无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (7): 800-806.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220736 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20220736
所属专题: 【能源环境】热电材料(202506)
肖娅妮1( ), 吕嘉南1,2, 李振明3, 刘铭扬3, 刘伟3, 任志刚4, 刘弘景4, 杨东旺1(
), 吕嘉南1,2, 李振明3, 刘铭扬3, 刘伟3, 任志刚4, 刘弘景4, 杨东旺1( ), 鄢永高1(
), 鄢永高1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-05
修回日期:2023-02-23
出版日期:2023-03-15
网络出版日期:2023-03-15
通讯作者:
杨东旺, 助理研究员. E-mail: ydongwang@whut.edu.cn;作者简介:肖娅妮(1999-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 303587@whut.edu.cn
基金资助:
XIAO Yani1( ), LYU Jianan1,2, LI Zhenming3, LIU Mingyang3, LIU Wei3, REN Zhigang4, LIU Hongjing4, YANG Dongwang1(
), LYU Jianan1,2, LI Zhenming3, LIU Mingyang3, LIU Wei3, REN Zhigang4, LIU Hongjing4, YANG Dongwang1( ), YAN Yonggao1(
), YAN Yonggao1( )
)
Received:2022-12-05
Revised:2023-02-23
Published:2023-03-15
Online:2023-03-15
Contact:
YANG Dongwang, research assistant. E-mail: ydongwang@whut.edu.cn;About author:XIAO Yani (1999-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 303587@whut.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
Bi2Te3基化合物是目前得到广泛商业应用的热电材料, 其湿热稳定性直接影响着热电器件的服役可靠性。本工作探究了商用n型Bi2Se0.21Te2.79和p型Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3热电材料存储于85 ℃, 85% RH(相对湿度)湿热环境600 h期间的降解行为。在湿热处理600 h后, n型Bi2Se0.21Te2.79和p型Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3材料表面均被氧化, 反应过程分别为Bi2Te3+O2→Bi2O3+TeO2和Bi2Te3+Sb2Te3+O2→Bi2O3+Sb2O3+TeO2。氧化过程在材料内部产生了纳米级孔洞, 甚至微裂纹, 导致材料的电、热性能全面劣化。在室温时, n型Bi2Se0.21Te2.79材料的电导率从存储前的9.45×104 S·m-1显著下降到7.79×104 S·m-1, ZT则从0.97下降至0.79; p型Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3材料的Seebeck系数从243 μV·K-1明显减小至220 μV·K-1, ZT则从1.24降低到0.97。综上所述, Bi2Te3基热电材料的湿热稳定性极差, 微型热电器件在服役过程中需要进行严格封装, 以阻止热电材料自身与环境中的水汽、空气发生复杂的氧化还原反应。
中图分类号:
肖娅妮, 吕嘉南, 李振明, 刘铭扬, 刘伟, 任志刚, 刘弘景, 杨东旺, 鄢永高. Bi2Te3基热电材料的湿热稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(7): 800-806.
XIAO Yani, LYU Jianan, LI Zhenming, LIU Mingyang, LIU Wei, REN Zhigang, LIU Hongjing, YANG Dongwang, YAN Yonggao. Hygrothermal Stability of Bi2Te3-based Thermoelectric Materials[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(7): 800-806.
