无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 449-456.DOI: 10.15541/jim230501 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim230501
所属专题: 【信息功能】发光材料与器件(202506); 【能源环境】量子点(202412); 【能源环境】钙钛矿(202506)
• 研究快报 • 上一篇
岳仔豪1,2( ), 杨小兔1, 张正亮1, 邓瑞翔1(
), 杨小兔1, 张正亮1, 邓瑞翔1( ), 张涛1(
), 张涛1( ), 宋力昕1,2
), 宋力昕1,2
收稿日期:2023-10-30
修回日期:2023-12-05
出版日期:2024-04-20
网络出版日期:2024-04-09
通讯作者:
邓瑞翔. E-mail: dengruixiang@mail.sic.ac.cn;作者简介:岳仔豪(1994-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: yuezh@shanghaitech.edu.cn
YUE Zihao1,2( ), YANG Xiaotu1, ZHANG Zhengliang1, DENG Ruixiang1(
), YANG Xiaotu1, ZHANG Zhengliang1, DENG Ruixiang1( ), ZHANG Tao1(
), ZHANG Tao1( ), SONG Lixin1,2
), SONG Lixin1,2
Received:2023-10-30
Revised:2023-12-05
Published:2024-04-20
Online:2024-04-09
Contact:
DENG Ruixiang. E-mail: dengruixiang@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:YUE Zihao (1994-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: yuezh@shanghaitech.edu.cn
摘要:
硼硅酸盐玻璃包覆钙钛矿CsPbBr3量子点(PQDs@glass)能够大幅提高PQDs的稳定性, 使其在LED照明和显示技术中拥有广泛的应用空间。然而, 玻璃包覆的同时也导致了PQDs发光强度与量子产率降低。本工作为提高其发光强度探讨了热诱导温度及Pb2+的含量对PQDs@glass结构的影响,当热诱导温度为460 ℃,Pb2+浓度为6 mol时,其发光强度最高。研究发现,Pb2+浓度的增加会导致玻璃网状结构的致密化,改变玻璃组分的扩散行为,影响PQDs的析晶过程,导致PQDs@glass发光强度的变化。本工作得到量子产率高达95.6%的PQDs@glass,并实现了硼硅酸盐玻璃基质内PQDs的尺寸可控制备。结果表明, PQDs尺寸分布在10 nm左右, 超过86%的颗粒尺寸在6~14 nm内, 且具有优越的稳定性, 经历10次室温至200 ℃热循环后, 发光强度仍能保持初始强度的98.9%。最后, 为了验证其在LED照明及显示领域的应用, 将制备的量子点微晶玻璃粉料与二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)混合, 得到的LED器件性能优异, 色域范围覆盖110% sRGB。本研究为PQDs@glass的大规模制备及其在LED器件领域的应用奠定了基础。
中图分类号:
岳仔豪, 杨小兔, 张正亮, 邓瑞翔, 张涛, 宋力昕. Pb2+对掺杂硼硅酸盐玻璃中CsPbBr3钙钛矿量子点发光性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 449-456.
YUE Zihao, YANG Xiaotu, ZHANG Zhengliang, DENG Ruixiang, ZHANG Tao, SONG Lixin. Effect of Pb2+ on the Luminescent Performance of Borosilicate Glass Coated CsPbBr3 Perovskite Quantum Dots[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 449-456.
