无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 433-339.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240426 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240426
所属专题: 【信息功能】发光材料与器件(202506)
陈梓1( ), 张爱迪1,2(
), 张爱迪1,2( ), 龚克2, 刘海华1, 禹钢3, 单青松4, 刘勇2, 曾海波4(
), 龚克2, 刘海华1, 禹钢3, 单青松4, 刘勇2, 曾海波4( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-08
修回日期:2024-11-15
出版日期:2025-04-20
网络出版日期:2024-12-16
通讯作者:
张爱迪, 高级工程师. E-mail: zhangaidi@bready.cn;作者简介:陈 梓(1985-), 女, 博士. E-mail: chenzi@hyit.edu.cn
CHEN Zi1( ), ZHANG Aidi1,2(
), ZHANG Aidi1,2( ), GONG Ke2, LIU Haihua1, YU Gang3, SHAN Qingsong4, LIU Yong2, ZENG Haibo4(
), GONG Ke2, LIU Haihua1, YU Gang3, SHAN Qingsong4, LIU Yong2, ZENG Haibo4( )
)
Received:2024-10-08
Revised:2024-11-15
Published:2025-04-20
Online:2024-12-16
Contact:
ZHANG Aidi, senior engineer. E-mail: zhangaidi@bready.cn;About author:CHEN Zi (1985-), female, PhD. E-mail: chenzi@hyit.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
作为环境友好型发光量子点(QDs)的重要替代材料, CuInS基核/壳量子点近年来受到越来越多的关注。然而, 这类量子点的一些缺点仍然阻碍了它们的工业化应用, 比如较低的光致发光量子产率(PLQY)、复杂的合成途径、发射光谱易失去控制、光稳定性不足等。本研究通过一锅/三步法合成策略成功制备了CuInZnS@ZnS核/壳量子点, 并精确调控其荧光发射光谱, 然后系统研究了CuInZnS@ZnS量子点在晶核形成、合金化和ZnS壳层生长过程中的集合体光谱特性。通过控制Cu/In元素的化学计量比、Zn2+掺杂以及ZnS壳层生长, 实现了量子点荧光发射峰在530~850 nm范围内的精准调控。CuInZnS@ZnS量子点具有明显的长荧光发射寿命(长达750 ns)、高PLQY(高达85%)和优异的结晶度。基于Cu缺陷相关的分子内定域能级发射模型阐释了集合体光谱演变规律。通过控制Cu/In元素的化学计量比, 并且基于Cu缺陷的不同氧化态, 提出了两种不同的Cu缺陷相关发射途径。本工作为制备高荧光效率的三元或四元合金量子点提供了更深入的见解。
中图分类号:
陈梓, 张爱迪, 龚克, 刘海华, 禹钢, 单青松, 刘勇, 曾海波. 具有可调谐和长寿命荧光发射的高亮度、单分散四元CuInZnS@ZnS量子点[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 433-339.
CHEN Zi, ZHANG Aidi, GONG Ke, LIU Haihua, YU Gang, SHAN Qingsong, LIU Yong, ZENG Haibo. High-brightness and Monodisperse Quaternary CuInZnS@ZnS Quantum Dots with Tunable and Long-lived Emission[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 433-339.
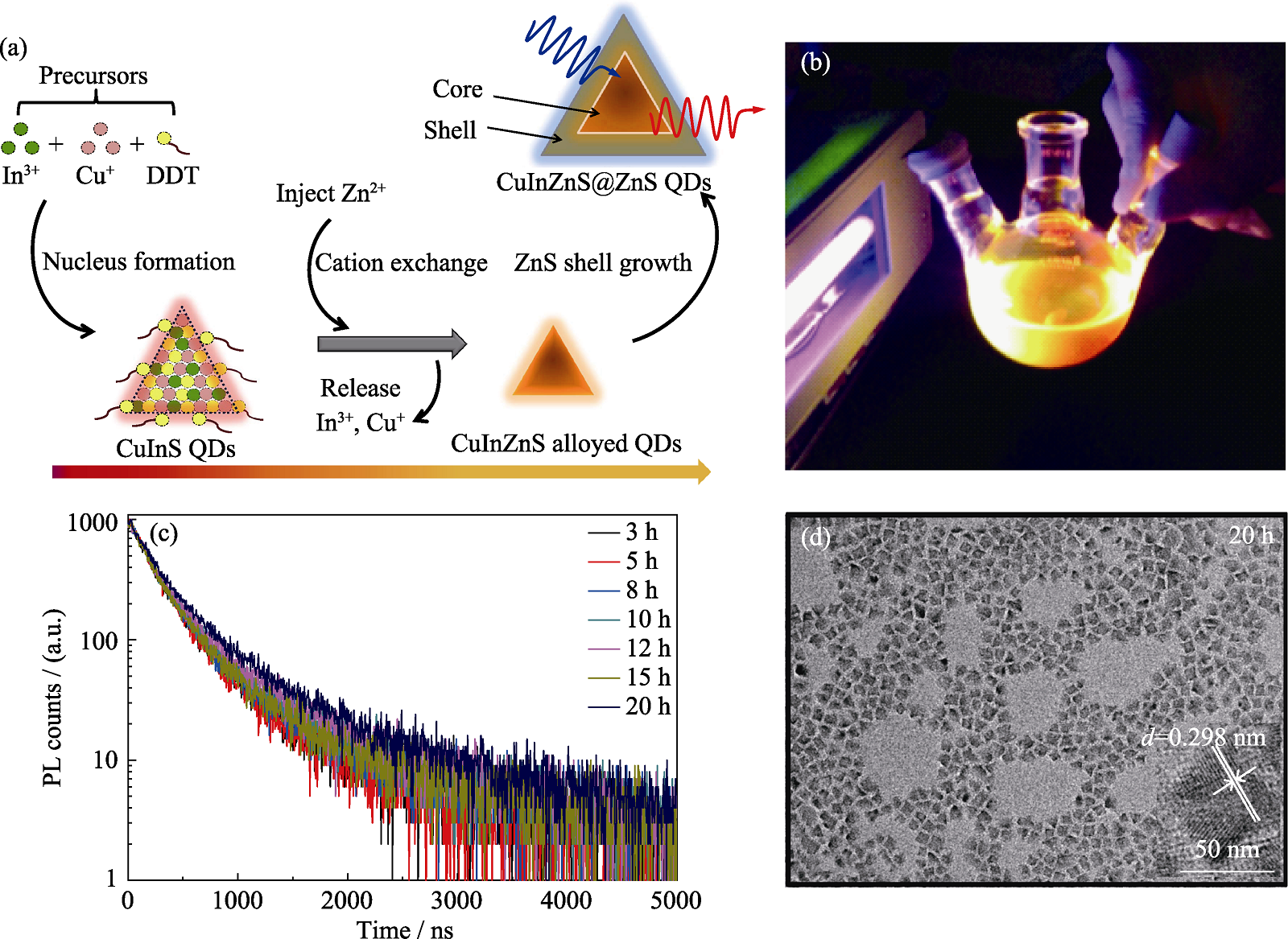
