
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 153-161.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170414
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
NIE Heng-Chang1, WANG Yong-Ling1, HE Hong-Liang2, WANG Gen-Shui1, DONG Xian-Lin1
Received:2017-08-25
Revised:2017-11-13
Published:2018-02-26
Online:2018-01-26
CLC Number:
NIE Heng-Chang, WANG Yong-Ling, HE Hong-Liang, WANG Gen-Shui, DONG Xian-Lin. Recent Progress of Porous PZT95/5 Ferroelectric Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(2): 153-161.

Fig. 3 SEM images of (a) Dextrin, (b) PMMA, (c) PZT 95/5 ceramics with Dextrin as pore formers and (d) PZT 95/5 ceramics with PMMA as pore formers[28-29]

Fig. 4 SEM images of the porous PZT95/5 ceramics with different pore sizes[37] (a) 1.8 mm PMMA spheres; (b) 5 μm PMMA spheres; (c) 15 μm PMMA spheres; (d) 60 μm PMMA spheres
| Property | Dense PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics | Porous PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk density/(g•cm-3) | ~7.6 | ~7.3 |
| Effective permittivity | 280-300 | 250-260 |
| Piezoelectric constant/(pC•N-1) | 66-70 | 66-70 |
| Bulk resistivity/(Ω•cm) | 1011-12 | 1011-12 |
| Tangent loss/% | 1.7-2.0 | 1.5-1.8 |
| Remnant polarization/(μC•cm-2) | ~35 | ~30 |
Table 1 Physical property comparison between dense and porous PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics with disperse distribution[39-40]
| Property | Dense PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics | Porous PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk density/(g•cm-3) | ~7.6 | ~7.3 |
| Effective permittivity | 280-300 | 250-260 |
| Piezoelectric constant/(pC•N-1) | 66-70 | 66-70 |
| Bulk resistivity/(Ω•cm) | 1011-12 | 1011-12 |
| Tangent loss/% | 1.7-2.0 | 1.5-1.8 |
| Remnant polarization/(μC•cm-2) | ~35 | ~30 |
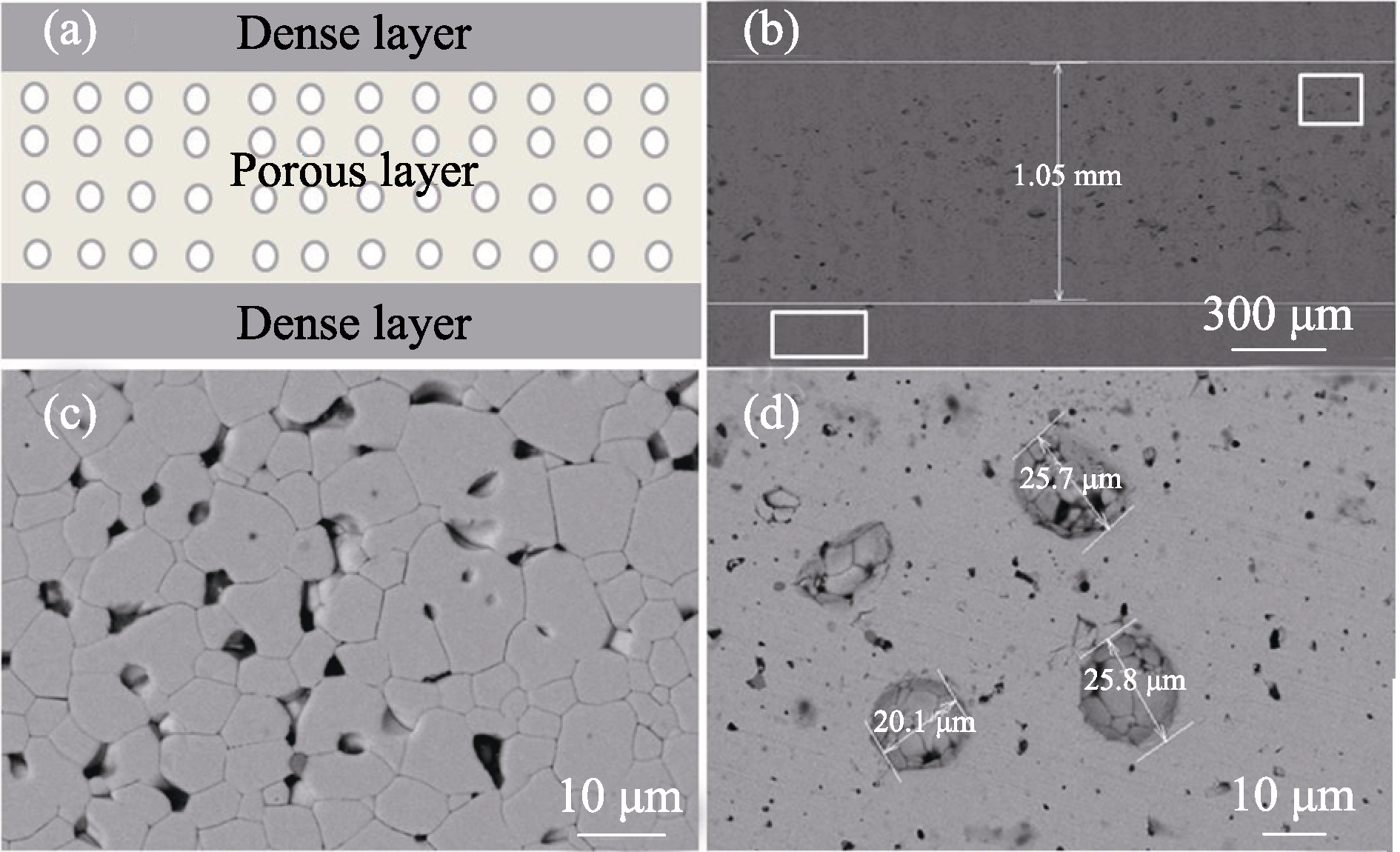
Fig. 7 Schematic diagram (a) and SEM images of polished fracture cross section of sandwich structure PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramic: (b) full cross section; (c) dense layer; (d) porous layer[42]
| Catalogue | Property |
|---|---|
| Type I (not dependent on porosity) | Curie temperature, Spontaneous polarization |
| Type II (depend only on the amount of porosity) | Remnant polarization, bulk density, effective permittivity, piezoelectric constant, tangent loss, Young’s modulus, Dynamic yielding threshold |
| Type III (depend on both the amount and one or more characteristics of porosity) | Shock plasticity, Dielectric strength |
Table 2 Relationship catalogue between physical property and pore of PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics
| Catalogue | Property |
|---|---|
| Type I (not dependent on porosity) | Curie temperature, Spontaneous polarization |
| Type II (depend only on the amount of porosity) | Remnant polarization, bulk density, effective permittivity, piezoelectric constant, tangent loss, Young’s modulus, Dynamic yielding threshold |
| Type III (depend on both the amount and one or more characteristics of porosity) | Shock plasticity, Dielectric strength |
| [1] | 钟维烈. 铁电体物理学. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998. |
| [2] | 王永龄. 功能陶瓷性能与应用. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003. |