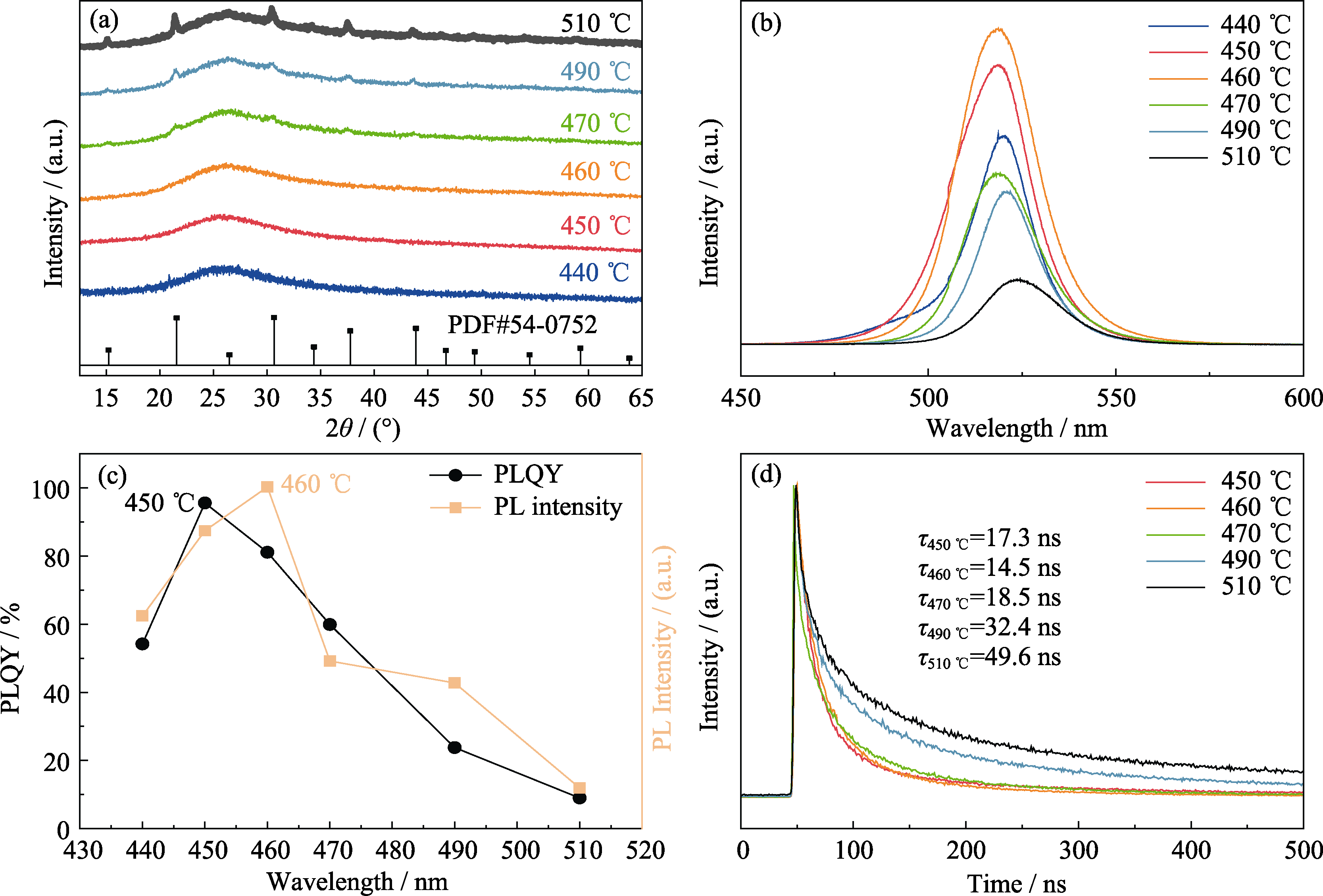
Fig. 2 Crystal structures and optical properties of PQDs@glass at different temperatures for 2 h (a) XRD patterns; (b) PL spectra; (c) PLQY and PL intensity; (d) Fluorescence lifetime curves Colorful images are available on website
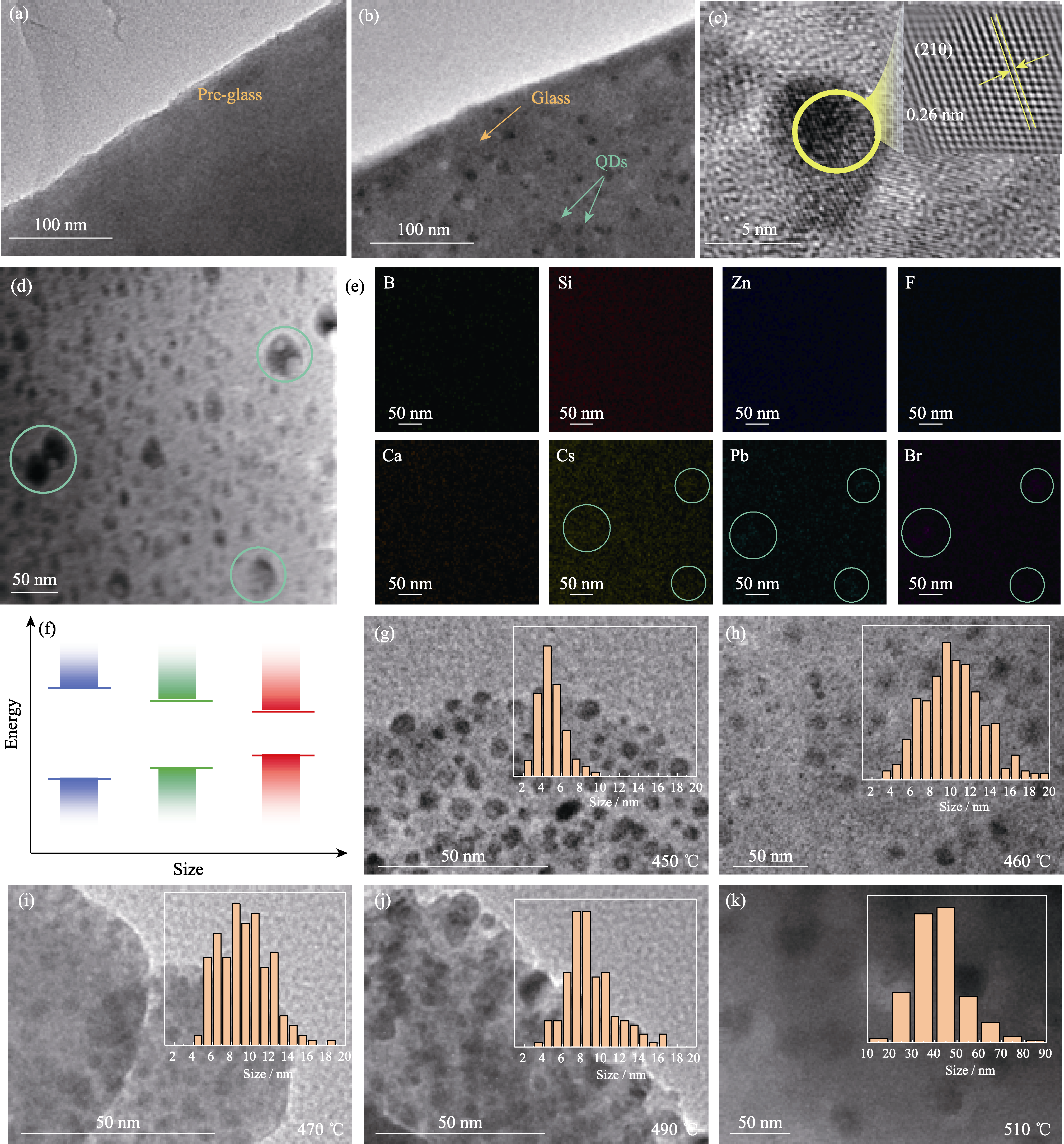
Fig. 3 TEM characterization and size distribution analyses of PQDs@glass (a, b) TEM images before (a) and after (b) heat-treatment; (c) High-resolution TEM image; (d, e) TEM image and EDS mappings; (f) Schematic diagram of the relationship between size and band gap of CsPbBr3 QDs; (g-k) TEM images and size statistics
| Code | SiO2 | H3BO3 | ZnO | CaF2 | Cs2CO3 | PbBr2 | NaBr | PbO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb-1 | 85 | 170 | 55 | 5 | 16 | 4 | 17 | 0.5 |
| Pb-2 | 85 | 170 | 55 | 5 | 16 | 5 | 15 | 0.5 |
| Pb-3 | 85 | 170 | 55 | 5 | 16 | 6 | 13 | 0.5 |
| Pb-4 | 85 | 170 | 55 | 5 | 16 | 7 | 11 | 0.5 |
Table 1 Component regulation of Pb2+ ions (all data in molar ratios)