Fig. 1 Optical and morphology characterization of the CuInS-based QDs (a) Synthetic route of the CuInS-based QDs; (b) Photograph of the CuInZnS@ZnS QDs with shell growth of 20 h (Cu : In : Zn is 1 : 2 : 3) under 365 nm showing brilliant luminescence; (c) Transient PL decays of the CuInZnS@ZnS QDs with different shell growth time (Cu : In : Zn is 1 : 2 : 3); (d) TEM images of the CuInZnS/ZnS QDs (Cu : In : Zn is 1 : 2 : 3) with shell growth of 20 h. Colorful figures are available on website
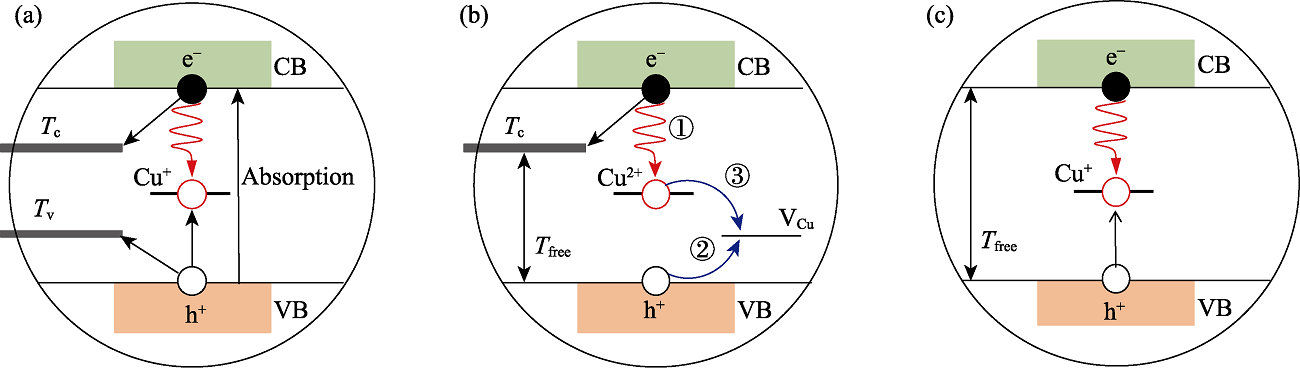
Fig. 2 Schematic depictions of relaxation processes in stoichiometric CuInS QDs (a), Cu-deficient CuInS QDs (b), and Cu-deficient CuInZnS@ZnS core/shell QDs (c) (a) Photon absorption is mainly due to the VB to CB transition. For the CuInS QDs with Cu/In ratio close to stoichiometric, the PL emission was due to radiative recombination of the CB electron with the hole existing in the intragap Cu+ state. (b) For the Cu-deficient CuInS QDs, there are three main processes. Process ①: a hole existing in the ground state forms Cu2+ defect, and it can directly recombine with the CB electron. Process ②: the recombination process was slow with the lifetime lasting hundreds of nanoseconds. To dominate the PL emission, another Cu vacancy trap (noted as VCu) quickly captured the photogenerated hole from the VB state, and formed a charge-compensated pair with the Cu2+ defect. Process ③: the trapped hole at VCu center radiatively recombined with the electron and finished the whole recombination process. (c) For the Cu-deficient core/shell QDs, the diffusion of Zn2+ ions occupied and decreased the VCu intragap states, and the thick ZnS shell eliminated the electron trap bands associated with the CB. The recombination of hot electron at CB edge and hole located at the intragap state (Cu+) dominated the PL decay process.
