无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (11): 1229-1236.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250092 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250092
胡学敏1,2( ), 张行健1, 蒋志豪1, 黄丽雯1, 丁开宁3, 张胜利2(
), 张行健1, 蒋志豪1, 黄丽雯1, 丁开宁3, 张胜利2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-03
修回日期:2025-05-18
出版日期:2025-11-20
网络出版日期:2025-06-03
通讯作者:
张胜利, 教授. E-mail: zhangslvip@njust.edu.cn作者简介:胡学敏(1986-), 女, 博士. E-mail: huxm@jit.edu.cn
基金资助:
HU Xuemin1,2( ), ZHANG Xingjian1, JIANG Zhihao1, HUANG Liwen1, DING Kaining3, ZHANG Shengli2(
), ZHANG Xingjian1, JIANG Zhihao1, HUANG Liwen1, DING Kaining3, ZHANG Shengli2( )
)
Received:2025-03-03
Revised:2025-05-18
Published:2025-11-20
Online:2025-06-03
Contact:
ZHANG Shengli, professor. E-mail: zhangslvip@njust.edu.cnAbout author:HU Xuemin (1986-), female, PhD. E-mail: huxm@jit.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
二维CoPS3电催化剂面内金属活性位点稀缺, 用于阳极析氧反应(OER)的动力学过程缓慢, 这限制了整体电解水制氢的效率。针对这一问题, 本研究提出通过量子限域效应与边缘化学修饰协同提升催化活性的新策略。首先构建了两种典型的具有高边缘位点密度的CoPS3量子点(CoPS3-QDs)结构模型, 通过结合能和键能计算筛选出热力学稳定的结构(CoPS3-QDs1), 其边缘Co2位点较其它边缘位点展现出最优OER活性(速率决定步骤的吉布斯自由能ΔG=1.68 eV)。进一步在CoPS3-QDs1的Co2位点及邻近硫原子引入氧(O)修饰, 构建五种O-CoPS3-QDs模型。理论计算表明, M4模型(O修饰于S3位点)的过电位(ηOER)仅为0.32 V, 较未修饰体系降低29%, 且显著优于文献报道的贵金属RuO2催化剂。局域态密度分析进一步揭示, O修饰诱导Co位点附近的电荷重新分布, 可以适度吸附氧中间体(*OH、*O、*OOH)。本研究阐明了量子点边缘态修饰在调控电子结构与反应动力学中的关键作用, 为设计高效、低成本的OER电催化剂提供了理论依据。
中图分类号:
胡学敏, 张行健, 蒋志豪, 黄丽雯, 丁开宁, 张胜利. 氧修饰的CoPS3量子点边缘态析氧活性的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1229-1236.
HU Xuemin, ZHANG Xingjian, JIANG Zhihao, HUANG Liwen, DING Kaining, ZHANG Shengli. First-principles Study on Oxygen Evolution Reaction Activity of CoPS3 Quantum Dots Edge States Modified with Oxygen[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1229-1236.
