无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 481-488.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240495 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240495
所属专题: 【能源环境】污染物催化去除(202506)
范小暄( ), 郑永炅, 徐丽荣, 姚子敏, 曹硕, 王可心(
), 郑永炅, 徐丽荣, 姚子敏, 曹硕, 王可心( ), 王绩伟(
), 王绩伟( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-27
修回日期:2025-01-24
出版日期:2025-05-20
网络出版日期:2025-02-13
通讯作者:
王可心, 讲师. E-mail: wyf93jl@163.com;作者简介:范小暄(1997-), 女, 博士研究生. E-mail: fanxiaoxuan0314@163.com
基金资助:
FAN Xiaoxuan( ), ZHENG Yonggui, XU Lirong, YAO Zimin, CAO Shuo, WANG Kexin(
), ZHENG Yonggui, XU Lirong, YAO Zimin, CAO Shuo, WANG Kexin( ), WANG Jiwei(
), WANG Jiwei( )
)
Received:2024-11-27
Revised:2025-01-24
Published:2025-05-20
Online:2025-02-13
Contact:
WANG Kexin, lecturer. E-mail: wyf93jl@163.com;About author:FAN Xiaoxuan (1997-), female, PhD candidate. E-mail: fanxiaoxuan0314@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
自激活长余辉光催化剂在全天候污水处理方面表现出巨大的潜力, 即使在黑暗条件下也具有持续的光催化活性。然而, 由于余辉发光的辐射复合与光催化降解反应对光生载流子的竞争性利用会降低余辉持续时间, 并引起空穴过量积累, 这极大地限制了长余辉驱动的光催化降解反应。本研究制备了一种基于氧空位(VO)LiYGeO4: Bi3+的长余辉光催化剂(VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+), 该催化剂被紫外光辐照激活后, 能够在无光照环境中持续释放紫外余辉, 并在自身释放余辉激活下光催化降解有机污染物。结果表明, 利用氧空位工程和晶体场工程可增大VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+陷阱浓度, 进而延长余辉衰减时间并增强余辉发光强度。通过构建芬顿反应体系, 增大了活性物种浓度, 进一步提升了VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+在余辉持续时间内的光降解效率。经过10 min光辐照激活后, VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+在无光照环境中能持续释放紫外余辉1 h并光催化降解罗丹明B(RhB), 在芬顿环境中的最大降解率可达63%。相较于无芬顿环境中的LiYScGeO4: Bi3+, 芬顿环境中的VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+对RhB的降解率提升了3.5倍。本工作为长余辉光催化剂的设计及其在污水处理领域中的应用提供了新的思路。
中图分类号:
范小暄, 郑永炅, 徐丽荣, 姚子敏, 曹硕, 王可心, 王绩伟. 基于富氧空位LiYScGeO4: Bi3+长余辉光催化剂的自激活余辉驱动有机污染物芬顿降解[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 481-488.
FAN Xiaoxuan, ZHENG Yonggui, XU Lirong, YAO Zimin, CAO Shuo, WANG Kexin, WANG Jiwei. Organic Pollutant Fenton Degradation Driven by Self-activated Afterglow from Oxygen-vacancy-rich LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ Long Afterglow Phosphor[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 481-488.