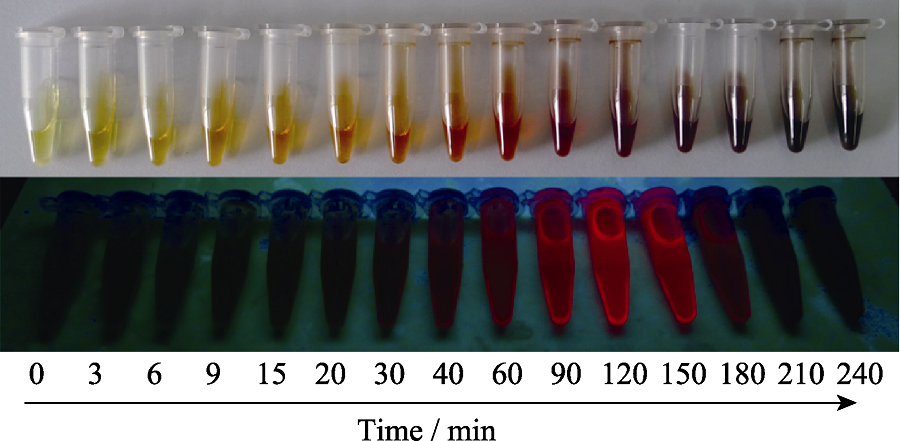
Fig. S2 Digital photographs of CuInS QDs in a typical nucleation growth process under daylight lamp and UV lamp (365 nm) DDT was chosen as the sulfur source, surface ligand, and solvent. The reaction temperature was 200 ℃
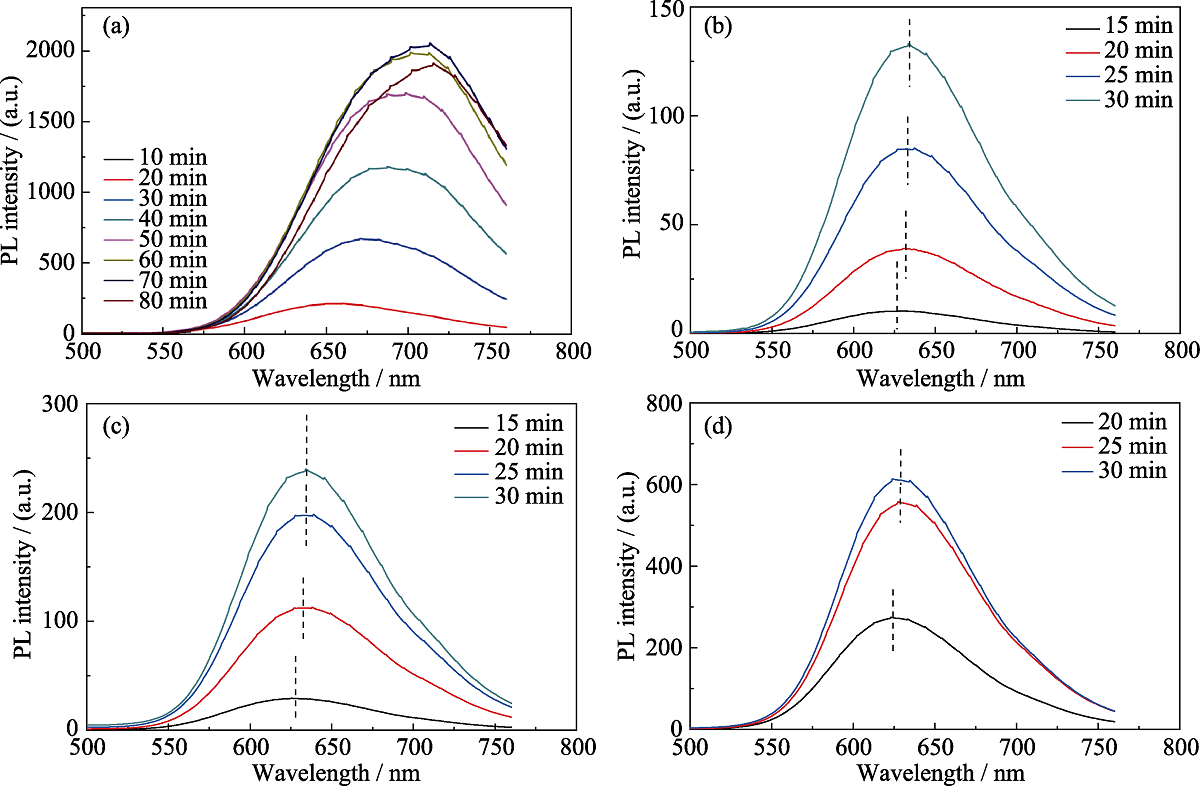
Fig. S4 Temporal evolution of PL emission spectra of CuInS QDs synthesized with different molar stoichiometric ratios of Cu : In precursors (a-d) stand for 1 : 1, 1 : 2, 1 : 4, and 1 : 6. DDT was chosen as the sulfur source. The aliquots of QDs samples for the PL intensity test were fixed. PL spectra were recorded with excitation at 450 nm
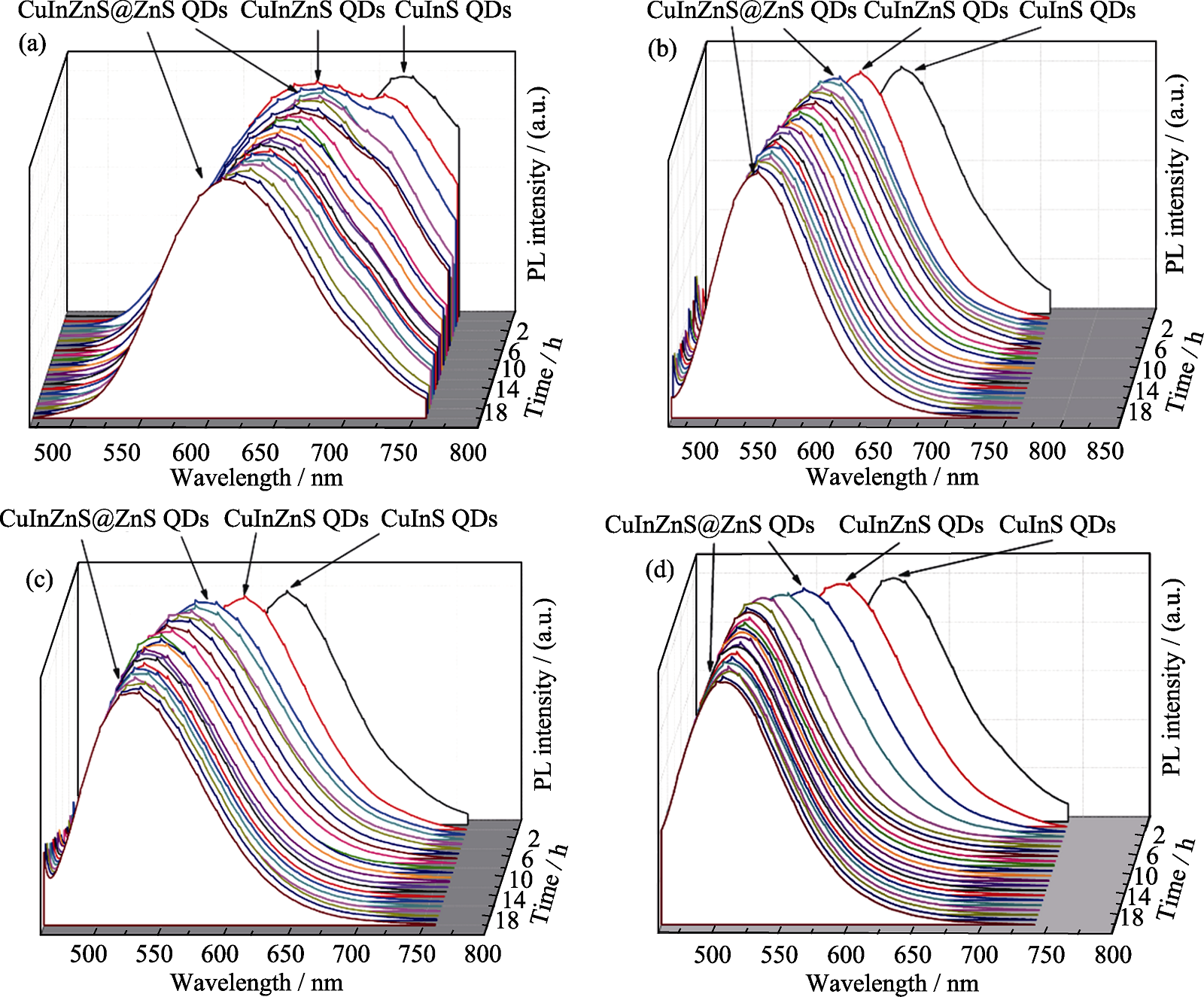
Fig. S5 Temporal evolution of PL spectra of CuInS QDs, CuInZnS QDs, and CuInZnS@ZnS QDs with different growth time (a-d) stand for the stoichiometric ratio of Cu : In at 1 : 1, 1 : 2, 1 : 4, and 1 : 6. PL spectra were recorded with excitation at 450 nm
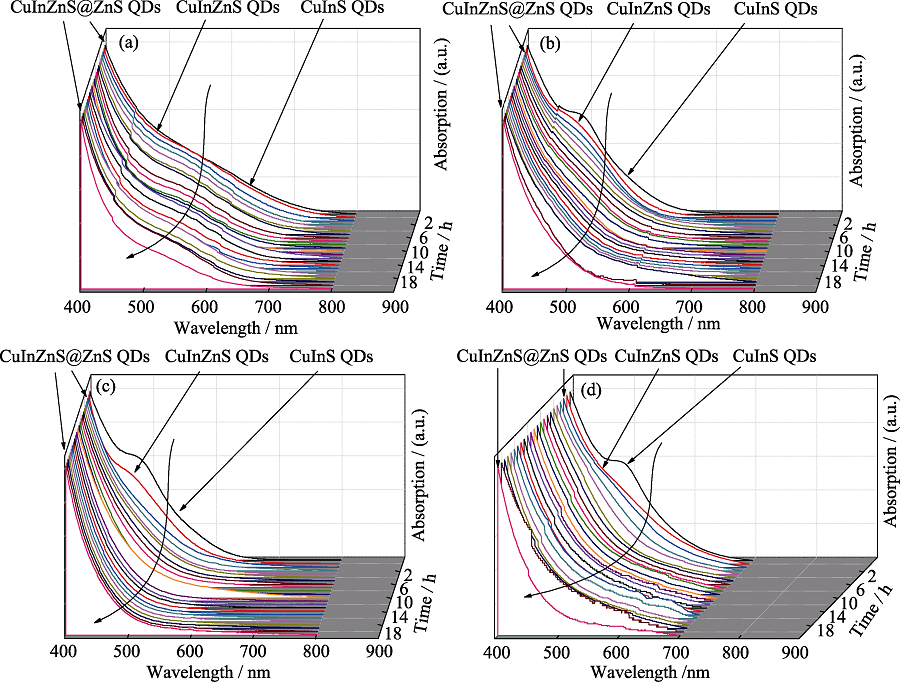
