无机材料学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (11): 1156-1160.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190031 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20190031
收稿日期:2019-01-16
修回日期:2019-04-18
出版日期:2019-11-20
网络出版日期:2019-05-29
作者简介:王君诚(1993-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: wangjuncheng@whut.edu.cn
基金资助:
WANG Jun-Cheng1,YANG Fei-Fei2,GAO Guan-Bin1( ),SUN Tao-Lei1,2(
),SUN Tao-Lei1,2( )
)
Received:2019-01-16
Revised:2019-04-18
Published:2019-11-20
Online:2019-05-29
Supported by:摘要:
近红外荧光特别是近红外Ⅱ区(1000~1700 nm)荧光在生物体内具有高组织渗透率、高时空分辨率、低背景荧光干扰和低光损伤的特点, 因此发展水溶性与生物相容性良好、量子产率高的长波段近红外荧光探针意义重大。本研究制备了不同荧光发射的Ag掺杂HgS量子点(HgAgS量子点)。在不同pH溶液中制备的HgAgS量子点荧光发射峰位于近红外Ⅱ区, 且呈现规律性变化; 随pH的增大, HgAgS量子点荧光发射峰先红移而后蓝移, 发射波长在pH 6时达到最大1110 nm; 原子吸收光谱表明在不同pH溶液中制备的HgAgS量子点, Ag的掺杂量(Ag/Hg比值)呈现出与荧光发射峰相同的规律性变化, 证明通过pH调控Ag的掺杂量从而调谐荧光发射峰的位置。HgAgS量子点的量子产率随pH先增加后降低, 在pH 7时达到最大13.23%(λem=1100 nm)。细胞毒性实验表明Ag的掺杂量对HgAgS量子点的细胞毒性无明显影响, 在1~50 μg/L浓度范围内均无明显细胞毒性。本研究结果不仅为体内进行近红外荧光成像提供了基础研究数据, 而且为荧光纳米探针的设计与制备提出了新的见解。
中图分类号:
王君诚, 杨菲菲, 高冠斌, 孙涛垒. Ag掺杂HgS量子点: 一种pH调谐的近红外Ⅱ区荧光纳米探针[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(11): 1156-1160.
WANG Jun-Cheng, YANG Fei-Fei, GAO Guan-Bin, SUN Tao-Lei. Ag doped HgS Quantum Dots: a pH-tunable Near-infrared-Ⅱ Fluorescent Nanoprobe[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(11): 1156-1160.
