无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (6): 708-716.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220742 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20220742
所属专题: 【生物材料】骨骼与齿类组织修复(202506)
• 研究快报 • 上一篇
吴锐1( ), 张敏慧1, 金成韵1, 林健1,2(
), 张敏慧1, 金成韵1, 林健1,2( ), 王德平1,2
), 王德平1,2
收稿日期:2022-12-06
修回日期:2022-12-26
出版日期:2023-01-18
网络出版日期:2023-01-18
通讯作者:
林健, 教授. E-mail: lin_jian@tongji.edu.cn作者简介:吴锐(1998-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 2030621@tongji.edu.cn
WU Rui1( ), ZHANG Minhui1, JIN Chenyun1, LIN Jian1,2(
), ZHANG Minhui1, JIN Chenyun1, LIN Jian1,2( ), WANG Deping1,2
), WANG Deping1,2
Received:2022-12-06
Revised:2022-12-26
Published:2023-01-18
Online:2023-01-18
Contact:
LIN Jian, professor. E-mail: lin_jian@tongji.edu.cn.About author:WU Rui (1998-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 2030621@tongji.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
硼硅酸盐生物玻璃以其稳定的结构和优异的生物活性而受到广泛关注, 但生物玻璃在矿化过程中活性呈现初期快而中后期慢的趋势, 造成后期的活性降低。光热可加速生物玻璃降解, 本研究制备了以氮化钛为核、生物玻璃(40SiO2-20B2O3-36CaO-4P2O5)为壳的复合生物玻璃, 利用光热场干预生物玻璃的矿化过程。结果表明, 生物玻璃具有显著的光热效应, 光热能力随氮化钛掺杂量和激光功率密度的增加而提高;在体外浸泡中, 近红外光辐照促进了生物玻璃的降解, 浸泡7 d后模拟体液中钙、硼的含量分别增加12%~16%和8%~11%, 加速了羟基磷灰石的生成;细胞增殖活性实验表明样品有良好的生物安全性。因此, 光热场可促进生物玻璃降解和矿化, 对周围细胞影响小, 有望在保障初期生物安全的同时发挥调节作用。
中图分类号:
吴锐, 张敏慧, 金成韵, 林健, 王德平. 光热核壳TiN@硼硅酸盐生物玻璃纳米颗粒的降解和矿化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 708-716.
WU Rui, ZHANG Minhui, JIN Chenyun, LIN Jian, WANG Deping. Photothermal Core-Shell TiN@Borosilicate Bioglass Nanoparticles: Degradation and Mineralization[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 708-716.
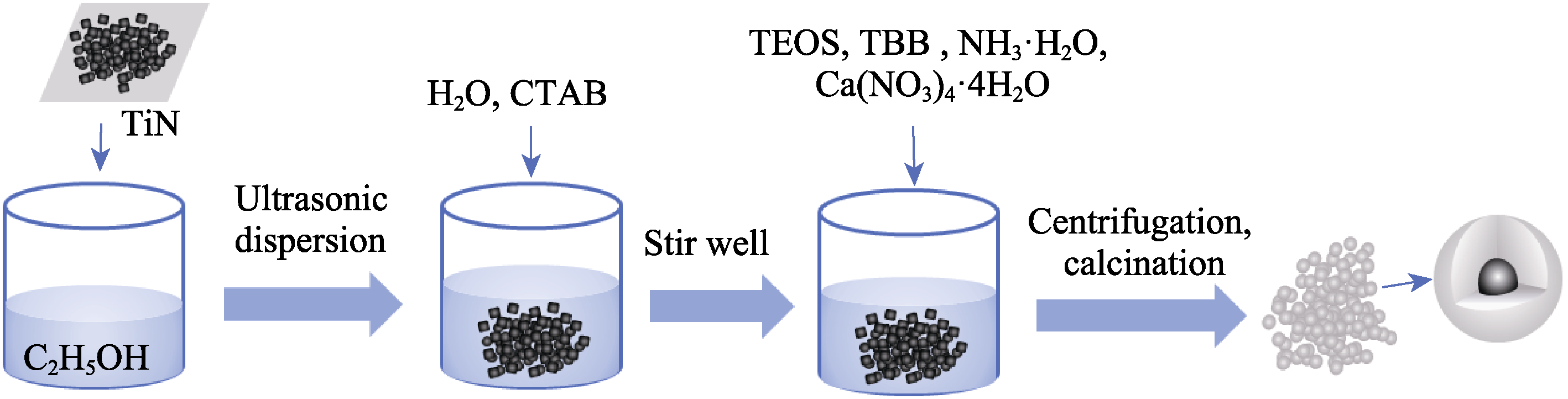
Fig. 1 Preparation process of core-shell xTiN@58S-20B nanoparticles CTAB: Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide; TEOS: Tetraethyl orthosilicate; TBB: Tributyl borate
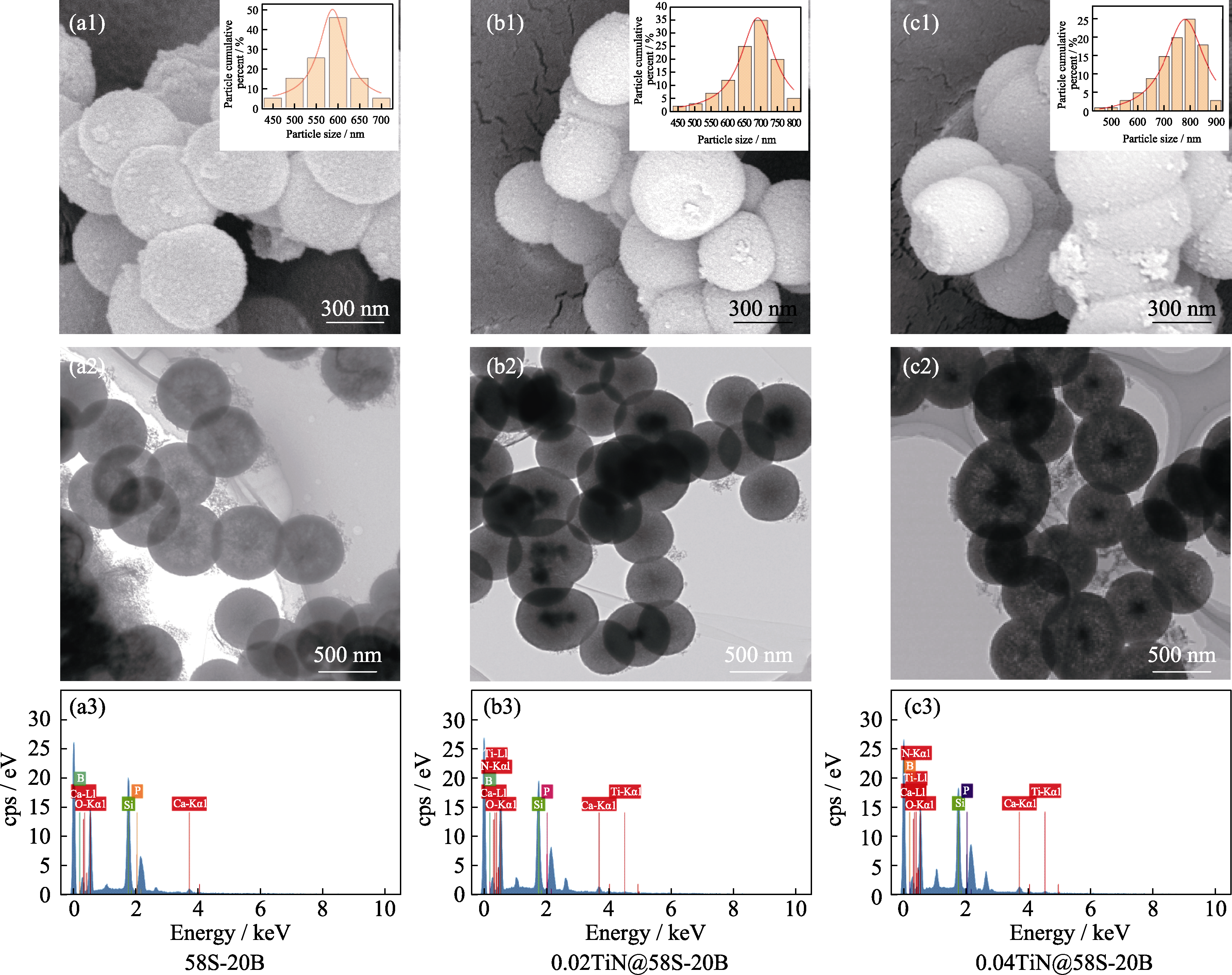
Fig. 3 Micrographs of xTiN@58S-20B (x=0, 0.02, 0.04) with insets showing the corresponding particle size distributions (a1, b1, c1) SEM images; (a2, b2, c2) TEM images; (a3, b3, c3) EDS spectra
