
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 348-362.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240368
Special Issue: 【能源环境】储能电池(202506)
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Jiguo( ), WU Tian, ZHAO Xu, YANG Fan, XIA Tian, SUN Shien(
), WU Tian, ZHAO Xu, YANG Fan, XIA Tian, SUN Shien( )
)
Received:2024-08-12
Revised:2024-11-05
Published:2025-04-20
Online:2024-11-29
Contact:
SUN Shien, professor. E-mail: shiensun@126.comAbout author:ZHANG Jiguo (1988-), male, engineer. E-mail: zhangjiguo@zjenergy.com.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHANG Jiguo, WU Tian, ZHAO Xu, YANG Fan, XIA Tian, SUN Shien. Improvement of Cycling Stability of Cathode Materials and Industrialization Process for Sodium-ion Batteries[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 348-362.
| Charge carrier | Li+ | Na+ |
|---|---|---|
| Ionic radius/Å | 0.76 | 1.02 |
| Electronic polarizability of ion/Å3 | 0.03 | 0.2-0.3 |
| Relative atomic mass | 6.94 | 23.00 |
| Ionization energy/eV | 5.39 | 5.14 |
| Melting point/℃ | 180.5 | 97.7 |
| Desolvation-energy in propylene carbonate/ (kJ·mol-1) | 215.8 | 158.2 |
| E0/V(vs. SHE) | -3.04 | -2.71 |
| Electronegativity | 0.98 | 0.93 |
| Molar mass/(g·mol-1) | 6.9 | 23.0 |
Table 1 Comparison of characteristics of Li+ and Na+ as charge carriers[6-7]
| Charge carrier | Li+ | Na+ |
|---|---|---|
| Ionic radius/Å | 0.76 | 1.02 |
| Electronic polarizability of ion/Å3 | 0.03 | 0.2-0.3 |
| Relative atomic mass | 6.94 | 23.00 |
| Ionization energy/eV | 5.39 | 5.14 |
| Melting point/℃ | 180.5 | 97.7 |
| Desolvation-energy in propylene carbonate/ (kJ·mol-1) | 215.8 | 158.2 |
| E0/V(vs. SHE) | -3.04 | -2.71 |
| Electronegativity | 0.98 | 0.93 |
| Molar mass/(g·mol-1) | 6.9 | 23.0 |
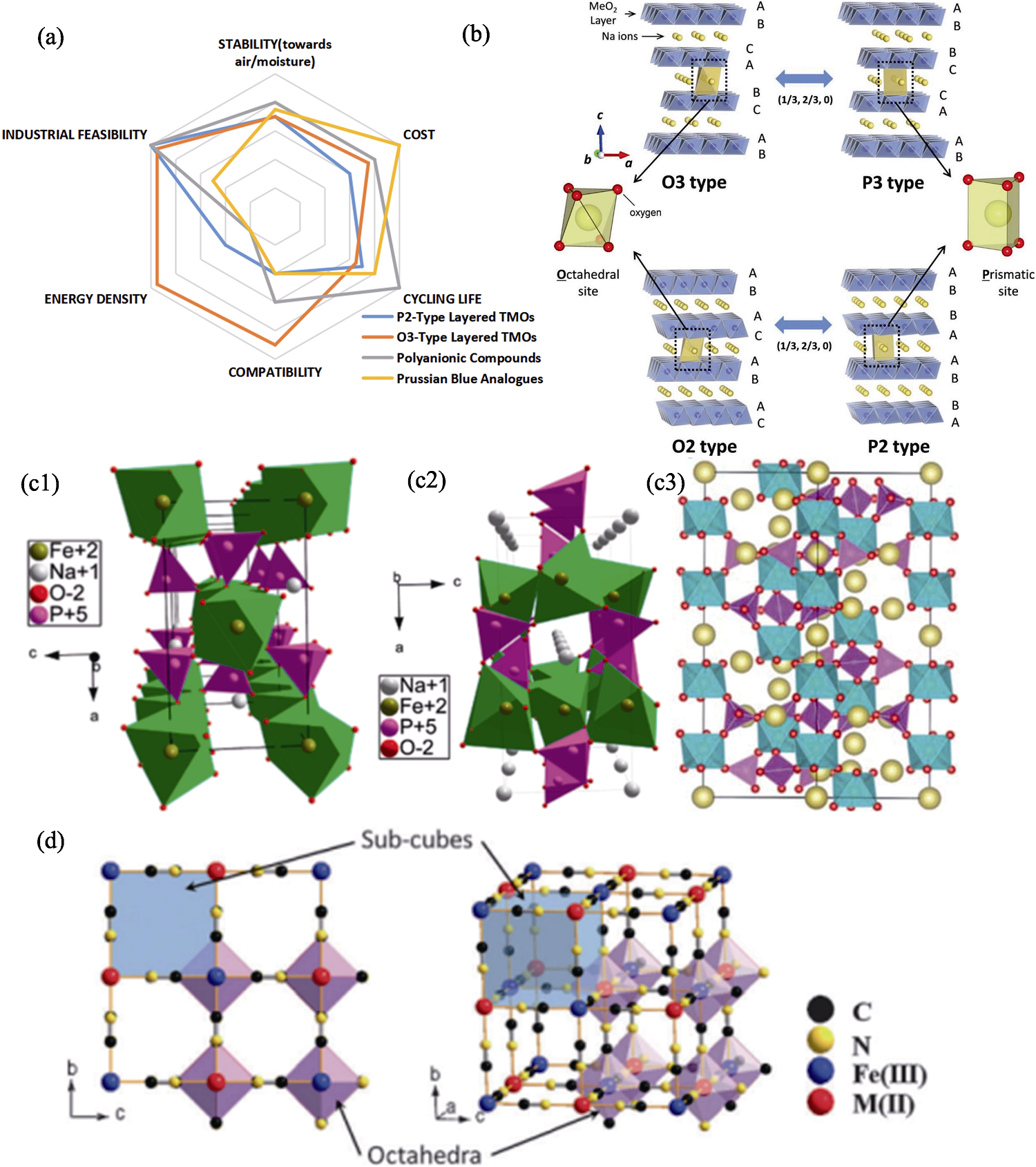
Fig. 2 Properties and structures of cathode materials for Na+ battery[10,13⇓⇓⇓ -17] (a) Properties of cathode materials[13-14]; (b) Classification and phase transition processes of layered materials[10]; (c) Structures of (c1) maricite NaFePO4[15], (c2) olivine NaFePO4[15] and (c3) NASICON-Na3V2(PO4)3[16]; (d) Framework of Prussian blue analogues[17]
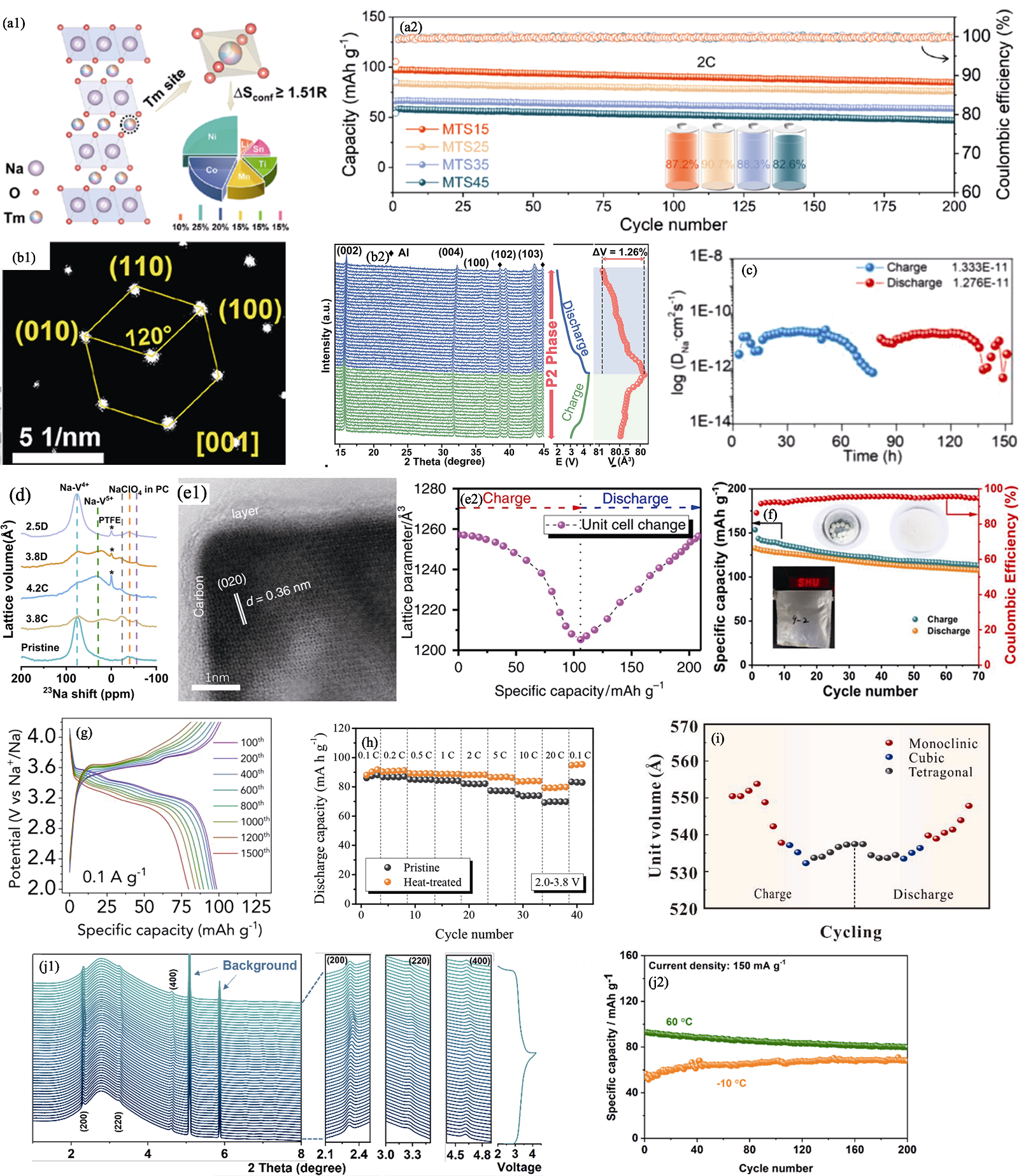
Fig. 3 Strategies of structural optimization[34⇓⇓⇓-38,40,42⇓⇓ -45] (a1) Crystal structure schematic of MTS15 and (a2) cycling performance of MTS15, MTS25, MTS35, and MTS45[34]; (b1) Selected area electron diffraction pattern of P2-NCLMO[35]; (b2) In situ XRD patterns and corresponding volume variations of P2-NCLMO electrode in the first cycle at 0.2C[35]; (c) Calculated diffusion coefficient of Na+ in P2/O3-NaMnNiCuFeTiOF[36]; (d) High-resolution ex situ solid-state 23Na nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of Na3(VOPO4)2F/8% Ketjen black electrode under various states[37]; (e1) Bright field TEM image of nanosized Na4Fe3(PO4)2(P2O7) plates (NFPP-E) with carbon layers and (e2) volume change details during the charge/discharge process of NFPP-E[38]; (f) Cycling performance of full-cell based on MnHCF-S-170 cathode and soft carbon anode[40]; (g) Charge-discharge curves of KMF in different cycles at 0.1 A·g−1[42]; (h) Rate performances of pristine and HT samples under current densities from 0.1C to 20C[43]; (i) Unit volume of SC-HEPBA during charge and discharge process[44]; (j1) In-situ synchrotron-based powder XRD patterns with charge-discharge curves and (j2) cycling performance under 150 mA·g−1 and different temperatures[45]
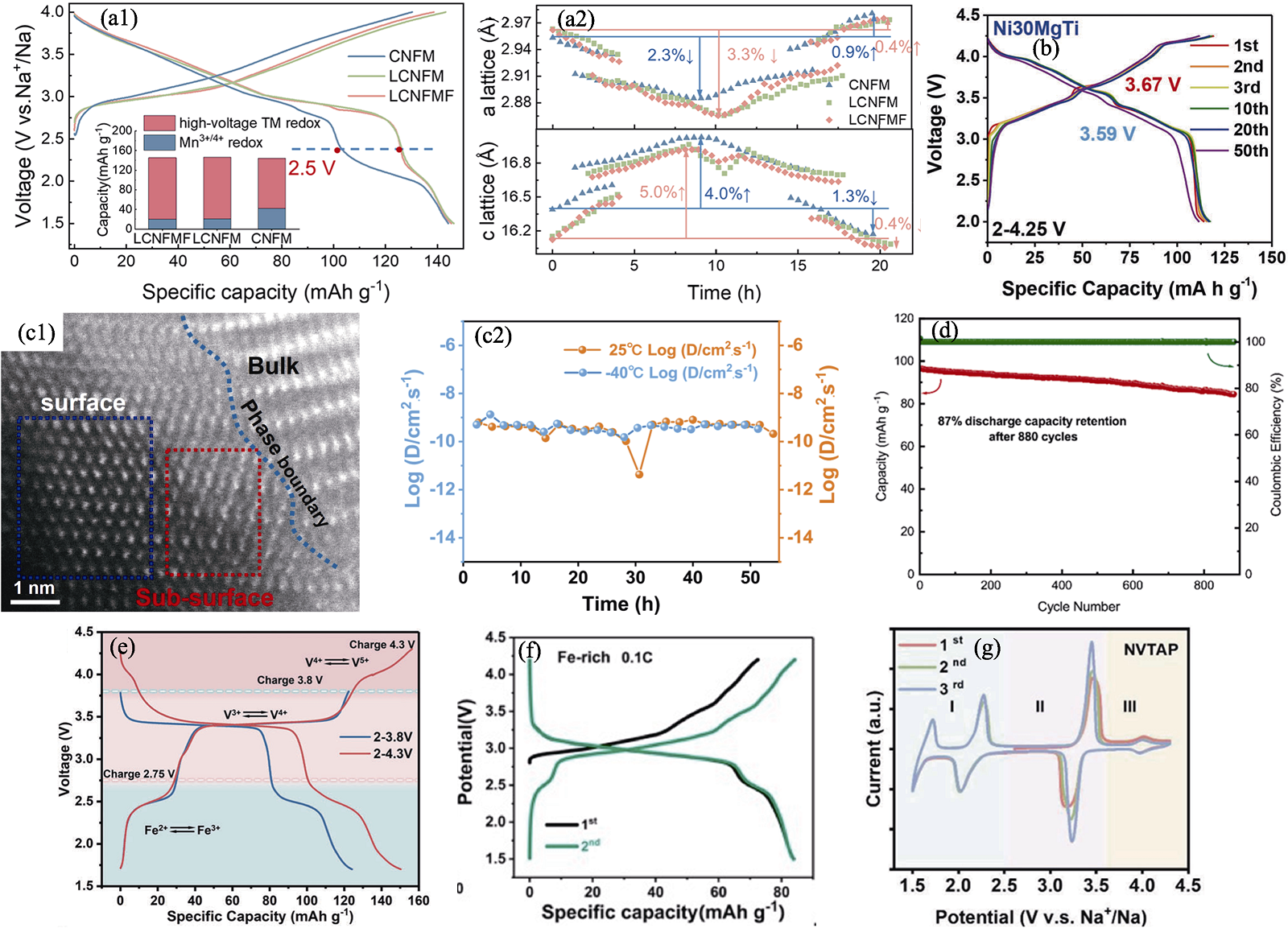
