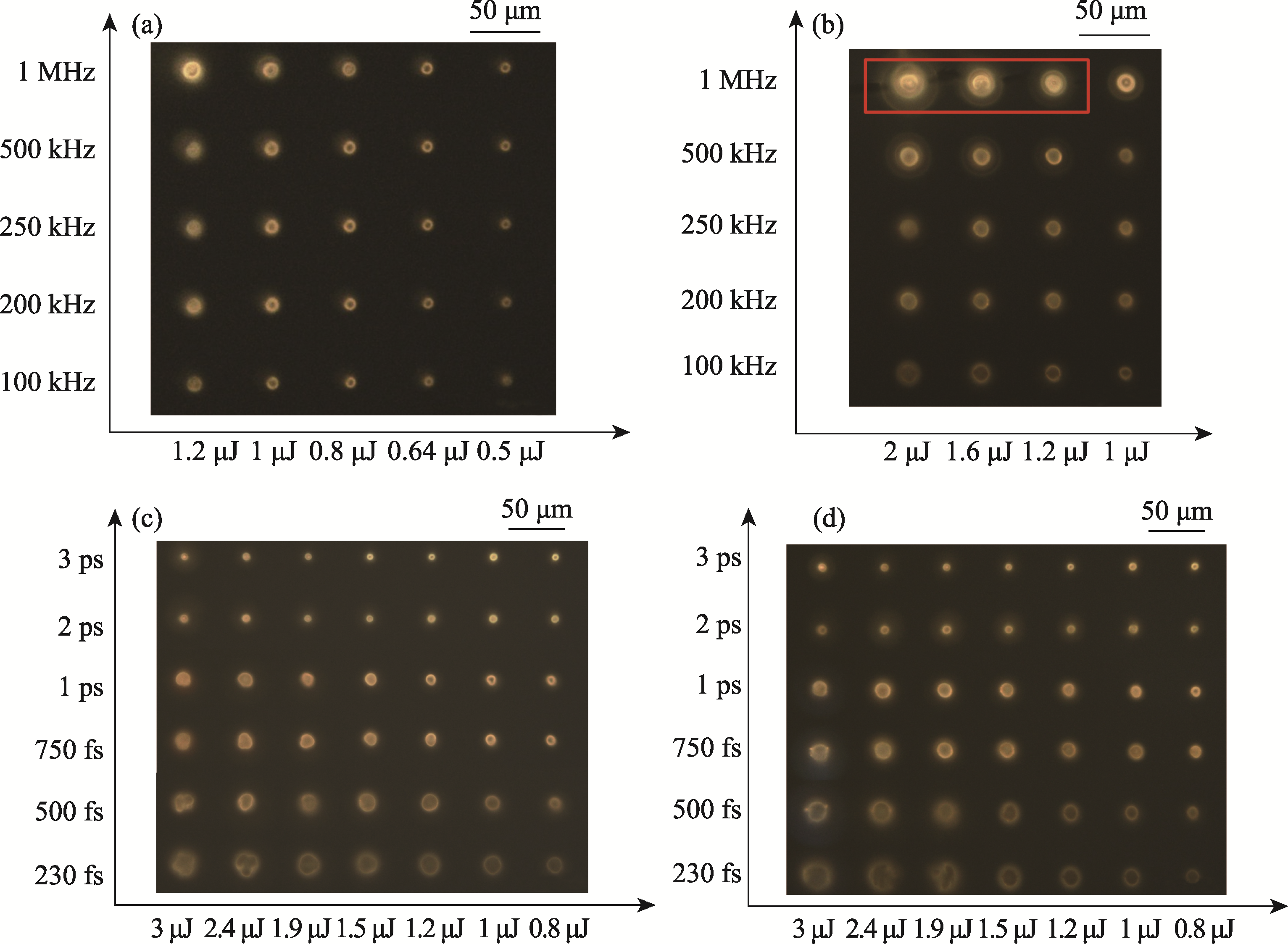
Fig. 3 Fluorescence micrograph of femtosecond laser direct writing of CdS quantum dots under different repetition rates, pulse widths and pulse energies (a) SC0.5 sample; (b, c) SC1.5 sample; (d) SC0.7 sample
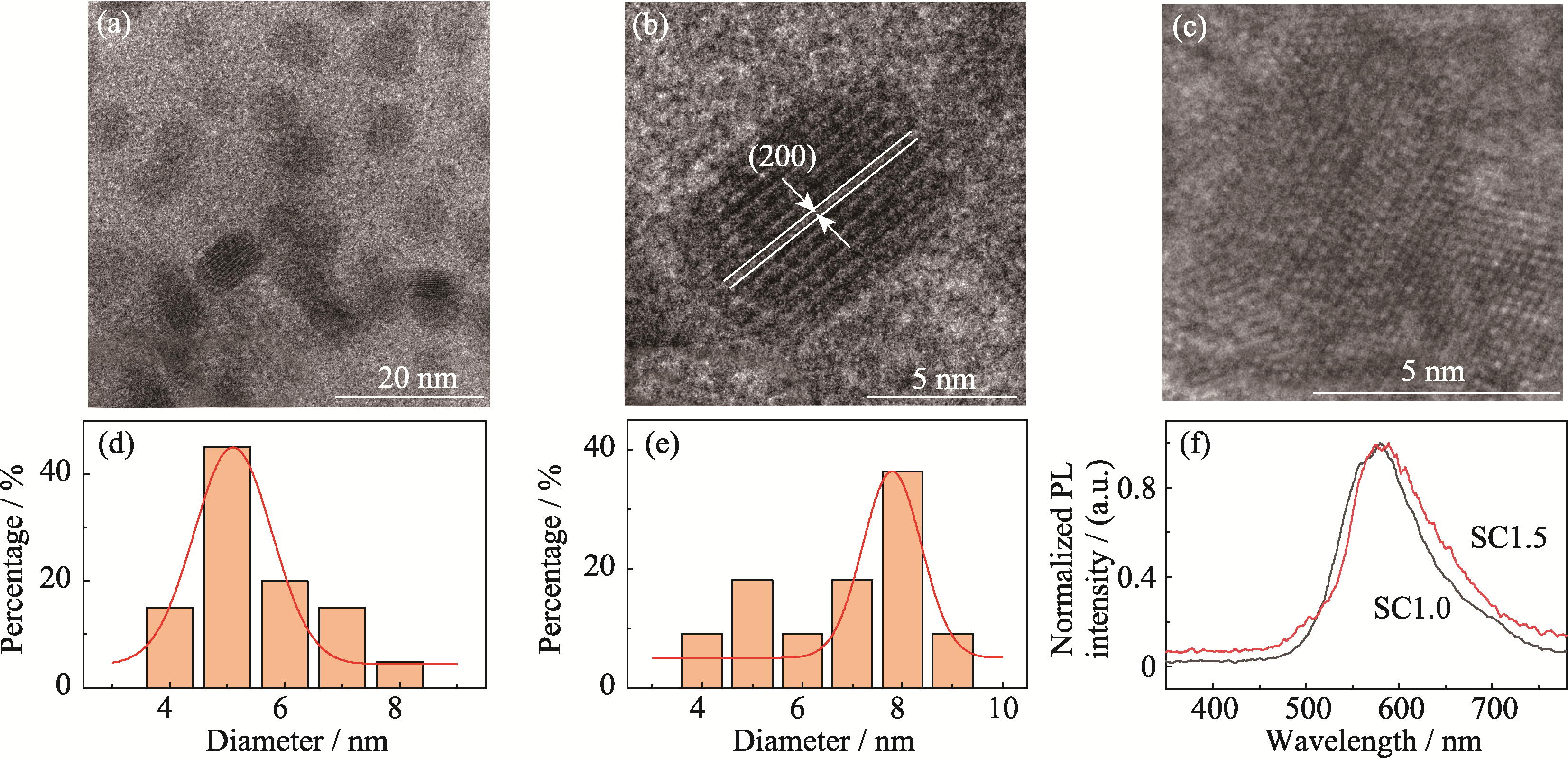
Fig. 5 TEM images, size distribution histograms of CdS quantum dots, and PL spectra for SC1.0 and SC1.5 sweep