无机材料学报 ›› 2014, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (7): 687-694.DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2014.13494 CSTR: 32189.14.SP.J.1077.2014.13494
徐 润1, 李忻达1, 李志强1, 赵仁宇1, 范根莲1, 熊定邦1, 唐 婕1, 许 勇2, 张 荻1
收稿日期:2013-09-29
修回日期:2013-12-25
出版日期:2014-07-20
网络出版日期:2014-06-20
作者简介:徐 润(1991-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: x.r.my.mail@gmail.com
基金资助:XU Run1, LI Xin-Da1, LI Zhi-Qiang1, ZHAO Ren-Yu1, FAN Gen-Lian1, XIONG Ding-Bang1, TANG Jie1, XU Yong2, ZHANG Di1
Received:2013-09-29
Revised:2013-12-25
Published:2014-07-20
Online:2014-06-20
About author:XU Run. E-mail: x.r.my.mail@gmail.com
Supported by:摘要:
采用聚合物热解化学气相沉积(PP-CVD)法, 通过聚乙二醇(PEG)的原位热解提供碳源、柠檬酸(CA)和硝酸钴反应产生催化剂纳米粒子, 在微纳米级的片状铝粉基底上原位生长碳纳米管(CNTs)。通过实验和反应动力学建模研究了PP-CVD反应机理, 揭示了PEG热解气相成分和催化剂纳米粒子表面气-固反应对CNTs生长速率的影响规律。CO初始分压和反应温度提高, CNTs生长速率提高; H2初始分压和催化剂密度提高, CNTs生长速率降低。模型预测的CNTs平均长度随反应温度和反应时间的变化趋势符合实验结果。因此, 本研究为进一步优化CNTs/铝复合粉末制备工艺提供了新的理论依据。
中图分类号:
徐 润, 李忻达, 李志强, 赵仁宇, 范根莲, 熊定邦, 唐 婕, 许 勇, 张 荻. 聚合物热解法制备碳纳米管/铝复合粉末及其反应动力学研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(7): 687-694.
XU Run, LI Xin-Da, LI Zhi-Qiang, ZHAO Ren-Yu, FAN Gen-Lian, XIONG Ding-Bang, TANG Jie, XU Yong, ZHANG Di. Preparation and Reaction Kinetics of Carbon Nanotubes/Aluminum Composite Powders Using Polymer Pyrolysis Method[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(7): 687-694.
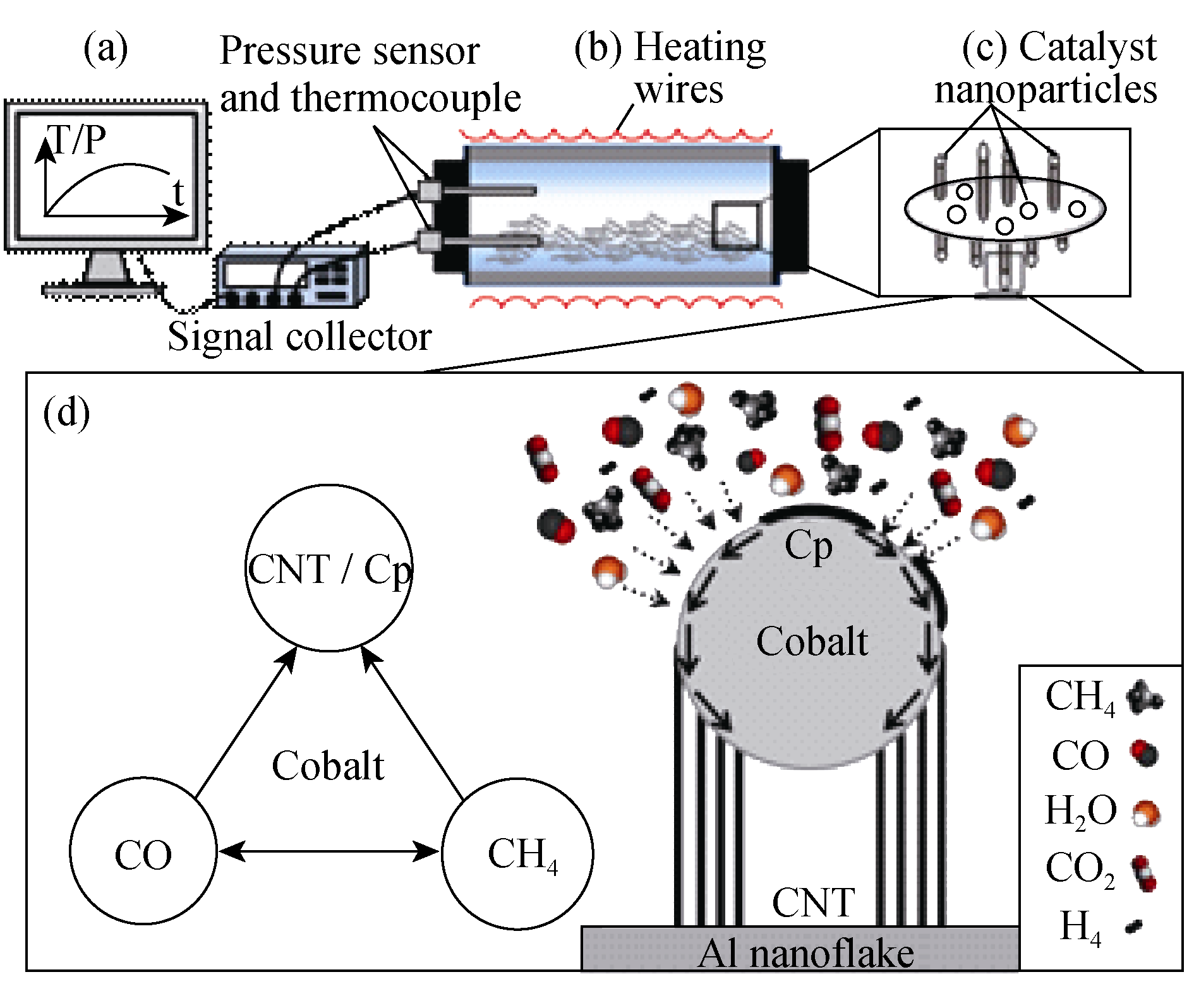
图1 PP-CVD生长CNTs示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic drawing of CNTs grown by PP-CVD (a) The temperature and pressure monitoring system; (b) The closed batch reactor; (c) Al nanoflakes with Co nanoparticles and CNTs as grown; (d) The gas-solid reaction pathway and tip growth mode of CNTs. The dashed arrows represent collision of gaseous species and the solid arrows represent surface diffusion of carbon atoms around the Co nanoparticle