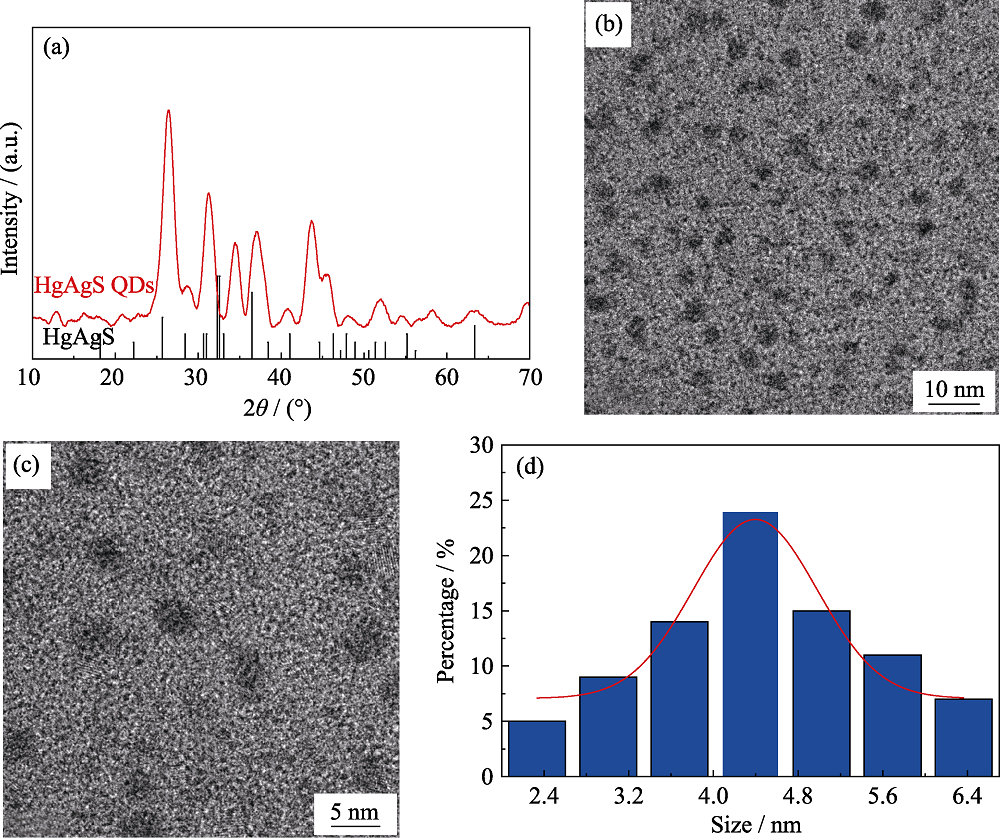
图1 HgAgS量子点的X射线衍射图谱(a), 透射电子显微镜照片(b), 高分辨透射电镜照片(c)和粒径统计分布图(d)
Fig. 1 XRD pattern (a), TEM image (b), HR-TEM image (c), and size distribution (d) of HgAgS QDs
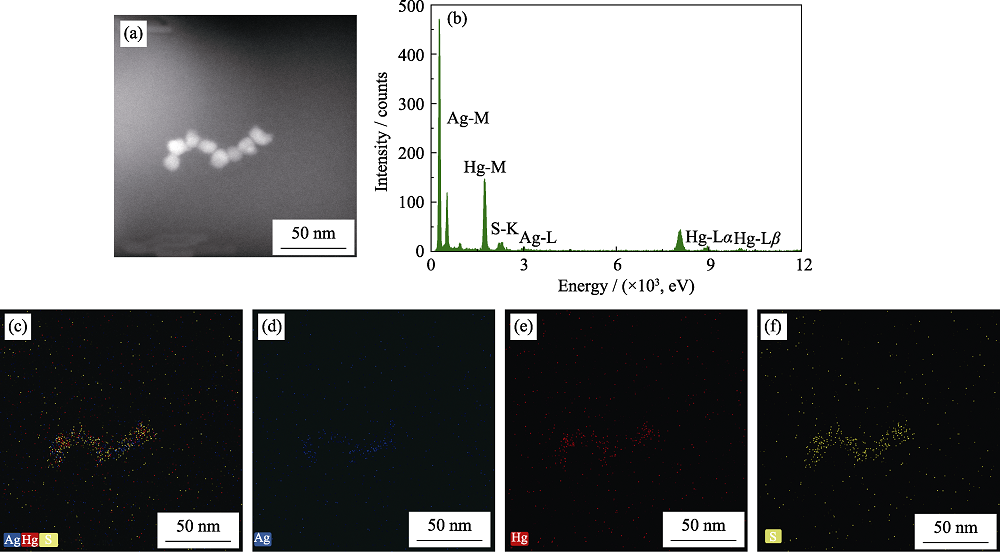
图2 HgAgS量子点的扫描透射电子显微镜高角环形暗场照片(HAADF) (a)和能谱图(b), 及其Ag(蓝色)、Hg(红色)和S(黄色)三种元素混合(c)和对应的单一元素Ag(d)、Hg(e)和S(f)分布图
Fig. 2 High-angle annular dark field (HAADF), STEM image (a) and EDS (b) of HgAgS QDs; Mixed elements mapping of HgAgS QDs (c) with corresponding single element Ag(blue) (d), Hg(red) (e) and S(yellow) (f) elements distribution
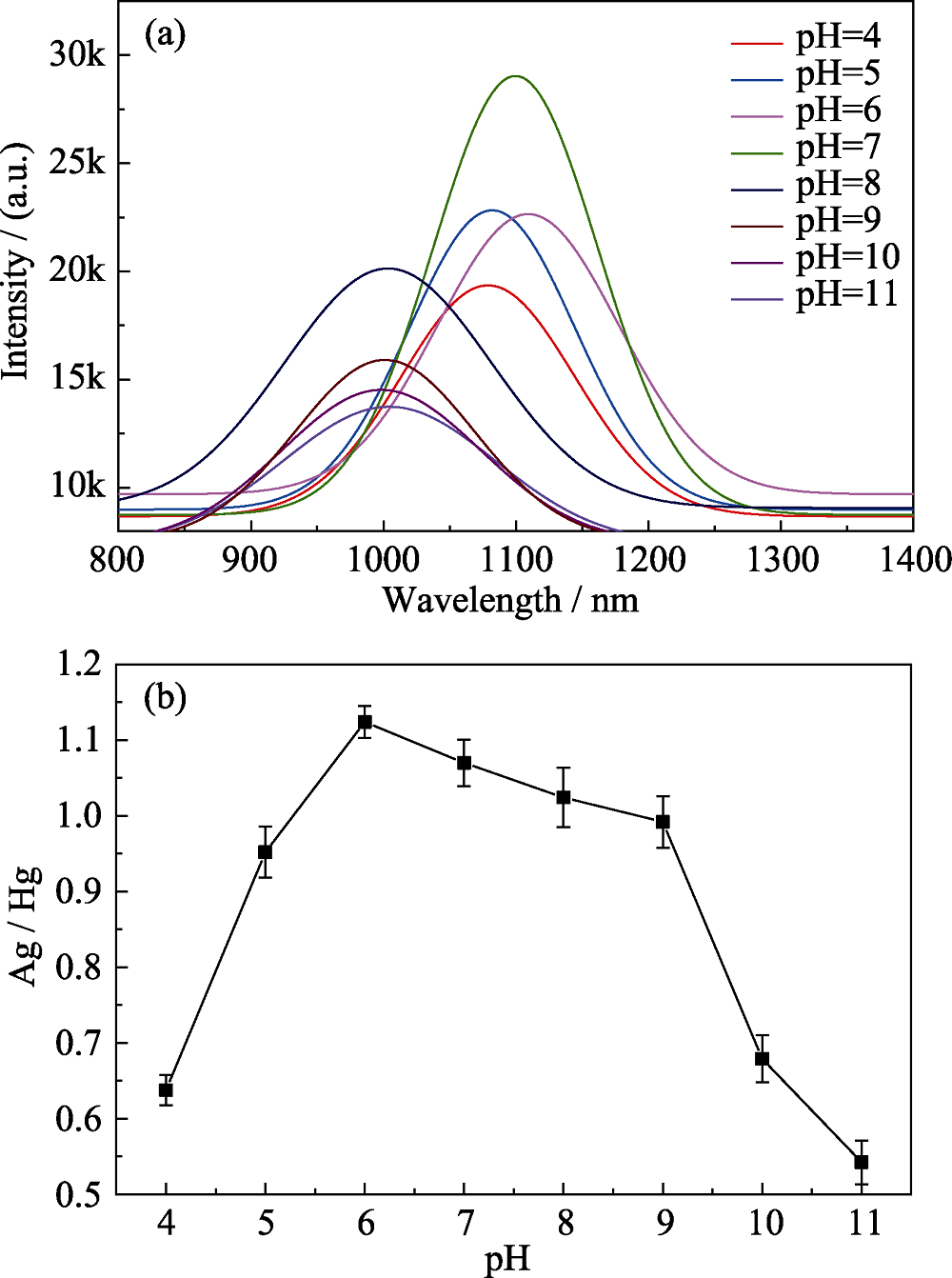
图4 激发波长为400 nm时在不同pH下制备的HgAgS量子点的荧光光谱(a)及其Ag/Hg值变化(彩图见网页)
Fig. 4 Fluorescence (a) and Ag/Hg value (b) of HgAgS QDs with different synthetic pH (Ex=400 nm) (colourful edition is available on website)
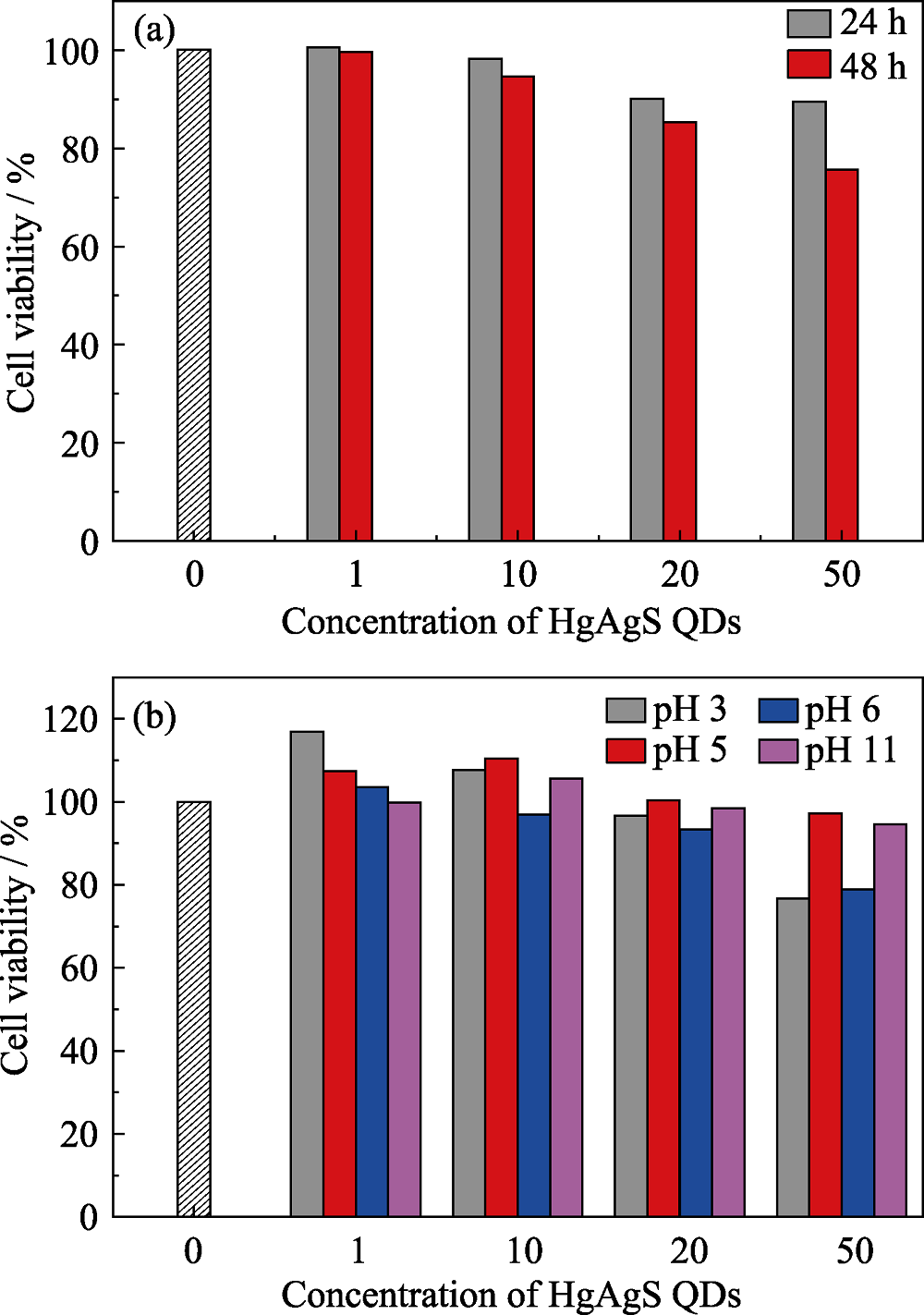
图5 HgAgS量子点(pH=6.0制备)在不同时间下对INS-1细胞的细胞活性影响(a)和不同pH条件下制备的HgAgS量子点对PC12细胞的活性影响(b)
Fig. 5 Cell viability of HgAgS QDs prepared at pH 6.0 on INS-1 cells for 24 and 48 h (a), and cell viability of HgAgS QDs prepared at pH=3.0, 5.0, 6.0 and 11.0 on PC12 cells (b). Concentrations of HgAgS QDs were 0, 1, 10, 20 and 50 μg/L
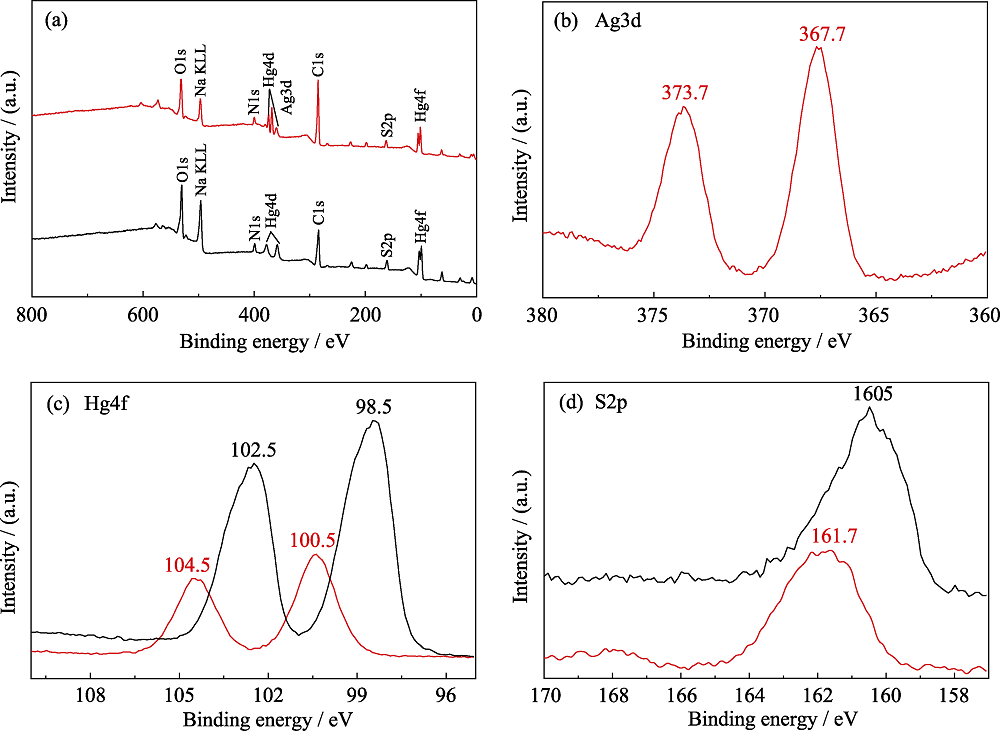
图8 图S3 HgS量子点(黑色曲线)和HgAgS量子点(红色曲线)的全谱(a)、Ag3d(b)、Hg4f(c)和S2p(d)的特征谱
Fig. 8 Fig. S3 Survey spectra (a), Ag3d (b), Hg4f (c) and S2p (d) spectra of HgS QDs (black curves) and HgAgS QDs (red curves)
