
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 234-244.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250180
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
NIE Xiaoshuang1,2( ), LI Dandan1, WANG Fang1,2, OUYANG Liping3, LI Heng1(
), LI Dandan1, WANG Fang1,2, OUYANG Liping3, LI Heng1( ), QIU Jiajun1(
), QIU Jiajun1( )
)
Received:2025-04-27
Revised:2025-05-19
Published:2026-02-20
Online:2025-06-05
Contact:
LI Heng, associate professor. E-mail: liheng@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:NIE Xiaoshuang (2000-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: niexiaoshuang0908@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
NIE Xiaoshuang, LI Dandan, WANG Fang, OUYANG Liping, LI Heng, QIU Jiajun. Ti3C2Tx Piezoelectric Composite Hydrogels for Bacterial-infected Skin Wound Healing[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 234-244.
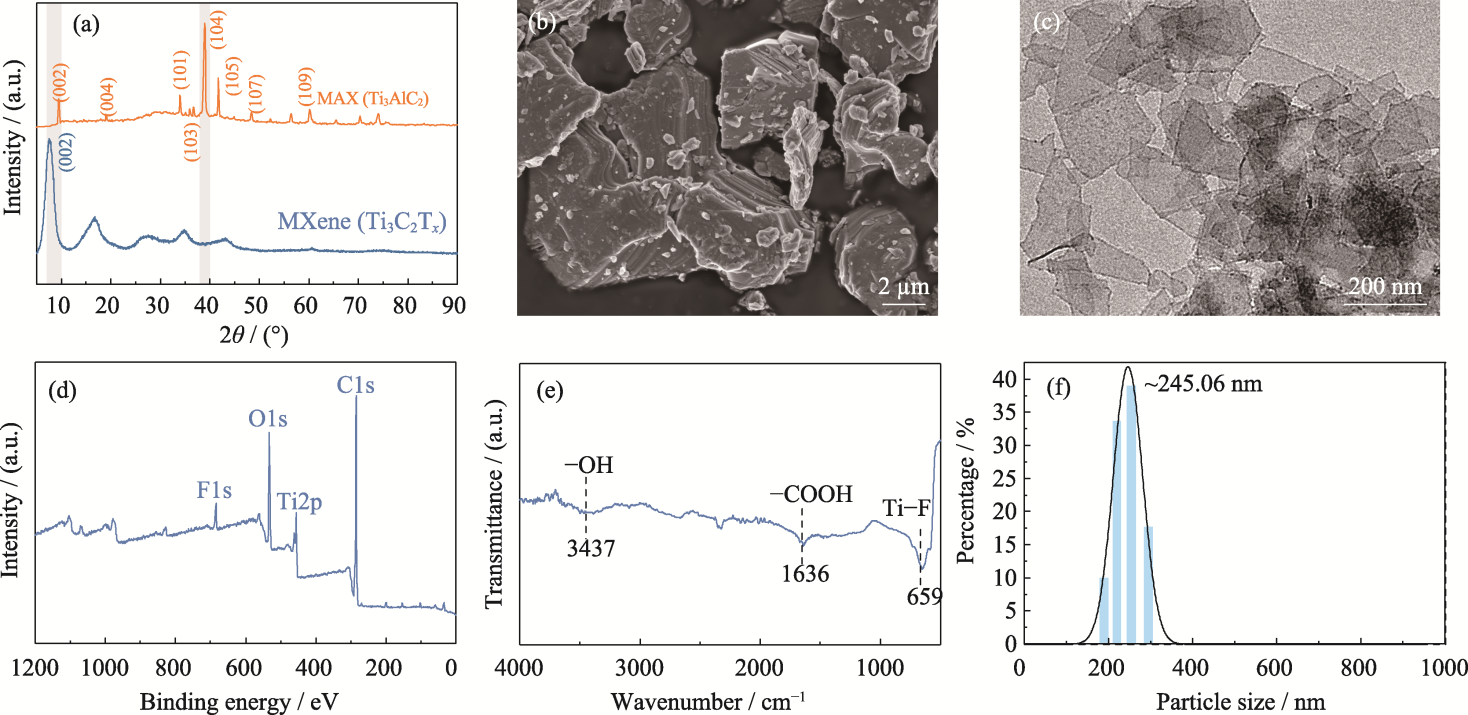