| Parameter at room temperature | n-type Bi2Se0.21Te2.79 | p-type Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 600 h | 0 h | 600 h | ||
| σ / (×104, S·m-1) | 9.45 | 7.79 | 9.12 | 8.69 | |
| S / (μV·K-1) | 219 | 224 | 243 | 220 | |
| n / (×1019, cm-3) | 1.25 | 1.32 | 1.52 | 1.47 | |
| μ / (cm2·V-1·s-1) | 470 | 369 | 375 | 370 | |
| PF / (mW·m-1·K-2) | 4.54 | 3.90 | 5.41 | 4.21 | |
| κ / (W·m-1·K-1) | 1.40 | 1.48 | 1.31 | 1.29 | |
| ZT | 0.97 | 0.79 | 1.24 | 0.97 | |
表1 n型Bi2Se0.21Te2.79和p型Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3材料在湿热环境(85 ℃, 85% RH)存储600 h前后的室温热电性能
Table 1 Room temperature thermoelectric performance of n-type Bi2Se0.21Te2.79 and p-type Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 materials before and after storage in hygrothermal environment (85 ℃, 85% RH) for 600 h
| Parameter at room temperature | n-type Bi2Se0.21Te2.79 | p-type Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 600 h | 0 h | 600 h | ||
| σ / (×104, S·m-1) | 9.45 | 7.79 | 9.12 | 8.69 | |
| S / (μV·K-1) | 219 | 224 | 243 | 220 | |
| n / (×1019, cm-3) | 1.25 | 1.32 | 1.52 | 1.47 | |
| μ / (cm2·V-1·s-1) | 470 | 369 | 375 | 370 | |
| PF / (mW·m-1·K-2) | 4.54 | 3.90 | 5.41 | 4.21 | |
| κ / (W·m-1·K-1) | 1.40 | 1.48 | 1.31 | 1.29 | |
| ZT | 0.97 | 0.79 | 1.24 | 0.97 | |
