无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (10): 1159-1166.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240062 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240062
所属专题: 【能源环境】热电材料(202506)
收稿日期:2024-02-02
修回日期:2024-04-23
出版日期:2024-10-20
网络出版日期:2024-05-16
通讯作者:
周 敏, 研究员. E-mail: mzhou@mail.ipc.ac.cn作者简介:苏浩健(1995-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: suhaojian19@mails.ucas.ac.cn
基金资助:
SU Haojian1,2( ), ZHOU Min1(
), ZHOU Min1( ), LI Laifeng1
), LI Laifeng1
Received:2024-02-02
Revised:2024-04-23
Published:2024-10-20
Online:2024-05-16
Contact:
ZHOU Min, professor. E-mail: mzhou@mail.ipc.ac.cnAbout author:SU Haojian (1995-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: suhaojian19@mails.ucas.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
热电材料可实现热能和电能的直接相互转换, 在温差发电和半导体制冷领域具有广阔的应用前景。SnTe作为PbTe的无毒同族类似物, 是一种极具潜力的中温区热电材料。本研究采用超重力场辅助燃烧合成(HG-CS)技术, 结合放电等离子体烧结(SPS)制备多元素掺杂的SnTe基热电材料, 系统研究了多元素掺杂对SnTe热电性能的影响规律和作用机制。在SnTe的阳离子位引入等价离子Ge2+和Pb2+, 阴离子位引入S2-和Se2-, 多元素掺杂引起大量晶格畸变点缺陷。同时, 在超重力场下快速凝固带来的塑性变形引入了应力场和大量位错, 从而形成了多级微观结构缺陷, 强烈散射中高频声子, 室温热导率从7.28 W·m-1·K-1 (未掺杂SnTe)大幅下降到2.74 W·m-1·K-1 (Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te0.80Se0.10S0.10), 在873 K时, 其最小热导率仅为1.38 W·m-1·K-1。这些微结构缺陷散射声子的同时也散射载流子, 导致载流子迁移率和电导率降低。值得一提的是, 掺杂使SnTe的带隙减小, Seebeck系数提高, 因此掺杂后材料的功率因子仍保持较高值。实验得到Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te0.80Se0.10S0.10的最大热电优值(ZT)达到1.02(873 K), 与未掺杂的SnTe相比得到大幅提高。
中图分类号:
苏浩健, 周敏, 李来风. 多元素掺杂优化SnTe的热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1159-1166.
SU Haojian, ZHOU Min, LI Laifeng. Optimization of Thermoelectric Properties of SnTe via Multi-element Doping[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1159-1166.
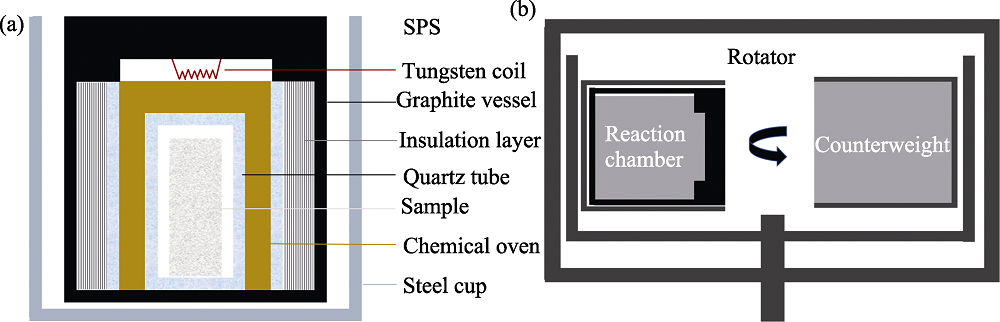
图1 实验方法原理示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagrams of preparative principles (a) Raw material filling in the reaction chamber; (b) Equipment for high gravity field assisted combustion synthesis

图2 样品Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te1-2xSexSx(x=0.05, 0.07, 0.10)的XRD图谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te1-2xSexSx (x=0.05, 0.07, 0.10) samples (b) Magnified patterns of 2θ=28°-30°