| [1] | LIU SHI-YU, XIONG HAO, LI RONG-RONG , et al. Activity- based near-infrared fluorogenic probe enables in vitro and in vivo profiling of neutrophil elastase. Analytical Chemistry, 2019,91(6):3877-3884. |
| [2] | NING JING, LIU TAO, DONG PEI-PEI , et al. Molecular design strategy to construct the near-infrared fluorescent probe for selectively sensing human cytochrome P450 2J2. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019,141(2):1126-1134. |
| [3] | LIU TZU-MING, CONDE JOAO, LIPINSKI TOMASZ , et al. Revisiting the classification of NIR-absorbing/emitting nanomaterials for in vivo bioapplications. NPG Asia Materials, 2016,8:25. |
| [4] | BHATTARAI DEVAL-PRASAD, TIWARI ARJUN-PRASAD, MAHARJAN BIKENDRA , et al. Sacrificial template-based synthetic approach of polypyrrole hollow fibers for photothermal therapy. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019,534:447-458. |
| [5] | TIAN YE, RAN RAN, JIAO YUN-FENG , et al. Redox stimuli- responsive hollow mesoporous silica nanocarriers for targeted drug delivery in cancer therapy. Nanoscale Horizons, 2016,1(6):480-487. |
| [6] | LIU YANG, SONG NAN, LI ZHEN-SHENG , et al. Near-infrared nanoparticles based on aza-BDP for photodynamic and photothermal therapy. Dyes and Pigments, 2019,160:71-78. |
