无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 379-387.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240402 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240402
所属专题: 【能源环境】燃料电池(202506)
信震宇1,2,3( ), 郭瑞华1,2,3(
), 郭瑞华1,2,3( ), 乌仁托亚1,2,3, 王艳4, 安胜利1,2,3, 张国芳1, 关丽丽1,2
), 乌仁托亚1,2,3, 王艳4, 安胜利1,2,3, 张国芳1, 关丽丽1,2
收稿日期:2024-09-09
修回日期:2024-11-29
出版日期:2025-04-20
网络出版日期:2024-12-12
通讯作者:
郭瑞华, 教授. E-mail: grh7810@163.com作者简介:信震宇(1998-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 2670680269@qq.com
基金资助:
XIN Zhenyu1,2,3( ), GUO Ruihua1,2,3(
), GUO Ruihua1,2,3( ), WUREN Tuoya1,2,3, WANG Yan4, AN Shengli1,2,3, ZHANG Guofang1, GUAN Lili1,2
), WUREN Tuoya1,2,3, WANG Yan4, AN Shengli1,2,3, ZHANG Guofang1, GUAN Lili1,2
Received:2024-09-09
Revised:2024-11-29
Published:2025-04-20
Online:2024-12-12
Contact:
GUO Ruihua, professor. E-mail: grh7810@163.comAbout author:XIN Zhenyu (1998-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 2670680269@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
直接乙醇燃料电池(DEFC)因其能量转换效率高、噪声低以及友好环境而受到广泛关注。然而, 这类电池仍面临催化剂成本高、稳定性差及催化活性低等问题。本研究选用氧化石墨烯(GO)作为载体, 以乙二醇为还原剂, 六水合氯铂酸为前驱体, 并引入非贵金属Fe, 通过调节Pt与Fe的摩尔比, 利用微波加热合成法制备出二元合金催化剂PtFex/GO(x=1/6、1/5、1/4、1/3、1/2、1), 在GO载体上原位负载纳米晶粒。原子半径小的Fe固溶到Pt晶格中, 导致Pt晶格的相邻原子间距缩小, 晶格收缩, 从而形成Pt-Fe合金。当x=1/3时, 催化剂表现出最优的催化活性, 其电催化活性面积为69.84 m2/g, 氧化峰值电流密度为858.42 A/g, 并且Tafel斜率较小。1100 s的计时电流测试下, PtFe1/3/GO催化剂的稳态电流密度为194.80 A/g, CO的氧化峰电位为0.554 V, 活化能为18.37 kJ/mol, 800圈测试后电流密度保持率为80.48%, 优于商业Pt/C(JM)催化剂。研究表明, 引入非贵金属Fe能够显著提升Pt基催化剂的催化活性和稳定性, 为Pt基催化剂材料的设计与潜在应用提供了重要的理论依据。
中图分类号:
信震宇, 郭瑞华, 乌仁托亚, 王艳, 安胜利, 张国芳, 关丽丽. Pt-Fe/GO纳米催化剂的制备及其电催化乙醇氧化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 379-387.