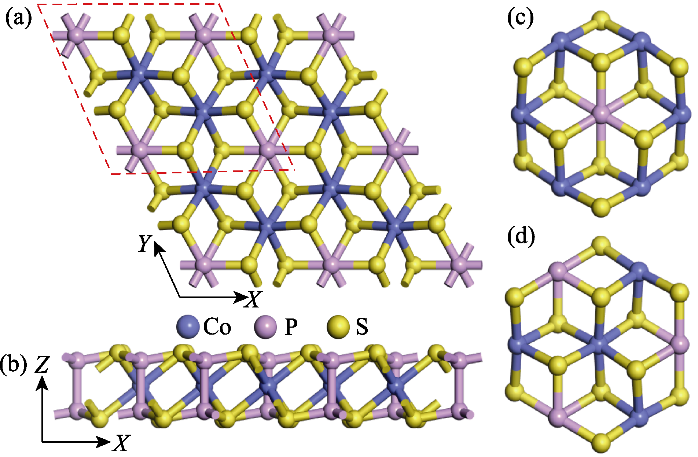
图1 CoPS3的单层晶体结构模型和量子点结构模型
Fig. 1 Monolayer crystal structure model and quantum dots model of CoPS3 (a) Top and (b) side views of the monolayer CoPS3 structure model; (c, d) Top views of (c) CoPS3-QDs1 and (d) CoPS3-QDs2; Red dashed line in (a) indicating unit cell of CoPS3
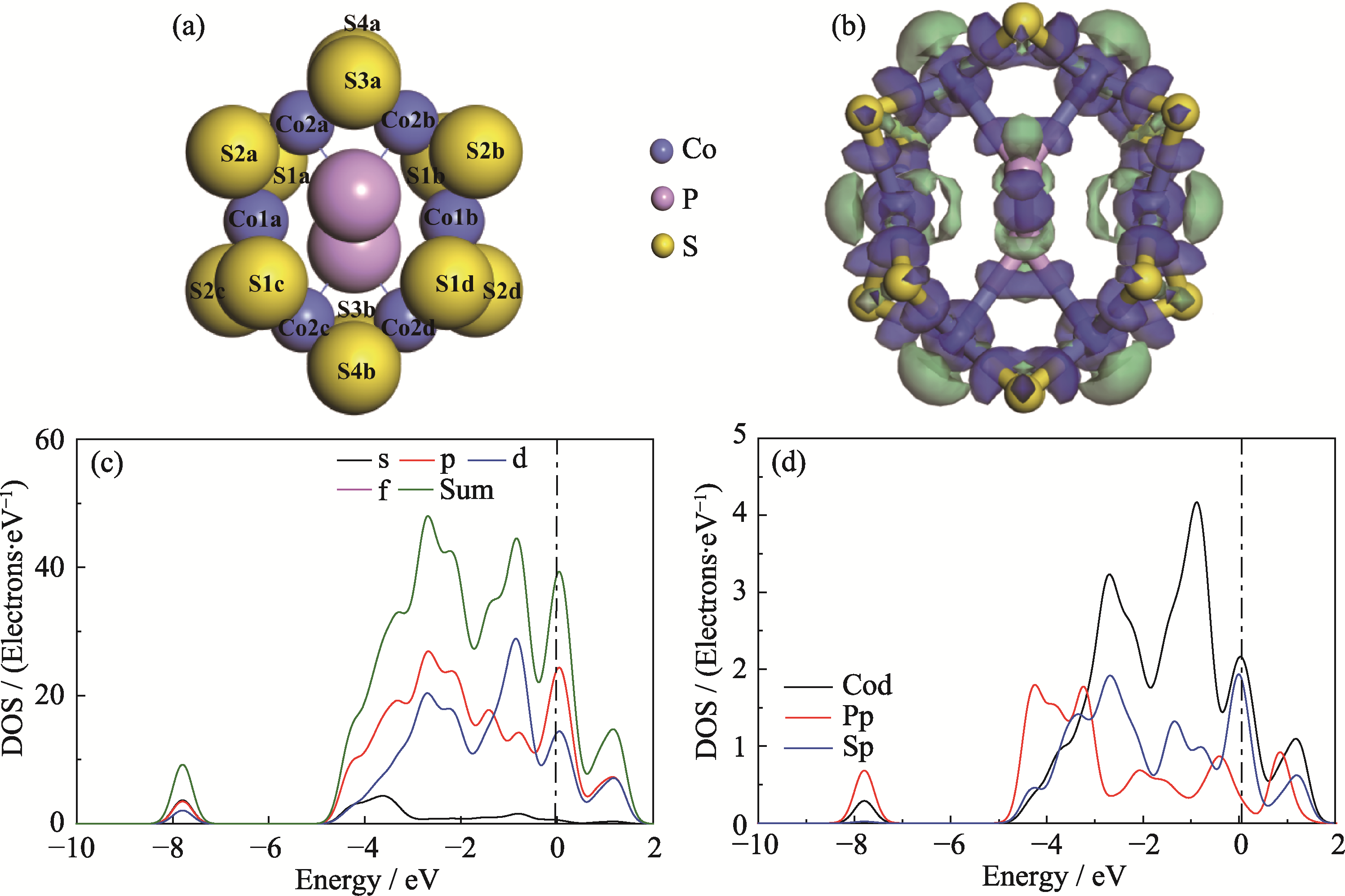
图2 几何优化后CoPS3-QDs1的结构模型和电子性质数据
Fig. 2 Optimized structure model and electronic property data of CoPS3-QDs1 (a) Top view of the optimized CoPS3-QDs1 structure model, where S1-S4, Co1, and Co2 represent six inequivalent edge atomic positions obtained from Mulliken charge calculations; (b) Charge density difference map of CoPS3-QDs1, where blue regions indicate electron accumulation and green regions indicate electron depletion, with isovalue=0.048 e/Å3; (c) Orbital-resolved