line samples (a-c) TEM images of CdS quantum dots in the (a, b) SC1.0 and (c) SC1.5 sweep line samples; (d, e) Size distribution histograms of CdS quantum dots in the (d) SC1.0 and (e) SC1.5 sweep line samples; (f) PL spectra of SC1.0 and SC1.5 sweep line samples
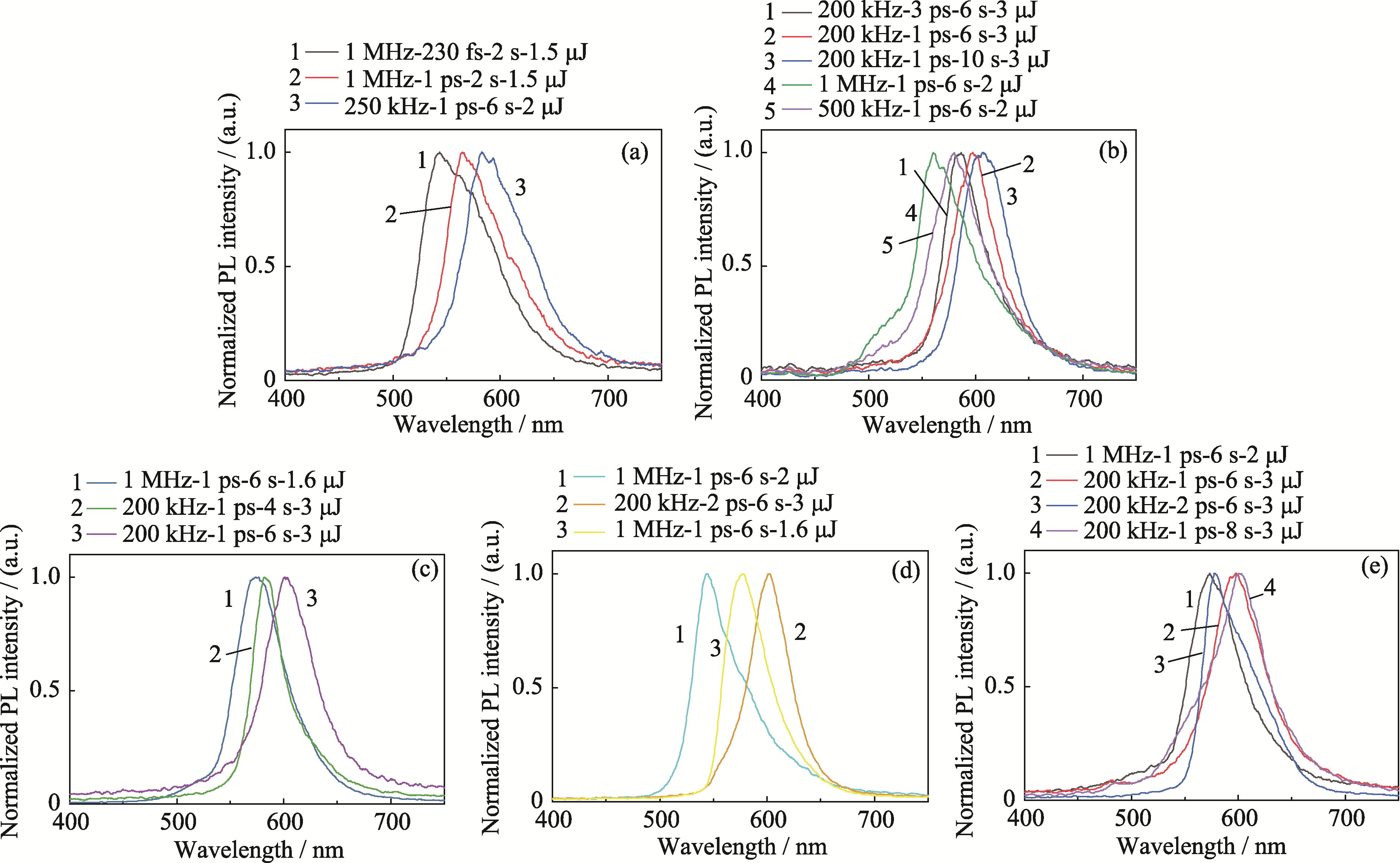
Fig. 6 PL spectra of CdS quantum dot glasses with different femtosecond laser processing parameters (a) SC0.3 sample; (b) SC0.5 sample; (c) SC0.7 sample; (d) SC1.0 sample; (e) SC1.5 sample
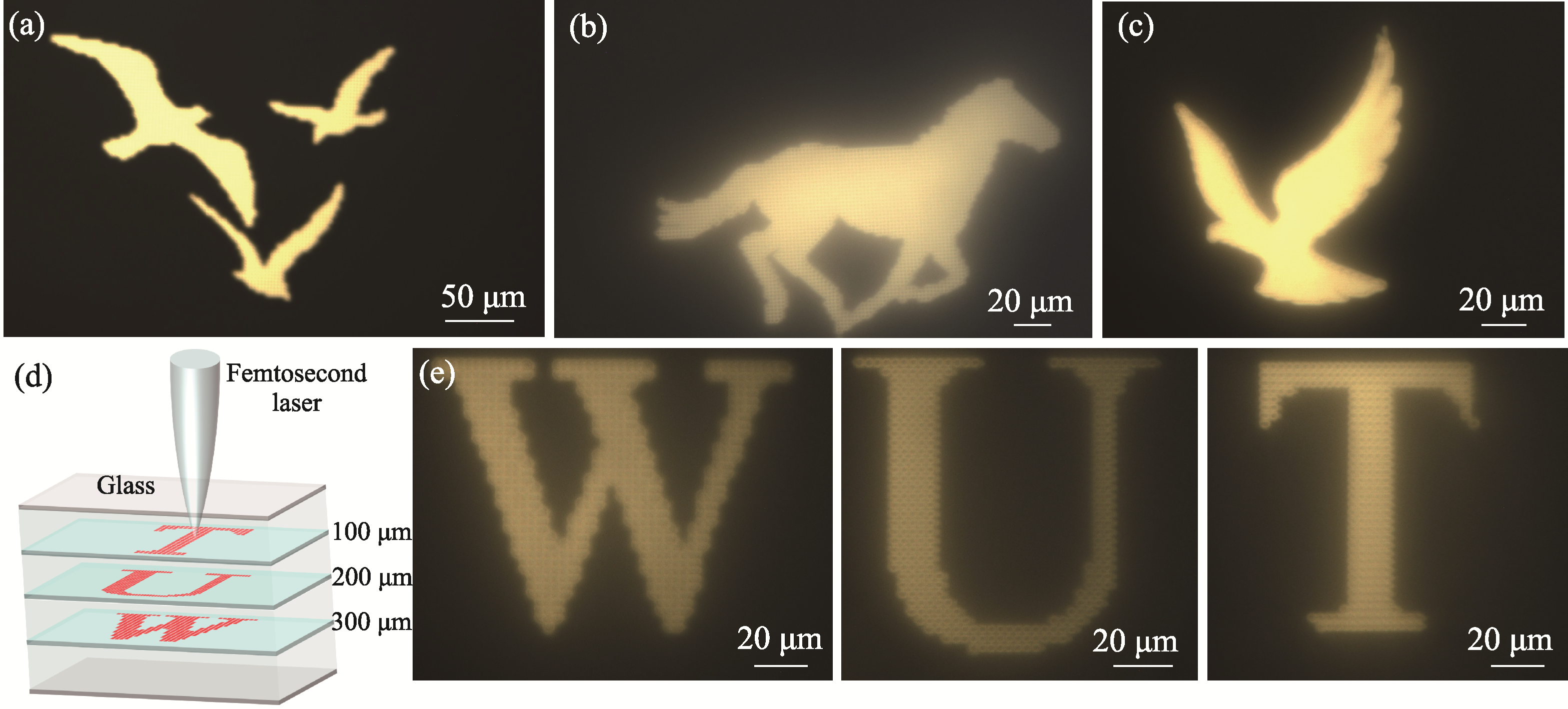
Fig. 7 Application of femtosecond laser direct writing CdS quantum dots glass (a-c) Femtosecond laser direct writing patterns; (d) Three-dimensional schematic diagram of information storage; (e) Femtosecond laser writes the letters W, U, and T
| [1] |
HAN Y X, YANG C L, SUN Y T, et al. The novel optical properties of CdS caused by concentration of impurity Co. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 585: 503.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 徐小齐. 半导体纳米CdS的制备及其性能研究. 南京: 南京航空航天大学硕士学位论文, 2009. |
| [3] |
AKIMOV V A, KOZLOVSKII V I, KOROSTELIN Y V, et al. A Cr2+:CdS laser tunable between 2.2 and 3.3 μm. Quantum Electronics, 2008, 38(9): 803.