Fig. 1 Synthesis and characterization of Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets (a) XRD patterns of MAX and MXene nanosheets; (b) SEM image of MAX; (c) TEM image, (d) XPS spectrum, (e) FT-IR spectrum and (f) particle size of MXene
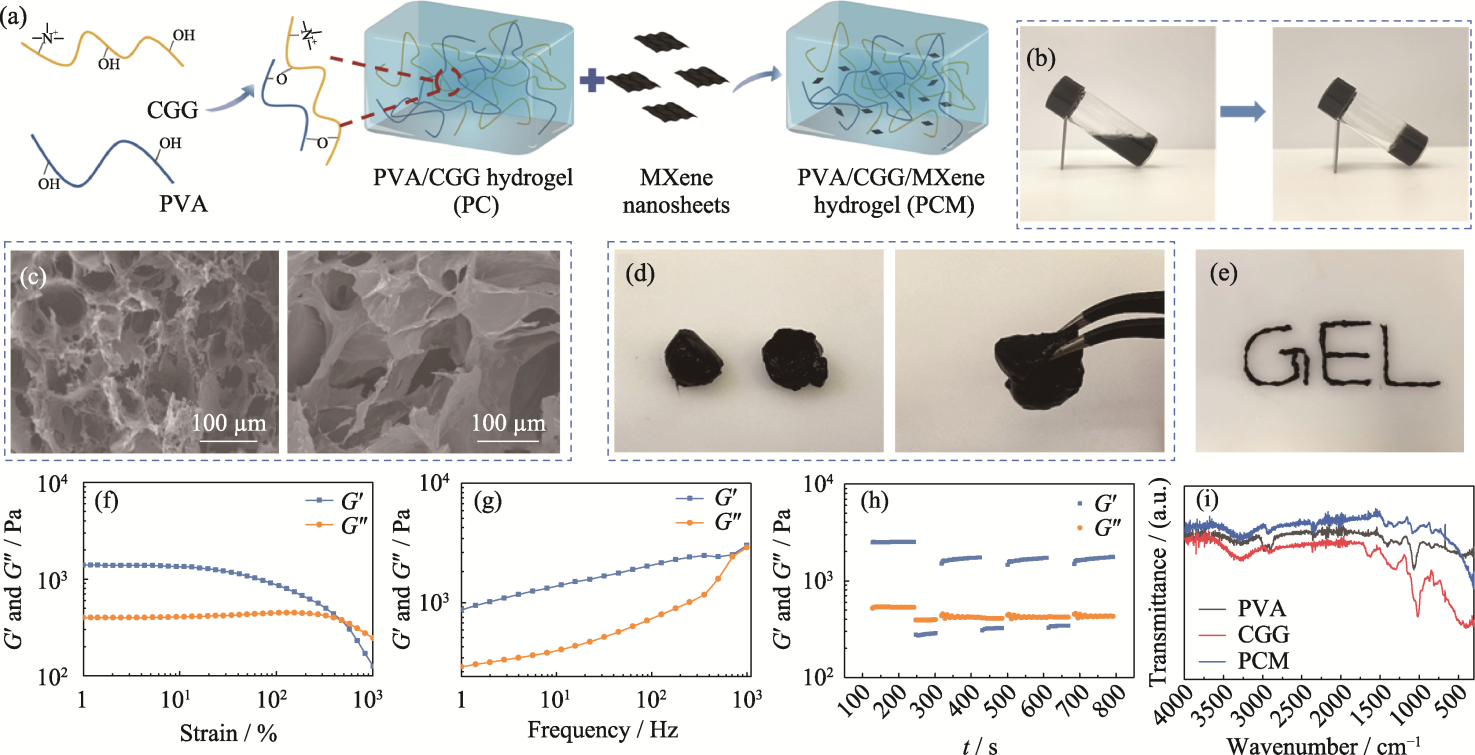
Fig. 2 Preparation and characterization of PCM composite hydrogel (a) Schematic representation of preparation of the PCM hydrogel; (b) Optical image depicting transition of the PCM hydrogel from sol state to gel state; (c) SEM images of the PC (left) and the PCM (right) hydrogels; (d) Self-healing and (e) injectable properties of the PCM hydrogel; (f-h) Rheological properties of the PCM hydrogel: (f) strain scan, (g) frequency scan, (h) cyclic strain scan, and (i) FT-IR spectra of hydrogels. Colorful figures are available on website
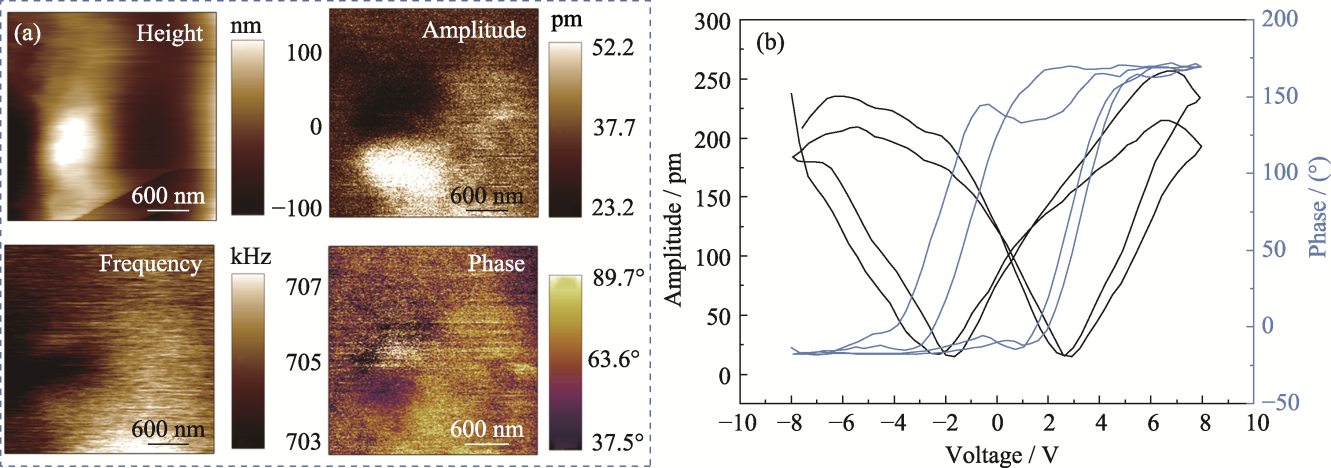
Fig. 4 Piezoelectric properties of PCM hydrogel (a) Surface topography, phase, frequency, and phase liner plots; (b) Butterfly pressure-amplitude curves and hysteresis loops
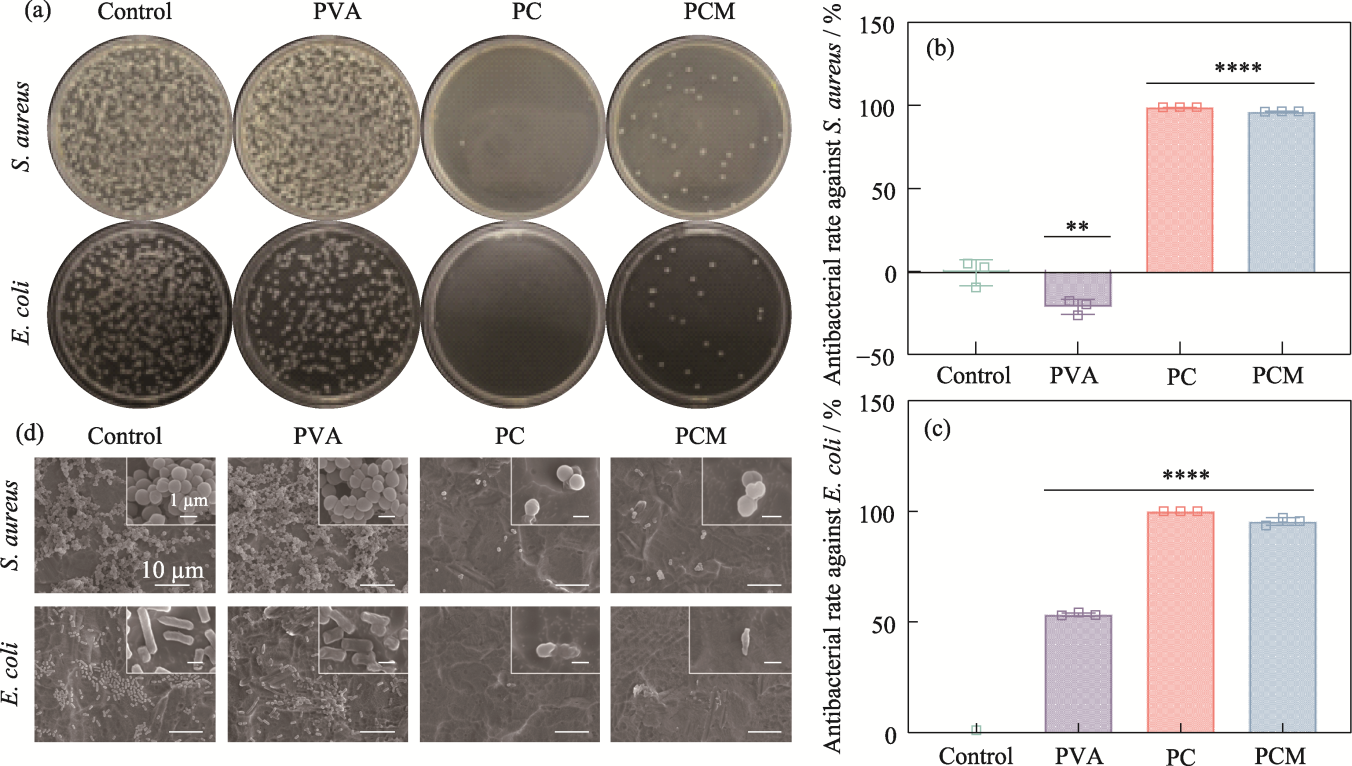