| Symbols | Definition |
|---|---|
| Cp | Encapsulating carbon |
| (S) | Surface species |
| C(S) | Active carbon atom |
| | The forward (f ) reaction rate constant of the i th reaction |
| | The reverse (r) reaction rate constant of the i th reaction |
| A | The Arrhenius pre-exponential factor |
| | The Arrhenius temperature coefficient |
| Ei | The activation energy of the i th reaction |
| R | The universal gas constant |
| | The change in the Gibbs free energy of formation as a result of the reaction |
| | The net stoichiometric coefficient for species j in i th reaction |
| qi | The rate of progress of the i th reaction |
| Rj | The net rate of production of species j |
| Cj | The volumetric concentration of species j |
| Vdeposited | The volume of deposited carbon atoms |
| | The volume of encapsulating carbon |
| VC | The volume of a carbon atom |
| | The density of Co nanoparticles |
| | CNTs growth rate |
| d | The diameter of Co nanoparticles |
| NA | Avogadro constant |
| Do | The surface diffusion coefficient of carbon atoms |
表1 模型中使用的符号定义
Table 1 Nomenclature of the symbols used in the modeling
| Symbols | Definition |
|---|---|
| Cp | Encapsulating carbon |
| (S) | Surface species |
| C(S) | Active carbon atom |
| | The forward (f ) reaction rate constant of the i th reaction |
| | The reverse (r) reaction rate constant of the i th reaction |
| A | The Arrhenius pre-exponential factor |
| | The Arrhenius temperature coefficient |
