无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 195-203.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230437 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20230437
所属专题: 【信息功能】敏感陶瓷(202506); 【制备方法】3D打印(202506); 【结构材料】吸波材料(202506); 【信息功能】MAX、MXene及其他二维材料(202506)
收稿日期:2023-09-24
修回日期:2023-10-15
出版日期:2023-11-10
网络出版日期:2023-11-10
通讯作者:
张传芳, 教授. E-mail: chuanfang.zhang@scu.edu.cn作者简介:邓顺桂(1996-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: shungui.deng@empa.ch
基金资助:
DENG Shungui1,2( ), ZHANG Chuanfang1(
), ZHANG Chuanfang1( )
)
Received:2023-09-24
Revised:2023-10-15
Published:2023-11-10
Online:2023-11-10
Contact:
ZHANG Chuanfang, professor. E-mail: chuanfang.zhang@scu.edu.cnAbout author:DENG Shungui (1996-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: shungui.deng@empa.ch
Supported by:摘要:
基于功能油墨的先进印刷技术(打印、涂布), 能够突破传统制造手段的瓶颈, 实现具有复杂结构和特定功能的个性化薄膜及电子器件的快速成型, 在可穿戴智能识别、能源存储、电磁屏蔽及吸波、触摸显示等领域展现出巨大的应用前景。印刷先进能源及电子器件的关键在于, 开发先进功能油墨材料和与之相匹配的先进印刷技术。2011年发现的MXene材料, 是一类由过渡金属碳化物、氮化物或碳氮化物所组成的二维大家族的总称, 因其卓越的物理和化学性质(如高电导率、出色的亲水性和丰富的表面化学)而受到广泛关注, 特别适合作为印刷电子器件的油墨材料。探索MXene油墨的印刷行为特征并厘清MXene油墨在印刷关键环节中的机理, 不仅有助于获得高精度的MXene油墨印刷图案, 而且可以为印刷多尺度、多材料的多功能薄膜和电子器件打下了坚实基础。本文首先介绍了MXene的制备及其片层胶体的化学稳定性, 并对其流变学特性、可打印油墨的形成、油墨印刷行为以及与之适配的打印方法进行了讨论, 着眼于MXene油墨在能源、健康监测和传感应用方面的最新进展, 分析了该领域面临的挑战和未来的发展方向, 为该领域的研究者提供新的视角和启示。
中图分类号:
邓顺桂, 张传芳. 多功能MXene油墨:面向印刷能源及电子器件的新视角[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 195-203.
DENG Shungui, ZHANG Chuanfang. MXene Multifunctional Inks: a New Perspective toward Printable Energy-related Electronic Devices[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(2): 195-203.

图2 MXene油墨的四种主要印刷技术的示意图
Fig. 2 Diagram of the four main printing technologies for MXene ink Screen printing[37], inkjet printing[38], transfer printing[39] and extrusion printing[40]

图4 MXene油墨打印示意图[38]
Fig. 4 Schematic illustration of direct MXene ink printing[38] Aqueous Ti3C2Tx inks are designed for extrusion printing while the Ti3C2Tx organic inks are used for inkjet printing
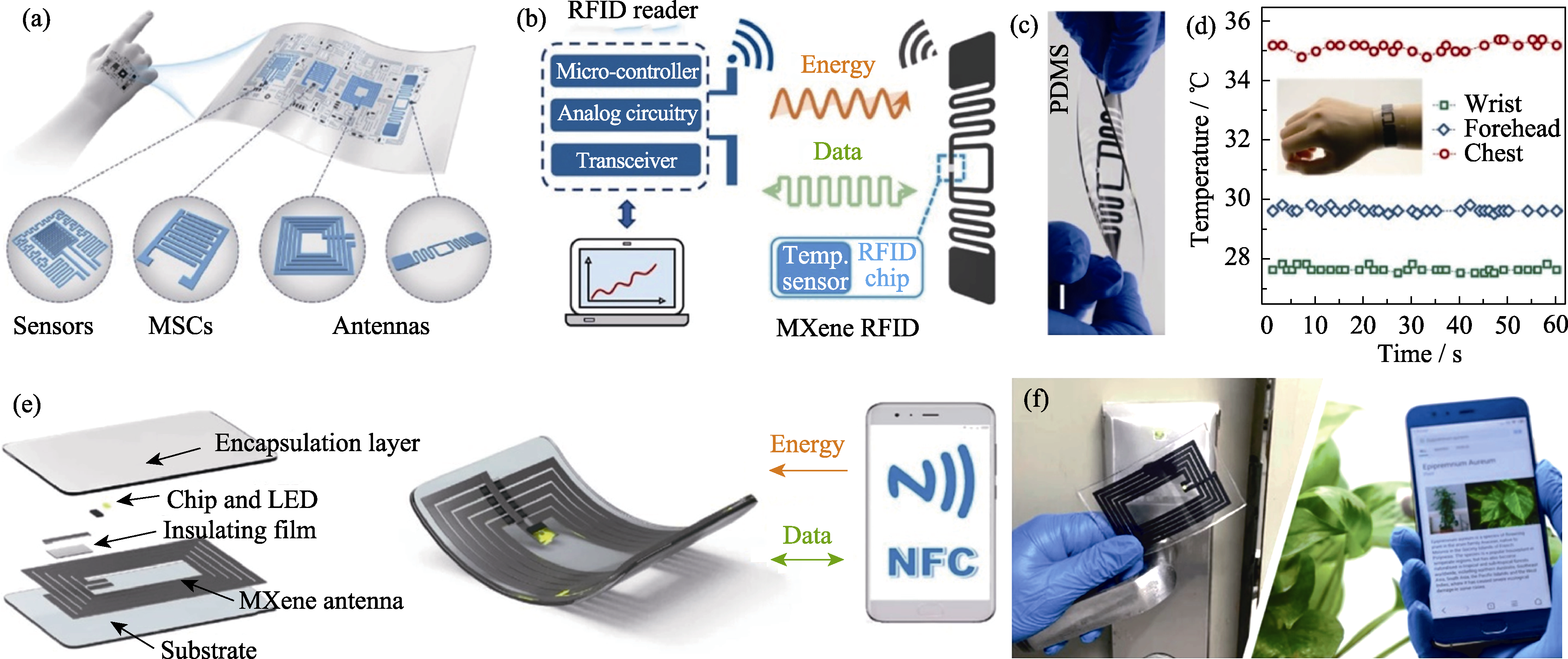
图6 (a)用于柔性无线电子的室温直接打印的MXene油墨; (b)MXene RFID传感器及(c)其照片; (d)MXene RFID传感器监测表面温度示例; (e)MXene NFC的制作及(f)应用示例[53]
Fig. 6 (a) Schematic illustration of room-temperature direct printing of additive-free MXene inks for flexible wireless electronics; (b) Mechanism and (c) optical image of flexible MXene RFID temperature tag; (d) MXene RFID sensors to monitor surface temperature; (e) Fabrication of MXene NFC tags and (f) examples of application[53]
| [1] |
LI N, PENG J H, ONG W J, et al. Mxenes: an emerging platform for wearable electronics and looking beyond. Matter, 2021, 4(2): 377.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ABDOLHOSSEINZADEH S, ZHANG C F, SCHNEIDER R, et al. A universal approach for room-temperature printing and coating of 2d materials. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(4): 2103660.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CAI X K, LUO Y T, LIU B, et al. Preparation of 2d material dispersions and their applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(16): 6224.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