XIN Zhenyu, GUO Ruihua, WUREN Tuoya, WANG Yan, AN Shengli, ZHANG Guofang, GUAN Lili. Pt-Fe/GO Nanocatalysts: Preparation and Electrocatalytic Performance on Ethanol Oxidation[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 379-387.
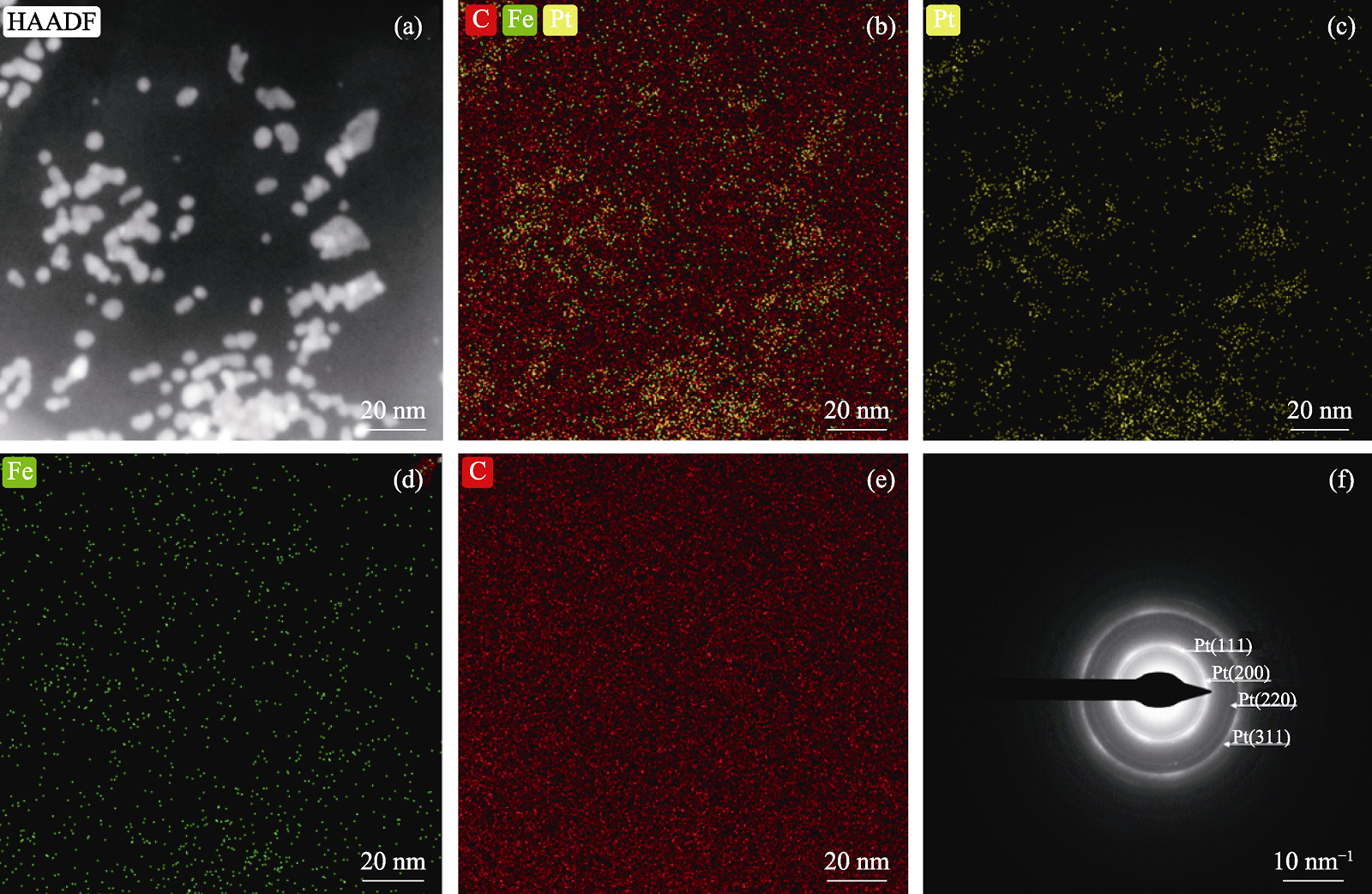
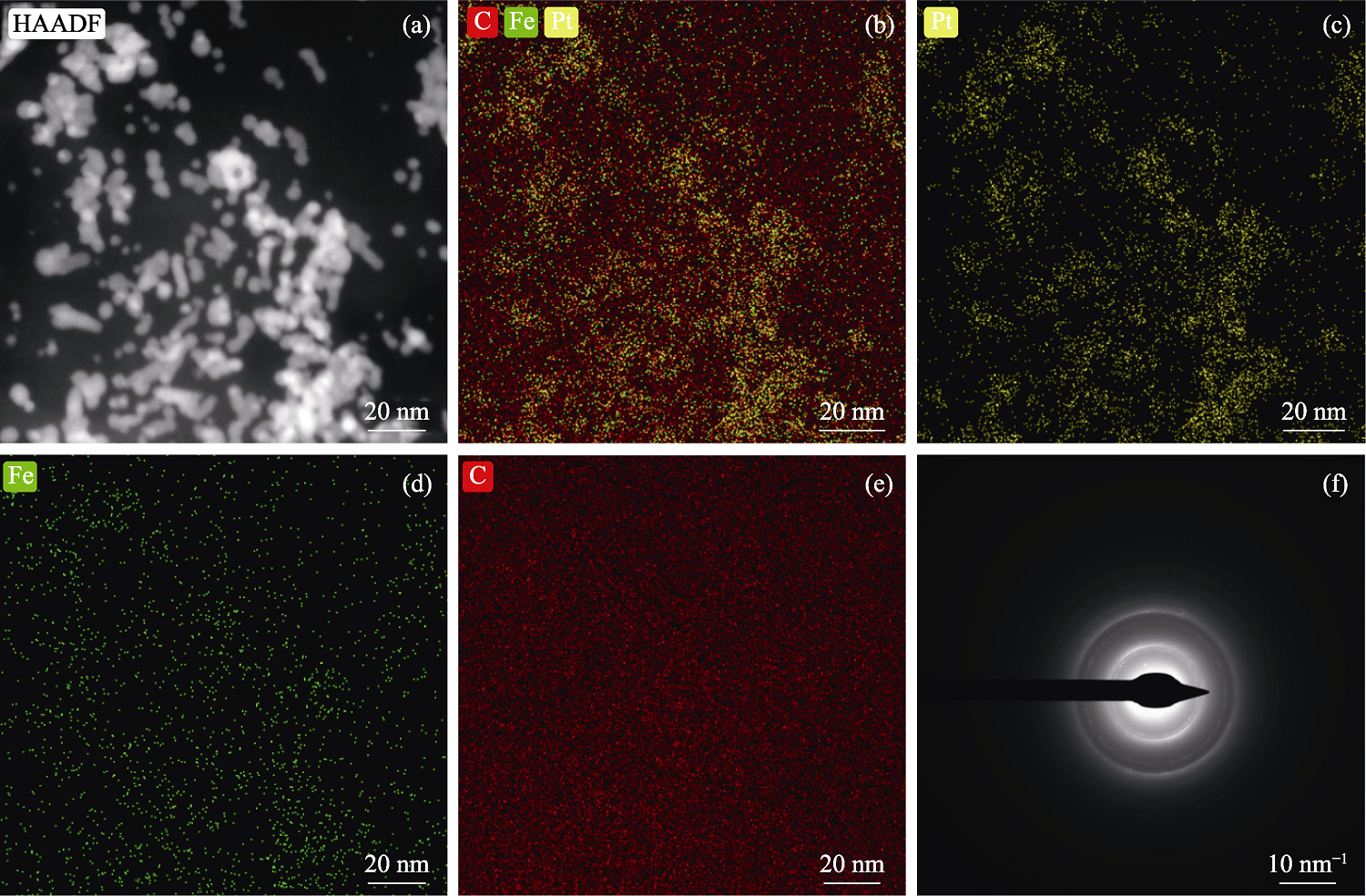
图2 PtFe1/3/GO催化剂的(a)面扫TEM照片、(b~e) EDS元素图和(f) SAED图案
Fig. 2 (a) Surface scaning TEM image, (b-e) EDS elemental mappings and (f) SAED pattern of PtFe1/3/GO catalyst
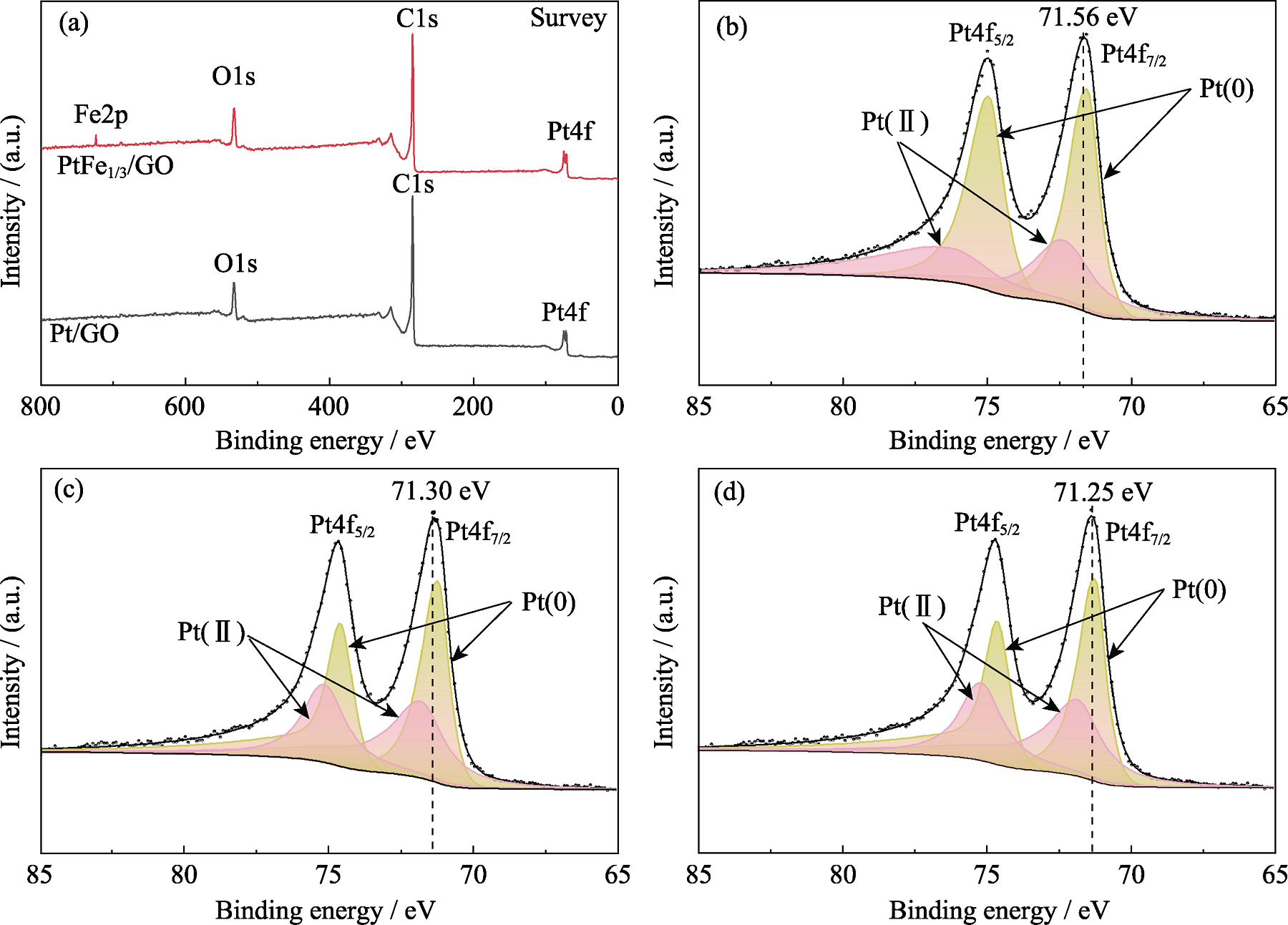
图3 催化剂的XPS图谱
Fig. 3 XPS spectra of catalysts (a) Survey spectra of Pt/GO and PtFe1/3/GO; (b-d) Pt4f spectra of (b) Pt/C(JM), (c) Pt/GO, and (d) PtFe1/3/GO
| Catalyst | Pt(0)/eV | Relative ratio/% | Pt(II)/eV | Relative ratio/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt/C(JM) | 71.56, 74.94 | 61.22 | 72.39, 76.28 | 38.78 |
| Pt/GO | 71.30, 74.77 | 56.10 | 71.97, 76.50 | 43.89 |
| PtFe1/3/GO | 71.25, 74.63 | 57.41 | 71.87, 75.17 | 42.59 |
表1 催化剂的Pt(0)和Pt(II)含量拟合结果
Table 1 Fitting results of Pt(0) and Pt(II) contents in catalysts
| Catalyst | Pt(0)/eV | Relative ratio/% | Pt(II)/eV | Relative ratio/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt/C(JM) | 71.56, 74.94 | 61.22 | 72.39, 76.28 | 38.78 |
| Pt/GO | 71.30, 74.77 | 56.10 | 71.97, 76.50 | 43.89 |
| PtFe1/3/GO | 71.25, 74.63 | 57.41 | 71.87, 75.17 | 42.59 |
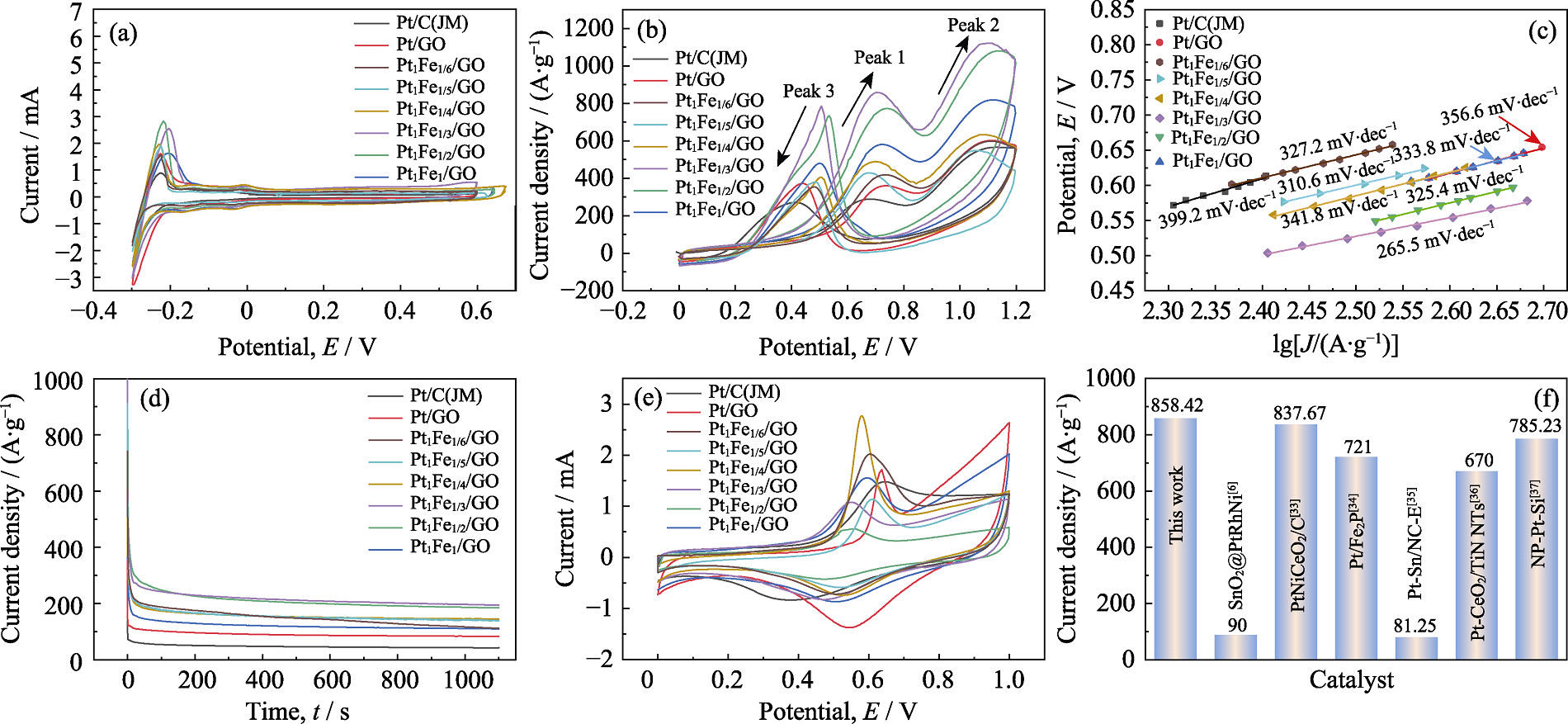
图4 不同催化剂样品的(a)活性表面积曲线、(b)循环伏安曲线、(c) Tafel 斜率、(d) I-t曲线和(e) CO溶出曲线; (f)本研究与文献的峰值电流密度比较[6,33⇓⇓⇓ -37]
Fig. 4 (a) Active surface area curves, (b) cyclic voltammetry curves, (c) Tafel slopes, (d) I-t curves, and (e) CO dissolution curves for different catalyst samples; (f) Peak current density of this work compared with literature[6,33⇓⇓⇓ -37] Colorful figures are available on website
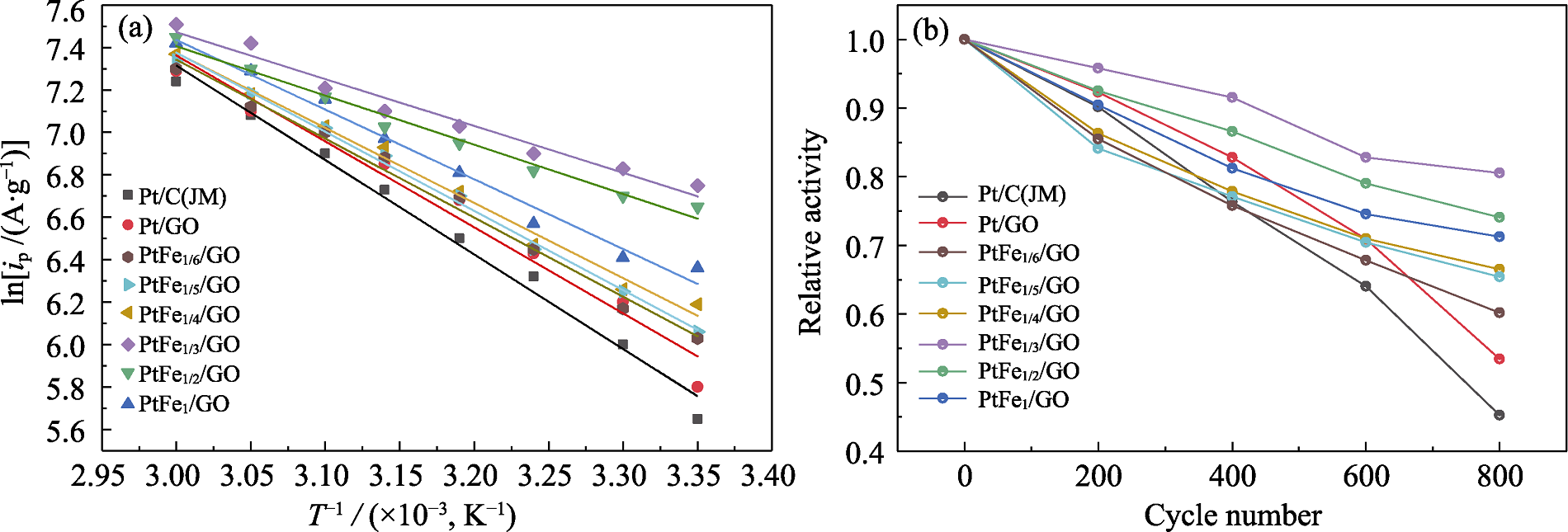