Fig. 6 Antimicrobial properties of the hydrogels (a) Agar plate images; (b, c) Antibacterial rates against (b) S. aureus and (c) E. coli, n=3, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001; (d) SEM images of S. aureus and E. coli from hydrogels
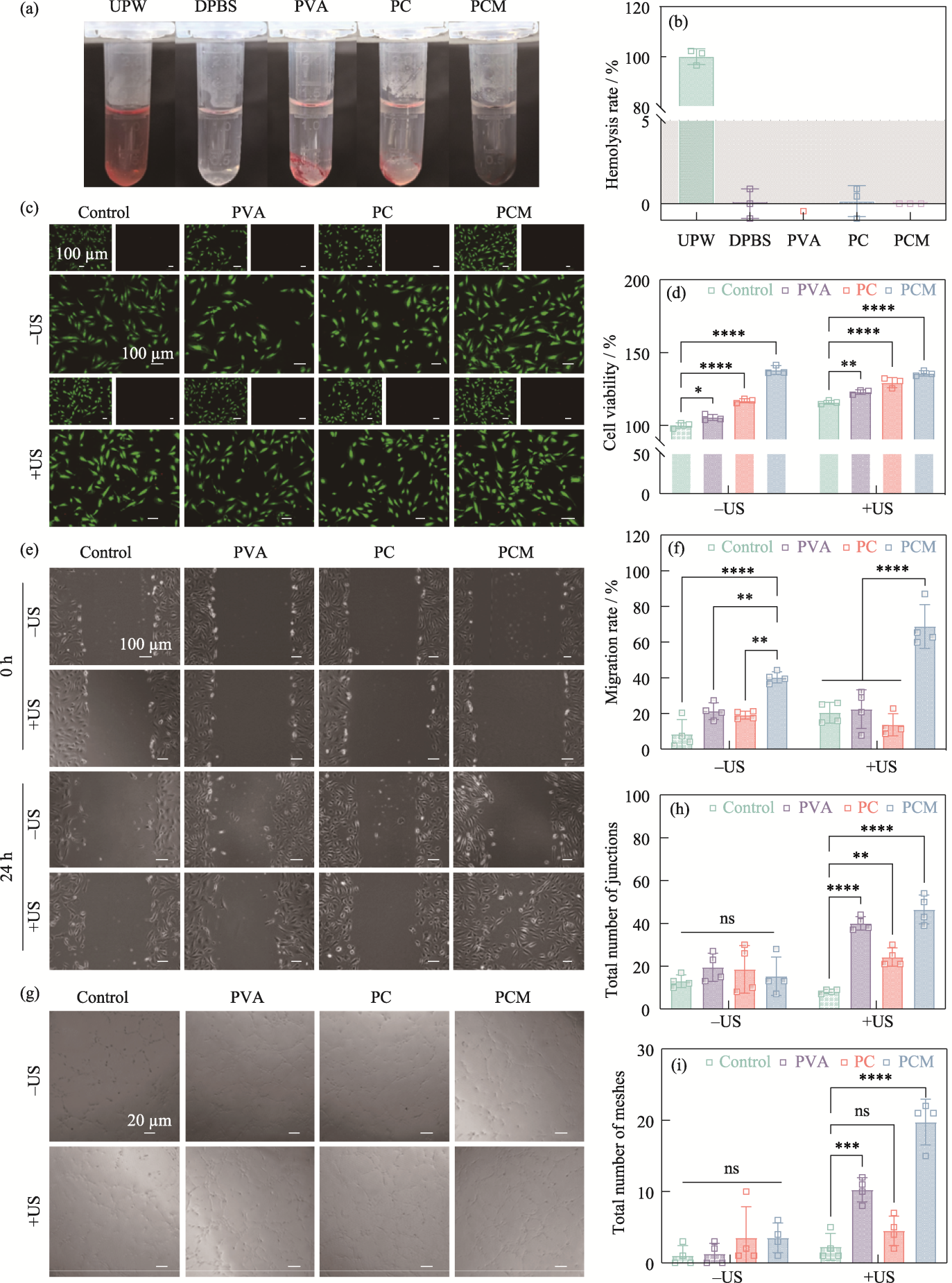
Fig. 7 Biocompatibility and regulation of cellular behaviors of the hydrogels (a) Optical images of the hemolysis experiments; (b) Hemolysis rates of UPW, DPBS, PVA, PC, and PCM hydrogels; (c) Live/dead staining fluorescent images and (d) cell viability of HUVECs from the control, PVA, PC, and PCM groups with or without ultrasound stimulation; (e) Cell migration images of HUVECs from the control, PVA, PC, and PCM groups with or without ultrasound stimulation and (f) corresponding migration rate; (g) Images of tube formation assay at 0 and 24 h from the control, PVA, PC, and PCM groups with or without ultrasound stimulation and corresponding total number of (h) junctions and (i) meshes n=3, **p< 0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. Colorful figures are available on website