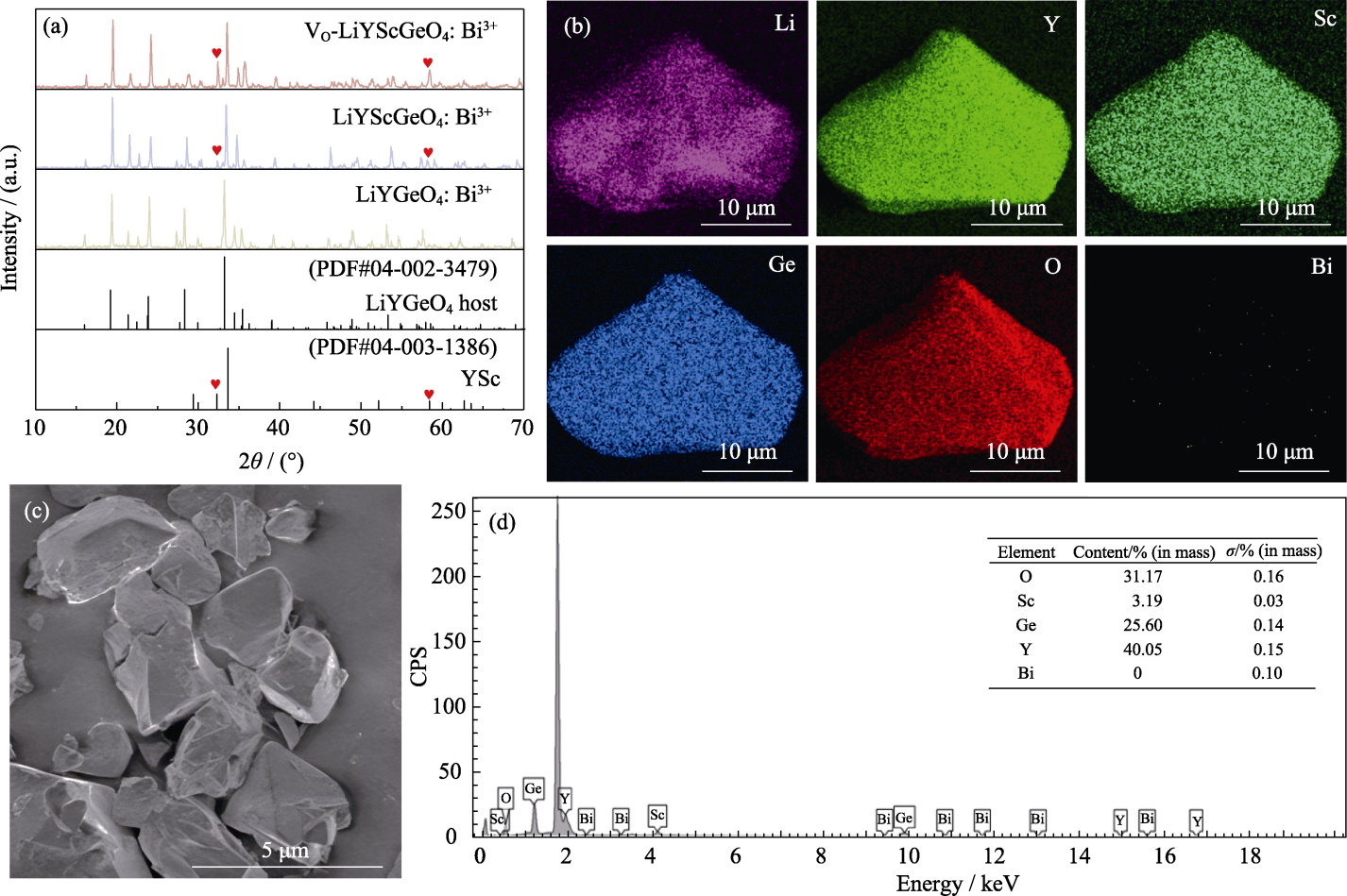
图1 催化剂的物相与形貌分析
Fig. 1 Phase and morphology analyses of catalysts (a) XRD patterns of LiYGeO4: Bi3+, LiYScGeO4: Bi3+, and VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+; (b) EDS elemental mappings of VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+; (c) SEM image of VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+; (d) EDS spectrum of VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+
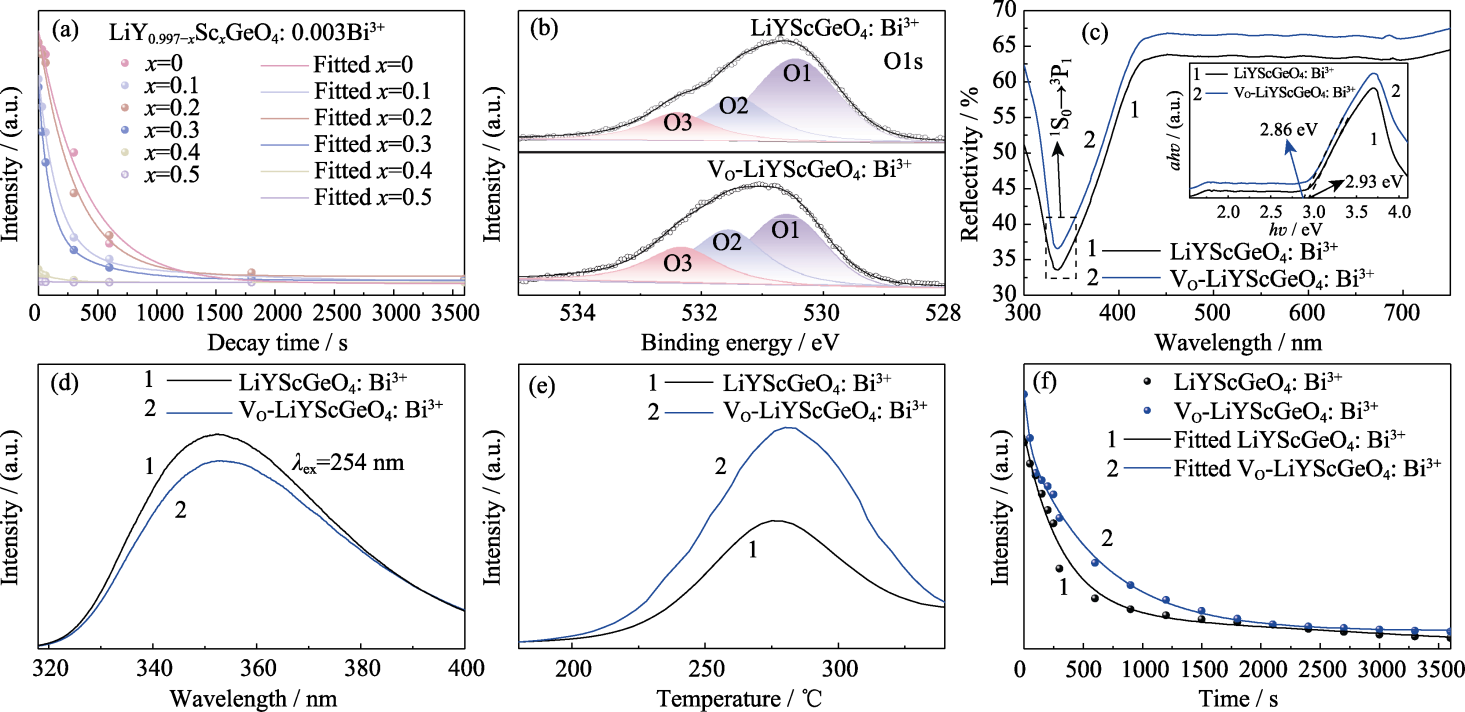
图2 LiYScGeO4: Bi3+和VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+的光学性质分析
Fig. 2 Optical properties of LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ and VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ (a) Long afterglow decay curves of LiY0.997-xScxGeO4: 0.003Bi3+ phosphors recorded at 355 nm after irradiation with 254 nm UV lamp for 10 min; (b) Fitted O1s XPS spectra; (c) UV-Vis DRS spectra with inset showing Tauc plots; (d) Emission spectra under 254 nm excitation; (e) TL spectra; (f) Afterglow decay curves Colorful figures are available on website
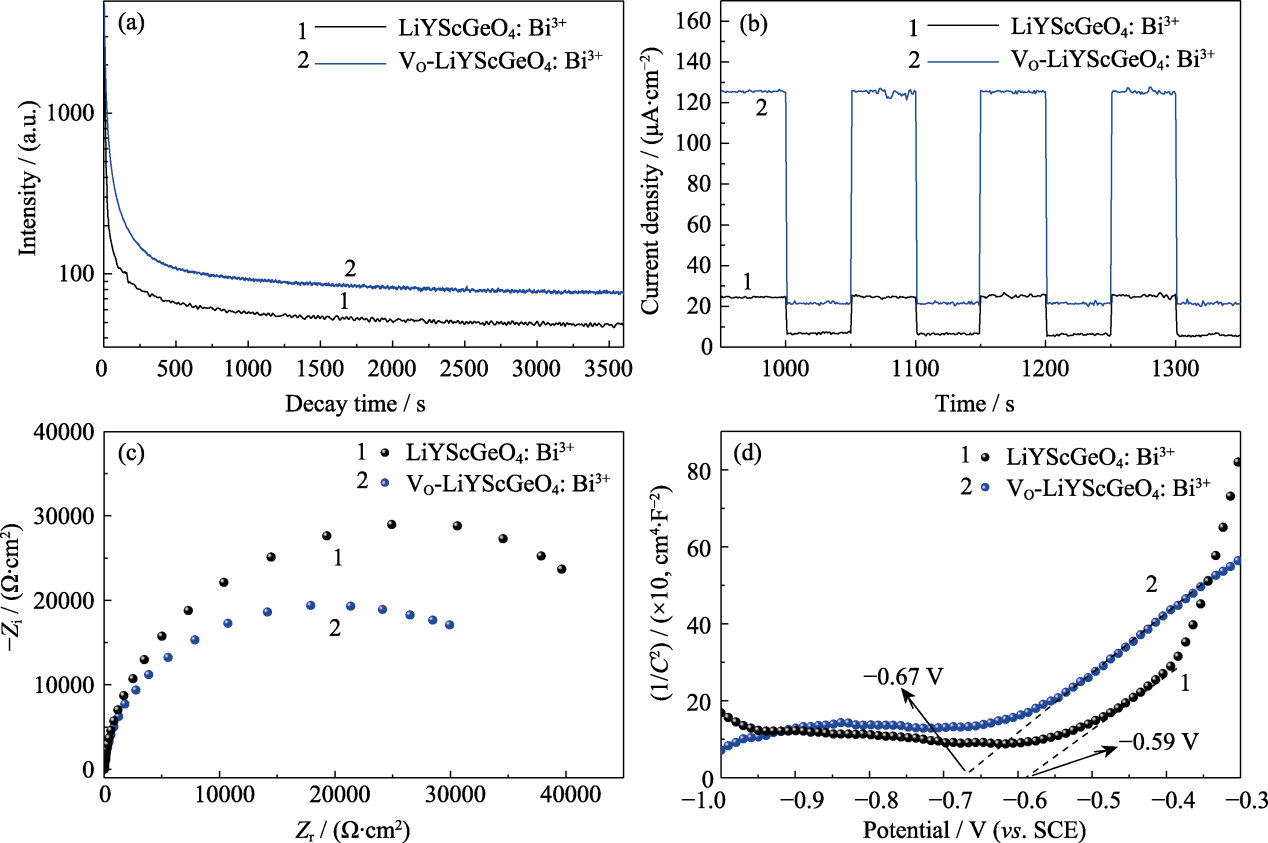
图3 LiYScGeO4: Bi3+和Vo-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+的电化学性能
Fig. 3 Electrochemical performance of LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ and Vo-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ (a) Afterglow photocurrent; (b) Steady-state photocurrent response; (c) Electrochemical impedance spectra; (d) Mott-Schottky plots
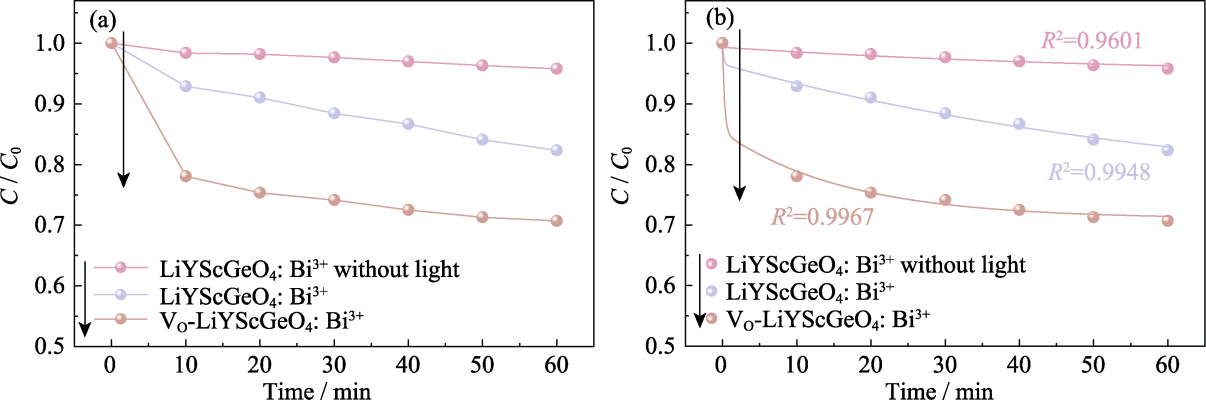
图4 LiYScGeO4: Bi3+和VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+对RhB的(a)光催化降解率和(b)动力学曲线
Fig. 4 (a) Photocatalytic degradation efficiency and (b) kinetic curves of LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ and VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+on RhB