| Code | SiO2 | H3BO3 | ZnO | CaF2 | Cs2CO3 | PbBr2 | NaBr | PbO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb-1 | 85 | 170 | 55 | 5 | 16 | 4 | 17 | 0.5 |
| Pb-2 | 85 | 170 | 55 | 5 | 16 | 5 | 15 | 0.5 |
| Pb-3 | 85 | 170 | 55 | 5 | 16 | 6 | 13 | 0.5 |
| Pb-4 | 85 | 170 | 55 | 5 | 16 | 7 | 11 | 0.5 |
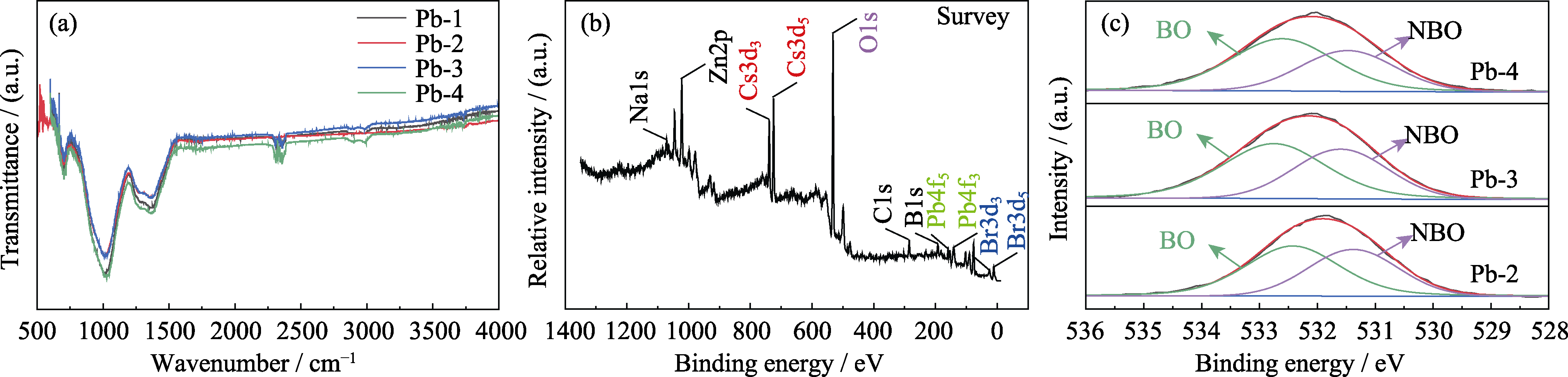
Fig. 5 Structural characterization of PQDs@glass at different Pb2+ concentrations (a, b) FT-IR and XPS spectra, and (c) the ratio of bridging to non-bridging oxygen bonds; Colorful figures are available on website
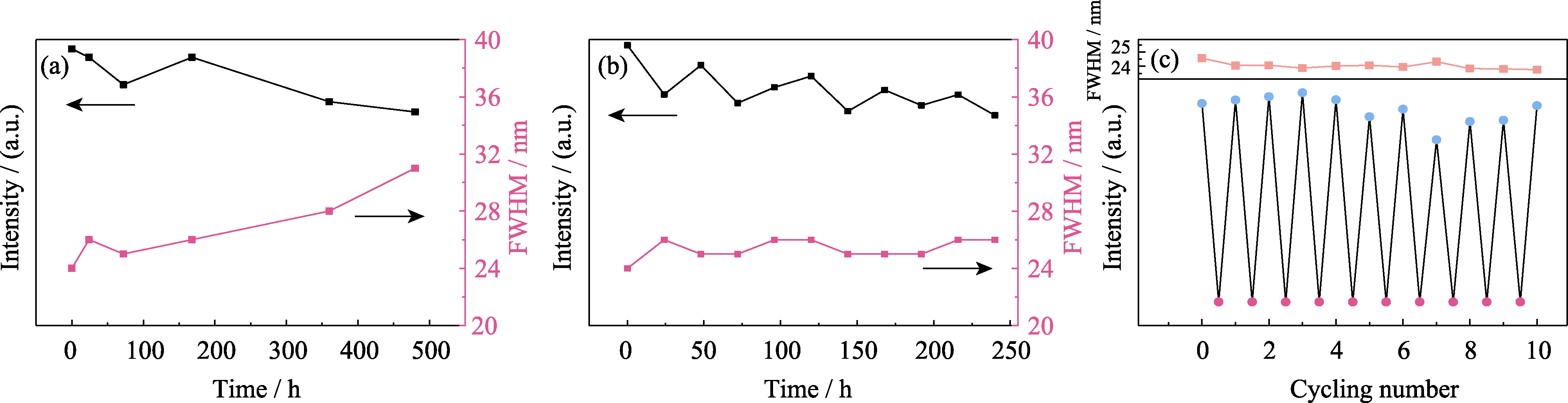
Fig. 6 Stability experiments of PQDs@glass (a, b) Variations in PL intensity and FWHM of water resistance (a) and UV stability (b), and (c) experimental results of thermal cycling stability
| [1] |
SU W, TENG Q, YUAN F. All-thermally evaporated perovskite LEDs toward high-resolution active-matrix displays. Matter, 2023, 6(8): 2539.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
KIM D, PARK S, CHOI B C, et al. The tetravalent manganese activated SrLaMgTaO6 phosphor for w-LED applications. Materials Research Bulletin, 2018, 97: 115.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHRISTENSEN A, GRAHAM S. Thermal effects in packaging high power light emitting diode arrays. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2009, 29(2/3): 364.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
WEN Z, XIE F, CHOY W C H. Stability of electroluminescent perovskite quantum dots light-emitting diode. Nano Select, 2021, 3(3): 505.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
WANG S, BI C, YUAN J, et al. Original core-shell structure of cubic CsPbBr3@Amorphous CsPbBrx perovskite quantum dots with a high blue photoluminescence quantum yield of over 80%. ACS Energy Letters, 2017, 3(1): 245.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
RAIN G, YAZDANI N, BOEHME S C, et al. Ultra-narrow room-temperature emission from single CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 2587.
