
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 1269-1278.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160234
• Orginal Article • Next Articles
BAO Yan, WANG Tong
Received:2016-04-06
Revised:2016-06-15
Published:2016-12-16
Online:2016-11-23
Supported by:CLC Number:
BAO Yan, WANG Tong. Recent Advances in Fabrication and Sustained/Controlled-release Application of Hollow Silica Microspheres[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(12): 1269-1278.
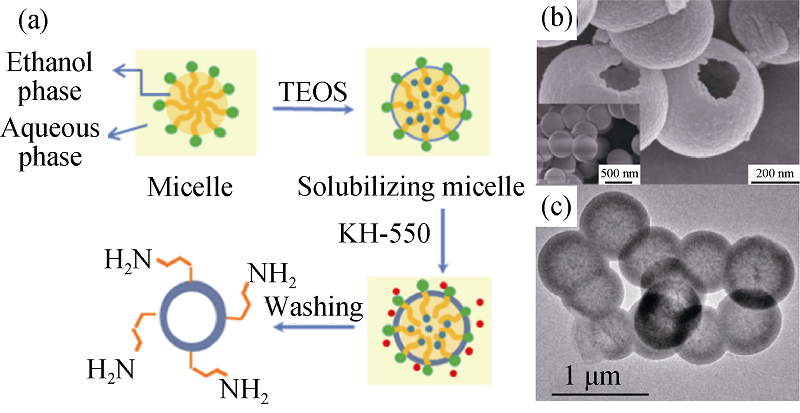
Fig. 3 (a) A schematic of the process for hollow silica microspheres preparation via soft-templating method; (b) SEM and (c)TEM images of hollow silica microspheres[44]
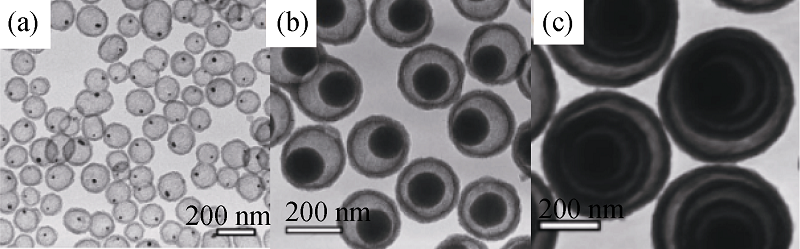
Fig. 4 TEM images of (a) Au/SiO2 yolk/shell hollow silica microspheres, (b) SiO2/SiO2 yolk/shell hollow silica microspheres and (c) SiO2/SiO2 multilayer shell hollow silica microspheres[46]
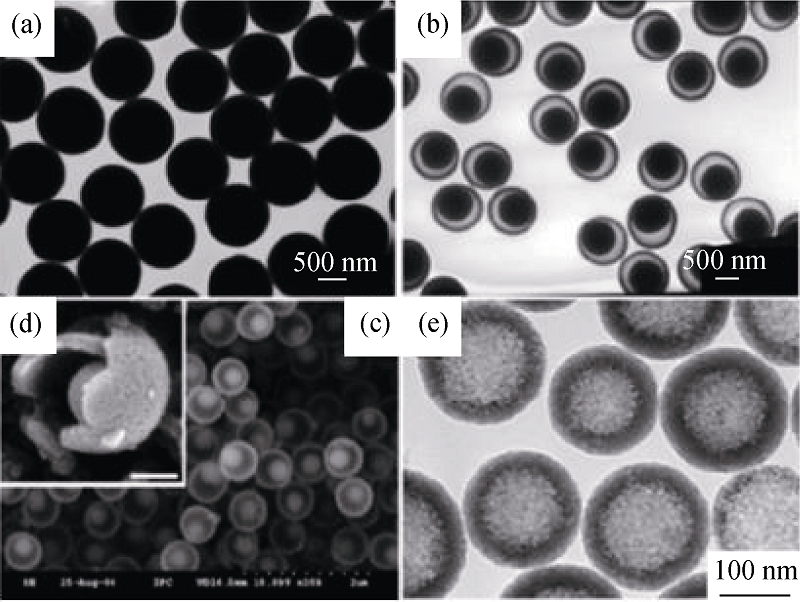
Fig. 6 (a) TEM image of solid silica spheres, (b) TEM and (c, d) SEM images of mesoporous hollow silica nanorattles, (e) TEM image of mesoporous hollow silica microspheres[58]
| Method | Characteristic | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Hard template | ① Adjustable particle size; ② Well-defined structure; ③ Uniform product morphology; ④ Foreseeable and high repetition rate | ① Difficult to remove the templates ② The shell easy to collapse; ③ Time-consuming and money-consuming |
| Soft template | ① Easy to prepare and remove the templates ② Simple technology; ③ Time-saving | ① Poor structural stability and monodispersity; ② Not easy to control shell thickness; ③ Wide particle size distribution; ④ Low efficiency |
| Self template | ① No additional template; ② Simple step and time-saving synthetic; ③ High repetition rate; ④ Controllable morphology | ① Various and complex influence factors; ② Large dependability on environment |
Table 1 Characteristics and limitations of various preparation methods
| Method | Characteristic | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Hard template | ① Adjustable particle size; ② Well-defined structure; ③ Uniform product morphology; ④ Foreseeable and high repetition rate | ① Difficult to remove the templates ② The shell easy to collapse; ③ Time-consuming and money-consuming |
| Soft template | ① Easy to prepare and remove the templates ② Simple technology; ③ Time-saving | ① Poor structural stability and monodispersity; ② Not easy to control shell thickness; ③ Wide particle size distribution; ④ Low efficiency |
| Self template | ① No additional template; ② Simple step and time-saving synthetic; ③ High repetition rate; ④ Controllable morphology | ① Various and complex influence factors; ② Large dependability on environment |
| [1] | LIU J, LIU F, GAO K,et al. Recent developments in the chemical synthesis of inorganic porous capsules. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2009, 19(34): 6073-6084. |
| [2] | ZHANG C, HOU T, CHEN J,et al. Preparation of mesoporous silica microspheres with multi-hollow cores and their application in sustained drug release. Particuology, 2010, 8(5): 447-452. |
| [3] | ZHU Y, SHI J, CHEN H,et al. A facile method to synthesize novel hollow mesoporous silica spheres and advanced storage property. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2005, 84(1): 218-222. |
| [4] | YANG X L, YAO K, ZHU Y H.Fabrication and sustained release property of nanostruetured hollow silica microspheres.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2005, 20(6): 1403-1408. |
| [5] | 鲍艳, 杨永强, 马建中, 等. 一种聚丙烯酸酯/ 中空二氧化硅纳米复合皮革涂饰剂的制备方法: 中国, 102704273A.2012-10-03. |
