无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 225-233.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250169 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20250169
王政1,2,3( ), 侯小琪1,3(
), 侯小琪1,3( ), 刘宣勇1,2,3(
), 刘宣勇1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-23
修回日期:2025-05-27
出版日期:2026-02-20
网络出版日期:2025-06-05
通讯作者:
侯小琪, 副研究员. E-mail: houxiaoqi@ucas.ac.cn;作者简介:王 政(2000-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: wangzheng22@mails.ucas.ac.cn
基金资助:
WANG Zheng1,2,3( ), HOU Xiaoqi1,3(
), HOU Xiaoqi1,3( ), LIU Xuanyong1,2,3(
), LIU Xuanyong1,2,3( )
)
Received:2025-04-23
Revised:2025-05-27
Published:2026-02-20
Online:2025-06-05
Contact:
HOU Xiaoqi, associate professor. E-mail: houxiaoqi@ucas.ac.cn;About author:WANG Zheng (2000-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: wangzheng22@mails.ucas.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
量子点(Quantum Dots, QDs)凭借其优异的光致发光特性, 在生物检测领域展现出重要的应用价值。其中, pH作为调控生理功能的关键参数, 其高灵敏度响应具有重要意义。然而, 传统pH荧光探针常受限于灵敏度不足或稳定性较差的问题。基于此, 本研究采用能带工程优化设计, 构建CdSe/CdS/ZnS核壳结构QDs, 以提高其荧光量子产率和稳定性。进一步通过巯基乙胺(Mercaptoethylamine, MEA)和多巴胺异硫氰酸酯(Dopamine-isothiocyanate, DA-ITC)修饰, 制备得到具有高灵敏度pH响应的QDs荧光探针。实验结果表明: 氨基化的CdSe/CdS/ZnS QDs具有优异的光学性质。经DA-ITC修饰后, 探针表现出高灵敏度的pH响应性能, 其响应机制源于碱性条件下表面配体氧化形成的多巴胺醌(Dopamine Quinone, DQ)对QDs的荧光猝灭作用。对于1 nmol QDs, DA-ITC投入量为4~40 μg/nmol时, 在pH 5.0~10.0范围内, 探针的荧光强度呈现随pH增加而线性降低的趋势(线性拟合常数R2>0.90)。当DA-ITC投入量为20 μg/nmol时, 探针的pH响应效果最佳, 其线性拟合常数为0.9869。此外, 该探针具有良好的细胞相容性, 能够有效应用于细胞pH荧光成像监测研究。