Fig. S6 Temporal evolution of UV-Vis absorption spectra of CuInS QDs, CuInZnS QDs, CuInZnS@ZnS QDs synthesized with different molar stoichiometric ratios of Cu : In precursors (a-d) stand for the stoichiometric ratio of Cu : In at 1 : 1, 1 : 2, 1 : 4, and 1 : 6. The absorption shoulder/onset is more blue-shifted with less Cu/In ratio
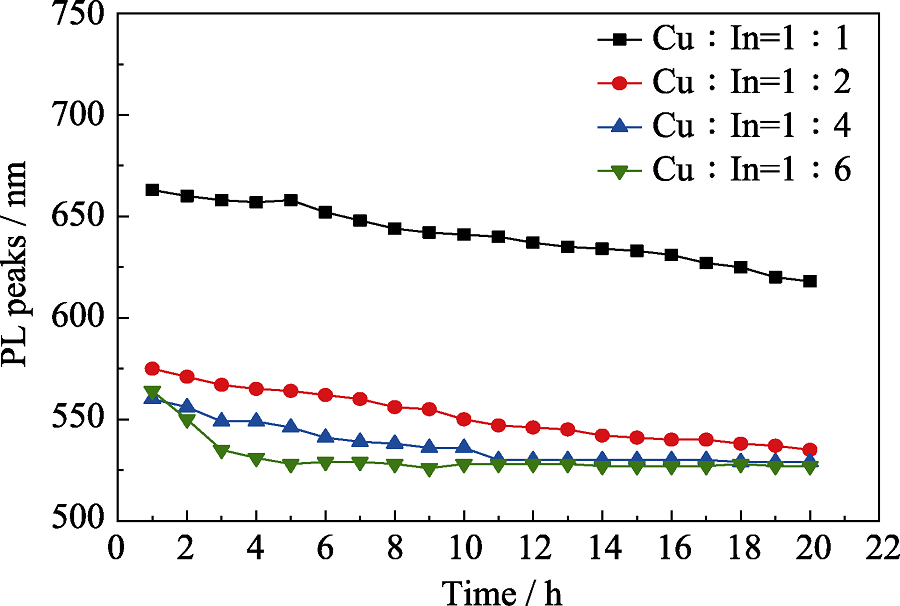
Fig. S7 Temporal evolution of PL central emission peaks for CuInZnS@ZnS QDs with different shell growth time The stoichiometric ratios of Cu : In are 1 : 1, 1 : 2, 1 : 4, and 1 : 6
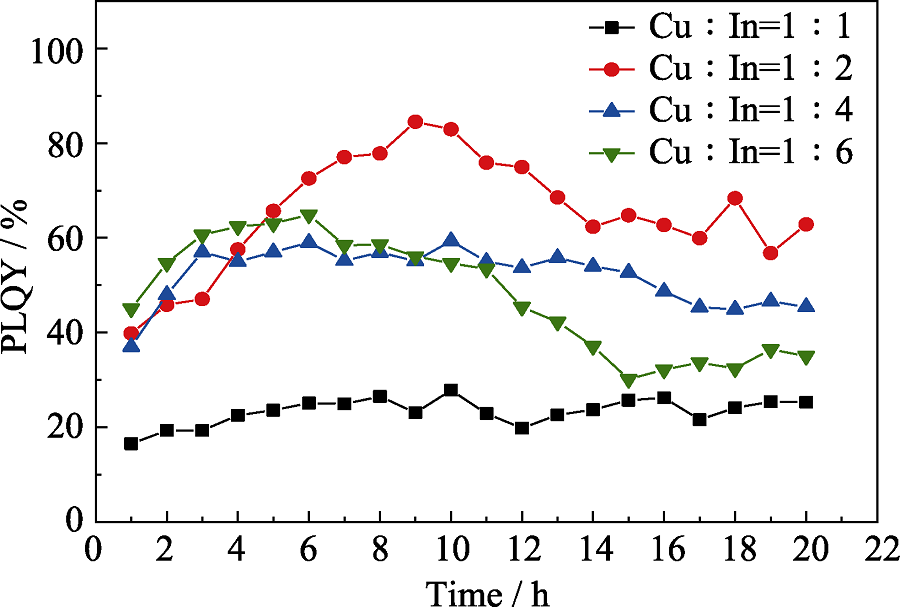
Fig. S8 Temporal evolution of PLQY for CuInZnS@ZnS QDs with different shell growth time The stoichiometric ratios of Cu : In are 1 : 1, 1 : 2, 1 : 4, and 1 : 6
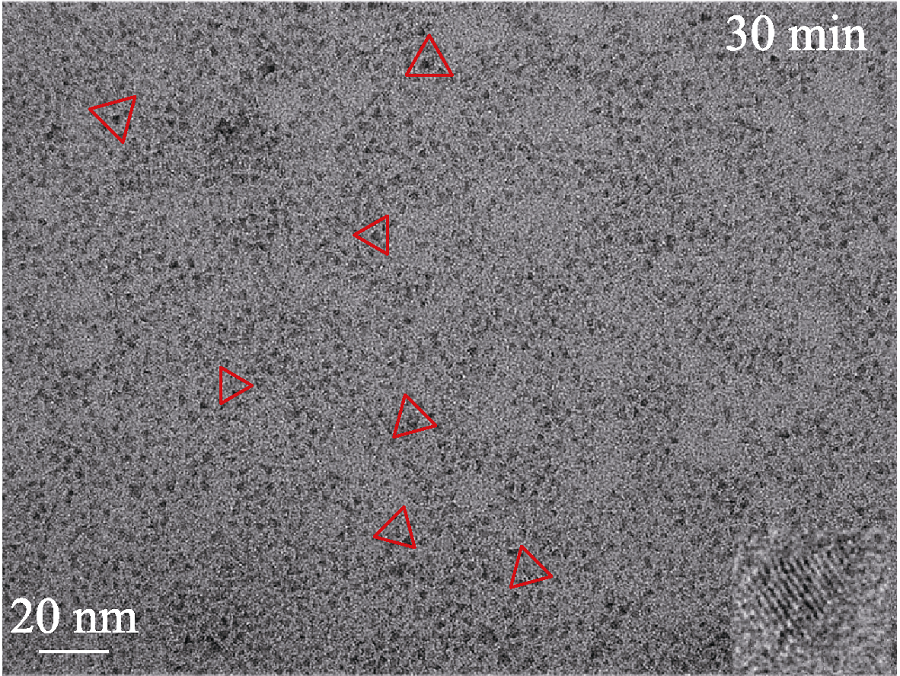
Fig. S11 TEM image of CuInS QDs (the stoichiometric ratio of Cu : In at 1 : 2) with reaction time of 30 min The red triangle frames indicate the shapes of the CuInS QDs
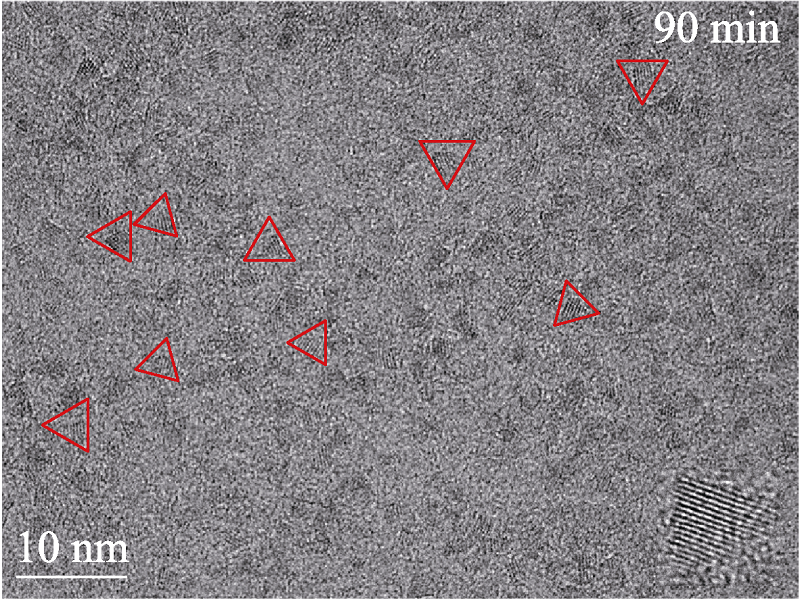
Fig. S12 TEM image of CuInZnS QDs (the stoichiometric ratio of Cu : In : Zn at 1 : 2 : 3) with Zn etching time of 90 min The red triangle frames indicate the shapes of the CuInZnS QDs