| [6] | ZHAO Y, SUN Y L, WANG H,et al. The application of hollow microspheres . Science and Technology in Chemical Industry, 2014, 22(5): 68-72. |
| [7] | CHEN J F, DING H M, WANG J X,et al. Preparation and characterization of porous hollow silica nanoparticles for drug delivery application . Biomaterials, 2004, 25(4): 723-727. |
| [8] | FENG X F, JIN W G, LIU F,et al. Advance in preparation of hollow mesoporous silica-based microsphere . Inorganic Chemical Industry, 2008, 40(12): 12-14. |
| [9] | WANG J X, WANG Z H, CHEN J F,et al. Direct encapsulation of water-soluble drug into silica microcapsules for sustained release applications . Materials Research Bulletin, 2008, 43(12): 3374-3381. |
| [10] | SLOWING I, VIVERO E J, WU C,et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as controlled release drug delivery and gene transfection carriers . Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2008, 60(11): 1278-1288. |
| [11] | ZHU Y, SHI J, SHEN W,et al. Stimuli-responsive controlled drug release from a hollow mesoporous silica sphere/polyelectrolyte multilayer core-shell structure. Angewandte Chemie, 2005, 117(32): 5213-5217. |
| [12] | LEE C, CHENG S, HUANG I,et al. Intracellular pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the controlled release of anticancer chemotherapeutics. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 122(44): 8390-8395. |
| [13] | CHANG F P, HUNG Y, CHANG J H,et al. Enzyme encapsulated hollow silica nanospheres for intracellular biocatalysis. ACS applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(9): 6883-6890. |
| [14] | CHEN Y, MENG Q, WU M,et al. Hollow mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles: a generic intelligent framework- hybridization approach for biomedicine. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(46): 16326-16334. |
| [15] | RETSCH M, SCHMELAEISEN M, BUTT H J,et al. Visible Mie scattering in nonabsorbing hollow sphere powders. Nano Letters, 2011, 11(3): 1389-1394. |
| [16] | JIN L, XU L, MOREIN C,et al. Titanium containing γ‐MnO2(TM) hollow spheres: one-step synthesis and catalytic activities in Li/Air batteries and oxidative chemical reactions. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010, 20(19): 3373-3382. |
| [17] | ZHU Y, FANG Y, KASKEL S.Folate-conjugated Fe3O4@SiO2 hollow mesoporous spheres for targeted anticancer drug delivery.The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(39): 16382-16388. |
| [18] | KOWALSKI A, VOGEL M, BLANKENSHIP R M.US Patent4, 427, 836, 1884. |
| [19] | ZHANG S, XU L, LIU H,et al. A dual template method for synthesizing hollow silica spheres with mesoporous shells. Materials Letters, 2009, 63(2): 258-259. |
| [20] | WANG Y, TANG C, DENG Q,et al. A versatile method for controlled synthesis of porous hollow spheres. Langmuir, 2010, 26(18): 14830-14834. |
| [21] | KATO N, KATO N.High-yield hydrothermal synthesis of mesoporous silica hollow capsules.Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2016, 219: 230-239. |
| [22] | DUAN Y W, YU A H, ZHAI G X.Progress of preparation methods of hollow microspheres.Chinese Journal of Pharmaceuticals, 2015, 46(6): 639-646. |
| [23] | SCHMID A, FUJII S, ARMES S P.Polystyrene silica nanocomposite particlesvia alcoholic dispersion polymerization using a cationic azo initiator. Langmuir, 2006, 22(11): 4923-4927. |
| [24] | SEN D, KHAN A, BAHADUR J,et al. Use of small-angel neutron scattering to investigate modifications of internal structure in self-assembled grains of nanoparticles synthesized by spray drying. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 347(1): 25-30. |