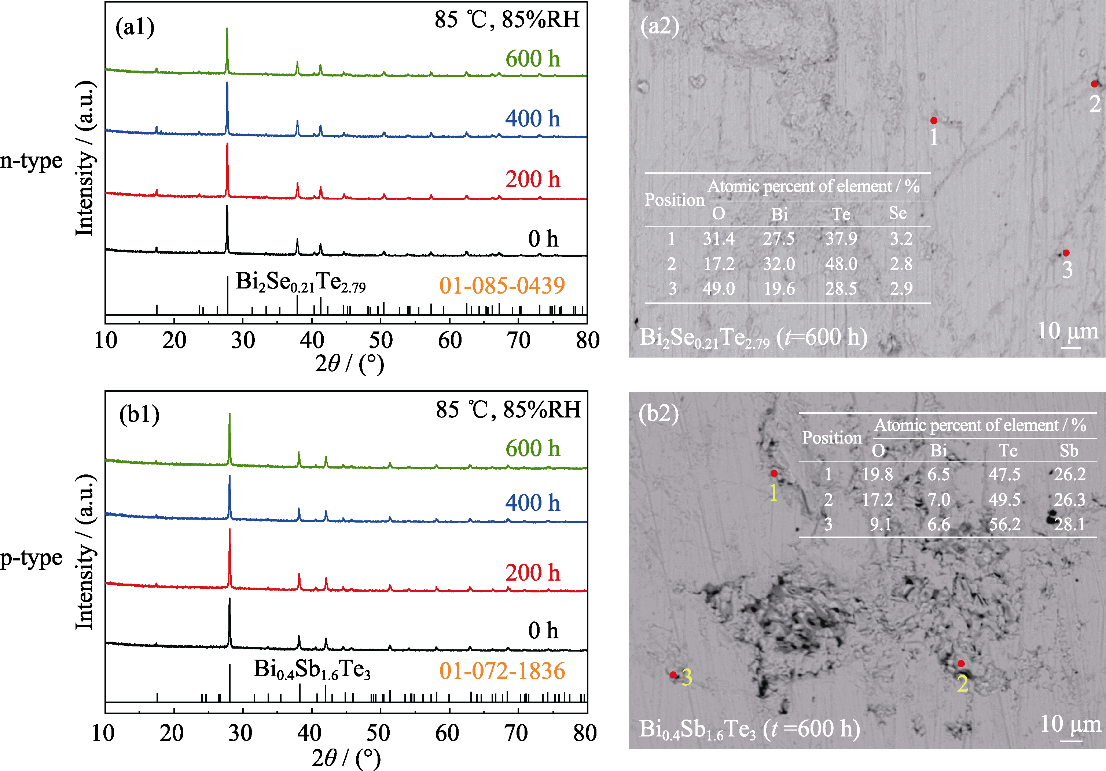
图1 (a1, b1)在湿热环境存储不同时间后材料的XRD谱图及(a2, b2)存储600 h后材料的表面EDS能谱
Fig. 1 (a1, b1) XRD patterns of samples after storage in hygrothermal environment for different time with (a2, b2) EDS results of material surface after storage in hygrothermal environment for 600 h (a1, a2) n-type Bi2Se0.21Te2.79; (b1, b2) p-type Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3
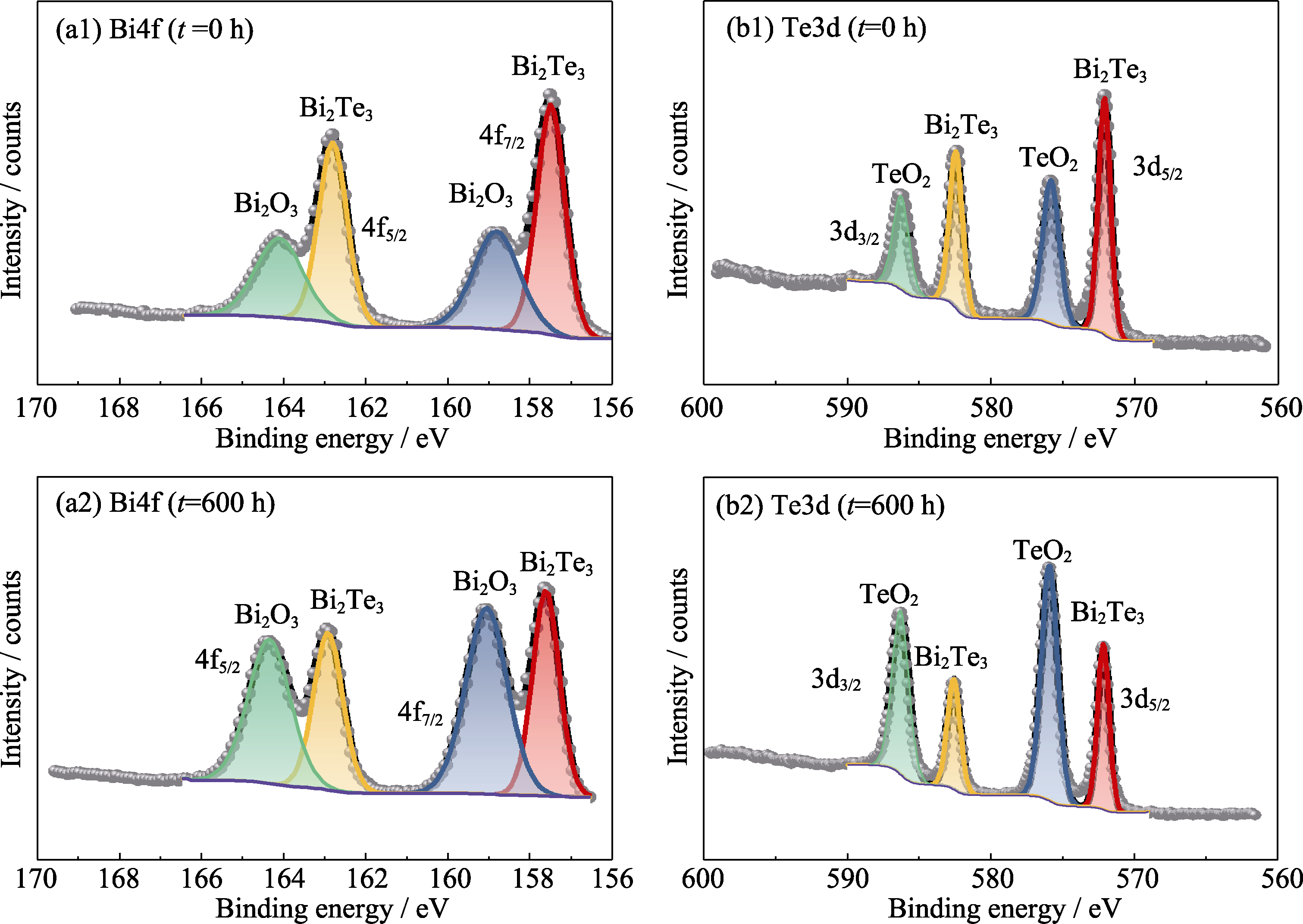
图2 n型Bi2Se0.21Te2.79材料在湿热环境存储600 h(a1~b1)前(a2~b2)后的表面XPS谱图
Fig. 2 Surface XPS spectra of n-type Bi2Se0.21Te2.79 material (a1-b1) before and (a2-b2) after storage in hygrothermal environment for 600 h (a1, a2) Bi4f; (b1, b2) Te3d
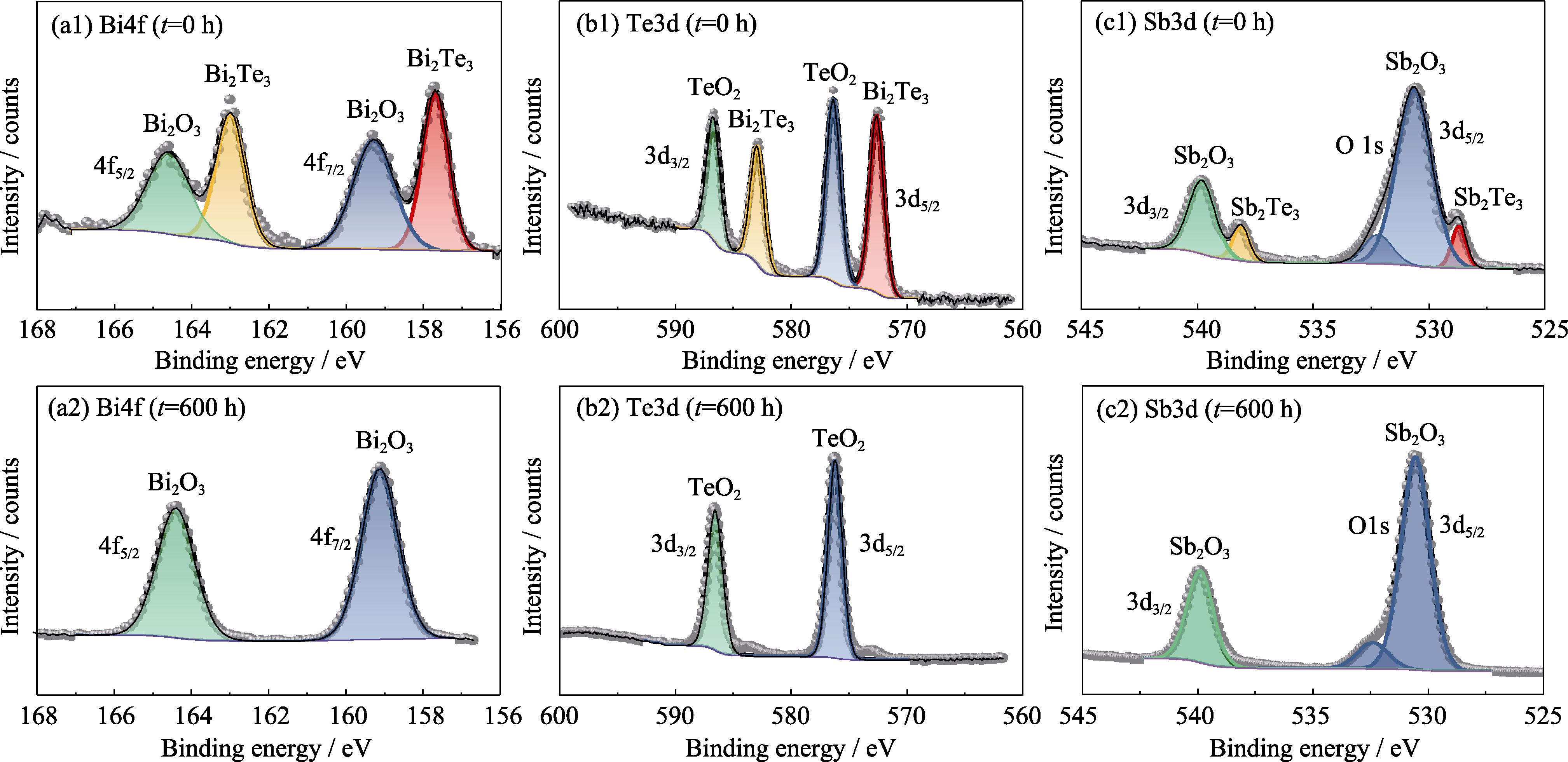
图3 p型Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3材料在湿热环境存储600 h(a1~c1)前(a2~c2)后的表面XPS谱图
Fig. 3 Surface XPS spectra of p-type Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 material (a1-c1) before and (a2-c2) after storage in hygrothermal environment for 600 h (a1, a2) Bi4f; (b1, b2) Te3d; (c1, c2) Sb3d

图4 (a1, a2) n型Bi2Se0.21Te2.79和(b1, b2) p型Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3材料在湿热环境存储600 h(a1, b1)前(a2, b2)后的FESEM照片
Fig. 4 FESEM images of (a1, a2) n-type Bi2Se0.21Te2.79 and (b1, b2) p-type Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 material (a1, b1) before and (a2, b2) after storage in hygrothermal environment for 600 h