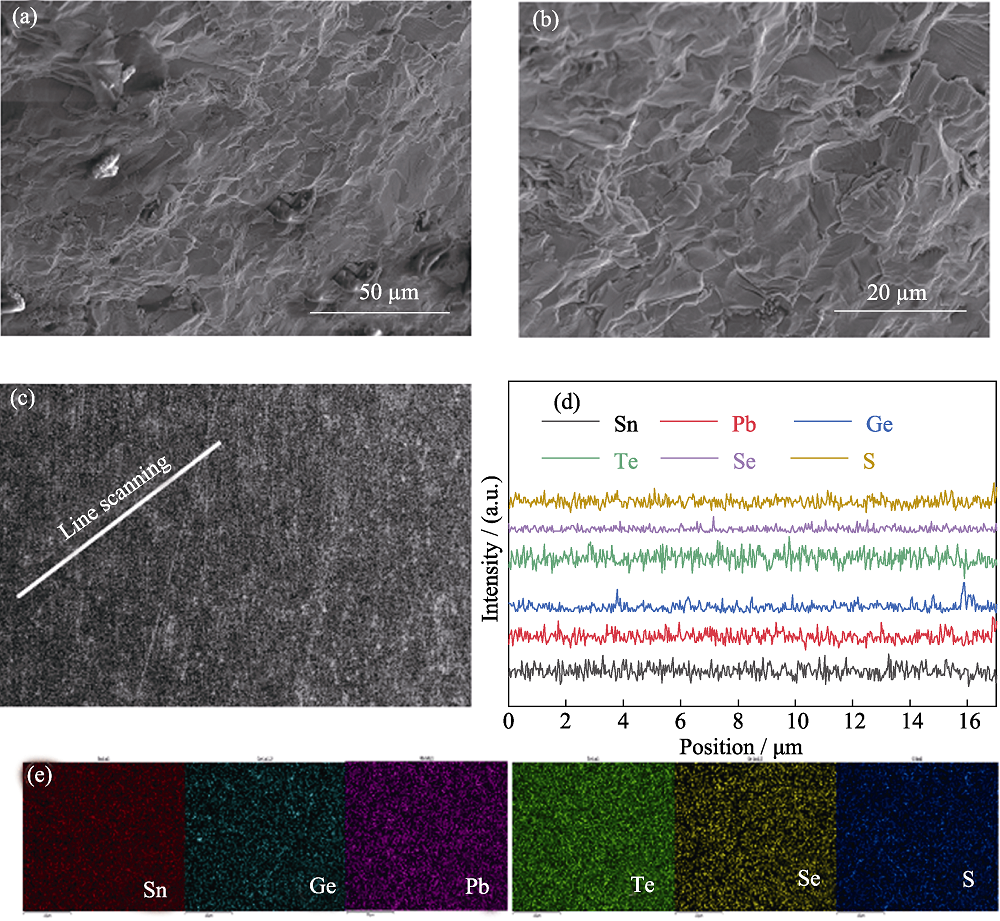
图3 Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te0.80Se0.10S0.10样品的(a~c)SEM照片和(d~e)EDS能谱结果
Fig. 3 SEM images (a-c) and EDS spectra (d-e) of Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te0.80Se0.10S0.10 Colorful figures are available on website

图4 熵变(∆S)与Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te1-2xSexSx中x的关系
Fig. 4 Relationship of entropy change (∆S) and x in Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te1-2xSexSx ∆S1: Entropy change of SnTe; ∆S2: Entropy change of Sn0.85Ge0.15Te; R: Gas constant, 8.314 J·mol-1·K-1

图5 SnTe, Sn0.85Ge0.15Te, Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te和Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te1-2xSexSx (x=0.05, 0.07, 0.10)的电输运性能
Fig. 5 Electrical transport performance for bulk SnTe, Sn0.85Ge0.15Te, Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te and Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te1-2xSexSx (x=0.05, 0.07, 0.10) samples (a, c, d) Temperature dependence of (a) Seebeck coefficient, (c) electrical conductivity and (d) power factor; (b) Dependence of Seebeck coefficient on the entropy change
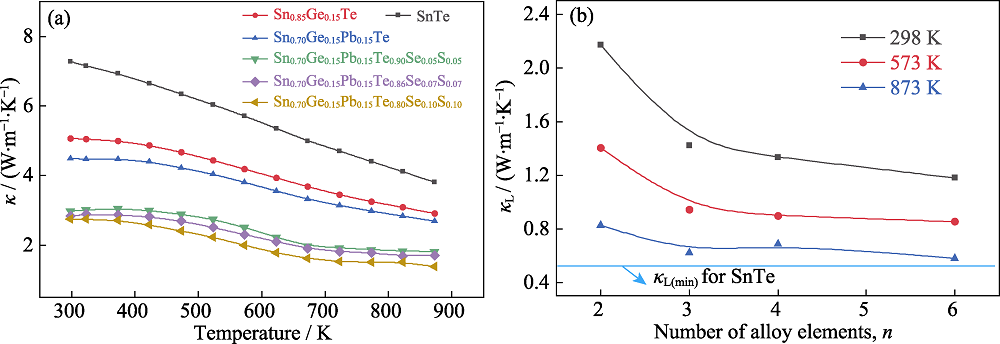
图6 SnTe, Sn0.85Ge0.15Te, Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te和Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te1-2xSexSx (x=0.05, 0.07, 0.10)的热输运性能
Fig. 6 Thermal transport performance for bulk SnTe, Sn0.85Ge0.15Te, Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te and Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te1-2xSexSx (x=0.05, 0.07, 0.10) samples (a) Temperature dependence of thermal conductivity; (b) Lattice thermal conductivities at 298, 573 and 873 K as a function of the number of alloying elements
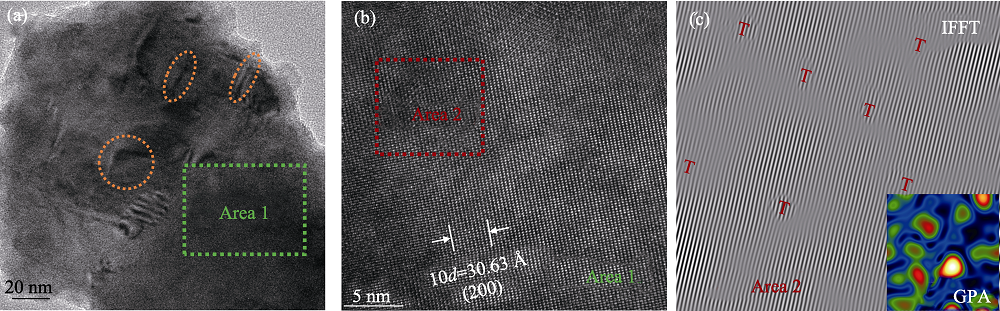
图7 样品Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te0.80Se0.10S0.10的微观结构
Fig. 7 Microstructure of the sample Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te0.80Se0.10S0.10 (a) Low magnification TEM image; (b) HRTEM image of the selected area 1 in (a); (c) Inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) and geometric phase analysis (GPA) images of the selected area 2 in (b)
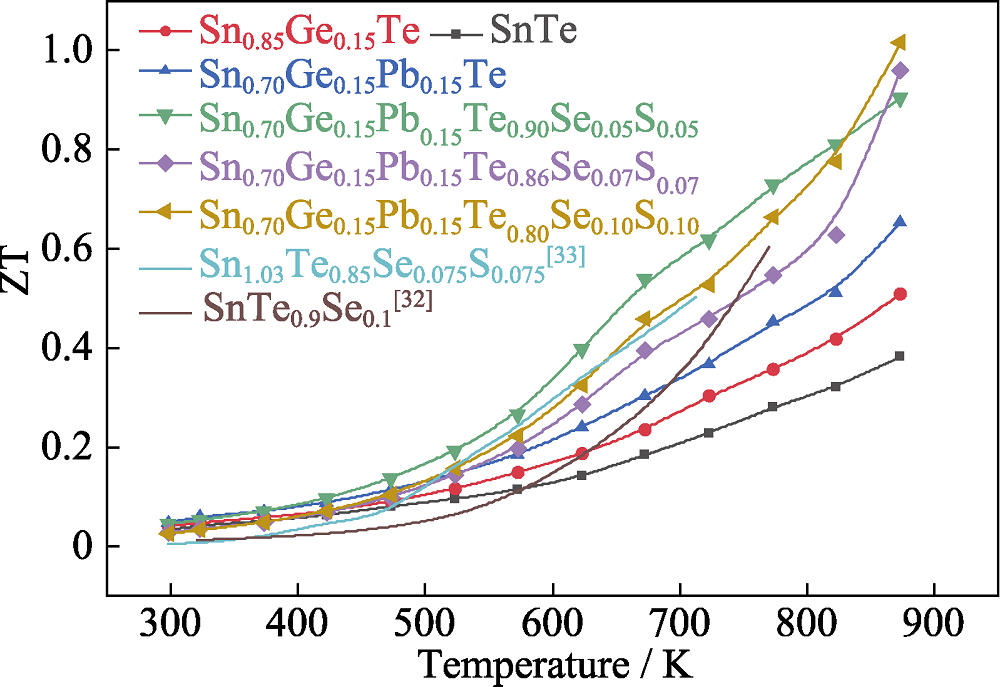