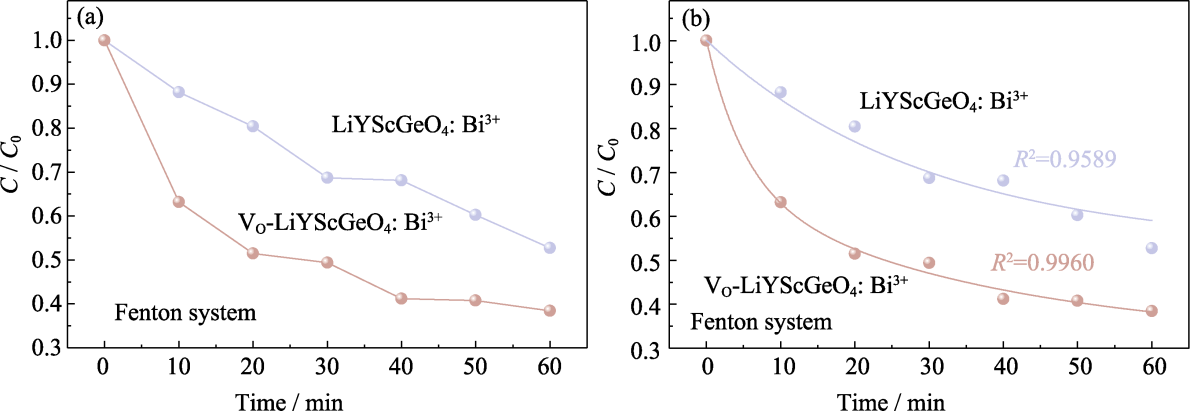
图5 LiYScGeO4: Bi3+和VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+在芬顿环境下对RhB的(a)光催化降解率和(b)动力学曲线
Fig. 5 (a) Photocatalytic degradation efficiency and (b) kinetic curves of LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ and VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+on RhB in Fenton environment
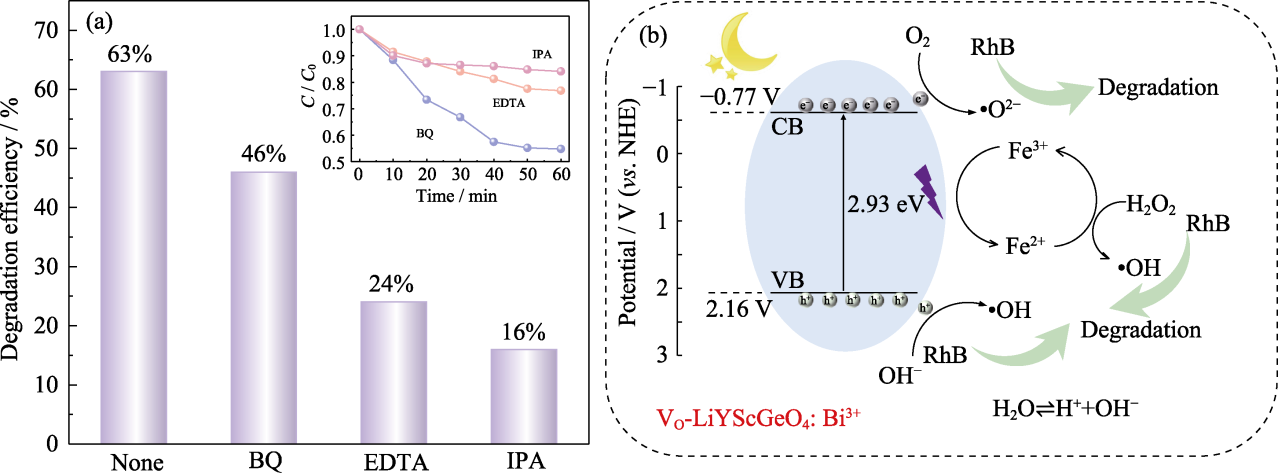
图6 光催化降解机制分析
Fig. 6 Analysis of photocatalytic degradation mechanism (a) Degradation efficiency of VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ on RhB with addition of reactive species scavengers BQ, EDTA and IPA, with inset showing degradation curves; (b) Schematic diagram of degradation process of long afterglow luminescence photocatalyst VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ in dark environment
| Sample | A1 | τ1/s | A2 | τ2/s | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ | 1.59×105 | 592 | 1.17×109 | 283 | 0.9834 |
| VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ | 4.11×104 | 518 | 1.69×105 | 573 | 0.9967 |
表S1 LiYScGeO4: Bi3+和VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+的余辉衰减参数
Table S1 Afterglow decay parameters of LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ and VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+
| Sample | A1 | τ1/s | A2 | τ2/s | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ | 1.59×105 | 592 | 1.17×109 | 283 | 0.9834 |
| VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ | 4.11×104 | 518 | 1.69×105 | 573 | 0.9967 |
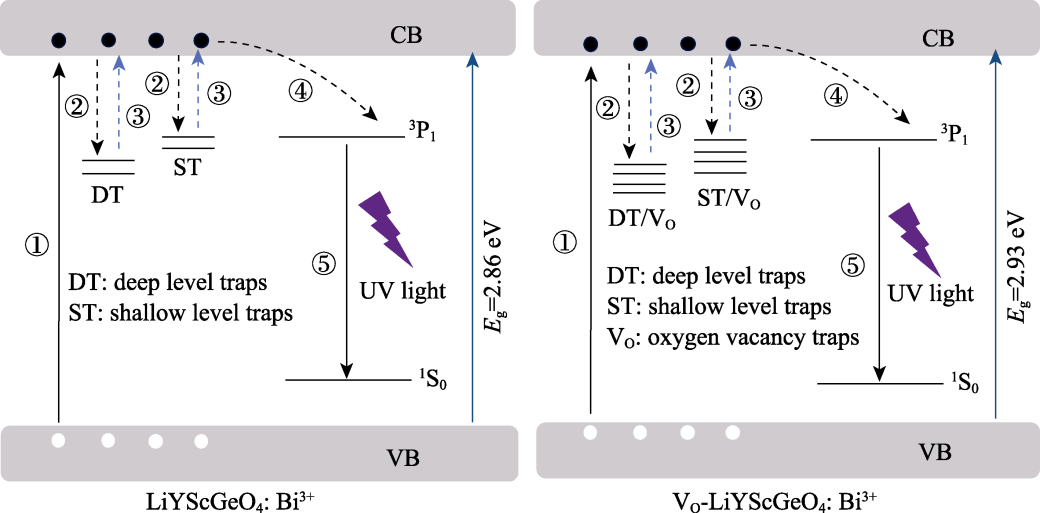
图S1 LiYScGeO4: Bi3+和VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+光催化剂的紫外长余辉发光机制示意图
Fig. S1 Schematic illustration of UV long afterglow luminescence mechanism for LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ and VO-LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ photocatalysts