| Ei | The activation energy of the i th reaction |
| R | The universal gas constant |
| | The change in the Gibbs free energy of formation as a result of the reaction |
| | The net stoichiometric coefficient for species j in i th reaction |
| qi | The rate of progress of the i th reaction |
| Rj | The net rate of production of species j |
| Cj | The volumetric concentration of species j |
| Vdeposited | The volume of deposited carbon atoms |
| | The volume of encapsulating carbon |
| VC | The volume of a carbon atom |
| | The density of Co nanoparticles |
| | CNTs growth rate |
| d | The diameter of Co nanoparticles |
| NA | Avogadro constant |
| Do | The surface diffusion coefficient of carbon atoms |
| The initial pressure /(1.013×105, Pa) | The initial partial pressure /(1.013×105, Pa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | CO | CO2 | H2O | H2 | |
| 22 | 1.61 | 6.24 | 6.18 | 5.65 | 1.53 |
表2 密闭反应器中PEG-CA-Co(II)热解气体组成
Table 2 Composition of the PEG-CA-Co(II) pyrolysis gases in the batch reactor
| The initial pressure /(1.013×105, Pa) | The initial partial pressure /(1.013×105, Pa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | CO | CO2 | H2O | H2 | |
| 22 | 1.61 | 6.24 | 6.18 | 5.65 | 1.53 |
| Species | CH4 | CO | CO2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Projected areaa | 2.43×10-2 | 2.01×10-2 | 3.45×10-2 |
| Ratiob | 3656 | 4388 | 2531 |
| Active site density c | 1.72×10-9 | 2.06×10-9 | 1.19×10-9 |
Table 3 The ratio of Co nanoparticle surface area to the projected area of carbon source gas molecules
| Species | CH4 | CO | CO2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Projected areaa | 2.43×10-2 | 2.01×10-2 | 3.45×10-2 |