partial density of states (PDOS) and (d) atom-resolved PDOS of CoPS3-QDs1. Colorful figures are available on website
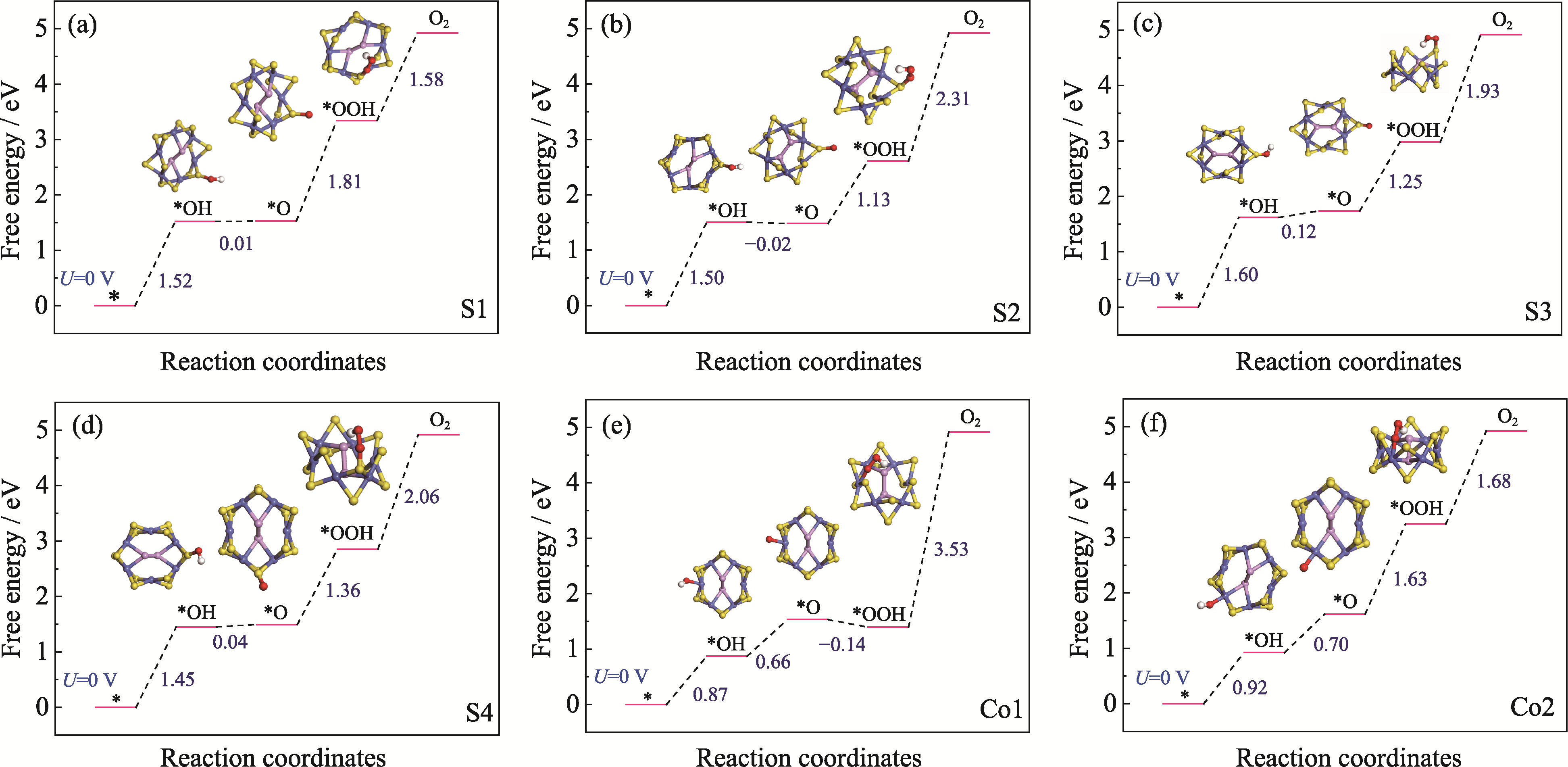
图3 CoPS3-QDs1六种吸附位点的OER吉布斯自由能台阶图及各吸附中间体模型示意图
Fig. 3 Step diagrams of Gibbs free energy for the OER at six adsorption sites of CoPS3-QDs1 and schematic illustrations of the adsorbed intermediate models (a) S1 site; (b) S2 site; (c) S3 site; (d) S4 site; (e) Co1 site; (f) Co2 site
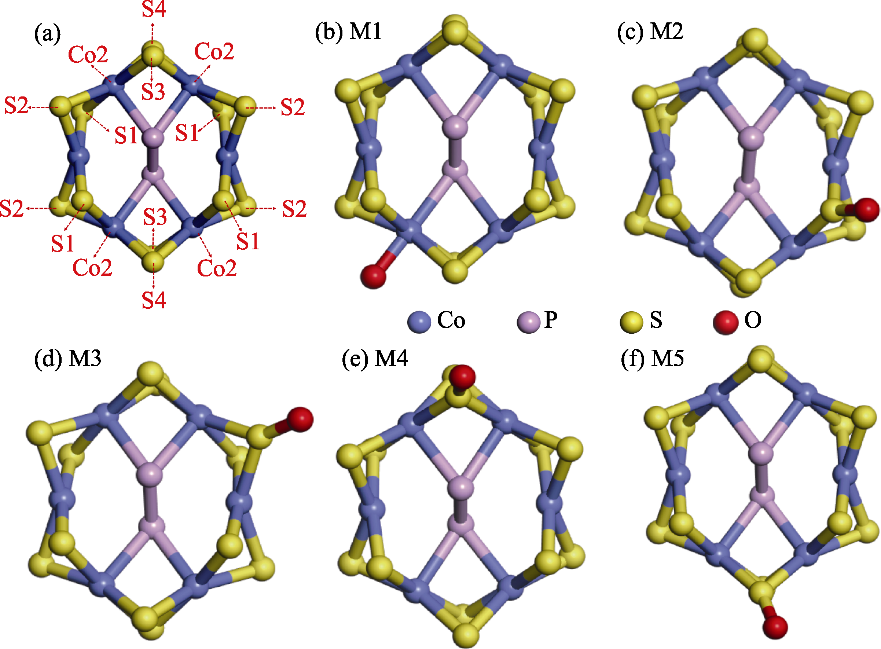
图4 O修饰CoPS3-QDs1 Co2位点及其周边四个不等价S原子的结构模型
Fig. 4 Structural models of O modification at the Co2 site of CoPS3-QDs1 and its surrounding four inequivalent S atoms (a) Distribution of Co2 site and its surrounding four S atomic sites; (b) Model M1 with O modification at the Co2 site; (c) Model M2 with O modification at the S1 site; (d) Model