Fig. 4 Strategies of chemical elements doping[16,46⇓⇓⇓⇓ -51] (a1) Initial charge-discharge curves of CNFM, Na0.89Li0.05Cu0.11Ni0.11Fe0.3Mn0.43O2 (LCNFM), and LCNFMF at 0.1C in a voltage range of 1.5-4.0 V with inset showing quantitative analysis results of reversible capacity contributions[46]; (a2) Changes of a/c-lattice parameters in three samples obtained by fitting in situ XRD data[46]; (b) Charge-discharge curves of Ni30MgTi[47]; (c1) STEM-HAADF image of interface between preconstructed layer and bulk phase and (c2) corresponding sodium ion diffusion coefficients of P2-NaMNNb calculated from GITT (galvanostatic intermittent titration technique) formula under 25 and −40 ℃[48]; (d) Cycling performance of NFVNP//HC at 5C in a voltage range of 1.5-3.8 V[49]; (e) Galvanostatic charge-discharge profiles at 0.5C in different voltage windows of 1.7-3.8 V and 1.7-4.3 V[16]; (f) Galvanostatic charge/discharge profiles of Fe-rich electrode at 0.1C from 1.5 V to 4.2 V[50]; (g) CV curves of NVTAP at 0.2 mV·s-1[51]
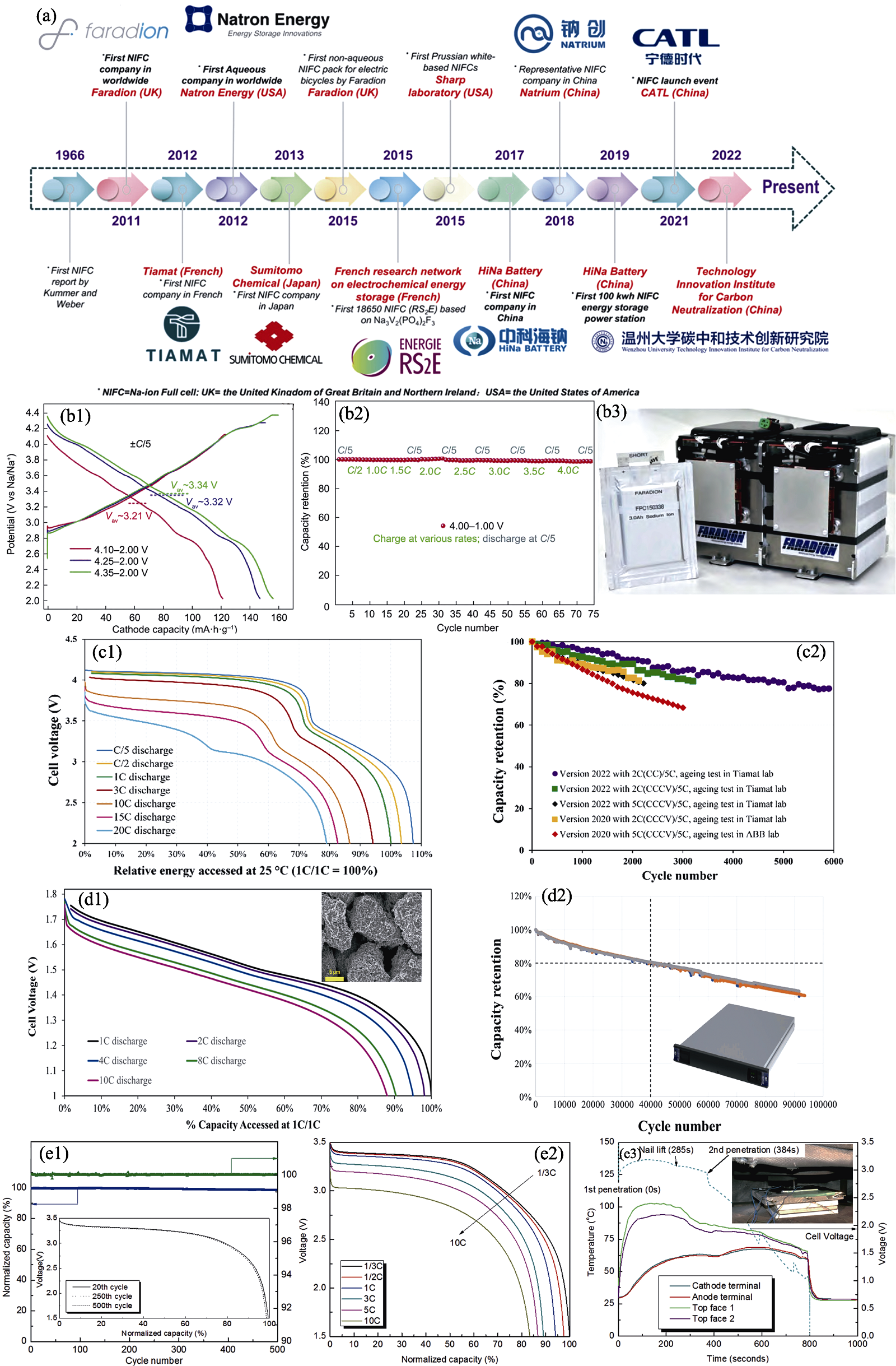
Fig. 5 International Industrialization process of sodium-ion batteries[83,85 -86,90 -91] (a) Worldwide development history of sodium-ion batteries[85]; (b1) Charge/discharge profiles of Faradion’s second-generation cathode material at 0.2C within different voltage windows[86]; (b2) Fast-charge performance of Faradion’s second-generation cathode material||HC 0.1 Ah full cell, charging at 4C (15 min total charge) without obvious capacity drop[86]; (b3) Faradion 3.0 Ah Na-ion pouch cell with 400 Wh battery pack system[86]; (c1) Discharge voltage profiles at different discharge rates as a function of relative energy accessed under 25 ℃ (1C/1C=100%) and (c2) cycling life measured on different versions of Tiamat Na-ion cells at 25 ℃ and 100% DOD[90]; (d1) Discharge voltage profiles of Natron cell at various discharge C rates as a function of percentage of discharge capacity accessed at 1C/1C and (d2) cycling performance at 25 ℃, 10C/10C, and 100% DOD performed in Natron’s lab with inset showing photo of ABB-Natron pluggable battery module containing 32 Natron’s 4.6 Ah sodium-ion pouch cells[91]; (e1) Cycling performance, (e2) rate capability at room temperature and (e3) safety evaluation of Novasis pouch cells[83]
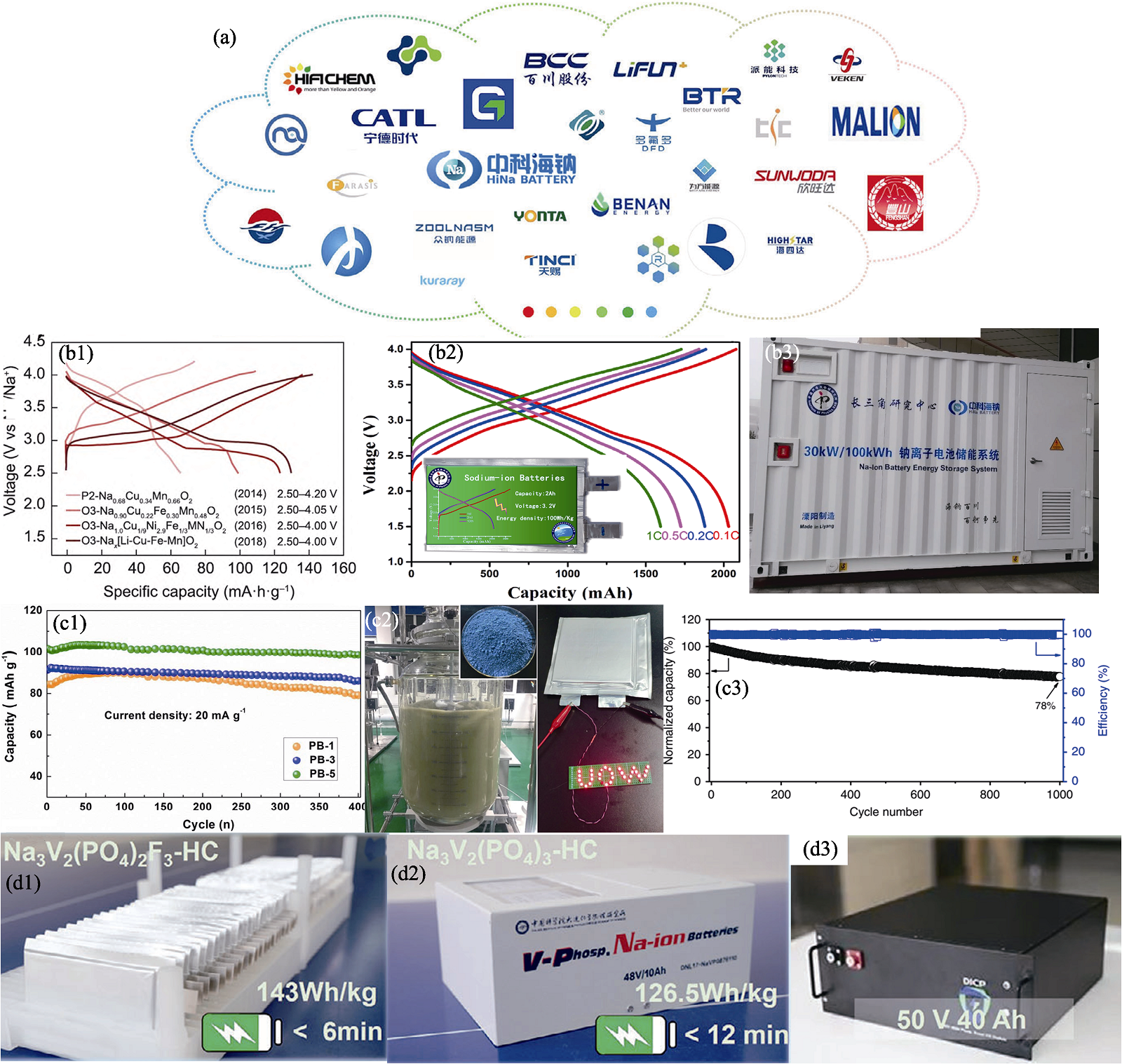
Fig. 6 Domestic industrialization process of sodium-ion batteries[97,99⇓ -101,104 -105,107] (a) Companies dedicated to advancing sodium-ion batteries[97]; (b1) Typical first charge/discharge profiles of several Cu-based oxide cathode materials[99], (b2) rate capability at various constant rates from 0.1C to 1C[100] and (b3) first 30 kW/100 kWh Na-ion battery system for energy storage[101]; (c1) Cycling performance of Na1+xFe[Fe(CN)6] electrodes[104], (c2) digital images of synthesis of Prussian white Na2−xFeFe(CN)6 in 100 L reactor and powder of final product and (c3) cycling performance of pouch full cell[105]; (d1-d3) Practical application of sodium-ion batteries with polyanionic materials as cathodes[107]
| [1] | LI M, LU J, CHEN Z, et al. 30 years of lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(33):1800561. |
| [2] | HU M, HUANG L, LI H, et al. Research progress on hard carbon anode for Li/Na-ion batteries. J. Inorg. Mater., 2024, 39(1):32. |
| [3] | YANG B, QIAN Y, LI Q, et al. Critical summary and perspectives on state-of-health of lithium-ion battery. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 2024, 190: 114077. |
| [4] | SHAO R, SUN Z, WANG L, et al. Resolving the origins of superior cycling performance of antimony anode in sodium-ion batteries: a comparison with lithium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2024, 136(11):e202320183. |
