无机材料学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (11): 1167-1174.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180540 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20180540
邹爱华,周贤良,康志兵,饶有海,吴开阳
收稿日期:2018-11-12
修回日期:2019-03-08
出版日期:2019-11-20
网络出版日期:2019-05-29
作者简介:邹爱华(1980-), 女, 博士, 副教授. E-mail: aihua553030@163.com
基金资助:ZOU Ai-Hua,ZHOU Xian-Liang,KANG Zhi-Bing,RAO You-Hai,WU Kai-Yang
Received:2018-11-12
Revised:2019-03-08
Published:2019-11-20
Online:2019-05-29
Supported by:摘要:
采用基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理及实验相结合的方法, 探讨了Al基体中分别掺杂Mg、Si、Cu合金元素对SiC/Al界面结合的影响, 重点考察了合金元素在界面偏聚时的电子结构和成键情况。研究表明: 在未掺杂Al/SiC体系界面结构优化时, 以Si原子为终止面的Brigde结构是最稳定的结合方式; 当合金元素分别替换界面处的Al原子后, 界面处原子的分波态密度、Muliken电荷及成键原子集居数等电子结构参数均有不同程度的变化, 这不仅增加了界面处 Si与Al原子结合, 同时也增强了界面处和亚界面处的Al基体和SiC增强相原子之间的相互作用, 使体系更加稳定, 界面黏着功均有不同提升; 其中掺Mg提升效果最明显, 其次为掺Cu和掺Si; 利用第一性原理计算的掺杂Al/SiC体系黏着功和实验值较为接近且变化规律相同。
中图分类号:
邹爱华, 周贤良, 康志兵, 饶有海, 吴开阳. 基体合金元素对SiC/Al界面结合影响的第一性原理及实验研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(11): 1167-1174.
ZOU Ai-Hua, ZHOU Xian-Liang, KANG Zhi-Bing, RAO You-Hai, WU Kai-Yang. Alloy Elements on SiC/Al Interface: a First-principle and Experimental Study[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(11): 1167-1174.
| Size | Purity/wt% | Relative density/% | Roughness /nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Φ20 mm×5 mm | >98.5 | >97 | 19 |
表1 SiC基板的基本参数
Table 1 Basic parameters of SiC substrate
| Size | Purity/wt% | Relative density/% | Roughness /nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Φ20 mm×5 mm | >98.5 | >97 | 19 |
| Alsurf | (100) | (110) | (111) | (211) | SiCsurf | (001) | (011) | (111) | (211) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esurf /(J·m-2) | 1.51 | 1.78 | 1.45 | 1.75 | Esurf/(J·m-2) | 5.42 | 5.96 | 6.49 | 8.41 |
表2 Al以及4H-SiC晶体表面的表面能