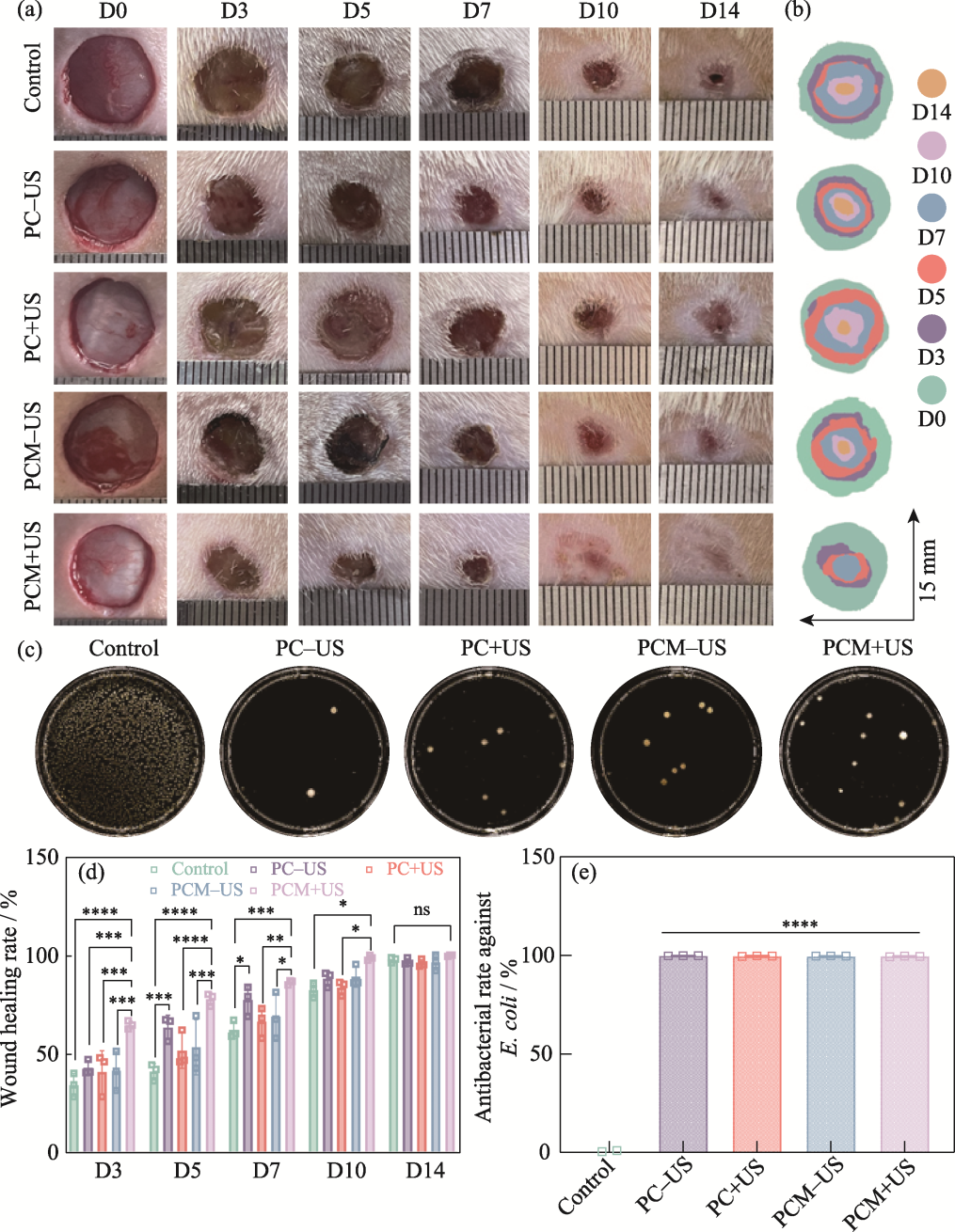
Fig. 8 Evaluation of in vivo therapeutic effect of the hydrogels (a) Representative digital photographs of skin wounds on 0, 3, 5, 7, 10, and 14 d; (b) Schematic diagram of the wounds treated with different groups for 14 d; (c) Agar plate images of E. coli from the control, PC-US, PC+US, PCM-US, and PCM+US groups; (d) Quantitative analysis of the wound healing rates in various groups on 3, 5, 7, 10, and 14 d; (e) Antibacterial rates of the control, PC-US, PC+US, PCM-US, and PCM+US groups against E. coli n=3, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. Colorful figures are available on website
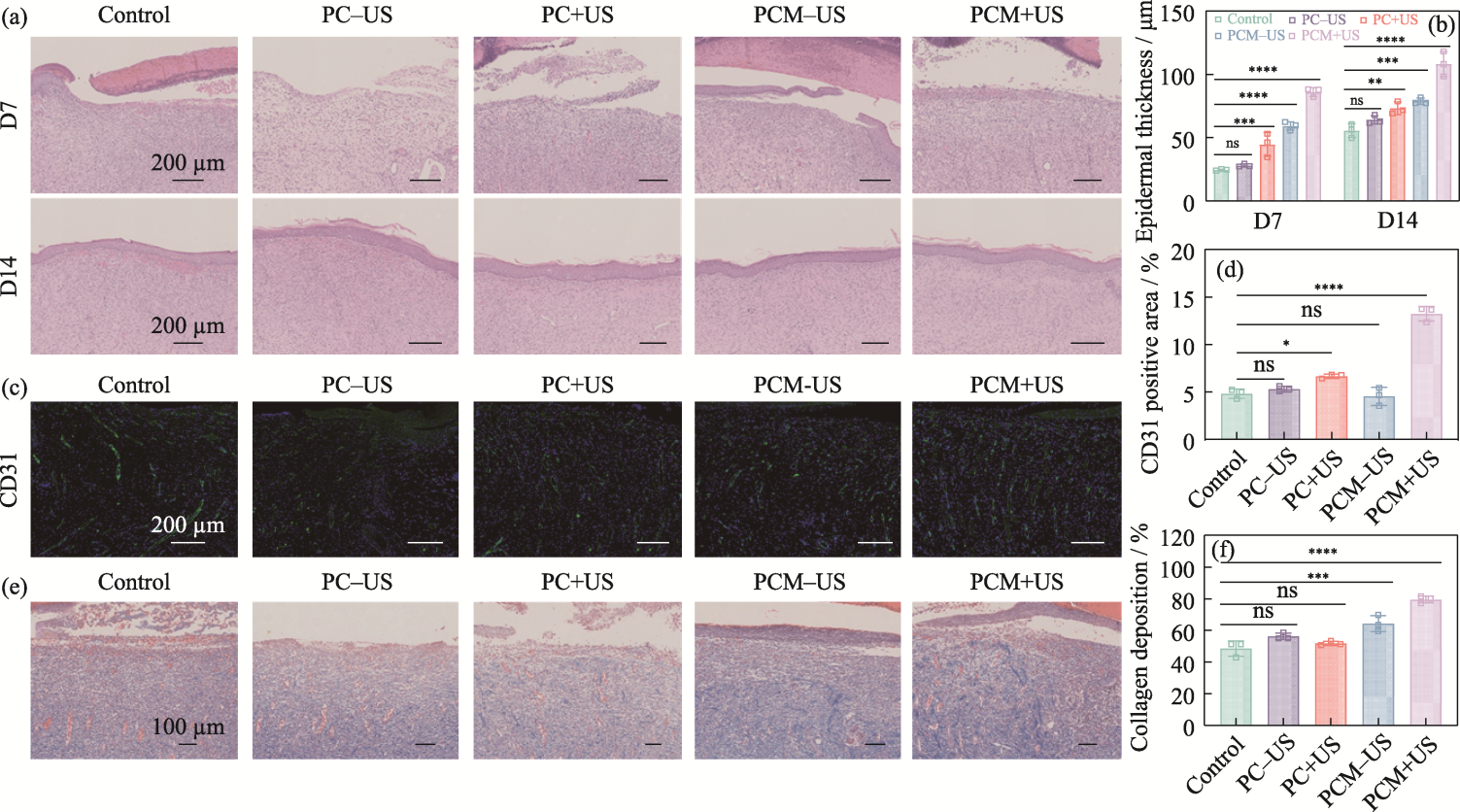
Fig. 9 Histologic evaluation of in vivo efficacy of the hydrogels (a) H&E staining of wound tissues on 7 and 14 d; (b) Epidermal thickness of skin tissues on 7 and 14 d; (c) CD31 staining of wound tissues on 7 d; (d) Area proportion of CD31-positive skin tissue on 7 