| [7] | WANG XUAN, LI ZHONG-LIANG, NAN NAN , et al. A simple system of swept source optical coherence tomography for a large imaging depth range. Optics Communications, 2019,431:51-57. |
| [8] | HANKIEWICZ J H, STOLL J A, STROUD J , et al. Nano-sized ferrite particles for magnetic resonance imaging thermometry. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2019,469:550-557. |
| [9] | LAN XIANG, WANG QIANG-BIN . Optically active AuNR@Ag core-shell nanoparticles and hierarchical assembly via DNA-mediated surface chemistry. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016,8(50):34598-34602. |
| [10] | KONG YI-FEI, CHEN JUN, FANG HONG-WEI , et al. Highly fluorescent ribonuclease-A-encapsulated lead sulfide quantum dots for ultrasensitive fluorescence in vivo imaging in the second near- infrared window. Chemistry of Materials, 2016,28(9):3041-3050. |
| [11] | LIN SHU, FENG YU, WEN XIAO-MING , et al. Theoretical and experimental investigation of the electronic structure and quantum confinement of wet-chemistry synthesized Ag2S nanocrystals. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014,119(1):867-872. |
| [12] | YANG JING, HU YAO-PING, TAN JIANG-WEI , et al. Ultra- bright near-infrared-emitting HgS/ZnS core/shell nanocrystals for in vitro and in vivo imaging. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2015,3(34):6928-6938. |