TORRISI F, HASAN T, WU W P, et al. Inkjet-printed graphene electronics. ACS Nano, 2012, 6 (4): 2992.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
ZHANG Y Z, WANG Y, CHENG T, et al. Printed supercapacitors: Materials, printing and applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 2019, 48(12): 3229.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
SECOR E B, AHN B Y, GAO T Z, et al. Rapid and versatile photonic annealing of graphene inks for flexible printed electronics. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(42): 6683.
DOI |
| [7] |
LI J T, NAIINI M M, VAZIRI S, et al. Inkjet printing of MoS2. Advanced Functional Materials, 2014, 24(41): 6524.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
JUN H Y, RYU S O, KIM S H, et al. Inkjet printing of few-layer enriched black phosphorus nanosheets for electronic devices. Advanced Electronic Materials, 2021, 7(10): 2100577.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
UZUN S, SCHELLING M, HANTANASIRISAKUL K, et al. Additive-free aqueous mxene inks for thermal inkjet printing on textiles. Small, 2021, 17(1): 2006376.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
WANG Z, LIANG X W, ZHAO T, et al. Facile synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles for screen printing conductive inks. Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics, 2017, 28(22): 16939.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LIU F X, QIU X B, XU J F, et al. High conductivity and transparency of graphene-based conductive ink: prepared from a multi-component synergistic stabilization method. Progress in Organic Coatings, 2019, 133: 125.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LI X K, LI M J, ZONG L, et al. Liquid metal droplets wrapped with polysaccharide microgel as biocompatible aqueous ink for flexible conductive devices. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(39): 1804197.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ZHAO L H, HONG C Y, WANG C H, et al. Enhancement of the adhesion strength of water-based ink binder based on waterborne polyurethane. Progress in Organic Coatings, 2023, 183: 107765.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
AGHAYAR Z, MALAKI M, ZHANG Y Z. MXene-based ink design for printed applications. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12 (23): 4346.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ZHANG C F. Interfacial assembly of two-dimensional MXenes. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 60: 417.