图8 SnTe、Sn0.85Ge0.15Te、Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te、Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te1-2xSexSx (x=0.05, 0.07, 0.10)及相关文献[32-33]样品的ZT值随温度的变化关系
Fig. 8 Temperature dependence of ZT for bulk SnTe, Sn0.85Ge0.15Te, Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te, Sn0.70Ge0.15Pb0.15Te1-2xSexSx (x=0.05, 0.07, 0.10), and samples in literature[32-33] Colorful figure is available on website
| [1] | ZHU T J, LIU Y T, FU C G, et al. Compromise and synergy in high-efficiency thermoelectric materials. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(14): 1606884. |
| [2] | WANG H, LALONDE A D, PEI Y Z, et al. The criteria for beneficial disorder in thermoelectric solid solutions. Advanced Functional Materials, 2013, 23(12): 1586. |
| [3] | HONG M, CHEN Z G, YANG L, et al. Realizing ZT of 2.3 in Ge1-x-ySbxInyTe via reducing the phase-transition temperature and introducing resonant energy doping. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(11): 1705942. |
| [4] | ZHOU Y M, ZHAO L D. Promising thermoelectric bulk materials with 2D structures. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(45): 1702676. |
| [5] | SU H J, MIAO Z C, PENG Y, et al. SnTe thermoelectric materials with low lattice thermal conductivity synthesized by a self- propagating method under a high-gravity field. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2022, 24(47): 29186. |
| [6] | ZHAO L D, HAO S Q, LO S H, et al. High thermoelectric performance via hierarchical compositionally alloyed nanostructures. Journal of American Chemistry Society, 2013, 135(19): 7364. |
| [7] | BANIK A, VISHAL B, PERUMAL S, et al. The origin of low thermal conductivity in Sn1-xSbxTe: phonon scattering via layered intergrowth nanostructures. Energy & Environmental Science, 2016, 9(6): 2011. |
| [8] | SHI X, YANG J, SALVADOR J R, et al. Multiple-filled skutterudites: high thermoelectric figure of merit through separately optimizing electrical and thermal transports. Journal of American Chemistry Society, 2011, 133(20): 7837. |
| [9] | LIU H L, SHI X, ZHANG L L, et al. Copper ion liquid-like thermoelectrics. Nature Materials, 2012, 11(5): 422. |