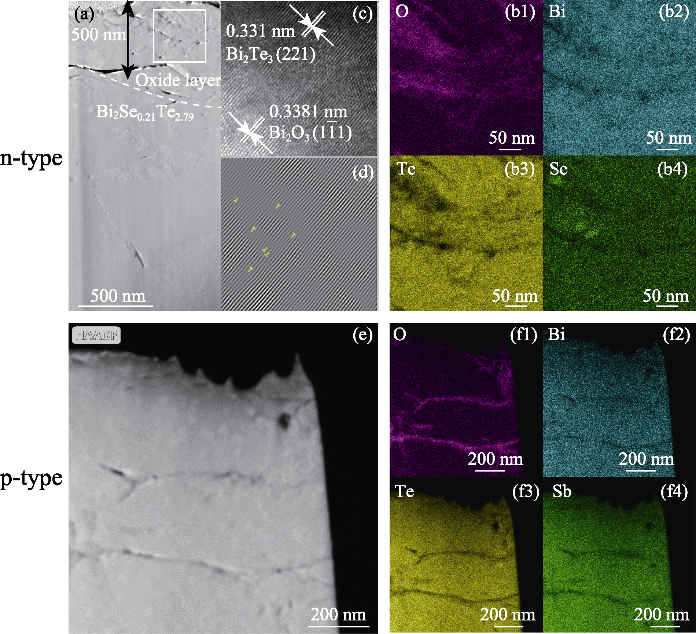
图5 (a) 湿热环境存储600 h的n型Bi2Se0.21Te2.79材料靠近表面区域的TEM照片; (b) 图(a)中方框区域的元素面分布图谱; (c) 图(a)中方框区域的HRTEM照片; (d) 图(c)的IFFT图;湿热环境存储600 h的p型Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3材料靠近表面的(e) HAADF-STEM照片和(f)元素面分布图谱
Fig. 5 (a) TEM image of the area close to the surface of n-type Bi2Se0.21Te2.79 material exposed to hygrothermal environment for 600 h; (b) elemental surface distribution profiles of the square region in (a); (c) HRTEM image of the square region in (a); (d) IFFT image of (c); (e) HAADF-STEM image of the area close to the surface of p-type Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 material exposed to hygrothermal environment and (f) its elemental surface distribution profiles of the region (b1, f1) O; (b2, f2) Bi; (b3, f3) Te; (b4)Se; (f4) Sb

图S1 湿热环境(85 ℃, 85% RH)条件下n型Bi2Se0.21Te2.79的热电性能
Fig. S1 Thermoelectric performance of n-type Bi2Se0.21Te2.79 in hygrothermal environment (85 ℃, 85% RH) (a) Electrical conductivity; (b) Seebeck coefficient; (c) Room temperature carrier concentration and carrier mobility; (d) Power factor; (e) Thermal conductivity; (f) ZT

图S2 湿热环境(85 ℃, 85% RH)条件下p型Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3的热电性能