中图分类号:
王政, 侯小琪, 刘宣勇. 多巴胺醌功能化的量子点荧光探针构建及其pH响应研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(2): 225-233.
WANG Zheng, HOU Xiaoqi, LIU Xuanyong. Functionalized Quantum Dot Fluorescent Probes with Dopamine Quinone: Construction and pH Response[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 225-233.
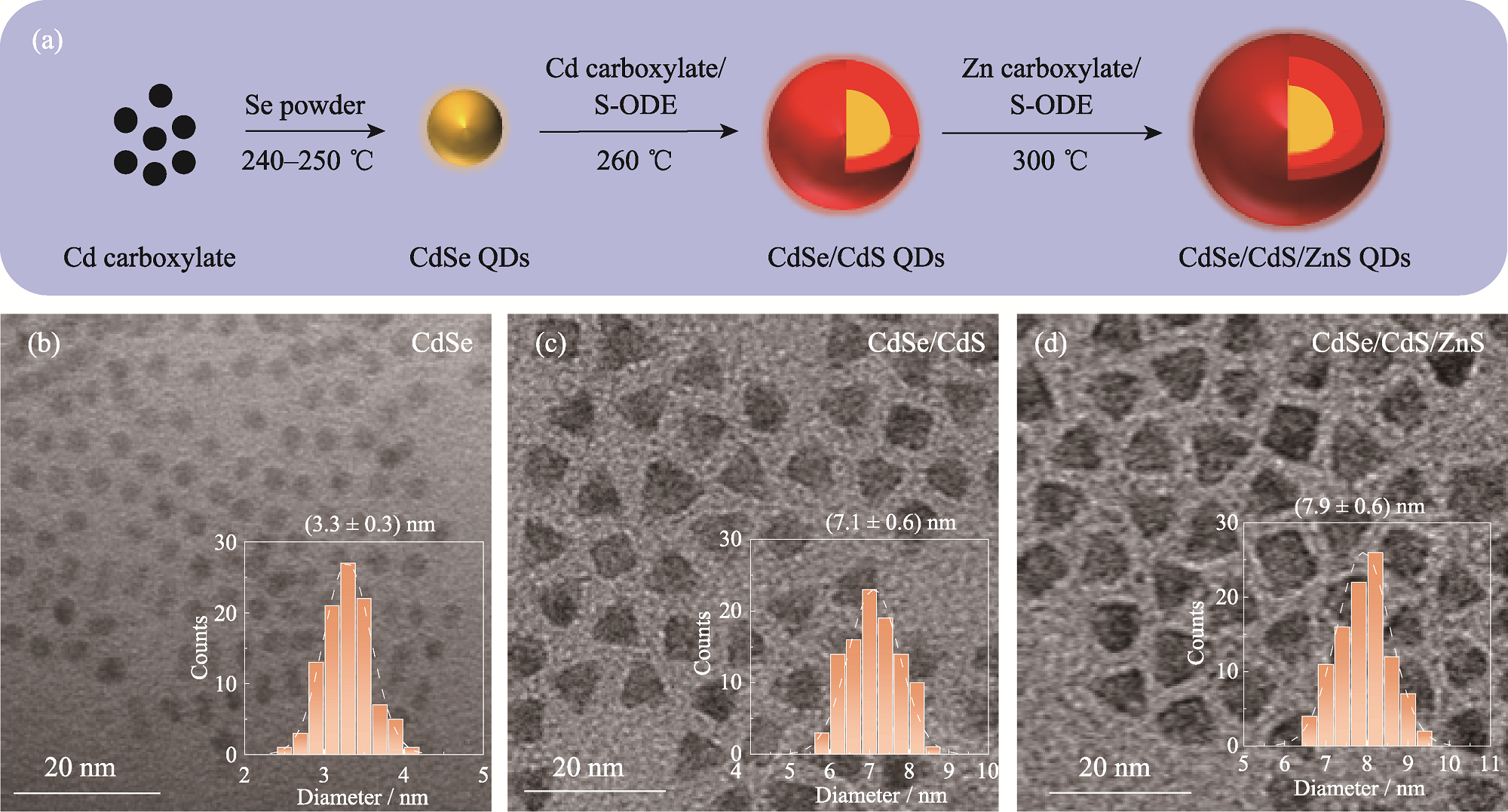
图1 QDs的制备过程、微观形貌及尺寸分布
Fig. 1 Schematic of preparation, micromorphologies and size distributions of QDs (a) Preparation process of QDs; (b-d) TEM images of CdSe QDs (b), CdSe/CdS QDs (c) and CdSe/CdS/ZnS QDs (d),with insets showing size distribution histograms
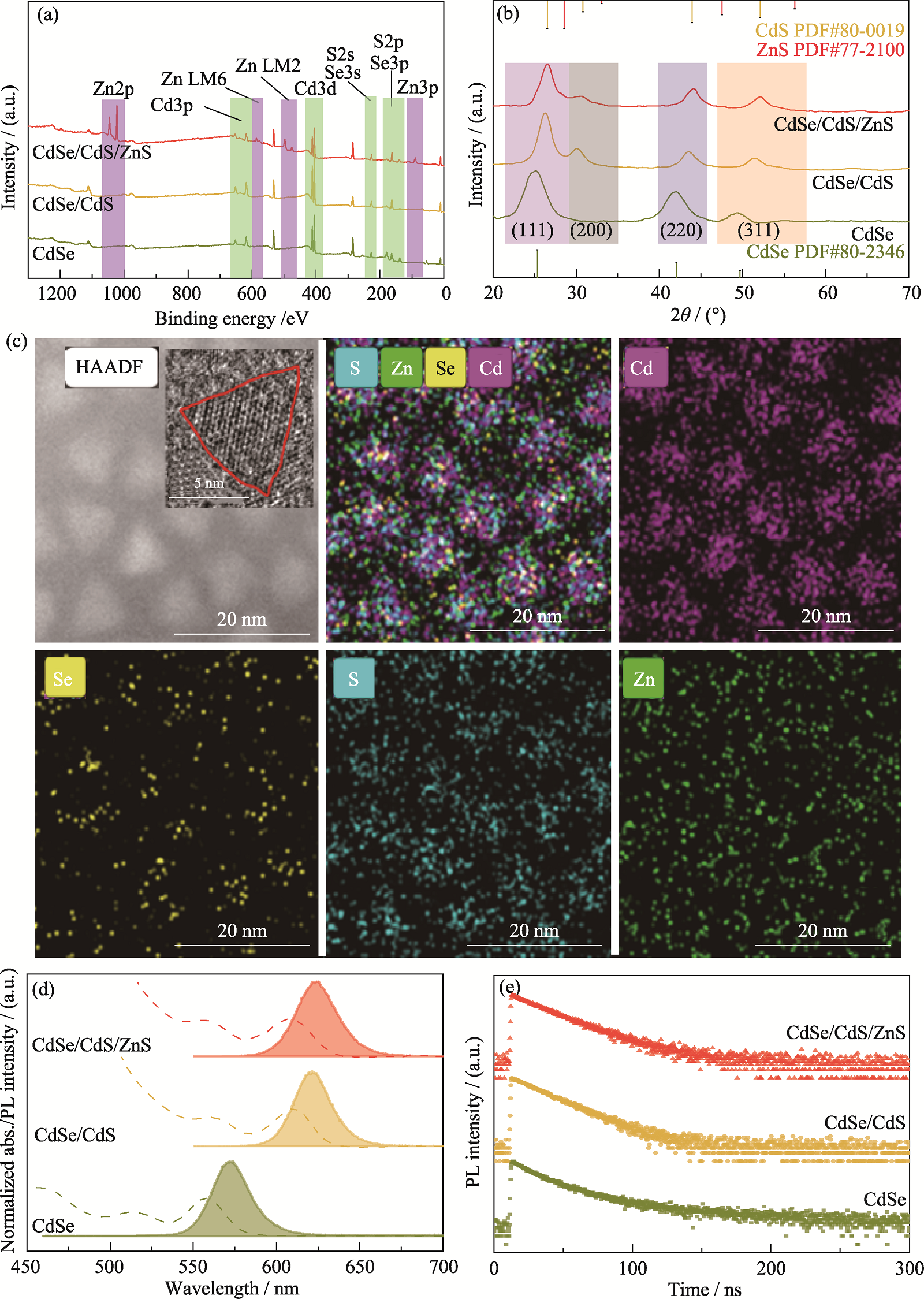
图2 QDs的结构表征、元素分布及光学性质
Fig. 2 Structural characterization, element distribution and optical properties of QDs (a) XPS spectra, (b) XRD patterns, (d) PL and UV-Vis spectra, and (e) transient PL spectra of QDs;(c) EDS mappings of CdSe/CdS/ZnS QDs with inset showing HRTEM image
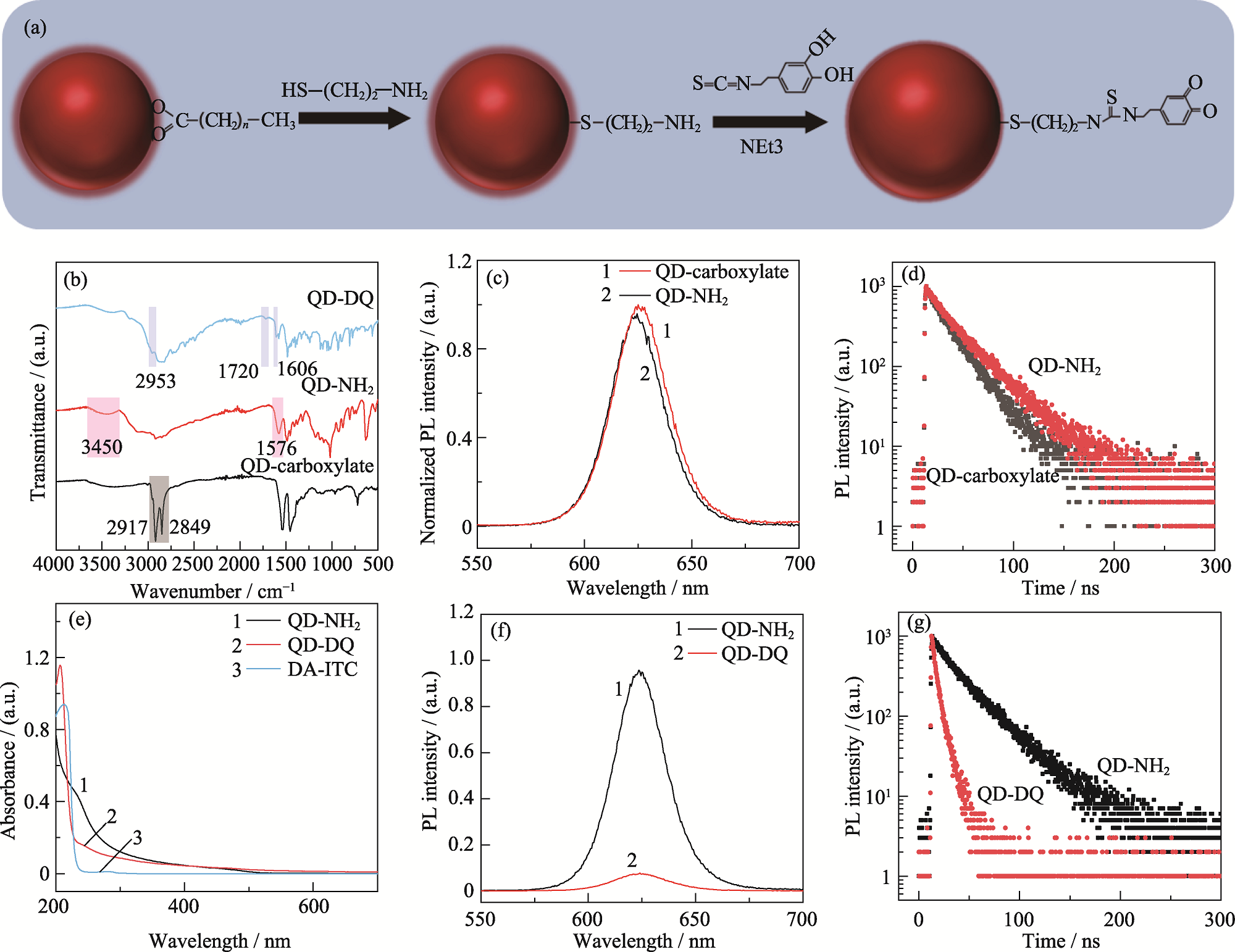
图3 QDs基pH响应探针的制备过程、表征和光学性质