| [5] | VAALMA C, BUCHHOLZ D, WEIL M, et al. A cost and resource analysis of sodium-ion batteries. Nat. Rev. Mater., 2018, 3(4):18013. |
| [6] | KUBOTA K, DAHBI M, HOSAKA T, et al. Towards K-ion and Na-ion batteries as “beyond Li-ion”. Chem. Rec., 2018, 18(4):459. |
| [7] | USISKIN R, LU Y, POPOVIC J, et al. Fundamentals, status and promise of sodium-based batteries. Nat. Rev. Mater., 2021, 6(11):1020. |
| [8] |
WANG J, ZHU Y F, SU Y, et al. Routes to high-performance layered oxide cathodes for sodium-ion batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2024, 53(8):4230.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | ZHANG H, GAO Y, LIU X, et al. Long-cycle-life cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries toward large-scale energy storage systems. Adv. Energy Mater., 2023, 13(23):2300149. |
| [10] | LIU Q, HU Z, CHEN M, et al. Recent progress of layered transition metal oxide cathodes for sodium-ion batteries. Small, 2019, 15(32):1805381. |
| [11] |
GUPTA P, PUSHPAKANTH S, HAIDER M A, et al. Understanding the design of cathode materials for Na-ion batteries. ACS Omega, 2022, 7(7):5605.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | LI Y, CHEN M, LIU B, et al. Heteroatom doping: an effective way to boost sodium ion storage. Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10(27):2000927. |
| [13] | DENG J, LUO W B, CHOU S L, et al. Sodium-ion batteries: from academic research to practical commercialization. Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(4):1701428. |
| [14] | HWANG J Y, MYUNG S T, SUN Y K. Sodium-ion batteries: present and future. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46: 3529. |
| [15] | HAO Z, SHI X, YANG Z, et al. The distance between phosphate- based polyanionic compounds and their practical application for sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater., 2024, 36(7):2305135. |
| [16] | ZHOU Y, XU G, LIN J, et al. Reversible multielectron redox chemistry in a NASICON-type cathode toward high-energy- density and long-life sodium-ion full batteries. Adv. Mater., 2023, 35(44):2304428. |
| [17] | LU Y, WANG L, CHENG J, et al. Prussian blue: a new framework of electrode materials for sodium batteries. Chem. Commun., 2012, 48(52):6544. |
| [18] | WANG J, DREYER S L, WANG K, et al. P2-type layered high- entropy oxides as sodium-ion cathode materials. Mater. Futures, 2022, 1(3):172. |
| [19] | ZHOU P, CHE Z, MA F, et al. Designing water air-stable P2-layered cathodes with delayed P2-O2 phase transition by composition and structure engineering for sodium-ion batteries at high voltage. Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 420: 127667. |
| [20] | SUN Y K. Direction for commercialization of O3-type layered cathodes for sodium-ion batteries. ACS Energy Lett., 2020, 5(4):1278. |
| [21] | ZHANG C, GAO R, ZHENG L, et al. New insights into the roles of Mg in improving the rate capability and cycling stability of O3-NaMn0.48Ni0.2Fe0.3Mg0.02O2 for sodium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10(13):10819. |
| [22] | GAO R M, ZHENG Z J, WANG P F, et al. Recent advances and prospects of layered transition metal oxide cathodes for sodium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater., 2020, 30: 9. |
| [23] | LIU J, KAN W H, LING C D. Insights into the high voltage layered oxide cathode materials in sodium-ion batteries: structural evolution and anion redox. J. Power Sources, 2021, 481: 229139. |