Fig. S2 Thermoelectric performance of p-type Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 in hygrothermal environment (85 ℃, 85% RH) (a) Electrical conductivity; (b) Seebeck coefficient; (c) Room temperature carrier concentration and carrier mobility; (d) Power factor; (e) Thermal conductivity; (f) ZT
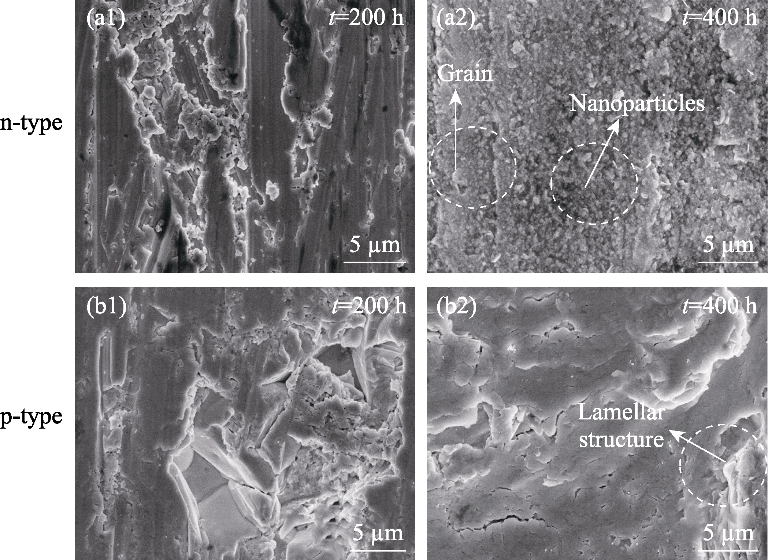
图S3 n型Bi2Se0.21Te2.79和p型Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3材料在湿热环境存储不同时间的FESEM照片
Fig. S3 FESEM images of samples exposed to hygrothermal environment for different time n-type Bi2Se0.21Te2.79: (a1) 200 h; (a2) 400 h; p-type Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3: (b1) 200 h; (b2) 400 h
| [1] |
CORNETT J, CHEN B, HAIDAR S, et al. Fabrication and characterization of Bi2Te3-based chip-scale thermoelectric energy harvesting devices. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2016, 46(5):2844.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
LIU C, ZHAO K, FAN Y, et al. A flexible thermoelectric film based on Bi2Te3 for wearable applications. Functional Materials Letters, 2021, 15(1):2251005.
DOI URL |
| [3] | NOZARIASBMARZ A, DYCUS J H, CABRAL M J, et al. Efficient self-powered wearable electronic systems enabled by microwave processed thermoelectric materials. Applied Energy, 2021, 283: 116211. |