d; (e) Masson staining of wound tissues on 7 d;(f) Proportion of collagen deposition from skin tissues on 7 d n=3, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. Colorful figures are available on website
| Component | PVA/(mg·mL-1) | CGG/(mg·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|
| PVA | 52.5 | 0 |
| PC1 | 52.5 | 10 |
| PC2 | 52.5 | 20 |
| PC3 | 52.5 | 30 |
| PC4 | 52.5 | 40 |
| PC5 | 52.5 | 50 |
| PC6 | 52.5 | 60 |
Table S1 Volume of each component in PCx hydrogels
| Component | PVA/(mg·mL-1) | CGG/(mg·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|
| PVA | 52.5 | 0 |
| PC1 | 52.5 | 10 |
| PC2 | 52.5 | 20 |
| PC3 | 52.5 | 30 |
| PC4 | 52.5 | 40 |
| PC5 | 52.5 | 50 |
| PC6 | 52.5 | 60 |
| Component | PVA/ (mg·mL-1) | CGG/ (mg·mL-1) | MXene/ (mg·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVA | 52.5 | 0 | 0 |
| PC | 52.5 | 40 | 0 |
| PCM1 | 52.5 | 40 | 1 |
| PCM2 | 52.5 | 40 | 2 |
| PCM3 | 52.5 | 40 | 3 |
| PCM4 | 52.5 | 40 | 4 |
| PCM5 | 52.5 | 40 | 5 |