Table 2 Surface energy of Al and 4H-SiC crystal
| Alsurf | (100) | (110) | (111) | (211) | SiCsurf | (001) | (011) | (111) | (211) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esurf /(J·m-2) | 1.51 | 1.78 | 1.45 | 1.75 | Esurf/(J·m-2) | 5.42 | 5.96 | 6.49 | 8.41 |
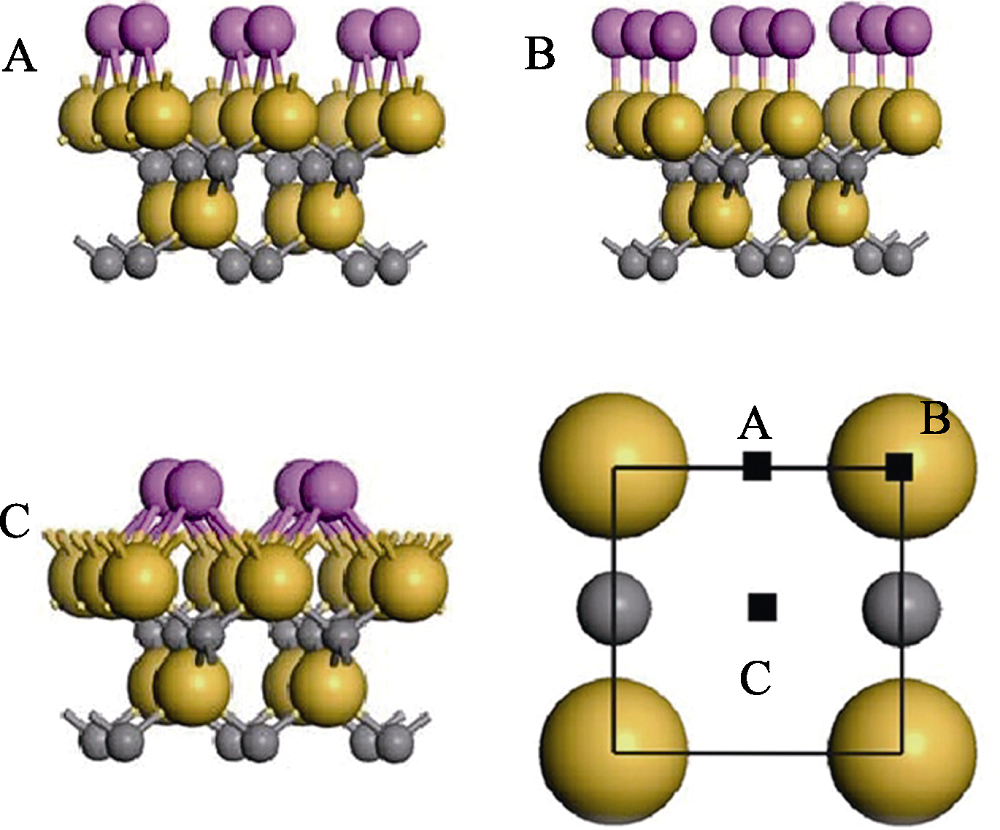
图1 以Si为终端的SiC(001)/Al(111)界面原子结构, A、B、C位分别记作桥位、顶位和空位
Fig. 1 Atomic structures of SiC (001) /Al (111) interfaces with Si-terminated, A, B and C sites as bridge, top and vacancy, respectively
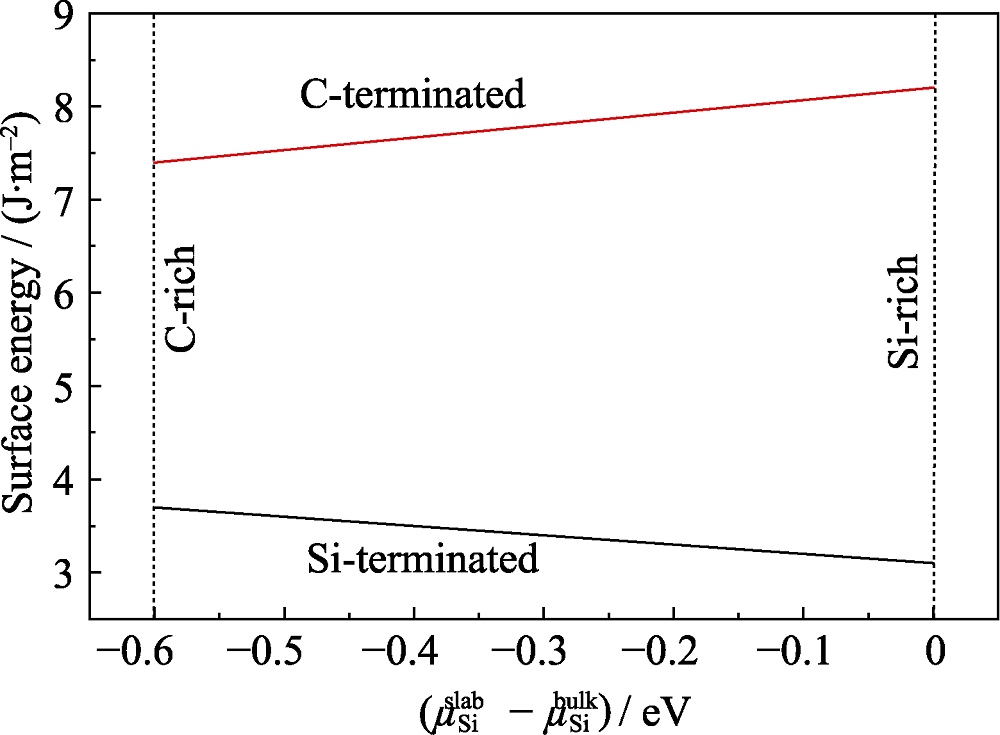
图2 SiC(001)表面能随$\mu _{\text{Si}}^{\text{slab}}-\mu _{\text{Si}}^{\text{bulk}}$变化的关系图
Fig. 2 Surface energy curves of SiC(001) with different $\mu _{\text{Si}}^{\text{slab}}-\mu _{\text{Si}}^{\text{bulk}}$
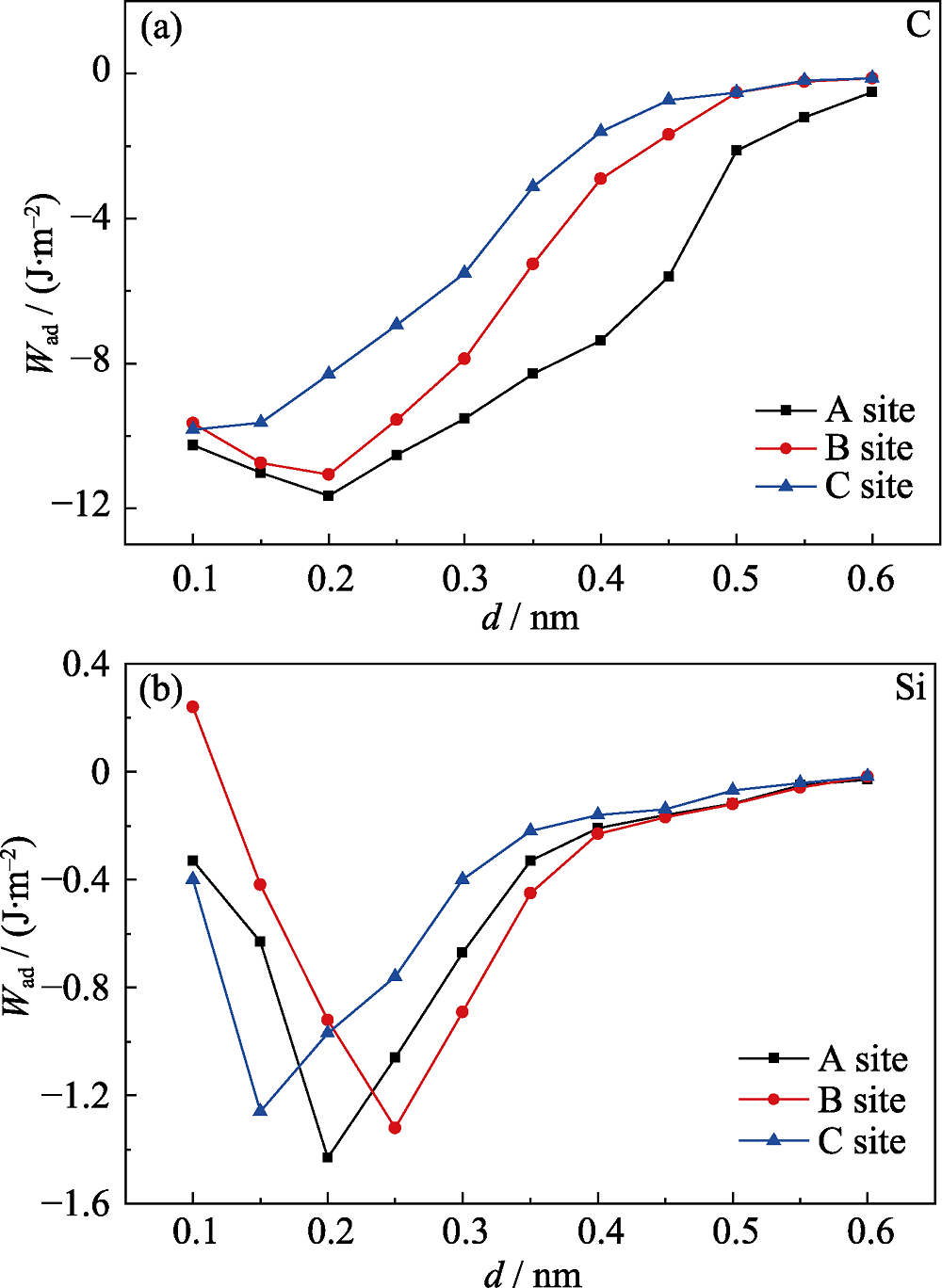
图3 SiC(001)/Al(111)界面分离功与界面距离的关系曲线
Fig. 3 Adhesion work curves of SiC(001)/Al(111) with different interfacial distance (a) C-terminated, (b) Si-terminated
| Model | Add number | Total energy/eV | Wad/(mJ·m-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al/SiC | 0 | -6573.7404 | 851 |
| Al-Mg/SiC | 1 | -7491.2968 | 1140 |
| 2 | -8408.7099 | 1342 | |
| 4 | -10243.2359 | 1015 | |
| Al-Si/SiC | 1 | -6624.1431 | 1024 |
| 2 | -6674.512 | 1242 | |
| 4 | -6775.2566 | 936 | |
| Al-Cu/SiC | 1 | -7993.8884 | 1088 |
| 2 | -9413.8768 | 1254 | |
| 4 | -12254.1254 | 642 |
表3 合金原子(Mg、Si、Cu)掺杂前后SiC/Al界面粘着功的变化
Table 3 Adhesion work of SiC/Al interface before and after doping Mg, Si and Cu
| Model | Add number | Total energy/eV | Wad/(mJ·m-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al/SiC | 0 | -6573.7404 | 851 |
| Al-Mg/SiC | 1 | -7491.2968 | 1140 |
| 2 | -8408.7099 | 1342 | |
| 4 | -10243.2359 | 1015 | |
| Al-Si/SiC | 1 | -6624.1431 | 1024 |
| 2 | -6674.512 | 1242 | |
| 4 | -6775.2566 | 936 | |
| Al-Cu/SiC | 1 | -7993.8884 | 1088 |