| [25] | HAGURA N, NANDIYANTO A B D, ISKANDAR F,et al. A role of template surface charge in the preparation of porous and hollow particles using spray-drying. Chemistry Letters, 2009, 38(11): 1076-1077. |
| [26] | HU W, DU X, WU Y,et al. Novel -Cu0.95V2O5 hollow microspheres and α-CuV2O6 nanograins: Facile synthesis and application in lithium-ion batteriesv. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 237(237): 112-118. |
| [27] | WEI J, DU A, JIN F,et al. The preparation and high-frequency electromagnetic properties of ferrimagnetic bisphthalonitrile-Fe3O4 core-shell hollow microspheres. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2013, 340(8): 70-75. |
| [28] | 杨永强. 聚丙烯酸酯/中空二氧化硅纳米复合皮革涂饰剂的制备及应用研究. 陕西科技大学, 2014. |
| [29] | GU W J, LIAO Y, WU W B,et al. Progress in the preparation of hollow silica spheres. Silicone Material, 2009, 23(4): 257-264. |
| [30] | TENG Z, HAN Y, LI J,et al. Preparation of hollow mesoporous silica spheres by a Sol-Gel/emulsion approach. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2010, 127(1): 67-72. |
| [31] | BECKER AL, JOHNSTON APR, CARUSO F.Layer-by-layer- assembled capsules and films for therapeutic delivery.Small, 2010, 6(17): 1836-1852. |
| [32] | XIE F, QI M Z, LI W J,et al. Classification, fabrication methods and applications of inorganic hollow spheres. Progress in Chemistry, 2011, 23(12): 2522-2533. |
| [33] | MALGRAS V, JI Q, KAMACHI Y,et al. Templated synthesis for nanoarchitectured porous materials. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 2015, 88(9): 1171-1200. |
| [34] | HSUEH H Y, YAO C T, HO R M.Well-ordered nanohybrids and nanoporous materials from gyroid block copolymer templates.Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(7): 1974-2018. |
| [35] | NANDIYANTO A B D, KIM S G, ISKANDAR F,et al. Synthesis of spherical mesoporous silica nanoparticles with nanometer-size controllable pores and outer diameters. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2009, 120(3): 447-453. |
| [36] | YANG Z, CONG H, CAO W.Narrowly dispersed micrometer- sized composite spheres based on diazonium-polystyrene.Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 2004, 42(17): 4284-4288. |
| [37] | ZOU H, WU S, RAN Q,et al. A simple and low-cost method for the preparation of monodisperse hollow silica spheres. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112(31): 11623-11629. |
| [38] | BAO Y, YANG Y Q, MA J Z.Fabrication of monodisperse hollow silica spheres and effect on water vapor permeability of polyacrylate membrane.Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2013, 407(10): 155-163. |
| [39] | SUHENDI A, NANDIYANTO A B, MUNIR M M,et al.Preparation of agglomeration-free spherical hollow silica particles using an electrospray method with colloidal templating. Materials Letters, 2013, 106(9): 432-435. |
| [40] | CHEN Z, CUI Z M, NIU F,et al. Pd nanoparticles in silica hollow spheres with mesoporous walls: a nanoreactor with extremely high activity. Chem. Commun., 2010, 46(35): 6524-6526. |
| [41] | BAO Y, YANG Y Q, MA J Z,et al. Fabrication of hollow silica microsphere using zinc oxide as template and its effect on polyacrylate film properies. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2014, 42(7): 914-925. |
| [42] | CAO F, LI D X, GUAN Z S.Preparation of silica hollow microspheres with special surface morphology by biotemplate method.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(3): 501-506. |
| [43] | WANG X, MIAO X R, LI Z M,et al. Fabrication of microporous hollow silica spheres templated by NP-10 micelles without calcinations. Applied Surface Science, 2011, 257(7): 2481-2488. |