Table S2 Volume of each component in PCMx hydrogels
| Component | PVA/ (mg·mL-1) | CGG/ (mg·mL-1) | MXene/ (mg·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVA | 52.5 | 0 | 0 |
| PC | 52.5 | 40 | 0 |
| PCM1 | 52.5 | 40 | 1 |
| PCM2 | 52.5 | 40 | 2 |
| PCM3 | 52.5 | 40 | 3 |
| PCM4 | 52.5 | 40 | 4 |
| PCM5 | 52.5 | 40 | 5 |
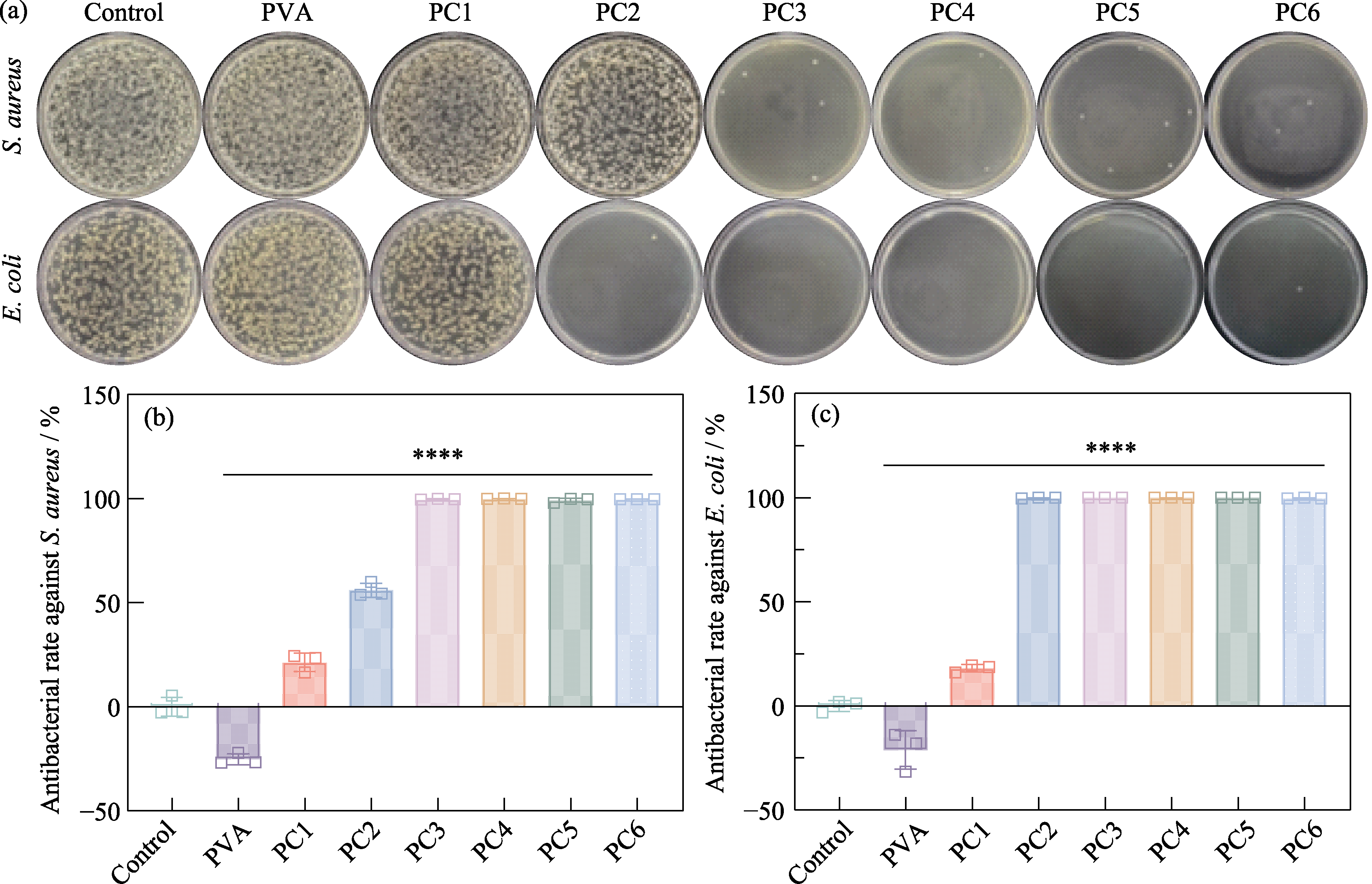
Fig. S5 Antibacterial performance testing of PCx hydrogels (a) Agar plate images of S. aureus and E. coli from control, PVA, PC1, PC2, PC3, PC4, PC5, and PC6 groups, respectively, and corresponding antibacterial rates against (b) S. aureus and (c) E. coli

Fig. S6 Comparison of gelation time for hydrogels After 30 min of freezing, the PC4 hydrogel (left) has formed a gel, while the PC3 hydrogel (right) is still in a thick, soluble state after 1 h of freezing
| [1] |
GÜIZA-ARGÜELLO V R, SOLARTE-DAVID V A, PINZÓN- MORA A V, et al. Current advances in the development of hydrogel-based wound dressings for diabetic foot ulcer treatment. Polymers, 2022, 14(14): 2764.