| [10] | LIU R H, CHEN H Y, ZHAO K P, et al. Entropy as a gene-like performance indicator promoting thermoelectric materials. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(38): 1702712. |
| [11] | CHEN Z W, JIAN Z Z, LI W, et al. Lattice dislocations enhancing thermoelectric PbTe in addition to band convergence. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(23): 1606768. |
| [12] | PEI Y Z, GIBBS Z M, GLOSKOVSKII A, et al. Optimum carrier concentration in n-type PbTe thermoelectrics. Advanced Energy Materials, 2014, 4(13): 1400486. |
| [13] | LI W, ZHENG L L, GE B H, et al. Promoting SnTe as an eco- friendly solution for p-PbTe thermoelectric via band convergence and interstitial defects. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(17): 1605887. |
| [14] | TANG J, YAO Z, CHEN Z, et al. Maximization of transporting bands for high-performance SnTe alloy thermoelectrics. Materials Today Physics, 2019, 9: 100091. |
| [15] | JIANG Q H, HU H S, YANG J Y, et al. High thermoelectric performance in SnTe nanocomposites with all-scale hierarchical structures. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(20): 23102. |
| [16] | WU H J, CHANG C, FENG D, et al. Synergistically optimized electrical and thermal transport properties of SnTe via alloying high- solubility MnTe. Energy & Environmental Science, 2015, 8(11): 3298. |
| [17] | TAN X J, SHAO H Z, HE J, et al. Band engineering and improved thermoelectric performance in M-doped SnTe (M = Mg, Mn, Cd, and Hg). Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016, 18(10): 7141. |
| [18] | TAN G J, SHI F Y, DOAK J W, et al. Extraordinary role of Hg in enhancing the thermoelectric performance of p-type SnTe. Energy & Environmental Science, 2015, 8(1): 267. |
| [19] | TAN G J, SHI F Y, HAO S Q, et al. Codoping in SnTe: enhancement of thermoelectric performance through synergy of resonance levels and band convergence. Journal of American Chemistry Society, 2015, 137(15): 5100. |
| [20] | PEI Y Z, ZHENG L L, LI W, et al. Interstitial point defect scattering contributing to high thermoelectric performance in SnTe. Advanced Electronic Materials, 2016, 2(6): 1600019. |