图5 不同催化剂的(a)变温循环伏安拟合曲线和(b)衰竭循环伏安拟合曲线
Fig. 5 (a) Variable temperature cyclic voltammetry fitting curves and (b) depletion cyclic voltammetry fitting curves for different catalysts Colorful figures are available on website
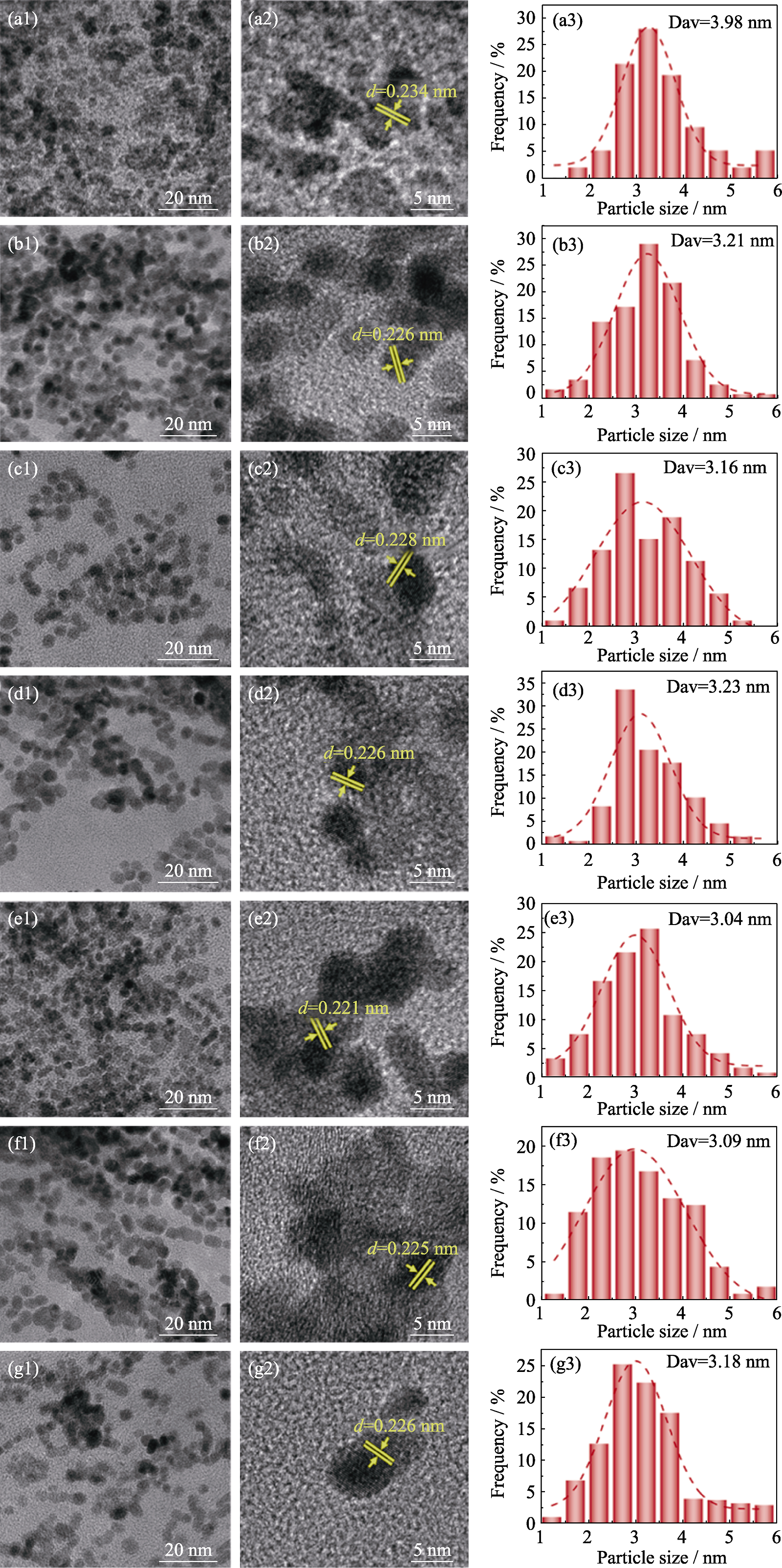
图S3 Pt/GO和PtFex/GO催化剂的TEM、HRTEM照片及粒径分布直方图
Fig. S3 TEM, HRTEM images and particle size distribution histograms of Pt/GO and PtFex/GO catalysts (a1-a3) Pt/GO; (b1-b3) PtFe1/6/GO; (c1-c3) PtFe1/5/GO; (d1-d3) PtFe1/4/GO; (e1-e3) PtFe1/3/GO; (f1-f3) PtFe1/2/GO; (g1-g3) PtFe1/GO

图S4 催化剂的变温循环伏安曲线
Fig. S4 Variable temperature cyclic voltammetry curves of catalysts (a) Pt/C(JM); (b) Pt/GO; (c) PtFe1/6/GO; (d) PtFe1/5/GO; (e) PtFe1/4/GO; (f) PtFe1/3/GO; (g) PtFe1/2/GO; (h) PtFe1/GO

图S5 催化剂的衰竭循环伏安曲线
Fig. S5 Attenuated cyclic voltammetry curves of catalysts (a) Pt/C(JM); (b) Pt/GO; (c) PtFe1/6/GO; (d) PtFe1/5/GO; (e) PtFe1/4/GO; (f) PtFe1/3/GO; (g) PtFe1/2/GO; (h) PtFe1/GO
| Sample | Active area/(m2·g-1) | Peak current density/(A·g-1) | Steady-state current density/(A·g-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PtFe1/3/GO | 69.84 | 858.42 | 194.80 | This Work |
| PtNiCeO2/C | 90.41 | 837.67 | 178.33 | [S1] |
| Pt/Fe2P | 80 | 721 | - | [S2] |
| Pt-Sn/NC-E | 121.5 | 81.25 | - | [S3] |
| SnO2@PtRhNi | 18 | 90 | - | [S4] |
| Pt-CeO2/TiNNTs | - | 670 | - | [S5] |
| NP-Pt-Si | - | 785.23 | 87.56 | [S6] |
表S1 本研究与文献报道的Pt催化剂性能对比
Table S1 Comparison of performance of Pt-catalysts in this work and in literature
| Sample | Active area/(m2·g-1) | Peak current density/(A·g-1) | Steady-state current density/(A·g-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PtFe1/3/GO | 69.84 | 858.42 | 194.80 | This Work |
| PtNiCeO2/C | 90.41 | 837.67 | 178.33 | [S1] |