| [3] | 贺元吉, 张亚洲, 李传胪. 爆电换能的理论分析. 国防科技大学学报, 2000, 22(z1): 43-48. |
| [4] | 刘高旻, 刘雨生, 张毅, 等. PZT铁电陶瓷及其在脉冲能源中的应用. 材料导报, 2006, 20(6): 74-77. |
| [5] | NEILSON F W.Effects of strong shocks in ferroelectric materials.Bull. Am. Phys. Soc., 1957, 2(2): 302. |
| [6] | BERLINCOURT D, JAFFE H, KRUEGER H H A, et al. Release of electric energy in PbNb(Zr,Ti,Sn)O3 by temperature-and by pressure-enforced phase transitions.Applied Physics Letters, 1963, 3(5): 90-92. |
| [7] | LYSNE P C, PERCIVAL C M.Electric energy generation by shock compression of ferroelectric ceramics: normal-mode response of PZT 95/5.Journal of Applied Physics, 1975, 46(4): 1519-1525. |
| [8] | STORZ L J, DUNGAN R H.A Study of the Electrical, Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of 95/5 PZT as Function of Pore Former Type and Concentration, Sandia Report, SAND85-1612[R]. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1985. |
| [9] | YONGLING W, WAN-ZONG Y, GUO-RONG H, et al.Study on shock wave-explosive energy converter of PZT 95/5 ferroelectric ceramics.Ferroelectrics, 1983, 49(1): 169-176. |
| [10] | FRITZ I J, KECK J D.Pressure-temperature phase diagrams for several modified lead zirconate ceramics.Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 1978, 39(11): 1163-1167. |
| [11] | ALTGILBERS L L, BAIRD J, FREEMAN B, et al.Explosive Pulsed Power. London: Imperial College Press, 2010. |
| [12] | SHKURATOV S I, BAIRD J, ANTIPOV V G, et al.Depolarization mechanisms of PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3 and PbZr0.95Ti0.05O3 poled ferroelectrics under high strain rate loading.Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104(21): 212901. |
| [13] | SHKURATOV S I, BAIRD J, TALANTSEV E F.Note: utilizing Pb(Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 ferroelectric ceramics to scale down autonomous explosive-driven shock-wave ferroelectric generators.Review of Scientific Instruments, 2012, 83(7): 076104. |
| [14] | ALTGILBERS L L, STULTS A H, KRISTIANSEN M, et al.Recent advances in explosive pulsed power.Journal of Directed Energy, 2009, 3(2): 149-191. |
| [15] | VALADEZ J C, SAHUL R, ALBERTA E, et al.The effect of a hydrostatic pressure induced phase transformation on the unipolar electrical response of Nb modified 95/5 lead zirconate titanate.Journal of applied physics, 2012, 111(2): 024109. |
| [16] | JAFFE B, COOK W K, JAFFE H, et al.Piezoelectric ceramics. Academic Press, 1971. |
| [17] | LOCKWOOD STEVE, VOIGHT JIM, PIKE RICK, et al.PZT Supply Team Goes from Basic Research to WR Production. MFG S&T Quarterly, 2003, 11: 2. |
| [18] | DUNGAN R H, STORZ L J.Relation between chemical, mechanical, and electrical properties of Nb2O5-modified 95mol% PbZrO3-5mol% PbTiO3.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1985, 68(10): 530-533. |
| [19] | TUTTLE B, VOIGT J, MOORE R.Structure-property Relationships of Antiferroelectric Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 Based Materials: Hydrostatic Depoling Characteristics. Sandia National Labs., Albuquerque, NM(United States), 1997. |
| [20] | TUTTLE B A, YANG P, GIESKE J H, et al.Pressure-induced phase transformation of controlled-porosity Pb(Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 ceramics.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2001, 84(6): 1260-1264. |