| Ratiob | 3656 | 4388 | 2531 |
| Active site density c | 1.72×10-9 | 2.06×10-9 | 1.19×10-9 |
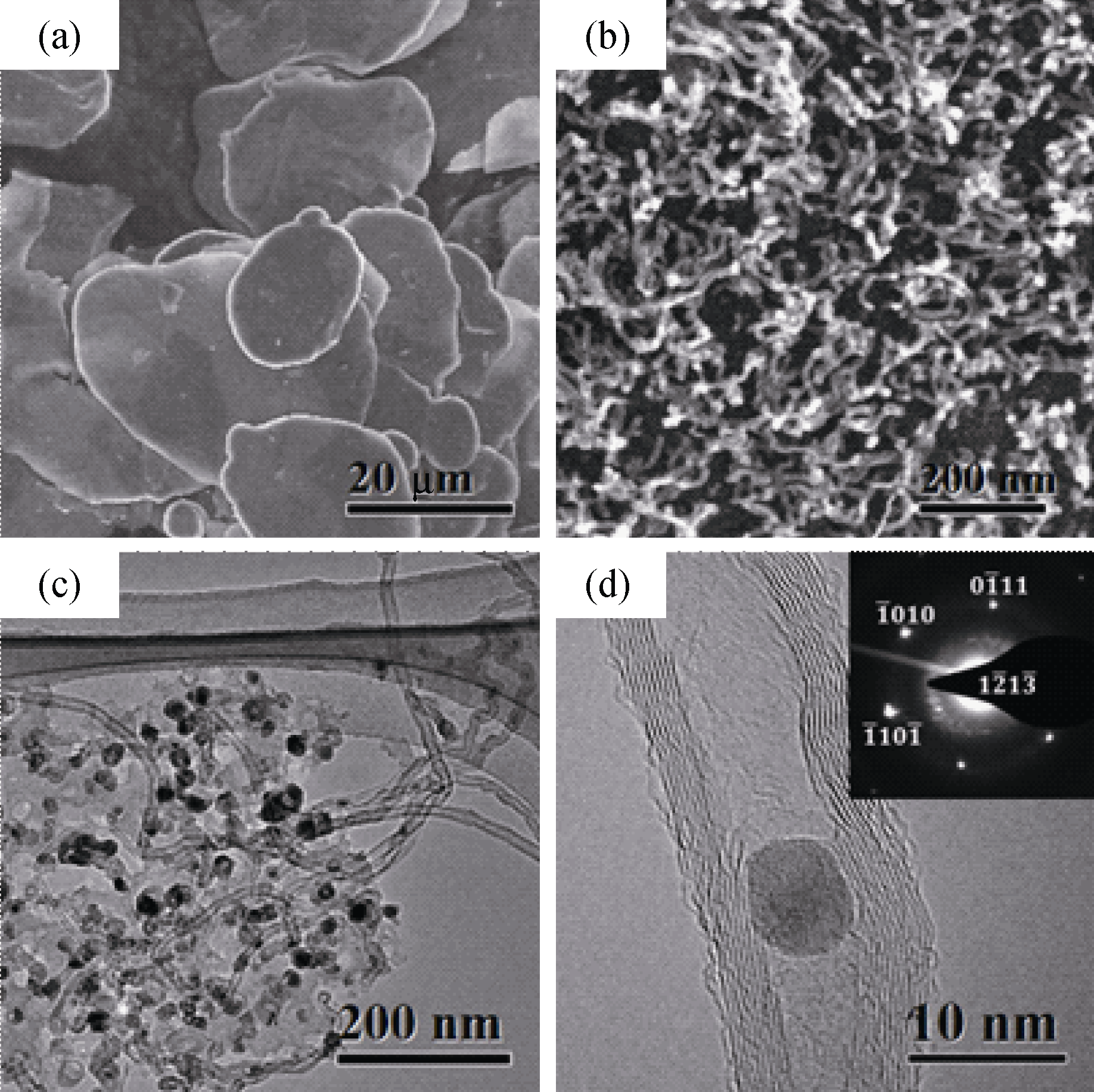
图3 不同尺度下的CNTs形貌
Fig. 3 Morphologies of CNTs at different scales (a) SEM image of the Al flake substrates; (b) SEM image of the CNTs; (c) TEM image of the CNTs; (d) HRTEM image of the CNTs and SEAD pattern of catalyst particle
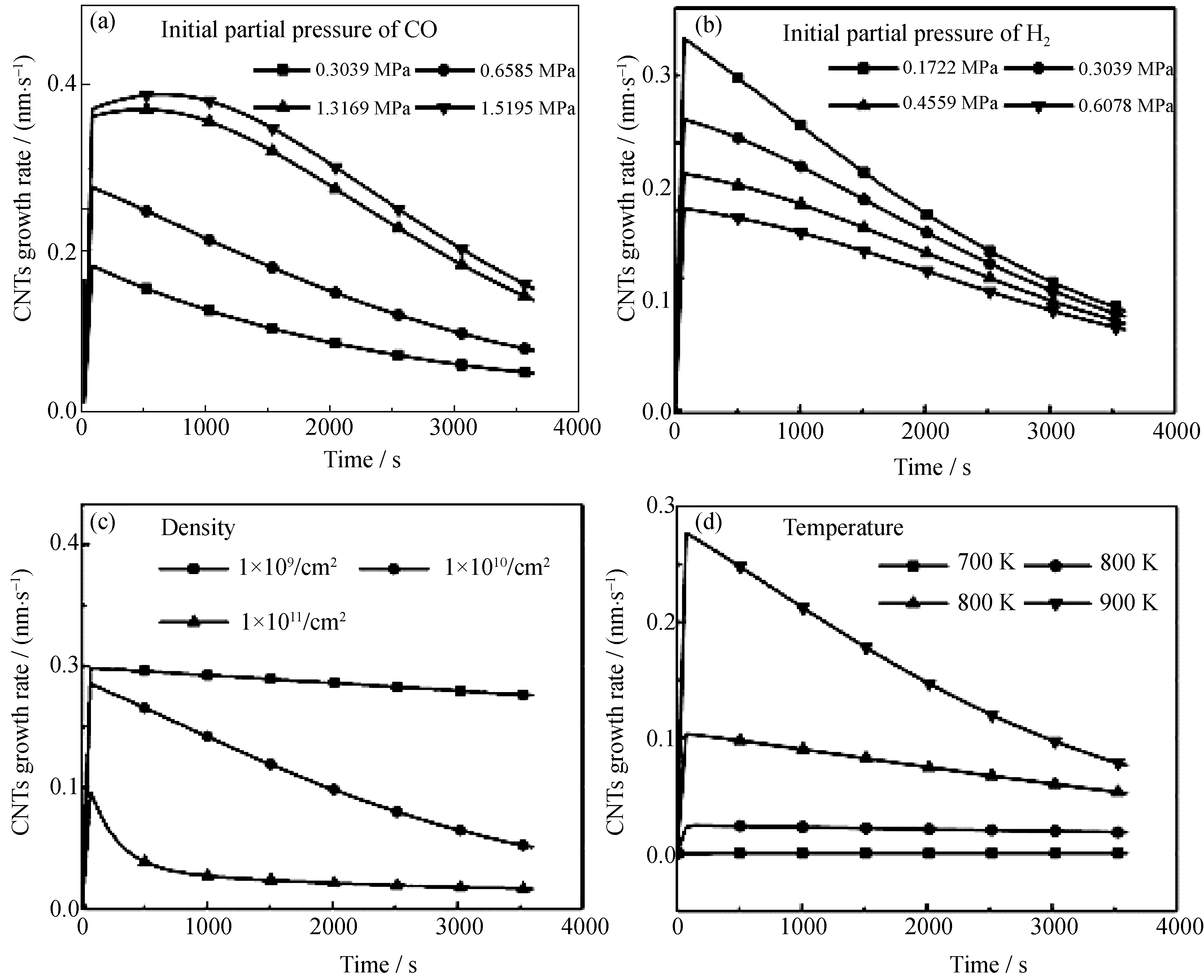
图4 模型中各项变量对于CNTs生长速率的影响(60 min内)
Fig.4 Effects of different vatiables in the modeling on the CNT growth rates in 60 min (a) Partial pressure of CO; (b) Partial pressure of H2; (c) Co nanoparticles density; (c) Reaction temperature
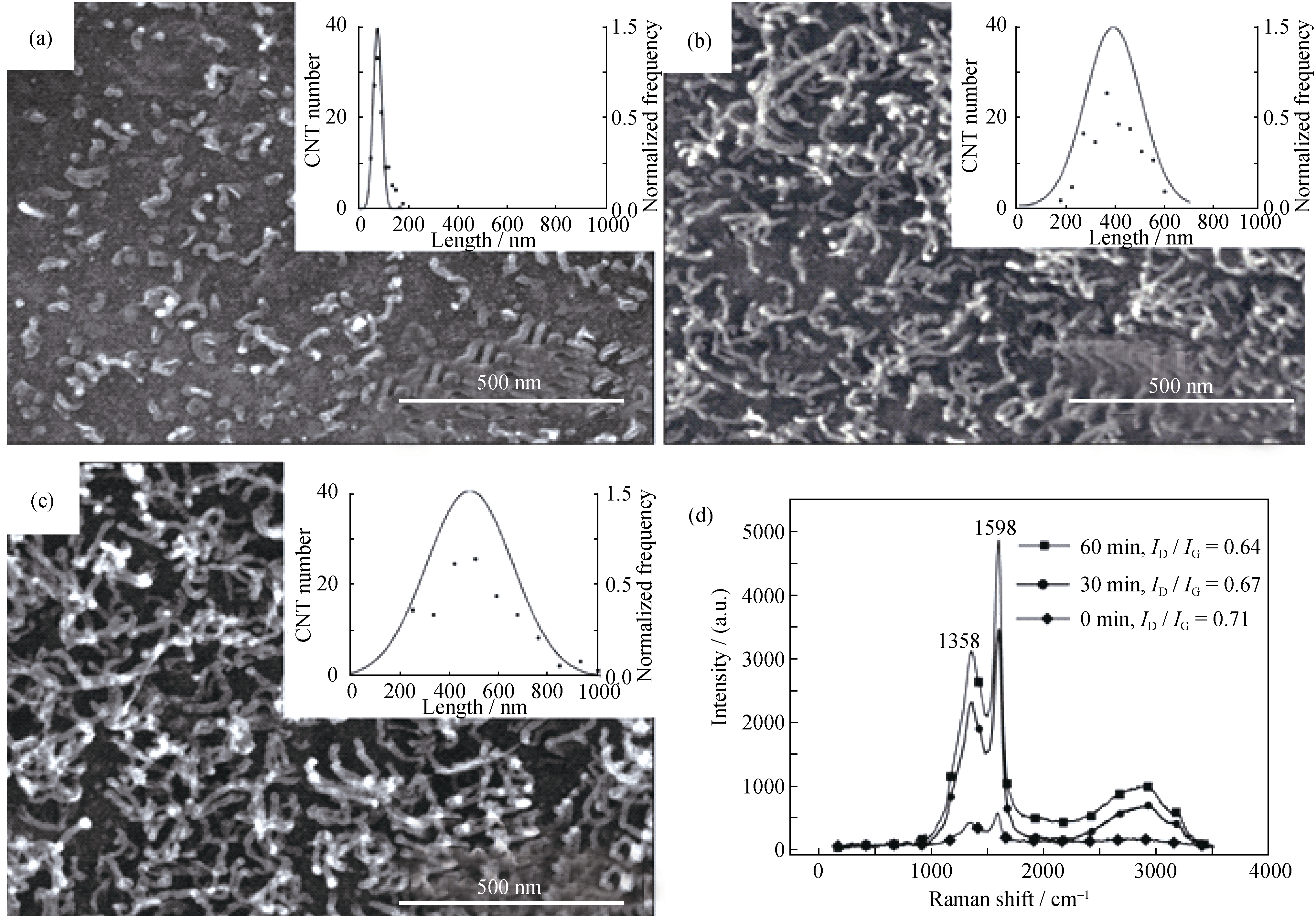
图6 在873 K反应(a)0 min、(b)30 min、(c)60 min后CNTs的SEM形貌和长度分布以及(d)不同反应时间CNTs/Al复合粉末的拉曼光谱
Fig.6 SEM images with length and normalized frequency statistic (inset) of the CNTs after grown at 873 K for (a) 0 min, (b) 30 min and (c) 60 min. (d) Raman spectra of the CNT/Al composite powders The lengths of CNTs were measured on the corresponding SEM images randomly, and 120 CNTs were counted at each reaction time
| [1] | TREACY M M J, EBBESEN T W, GIBSON J M. Exceptionally high Young’s modulus observed for individual carbon nanotubes. Nature, 1996, 381: 678-680. |
| [2] | ESAWI A M K, MORSI K, SAYED A, et al. Effect of carbon nanotube (CNT) content on the mechanical properties of CNT-reinforced aluminium composites. Composites Science and Technology, 2010, 70(16): 2237-2241. |
| [3] | GEORGE R, KASHYAP K T, RAHUL R, et al. Strengthening in carbon nanotube/aluminium (CNT/Al) composites. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 53(10): 1159-1163. |