| [44] | BAO Y, SHI C H, MA J Z.Fabrication of hollow silica spheres and their effect on water vapor permeability of waterborne polyurethane film.Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2015, 43(1): 35-41. |
| [45] | 李敏. 双子表面活性剂为模板制备中空二氧化硅纳米球及其载药性能研究. 湖北: 华中科技大学博士学位, 2013. |
| [46] | WU X J, XU D.Soft template synthesis of yolk/silica shell particles.Advanced Materials, 2010, 22(13): 1516-1520. |
| [47] | JAFELICCI JR M, DAVOLOS M R, DOS SANTOS F J,et al. Hollow silica particles from microemulsion. Journal of Non- crystalline Solids, 1999, 247(1): 98-102. |
| [48] | SINGH R K, GARG A, BANDYOPADHYAYA R,et al. Density fractionated hollow silica microspheres with high-yield by non-polymeric Sol-Gel/ emulsion route. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2007, 310(1): 39-45. |
| [49] | TENG Z, HAN Y, LI J,et al. Preparation of hollow mesoporous silica spheres by a Sol-Gel/ emulsion approach. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2010, 127(1): 67-72. |
| [50] | JZHANG C, HOU T, CHEN J,et al. Preparation of mesoporous silica microspheres with multi-hollow cores and their application in sustained drug release. Particuology, 2010, 8(5): 447-452. |
| [51] | CHUL O, CHUNG S, SHIN S,et al. Distribution of macropores in silica particles prepared by using multiple emulsions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2002, 254(1): 79-86. |
| [52] | WU W, XIAO X H, ZHANG S F,et al. One-pot reaction and subsequent annealing to synthesis hollow spherical magnetite and maghemite nanocages. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2009, 4(8): 926-931. |
| [53] | FANG X, ZHAO X, FANG W,et al.Self-templating synthesis of hollow mesoporous silica and their applications in catalysis and drug delivery. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(6): 2205-2218. |
| [54] | WANG Q, LIU Y, YAN H.Mechanism of aself-templatingsynthesis of monodispersed hollow silica nanospheres with tunable size and shell thickness.Chemical Communications, 2007(23): 2339-2341. |
| [55] | BAO Y, YANG Y Q, MA J Z.Research progress of hollow structural materials prepared via templating method.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(5): 459-468. |
| [56] | ZHANG Q, ZHANG T, GE J,et al. Permeable silica shell through surface-protected etching. Nano letters, 2008, 8(9): 2867-2871. |
| [57] | HU J, WANG X, LIU L,et al. A facile and general fabrication method for organic silica hollow spheres and their excellent adsorption properties for heavy metal ions. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(46): 19771-19777. |
| [58] | CHEN D, LI L, TANG F,et al. Facile and scalable synthesis of tailored silica “nanorattle” structures. Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(37): 3804-3807. |
| [59] | CHEN Y, CHEN H R, SHI J L.Construction of homogenous/heterogeneous hollow mesoporous silica nanostructures by silica- etching chemistry: principles, synthesis, and applications.Accounts of Chemical Research, 2013, 47(1): 125-137. |
| [60] | CHEN Y, XU P, CHEN H,et al. Colloidal HPMO nanoparticles: silica-etching chemistry tailoring, topological transformation, and nano-biomedical applications. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(22): 3100-3105. |
| [61] | JI Q, GUO C, YU X,et al. Flake-shell capsules: adjustable inorganic structures. Small, 2012, 8(15): 2345-2349. |
| [62] | TERENTYEVA T G, MATRAS A, VAN ROSSOM W,et al. Bioactive flake-shell capsules: soft silica nanoparticles for efficient enzyme immobilization. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2013, 1(26): 3248-3256. |