Fig. 3 Schematic of preparation, characterization and optical properties of QDs-based pH probes (a) Preparation of pH probe; (b) FT-IR spectra of pH probe at different phases; (c) PL spectra and (d) transient PL spectra of QDs before and after MEA ligand exchange; (e) UV-Vis spectra, (f) PL spectra and (g) transient PL spectra of QDs before and after linking DA-ITC (40 μg/nmol)
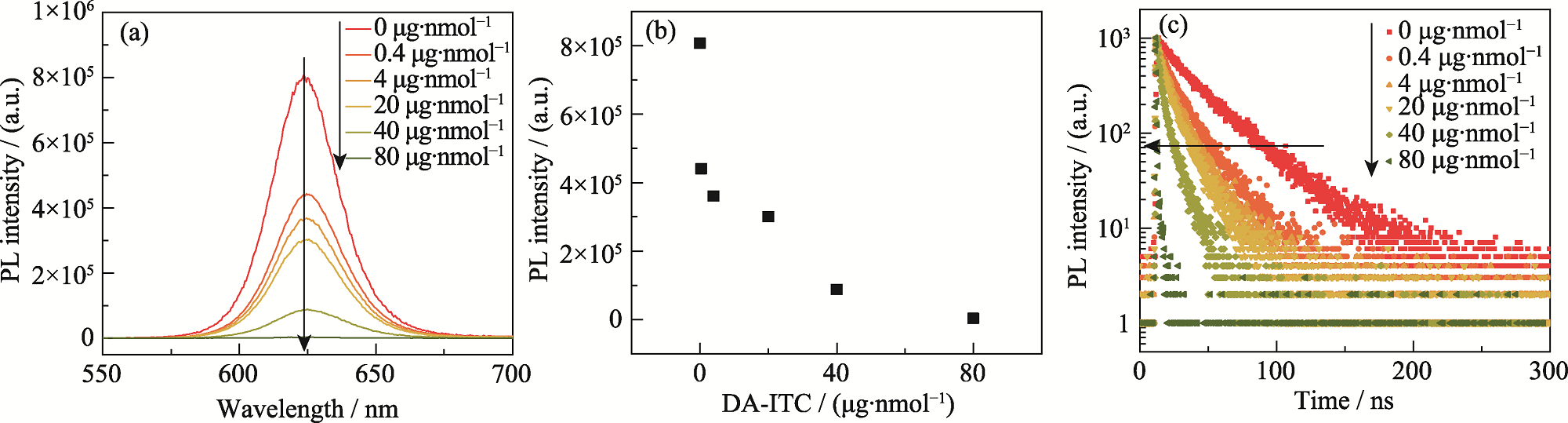
图4 DA-ITC投入量对QDs基pH响应探针光学性质的影响
Fig. 4 Effect of DA-ITC input on optical properties of QDs-based pH probes (a) PL spectra; (b) Variation of PL peak intensity; (c) Transient PL spectra
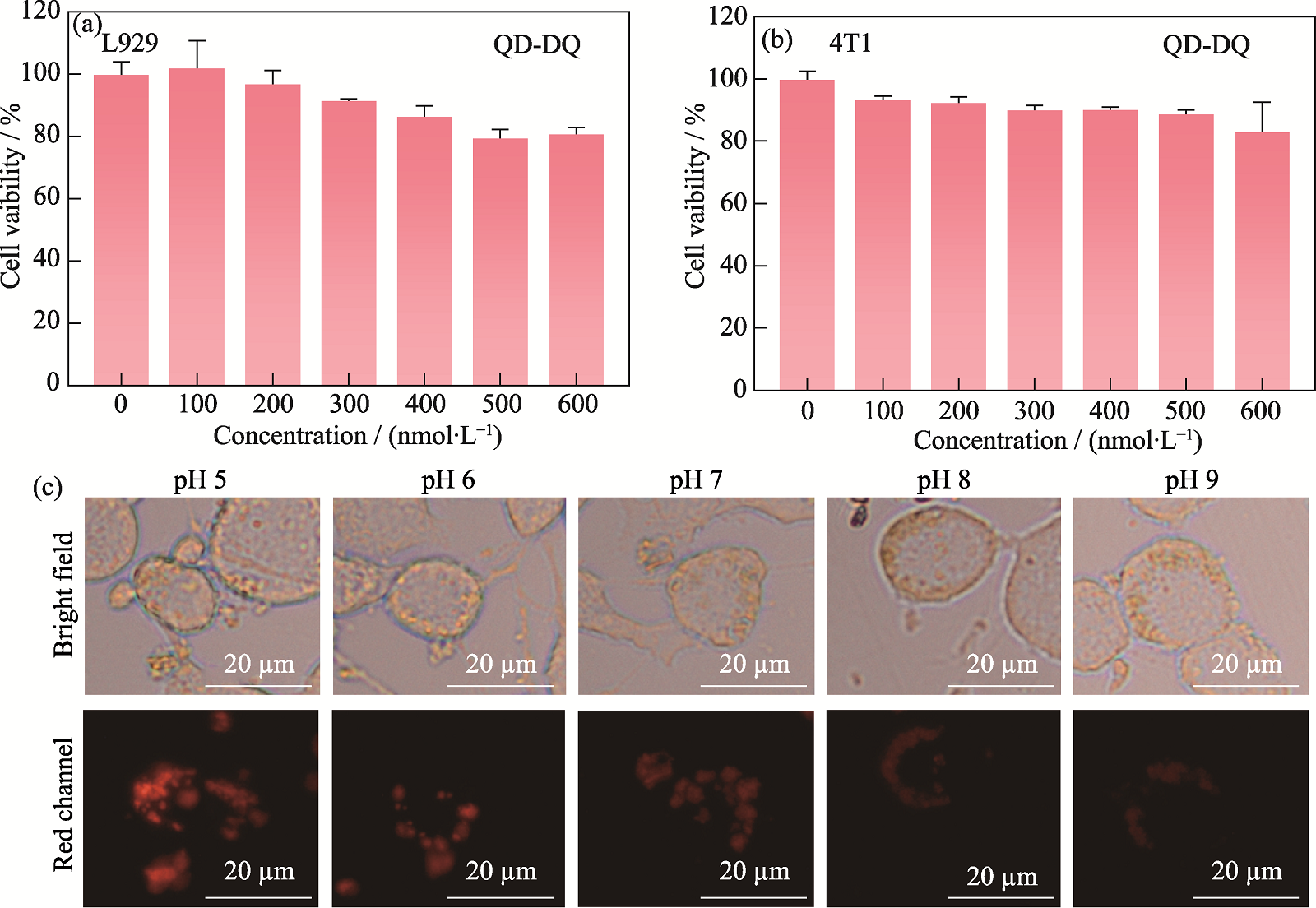
图6 探针的细胞毒性及其在细胞体系中的pH响应效果
Fig. 6 Cytotoxicity of probe and its pH response effect in the cellular system (a, b) Cytotoxicity of probe to L929 cells (a) and 4T1 cells (b); (c) Fluorescence imaging of probe responses to intracellular pH change
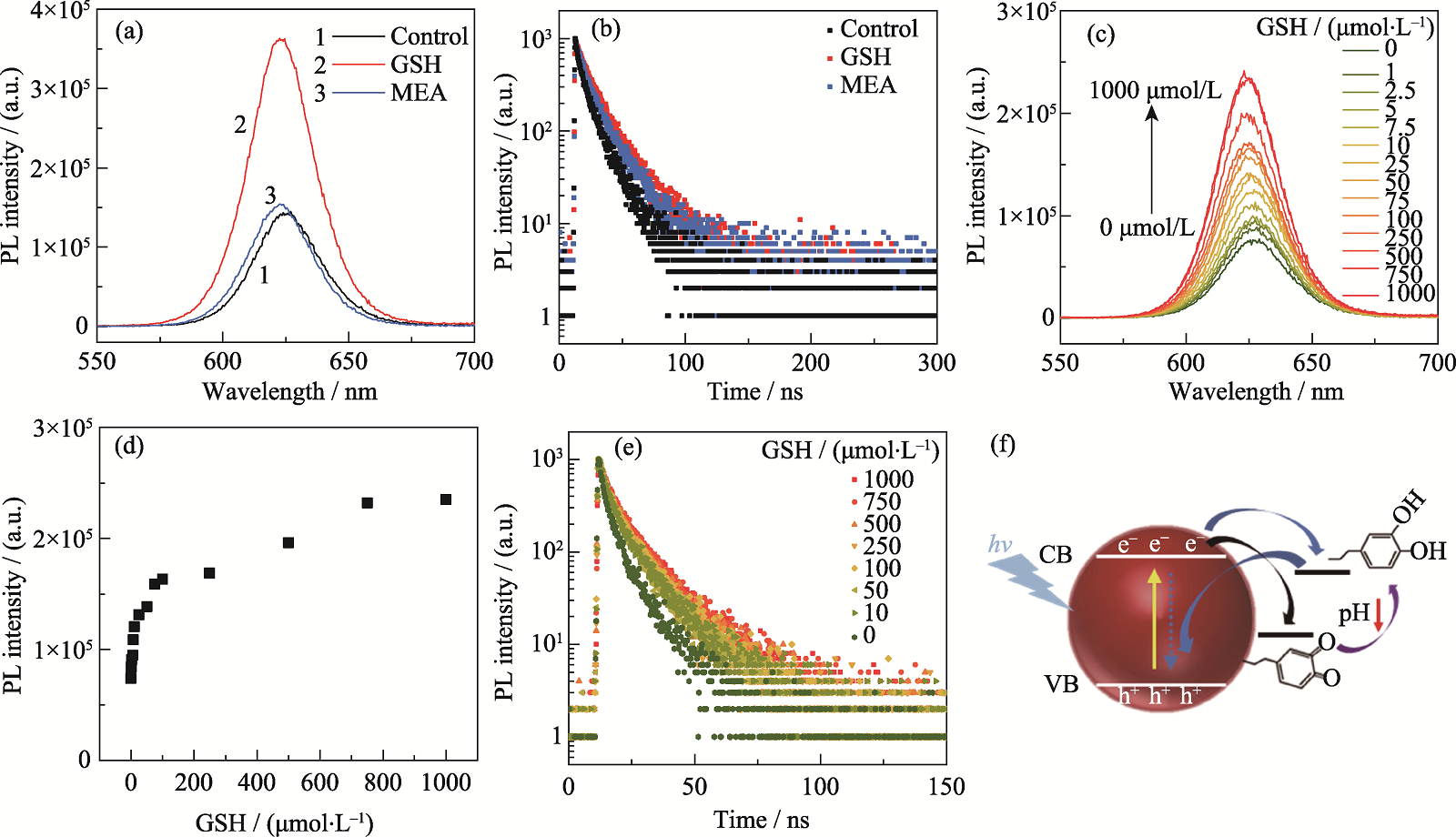
图7 GSH对荧光探针光学性质的影响及荧光探针pH响应机制
Fig. 7 Effect of GSH on the optical properties of fluorescent probes and pH response mechanism of probes (a, b) Same concentration of GSH and MEA incubated with probe for 30 min: (a) PL spectra and (b) transient PL spectra of probe; (c-e) Different concentration of GSH incubated with probe for 30 min: (c) PL spectra, (d) variation of PL peak intensity and (e) transient PL spectra of probe; (f) Schematic of the mechanism of fluorescence probe response to pH change. Colorful figures are available on website