| [4] | JIANG L, LI Z, FAN G, et al. The use of flake powder metallurgy to produce carbon nanotube (CNT)/aluminum composites with a homogenous CNT distribution. Carbon, 2012, 50(5): 1993-1998. |
| [5] | DENG C, ZHANG X X, WANG D, et al. Preparation and characterization of carbon nanotubes/aluminum matrix composites. Materials Letters, 2007, 61(8): 1725-1728. |
| [6] | BAKSHI S R, AGARWAL A. An analysis of the factors affecting strengthening in carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum composites. Carbon, 2011, 49(2): 533-544. |
| [7] | BAKSHI S R, LAHIRI D, AGARWAL A. Carbon nanotube reinforced metal matrix composites: a review. International Materials Reviews, 2010, 55(1): 41-64. |
| [8] | WANG L, CHOI H, MYOUNG J M, et al. Mechanical alloying of multi-walled carbon nanotubes and aluminium powders for the preparation of carbon/metal composites. Carbon, 2009, 47(15): 3427-3433. |
| [9] | POIRIER D, GAUVIN R, DREW R A L. Structural characterization of a mechanically milled carbon nanotube/aluminum mixture. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2009, 40(9): 1482-1489. |
| [10] | CHA S I, KIM K T, ARSHAD S N, et al. Extraordinary strengthening effect of carbon nanotubes in metal-matrix nanocomposites processed by molecular-level mixing. Advanced Materials, 2005, 17(11): 1377-1381. |
| [11] | HE C, ZHAO N, SHI C, et al. An approach to obtaining homogeneously dispersed carbon nanotubes in al powders for preparing reinforced al-matrix composites. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(8): 1128-1132. |
| [12] | CAO L, LI Z, FAN G, et al. The growth of carbon nanotubes in aluminum powders by the catalytic pyrolysis of polyethylene glycol. Carbon, 2012, 50(3): 1057-1062. |