| [13] | ZHANG MING-XI, YUE JING-YING, CUI RAN , et al. Bright quantum dots emitting at similar to 1,600 nm in the NIR-IIb window for deep tissue fluorescence imaging. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018,115(26):6590-6595. |
| [14] | XIONG HU, ZHOU KE-JIN, YAN YUN-FENG , et al. Tumor- activated water-soluble photosensitizers for near-infrared photodynamic cancer therapy. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018,10(19):16335-16343. |
| [15] | YANG ZHEN, TIAN RUI, WU JIN-JUN , et al. Impact of semiconducting perylene diimide nanoparticle size on lymph node mapping and cancer imaging. ACS Nano, 2017,11(4):4247-4255. |
| [16] | BRAUN MARKUS, BURDA CLEMENS, EI-SAYED MOSTAFA-A . Variation of the thickness and number of wells in the CdS/ HgS/CdS quantum dot quantum well system. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2001,105(22):5548-5551. |
| [17] | ZHANG WEN-HAO, YANG JING, YU JUN-SHENG . Synthesis of stable near-infrared emitting HgTe/CdS core/shell nanocrystals using dihydrolipoic acid as stabilizer. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012,22(13):6383-6388. |
| [18] | SUN TING-TING, DOU JIN-HU, LIU SHI , et al. Second near-infrared conjugated polymer nanoparticles for photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018,10(9):7919-7926. |
