无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (7): 808-816.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250008 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250008
余乐洋阳1,2( ), 赵芳霞1(
), 赵芳霞1( ), 张舒心2, 徐以祥2, 牛亚然2(
), 张舒心2, 徐以祥2, 牛亚然2( ), 张振忠1, 郑学斌2
), 张振忠1, 郑学斌2
收稿日期:2025-01-07
修回日期:2025-02-21
出版日期:2025-07-20
网络出版日期:2025-03-06
通讯作者:
赵芳霞, 教授. E-mail: fangxiazhao@126.com;作者简介:余乐洋阳(1999-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: leyangyangyu@126.com
YU Leyangyang1,2( ), ZHAO Fangxia1(
), ZHAO Fangxia1( ), ZHANG Shuxin2, XU Yixiang2, NIU Yaran2(
), ZHANG Shuxin2, XU Yixiang2, NIU Yaran2( ), ZHANG Zhenzhong1, ZHENG Xuebin2
), ZHANG Zhenzhong1, ZHENG Xuebin2
Received:2025-01-07
Revised:2025-02-21
Published:2025-07-20
Online:2025-03-06
Contact:
ZHAO Fangxia, professor. E-mail: fangxiazhao@126.com;About author:YU Leyangyang (1999-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: leyangyangyu@126.com
摘要:
原料粉体的制备是直接影响等离子喷涂涂层结构与性能的关键技术之一。目前, 制备高熵硼化物粉体的常用方法——硼热还原法存在制备周期长、产物含杂质及用于喷涂的粉体无法直接得到等缺点。本工作采用感应等离子球化(Inductive plasma spheroidization, IPS)工艺制备了喷涂用(Zr1/4Hf1/4Ta1/4Ti1/4)B2高熵粉体, 并与两种传统粉体制备工艺进行了比较。研究表征了不同工艺粉体的形貌、内部结构以及粒径、密度等基本性能, 探究了不同粉体制备工艺对高熵硼化物粉体显微结构及基本性能的影响, 并验证了IPS工艺制备高熵硼化物粉体的普适性。结果表明, 以商用微米级硼化物粉体为原料, 通过混合-造粒-烧结-IPS工艺可制备元素分布均匀的高熵粉体, 该粉体还具有表面光滑、球形形状、内部致密, 且松装密度和振实密度高的特征。采用IPS工艺制备不同组元种类和含量的高熵硼化物粉体, 进一步验证了该工艺具有良好的普适性。结合第一性原理计算和IPS技术的特点, 深入分析了粉体组元固溶高熵化的形成机制。本工作有望为喷涂用高熵陶瓷粉体的制备提供一种新的方法。
中图分类号:
余乐洋阳, 赵芳霞, 张舒心, 徐以祥, 牛亚然, 张振忠, 郑学斌. 感应等离子球化技术制备喷涂用高熵硼化物粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 808-816.
YU Leyangyang, ZHAO Fangxia, ZHANG Shuxin, XU Yixiang, NIU Yaran, ZHANG Zhenzhong, ZHENG Xuebin. Preparation of High-entropy Boride Powders for Plasma Spraying by Inductive Plasma Spheroidization[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 808-816.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Second gas (H2)/slpm | 30-60 |
| Primary gas (Ar)/slpm | 120-150 |
| Chamber pressure/psig | 3-7 |
| Powder feed rate/(g·min-1) | 20-40 |
表1 感应等离子球化制备粉体的工艺参数
Table 1 Process parameters for powder preparation by inductive plasma spheroidization
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Second gas (H2)/slpm | 30-60 |
| Primary gas (Ar)/slpm | 120-150 |
| Chamber pressure/psig | 3-7 |