DOI |
| [7] |
ZHOU X, CHANG Q, XIANG G, et al. A and B sites dual substitution by Na+ and Cu2+ co-doping in CsPbBr3 quantum dots to achieve bright and stable blue light emitting diodes. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2023, 300: 122773.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
WU W, ZHAO C, HU M, et al. CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots grown within Fe-doped zeolite X with improved stability for sensitive NH3 detection. Nanoscale, 2023, 15(12): 5705.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LIN C Q, LIU M L, YANG Z, et al. Mn2+ doped CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots with high quantum yield and stability for flexible array displays. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2023, 327: 124295.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LIU S, SHAO G, DING L, et al. Sn-doped CsPbBr3 QDs glasses with excellent stability and optical properties for WLED. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 361: 937.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
HUANG D, BO J, ZHENG R, et al. Luminescence and stability enhancement of CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots through surface sacrificial coating. Advanced Optical Materials, 2021, 9(16): 2100474.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ZOU L, LI X, YANG M, et al. ZnPc/CsPbBr3 QDs collaborative interface modification to improve the performance of CsPbBr3 perovskite solar cells. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2023, 251: 112157.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
XU Y, YU L, PENG K, et al. Ultra-stable perovskite quantum dot composites encapsulated with mesoporous SiO2 and PbBr(OH) for white light-emitting diodes. Luminescence, 2023, 38(5): 536.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
REN J, LI T, ZHOU X, et al. Encapsulating all-inorganic perovskite quantum dots into mesoporous metal organic frameworks with significantly enhanced stability for optoelectronic applications. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 358: 30.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LV W, LI L, XU M, et al. Improving the stability of metal halide perovskite quantum dots by encapsulation. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(28): 1900682.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LI S, NIE L, MA S, et al. Environmentally friendly CsPbBr3 QDs multicomponent glass with super-stability for optoelectronic devices and up-converted lasing. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(8): 3270.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
YANG B, MEI S, ZHU Y, et al. Precipitation promotion of highly emissive and stable CsPbX3 (Cl, Br, I) perovskite quantum dots in borosilicate glass with alkaline earth modification. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(4): 6720.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
TONG Y, WANG Q, LIU X, et al. The promotion of TiO2 induction for finely tunable self-crystallized CsPbX3(X = Cl, Br and I) nanocrystal glasses for LED backlighting display. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 429: 132391.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SHAO G, LIU S, DING L, et al. KxCs1-xPbBr3 NCs glasses possessing super optical properties and stability for white light emitting diodes. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 375: 122031.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LIU S, HE M, DI X, et al. Precipitation and tunable emission of cesium lead halide perovskites (CsPbX3, X = Br, I) QDs in borosilicate glass. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(4): 4496.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
LIU J, SHEN L, CHEN Y, et al. Highly luminescent and ultrastable cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystal glass for plant-growth lighting engineering. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(43): 13606.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