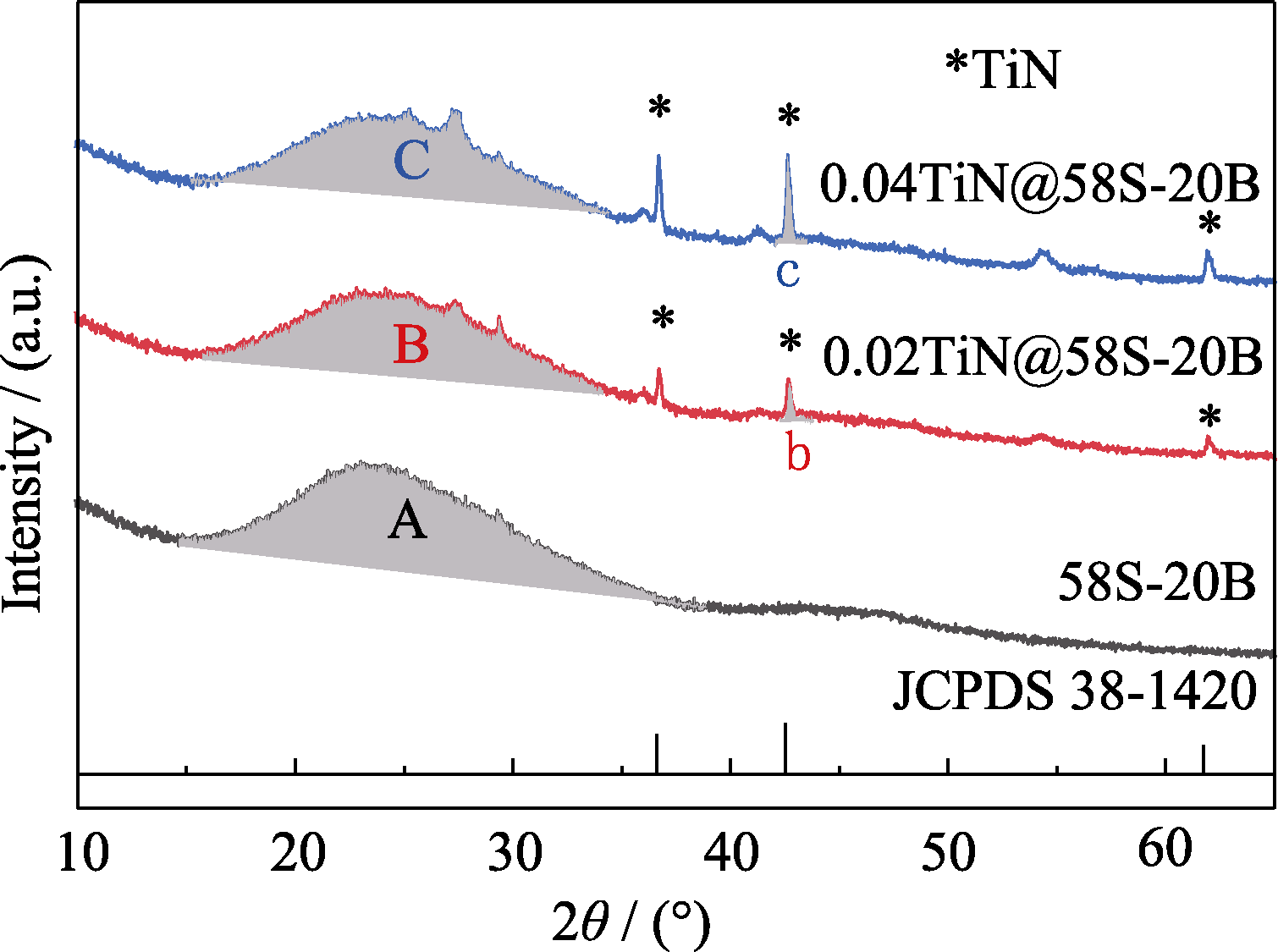
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of xTiN@58S-20B (x=0, 0.02, 0.04), with gray shaded parts A, B, and C showing the glass peak areas, while b and c showing the strongest peak area of the TiN NPs
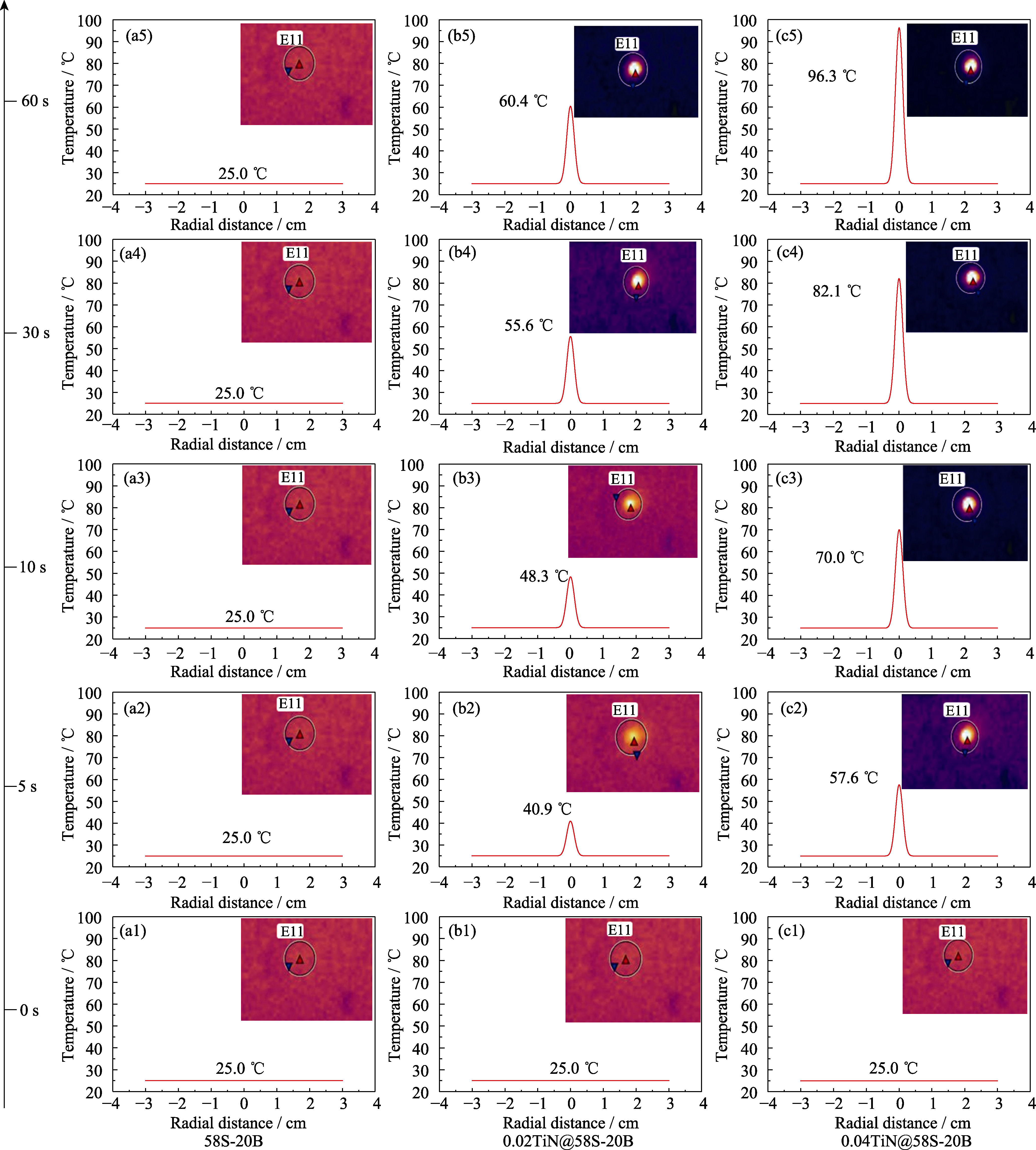
Fig. 5 Temperature rise diagrams of three samples in air with 1064 nm NIR laser at a power density of 1.0 W/cm2 for 60 s, with insets showing the infrared images correspondingly at each time point, X axial representing the radial distance extending to both sides from the sample center, and the Y axial representing the temperature
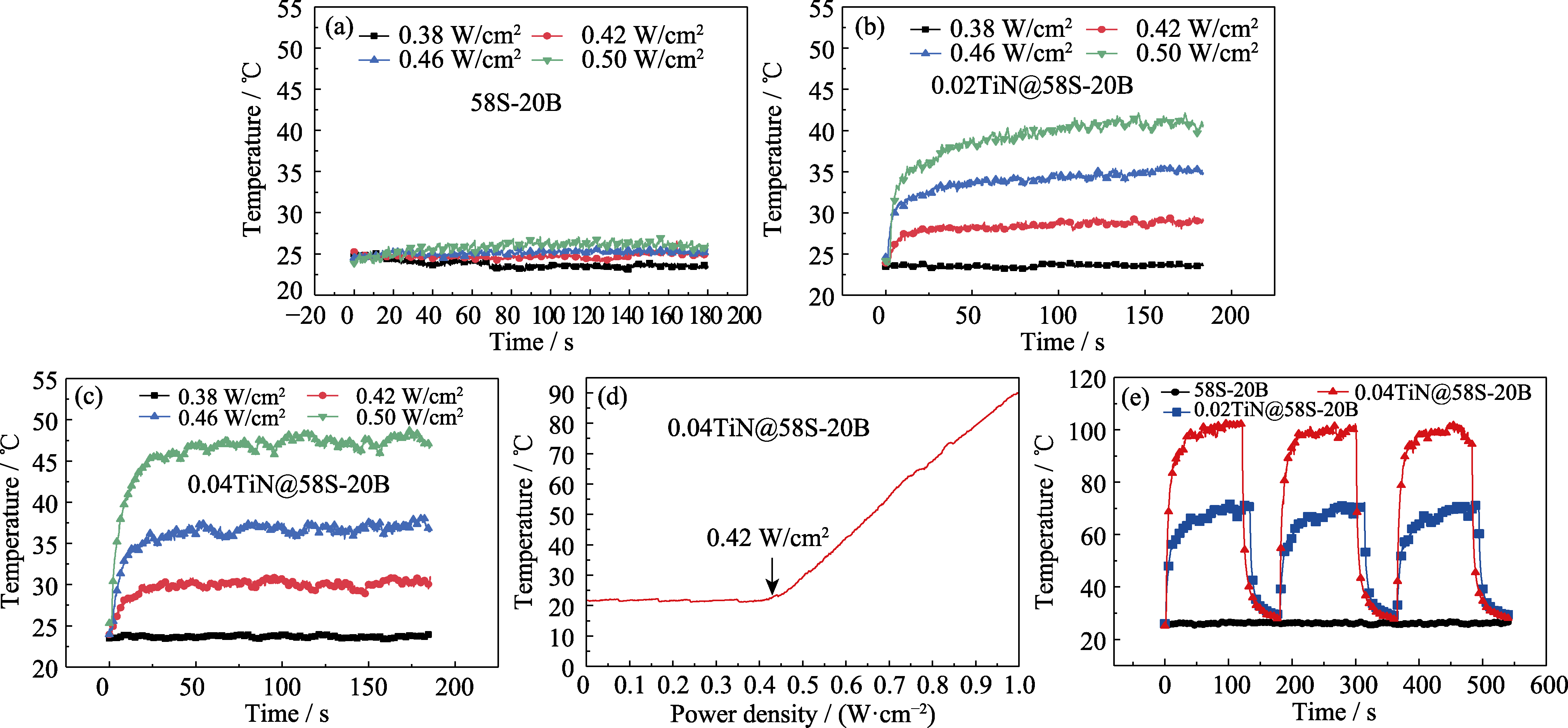
Fig. 6 Temperature changes of bioglass (a-c) Temperature changes of 58S-20B (a), 0.02TiN@58S-20B (b), 0.04TiN@58S-20B (c) irradiated by 1064 nm NIR laser at different power density (0.38, 0.42, 0.46, 0.50 W/cm2) for 3 min; (d)Temperature versus power density; (e) Heating curves of three samples under 1064 nm laser irradiation (1.0 W/cm2)