| Powder feed rate/(g·min-1) | 20-40 |
| Powder | D10/μm | D50/μm | D90/μm | D97/μm | Apparent density/(g·cm-3) | Tap density/(g·cm-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIX | 16.53 | 33.14 | 61.72 | 77.85 | 1.93 | 2.38 |
| BTR | 19.65 | 34.92 | 66.66 | 79.61 | 2.25 | 2.82 |
| IPS | 11.08 | 28.65 | 56.61 | 73.30 | 4.40 | 4.77 |
表2 三种(Zr1/4Hf1/4Ta1/4Ti1/4)B2粉体的粒径分布、松装密度及振实密度
Table 2 Particle size distribution, apparent and tap densities of three kinds of (Zr1/4Hf1/4Ta1/4Ti1/4)B2 powders
| Powder | D10/μm | D50/μm | D90/μm | D97/μm | Apparent density/(g·cm-3) | Tap density/(g·cm-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIX | 16.53 | 33.14 | 61.72 | 77.85 | 1.93 | 2.38 |
| BTR | 19.65 | 34.92 | 66.66 | 79.61 | 2.25 | 2.82 |
| IPS | 11.08 | 28.65 | 56.61 | 73.30 | 4.40 | 4.77 |

图5 三种工艺制备的(Zr1/4Hf1/4Ta1/4Ti1/4)B2粉体的TG-DSC曲线(a)与单组元硼化物氧化反应的吉布斯自由能(b)
Fig. 5 TG-DSC curves of (Zr1/4Hf1/4Ta1/4Ti1/4)B2 powders prepared by three processes (a) and Gibbs free energy for the oxidation reaction of single-component borides (b) Colorful figures are available on website
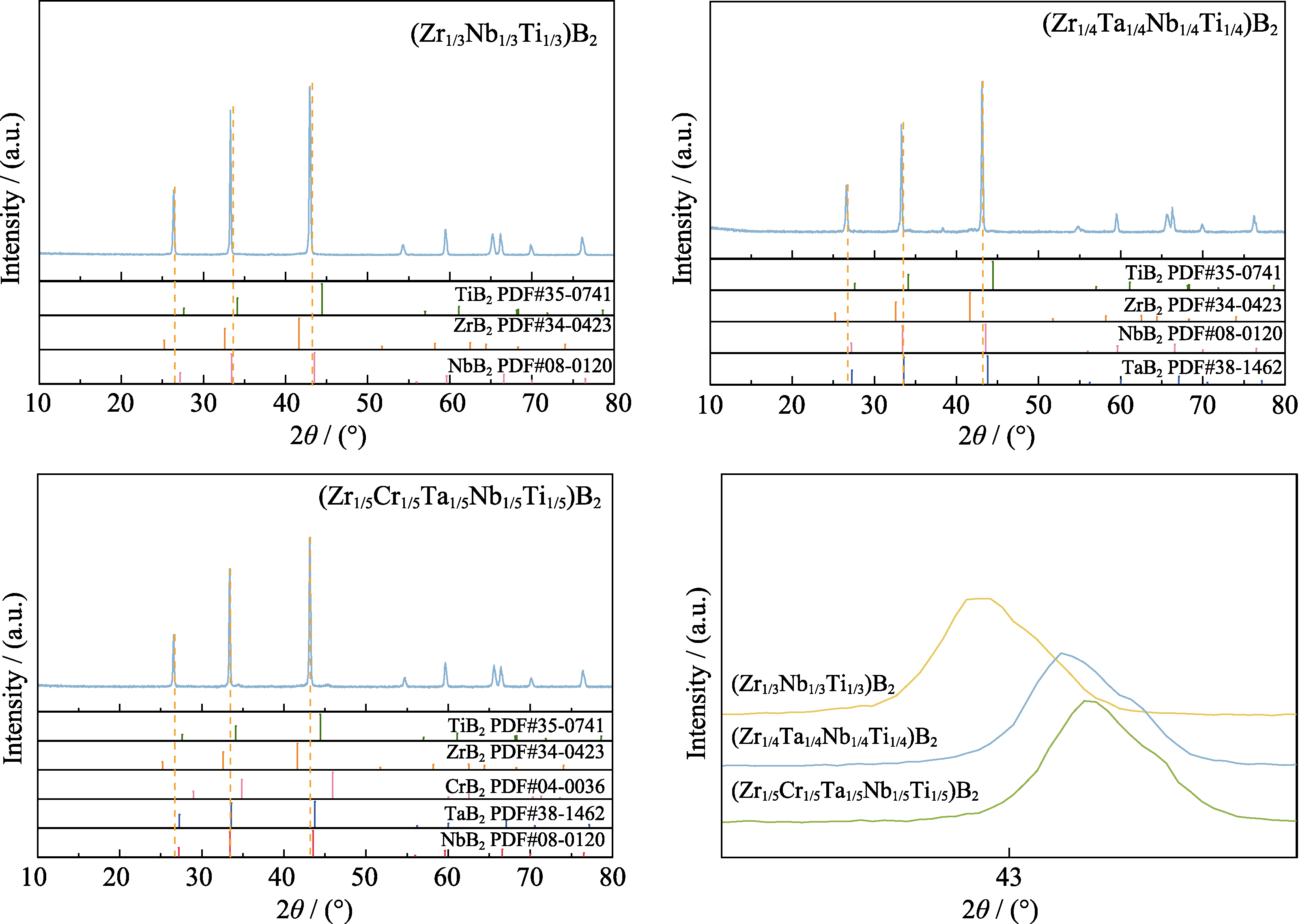
图6 IPS制备的(Zr1/3Nb1/3Ti1/3)B2、(Zr1/4Ta1/4Nb1/4Ti1/4)B2、(Zr1/5Cr1/5Ta1/5Nb1/5Ti1/5)B2粉体的XRD图谱
Fig. 6 XRD patterns of (Zr1/3Nb1/3Ti1/3)B2, (Zr1/4Ta1/4Nb1/4Ti1/4)B2, and (Zr1/5Cr1/5Ta1/5Nb1/5Ti1/5)B2 powders prepared by IPS

图7 IPS制备的(Zr1/3Nb1/3Ti1/3)B2 (a)、(Zr1/4Ta1/4Nb1/4Ti1/4)B2 (b)、(Zr1/5Cr1/5Ta1/5Nb1/5Ti1/5)B2 (c)粉体的SEM照片和EDS分析
Fig. 7 SEM images and EDS mappings of (Zr1/3Nb1/3Ti1/3)B2 (a), (Zr1/4Ta1/4Nb1/4Ti1/4)B2 (b), and (Zr1/5Cr1/5Ta1/5Nb1/5Ti1/5)B2 (c) powders prepared by IPS Table shows the corresponding element contents (in atom) of spot 1-spot 6
| (Me0.5Zr0.5)B2 | Etot/(eV·atom-1) | Ecoh/(eV·atom-1) |
|---|---|---|
| (Ti0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -49.14 | -7.29 |
| (V0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -49.06 | -7.06 |
| (Cr0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -48.38 | -6.62 |
| (Nb0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -50.57 | -7.37 |
| (Mo0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -50.22 | -7.07 |
| (Hf0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -51.37 | -7.49 |
| (Ta0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -52.20 | -7.59 |