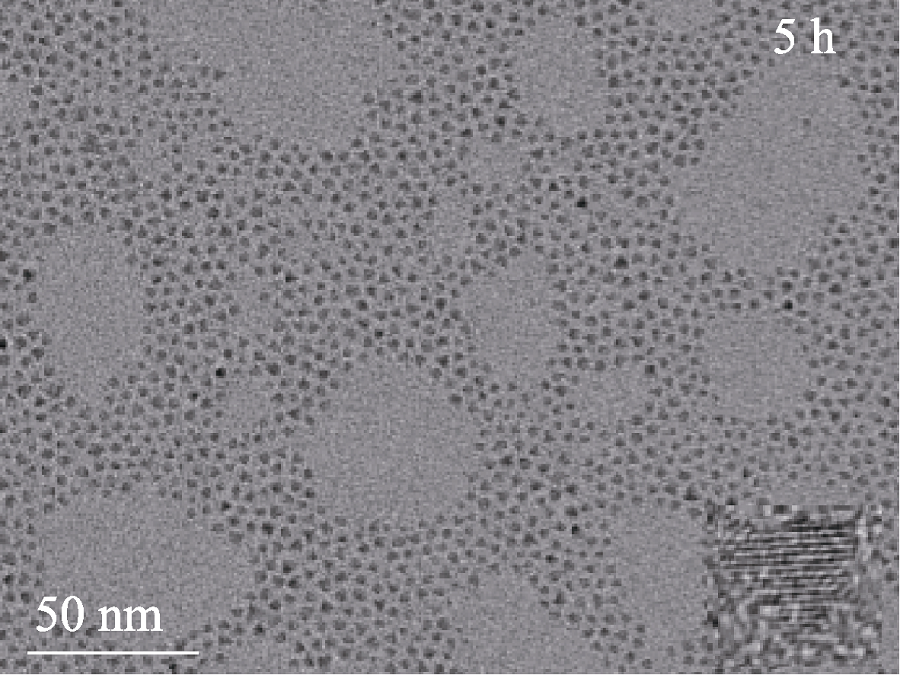
Fig. S13 TEM images of CuInZnS@ZnS QDs (the stoichioetric ratio of Cu : In : Zn at 1 : 2 : 3) with ZnS shell growth time of 5 h The insert showing their representative high- esolution TEM images
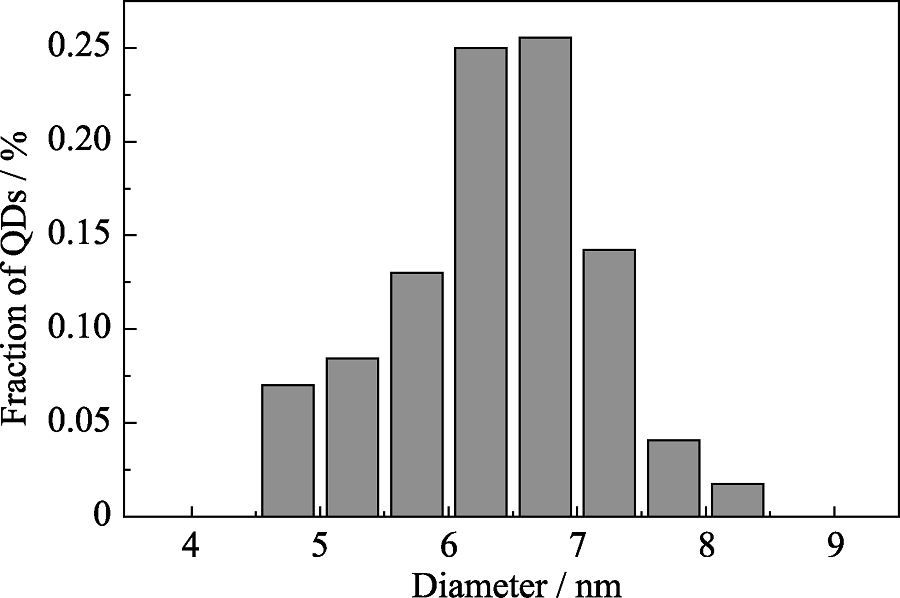
Fig. S14 Size distribution histograms for CuInZnS/ZnS QDs (Cu : In : Zn at 1 : 2 : 3) with shell growth of 20 h To build the histograms, over 100 particles were measured
| Cu : In precursor | λem/nm | PLQY/% | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 : 1 | 710 | 3.3 | 264 (65) |
| 1 : 2 | 633 | 8.8 | 270 (71) |
| 1 : 4 | 625 | 18.9 | 293 (86) |
| 1 : 6 | 618 | 21.0 | 299 (95) |
Table S1 Relevant parameters for CuInS QDs synthesized with different molar stoichiometric ratios of Cu : In. λem at the PL central emission peak from the QDs solution when excited at 450 nm. The amounts of DDT (10 mL) and CuI (0.1 mmol) were held fixed
| Cu : In precursor | λem/nm | PLQY/% | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 : 1 | 710 | 3.3 | 264 (65) |
| 1 : 2 | 633 | 8.8 | 270 (71) |
| 1 : 4 | 625 | 18.9 | 293 (86) |