| QDs | The first exciton absorption peak/nm | PL peak/nm | FHWM/nm | PL decay lifetime/ns | χR2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CdSe | 558.0 | 571.5 | 26.0 | / | / |
| CdSe/CdS | 609.5 | 622.0 | 25.3 | 19.35 | 0.95 |
| CdSe/CdS/ZnS | 609.0 | 625.0 | 28.4 | 21.20 | 1.24 |
表S1 油溶性量子点的光学性质
Table S1 Optical properties of oil-soluble QDs
| QDs | The first exciton absorption peak/nm | PL peak/nm | FHWM/nm | PL decay lifetime/ns | χR2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CdSe | 558.0 | 571.5 | 26.0 | / | / |
| CdSe/CdS | 609.5 | 622.0 | 25.3 | 19.35 | 0.95 |
| CdSe/CdS/ZnS | 609.0 | 625.0 | 28.4 | 21.20 | 1.24 |
| Amount of input/(μg·nmol-1) | y = b×x + a | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 0.4 | y = -28309x + 587440 | 0.4777 |
| 4 | y = -56370x + 670873 | 0.9097 |
| 20 | y = -44246x + 522045 | 0.9869 |
| 40 | y = -11429x + 141699 | 0.9667 |
| 80 | y = -53.148x + 4116.5 | 0.0249 |
表S2 不同DA-ITC投入量的探针荧光响应pH的拟合
Table S2 Fitting of probe fluorescence response pH under different DA-ITC input amounts
| Amount of input/(μg·nmol-1) | y = b×x + a | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 0.4 | y = -28309x + 587440 | 0.4777 |
| 4 | y = -56370x + 670873 | 0.9097 |
| 20 | y = -44246x + 522045 | 0.9869 |
| 40 | y = -11429x + 141699 | 0.9667 |
| 80 | y = -53.148x + 4116.5 | 0.0249 |