| [4] | HOU C C, VAN TOAN N, ONO T. High density micro-thermoelectric generator based on electrodeposition of Bi2Te3 and Sb2Te3. 2022 IEEE 35th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems Conference (MEMS), Tokyo, 2022: 600-603. |
| [5] |
YAN Q, KANATZIDIS M G. High-performance thermoelectrics and challenges for practical devices. Nature Materials, 2022, 21(5):503.
DOI |
| [6] | YUAN X, L Z, SHAO Y, et al. Bi2Te3-based wearable thermoelectric generator with high power density: from structure design to application. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2022, 10: 6456. |
| [7] |
FRANCIOSO L, DE PASCALI C, FARELLA I, et al. Flexible thermoelectric generator for ambient assisted living wearable biometric sensors. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(6):3239.
DOI URL |
| [8] | LU Z, ZHANG H, MAO C, et al. Silk fabric-based wearable thermoelectric generator for energy harvesting from the human body. Applied Energy, 2016, 164: 57. |
| [9] | WANG Y, SHI Y, MEI D, et al. Wearable thermoelectric generator to harvest body heat for powering a miniaturized accelerometer. Applied Energy, 2018, 215: 690. |
| [10] |
ZOU Q, SHANG H, HUANG D, et al. Bi2Te3-based flexible thermoelectric generator for wearable electronics. Applied Physics Letters, 2022, 120(2):023903.