| [21] | ZHAO L D, ZHANG X, WU H J, et al. Enhanced thermoelectric properties in the counter-doped SnTe system with strained endotaxial SrTe. Journal of American Chemistry Society, 2016, 138(7): 2366. |
| [22] | WEI P X, LIAO C E, WU H A, et al. Thermodynamic routes to ultralow thermal conductivity and high thermoelectric performance. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(12): 1906457. |
| [23] | SHAFEIE S, GUO S, HU Q, et al. High-entropy alloys as high-temperature thermoelectric materials. Journal of Applied Physics, 2015, 118(18): 105. |
| [24] | HU L, ZHANG Y, WU H, et al. Entropy engineering of SnTe: multi-principal-element alloying leading to ultralow lattice thermal conductivity and state-of-the-art thermoelectric performance. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(29): 1802116. |
| [25] | PEI Y Z, LALONDE A D, WANG H, et al. Low effective mass leading to high thermoelectric performance. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(7): 7963. |
| [26] | BLACHNIK R, IGEL R. Thermodynamic properties of IV-VI compounds lead chalcogenides. Zeitschrift Fur Naturforschung B, 1974, 29(7): 633. |
| [27] | ZHANG Q, GUO Z, WANG R Y, et al. High-performance thermoelectric material and module driven by medium-entropy engineering in SnTe. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(35): 2205458. |
| [28] | SU H J, HAN Y M, XIE L C, et al. Fast fabrication of SnTe via a non-equilibrium method and enhanced thermoelectric properties by medium-entropy engineering. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2023, 11(16): 5363. |
| [29] | KIM H S, GIBBS Z M, TANG Y, et al. Characterization of Lorenz number with Seebeck coefficient measurement. APL Materials, 2015, 3(4): 041506. |
| [30] | YANG Q, QIU P, SHI X, et al. Application of entropy engineering in thermoelectrics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 347. |
| [31] | KIM Y M, CHUNG K, YOO J, et al. Effect of fine boron powders prepared with a self-propagating high temperature synthesis on flux pinning properties of the MgB2/Fe composite wires. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 485(1): 44. |
| [32] | WANG L J, CHANG S Y, ZHENG S Q, et al. Thermoelectric performance of Se/Cd codoped SnTe via microwave solvothermal method. ACS Applied Materials Interfaces, 2017, 9(27): 612. |