| 1 : 6 | 618 | 21.0 | 299 (95) |
| Cu : In precursor | λem/nm | PLQY/% | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 : 1 | 675 | 14.7 | 277 (102) |
| 1 : 2 | 596 | 16.8 | 284 (101) |
| 1 : 4 | 590 | 24.8 | 284 (110) |
| 1 : 6 | 581 | 36.3 | 282 (112) |
Table S2 Relevant parameters for CuInZnS alloyed QDs synthesized with differnt molar stoichiometric ratios of Cu : In. λem is the PL central emission peak from the QDs solution when excited at 450 nm. The amounts of DDT (10 mL) and CuI (0.1 mmol) were held fixed
| Cu : In precursor | λem/nm | PLQY/% | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 : 1 | 675 | 14.7 | 277 (102) |
| 1 : 2 | 596 | 16.8 | 284 (101) |
| 1 : 4 | 590 | 24.8 | 284 (110) |
| 1 : 6 | 581 | 36.3 | 282 (112) |
| Shell reaction time/h | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|
| 3 | 588 (204) |
| 5 | 647 (208) |
| 8 | 714 (214) |
| 10 | 724 (211) |
| 12 | 729 (219) |
| 15 | 751 (222) |
| 20 | 755 (231) |
Table S3 PL lifetime of CuInZnS@ZnS QDs with the stoichiometric ratio of Cu : In at 1 : 2 after excited at 450 nm.