DOI URL |
| [11] | YOU H, LI Z, SHAO Y, et al. Flexible Bi2Te3-based thermoelectric generator with an ultra-high power density. Applied Thermal Engineering 2022, 202: 117818. |
| [12] |
XU Z, YANG D, YUAN X, et al. Objective evaluation of wearable thermoelectric generator: from platform building to performance verification. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2022, 93(4):045105.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
HENDRICKS T J, KARRI N K. Micro- and nano-technology: a critical design key in advanced thermoelectric cooling systems. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2009, 38(7):1257.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
TANG X, LI Z, LIU W, et al. A comprehensive review on Bi2Te3- based thin films: thermoelectrics and beyond. Interdisciplinary Materials, 2022, 1(1):88.
DOI URL |
| [15] | MAMUR H, BHUIYAN M R A, KORKMAZ F, et al. A review on bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) nanostructure for thermoelectric applications. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 82: 4159. |
| [16] | ZHU W, WEI P, ZHANG J, et al. Fabrication and excellent performances of bismuth telluride-based thermoelectric devices. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(10):12276. |
| [17] | LIN Y, WU X, LI Y, et al. Revealing multi-stage growth mechanism of Kirkendall voids at electrode interfaces of Bi2Te3-based thermoelectric devices with in-situ TEM technique. Nano Energy, 2022, 102: 107736. |
| [18] |
TASHIRO M, SUKENAGA S, IKEMOTO K, et al. Interfacial reactions between pure Cu, Ni, and Ni-Cu alloys and p-type Bi2Te3bulk thermoelectric material. Journal of Materials Science, 2021, 56(29):16545.
DOI |
| [19] |
CHEN L, BAI S, SHI X, et al. High temperature interfacial stability of Fe/Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3thermoelectric elements. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2):197.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
ZHENG Y, TAN X Y, WAN X, et al. Thermal stability and mechanical response of Bi2Te3-based materials for thermoelectric applications. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2019, 3(3): 2078.
DOI URL |
| [21] | LIN C F, HAU N Y, HUANG Y T, et al. Synergetic effect of Bi2Te3 alloys and electrodeposition of Ni for interfacial reactions at solder/Ni/Bi2Te3 joints. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 708: 220. |
| [22] |
JIANG C, FAN X A, HU J, et al. Thermal stability of zone melting p-type (Bi, Sb)2Te3 ingots and comparison with the corresponding powder metallurgy samples. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2018, 47(7):4038.
DOI |
| [23] | JIANG C, FAN X A, FENG B, et al. Thermal stability of p-type polycrystalline Bi2Te3-based bulks for the application on thermoelectric power generation. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 692: 885. |
| [24] |
HU X, FAN X A, JIANG C, et al. Thermal stability of n-type zone- melting Bi2(Te, Se)3 alloys for thermoelectric generation. Materials Research Express, 2018, 6(3):035907.
DOI URL |
| [25] | TANG H, HUI B, YANG X, et al. Thermal stability and interfacial structure evolution of Bi2Te3-based micro thermoelectric devices. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 896: 163090. |
| [26] | ARUN P, TYAGI P, VEDESHWAR, et al. Ageing effect of Sb2Te3 thin films ageing effect of Sb2Te3 thin films. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2001, 307: 105. |
| [27] | BANDO H, KOIZUMI K, OIKAWA Y, et al. The time-dependent process of oxidation of the surface of Bi2Te3 studied by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2000, 12: 5607. |
| [28] | GUO J H, QIU F, ZHANG Y, et al. Surface oxidation properties in a topological insulator Bi2Te3 film. Chinese Physics Letters, 2013, 30: 106801. |
| [29] | MUSIC D, CHANG K, SCHMIDT P, et al. On atomic mechanisms governing the oxidation of Bi2Te3. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2017, 29: 485705. |
| [30] | SIROTINA A P, CALLAERT C, VOLYKHOV A A, et al. Mechanistic studies of gas reactions with multicomponent solids: what can we learn by combining NAP XPS and atomic resolution STEM/EDX? The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2019, 123: 26201. |
| [31] | THOMAS C R, VALLON M K, FRITH M G, et al. Surface oxidation of Bi2(Te,Se)3 topological insulators depends on cleavage accuracy. Chemistry of Materials, 2016, 28: 35. |
| [32] | QU Q, LIU B, LIANG J, et al. Expediting hydrogen evolution through topological surface states on Bi2Te3. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10: 1656. |
| [33] | SHARMA P A, OHTA T, BRUMBACH M T, et al. Ex Situ photoelectron emission microscopy of polycrystalline bismuth and antimony telluride surfaces exposed to ambient oxidation. Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13: 18218. |
| [34] | LU B, HU S, LI W E, et al. Preparation and characterization of Sb2Te3 thin films by coevaporation. International Journal of Photoenergy, 2010, 4: 476589. |
| [35] |
NORIMASA O, KUROKAWA T, EGUCHI R, et al. Evaluation of thermoelectric performance of Bi2Te3 films as a function of temperature increase rate during heat treatment. Coatings, 2021, 11(1):38.