M3 with O modification at the S2 site; (e) Model M4 with O modification at the S3 site; (f) Model M5 with O modification at the S4 site. Colorful figures are available on website
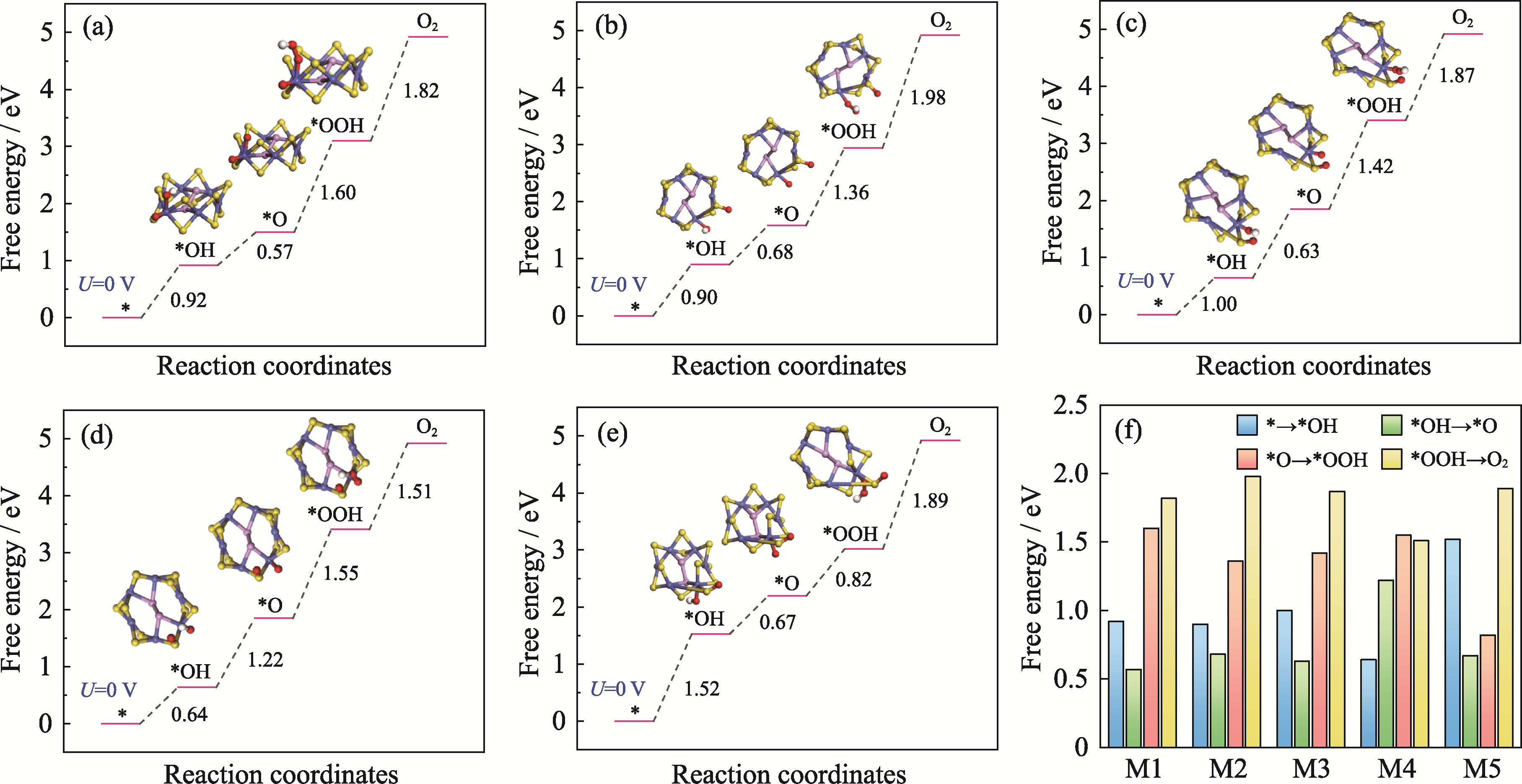
图5 O修饰得到的M1~M5模型的OER活性对比
Fig. 5 OER activity comparisons of M1-M5 models with O modification (a-e) Gibbs free energy diagrams for OER on (a) M1, (b) M2, (c) M3, (d) M4, and (e) M5 models with O modification; (f) Comparisons of the Gibbs free energy differences for the four electron transfer steps in the OER process for M1-M5 models. Colorful figures are available on website
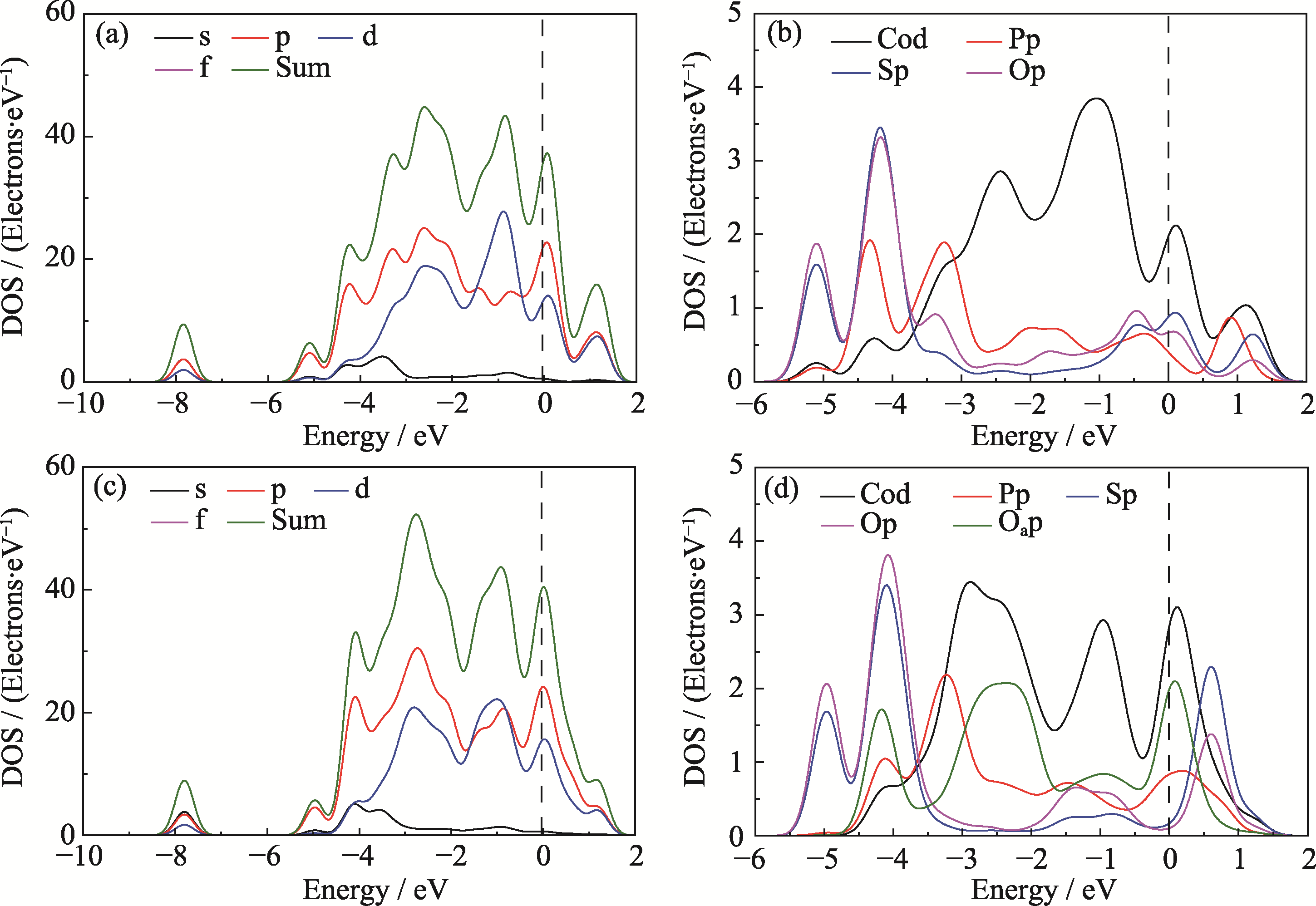
图6 M4模型吸附OOH中间体前、后的态密度图对比
Fig. 6 Comparison of density of states for M4 model before and after adsorption of OOH (a) Total PDOS and (b) atom-resolved PDOS of M4 model; (c) Total PDOS and (d) atom-resolved PDOS of M4 model after adsorbing *OOH. Colorful figures are available on website