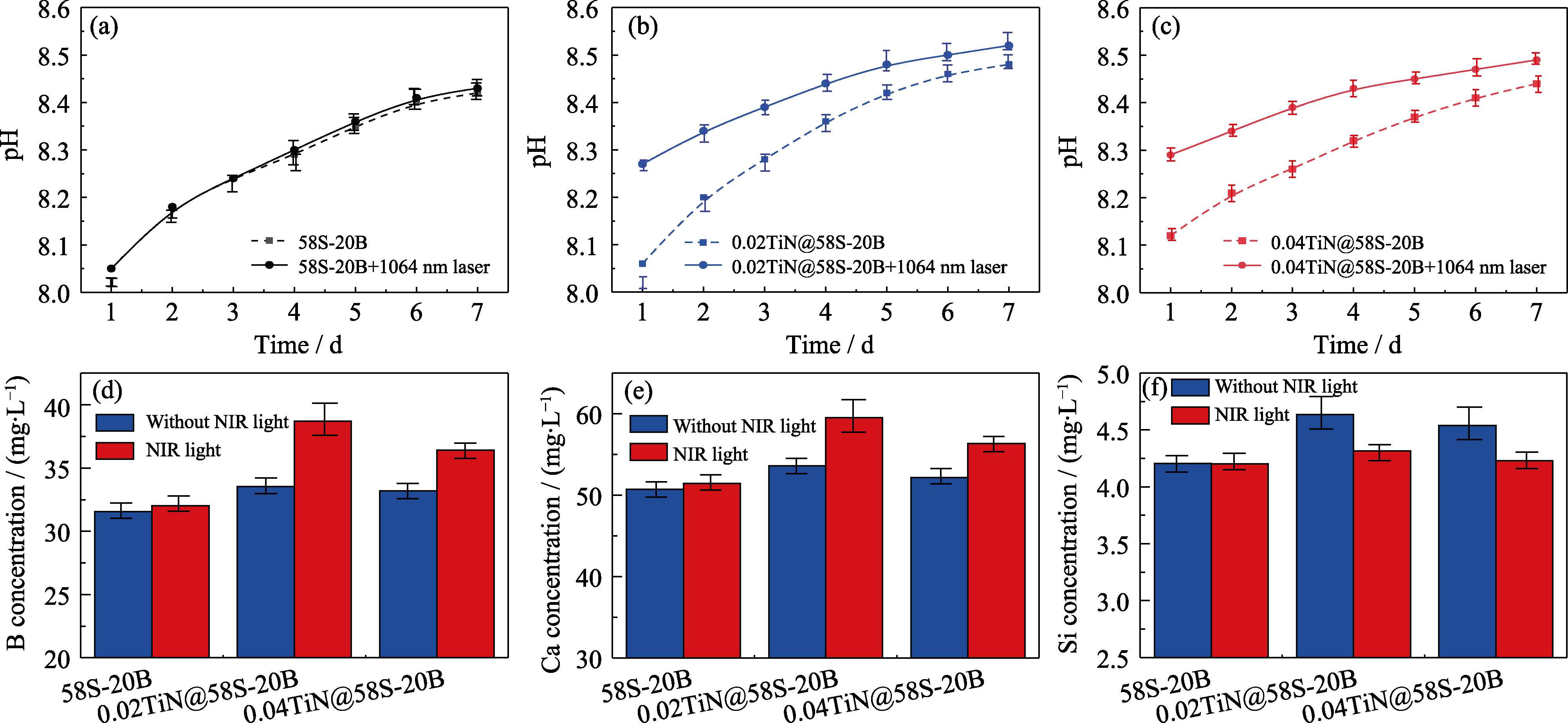
Fig. 7 pH changes and ions release of bioglass samples immersed in SBF at 37 ℃ for 7 d (a-c) pH changes within 7 d; (d-f) Ion release profiles of B, Ca, Si on the 7th day
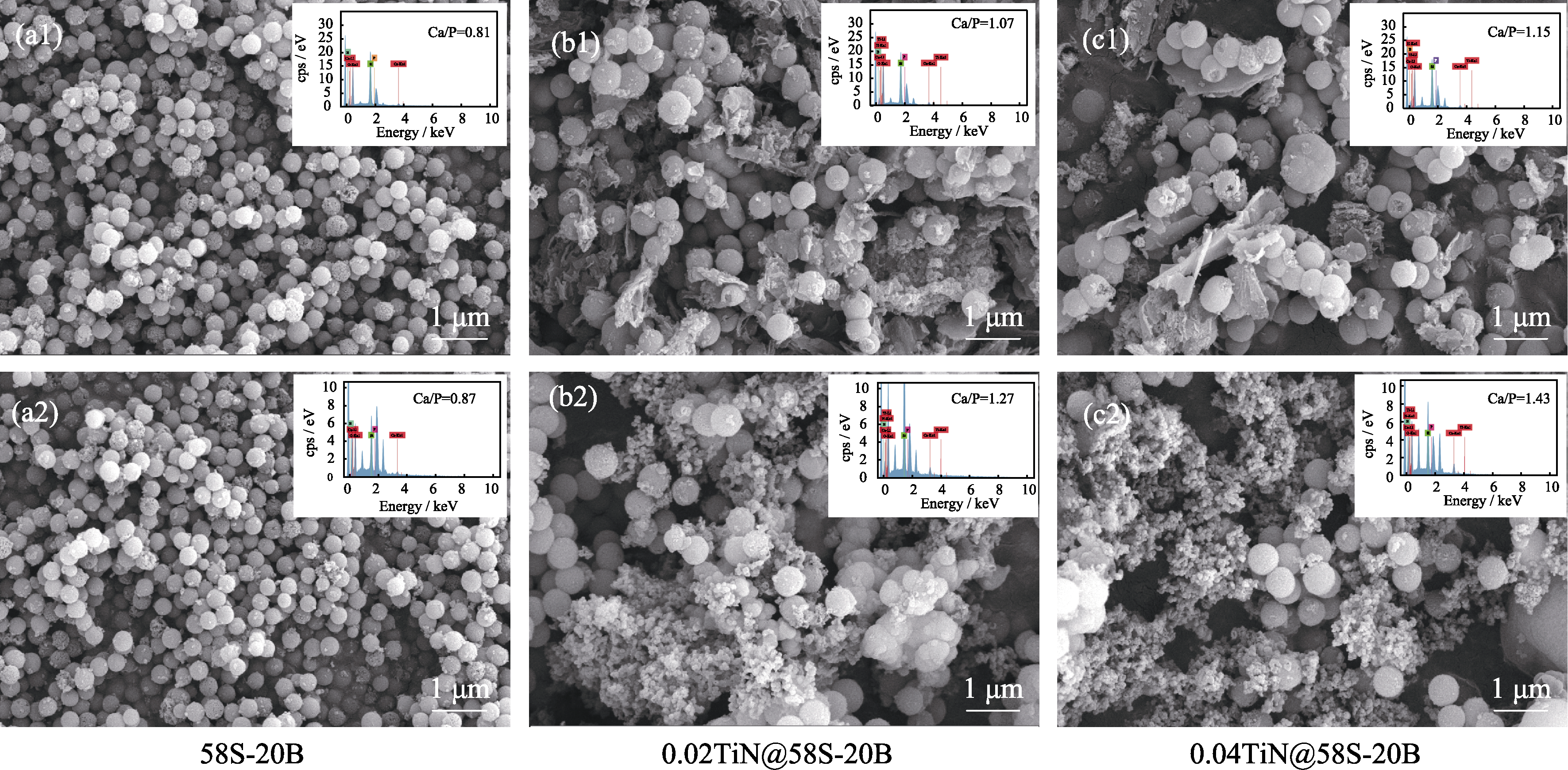
Fig. 8 SEM images of borosilicate samples immersed in SBF for 7 d with insets showing corresponding EDS spectra (a1, b1, c1) Without NIR laser irradiation; (a2, b2, c2) With NIR laser irradiation
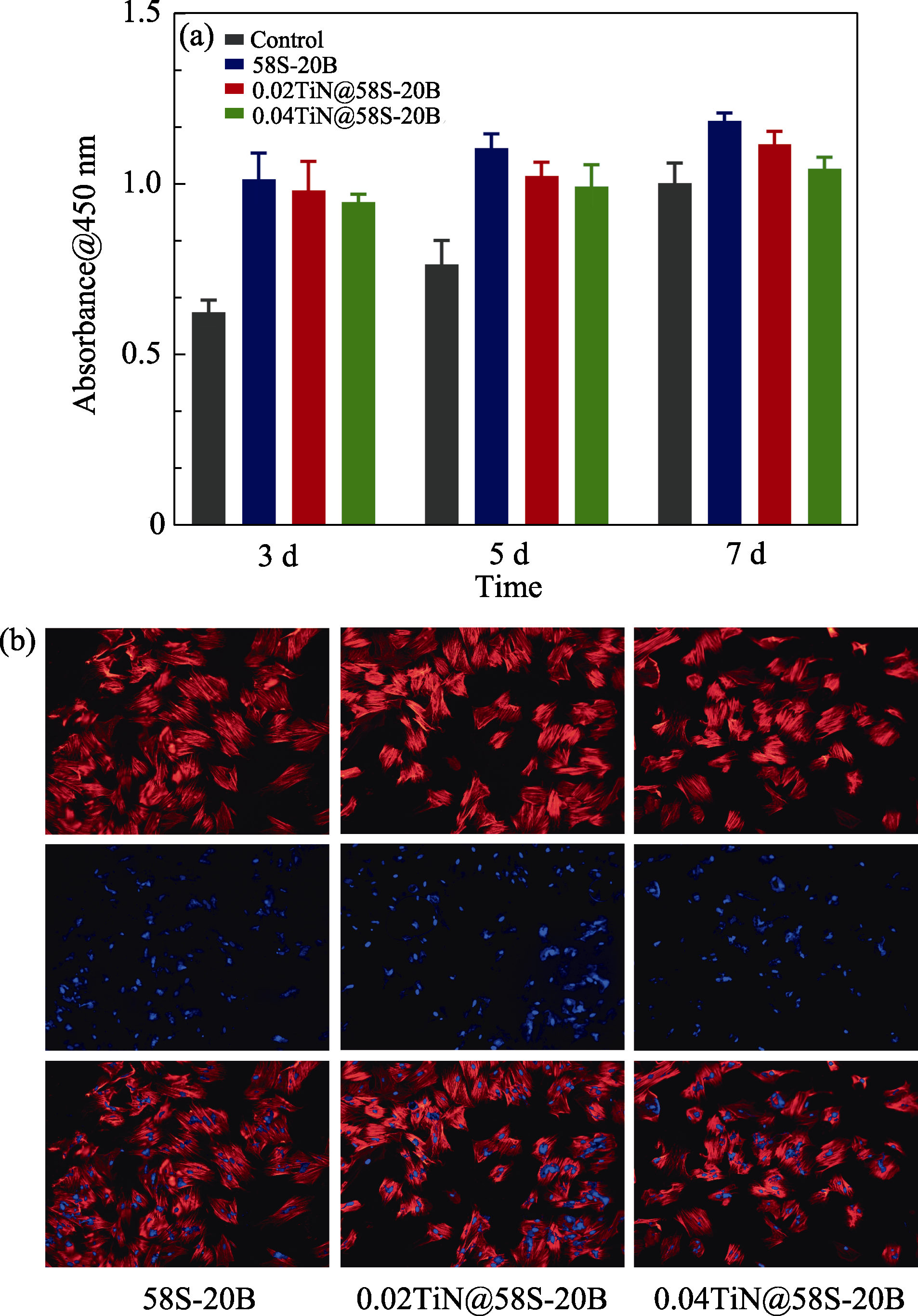
Fig. 10 Cell proliferation activity and cell morphology analysis of control, 58S-20B, 0.02TiN@58S-20B, and 0.04TiN@58S-20B (a) CCK-8 analysis; (b) Fluorescent images of cell morphology. Blue indicates the cell nucleus and red indicates the cell cytoskeleton
| [1] |
DESCHASEAUX F, SENSÉBÉ L, HEYMANN D, et al. Mechanisms of bone repair and regeneration. Trends in Molecular Medicine, 2009, 15(9):417.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