| (W0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -51.72 | -7.32 |
表3 (Me0.5Zr0.5)B2的密度泛函理论能Etot和结合能Ecoh
Table 3 Density functional theory energies (Etot) and cohesive energies (Ecoh) of (Me0.5Zr0.5)B2
| (Me0.5Zr0.5)B2 | Etot/(eV·atom-1) | Ecoh/(eV·atom-1) |
|---|---|---|
| (Ti0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -49.14 | -7.29 |
| (V0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -49.06 | -7.06 |
| (Cr0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -48.38 | -6.62 |
| (Nb0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -50.57 | -7.37 |
| (Mo0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -50.22 | -7.07 |
| (Hf0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -51.37 | -7.49 |
| (Ta0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -52.20 | -7.59 |
| (W0.5Zr0.5)B2 | -51.72 | -7.32 |
| [1] | 陈玉峰, 洪长青, 胡成龙, 等. 空天飞行器用热防护陶瓷材料. 现代技术陶瓷, 2017, 38(5): 311. |
| [2] |
PADTURE N P. Advanced structural ceramics in aerospace propulsion. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(8): 804.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | JIN X, FAN X, LU C, et al. Advances in oxidation and ablation resistance of high and ultra-high temperature ceramics modified or coated carbon/carbon composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(1): 1. |
| [4] | NI D, CHENG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Advances in ultra-high temperature ceramics, composites, and coatings. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2022, 11(1): 1. |
| [5] | OSES C, TOHER C, CURTAROLO S. High-entropy ceramics. Nature Reviews Materials, 2020, 5(4): 295. |
| [6] | CAI F Y, NI D W, DONG S M. Research progress of high-entropy carbide ultra-high temperature ceramics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 591. |
| [7] | HOQUE M S B, MILICH M, AKHANDA M S, et al. Thermal and ablation properties of a high-entropy metal diboride: (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ti0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2)B2. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(11): 4581. |
| [8] |
WANG H X, LIU Q M, WANG Y G. Research progress of high entropy transition metal carbide ceramics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 355.