| [63] | SLOWING I, VIVERRO E J, WU C,et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as controlled release drug delivery and gene transfection carriers. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2008, 60(11): 1278-1288. |
| [64] | LEE C, CHENG S, HUANG I,et al. Intracellular pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the controlled release of anticancer chemotherapeutics. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 122(44): 8390-8395. |
| [65] | HWANG Y J, OH C, OH S G.Controlled release of retinol from silica particles prepared in O/W/O emulsion: The effects of surfactants and polymers.Journal of Controlled Release, 2005, 106(3): 339-349. |
| [66] | THEISINGER S, SCHOELLER K, OSBORN B,et al. Encapsulation of a fragrance via miniemulsion polymerization for temperature-controlled release. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics, 2009, 210(6): 411-420. |
| [67] | VALLET-REGI M, BALAS F, COLILLA M,et al. bone-regenerative bioceramic implants with drug and protein controlled delivery capability. Progress in Solid State Chemistry, 2008, 36(3): 163-191. |
| [68] | SHE X, CHEN L, VELLEMAN L,et al. Fabrication of high specificity hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles assisted by Eudragit for targeted drug delivery. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2015, 445: 151-160. |
| [69] | LI Z Z, WEN L X, SHAO L,et al. Fabrication of porous hollow silica nanoparticles and their applications in drug release control. Journal of Controlled Release, 2004, 98(2): 245-254. |
| [70] | BOTTERHUIS N E, SUN Q, MAGUSIN P C M M,et al. Hollow silica spheres with an ordered pore structure and their application in controlled release studies. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2006, 12(5): 1448-1456. |
| [71] | CHEN J F, DING H M, WANG J X,et al. Preparation and characterization of porous hollow silica nanoparticles for drug delivery application. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(4): 723-727. |
| [72] | HUDSON S P, PADERERA R F, LANGER R,et al. The biocompatibility of mesoporous silicates. Biomaterials, 2008, 29(30): 4045-4055. |
| [73] | WANG J X, WANG Z H, CHEN J F,et al. Direct encapsulation of water-soluble drug into silica microcapsules for sustained release applications. Materials Research Bulletin, 2008, 43(12): 3374-3381. |
| [74] | LANGER R.Polymer-controlled drug delivery systems.Accounts of Chemical Research, 1993, 26(10): 537-542. |
| [75] | JONES M N.Carbohydrate-mediated liposomal targeting and drug delivery.Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 1994, 13(3): 215-249. |
| [76] | LIU G, ZHU C, XU J,et al. Thermo-responsive hollow silica microgels with controlled drug release properties. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2013, 111(6): 7-14. |
| [77] | CHEN F, ZHU Y.Chitosan enclosed mesoporous silica nanoparticles as drug nano-carriers: sensitive response to the narrow pH range.Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2012, 150(1): 83-89. |
| [78] | XUE M, FINDENEGG G H.Lysozyme as a pH-responsive valve for the controlled release of guest molecules from mesoporous silica.Langmuir, 2012, 28(50): 17578-17584. |
| [79] | YOU Y Z, KALEBAILA K K, BROCK S L.Temperature- controlled uptake and release in PNIPAM-modified porous silica nanoparticles.Chemistry of Materials, 2008, 20(10): 3354-3359. |
| [80] | CHEN L, WANG W, SU B,et al. A light-responsive release platform by controlling the wetting behavior of hydrophobic surface. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(1): 744-751. |
| [81] | CHEN M, HUANG C, HE C,et al. A glucose-responsive controlled release system using glucose oxidase-gated mesoporous silica nanocontainers. Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(76): 9522-9524. |