| [1] | PARUL, KAUR K, BADRU R, et al. Photodegradation of organic pollutants using heterojunctions: a review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(2): 103666. |
| [2] | HU M, QUAN Y, YANG S, et al. Self-cleaning semiconductor heterojunction substrate: ultrasensitive detection and photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants for environmental remediation. Microsystems & Nanoengineering, 2020, 6: 111. |
| [3] | QIAN J, XUE Y, AO Y, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of CeO2/NaNbO3 composites with enhanced photocatalytic performance. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2018, 39(4): 682. |
| [4] | CHEN D, CHENG Y, ZHOU N, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants using TiO2-based photocatalysts: a review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 268: 121725. |
| [5] | 梁平平, 刘帅, 李红艺, 等. PVDF-CNT自漂浮多孔微珠的制备及在高效太阳能驱动界面水蒸发中的应用. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2689. |
| [6] | TANG J, LIU Y, ZHANG X, et al. Fabrication of loaded Ag sensitized round-the-clock highly active Z-scheme BiFeO3/Ag/ Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+, Dy3+/Ag photocatalyst for metronidazole degradation and hydrogen production. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 580: 233433. |
| [7] | HAI O, PEI M, YANG E, et al. Exploration of long afterglow luminescence materials work as round-the-clock photocatalysts. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 866: 158752. |
| [8] | XIAO B, TONG S, YAN L, et al. Round-the-clock photocatalysis of plasmonic Ag-enhanced Z-scheme heterojunction material Sr2MgSi2O7: (Eu, Dy)/g-C3N4@Ag under visible-light irradiation. Molecular Catalysis, 2024, 552: 113674. |