| Pt/Fe2P | 80 | 721 | - | [S2] |
| Pt-Sn/NC-E | 121.5 | 81.25 | - | [S3] |
| SnO2@PtRhNi | 18 | 90 | - | [S4] |
| Pt-CeO2/TiNNTs | - | 670 | - | [S5] |
| NP-Pt-Si | - | 785.23 | 87.56 | [S6] |
图S6 循环测试后PtFe1/3/GO催化剂的TEM照片
Fig. S6 TEM images of PtFe1/3/GO after cyclic testing (a) Surface scanning TEM image; (b-e) Surface EDS elemental mappings; (f) SAED pattern

图S7 循环测试后PtFe1/3/GO催化剂的(a)TEM、(b)HRTEM照片及(c)粒径分布直方图
Fig. S7 (a) TEM, (b) HRTEM images and (c) particle size distribution histogram of PtFe1/3/GO catalyst after cyclic testing
| [1] | SHI Y. Research on energy saving management models for coal- fired power plants in the context of new energy. Smart Systems and Green Energy, 2023, 5(1):17. |
| [2] | LAERO C, FERRARI M D. Sweet potato as a bioenergy crop for fuel ethanol production:perspectives and challenges//RAY R C, RAMACHANDRAN S. Bioethanol production from food crops. London: Elsevier, 2019: 115- 147. |
| [3] |
HUANG L, ZAMAN S, TIAN X, et al. Advanced platinum-based oxygen reduction electrocatalysts for fuel cells. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2021, 54(2):311.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
WANG Y, CHU F, ZENG J, et al. Single atom catalysts for fuel cells and rechargeable batteries: principles, advances, and opportunities. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(1):210.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | SUN H, ZHAO L, YU F. Synthesis and characterization of Pt-V- SnO2/C electrocatalysts for ethanol oxidation in acidic media. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2013, 8(2):2768. |
| [6] | GRUZEŁ G, PIEKARZ P, PAWLYTA M, et al. Preparation of Pt-skin PtRhNi nanoframes decorated with small SnO2 nanoparticles as an efficient catalyst for ethanol oxidation reaction. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(25):22352. |