BOSE S, ROY M, BANDYOPADHYAY A, et al. Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Trends in Biotechnology, 2012, 30(10):546.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
LARRY L, HENCH L L. Bioactive materials: the potential for tissue regeneration. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 1998, 41(4):511.
PMID |
| [4] |
KOKUBO T, ITO S, HUANG Z T, et al. Ca, P-rich layer formed on high-strength bioactive glass-ceramic A-W. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 1990, 24(3):331.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
HENCH L L, PASCHALL H A. Direct chemical bond of bioactive glass-ceramic materials to bone and muscle. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 1973, 7(3):25.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
SAEID K, FRANCESCO B, SEPIDEH H, et al. Bioactive glasses entering the mainstream. Drug Discovery Today, 2018, 23(10):1700.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
SAQIB A, IMRAN F, KEFI I, et al. A review of the effect of various ions on the properties and the clinical applications of novel bioactive glasses in medicine and dentistry. Saudi Dental Journal, 2014, 26(1):1.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | HU H R, TANG Y. Angiogenesis and full-thickness wound healing efficiency of a copper-doped borate bioactive glass/poly(lactic-co- glycolic acid) dressing loaded with vitamin E in vivo and in vitro. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(27):22939. |
| [9] |
LI J, ZHANG C, GONG S, et al. A nanoscale photothermal agent based on a metal-organic coordination polymer as a drug-loading framework for effective combination therapy. Acta Biomaterialia, 2019, 94: 435.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
ZHANG T, JIANG Z, XVE T, et al. One-pot synthesis of hollow PDA@DOX nanoparticles for ultrasound imaging and chemo- thermal therapy in breast cancer. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(45):21759.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
CAO Z X, WANG R G, YANG F, et al. Photothermal healing of a glass fiber reinforced composite interface by gold nanoparticles. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(124):102167.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
PINHEIRO A N L B, SOARES L G P, DA SILVA A C P, et al. Laser/LED phototherapy on the repair of tibial fracture treated with wire osteosynthesis evaluated by Raman spectroscopy. Lasers in Medical Science, 2018, 33: 1657.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
SMITH A M, MANCINI M C, NIE S, et al. Bioimaging: second window for in vivo imaging. Nature Nanotechnology, 2009, 4(11):710.
DOI |
| [14] |
JIANG W, FU Q, WEI H, et al. TiN nanoparticles: synthesis and application as near-infrared photothermal agents for cancer therapy. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54: 5743.