| [9] | VAIDYANATHAN S. Recent progress on lanthanide-based long persistent phosphors: an overview. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2023, 11(26): 8649. |
| [10] | DING Y, YE Y, WANG C, et al. “Light battery” role of long afterglow phosphor for round-the-clock environmental photocatalysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 450: 142041. |
| [11] | LI Y, GUO C, YUAN J, et al. Recent advances and prospects of persistent luminescent materials in public health applications. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 487: 150424. |
| [12] | JANY H F, KARLA V L, PETER H, et al. Wastewater sludge recycling: an efficient catalyst for photo-Fenton degradation of antibiotics and effluent disinfection. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 467: 143380. |
| [13] | DU C, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Fe-based metal organic frameworks (Fe-MOFs) for organic pollutants removal via photo- Fenton: a review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 431: 133932. |
| [14] | LIU X, ZHOU Y, ZHANG J, et al. Insight into electro-Fenton and photo-Fenton for the degradation of antibiotics: mechanism study and research gaps. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 347: 379. |
| [15] | CAO Z, ZHANG J, ZHOU J, et al. Electroplating sludge derived zinc-ferrite catalyst for the efficient photo-Fenton degradation of dye. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 193: 146. |
| [16] | PEI L, MA Z, ZHONG J, et al. Oxygen vacancy-rich Sr2MgSi2O7: Eu2+, Dy3+ long afterglow phosphor as a round-the-clock catalyst for selective reduction of CO2 to CO. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(49): 2208565. |
| [17] | JIANG T, XIE W, GENG S, et al. Constructing oxygen vacancy- regulated cobalt molybdate nanoflakes for efficient oxygen evolution reaction catalysis. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2022, 43(9): 2434. |