| [7] | ZHANG W, YANG Y, HUANG B, et al. Ultrathin PtNiM (M=Rh, Os, and Ir) nanowires as efficient fuel oxidation electrocatalytic materials. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(15):1805833. |
| [8] | 黄思玉, 赵杰, 陈卫祥, 等. 空心PtCo/CNTs催化剂的合成及其电催化性能. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2008, 42(7):1218. |
| [9] | 王帅. 微波合成Pt-M/C催化剂及其催化性能比较. 山东工业技术, 2017(13): 276. |
| [10] | LI L, YUAN X, XIA X, et al. The effect of Mo doping on the catalytic performance of Pt/C catalyst for ethanol oxidation. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(10):1044. |
| [11] | GUO R, WANG J, AN S, et al. Effect of cerium oxide prepared under different hydrothermal time on electrocatalytic performance of Pt-based anode catalysts. Journal of Rare Earths, 2020, 38(4):384. |
| [12] | YI L, YU B, YI W, et al. Carbon-supported bimetallic platinum-iron nanocatalysts: application in direct borohydride/hydrogen peroxide fuel cell. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(7):8142. |
| [13] | TU W Z, LUO W J, CHEN C L, et al. Tungsten as “adhesive” in Pt2CuW0.25 ternary alloy for highly durable oxygen reduction electrocatalysis. Advanced Functioanal Materials, 2020, 30(6):1908230. |
| [14] | CHEN Y, ZHOU Y, TANG Y, et al. Electrocatalytic properties of carbon-supported Pt-Ru catalysts with the high alloying degree for formic acid electrooxidation. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195(13):4129. |
| [15] | ZHENG H, DENG D, ZHENG X, et al. Highly reversible Zn-air batteries enabled by tuned valence electron and steric hindrance on atomic Fe-N4-C sites. Nano Letters, 2024, 24(15):4672. |