| 2 | -9413.8768 | 1254 | |
| 4 | -12254.1254 | 642 |
| Atom number | Model | Charge population | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s(Mg,Si,Cu) | p(Mg,Si,Cu) | d(Si, Cu) | Total(Mg, Si, Cu) | ||
| Al(1) | Without Mg,Si,Cu | 1.11,1.11,1.11 | 1.76,1.76,1.76 | 0, 0 | 2.87, 2.87, 2.87 |
| With Mg,Si,Cu | 1.15,1.14,1.14 | 1.84,1.74,1.75 | 0, 0 | 2.99, 2.88, 2.89 | |
| Al(2)/(Mg,Si,Cu) | Without Mg,Si,Cu | 1.11,1.11,1.11 | 1.76,1.76,1.76 | 0, 0 | 2.87, 2.87, 2.87 |
| With Mg,Si,Cu | 0.52,1.58,0.68 | 6.54, 2.5, 0.84 | 0, 9.76 | 7.07, 4.08, 9.76 | |
| Al(4) | Without Mg,Si,Cu | 1.11,1.11,1.11 | 1.76,1.76,1.76 | 0, 0 | 2.87, 2.87, 2.87 |
| With Mg,Si,Cu | 1.14,1.12,1.11 | 1.85,1.8,1.83 | 0, 0 | 2.99, 2.92, 2.94 | |
| Si(2) | Without Mg,Si,Cu | 1.39,1.39,1.39 | 2.5, 2.5, 2.5 | 0, 0 | 3.98, 3.98, 3.98 |
| With Mg,Si,Cu | 1.5,1.42,1.45 | 2.54, 2.56, 2.54 | 0, 0 | 4.04, 3.98, 3.99 | |
| Si(4) | Without Mg,Si,Cu | 1.39,1.39,1.39 | 2.5, 2.5, 2.5 | 0, 0 | 3.89, 3.89, 3.89 |
| With Mg,Si,Cu | 1.4,1.4,1.39 | 2.55, 2.5, 2.53 | 0, 0 | 3.95, 3.9, 3.92 | |
表4 合金原子(Mg、Si、Cu)掺杂前后SiC/Al界面处原子Millken电荷
Table 4 Millken charge of atom at SiC/Al interface before and after doping Mg, Si and Cu
| Atom number | Model | Charge population | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s(Mg,Si,Cu) | p(Mg,Si,Cu) | d(Si, Cu) | Total(Mg, Si, Cu) | ||
| Al(1) | Without Mg,Si,Cu | 1.11,1.11,1.11 | 1.76,1.76,1.76 | 0, 0 | 2.87, 2.87, 2.87 |
| With Mg,Si,Cu | 1.15,1.14,1.14 | 1.84,1.74,1.75 | 0, 0 | 2.99, 2.88, 2.89 | |
| Al(2)/(Mg,Si,Cu) | Without Mg,Si,Cu | 1.11,1.11,1.11 | 1.76,1.76,1.76 | 0, 0 | 2.87, 2.87, 2.87 |
| With Mg,Si,Cu | 0.52,1.58,0.68 | 6.54, 2.5, 0.84 | 0, 9.76 | 7.07, 4.08, 9.76 | |
| Al(4) | Without Mg,Si,Cu | 1.11,1.11,1.11 | 1.76,1.76,1.76 | 0, 0 | 2.87, 2.87, 2.87 |
| With Mg,Si,Cu | 1.14,1.12,1.11 | 1.85,1.8,1.83 | 0, 0 | 2.99, 2.92, 2.94 | |