| [18] | ZHAO W, WEI Z, LI C, et al. An oxygen-vacancy rich ZnFe2O4/BiOI/AgI heterojunction for enhanced photocatalytic and photo-Fenton performance via double Z-scheme structure. Materials Research Bulletin, 2024, 169: 112508. |
| [19] | KONG Y, CHEN S, HE J, et al. Oxygen-vacancy rich in melilite to modulate the persistent luminescence for multi-functional applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2023, 11(27): 9262. |
| [20] | YANG T, JIANG H, HAI O, et al. Effect of oxygen vacancies on the persistent luminescence of Y3Al2Ga3O12: Ce3+,Yb3+ phosphors. Inorganic Chemistry, 2021, 60(23): 17797. |
| [21] | FAN X, XU L, LIU W, et al. Energy transfer in dual-emission LiY6(BO3)3O5: Bi3+, Eu3+ phosphors for temperature sensing applications. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(18): 32583. |
| [22] | ZHU Y, LIANG Y, LIU S, et al. Narrow-band green-emitting Sr2MgAl22O36:Mn2+ phosphors with superior thermal stability and wide color gamut for backlighting display applications. Advanced Optical Materials, 2019, 7(6): 1801419. |
| [23] | WANG S, WU H, FAN Y, et al. A highly efficient narrow-band blue phosphor of Bi3+-activated cubic borate Ba3Lu2B6O15 towards backlight display applications. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 432: 134265. |
| [24] | HAI O, PEI M, REN Q, et al. Ag nanoparticles significantly improve the slow decay brightness of SrAl2O4: Eu2+, Dy3+ by the surface plasmon effect. Dalton Transactions, 2022, 51(6): 2287. |
| [25] | YANG E, HAI O, REN Q, et al. Improved trap capability of shallow traps of Sr2MgSi2O7: Eu2, Dy3+ through depositing Au nanoparticles. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 858: 157705. |