DOI |
| [16] |
NAGUIB M, MASHTALIR O, CARLE J, et al. Two-dimensional transition metal carbides. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(2): 1322.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | COME J, NAGUIB M, ROZIER P, et al. A non-aqueous asymmetric cell with a Ti2C-based two-dimensional negative electrode. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(8): 1368. |
| [18] |
ZHANG C, MA Y L, ZHANG X T, et al. Two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes): synthesis, properties, and electrochemical energy storage applications. Energy & Environmental Materials, 2020, 3(1): 29.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ABDOLHOSSEINZADEH S, JIANG X T, ZHANG H, et al. Perspectives on solution processing of two-dimensional MXenes. Materials Today, 2021, 48: 214.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
ZHANG Y Z, WANG Y, JIANG Q, et al. Mxene printing and patterned coating for device applications. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(21): 1908486.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ALHABEB M, MALESKI K, ANASORI B, et al. Guidelines for synthesis and processing of two-dimensional titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene). Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(18): 7633.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ABDOLHOSSEINZADEH S, HEIER J, ZHANG C F. Printing and coating mxenes for electrochemical energy storage devices. Journal of Physics-Energy, 2020, 2(3): 031004.
DOI |
| [23] |
SREENILAYAM S P, UL AHAD I, NICOLOSI V, et al. MXene materials based printed flexible devices for healthcare, biomedical and energy storage applications. Materials Today, 2021, 43: 99.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
NAGUIB M, KURTOGLU M, PRESSER V, et al. Two- dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(37): 4248.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
GHIDIU M, LUKATSKAYA M R, ZHAO M Q, et al. Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide 'clay' with high volumetric capacitance. Nature, 2014, 516(7529): 78.
DOI |
| [26] |
URBANKOWSKI P, ANASORI B, MAKARYAN T, et al. Synthesis of two-dimensional titanium nitride Ti4N3 (MXene). Nanoscale, 2016, 8(22): 11385.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
LI T F, YAO L L, LIU Q L, et al. Fluorine-free synthesis of high- purity Ti3C2Tx (T=OH, O) via alkali treatment. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(21): 6115.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
SHEN M, JIANG W Y, LIANG K, et al. One-pot green process to synthesize MXene with controllable surface terminations using molten salts. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(52): 27013.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
ZHANG C F J, PINILLA S, MCEYOY N, et al. Oxidation stability of colloidal two-dimensional titanium carbides (MXenes). Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(11): 4848.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
NATU V, HART J L, SOKOL M, et al. Edge capping of 2D-MXene sheets with polyanionic salts to mitigate oxidation in aqueous colloidal suspensions. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(36): 12655.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
ZHAO X F, VASHISTH A, PREHN E, et al. Antioxidants unlock shelf-stable Ti3C2Tx (MXene) nanosheet dispersions. Matter, 2019, 1(2): 513.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
FAN Z M, HE H Y, YU J X, et al. Binder-free Ti3C2Tx MXene doughs with high redispersibility. ACS Materials Letters, 2020, 2(12): 1598.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
DENG S G, GUO T Z, NUEESCH F, et al. Stable MXene dough with ultrahigh solid fraction and excellent redispersibility toward efficient solution processing and industrialization. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(19): 2300660.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
AKUZUM B, MALESKI K, ANASORI B, et al. Rheological characteristics of 2D titanium carbide (MXene) dispersions: a guide for processing mxenes. ACS Nano, 2018, 12 (3): 2685.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
GLASSER A, CLOUTET É, HADZIIOANNOU G, et al. Tuning the rheology of conducting polymer inks for various deposition processes. Chemistry of Materials, 2019, 31(17): 6936.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
LI H P, LIANG J J. Recent development of printed micro- supercapacitors: printable materials, printing technologies, and perspectives. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(3): 1805864.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ABDOLHOSSEINZADEH S, SCHNEIDER R, VERMA A, et al. Turning trash into treasure: additive free MXene sediment inks for screen-printed micro-supercapacitors. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(17): 2000716.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
ZHANG C F, MCKEON L, KREMER M P, et al. Additive-free MXene inks and direct printing of micro-supercapacitors. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1795.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
ZHANG C F, KREMER M P, SERAL-ASCASO A, et al. Stamping of flexible, coplanar micro-supercapacitors using MXene inks. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(9): 1705506.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
YANG W J, YANG J, BYUN J J, et al. 3D printing of freestanding MXene architectures for current-collector-free supercapacitors. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(37): 1902725.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
WU Z Y, LIU S R, HAO Z J, et al. MXene contact engineering for printed electronics. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(19): 2207174.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
LUOMA E, VALIMAKI M, OLLILA J, et al. Bio-based polymeric substrates for printed hybrid electronics. Polymers, 2022, 14(9): 1863.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
LINGHU C H, ZHANG S, WANG C J, et al. Transfer printing techniques for flexible and stretchable inorganic electronics. npj Flexible Electronics, 2018, 2: 26.