DOI |
| [15] |
GULER U, SHALAEV V M, BOLTASSEVA A, et al. Nanoparticle plasmonics: going practical with transition metal nitrides. Materials Today, 2015, 18(4):227.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ZHANG M, YAO A, LIN J, et al. Photothermally active borosilicate-based composite bone cement for near-infrared light controlled mineralisation. Materials Technology, 2021, 37(10):1243.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHU K P, SUN J, SONG Y E, et al. A novel hollow hydroxyapatite microspheres/chitosan composite drug carrier for controlled release. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(4):434.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LIANG Z, SUSHA A, CARUSO F, et al. Gold nanoparticle-based core-shell and hollow spheres and ordered assemblies thereof. Chemistry of Materials, 2003, 15(16):3176.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
KIM J, JI E L, LEE J, et al. Magnetic fluorescent delivery vehicle using uniform mesoporous silica spheres embedded with monodisperse magnetic and semiconductor nanocrystals. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006, 128(3):688.
PMID |
| [20] |
BALAS F, ARCOS D, PÉREZ-PARIENTE J, et al. Textural properties of SiO2·CaO·P2O5 glasses prepared by the Sol-Gel method. Journal of Materials Research, 2001, 16(5):1345.
DOI URL |
| [21] | SUN H Z, GE W J, GAO X, et al. Effect of SDT on the survival rate of endometrial cancer cells, assessed by the CCK-8 method. PLOS ONE, 2015, 11: 27. |
| [22] | GAO J, YE B, WU W H, et al. Tachyzoites of toxolasma gondii enhances the cytotoxicity of Etooside (V-16) to mouse colon cancer cell ct26 in vitro. Chinese Journal of Zoonoses, 2010, 26(8):720. |
| [23] |
JAQUE D, MAESTRO L M, ROSAL B D, et al. Nanoparticles for photothermal therapies. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(16):9494.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
MAESTRO L M, HARO-GONZÁLEZ P, ROSAL B D, et al. Heating efficiency of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in the first and second biological windows. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(17):7882.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
HENCH L L, WILSON J. Surface-active biomaterials. Science, 1984, 226(4675):630.
PMID |
| [26] | YAO A H, LIN J, DUAN X, et al. Formation mechanism of multilayered structure on surface of bioactive borosilicate glass. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2008, 24(7):1132. |
| [27] | ZHU X, SCHEIDELER L, EIBL O, et al. Characterization of nano hydroxyapatite/collagen surfaces and cellular behaviors. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 2006, 1(14):114. |
| [1] | 杨恩东, 李宝乐, 张珂, 谭鲁, 娄永兵. ZnCo2O4-ZnO@C@CoS核壳复合材料的制备及其在超级电容器中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 485-493. |
| [2] | 张婷婷, 王方园, 刘长友, 张国荣, 吕佳辉, 宋宇晨, 介万奇. 水热-烧结法制备Cr2+:ZnSe/ZnSe核壳结构纳米孪晶[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 409-415. |
| [3] | 岳全鑫, 郭瑞华, 王瑞芬, 安胜利, 张国芳, 关丽丽. 3D核壳结构NiMoO4@CoFe-LDH纳米棒的高效析氧及全解水性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1254-1264. |
| [4] | 马晓森, 张丽晨, 刘砚超, 汪全华, 郑家军, 李瑞丰. 13X@SiO2合成及其甲苯吸附性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [5] | 迟聪聪, 屈盼盼, 任超男, 许馨, 白飞飞, 张丹洁. SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2核壳结构的制备及其光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [6] | 陈铖, 丁晶鑫, 王会, 王德平. 掺钕介孔硼硅酸盐生物活性玻璃陶瓷骨水泥的制备与性能表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1245-1258. |
| [7] | 池哲人, 张辽, 郭志前, 李永生, 牛德超. 氧化硅基杂化胶束负载Flav7光热剂的合成与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1236-1244. |
| [8] | 陈小梅, 陈颖, 袁霞. 核壳材料Co3O4@SiO2催化环己基过氧化氢分解[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 65-71. |
| [9] | 朱子旻, 张敏慧, 张轩宇, 姚爱华, 林健, 王德平. 硼硅酸盐生物活性玻璃在直流电场下的体外矿化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 1006-1012. |
| [10] | 林子扬, 常宇辰, 吴章凡, 包荣, 林文庆, 王德平. 不同模拟体液对硼硅酸盐生物活性玻璃基骨水泥矿化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 745-752. |
| [11] | 常宇辰, 林子扬, 谢昕, 吴章凡, 姚爱华, 叶松, 林健, 王德平, 崔旭. 基于介孔硼硅酸盐生物活性玻璃微球的可注射复合骨水泥[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(12): 1398-1406. |
| [12] | 李孟夏, 陆越, 王利斌, 胡先罗. Mn3O4@ZnO核壳结构纳米片阵列的可控合成及其在水系锌离子电池中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(1): 86-92. |
| [13] | 肖文谦,张静,李克江,邹新宇,蔡昱东,李波,刘雪,廖晓玲. 荔枝状CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4磁性介孔多级微球的制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 925-932. |
| [14] | 宋晶晶, 陈波, 林开利. 核壳结构羟基磷灰石/介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒的制备及其药物释放研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(6): 623-628. |
| [15] | 周蓓莹, 陈东, 刘佳乐, 江莞, 罗维, 王连军. CuInS2/ZnS核壳结构量子点的水相制备与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(3): 279-283. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||