| [26] | LU J C, BAI X L, ZHAO Q Y, et al. Construction of AgI/PCN-224 Z-scheme heterojunction for efficient photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride: pathways, mechanism and theoretical calculations. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 456: 142364. |
| [27] | WEI B, WANG C, HE Y, et al. A novel FeS2@g-C3N4 composite with enhanced photo-Fenton catalytic activity for pollutant degradation. Composites Communications, 2021, 24: 100652. |
| [28] | LUO J, ZHAO J, XIE Y, et al. Surface modified Bi2SiO5 microflowers with Fe3+ doping for efficient degradation of organic contaminants. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 926: 166866. |
| [29] | GUAN F, YANG H, LI J, et al. Preparation of Na+/g-C3N4 materials and their photocatalytic degradation mechanism on methylene blue. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1143. |
| [30] | DU Z, LI K, ZHOU S, et al. Degradation of ofloxacin with heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyzed by biogenic Fe-Mn oxides. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 380: 122427. |
| [31] | RICARDO I A, PANIAGUA C E S, PAIVA V A B, et al. Degradation and initial mechanism pathway of chloramphenicol by photo-Fenton process at circumneutral pH. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 339: 531. |
| [32] | ZHOU D M, CHEN L J, ZHAO X, et al. Persistent production of multiple active species with copper doped zinc gallate nanoparticles for light-independent photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2024, 668: 540. |
| [33] | ZOU P, LI Z, JIA P, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of bismuth oxychloride by in-situ introducing oxygen vacancy. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2021, 623: 126705. |
| [1] | 李廷松, 王文丽, 刘强, 王雁斌, 周真真, 胡辰, 李江. Cr3+掺杂浓度对YAGG:Ce3+,Cr3+发光陶瓷余辉性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 1037-1044. |