DOI URL |
| [2] | GONZALEZ A C D O, COSTA T F, ANDRADE Z D A, et al. Wound healing-a literature review. Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia, 2016, 91(5): 614. |
| [3] |
TAVAKOLI S, KLAR A S. Advanced hydrogels as wound dressings. Biomolecules, 2020, 10(8): 1169.
DOI URL |
| [4] | WANG Y, WU Y, LONG L, et al. Inflammation-responsive drug-loaded hydrogels with sequential hemostasis, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory behavior for chronically infected diabetic wound treatment. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(28): 33584. |
| [5] |
LEAPER D, ASSADIAN O, EDMISTON C E. Approach to chronic wound infections. British Journal of Dermatology, 2015, 173(2): 351.
DOI URL |
| [6] | METCALF D G, BOWLER P G. Biofilm delays wound healing: a review of the evidence. Burns & Trauma, 2013, 1(1): 5. |
| [7] |
LINDLEY L E, STOJADINOVIC O, PASTAR I, et al. Biology and biomarkers for wound healing. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 2016, 138(3S): 18S.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
UBEROI A, MCCREADY-VANGI A, GRICE E A. The wound microbiota: microbial mechanisms of impaired wound healing and infection. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2024, 22(8): 507.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
MIZELLE R M. Diabetes, race, and amputations. The Lancet, 2021, 397(10281): 1256.
DOI URL |
| [10] | ARMSTRONG D G, TAN T, BOULTON A J M, et al. Diabetic foot ulcers: a review. Journal of the American Medical Association, 2023, 330(1): 62. |
| [11] |
SEN C K. Human wounds and its burden: an updated compendium of estimates. Advances in Wound Care, 2019, 8(2): 39.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
SEN C K. Human wound and its burden: updated 2020 compendium of estimates. Advances in Wound Care, 2021, 10(5): 281.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
DENG L, DU C, SONG P, et al. The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in diabetic wound healing. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2021, 2021(1): 8852759.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
PIETRAMAGGIORI G, SCHERER S S, MATHEWS J C, et al. Healing modulation induced by freeze-dried platelet-rich plasma and micronized allogenic dermis in a diabetic wound model. Wound Repair and Regeneration, 2008, 16(2): 218.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | MEYER M, MÜLLER A K, YANG J, et al. The role of chronic inflammation in cutaneous fibrosis:fibroblast growth factor receptor deficiency in keratinocytes as an example. Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings, 2011, 15(1): 48. |
| [16] |
TANAKA Y, SUTARLIE L, SU X. Detecting bacterial infections in wounds: a review of biosensors and wearable sensors in comparison with conventional laboratory methods. Analyst, 2022, 147(9): 1756.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
DENG Y, BOON C, CHEN S, et al. Cis-2-dodecenoic acid signal modulates virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa through interference with quorum sensing systems and T3SS. BMC Microbiology, 2013, 13: 231.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
JACOBS M R, FELMINGHAM D, APPELBAUM P C, et al. The Alexander project 1998-2000: susceptibility of pathogens isolated from community-acquired respiratory tract infection to commonly used antimicrobial agents. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 2003, 52(2): 229.
PMID |
| [19] |
YAGUPSKY P. Selection of antibiotic-resistant pathogens in the community. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal, 2006, 25(10): 974.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
FALAGAS M E, MAVROUDIS A D, VARDAKAS K Z. The antibiotic pipeline for multi-drug resistant gram negative bacteria: what can we expect? Expert Review of Anti-Infective Therapy, 2016, 14(8): 747.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
CHEN S, WANG H, SU Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-laden, personalized 3D scaffolds with controlled structure and fiber alignment promote diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomaterialia, 2020, 108: 153.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
LEE K, SILVA E A, MOONEY D J. Growth factor delivery-based tissue engineering: general approaches and a review of recent developments. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2011, 8(55): 153.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | CHENG B, YAN Y, QI J, et al. Cooperative assembly of a peptide gelator and silk fibroin afford an injectable hydrogel for tissue engineering. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(15): 12474. |
| [24] |
ZAREI F, SOLEIMANINEJAD M. Role of growth factors and biomaterials in wound healing. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology, 2018, 46(sup1): 906.
DOI |
| [25] |
NUCCITELLI R. A role for endogenous electric fields in wound healing. Current Topics in Developmental Biology, 2003, 58(2): 1.