| [24] | XU C, ZHAO J, YANG C, et al. Polyanionic cathode materials for practical Na-ion batteries toward high energy density and long cycle life. ACS Cent. Sci., 2023, 9(9):1721. |
| [25] | LI Y, HE W X, ZHENG X Y, et al. Prussian blue cathode materials for aqueous sodium-ion batteries: preparation and electrochemical performance. J. Inorg. Mater., 2019, 34(4):365. |
| [26] |
SONG J, WANG L, LU Y, et al. Removal of interstitial H2O in hexacyanometallates for a superior cathode of a sodium-ion battery. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(7):2658.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | WANG Y, FENG Z, CUI P, et al. Pillar-beam structures prevent layered cathode materials from destructive phase transitions. Nat. Commun., 2021, 12: 13. |
| [28] | BERSUKER I B. Jahn-Teller and pseudo-Jahn-Teller effects: from particular features to general tools in exploring molecular and solid state properties. Chem. Rev., 2020, 121(3):1463. |
| [29] | ESHETU G G, ELIA G A, ARMAND M, et al. Electrolytes and interphases in sodium-based rechargeable batteries: recent advances and perspectives. Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10(20):2000093. |
| [30] | WANG Q, MARIYAPPAN S, ROUSSE G, et al. Unlocking anionic redox activity in O3-type sodium 3d layered oxides via Li substitution. Nat. Mater., 2021, 20: 353. |
| [31] | REN M, ZHAO S, GAO S, et al. Homeostatic solid solution in layered transition-metal oxide cathodes of sodium-ion batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 145(1):224. |
| [32] | KIM Y, PARK H, SHIN K, et al. Rational design of coating ions via advantageous surface reconstruction in high-nickel layered oxide cathodes for lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater., 2021, 11(38):2101112. |
| [33] | ZHANG R, YANG S, LI H, et al. Air sensitivity of electrode materials in Li/Na ion batteries: issues and strategies. InfoMat, 2022, 4(6):e12305. |
| [34] | WANG H, GAO X, ZHANG S, et al. High-entropy Na-deficient layered oxides for sodium-ion batteries. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(13):12530. |
| [35] | WANG Y, ZHAO X, JIN J, et al. Boosting the reversibility and kinetics of anionic redox chemistry in sodium-ion oxide cathodes via reductive coupling mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145(41):22708. |
| [36] | ZHOU P, CHE Z, LIU J, et al. High-entropy P2/O3 biphasic cathode materials for wide-temperature rechargeable sodium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater., 2023, 57: 618. |
| [37] | SHEN X, ZHOU Q, HAN M, et al. Rapid mechanochemical synthesis of polyanionic cathode with improved electrochemical performance for Na-ion batteries. Nat. Commun., 2021, 12: 2848. |
| [38] | CHEN M, HUA W, XIAO J, et al. NASICON-type air-stable and all-climate cathode for sodium-ion batteries with low cost and high-power density. Nat. Commun., 2019, 10: 1480. |
| [39] | WANG K, LIU Z, LIN C, et al. Development of quasi-solid-state Na-ion battery based on water-minimal Prussian blue cathode. J. Inorg. Mater., 2024, 39(9):1005. |
| [40] | PENG J, GAO Y, ZHANG H, et al. Ball milling solid-state synthesis of highly crystalline Prussian blue analogue Na2-xMnFe(CN)6 cathodes for all-climate sodium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2022, 61(32):e202205867. |
| [41] | SHANG Y, LI X, SONG J, et al. Unconventional Mn vacancies in Mn-Fe Prussian blue analogs: suppressing Jahn-Teller distortion for ultrastable sodium storage. Chem, 2020, 6(7): 1804. |
| [42] |