| [2] | 李汶金, 娄程广, 张帅, 苏兴华. 金属Cu和5YSZ陶瓷的“闪连”研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 957-963. |
| [3] | 周阳阳, 张艳艳, 于子怡, 傅正钱, 许钫钫, 梁瑞虹, 周志勇. 通过Bi3+自掺杂增强CaBi4Ti4O15基陶瓷压电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 719-728. |
| [4] | 陈莉波, 盛盈, 伍明, 宋季岭, 蹇建, 宋二红. Na和O元素共掺杂氮化碳高效光催化制氢[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 552-562. |
| [5] | 孙雨萱, 王政, 时雪, 史颖, 杜文通, 满振勇, 郑嘹赢, 李国荣. 缺陷偶极子热稳定性对Fe掺杂PZT陶瓷机电性能影响研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 545-551. |
| [6] | 贾相华, 张辉霞, 刘艳凤, 左桂鸿. 湿化学法制备Cu2O/Cu空心球异质结光催化剂[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 397-404. |
| [7] | 马彬彬, 钟婉菱, 韩涧, 陈椋煜, 孙婧婧, 雷彩霞. ZIF-8/TiO2复合介观晶体的制备及光催化活性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 937-944. |
| [8] | 曹青青, 陈翔宇, 吴健豪, 王筱卓, 王乙炫, 王禹涵, 李春颜, 茹菲, 李兰, 陈智. SiO2增强自敏性氮化碳微球可见光降解盐酸四环素的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 787-792. |
| [9] | 王兆阳, 秦鹏, 蒋胤, 冯小波, 杨培志, 黄富强. 三明治结构钌插层二氧化钛光催化四环素降解性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 383-389. |
| [10] | 叶茂森, 王耀, 许冰, 王康康, 张胜楠, 冯建情. II/Z型Bi2MoO6/Ag2O/Bi2O3异质结可见光催化降解四环素[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 321-329. |
| [11] | 史瑞, 刘伟, 李林, 李欢, 张志军, 饶光辉, 赵景泰. BaSrGa4O8: Tb3+力致发光材料的制备及性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1107-1113. |
| [12] | 李秋实, 殷广明, 吕伟超, 王怀尧, 李婧琳, 杨红光, 关芳芳. Na+/g-C3N4材料的制备及光催化降解亚甲基蓝机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1143-1150. |
| [13] | 曾琦琦, 吴彦徵, 程煌裕, 邵康, 胡恬雨, 潘再法. 钙掺杂自激活锗酸锌长余辉材料的多色余辉及动态防伪应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 901-909. |
| [14] | 李跃军, 曹铁平, 孙大伟. S型异质结Bi4O5Br2/CeO2的制备及其光催化CO2还原性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 963-970. |
| [15] | 伍林, 胡明蕾, 王丽萍, 黄少萌, 周湘远. TiHAP@g-C3N4异质结的制备及光催化降解甲基橙[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||