| [13] | TANG J, FAN G, LI Z, et al. Synthesis of carbon nanotube/ aluminium composite powders by polymer pyrolysis chemical vapor deposition. Carbon, 2013, 55(1): 202-208. |
| [14] | GRUJICIC M, CAO G, GERSTEN B. Optimization of the chemical vapor deposition process for carbon nanotubes fabrication. Applied Surface Science, 2002, 191(1): 223-239. |
| [15] | GRUJICIC M, CAO G, GERSTEN B. An atomic-scale analysis of catalytically-assisted chemical vapor deposition of carbon nanotubes. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2002, 94(2): 247-259. |
| [16] | LOUCHEV O A, LAUDE T, SATO Y, et al. Diffusion-controlled kinetics of carbon nanotube forest growth by chemical vapor deposition. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2003, 118(16): 7622-7634. |
| [17] | MA H, PAN L, NAKAYAMA Y. Modelling the growth of carbon nanotubes produced by chemical vapor deposition. Carbon, 2011, 49(3): 854-861. |
| [18] | CHEN D, LØDENG R, ANUNDSKÅS A, et al. Deactivation during carbon dioxide reforming of methane over Ni catalyst: microkinetic analysis. Chemical Engineering Science, 2001, 56(4): 1371-1379. |
| [19] | KEE R J, RUPLEY F M, MILLER J A, et al. Chemkin Release 4.1, Reaction Design, San Diego, CA (2006). |
| [20] | CHASE M W. NIST-JANAF. Thermochemical Tables. 4th ed. Gaithersburg: ACS & AIP, 1998. |
| [21] | COLTRIN M E, DANDY D S. Analysis of diamond growth in subatmospheric dc plasma-gun reactors. Journal of Applied Physics, 1993, 74(9): 5803-5820. |
| [22] | FOGLER H. Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering. 4th edn. New York: Prentice Hall, 2006. |