| [16] | SUN L, WANG H, EID K, et al. Shape-controlled synthesis of porous AuPt nanoparticles and their superior electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction reaction. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2016, 17: 58. |
| [17] | FANG D, HE F, XIE J, et al. Calibration of binding energy positions with C1s for XPS results. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2020, 35: 711. |
| [18] | SHI H L, WANG R Y, LOU M R, et al. A novel Pt/pyridine ionic liquid polyoxometalate/rGO tri-component hybrid and its enhancedactivities for methanol electrooxidation. Electrochim Acta, 2019, 294: 93. |
| [19] | ZHANG J, WANG J, LIU Y, et al. High-performance lithium iron phosphate with phosphorus-doped carbon layers for lithium ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(5): 2043. |
| [20] | ZHU T, HENSEN E J M, VAN SANTEN R A, et al. Roughening of Pt nanoparticles induced bysurface-oxide formation. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2013, 15(7):2268. |
| [21] | HUANG M, JIANG Y, JIN C, et al. Pt-Cu alloy with high density of surface Pt defects for efficient catalysis of breaking C-C bond in ethanol. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 125: 29. |
| [22] | MAI T P, CHIKU M, HIGUCHI E, et al. Structure-controlled Rh/Sn/Pt ternary catalysts for complete oxidation reaction of ethanol to carbon dioxide. ECS Transaction, 2015, 69(17):675. |
| [23] | 郭瑞华, 朱国富, 安胜利, 等. 前驱体溶液pH对Pt基催化剂电催化性能的影响. 化工新型材料, 2021, 49(S1):224. |
| [24] | PENG H, REN J, WANG Y, et al. One-stone, two birds: alloying effect and surface defects induced by Pt on Cu2-xSe nanowires to boost CC bond cleavage for electrocatalytic ethanol oxidation. Nano Energy, 2021, 88: 106307. |