| [21] | SING K S W. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (recommendations 1984).Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1985, 57(4): 603-619. |
| [22] | STUDART A R, GONZENBACH U T, TERVOORT E, et al.Processing routes to macroporous ceramics: a review.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2006, 89(6): 1771-1789. |
| [23] | OHJI T, FUKUSHIMA M.Macro-porous ceramics: processing and properties.International Materials Reviews, 2012, 57(2): 115-131. |
| [24] | HAMMEL E C, IGHODARO O L R, OKOLI O I. Processing and properties of advanced porous ceramics: an application based review.Ceramics International, 2014, 40(10): 15351-15370. |
| [25] | 陈永. 多孔材料制备与表征. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2010. |
| [26] | YANG P, MOORE R H, LOCKWOOD S J BRUCE A, et al. Chem-prep PZT95/5 for Neutron Generator Applications: ehe Effect of Pore Former Type and Density on the Depoling Behavior of Chemically Prepared PZT 95/5 ceramics, Sandia Report SAND2003- 0537[R]. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2003. |
| [27] | SETCHELL R E, TUTTLE B A, VOIGT J A.Effects of Microstructural Variables on the Shock Wave Response of PZT 95/5. Sandia Report SAND2003-0537. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2003. |
| [28] | ZENG T, DONG X L, MAO C L, et al.Effects of pore shape and porosity on the properties of porous PZT 95/5 ceramics.Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2007, 27(4): 2025-2029. |
| [29] | ZENG T, WANG G, DONG X, et al.Investigation on FR(LT)-FR(HT) phase transition and pyroelectric properties of porous Zr-rich lead zirconate titante ceramics.Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2007, 140(1): 5-9. |
| [30] | NIE H C, DONG X L, FENG N B, et al.Quantitative dependence of the properties of Pb0.99(Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98Nb0.02O3 ferroelectric ceramics on porosity.Materials Research Bulletin, 2010, 45(5): 564-567. |
| [31] | 王永刚. 多孔未极化 Pb(Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 铁电陶瓷单轴压缩力学响应与相变. 物理学报, 2015, 64: 134601. |
| [32] | 蒋招绣, 申海艇, 辛铭之, 等. 多孔极化PZT95/5 铁电陶瓷单轴压缩力学响应与放电特性. 固体力学学报, 2016, 37(1): 50-58. |
| [33] | SETCHELL R E.Shock wave compression of the ferroelectric ceramic Pb0.99(Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98Nb0.02O3: Hugoniot states and constitutive mechanical properties.Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 94(1): 573-588. |
| [34] | SETCHELL R E.Shock wave compression of the ferroelectric ceramic Pb0.99(Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98Nb0.02O3: depoling currents.Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 97(1): 013507. |
| [35] | SETCHELL R E.Shock wave compression of the ferroelectric ceramic Pb0.99(Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98Nb0.02O3: microstructural effects. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 101(5): 053525. |
| [36] | FENG N, NIE H, CHEN X, et al.Depoling of porous Pb0.99(Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98Nb0.02O3 ferroelectric ceramics under shock wave load.Current Applied Physics, 2010, 10(6): 1387-1390. |