LI X, SHANG Y, YAN D, et al. Topotactic epitaxy self-assembly of potassium manganese hexacyanoferrate superstructures for highly reversible sodium-ion batteries. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(1):453.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | WANG W, GANG Y, PENG J, et al. Effect of eliminating water in Prussian blue cathode for sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(25):2111727. |
| [44] | HUANG Y, ZHANG X, JI L, et al. Boosting the sodium storage performance of Prussian blue analogs by single-crystal and high- entropy approach. Energy Storage Mater., 2023, 58: 1. |
| [45] | PENG J, ZHANG B, HUA W, et al. A disordered Rubik's cube-inspired framework for sodium-ion batteries with ultralong cycle lifespan. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2023, 62(6):e202215865. |
| [46] |
DING F, WANG H, ZHANG Q, et al. Tailoring electronic structure to achieve maximum utilization of transition metal redox for high-entropy Na layered oxide cathodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145(25):13592.
DOI PMID |
| [47] | LIU Z, WU J, ZENG J, et al. Co-free layered oxide cathode material with stable anionic redox reaction for sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater., 2023, 13(29):2301471. |
| [48] | SHI Q, QI R, FENG X, et al. Niobium-doped layered cathode material for high-power and low-temperature sodium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun., 2022, 13: 3205. |
| [49] | ZHAO Q Y, LI J Y, CHEN M J, et al. Bimetal substitution enabled energetic polyanion cathode for sodium-ion batteries. Nano Lett., 2022, 22(23):9685. |
| [50] | WANG J, ZENG W, ZHU J, et al. Fe-rich pyrophosphate with prolonged high-voltage-plateaus and suppressed voltage decay as sodium-ion battery cathode. Nano Energy, 2023, 116: 108822. |
| [51] | LI Z, SUN C, LI M, et al. Na2.5VTi0.5Al0.5(PO4)3 as long lifespan cathode for fast charging sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2024, 34(23):2315114. |
| [52] | BI Z, HUANG W, MU S, et al. Dual-interface reinforced flexible solid garnet batteries enabled by in-situ solidified gel polymer electrolytes. Nano Energy, 2021, 90: 106498. |
| [53] | SHI R, LIU K, ZUO M, et al. Interface-reinforced solid-state electrochromic Li-ion batteries enabled by in-situ liquid-solid transitional plastic glues. J. Energy Chem., 2024, 98: 96. |
| [54] | BI Z, SUN Q, JIA M, et al. Molten salt driven conversion reaction enabling lithiophilic and air-stable garnet surface for solid-state lithium batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(52):2208751. |
| [55] | BI Z, SHI R, LIU X, et al. In situ conversion reaction triggered alloy@antiperovskite hybrid layers for lithiophilic and robust lithium/garnet interfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2023, 33(43):2307701. |
| [56] | HUANG G, KONG Q, YAO W, et al. High proportion of active nitrogen-doped hard carbon based on mannich reaction as anode material for high-performance sodium-ion batteries. ChemSusChem, 2023, 16(7):e202202070. |
| [57] | HOU Z, ZHANG X, CHEN J, et al. Towards high-performance aqueous sodium ion batteries: constructing hollow NaTi2(PO4)3@C nanocube anode with Zn metal-induced pre-sodiation and deep eutectic electrolyte. Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12(14):2104053. |
| [58] | CHE C, WU F, LI Y, et al. Challenges and breakthroughs in enhancing temperature tolerance of sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater., 2024, 36(28):2402291. |
| [59] | ZHANG Y, XU J, LI Z, et al. All-climate aqueous Na-ion batteries using “water-in-salt” electrolyte. Sci. Bull., 2022, 67(2):161. |