DOI URL |
| [36] | LI A, NAN P, WANG Y, et al. Chemical stability and degradation mechanism of Mg3Sb2-Bi thermoelectrics towards room-temperature applications. Acta Materialia, 2022, 239: 118301. |
| [37] | ZHAO Y, BURDA C. Chemical synthesis of Bi(0.5)Sb(1.5)Te3 nanocrystals and their surface oxidation properties. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2009, 1(6):1259. |
| [38] | JEONG K, PARK D, MAENG I, et al. Modulation of optoelectronic properties of the Bi2Te3nanowire by controlling the formation of selective surface oxidation. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 548: 149069. |
| [1] | 程俊, 张家伟, 仇鹏飞, 陈立东, 史迅. P掺杂β-FeSi2材料的制备与热电输运性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 895-902. |
| [2] | 陈浩, 樊文浩, 安德成, 陈少平. 能带优化和载流子调控改善SnTe的热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 306-312. |
| [3] | 田震, 蒋全伟, 李建波, 于砺锋, 康慧君, 王同敏. 热变形协同优化BiSbSe1.50Te1.50材料电热输运[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1316-1324. |
| [4] | 张哲, 孙婷婷, 王连军, 江莞. 不同维度Ag2Se构筑柔性热电薄膜的性能优化与器件集成研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1221-1227. |
| [5] | 孟雨婷, 王雪梅, 章淑娴, 陈志炜, 裴艳中. Bi2Te3基热电材料的单带和双带传输特性转变[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1283-1291. |
| [6] | 苏浩健, 周敏, 李来风. 多元素掺杂优化SnTe的热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1159-1166. |
| [7] | 贺丹琪, 魏明旭, 刘蕤之, 汤志鑫, 翟鹏程, 赵文俞. 一步法制备重费米子YbAl3热电材料及其性能提升[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 577-582. |
| [8] | 华思恒, 杨东旺, 唐昊, 袁雄, 展若雨, 徐卓明, 吕嘉南, 肖娅妮, 鄢永高, 唐新峰. n型Bi2Te3基材料表面处理对热电单元性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 163-169. |
| [9] | 李建波, 田震, 蒋全伟, 于砺锋, 康慧君, 曹志强, 王同敏. 不同元素掺杂对CaTiO3微观结构及热电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1396-1404. |
| [10] | 王鹏将, 康慧君, 杨雄, 刘颖, 程成, 王同敏. 熵调控抑制ZrNiSn基half-Heusler热电材料的晶格热导率[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 717-723. |
| [11] | 程成, 李建波, 田震, 王鹏将, 康慧君, 王同敏. In2O3/InNbO4复合材料的热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 724-730. |
| [12] | 娄许诺, 邓后权, 李爽, 张青堂, 熊文杰, 唐国栋. Ge掺杂MnTe材料的热电输运性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 209-214. |
| [13] | 金敏, 白旭东, 张如林, 周丽娜, 李荣斌. 区熔法制备金属硫化物Ag2S及其热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 101-106. |
| [14] | 张岑岑, 王雪, 彭良明. 基于分步式双重调控n型(PbTe)1-x-y(PbS)x(Sb2Se3)y体系的热电传输特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 936-942. |
| [15] | 杨青雨, 仇鹏飞, 史迅, 陈立东. 熵工程在热电材料中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(4): 347-354. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||