| Si(2) | Without Mg,Si,Cu | 1.39,1.39,1.39 | 2.5, 2.5, 2.5 | 0, 0 | 3.98, 3.98, 3.98 |
| With Mg,Si,Cu | 1.5,1.42,1.45 | 2.54, 2.56, 2.54 | 0, 0 | 4.04, 3.98, 3.99 | |
| Si(4) | Without Mg,Si,Cu | 1.39,1.39,1.39 | 2.5, 2.5, 2.5 | 0, 0 | 3.89, 3.89, 3.89 |
| With Mg,Si,Cu | 1.4,1.4,1.39 | 2.55, 2.5, 2.53 | 0, 0 | 3.95, 3.9, 3.92 | |
| Bond type | Population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Mg | With Mg | Without Si | With Si | Without Cu | With Cu | |
| Al(1)-Si(1) | 0.36 | 0.4 | 0.36 | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.38 |
| Al(2)/(Mg,Si,Cu)-Si(2) | 0.36 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.31 |
| Al(3)-Si(3) | 0.36 | 0.39 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.37 |
| Al(4)-Si(4) | 0.36 | 0.4 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.37 |
| Al(4)-Al(5) | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.25 |
| Si(4)-C(4) | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.26 |
表5 合金原子(Mg、Si、Cu)掺杂前后SiC/Al界面及附近成键原子集居数
Table 5 Populations of atoms at and near SiC/Al interface before and after doping Mg, Si and Cu
| Bond type | Population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Mg | With Mg | Without Si | With Si | Without Cu | With Cu | |
| Al(1)-Si(1) | 0.36 | 0.4 | 0.36 | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.38 |
| Al(2)/(Mg,Si,Cu)-Si(2) | 0.36 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.31 |
| Al(3)-Si(3) | 0.36 | 0.39 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.37 |
| Al(4)-Si(4) | 0.36 | 0.4 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.37 |
| Al(4)-Al(5) | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.25 |
| Si(4)-C(4) | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.26 |
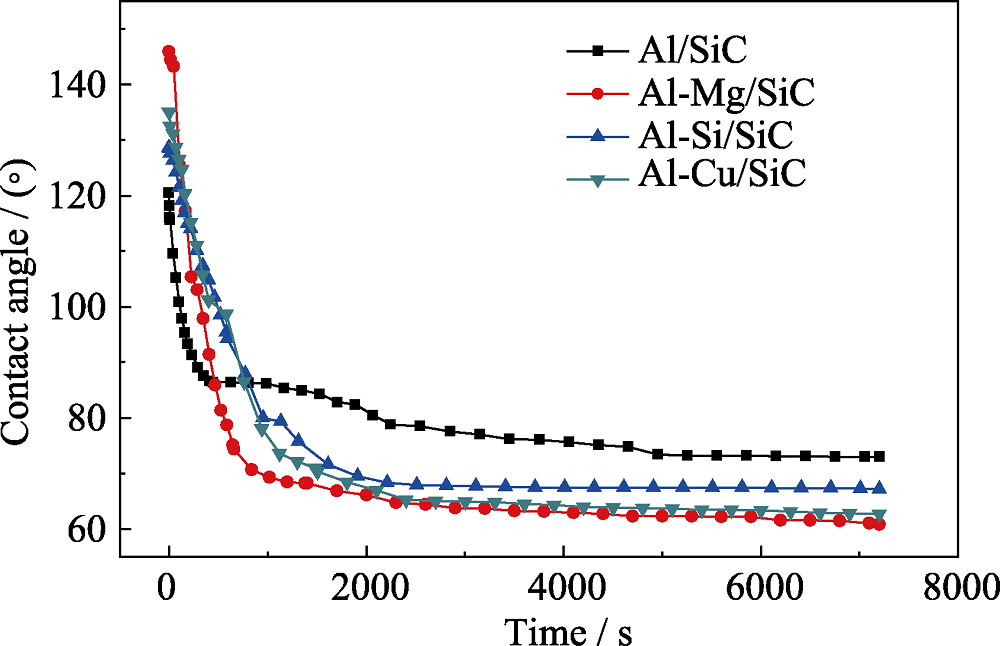