| [60] | LIU X, ZHENG X, QIN X, et al. Temperature-responsive solid- electrolyte-interphase enabling stable sodium metal batteries in a wide temperature range. Nano Energy, 2022, 103: 107746. |
| [61] | LIU M, YANG Z, SHEN Y, et al. Chemically presodiated Sb with a fluoride-rich interphase as a cycle-stable anode for high-energy sodium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9(9):5639. |
| [62] | MU J J, LIU Z M, LAI Q S, et al. An industrial pathway to emerging presodiation strategies for increasing the reversible ions in sodium-ion batteries and capacitors. Energy Mater., 2022, 2(6):200043. |
| [63] | LIU T, XIANG P, LI Y, et al. In situ forming Na-Sn alloy/Na2S interface layer for ultrastable solid state sodium batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2024, 34(32):2316528. |
| [64] | TIAN K, HE H, LI X, et al. Boosting electrochemical reaction and suppressing phase transition with a high-entropy O3-type layered oxide for sodium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10(28):14943. |
| [65] | DING F, ZHAO C, XIAO D, et al. Using high-entropy configuration strategy to design Na-ion layered oxide cathodes with superior electrochemical performance and thermal stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144(18):8286. |
| [66] | TANG Y, ZHANG Q, ZUO W, et al. Sustainable layered cathode with suppressed phase transition for long-life sodium-ion batteries. Nat. Sustain., 2024, 7(3):348. |
| [67] | FENG J, LIU Y, FANG D, et al. Reusing the steel slag to design a gradient-doped high-entropy oxide for high-performance sodium ion batteries. Nano Energy, 2023, 118: 109030. |
| [68] | MA S, ZOU P, XIN H L. Extending phase-variation voltage zones in P2-type sodium cathodes through high-entropy doping for enhanced cycling stability and rate capability. Mater. Today Energy, 2023, 38: 101446. |
| [69] | MU J, CAI T, DONG W, et al. Biphasic high-entropy layered oxide as a stable and high-rate cathode for sodium-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 471: 144403. |
| [70] | ZHOU Y, XU G, LIN J, et al. A multicationic-substituted configurational entropy-enabled NASICON cathode for high- power sodium-ion batteries. Nano Energy, 2024, 128: 109812. |
| [71] | LI M, SUN C, YUAN X, et al. A configuration entropy enabled high-performance polyanionic cathode for sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2024, 34(21):2314019. |
| [72] | SHEN X, HAN M, LI X, et al. Regulated synthesis of α-NaVOPO4 with an enhanced conductive network as a high-performance cathode for aqueous Na-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14(5):6841. |
| [73] | LING M, JIANG Q, LI T, et al. The mystery from tetragonal NaVPO4F to monoclinic NaVPO4F: crystal presentation, phase conversion, and Na-storage kinetics. Adv. Energy Mater., 2021, 11(21):2100627. |
| [74] | FAN Z, SONG W, YANG N, et al. Insights into the phase purity and storage mechanism of nonstoichiometric Na3.4Fe2.4(PO4)1.4P2O7 cathode for high-mass-loading and high-power-density sodium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2024, 63(8):e202316957. |
| [75] | ZHANG L M, HE X D, WANG S, et al. Hollow-sphere-structured Na4Fe3(PO4)2(P2O7)/C as a cathode material for sodium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13(22):25972. |
| [76] | TANG Y, LI W, FENG P, et al. High-performance manganese hexacyanoferrate with cubic structure as superior cathode material for sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30(10):1908754. |