DOI |
| [9] | GUO L X, TANG Y, HUANG S W, et al. Ablation resistance of high-entropy oxide coatings on C/C composites. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(1): 61. |
| [10] | XU Y, PAN X, HUANG S, et al. Effect of solid oxidation products on the ablation mechanisms of ZrC and HfC based coatings above 2000 ℃. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 22: 1900. |
| [11] | XU Y, ZHENG W, DAI M, et al. Effect of TaSi2 addition on long-term ablation behavior of HfB2-SiC coating. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(14): 5802. |
| [12] | XU Y, HUANG S, HAN D, et al. Effect of different SiC/TaSi2 contents on ablation behavior of ZrB2 coating. Corrosion Science, 2022, 205: 110424. |
| [13] | PAN X, NIU Y, LIU T, et al. Ablation behaviors of ZrC-TiC coatings prepared by vacuum plasma spray: above 2000 ℃. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(11): 3292. |
| [14] | 杜仲, 霍威, 赵帅, 等. YSZ粉末致密度对涂层性能的影响. 中国钨业, 2022, 37(1): 42. |
| [15] | 陈伟文. 粉末球形度对超音速火焰喷涂制备不锈钢涂层组织及性能的影响. 中国机械, 2019(11): 50. |
| [16] | GAO P H, YANG G J, CAO S T, et al. Heredity and variation of hollow structure from powders to coatings through atmospheric plasma spraying. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2016, 305: 76. |
| [17] | SUN S, LIU Y, MA Z, et al. Fabrication of ZrB2-SiC powder with a eutectic phase for sintering or plasma spraying. Powder Technology, 2020, 372: 506. |
| [18] | LI G, WANG D, WU Y, et al. The solid solution and microstructural evolution of WC doped Hf-Ta-C powders by induction plasma spheroidization. Powder Technology, 2023, 419: 118338. |
| [19] | PAN X, XU X, NIU Y, et al. Relationship analysis on particle-coating-ablation property of UHTC coatings fabricated by plasma spray technique. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(3): 3808. |
| [20] | LIU B, DUAN H, LI L, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ultra-hard spherical refractory high-entropy alloy powders fabricated by plasma spheroidization. Powder Technology, 2021, 382: 550. |
| [21] | SHEN X Q, LIU J X, LI F, et al. Preparation and characterization of diboride-based high entropy (Ti0.2Zr0.2Hf0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)B2-SiC particulate composites. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(18): 24508. |
| [22] | XU Y, YU L, ZHAO T, et al. Composition design of oxidation resistant non-equimolar high-entropy ceramic materials: an example of (Zr-Hf-Ta-Ti)B2 ultra-high temperature ceramics. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2024, 13(12): 2087. |
| [23] | POST B, GLASER F W, MOSKOWITZ D. Transition metal diborides. Acta Metallurgica, 1954, 2(1): 20. |
| [24] | LIU H, ZHAO X. Thermal conductivity analysis of high porosity structures with open and closed pores. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 183: 122089. |
| [25] |
BABAEI H, MCGAUGHEY A J H, WILMER C E. Effect of pore size and shape on the thermal conductivity of metal-organic frameworks. Chemical Science, 2017, 8(1): 583.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | LIU G A, WANG H L, FANG C, et al. Effect of B4C content on mechanical properties and oxidation resistance of (Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C ceramics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 697. |
| [27] | HOU X, CHOU K C. Quantitative investigation of oxidation behavior of boron carbide powders in air. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 573: 182. |
| [1] | 刘国昂, 王海龙, 方成, 黄飞龙, 杨欢. B4C含量对(Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C陶瓷力学性能及抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 697-706. |
| [2] | 张宇晨, 陆知遥, 赫晓东, 宋广平, 朱春城, 郑永挺, 柏跃磊. 硫族MAX相硼化物的物相稳定性和性能预测[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 225-232. |
| [3] | 李高然, 李红阳, 曾海波. 硼基材料在锂硫电池中的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 152-162. |
| [4] | 邹灿辉, 龙莹, 郑鑫, 张锦阳, 林华泰. 三元过渡金属硼化物Os1-xRuxB2的制备及其结构和性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(7): 787-792. |
| [5] | 潘 宇, 路 新, 魏治国, 王国庆, 曲选辉. 二元钒硼化物的反应合成及其放电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(4): 407-412. |
| [6] | 梁超龙, 张 忻, 张久兴, 张繁星, 王 杨. La1-xNdxB6阴极材料的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(4): 363-368. |
| [7] | 包黎红, 明 明, 特古斯. Eu-掺杂CeB6纳米晶的合成与光吸收研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(10): 1110-1114. |
| [8] | 张国军, 邹 冀, 倪德伟, 刘海涛, 阚艳梅. 硼化物陶瓷: 烧结致密化、微结构调控与性能提升[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(3): 225-233. |
| [9] | 包黎红, 张久兴, 周身林. Ba掺杂对稀土硼化物GdB6结构, 晶粒取向和热发射性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(10): 1116-1120. |
| [10] | 王永国,李兆前,张荻. 新型三元硼化物基金属陶瓷的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2003, 18(6): 1217-1221. |
| [11] | 张涛,李兆前,黄传真. 三元硼化物基金属陶瓷的液相烧结及其应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2002, 17(1): 17-23. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||