图6 900 ℃时纯Al及其合金(Al-Mg、Si、Cu)在α-SiC基板上接触角随时间的变化
Fig. 6 Contact angle of pure Al and its alloy (Al-Mg, Si, Cu) on α-SiC substrate at 900 ℃ varies with time
| Model | This experiment/ (mJ·m-2) | First principles/ (mJ·m-2) |
|---|---|---|
| SiC/Al | 839 | 851 |
| SiC/Al-Mg | 1246 | 1140 |
| SiC/Al-Si | 1167 | 1024 |
| SiC/Al-Cu | 1220 | 1088 |
表6 不同体系界面黏着功
Table 6 Adhesion work of different interface systems
| Model | This experiment/ (mJ·m-2) | First principles/ (mJ·m-2) |
|---|---|---|
| SiC/Al | 839 | 851 |
| SiC/Al-Mg | 1246 | 1140 |
| SiC/Al-Si | 1167 | 1024 |
| SiC/Al-Cu | 1220 | 1088 |
| [1] | SONG M, HE Y H . Effects of die-pressing pressure andextrusion on the microstructures and mechanical properties of SiC reinforced pure aluminium composites. Mater. Design, 2010,31(2):985-989. |
| [2] | FOX R T, NEWMAN R A, PYZIK A J , et al. Al2O3-B4C-Al composite material system via pressure less infiltration methods. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol., 2010,7(6):837-845. |
| [3] | LEE H S, JEON K Y, KIM H Y , et al. Fabrication process and thermal properties of SiCp/Al metal matrix composites for electronic packaging applications. J. Mater. Sci., 2000,35(24):6231-6236. |
| [4] | LI C Y, HU Y K, ZHENG X J , et al. Study of microstructure of SiCp/ZL101A composites by vacuum hot-pressing sintering processing. Rare Metal Mater. Eng., 2014,41(2):413-416. |
| [5] | HE P, HUANG S Y, WANG H C , et al. Electroless nickel -phosphorus plating on silicon carbide particles for metal matrix composites. Ceram. Int., 2014,40(10):16653-16664. |
| [6] | BHUSHAN R K, KUMAR S, DAS S . Optimisation of porosity of 7075 Al alloy 10% SiC composite produced by stir casting process through Taguchi method. Int. J. Mater. Eng. Innov., 2009,1(1):116-129. |