| [37] | NIE H C, DONG X, FENG N, et al.Microgeometry effect on the properties of Pb0.99(Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98Nb0.02O3 ferroelectric ceramics.Materials Research Bulletin, 2011, 46(8): 1243-1246. |
| [38] | NIE H C, FENG N B, CHEN X F, et al.Enhanced ferroelectric properties of intragranular-porous Pb (Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 ceramic fabricated with carbon nanotubes.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2010, 93(3): 642-645. |
| [39] | NIE H C, DONG X, CHEN X, et al.Formation mechanism of intragranular pores in Pb(Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 ferroelectric ceramic.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2012, 95(1): 223-226. |
| [40] | NIE H C, YU Y, LIU Y, et al. Enhanced shock performance by disperse porous structure: a case study in PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, DOI:10.1111/ jace.15097, 2017, 1-7. |
| [41] | MOORE R H, HUTCHINSON M A, MONTOYA T V, et al. Method of Making and Ceramic Articles with Multiple Regions of Distinct Density: U.S. Patent 8,212,456.2012-7-3. |
| [42] | NIE H C, DONG X, CHEN X, et al.Enhanced performances of sandwich structure Pb0.99 (Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98Nb0.02O3 ferroelectric ceramics for pulsed power application. Materials Research Bulletin, 2014, 51(9): 167-170. |
| [43] | LYSNE P C.Dielectric breakdown of shock-loaded PZT 65/35.Journal of Applied Physics, 1973, 44(2): 577-582. |
| [44] | LYSNE P C.Dielectric properties of shock-wave-compressed PZT 95/5.Journal of Applied Physics, 1977, 48(3): 1020-1023. |
| [45] | LYSNE P C.Resistivity of shock-wave-compressed PZT 95/5.Journal of Applied Physics, 1977, 48(11): 4565-4568. |
| [46] | CHHABILDAS L C.Dynamic Shock Studies of PZT 95/5 Ferroelectric Ceramic. Sandia Report, SAND84-1729. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1984. |
| [47] | CHHABILDAS L C, CARR M J, KUNZ S C, et al.Shock Recovery Experiments on PZT 95/5. Sandia Report, SAND85-0406C. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1985. |
| [48] | HALPIN W J.Resistivity estimates for some shocked ferroelectrics.Journal of Applied Physics, 1968, 39(8): 3821-3826. |
| [49] | TKACH Y, SHKURATOV S I, TALANTSEV E F, et al.Theoretical treatment of explosive-driven ferroelectric generators.IEEE Transactions On Plasma Science, 2002, 30(5): 1665-1673. |
| [50] | ZHANG F, HE H, LIU G, et al.Failure behavior of Pb (Zr0.95Ti0.05) O3 ferroelectric ceramics under shock compression.Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 113(18): 183501. |
| [51] | ZHANG F, LIU Y, XIE Q, et al.Electrical response of Pb (Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 under shock compressions.Journal of Applied Physics, 2015, 117(13): 134104. |
| [52] | NIE H C, YANG J, CHEN X, et al.Mechanical induced electrical failure of shock compressed PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics.Current Applied Physics, 2017, 17(4): 448-453. |
| [53] | 喻寅, 王文强, 杨佳, 等. 多孔脆性介质冲击波压缩破坏的细观机理和图像. 物理学报, 2012, 61(4): 48103. |
| [54] | YU Y, WANG W, HE H, et al.Mesoscopic deformation features of shocked porous ceramic: polycrystalline modeling and experimental observations.Journal of Applied Physics, 2015, 117(12): 125901. |