PMID |
| [26] |
THRIVIKRAMAN G, BODA S K, BASU B. Unraveling the mechanistic effects of electric field stimulation towards directing stem cell fate and function: a tissue engineering perspective. Biomaterials, 2018, 150: 60.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
SNYDER A R, PEROTTI A L, LAM K C, et al. The influence of high-voltage electrical stimulation on edema formation after acute injury: a systematic review. Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2010, 19(4): 436.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
SEBASTIAN A, SYED F, PERRY D, et al. Acceleration of cutaneous healing by electrical stimulation: degenerate electrical waveform down-regulates inflammation, up-regulates angiogenesis and advances remodeling in temporal punch biopsies in a human volunteer study. Wound Repair and Regeneration, 2011, 19(6): 693.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | GUO Z, SAW P E, JON S. Non-invasive physical stimulation to modulate the tumor microenvironment: unveiling a new frontier in cancer therapy. BIO Integration, 2024, 5(1): 986. |
| [30] |
SALATINO J W, LUDWIG K A, KOZAI T D, et al. Glial responses to implanted electrodes in the brain. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 1(11): 862.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
HUANG D, CHENG Y, CHEN G, et al. 3D-printed Janus piezoelectric patches for sonodynamic bacteria elimination and wound healing. Research, 2023, 6: 0022.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
ZHANG Y, RUAN K, GU J. Flexible sandwich-structured electromagnetic interference shielding nanocomposite films with excellent thermal conductivities. Small, 2021, 17(42): 2101951.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
ZENG Z, WANG C, SIQUEIRA G, et al. Nanocellulose-MXene biomimetic aerogels with orientation-tunable electromagnetic interference shielding performance. Advanced Science, 2020, 7(15): 2000979.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
ZHANG Y, HU Y, XIE B, et al. Hoffmeister effect optimized hydrogel electrodes with enhanced electrical and mechanical properties for nerve conduction studies. Research, 2024, 7: 0453.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
ZHOU H, CHEN L, HUANG C, et al. Endogenous electric field coupling MXene sponge for diabetic wound management: haemostatic, antibacterial, and healing. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2024, 22(1): 530.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
DONG S, ZHANG Y, MEI Y, et al. Researching progress on bio-reactive electrogenic materials with electrophysiological activity for enhanced bone regeneration. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022, 10: 921284.
DOI URL |
| [1] | WANG Yutong, CHANG Jiang, XU He, WU Chengtie. Advances in Silicate Bioceramic/Bioglass for Wound Healing: Effects, Mechanisms and Application Ways [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [2] | ZHAO Lihua, WANG Yanshuai, YIN Xinwu, MAO Yeqiong, NIU Dechao. Bismuth Sulfide Nanoclusters-loaded Silica-based Hybrid Micelles: Preparation and Photothermal Antibacterial Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1129-1136. |
| [3] | ZHANG Bo, FU Yimin, CHEN Zheng, SHI Ao, ZHU Min. Near-infrared Responsive Biphasic Antibacterial Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Composite Scaffolds: Preparation and Antibacterial Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1137-1144. |
| [4] | WANG Yueyue, HUANG Jiahui, KONG Hongxing, LI Huaizhu, YAO Xiaohong. Silver Loaded Radial Mesoporous Silica: Preparation and Application in Dental Resins [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 77-83. |
| [5] | LI Chengyu, DING Ziyou, HAN Yingchao. In vitro Antibacterial and Osteogenic Properties of Manganese Doped Nano Hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 313-320. |
| [6] | ZHANG Zhimin, GE Min, LIN Han, SHI Jianlin. Novel Magnetoelectric Catalytic Nanoparticles: RNS Release and Antibacterial Efficiency [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1114-1124. |
| [7] | ZHANG Shumin, XI Xiaowen, SUN Lei, SUN Ping, WANG Deqiang, WEI Jie. Sonodynamic and Enzyme-like Activities of Niobium-based Coatings: Antimicrobial, Cell Proliferation and Cell Differentiation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1125-1134. |
| [8] | XIE Jiaye, LI Liwen, ZHU Qiang. Contrastive Study on in Vitro Antibacterial Property and Biocompatibility of Three Clinical Pulp Capping Agents [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1449-1456. |
| [9] | DU Jiaheng, FAN Xinli, XIAO Dongqin, YIN Yiran, LI Zhong, HE Kui, DUAN Ke. Electrophoretic Coating of Magnesium Oxide on Microarc-oxidized Titanium and Its Biological Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1441-1448. |
| [10] | WU Xuetong, ZHANG Ruofei, YAN Xiyun, FAN Kelong. Nanozyme: a New Approach for Anti-microbial Infections [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 43-54. |
| [11] | SHENG Lili, CHANG Jiang. Photo/Magnetic Thermal Fe2SiO4/Fe3O4 Biphasic Bioceramic and Its Composite Electrospun Membrane: Preparation and Antibacterial [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 983-990. |
| [12] | WANG Xiaojun, XU Wen, LIU Runlu, PAN Hui, ZHU Shenmin. Preparation and Properties of Ag@C3N4 Photocatalyst Supported by Hydrogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| [13] | WEI Ziqin, XIA Xiang, LI Qin, LI Guorong, CHANG Jiang. Preparation and Properties of Barium Titanate/Calcium Silicate Composite Bioactive Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 617-622. |
| [14] | WU Aijun, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Copper-incorporated Calcium Silicate Nanorods Composite Hydrogels for Tumor Therapy and Skin Wound Healing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1203-1216. |
| [15] | XIANG Hui, QUAN Hui, HU Yiyuan, ZHAO Weiqian, XU Bo, YIN Jiang. Piezoelectricity of Graphene-like Monolayer ZnO and GaN [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 492-496. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||