| [7] | MANDALl D, VISWANATHAN S . Effect of re-melting on particles distribution and interface formation in SiC reinforced 2124Al matric composite. Mater. Charact., 2013,86:21-27. |
| [8] | RATNAPARKHI P L, HOWE J M . Characterization of a diffusion- bonded Al-Mg alloy/SiC interface by high resolution and analytical electron microscopy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1994,25(3):617-627. |
| [9] | LUO Z P . Crystallography of SiC/MgAl2O4/Al interfaces in a pre-oxidizied SiC reinforced SiC/Al composite. Acta Mater., 2006,54(1):47-58. |
| [10] | MANDALl D, VISWANATHAN S . Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and interface of SiC particle reinforced 2124 Al matrix composite. Mater. Charact., 2013,85:73-81. |
| [11] | AGUILAR-MARTÍNEZ J A, PECH-CANUL M I, RODRÍGUEZ- REYES M , et al. Effect of Mg and SiC type on the processing of two-layer Al/SiCp composites by pressureless infiltration. J. Mater. Sci., 2004,39(3):1025-1028. |
| [12] | EUSTATHOPOULOS N, LAURENT V, RADO C . Wetting kinetics and bonding of Al and Al alloys on α-SiC. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1996,205(1/2):1-8. |
| [13] | KOBASHI M, CHOH T . The wettability and the reaction for SiC particlce/Al alloy system. J. Mater. Sci., 1993,28(3):684-690. |
| [14] | FERRO A C, DERBY B . Wetting behavior in the Al-Si/SiC system: interface reactions and solubility effects. Acta Mater., 1995,43(8):3061-3073. |
| [15] | MA X C, WU J B . An investigation on wettability and interfacial phenomena of Al-SiC system. J. Mater. Sci. Eng., 1994,12(1):37-41. |
| [16] | ZHANG Q, JIA L T, WU G H . Fabrication of oxidized SiC particles reinforced aluminum matrix composite by pressureless infiltration technique. J. Inorg. Mater., 2012,27(4):353-357. |
| [17] | LIU J Y, LIU Y C, LIU G Q , et al. Oxidation behavior of silicon carbide particales and their interfacial characterization in aluminum matrix composites. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met., 2002,12(5):961-966. |