DOI URL |
| [4] | BAO Q, LI W, XU P, et al. On-chip single-mode CdS nanowire laser. Light: Science & Application, 2020, 9(1): 42. |
| [5] |
AGARWAL R, BARRELET C J, LIEBER C M. Lasing in single cadmium sulfide nanowire optical cavities. Nano Letters, 2005, 5(5): 917.
PMID |
| [6] |
BÖER K W. Cadmium sulfide enhances solar cell efficiency. Energy Conversion and Management, 2011, 52(1): 426.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
CHEN C, ZHAI Y, LI F, et al. High efficiency CH3NH3PbI3:CdS perovskite solar cells with CuInS2 as the hole transporting layer. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 341: 396.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ZHU G, SU F, LV T, et al. Au nanoparticles as interfacial layer for CdS quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2010, 5(11): 1749.
PMID |
| [9] | HUSSEIN W S, AHMED A F, AADIM K A. Influence of laser energy and annealing on structural and optical properties of CdS films prepared by laser induced plasma. Iraqi Journal of Science, 2020, 61(6): 1307. |
| [10] |
ULLRICH B. Thin-film CdS formed with pulsed-laser deposition towards optical and hybrid device applications. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2007, 18(11): 1105.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
SANZ M, NALDA R D, MARCO J F, et al. Femtosecond pulsed laser deposition of nanostructured CdS films. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(11): 4864.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
SEMONIN O E, LUTHER J M, BEARD M C. Quantum dots for next-generation photovoltaics. Materials Today, 2012, 15(11): 508.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
CHO S, KIM Y, LEE S, et al. Recent progress in blue-emitting semiconductor nanocrystal quantum dots for display applications. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2024, 41: 3359.
DOI |
| [14] |
LI X J, CHEN L Q, MAO D Q, et al. Low-threshold cavity-enhanced superfluorescence in polyhedral quantum dot superparticles. Nanoscale Advances, 2024, 6(12): 3220.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
ZAFAR A J, MITRA A, APALKOV V. High harmonic generation in graphene quantum dots. Journal of Physics-Condensed Matter, 2024, 36(21): 215302.
DOI |
| [16] |
KONDRATENKO T S, SMIRNOV M S, OVCHINNIKOV O V, et al. Size-dependent optical properties of colloidal CdS quantum dots passivated by thioglycolic acid. Semiconductors, 2018, 52(9): 1137.
DOI |
| [17] | KESHARI A K, PANDEY A C. Color tunability and Raman investigation in CdS quantum dots. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2009, 1147(1): 427. |
| [18] |
SUN L, LI Y, YAN J, et al. A review on pulsed laser preparation of quantum dots in colloids for the optimization of perovskite solar cells: advantages, challenges, and prospects. Nanomaterials, 2024, 14(19): 1550.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 袁春云. 半导体量子点的合成及性质研究. 吉林: 长春理工大学硕士学位论文, 2016. |
| [20] |
VETCHINNIKOV M P, LIPATIEV A S, SHAKHGILDYAN G Y, et al. Direct femtosecond laser-induced formation of CdS quantum dots inside silicate glass. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(11): 2519.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | LI X K, TAN D Z, LIU Y, et al. Ultrafast laser direct writing of nanocrystals inside glass and its applications. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2022, 41(11): 3781. |
| [22] |
SUN K, TAN D Z, FANG X Y, et al. Three-dimensional direct lithography of stable perovskite nanocrystals in glass. Science, 2022, 375(6578): 307.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
LI X K, SUN K, WU J J, et al. Thermal-triggered phase separation and ion exchange enables photoluminescence tuning of stable mixed-halide perovskite nanocrystals for dynamic display. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2024, 18(5): 2301244.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
SUN K, LI X K, TAN D Z, et al. Pure blue perovskites nanocrystals in glass: ultrafast laser direct writing and bandgap tuning. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2023, 17(5): 2200902.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SUN K, TAN D Z, SONG J, et al. Highly emissive deep-red perovskite quantum dots in glass: photoinduced thermal engineering and applications. Advanced Optical Materials, 2021, 9(11): 2100094.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