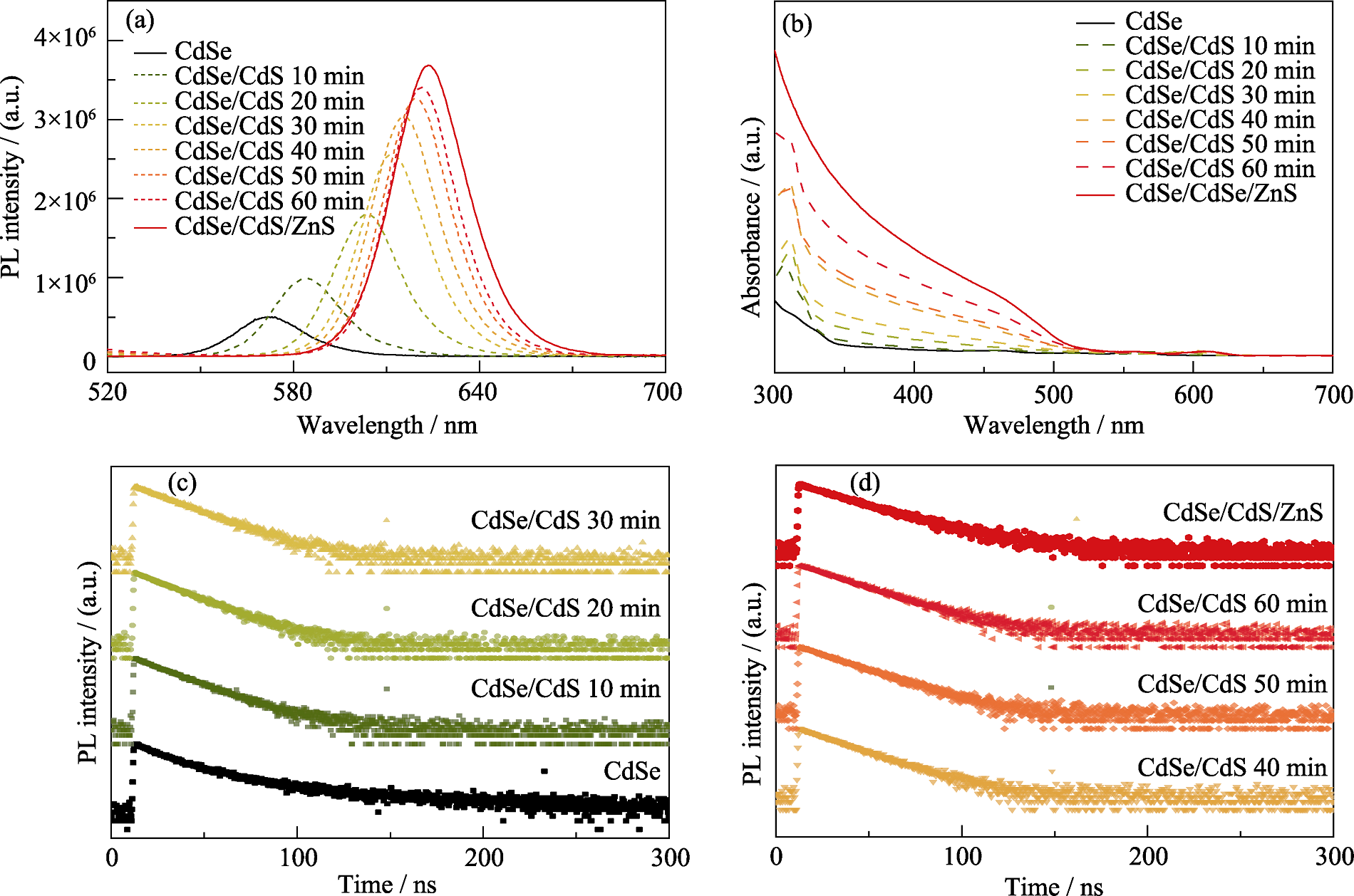
图S2 CdSe核QDs上生长CdS和ZnS层过程中的光学性质变化
Fig. S2 Variation of optical properties during growth of CdS and ZnS layers on CdSe core QDs (a) PL spectra; (b) UV-Vis spectra; (c, d) Transient PL spectra
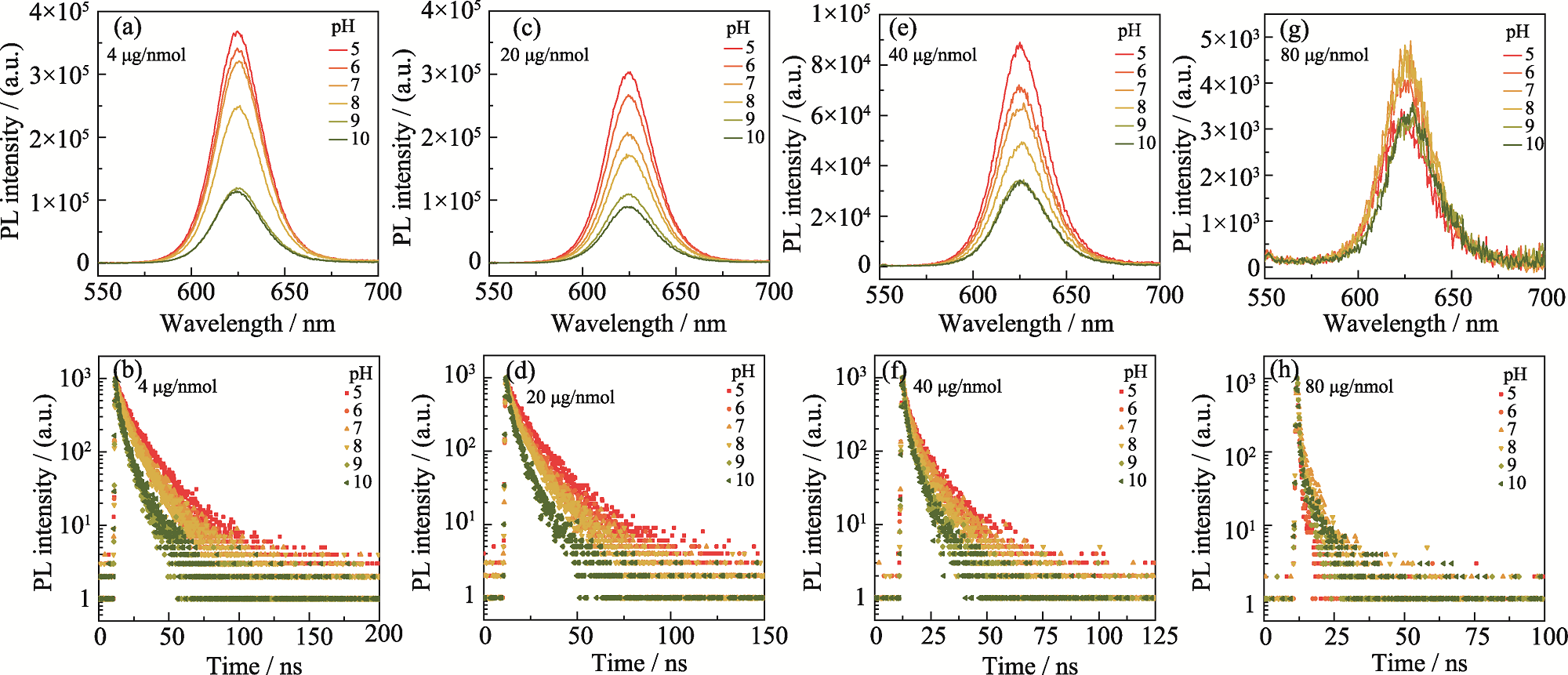
图S3 不同DA-ITC投入量的探针在不同pH环境中的光学性质变化
Fig. S3 Variation of optical properties of probes with different DA-ITC inputs in different pH environments (a, b) 4 μg/nmol; (c, d) 20 μg/nmol; (e, f) 40 μg/nmol; (g, h) 80 μg/nmol
| [1] |
ALIVISATOS A P. Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science, 1996, 271(5251): 933.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
EFROS A L, BRUS L E. Nanocrystal quantum dots: from discovery to modern development. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(4): 6192.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
BRUS L E. Electron-electron and electron-hole interactions in small semiconductor crystallites: the size dependence of the lowest excited electronic state. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1984, 80(9): 4403.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
MICHALET X, PINAUD F F, BENTOLILA L A, et al. Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science, 2005, 307: 538.
DOI URL |