| No. | Fractional coordinates | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | |
| Co1a | -0.251 | 0.002 | -0.005 |
| Co1b | 0.275 | 0.002 | -0.005 |
| Co2a | -0.128 | 0.266 | 0.015 |
| Co2b | 0.152 | 0.266 | 0.015 |
| Co2c | -0.128 | -0.263 | -0.026 |
| Co2d | 0.152 | -0.263 | -0.026 |
| S1a | -0.239 | 0.167 | -0.175 |
| S1b | 0.263 | 0.167 | -0.175 |
| S1c | -0.238 | -0.164 | 0.165 |
| S1d | 0.262 | -0.164 | 0.165 |
| S2a | -0.315 | 0.187 | 0.137 |
| S2b | 0.339 | 0.187 | 0.137 |
| S2c | -0.316 | -0.184 | -0.147 |
| S2d | 0.340 | -0.184 | -0.147 |
| S3a | 0.012 | 0.374 | 0.185 |
| S3b | 0.012 | -0.369 | -0.197 |
| S4a | 0.012 | 0.394 | -0.130 |
| S4b | 0.012 | -0.392 | 0.119 |
| P1 | 0.012 | 0.070 | 0.084 |
| P2 | 0.012 | -0.066 | -0.094 |
表S1 几何优化后CoPS3-QDs1各原子空间分布的分数坐标
Table S1 Fractional coordinates of each atom in the optimized geometrical structure model of CoPS3-QDs1
| No. | Fractional coordinates | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | |
| Co1a | -0.251 | 0.002 | -0.005 |
| Co1b | 0.275 | 0.002 | -0.005 |
| Co2a | -0.128 | 0.266 | 0.015 |
| Co2b | 0.152 | 0.266 | 0.015 |
| Co2c | -0.128 | -0.263 | -0.026 |
| Co2d | 0.152 | -0.263 | -0.026 |
| S1a | -0.239 | 0.167 | -0.175 |
| S1b | 0.263 | 0.167 | -0.175 |
| S1c | -0.238 | -0.164 | 0.165 |
| S1d | 0.262 | -0.164 | 0.165 |
| S2a | -0.315 | 0.187 | 0.137 |
| S2b | 0.339 | 0.187 | 0.137 |
| S2c | -0.316 | -0.184 | -0.147 |
| S2d | 0.340 | -0.184 | -0.147 |
| S3a | 0.012 | 0.374 | 0.185 |
| S3b | 0.012 | -0.369 | -0.197 |