| [25] | MO Y, GUO R, AN S, et al. Preparation of broom strong cerium oxide and its effect on the performance of Pt based anode catalysts. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 34(11): 1991. |
| [26] |
TIAN X L, ZHAO X, SU Y Q, et al. Engineering bunched Pt-Ni alloy nanocages for efficient oxygen reduction in practical fuel cells. Science, 2019, 366(6467):850.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | ZOU L L, FAN J, ZHOU Y, et al. Conversion of PtNi alloy from disordered to ordered for enhanced activity and durability in methanol- tolerant oxygen reduction reactions. NanoResearch, 2015, 8(8):2777. |
| [28] | SARAVANAN C, MARKOVIC N M, HEAD-GORDON M, et al. Stripping and bulk Co electro-oxidation at the Pt electrode interface: dynamic Monte Carlo simulations. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2001, 114(14):6404. |
| [29] | SHI Y, MA Z R, XIAO Y Y, et al. Electronic metal-support interaction modulates single-atom platinum catalysis for hydrogen evolution reaction. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 3021. |
| [30] | WEI Z Z, YAO Z H, ZHOU Q, et al. Optimizing alkyne hydrogenation performance of Pd on carbon in situ decorated with oxygen- deficient TiO2 by integrating the reaction and diffusion. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(12):10656. |
| [31] | ZHU Y M, BU L Z, SHAO Q, et al. Structurally ordered Pt3Sn nanofibers with highlighted antipoisoning property as efficient ethanol oxidation electrocatalysts. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(5):3455. |
| [32] | YAO Y, GUO R, AN S, et al. In situ loaded Pt-Co high index facets catalysts: preparation and electrocatalytic performance. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 71. |