TAN D, ZHANG B, QIU J. Ultrafast laser direct writing in glass: thermal accumulation engineering and applications. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2021, 15(9): 2000455.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
DAI Y, ZHU B, QIU J R, et al. Direct writing three dimensional Ba2TiSi2O8 crystalline pattern in glass with ultrashort pulse laser. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 90(18): 181109.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
DU X, ZHANG H, CHENG C, et al. Space-selective precipitation of ZnO crystals in glass by using high repetition rate femtosecond laser irradiation. Optics Express, 2014, 22(15): 17908.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | YUE Zihao, YANG Xiaotu, ZHANG Zhengliang, DENG Ruixiang, ZHANG Tao, SONG Lixin. Effect of Pb2+ on the Luminescent Performance of Borosilicate Glass Coated CsPbBr3 Perovskite Quantum Dots [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 449-456. |
| [2] | LUO Shuwen, MA Mingsheng, LIU Feng, LIU Zhifu. Corrosion Behavior and Mechanism of LTCC Materials in Ca-B-Si System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 553-560. |
| [3] | PANG Libin, WANG Deping. Drug Carrier Based on Mesoporous Borosilicate Glass Microspheres: Preparation and Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 780-786. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xiao-Yang, PENG Hai-Bo, LIU Feng-Fei, ZHAO Yan, SUN Meng-Li, GUAN Ming, ZHANG Bing-Tao, DU Xin, YUAN Wei, WANG Tie-Shan. Mechanical Properties of Borosilicate Glass with Different Irradiation of Heavy Ions [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(7): 741-747. |
| [5] | LI Ling, XIAO Jun-Ying, CUI Mi-Dou, TAI You-Yi, PANG Yong-Wen, HAN Song, LI Xiao-Wei. Boron and Sulfur Co-doped TiO2 Nanofilm as High Efficiency CdS Quantum-dot-sensitized Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(6): 627-633. |
| [6] | YIN De-Wu, LIU Zhen, YANG Xin-Yu, ZHANG Xi-Yan, XIANG Wei-Dong. Preparation and Optical Properties of AgIn Alloy Quantum Dots Doped Glass [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(10): 1034-1038. |
| [7] | ZHAO Xiu-Li, LIANG Xiao-Juan, LUO Hong-Yan, CHEN Zhao-Ping, XIANG Wei-Dong. Third-order Nonlinear Optical Properties of Silver Quantum Dots Doped in Sodium Borosilicate Glass [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(9): 1003-1008. |
| [8] | YANG Xin-Yu, XIANG Wei-Dong, ZHANG Xi-Yan, LIU Hai-Tao, ZHAO Hai-Jun, LIANG Xiao-Juan. Study on the Third-order Optical Nonlinear Absorption Properties of Bi2O3 Nanocrystals Glass [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(3): 317-322. |
| [9] | YANG Xin-Yu, , XIANG Wei-Dong, , ZHAO Hai-Jun,ZHANG Xi-Yan, LIANG Xiao-Juan, LIU Hai-Tao. Third-order Nonlinear Optical Properties of Bi2S3 Nanocrystals Embedded inSodium Borosilicate Glass [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(3): 290-294. |
| [10] | LU Bo,DAI Ye,MA Hong-Liang. Femtosecond Laser Induced Ba2TiSi2O8 Crystal Precipitation in Glass [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(4): 769-772. |
| [11] | CONG Ri-Min,LUO Yun-Jun,YU Huai-Qing. Study on the Resistance to Aging of CdS Quantum Dots Encapsulated by PAMAM Dendrimers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(2): 379-382. |
| [12] | DING Ting,BAO Jia-Xing,WANG Li,ZHOU Shi-Feng,QIU Jian-Rong. Femtosecond Laser Induced Micro-structure Change in Ag+-doped BK7 Glass [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(5): 807-810. |
| [13] | ZHOU You-Hua,LU Pei-Xian,YANG Guang,YANG Yi-Fa,ZHENG Qi-Guang. β-FeSi2 thin film prepared by femtosecond laser ablation and its optical characteristic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(3): 545-549. |
| [14] |
YU Ben-Hai,DAI Neng-Li,LI Yu-Hua,ZHENG Qi-Guang,LU Pei-Xiang.
Experimental Study on the Ablation of MgAl2O4 Transparent Ceramic by a Femtosecond Laser [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(2): 328-332. |
| [15] | JIANG Xiong-Wei,QIU Jian-Rong,ZENG Hui-Dan,ZHU Cong-Shan. Femtosecond Laser Induced Growth of LiNbO3 Crystal in Glass [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2004, 19(4): 935-938. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||