| Shell reaction time/h | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|
| 3 | 588 (204) |
| 5 | 647 (208) |
| 8 | 714 (214) |
| 10 | 724 (211) |
| 12 | 729 (219) |
| 15 | 751 (222) |
| 20 | 755 (231) |
| Shell reaction time/h | PL emission peak/nm | PLQY/% | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 546 | 57 | 509 (171) |
| 10 | 536 | 50 | 530 (177) |
| 15 | 531 | 53 | 558 (174) |
| 20 | 530 | 58 | 549 (165) |
Table S4 Relevant parameters for CuInZnS@ZnS QDs with the stoichiometric ratio of Cu : In at 1 : 4, synthesized with different ZnS shell growth time. λem is the PL central emission peak from the QDs solution when excited at 450 nm. The amounts of DDT (10 mL) and CuI (0.1 mmol) were held fixed.
| Shell reaction time/h | PL emission peak/nm | PLQY/% | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 546 | 57 | 509 (171) |
| 10 | 536 | 50 | 530 (177) |
| 15 | 531 | 53 | 558 (174) |
| 20 | 530 | 58 | 549 (165) |
| [1] | JAISWAL J K, MATTOUSSI H, MAURO J M, et al. Long-term multiple color imaging of live cells using quantum dot bioconjugates. Nature Biotechnology, 2002, 21: 47. |
| [2] |
CHAN W C, NIE S. Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science, 1998, 281(5385): 2016.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | ZHANG Y, LV Y, LI L S, et al. Aminophosphate precursors for the synthesis of near-unity emitting InP quantum dots and their application in liver cancer diagnosis. Exploration, 2022, 2(4):20220082. |
| [4] | WU R, WANG T, WU M, et al. Synthesis of highly stable CuInZnS/ZnS//ZnS quantum dots with thick shell and its application to quantitative immunoassay. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 348: 447. |
| [5] | MEINARDI F, COLOMBO A, VELIZHANIN K A, et al. Large- area luminescent solar concentrators based on ‘Stokes-shift- engineered’ nanocrystals in a mass-polymerized PMMA matrix. Nature Photonics, 2014, 8(5):392. |
| [6] | DONG H, RAN C, GAO W, et al. Metal halide perovskite for next-generation optoelectronics: progresses and prospects. eLight, 2023, 3: 3. |
| [7] | YUAN M, LIU M, SARGENT E H. Colloidal quantum dot solids for solution-processed solar cells. Nature Energy, 2016, 1(3):16016. |
| [8] | SARGENT E H. Colloidal quantum dot solar cells. Nature Photonics, 2012, 6(3):133. |
| [9] | CAO W, ZHANG W, DONG L, et al. Progress on quantum dot photocatalysts for biomass valorization. Exploration, 2023, 3(6):20220169. |
| [10] | DAI X, ZHANG Z, JIN Y, et al. Solution-processed, high- performance light-emitting diodes based on quantum dots. Nature, 2014, 515(7525):96. |
| [11] | SUN Q, WANG Y A, LI L S, et al. Bright, multicoloured light- emitting diodes based on quantum dots. Nature Photonics, 2007, 1(12):717. |
| [12] | DONG C, LIU H, ZHANG A, et al. Controllable blinking-to- nonblinking behavior of aqueous CdTeS alloyed quantum dots. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2014, 20(7): 1940. |
| [13] | ZHANG A, DONG C, LIU H, et al. Blinking behavior of CdSe/CdS quantum dots controlled by alkylthiols as surface trap modifiers. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(46):24592. |
| [14] |
MCDONALD S A, KONSTANTATOS G, ZHANG S, et al. Solution-processed PbS quantum dot infrared photodetectors and photovoltaics. Nature Materials, 2005, 4(2):138.
PMID |
| [15] | HUANG P, SUN S, LEI H, et al. Nonlocal interaction enhanced biexciton emission in large CsPbBr3 nanocrystals. eLight, 2023, 3: 10. |
| [16] | LIAN W, TU D, WENG X, et al. Near-Infrared nanophosphors based on CuInSe2 quantum dots with near-unity photoluminescence quantum yield for micro-LEDs applications. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(9):2311011. |
| [17] | DE TRIZIO L, PRATO M, GENOVESE A, et al. Strongly fluorescent quaternary Cu-In-Zn-S nanocrystals prepared from Cu1-xInS2 nanocrystals by partial cation exchange. Chemistry of Materials, 2012, 24(12):2400. |
| [18] | LI L, DAOU T J, TEXIER I, et al. Highly luminescent CuInS2/ ZnS core/shell nanocrystals: cadmium-free quantum dots for in vivo imaging. Chemistry of Materials, 2009, 21(12):2422. |
| [19] | ZHONG H, ZHOU Y, YE M, et al. Controlled synthesis and optical properties of colloidal ternary chalcogenide CuInS2 nanocrystals. Chemistry of Materials, 2008, 20(20):6434. |
| [20] | MCDANIEL H, FUKE N, PIETRYGA J M, et al. Engineered CuInSexS2-x quantum dots for sensitized solar cells. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2013, 4(3):355. |
| [21] |
LI L, PANDEY A, WERDER D J, et al. Efficient synthesis of highly luminescent copper indium sulfide-based core/shell nanocrystals with surprisingly long-lived emission. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(5):1176.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | ZHONG H, LO S S, MIRKOVIC T, et al. Noninjection gram-scale synthesis of monodisperse pyramidal CuInS2 nanocrystals and their size-dependent properties. ACS Nano, 2010, 4(9):5253.<br |
| [23] |
XIE R, RUTHERFORD M, PENG X. Formation of high-quality I-III-VI semiconductor nanocrystals by tuning relative reactivity of cationic precursors. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(15):5691.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | CHUANG P H, LIN C C, LIU R S. Emission-tunable CuInS2/ZnS quantum dots: structure, optical properties, and application in white light-emitting diodes with high color rendering index. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(17):15379. |