| [18] | ZHANG D, SHEN P, SHI L X . Wetting and evaporation behaviors of molten Mg on partially oxidized SiC substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2010,256(23):7043-7047. |
| [19] | JONES R O, GUNNARSSON O . Density-functional formalism: sources of error in local-density applications. Phys. Rev. Lett., 1989,61(3):689-746. |
| [20] | HONG T, SIMTH J R, SROLOVITZ D J . Theory of meta-ceramic adhesion. Acta Metall. Mater., 1995,43(7):2721-2730. |
| [21] | HAYES R L, ORTIZ M, CARTER E A . Universal binding-energy relation for crystals that accounts for surface relaxation. Phys. Rev. B, 2004,69(17):1324-1332. |
| [22] | SHI L X, SHEN P, ZHANG D, JIANG Q C . Wetting and evaporation behaviors of molten Mg-Al alloy drops on partially oxidized α-SiC substrates. Mater Z. Chem. Phys., 2011,130(3):1125-1133. |
| [23] | SAIZ E, CANNON R M, TOMSIA A P . Reactive spreading in ceramic/metal systems. Oil Gas Sci. Technol., 2001,56(1):89-96. |
| [24] | HOEKSTRA J, KOHYAMA M . Ab initio calculations of the β-SiC(001)/Al interface. Phys. Rev. B, 1998,57(4):2334-2341. |
| [25] | WINKLER B, PICKARD C J, SEGALL M D , et al. Density- functional study of charge disordering in Cs2Au(I)Au(Ⅲ)Cl6 under pressure. Phys. Rev. B, 2001,63(21):214103-214106. |
| [26] | LIU Y M, SHI J Y, LU Q Q , et al. Research progress of solid surface energy calculation based on Young's equation. Mater. Rev., 2013,23(11):123-129. |
| [27] | CANDAN E, ATKINSON H V, TUREN Y , et al. Wettability of aluminum-magnesium alloys on silicon carbide substrates. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2011,94(3):867-874. |
| [1] | 吴玉豪, 彭仁赐, 程春玉, 杨丽, 周益春. HfxTa1-xC体系力学性能及熔化曲线的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 761-768. |