| [5] | WEGNER K D, HILDEBRANDT N. Quantum dots: bright and versatile in vitro and in vivo fluorescence imaging biosensors. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(14): 4792. |
| [6] |
LIU H, WANG Z, LIU S, et al. Single-virus tracking with quantum dots in live cells. Nature Protocols, 2022, 18(2): 458.
DOI |
| [7] |
OU W, ZHU K, LU X, et al. Alloyed geometric structure strategy enables high-quality water-soluble quantum dots for ultrasensitive fluorescence immunoassay. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 502: 157799.
DOI URL |
| [8] | LIU Z, HOU X, YOU H, et al. Surface copassivation strategy for developing water-soluble InP colloidal quantum dots with high luminescence and suppressed blinking. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2025, 147(6): 4778. |
| [9] |
DING C, CHENG S, ZHANG C, et al. Ratiometric upconversion luminescence nanoprobe with near-infrared Ag2S nanodots as the energy acceptor for sensing and imaging of pH in vivo. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(11): 7181.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HOU S L, DONG J, TANG M H, et al. Triple-interpenetrated lanthanide-organic framework as dual wave bands self-calibrated pH luminescent probe. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(8): 5455.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
STEINEGGER A, WOLFBEIS O S, BORISOV S M. Optical sensing and imaging of pH values: spectroscopies, materials, and applications. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(22): 12357.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
YANG R, HE X, NIU G, et al. A single fluorescent pH probe for simultaneous two-color visualization of nuclei and mitochondria and monitoring cell apoptosis. ACS Sensors, 2021, 6(4): 1552.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | LYAGIN I, MASLOVA O, STEPANOV N, et al. Reassessing of enzymes degrading mycotoxins at acidic pH. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2025, 198: 105994. |
| [14] |
RUIZ-GUERRERO C D, ESTRADA-OSORIO D V, GUTIÉRREZ A, et al. Novel cobalt-based aerogels for uric acid detection in fluids at physiological pH. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2025, 267: 116850.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
CHEN H, YE Z, SUN L, et al. Synthesis of chitosan-based micelles for pH responsive drug release and antibacterial application. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2018, 189: 65.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
KAY E R, LEE J, NOCERA D G, et al. Conformational control of energy transfer: a mechanism for biocompatible nanocrystal-based sensors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 52(4): 1165.