| [25] | ZHANG A, DONG C, LI L, et al. Non-blinking (Zn)CuInS/ZnS quantum dots prepared by in situ interfacial alloying approach. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1):15227. |
| [26] | THUY U T D, REISS P, LIEM N Q. Luminescence properties of In(Zn)P alloy core/ZnS shell quantum dots. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 97(19):193104. |
| [27] | KIM Y K, AHN S H, CHUNG K, et al. The photoluminescence of CuInS2 nanocrystals: effect of non-stoichiometry and surface modification. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(4):1516. |
| [28] | PARK J, KIM S W. CuInS2/ZnS core/shell quantum dots by cation exchange and their blue-shifted photoluminescence. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(11):3745. |
| [29] | BOLDT K, KIRKWOOD N, BEANE G A, et al. Synthesis of highly luminescent and photo-stable, graded shell CdSe/CdxZn1-xS nanoparticles by in situ alloying. Chemistry of Materials, 2013, 25(23):4731. |
| [30] |
CHEN Y, LI S, HUANG L, et al. Green and facile synthesis of water-soluble Cu-In-S/ZnS core/shell quantum dots. Inorganic Chemistry, 2013, 52(14):7819.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
MAHLER B, SPINICELLI P, BUIL S, et al. Towards non-blinking colloidal quantum dots. Nature Materials, 2008, 7(8):659.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | SPERANSKAYA E S, BELOGLAZOVA N V, ABE S, et al. Hydrophilic, bright CuInS2 quantum dots as Cd-free fluorescent labels in quantitative immunoassay. Langmuir, 2014, 30(25):7567. |
| [33] | NAM D E, SONG W S, YANG H. Noninjection, one-pot synthesis of Cu-deficient CuInS2/ZnS core/shell quantum dots and their fluorescent properties. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2011, 361(2):491. |
| [34] | CHOI H S, KIM Y, PARK J C, et al. Highly luminescent, off-stoichiometric CuxInyS2/ZnS quantum dots for near-infrared fluorescence bio-imaging. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(54):43449. |
| [35] | PORTNIAGIN A S, NING J, WANG S, et al. Monodisperse CuInS2/CdS and CuInZnS2/CdS core-shell nanorods with a strong near-infrared emission. Advanced Optical Materials, 2022, 10(8):2102590. |
| [36] | LI J J, WANG Y A, GUO W, et al. Large-scale synthesis of nearly monodisperse CdSe/CdS core/shell nanocrystals using air-stable reagents via successive ion layer adsorption and reaction. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(41):12567. |
| [37] |
PENG Z A, PENG X. Formation of high-quality CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals using CdO as precursor. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2001, 123(1):183.
PMID |
| [38] | FUHR A S, YUN H J, MAKAROV N S, et al. Light emission mechanisms in CuInS2 quantum dots evaluated by spectral electrochemistry. ACS Photonics, 2017, 4(10):2425. |
| [39] | GONG K, KELLEY D F. Lattice strain limit for uniform shell deposition in zincblende CdSe/CdS quantum dots. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2015, 6(9):1559. |
| [40] | GONG K, BEANE G, KELLEY D F. Strain release in metastable CdSe/CdS quantum dots. Chemical Physics, 2016, 471: 18. |
| [41] | GONG K, KELLEY D F. A predictive model of shell morphology in CdSe/CdS core/shell quantum dots. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2014, 141(19):194704. |
| [1] | 吴华鑫, 张骐昊, YAN Haixue, 王连军, 江莞. 纳米复合MgAgSb基合金的热电输运性能优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 997-1004. |
| [2] | 信震宇, 郭瑞华, 乌仁托亚, 王艳, 安胜利, 张国芳, 关丽丽. Pt-Fe/GO纳米催化剂的制备及其电催化乙醇氧化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 379-387. |
| [3] | 郑元顺, 余健, 叶先峰, 梁栋, 朱婉婷, 聂晓蕾, 魏平, 赵文俞, 张清杰. V取代Al位提升全赫斯勒合金Fe2VAl的热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1425-1432. |
| [4] | 任先培, 李超, 凌芳, 胡启威, 于俊玲, 向晖, 彭跃红. 炭黑表面CoMoSSe异质结构合金的制备及其高效析氢研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1293-1299. |
| [5] | 张宇婷, 李晓斌, 刘尊义, 李宁, 赵鹬. 复合蛋黄壳型NiCo2V2O8@TiO2@NC材料用作锂离子电池负极研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1221-1228. |
| [6] | 胡学敏, 张行健, 蒋志豪, 黄丽雯, 丁开宁, 张胜利. 氧修饰的CoPS3量子点边缘态析氧活性的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1229-1236. |
| [7] | 吕昕怿, 相恒阳, 曾海波. 长程有序助力钙钛矿QLED高性能化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 111-112. |
| [8] | 杨恩东, 李宝乐, 张珂, 谭鲁, 娄永兵. ZnCo2O4-ZnO@C@CoS核壳复合材料的制备及其在超级电容器中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 485-493. |
| [9] | 张婷婷, 王方园, 刘长友, 张国荣, 吕佳辉, 宋宇晨, 介万奇. 水热-烧结法制备Cr2+:ZnSe/ZnSe核壳结构纳米孪晶[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 409-415. |
| [10] | 岳仔豪, 杨小兔, 张正亮, 邓瑞翔, 张涛, 宋力昕. Pb2+对掺杂硼硅酸盐玻璃中CsPbBr3钙钛矿量子点发光性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 449-456. |
| [11] | 陈浩, 樊文浩, 安德成, 陈少平. 能带优化和载流子调控改善SnTe的热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 306-312. |
| [12] | 岳全鑫, 郭瑞华, 王瑞芬, 安胜利, 张国芳, 关丽丽. 3D核壳结构NiMoO4@CoFe-LDH纳米棒的高效析氧及全解水性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1254-1264. |
| [13] | 孟雨婷, 王雪梅, 章淑娴, 陈志炜, 裴艳中. Bi2Te3基热电材料的单带和双带传输特性转变[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1283-1291. |
| [14] | 孙强强, 陈子璇, 杨子玥, 王毅梦, 曹宝月. 金属镍铜负载钒氧化物的高效电解产氢性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 647-655. |
| [15] | 吴锐, 张敏慧, 金成韵, 林健, 王德平. 光热核壳TiN@硼硅酸盐生物玻璃纳米颗粒的降解和矿化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 708-716. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||