DOI |
| [44] |
CAREY T, CACOVICH S, DIVITINI G, et al. Fully inkjet-printed two-dimensional material field-effect heterojunctions for wearable and textile electronics. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 1202.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
MA J X, ZHENG S H, CAO Y X, et al. Aqueous MXene/ph1000 hybrid inks for inkjet-printing micro-supercapacitors with unprecedented volumetric capacitance and modular self-powered microelectronics. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(23): 2100746.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
HU G H, KANG J, NG L W T, et al. Functional inks and printing of two-dimensional materials. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(9): 3265.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
SAADI M, MAGUIRE A, POTTACKAL N T, et al. Direct ink writing: a 3D printing technology for diverse materials. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(28): 2108855.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
AZADMANJIRI J, REDDY T N, KHEZRI B, et al. Prospective advances in MXene inks: screen printable sediments for flexible micro-supercapacitor applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(9): 4533.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
ZHANG C F, PARK S N, SERAL-ASCASO A, et al. High capacity silicon anodes enabled by MXene viscous aqueous ink. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 849.
DOI PMID |
| [50] |
TANG H, LI W L, PAN L M, et al. A robust, freestanding MXene-sulfur conductive paper for long-lifetime Li-S batteries. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(30): 1901907.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
TANG H, LI W L, PAN L M, et al. In situ formed protective barrier enabled by sulfur@titanium carbide MXene ink for achieving high-capacity, long lifetime Li-S batteries. Advanced Science, 2018, 5(9): 1800502.
DOI URL |
| [52] | CHEN M J, LI L L, DENG Z M, et al. Two-dimensional janus MXene inks for versatile functional coatings on arbitrary substrates. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(3): 4591. |
| [53] |
SHAO Y Z, WEI L S, WU X Y, et al. Room-temperature high-precision printing of flexible wireless electronics based on MXene inks. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 3223
DOI PMID |
| [54] | SONG Y, TAY R Y, LI J, et al. 3D-printed epifluidic electronic skin for machine learning-powered multimodal health surveillance. Science Advances, 2023, 9(37): 6492. |
| [1] | 刘会来, 李志豪, 孔德峰, 陈星. 酞菁铁/MXene复合阴极的制备及电芬顿降解磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 61-69. |
| [2] | 魏相霞, 张晓飞, 徐凯龙, 陈张伟. 增材制造柔性压电材料的现状与展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 965-978. |
| [3] | 陈乾, 苏海军, 姜浩, 申仲琳, 余明辉, 张卓. 超高温氧化物陶瓷激光增材制造及组织性能调控研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 741-753. |
| [4] | 李雷, 程群峰. 高性能MXenes纳米复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 153-161. |
| [5] | 徐向明, Husam N ALSHAREEF. MXetronics—MXene电子学[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 171-178. |
| [6] | 李腊, 沈国震. 二维MXenes材料在柔性光电探测器中的应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 186-194. |
| [7] | 巴坤, 王建禄, 韩美康. MXene的红外特性及其应用研究展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 162-170. |
| [8] | 尹建宇, 刘逆霜, 高义华. MXene在压力传感中的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 179-185. |
| [9] | 刘艳艳, 谢曦, 刘增乾, 张哲峰. MAX相陶瓷增强金属基复合材料: 制备、性能与仿生设计[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 145-152. |
| [10] | 陈泽, 支春义. MXene在锌离子电池中的应用: 研究进展与展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 204-214. |
| [11] | 丁浩明, 陈科, 李勉, 李友兵, 柴之芳, 黄庆. 无机材料的“化学剪刀”结构编辑策略[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 115-128. |
| [12] | 万胡杰, 肖旭. MXenes及其复合物的太赫兹电磁屏蔽与吸收[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 129-144. |
| [13] | 费玲, 雷蕾, 汪德高. 二维MXene材料在新型薄膜太阳能电池技术中的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 215-224. |
| [14] | 周云凯, 刁亚琪, 王明磊, 张宴会, 王利民. 聚苯胺改性Ti3C2(OH)2抗氧化性的第一性原理计算研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1151-1158. |
| [15] | 陶顺衍, 杨加胜, 邵芳, 吴应辰, 赵华玉, 董绍明, 张翔宇, 熊瑛. 航机CMC热端部件用热喷涂涂层的机遇与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1077-1083. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||