| [19] | QIN HAI-YAN, NIU YUAN, MENG REN-YANG , et al. Single- dot spectroscopy of zinc-blende CdSe/CdS core/shell nano-crystals: nonblinking and correlation with ensemble measurements. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014,136(1):179-187. |
| [20] | GAO GUAN-BIN, ZHANG MING-XI, GONG DE-JUN , et al. The size-effect of gold nanoparticles and nanoclusters in the inhibition of amyloid-beta fibrillation. Nanoscale, 2017,9(12):4107-4113. |
| [21] | SHEN GUO-HUA, GUYOT-SIONNEST PHILIPPE . HgS and HgS/CdS colloidal quantum dots with infrared intraband transitions and emergence of a surface plasmon. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016,120(21):11744-11753. |
| [22] | YANG FEI-FEI, GAO GUAN-BIN, WANG JUN-CHENG , et al. Chiral β-HgS quantum dots: aqueous synthesis, optical properties and cytocompatibility. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019,537:422-430. |
| [1] | 王晓波, 朱于良, 薛稳超, 史汝川, 骆柏锋, 罗骋韬. PT含量变化对PMN-PT单晶的大功率性能影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 840-846. |
| [2] | 汤新丽, 丁自友, 陈俊锐, 赵刚, 韩颖超. 基于稀土铕离子荧光标记的磷酸钙纳米材料体内分布与代谢研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 754-764. |
| [3] | 余乐洋阳, 赵芳霞, 张舒心, 徐以祥, 牛亚然, 张振忠, 郑学斌. 感应等离子球化技术制备喷涂用高熵硼化物粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 808-816. |
| [4] | 杨光, 张楠, 陈舒锦, 王义, 谢安, 严育杰. 基于多孔ITO电极的WO3薄膜的制备及其电致变色性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 781-789. |
| [5] | 孙晶, 李翔, 毛小建, 章健, 王士维. 月桂酸改性剂对氮化铝粉体抗水解性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 826-832. |