| [23] | TESSONNIER J P, SU D S. Recent progress on the growth mechanism of carbon nanotubes: a review. Chem. Sus. Chem., 2011, 4(7): 824-847. |
| [24] | KUMAR M, ANDO Y. Chemical vapor deposition of carbon nanotubes: a review on growth mechanism and mass production. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2010, 10(6): 3739-3758. |
| [25] | LYSAGHT A C, CHIU W K S. Modeling of the carbon nanotube chemical vapor deposition process using methane and acetylene precursor gases. Nanotechnology, 2008, 19(16): 165607. |
| [26] | STORSÆTER S, CHEN D, HOLMEN A. Microkinetic modelling of the formation of C1 and C2 products in the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis over cobalt catalysts. Surface Science, 2006, 600(10): 2051-2063. |
| [27] | ZADEH J S M, SMITH K J. Kinetics of CH4 decomposition on supported cobalt catalysts. Journal of Catalysis, 1998, 176: 115-124. |
| [28] | PURETZKY A A, GEOHEGAN D B, JESSE S, et al. In situ measurements and modeling of carbon nanotube array growth kinetics during chemical vapor deposition. Applied Physics A, 2005, 81(2): 223-240. |
| [29] | YOKOYAMA H, NUMAKURA H, KOIWA M. The solubility and diffusion of carbon in palladium. Acta Materialia, 1998, 46(8): 2823-2830. |
| [30] | HUANG C W, LI Y Y. In situ synthesis of platelet graphite nanofibers from thermal decomposition of poly (ethylene glycol). The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2006, 110(46): 23242-23246. |
| [31] | 宋玉强, 李世春, 杨泽亮. Al/Co相界面的扩散溶解层. 焊接学报, 2008, 29(12): 8-12. |
| [1] | 江宗玉, 黄红花, 清江, 王红宁, 姚超, 陈若愚. 铝离子掺杂MIL-101(Cr)的制备及其VOCs吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 747-753. |
| [2] | 孙晶, 李翔, 毛小建, 章健, 王士维. 月桂酸改性剂对氮化铝粉体抗水解性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 826-832. |