DOI URL |
| [17] | ORTE A, ALVAREZ-PEZ J M, RUEDAS-RAMA M J. fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy for the detection of intracellular pH with quantum dot. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(7): 6387. |
| [18] |
PAEK K, YANG H, LEE J, et al. Efficient colorimetric pH sensor based on responsive polymer quantum dot integrated graphene oxide. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(3): 2848.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SUSUMU K, FIELD L D, OH E, et al. Purple-, blue-, and green- emitting multishell alloyed quantum dots: synthesis, characterization, and application for ratiometric extracellular pH sensing. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(17): 7330.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
MEDINTZ I L, STEWART M H, TRAMMELL S A, et al. Quantum-dot/dopamine bioconjugates function as redox coupled assemblies for in vitro and intracellular pH sensing. Nature Materials, 2010, 9(8): 676.
DOI |
| [21] |
LI D, XU H, LI D, et al. p-Aminothiophenol-coated CdSe/ZnS quantum dots as a turn-on fluorescent probe for pH detection in aqueous media. Talanta, 2017, 166: 54.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
ZHOU J, ZHU M, MENG R, et al. Ideal CdSe/CdS core/shell nanocrystals enabled by entropic ligands and their core size-, shell thickness-, and ligand-dependent photoluminescence properties. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(46): 16556.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
HOU X, KANG J, QIN H, et al. Engineering Auger recombination in colloidal quantum dots via dielectric screening. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1750.
DOI |
| [24] |
HOU X, QIN H, PENG X. Enhancing dielectric screening for Auger suppression in CdSe/CdS quantum dots by epitaxial growth of ZnS shell. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(9): 3871.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
SNEE P T, SOMERS R C, NAIR G, et al. A ratiometric cdse ZnS nanocrystal pH sensor. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006, 128: 13320.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
SYKORA M, PETRUSKA M A, ALSTRUM-ACEVEDO J, et al. Photoinduced charge transfer between CdSe nanocrystal quantum dots and Ru-polypyridine complexes. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006, 128: 9984.
PMID |
| [27] |
MEDINTZ I L, PONS T, TRAMMELL S A, et al. Interactions between redox complexes and semiconductor quantum dots coupled via a peptide bridge. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130: 16745.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
SCHWABACHER J C, KODAIMATI M S, WEISS E A. Origin of the pH dependence of emission of aqueous dihydrolipoic acid-capped PbS quantum dots. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2019, 123(28): 17574.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
JI X, PALUI G, AVELLINI T, et al. On the pH-dependent quenching of quantum dot photoluminescence by redox active dopamine. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(13): 6006.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
BANERJEE S, KAR S, PEREZ J M, et al. Quantum dot based off on probe for detection of glutathione. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009, 113: 9659.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 袁子豪, 许银生, 李昕阔, 谭德志. 飞秒激光调控CdS量子点玻璃的发光性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 105-112. |
| [2] | 陈梓, 张爱迪, 龚克, 刘海华, 禹钢, 单青松, 刘勇, 曾海波. 具有可调谐和长寿命荧光发射的高亮度、单分散四元CuInZnS@ZnS量子点[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 433-339. |
| [3] | 高晨光, 孙晓亮, 陈君, 李达鑫, 陈庆庆, 贾德昌, 周玉. 基于湿法纺丝技术的SiBCN-rGO陶瓷纤维的组织结构、力学和吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [4] | 张宇婷, 李晓斌, 刘尊义, 李宁, 赵鹬. 复合蛋黄壳型NiCo2V2O8@TiO2@NC材料用作锂离子电池负极研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1221-1228. |
| [5] | 胡学敏, 张行健, 蒋志豪, 黄丽雯, 丁开宁, 张胜利. 氧修饰的CoPS3量子点边缘态析氧活性的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1229-1236. |
| [6] | 吕昕怿, 相恒阳, 曾海波. 长程有序助力钙钛矿QLED高性能化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 111-112. |
| [7] | 杨恩东, 李宝乐, 张珂, 谭鲁, 娄永兵. ZnCo2O4-ZnO@C@CoS核壳复合材料的制备及其在超级电容器中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 485-493. |
| [8] | 张婷婷, 王方园, 刘长友, 张国荣, 吕佳辉, 宋宇晨, 介万奇. 水热-烧结法制备Cr2+:ZnSe/ZnSe核壳结构纳米孪晶[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 409-415. |
| [9] | 岳仔豪, 杨小兔, 张正亮, 邓瑞翔, 张涛, 宋力昕. Pb2+对掺杂硼硅酸盐玻璃中CsPbBr3钙钛矿量子点发光性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 449-456. |
| [10] | 岳全鑫, 郭瑞华, 王瑞芬, 安胜利, 张国芳, 关丽丽. 3D核壳结构NiMoO4@CoFe-LDH纳米棒的高效析氧及全解水性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1254-1264. |
| [11] | 吴锐, 张敏慧, 金成韵, 林健, 王德平. 光热核壳TiN@硼硅酸盐生物玻璃纳米颗粒的降解和矿化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 708-716. |
| [12] | 马晓森, 张丽晨, 刘砚超, 汪全华, 郑家军, 李瑞丰. 13X@SiO2合成及其甲苯吸附性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [13] | 迟聪聪, 屈盼盼, 任超男, 许馨, 白飞飞, 张丹洁. SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2核壳结构的制备及其光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [14] | 张枫娟, 韩博宁, 曾海波. 钙钛矿量子点光伏与荧光聚光电池: 现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 117-128. |
| [15] | 陈小梅, 陈颖, 袁霞. 核壳材料Co3O4@SiO2催化环己基过氧化氢分解[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 65-71. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||