| [6] | 柴润宇, 张镇, 王孟龙, 夏长荣. 直接组装法制备氧化铈基金属支撑固体氧化物燃料电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 765-771. |
| [7] | 王鲁杰, 张玉新, 李彤阳, 于源, 任鹏伟, 王建章, 汤华国, 姚秀敏, 黄毅华, 刘学建, 乔竹辉. 深海服役环境下碳化硅陶瓷材料的腐蚀及磨损行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 799-807. |
| [8] | 李文元, 徐佳楠, 邓瀚澳, 常爱民, 张博. 钒取代对LaTaO4陶瓷微观结构和微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 697-703. |
| [9] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [10] | 董晨雨, 郑维杰, 马一帆, 郑春艳, 温峥. 压电力显微镜表征Pb(Mg,Nb)O3-PbTiO3超薄膜弛豫特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 675-682. |
| [11] | 何国强, 张恺恒, 王震涛, 包健, 席兆琛, 方振, 王昌昊, 王威, 王鑫, 姜佳沛, 李祥坤, 周迪. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: 一种被低估的K40微波介质陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 639-646. |
| [12] | 张家维, 陈宁, 程原, 王博, 朱建国, 金城. Bi4Ti3O12铋层状压电陶瓷的A/B位掺杂及其电学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 690-696. |
| [13] | 崔宁, 张玉新, 王鲁杰, 李彤阳, 于源, 汤华国, 乔竹辉. (TiVNbMoW)Cx高熵陶瓷的单相形成过程与碳空位调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [14] | 熊思宇, 莫尘, 朱肖伟, 朱国斌, 陈德钦, 刘来君, 施晓东, 李纯纯. 超低介电常数LiBxAl1-xSi2O6微波介质陶瓷的低温烧结[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 536-544. |
| [15] | 安然, 林锶, 郭世刚, 张冲, 祝顺, 韩颖超. 铁掺杂纳米羟基磷灰石的制备及紫外吸收性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 457-465. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||