| [55] | YU Y, WANG W, HE H, et al.Modeling multiscale evolution of numerous voids in shocked brittle material.Physical Review E, 2014, 89(4): 043309. |
| [56] | 喻寅, 贺红亮, 王文强, 等. 含微孔洞脆性材料的冲击响应特性与介观演化机制. 物理学报, 2014, 63(24): 246102. |
| [57] | 喻寅, 贺红亮, 王文强, 等. 多孔脆性材料对高能量密度脉冲的吸收和抵抗能力. 物理学报, 2015, 64(12): 124302. |
| [58] | JIANG T, YU Y, HE H, et al.Macroscopic shock plasticity of brittle material through designed void patterns.Journal of Applied Physics, 2016, 119(9): 095905. |
| [59] | RICE R W.The Porosity Dependence of Physical Properties of Materials: a Summary Review, Key Engineering Materials. Zürich Trans Tech Publications, 1996, 115: 1-20. |
| [60] | LIU Z, REN W, NIE H, et al.Pressure driven depolarization behavior of Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3 based lead-free ceramics.Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 110(21): 212901. |
| [61] | SHKURATOV S I, BAIRD J, ANTIPOV V G, et al.Ultrahigh energy density harvested from domain-engineered relaxor ferroelectric single crystals under high strain rate loading. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 46758. |
| [1] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | TIAN Ruizhi, LAN Zhengyi, YIN Jie, HAO Nanjing, CHEN Hangrong, MA Ming. Microfluidic Technology Based Synthesis of Inorganic Nano-biomaterials: Principles and Progress [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [8] | ZHANG Jiguo, WU Tian, ZHAO Xu, YANG Fan, XIA Tian, SUN Shien. Improvement of Cycling Stability of Cathode Materials and Industrialization Process for Sodium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [9] | YIN Jie, GENG Jiayi, WANG Kanglong, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Recent Advances in 3D Printing and Densification of SiC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [10] | CHEN Guangchang, DUAN Xiaoming, ZHU Jinrong, GONG Qing, CAI Delong, LI Yuhang, YANG Donglei, CHEN Biao, LI Xinmin, DENG Xudong, YU Jin, LIU Boya, HE Peigang, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. Advanced Ceramic Materials in Helicopter Special Structures: Research Progress and Application Prospect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [11] | FAN Xiaobo, ZU Mei, YANG Xiangfei, SONG Ce, CHEN Chen, WANG Zi, LUO Wenhua, CHENG Haifeng. Research Progress on Proton-regulated Electrochemical Ionic Synapses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [12] | HAIREGU Tuxun, GUO Le, DING Jiayi, ZHOU Jiaqi, ZHANG Xueliang, NUERNISHA Alifu. Research Progress of Optical Bioimaging Technology Assisted by Upconversion Fluorescence Probes in Tumor Imaging [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [13] | SUN Shujuan, ZHENG Nannan, PAN Haokun, MA Meng, CHEN Jun, HUANG Xiubing. Research Progress on Preparation Methods of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [14] | TAO Guilong, ZHI Guowei, LUO Tianyou, OUYANG Peidong, YI Xinyan, LI Guoqiang. Progress on Key Technologies of Cavity-structured Thin Film Bulk Acoustic Wave Filter [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| [15] | ZHOU Fan, TIAN Zhilin, LI Bin. Research Progress on Carbide Ultra-high Temperature Ceramic Anti-ablation Coatings for Thermal Protection System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 1-16. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||