| [82] | RADHAKRISHNAN K, GUPTA S, GNANADHAS D P,et al. Protamine-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for biologically triggered drug release. Particle & Particle Systems Characterization, 2014, 31(4): 449-458. |
| [83] | ZHANG Z, BALOGH D, WANG F,et al. Biocatalytic release of an anticancer drug from nucleic-acids-capped mesoporous SiO2 Using DNA or molecular biomarkers as triggering stimuli. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(10): 8455-8468. |
| [84] | GUI W Y, WANG W Q, JIAO X Y,et al. pH-response controlled release system based on hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles . Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2015, 45(7): 703-709. |
| [85] | HU J, LIU L, XIE Y,et al. Facile synthesis of thermal-responsive P(NIPAM-S)/SiO2 hybrid hollow spheres and their controllable release properties for fragrance. Polymer Chemistry, 2013, 4(11): 3293-3299. |
| [86] | HU J, CHEN M, TIAN H,et al. Preparation and pyrolysis characteristics of PNIPAM-grafted SiO2 hollow spheres loading vitamin C. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(99): 81134-81141. |
| [87] | ZHU Y, MENG W, GAO H,et al. Hollow mesoporous silica/poly (L-lysine) particles for codelivery of drug and gene with enzyme- triggered release property. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(28): 13630-13636. |
| [1] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | TIAN Ruizhi, LAN Zhengyi, YIN Jie, HAO Nanjing, CHEN Hangrong, MA Ming. Microfluidic Technology Based Synthesis of Inorganic Nano-biomaterials: Principles and Progress [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [8] | ZHANG Jiguo, WU Tian, ZHAO Xu, YANG Fan, XIA Tian, SUN Shien. Improvement of Cycling Stability of Cathode Materials and Industrialization Process for Sodium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [9] | YIN Jie, GENG Jiayi, WANG Kanglong, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Recent Advances in 3D Printing and Densification of SiC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [10] | CHEN Guangchang, DUAN Xiaoming, ZHU Jinrong, GONG Qing, CAI Delong, LI Yuhang, YANG Donglei, CHEN Biao, LI Xinmin, DENG Xudong, YU Jin, LIU Boya, HE Peigang, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. Advanced Ceramic Materials in Helicopter Special Structures: Research Progress and Application Prospect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [11] | FAN Xiaobo, ZU Mei, YANG Xiangfei, SONG Ce, CHEN Chen, WANG Zi, LUO Wenhua, CHENG Haifeng. Research Progress on Proton-regulated Electrochemical Ionic Synapses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [12] | HAIREGU Tuxun, GUO Le, DING Jiayi, ZHOU Jiaqi, ZHANG Xueliang, NUERNISHA Alifu. Research Progress of Optical Bioimaging Technology Assisted by Upconversion Fluorescence Probes in Tumor Imaging [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [13] | SUN Shujuan, ZHENG Nannan, PAN Haokun, MA Meng, CHEN Jun, HUANG Xiubing. Research Progress on Preparation Methods of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [14] | TAO Guilong, ZHI Guowei, LUO Tianyou, OUYANG Peidong, YI Xinyan, LI Guoqiang. Progress on Key Technologies of Cavity-structured Thin Film Bulk Acoustic Wave Filter [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| [15] | ZHOU Fan, TIAN Zhilin, LI Bin. Research Progress on Carbide Ultra-high Temperature Ceramic Anti-ablation Coatings for Thermal Protection System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 1-16. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||