| [33] | ROYCHOWDHURY S, BISWAS R K, DUTTA M. Phonon localization and entropy-driven point defects lead to ultralow thermal conductivity and enhanced thermoelectric performance in (SnTe)1-2x(SnSe)x(SnS)x. ACS Energy Letters, 2019, 4(7): 1658. |
| [1] | 程俊, 张家伟, 仇鹏飞, 陈立东, 史迅. P掺杂β-FeSi2材料的制备与热电输运性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 895-902. |
| [2] | 陈浩, 樊文浩, 安德成, 陈少平. 能带优化和载流子调控改善SnTe的热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 306-312. |
| [3] | 田震, 蒋全伟, 李建波, 于砺锋, 康慧君, 王同敏. 热变形协同优化BiSbSe1.50Te1.50材料电热输运[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1316-1324. |
| [4] | 张哲, 孙婷婷, 王连军, 江莞. 不同维度Ag2Se构筑柔性热电薄膜的性能优化与器件集成研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1221-1227. |
| [5] | 孟雨婷, 王雪梅, 章淑娴, 陈志炜, 裴艳中. Bi2Te3基热电材料的单带和双带传输特性转变[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1283-1291. |
| [6] | 肖娅妮, 吕嘉南, 李振明, 刘铭扬, 刘伟, 任志刚, 刘弘景, 杨东旺, 鄢永高. Bi2Te3基热电材料的湿热稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(7): 800-806. |
| [7] | 贺丹琪, 魏明旭, 刘蕤之, 汤志鑫, 翟鹏程, 赵文俞. 一步法制备重费米子YbAl3热电材料及其性能提升[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 577-582. |
| [8] | 李建波, 田震, 蒋全伟, 于砺锋, 康慧君, 曹志强, 王同敏. 不同元素掺杂对CaTiO3微观结构及热电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1396-1404. |
| [9] | 王鹏将, 康慧君, 杨雄, 刘颖, 程成, 王同敏. 熵调控抑制ZrNiSn基half-Heusler热电材料的晶格热导率[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 717-723. |
| [10] | 程成, 李建波, 田震, 王鹏将, 康慧君, 王同敏. In2O3/InNbO4复合材料的热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 724-730. |
| [11] | 娄许诺, 邓后权, 李爽, 张青堂, 熊文杰, 唐国栋. Ge掺杂MnTe材料的热电输运性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 209-214. |
| [12] | 金敏, 白旭东, 张如林, 周丽娜, 李荣斌. 区熔法制备金属硫化物Ag2S及其热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 101-106. |
| [13] | 张岑岑, 王雪, 彭良明. 基于分步式双重调控n型(PbTe)1-x-y(PbS)x(Sb2Se3)y体系的热电传输特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 936-942. |
| [14] | 杨东旺, 罗婷婷, 苏贤礼, 吴劲松, 唐新峰. 基于熵工程及SHS动力学的BiAgSeS本征低热导率起源探究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 991-998. |
| [15] | 杨青雨, 仇鹏飞, 史迅, 陈立东. 熵工程在热电材料中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(4): 347-354. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||