| [33] | 郭瑞华, 钱飞, 安胜利, 等. Ni添加对直接乙醇燃料电池Pt基催化剂催化性能的影响. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2019, 48(8):2683. |
| [34] | LIU J, ZHANG H, GONG H, et al. Polyethylene/polypropylene bicomponent spunbond air filtration materials containing magnesium stearate for efficient fine particle capture. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(43):40592. |
| [35] | 汤俊平, 黄郁夫, 吴鹏, 等. 直接乙醇燃料电池阳极催化材料研究进展. 材料导报, 2023, 37(S2):532. |
| [36] | ZHOU Q, PAN Z, WU D, et al. Pt-CeO2/TiN NTs derived from metal organic frameworks as high-performance electrocatalyst for methanol electrooxidation. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(21):10646. |
| [37] | 卢娜丽, 李尧, 张磊, 等. 纳米多孔Pt-Si合金对乙醇的电催化氧化研究. 常熟理工学院学报, 2018, 32(5):19. |
| [38] | LIU H, WANG S, JIA F. Conversion of commercial Pt/C to clean Pt-Cu/C catalyst with high activity toward methanol oxidation. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 184: 331. |
| [39] | SUN Q, KIM S. Synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene supported Pt nanoparticles catalysts and their catalytic activity for fuel cell. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 153(2):566. |
| [40] | RIBADENEIRA E, HOYOS B A. Evaluation of Pt-Ru-Ni and Pt-Sn-Ni catalysts as anodes indirect ethanol fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 180(1):238. |
| [41] | GUO R, MO Y, AN S, et al. Controllable synthesis of cerium oxide hollow spheres and their influence on the electrocatalytic performance of Pt based catalysts. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(7):779. |
| [1] | 郭瑞华, 莫逸杰, 安胜利, 张捷宇, 周国治. 氧化铈空心球可控合成及其对Pt基催化剂电催化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(7): 779-786. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||