| [77] | PAN T Y, WU C Y, NI C S, et al. Improvement in cycling stability of Prussian blue analog-based aqueous sodium-ion batteries by ligand substitution and electrolyte optimization. Electrochim. Acta, 2022, 427: 140778. |
| [78] | XU Z, SUN Y, XIE J, et al. Scalable preparation of Mn/Ni binary Prussian blue as sustainable cathode for harsh-condition-tolerant sodium- ion batteries. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2022, 10(40):13277. |
| [79] | XU Z, SUN Y, XIE J, et al. High-performance Ni/Fe-codoped manganese hexacyanoferrate by scale-up synthesis for practical Na-ion batteries. Mater. Today Sustain., 2022, 18: 100113. |
| [80] | SHEN L, JIANG Y, LIU Y, et al. High-stability monoclinic nickel hexacyanoferrate cathode materials for ultrafast aqueous sodium ion battery. Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 388: 124228. |
| [81] | TANG Y, WANG L, HU J, et al. Epitaxial nucleation of NaxFeFe(CN)6@rGO with improved lattice regularity as ultrahigh-rate cathode for sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater., 2024, 14(7):2303015. |
| [82] | ANG C, LU W, ZHANG Y, et al. Toward ultrahigh rate and cycling performance of cathode materials of sodium ion battery by introducing a bicontinuous porous structure. Adv. Mater., 2024, 36(26):2402005. |
| [83] | BAUER A, SONG J, VAIL S, et al. The scale-up and commercialization of nonaqueous Na-ion battery technologies. Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(17):1702869. |
| [84] | GOIKOLEA E, PALOMARES V, WANG S, et al. Na-ion batteries— approaching old and new challenges. Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10(44):2002055. |
| [85] | GAO Y, ZHANG H, PENG J, et al. A 30-year overview of sodium-ion batteries. Carbon Energy, 2024, 6(6):e464. |
| [86] | ZHAO L, ZHANG T, LI W, et al. Engineering of sodium-ion batteries: opportunities and challenges. Engineering, 2022, 24: 172. |
| [87] | RUDOLA A, RENNIE A J, HEAP R, et al. Commercialisation of high energy density sodium-ion batteries: Faradion's journey and outlook. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9(13):8279. |
| [88] | SAYERS R, BARKER J, HEAP R. Compositions containing doped nickelate compounds: WO2015177544A1. 2015-05-20. |
| [89] | EDELSTEIN S. Faradion electric bike: prototype powered by sodium-ion batteries. (2015-05-24)[2024-08-06]. http://www.greencarreports.com/news/1098434_faradion-electric-bike-prototype-powered-bysodium-ion-batteries. |
| [90] | HE M, MEJDOUBI A E, CHARTOUNI D, et al. High power NVPF/HC-based sodium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources, 2023, 588: 233741. |
| [91] | HE M, DAVIS R, CHARTOUNI D, et al. Assessment of the first commercial Prussian blue based sodium-ion battery. J. Power Sources, 2022, 548: 232036. |
| [92] | LIU Q, HU Z, CHEN M, et al. The cathode choice for commercialization of sodium-ion batteries: layered transition metal oxides versus Prussian blue analogs. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30(14):1909530. |
| [93] | KUZE S, KAGEURA J I, MATSUMOTO S, et al. Development of a sodium ion secondary battery. Sumitomo Kagaku, 2013, 2013: 1. |
| [94] | RS2E network. French researchers develop sodium-ion battery in 18650 format;performance comparable to Li-ion. (2015-11-27) [2024-08-06]. https://www.greencarcongress.com/2015/11/20151127-rs2e.html. |
| [95] | HALL N, BOULINEAU S, CROGUENNEC L, et al. Method for preparing a Na3V2(PO4)2F3 particulate material: WO2017/064189A1. 2017-04-20. |
| [96] |
WANG L, SONG J, QIAO R, et al. Rhombohedral Prussian white as cathode for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(7):2548.