| [2] | 靳宇翔, 宋二红, 朱永福. 3d过渡金属单原子掺杂石墨烯缺陷电催化还原CO2的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 845-852. |
| [3] | 王伟华, 张磊宁, 丁峰, 代兵, 韩杰才, 朱嘉琦, 贾怡, 杨宇. 铱衬底上金刚石外延形核与生长: 第一性原理计算[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 416-422. |
| [4] | 张宇晨, 陆知遥, 赫晓东, 宋广平, 朱春城, 郑永挺, 柏跃磊. 硫族MAX相硼化物的物相稳定性和性能预测[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 225-232. |
| [5] | 周靖渝, 李兴宇, 赵晓琳, 王有伟, 宋二红, 刘建军. Ti和Cu掺杂β-NaMnO2正极材料:钠离子电池的倍率和循环性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1404-1412. |
| [6] | 陈梦杰, 王倩倩, 吴成铁, 黄健. 基于DFT的描述符预测生物陶瓷的降解性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1175-1181. |
| [7] | 周云凯, 刁亚琪, 王明磊, 张宴会, 王利民. 聚苯胺改性Ti3C2(OH)2抗氧化性的第一性原理计算研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1151-1158. |
| [8] | 吴晓维, 张涵, 曾彪, 明辰, 孙宜阳. 杂化泛函HSE和PBE0计算CsPbI3缺陷性质的比较研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1110-1116. |
| [9] | 张守超, 陈洪雨, 刘洪飞, 杨羽, 李欣, 刘德峰. 6H-SiC中子辐照肿胀高温回复及光学特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 678-686. |
| [10] | 杨颖康, 邵怡晴, 李柏良, 吕志伟, 王路路, 王亮君, 曹逊, 吴宇宁, 黄荣, 杨长. Cl掺杂对CuI薄膜发光性能增强研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 687-692. |
| [11] | 华思恒, 杨东旺, 唐昊, 袁雄, 展若雨, 徐卓明, 吕嘉南, 肖娅妮, 鄢永高, 唐新峰. n型Bi2Te3基材料表面处理对热电单元性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 163-169. |
| [12] | 文志勤, 黄彬荣, 卢涛仪, 邹正光. 压力对PbTiO3结构和热物性质影响的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 787-794. |
| [13] | 孙铭, 邵溥真, 孙凯, 黄建华, 张强, 修子扬, 肖海英, 武高辉. RGO/Al复合材料界面性质第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 651-659. |
| [14] | 肖美霞, 李苗苗, 宋二红, 宋海洋, 李钊, 毕佳颖. 表面端基卤化Ti3C2 MXene应用于锂离子电池高容量电极材料的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 660-668. |
| [15] | 袁罡, 马新国, 贺华, 邓水全, 段汪洋, 程正旺, 邹维. 平面应变对二维单层MoSi2N4能带结构和光电性质的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 527-533. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||