STOCH P, STOCH A. Structure and properties of Cs containing borosilicate glasses studied by molecular dynamics simulations. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2015, 411: 106.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LIU Q, FENG L, SUN Y, et al. Effects of phosphate glass on Cs+ immobilization in geopolymer glass-ceramics. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(4): 6545.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
YANG B, MEI S, HE H, et al. Lead oxide enables lead volatilization pollution inhibition and phase purity modulation in perovskite quantum dots embedded borosilicate glass. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(1): 258.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
KAUR N, KHANNA A, G NZ LEZ-BARRIUSO M, et al. Effects of Al3+, W6+, Nb5+ and Pb2+ on the structure and properties of borotellurite glasses. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2015, 429: 153.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
OTHMAN H, TOPPER B, ELKHOLY H, et al. Structural, spectroscopic, and radiation shielding properties of Pb2+‐doped borate and phosphate glasses. International Journal of Applied Glass Science, 2023, 14(3): 408.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
LI P, TIAN Y, HUANG F, et al. Highly efficient photostimulated luminescence of Pb2+ doped SrAl2O4:Eu2+, Dy3+ borate glass for long-term stable optical information storage. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(12): 5065.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
EL-EGILI K, DOWEIDAR H, MOUSTAFA Y M, et al. Structure and some physical properties of PbO-P2O5 glasses. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2003, 339(4): 237.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
CHENG Y, XIAO H, GUO W, et al. Structure and crystallization kinetics of PbO-B2O3 glasses. Ceramics International, 2007, 33(7): 1341.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 陈梓, 张爱迪, 龚克, 刘海华, 禹钢, 单青松, 刘勇, 曾海波. 具有可调谐和长寿命荧光发射的高亮度、单分散四元CuInZnS@ZnS量子点[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 433-339. |
| [2] | 潘泽晟, 游雅萍, 郑雅, 陈海杰, 王连军, 江莞. 面向紫光激发白光LED用荧光材料的耐候性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 314-322. |
| [3] | 吕昕怿, 相恒阳, 曾海波. 长程有序助力钙钛矿QLED高性能化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 111-112. |
| [4] | 瞿牡静, 张淑兰, 朱梦梦, 丁浩杰, 段嘉欣, 代恒龙, 周国红, 李会利. CsPbBr3@MIL-53纳米复合荧光粉的合成、性能及其白光LEDs应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 1035-1043. |
| [5] | 樊家顺, 夏冬林, 刘保顺. 温度相关的CsPbBr3纳米晶瞬态光电导响应研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 893-900. |
| [6] | 罗淑文, 马名生, 刘峰, 刘志甫. Ca-B-Si体系LTCC材料腐蚀行为及腐蚀机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 553-560. |
| [7] | 陆晨辉, 葛万银, 宋盼盼, 张盼锋, 徐美美, 张伟. 用于白光LED稀土Eu掺杂SiAlON基荧光粉的发光性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 97-104. |
| [8] | 庞力斌, 王德平. 介孔硼硅酸盐玻璃微球药物载体的制备及其性能表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 780-786. |
| [9] | 张枫娟, 韩博宁, 曾海波. 钙钛矿量子点光伏与荧光聚光电池: 现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 117-128. |
| [10] | 杜傲宸, 杜琪源, 刘欣, 杨益民, 夏晨阳, 邹军, 李江. 高光效、大功率LEDs/LDs用Ce:YAG透明陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 883-892. |
| [11] | 肖翔, 郭少柯, 丁成, 张志洁, 黄海瑞, 徐家跃. CsPbBr3@TiO2核壳结构纳米复合材料用作水稳高效可见光催化剂[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 507-512. |
| [12] | 王兆武, 姬海鹏, 王飞翔, 侯星慧, 易莎莎, 周颖, 陈德良. 调控Al2O3晶型控制MgAl2O4:Mn4+荧光粉中Mn价态研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 513-520. |
| [13] | 田建建, 马霞, 王敏, 姚鹤良, 华子乐, 张玲霞. 锡量子点制备及其电催化还原二氧化碳产甲酸性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1337-1342. |
| [14] | 舒孟洋, 陆嘉琳, 张志洁, 沈涛, 徐家跃. CsPbBr3钙钛矿量子点/C3N4超薄纳米片0D/2D复合材料: 增强的稳定性和光催化活性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1217-1222. |
| [15] | 姬海鹏, 张宗涛, XU Jian, TANABE Setsuhisa, 陈德良, 解荣军. Mn4+激活氧氟化物红光荧光粉的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 847-856. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||