DOI PMID |
| [97] | LU X, LI S, LI Y, et al. From lab to application: challenges and opportunities in achieving fast charging with polyanionic cathodes for sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater., 2024, 36(36):2407359. |
| [98] | XU S Y, WU X Y, LI Y M, et al. Novel copper redox-based cathode materials for room-temperature sodium-ion batteries. Chin. Phys. B, 2014, 23(11):118202. |
| [99] | MU L, XU S, LI Y, et al. Prototype sodium-ion batteries using an air-stable and Co/Ni-free O3-layered metal oxide cathode. Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(43):6928. |
| [100] | LI Y, HU Y S, QI X, et al. Advanced sodium-ion batteries using superior low cost pyrolyzed anthracite anode: towards practical applications. Energy Storage Mater., 2016, 5: 191. |
| [101] | HU Y S, KOMABA S, FORSYTH M, et al. A new emerging technology: Na-ion batteries. Small Methods, 2019, 3(4):1900184. |
| [102] |
容晓晖, 陆雅翔, 戚兴国, 等. 钠离子电池: 从基础研究到工程化探索. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(2):515.
DOI |
| [103] | 电池网. Natrium energy signed a contract of 80,000 mt of sodium-ion battery cathode material project, further accelerating the industrialisation. (2022-06-14)[2024-08-06]. https://news.metal.com/newscontent/101860656/natrium-energy-signed-a-contract-of-80000-mt-of-sodiumion-battery-cathode-material-project-further-accelerating-the-industrialisation/. |
| [104] | LI W J, CHOU S L, WANG J Z, et al. Facile method to synthesize Na-enriched Na1+xFeFe(CN)6 frameworks as cathode with superior electrochemical performance for sodium-ion batteries. Chem. Mater., 2015, 27(6): 1997. |
| [105] |
WANG W, GANG Y, HU Z, et al. Reversible structural evolution of sodium-rich rhombohedral Prussian blue for sodium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1):980.
DOI PMID |
| [106] | Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Ltd. The first-generation sodium-ion battery launch event. (2021-07-29)[2024-08-06]. https://www.catl.com/en/news/685.html. |
| [107] | 邱艳玲, 韩建鑫, 王雨霄. 我部研制出48V/10Ah磷酸盐基钠离子电池储能系统并成功开展应用示范. (2021-11-24)[2024-08-06]. http://energystorage.dicp.ac.cn/info/1061/5239.htm. |
| [1] | YU Shengyang, SU Haijun, JIANG Hao, YU Minghui, YAO Jiatong, YANG Peixin. A Review of Pore Defects in Ultra-high Temperature Oxide Ceramics by Laser Additive Manufacturing: Formation and Suppression [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [2] | YAN Gongqin, WANG Chen, LAN Chunbo, HONG Yuxin, YE Weichao, FU Xianghui. Al-doped P2-type Na0.8Ni0.33Mn0.67-xAlxO2 as Cathode for Sodium-ion Batteries: Synthesis and Electrochemical Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 1005-1012. |
| [3] | LIU Jiangping, GUAN Xin, TANG Zhenjie, ZHU Wenjie, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Nitrogen-containing Volatile Organic Compounds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [4] | XIAO Xiaolin, WANG Yuxiang, GU Peiyang, ZHU Zhenrong, SUN Yong. Advances in Regulation of Damaged Skin Regeneration by Two-dimensional Inorganic Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [5] | MA Jingge, WU Chengtie. Application of Inorganic Bioceramics in Promoting Hair Follicle Regeneration and Hair Growth [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [6] | ZHANG Hongjian, ZHAO Ziyi, WU Chengtie. Inorganic Biomaterials on Regulating Neural Cell Function and Innervated Tissue Regeneration: A Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [7] | AI Minhui, LEI Bo. Micro-nanoscale Bioactive Glass: Functionalized Design and Angiogenic Skin Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [8] | WANG Yutong, CHANG Jiang, XU He, WU Chengtie. Advances in Silicate Bioceramic/Bioglass for Wound Healing: Effects, Mechanisms and Application Ways [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [9] | MA Wenping, HAN Yahui, WU Chengtie, LÜ Hongxu. Application of Inorganic Bioactive Materials in Organoid Research [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [10] | LUO Xiaomin, QIAO Zhilong, LIU Ying, YANG Chen, CHANG Jiang. Inorganic Bioactive Materials Regulating Myocardial Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [11] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [12] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [13] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [14] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [15] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||