| [3] | 陈义, 邱海鹏, 陈明伟, 徐昊, 崔恒. SiC/SiC复合材料基体硼改性方法及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [4] | 熊思宇, 莫尘, 朱肖伟, 朱国斌, 陈德钦, 刘来君, 施晓东, 李纯纯. 超低介电常数LiBxAl1-xSi2O6微波介质陶瓷的低温烧结[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 536-544. |
| [5] | 信震宇, 郭瑞华, 乌仁托亚, 王艳, 安胜利, 张国芳, 关丽丽. Pt-Fe/GO纳米催化剂的制备及其电催化乙醇氧化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 379-387. |
| [6] | 穆爽, 马沁, 张禹, 沈旭, 杨金山, 董绍明. Yb2Si2O7改性SiC/SiC复合材料的氧化行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 323-328. |
| [7] | 杨舒琪, 杨存国, 牛慧祝, 石唯一, 舒珂维. GeP3/科琴黑复合材料作为钠离子电池高性能负极材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 329-336. |
| [8] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [9] | 栾新刚, 何典蔚, 涂建勇, 成来飞. 2D平纹和3D针刺C/SiC复合材料的低速冲击破坏行为和失效机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 205-214. |
| [10] | 冯关正, 杨健, 周渡, 陈啟明, 许文涛, 周有福. 水热-碳热合成AlN纳米粉体的机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 104-110. |
| [11] | 王文婷, 徐敬军, 马科, 李美栓, 李兴超, 李同起. 原位反应/热压合成Ti2AlC-20TiB2复合材料在1000~1300 ℃空气中的高温氧化行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 31-38. |
| [12] | 王琨鹏, 刘兆林, 林存生, 王治宇. 基于低含水量普鲁士蓝正极的准固态钠离子电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 1005-1012. |
| [13] | 全文心, 余艺平, 方冰, 李伟, 王松. 管状C/SiC复合材料高温空气氧化行为与宏细观建模研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 920-928. |
| [14] | 何思哲, 王俊舟, 张勇, 费嘉维, 吴爱民, 陈意峰, 李强, 周晟, 黄昊. 高频低损耗的Fe/亚微米FeNi软磁复合材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 871-878. |
| [15] | 武向权, 滕家琛, 季祥旭, 郝禹博, 张忠明, 徐春杰. 织构化多孔Al2O3-SiO2复合陶瓷片-球混合浆料特性及光强分布仿真[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 769-778. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||