| S4a | 0.012 | 0.394 | -0.130 |
| S4b | 0.012 | -0.392 | 0.119 |
| P1 | 0.012 | 0.070 | 0.084 |
| P2 | 0.012 | -0.066 | -0.094 |

图S2 CoPS3-QDs1的六个活性位点(S1~S4、Co1和Co2)上分别吸附了*OOH、*OH和*O三个氧中间体的结构模型示意图,分别以(a)S1和(b)Co2位点为例
Fig. S2 Schematic structure models of six active sites (S1-S4, Co1 and Co2) of CoPS3-QDs1 adsorbing three oxygen intermediates (*OOH, *OH, and *O), illustrated using site S1 and Co2 as example
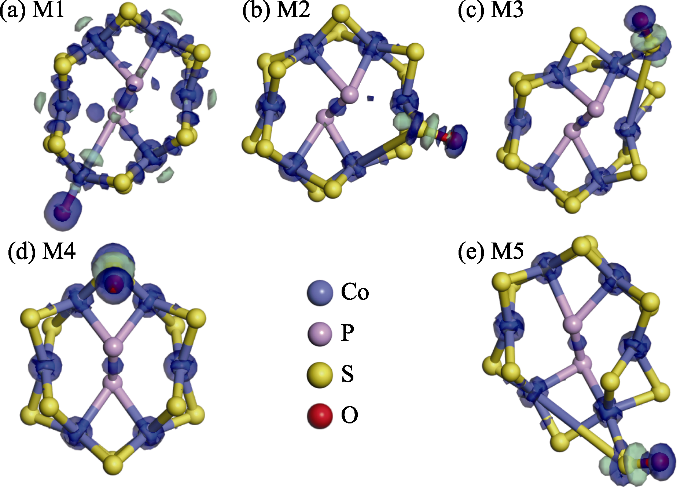
图S3 几何优化后O修饰CoPS3-QDs1的Co2位点及其周边四个不等价S原子的结构模型和差分电荷密度分布,其中蓝色区域表示电子聚集,绿色区域表示电子损耗isovalue=0.2 e/Å3
Fig. S3 Optimized structural models and charge density difference maps of O modification at the Co2 site of CoPS3-QDs1 and its surrounding four inequivalent S atoms, where blue regions indicate electron accumulation and green regions indicate electron depletion, with isovalue=0.2 e/Å3
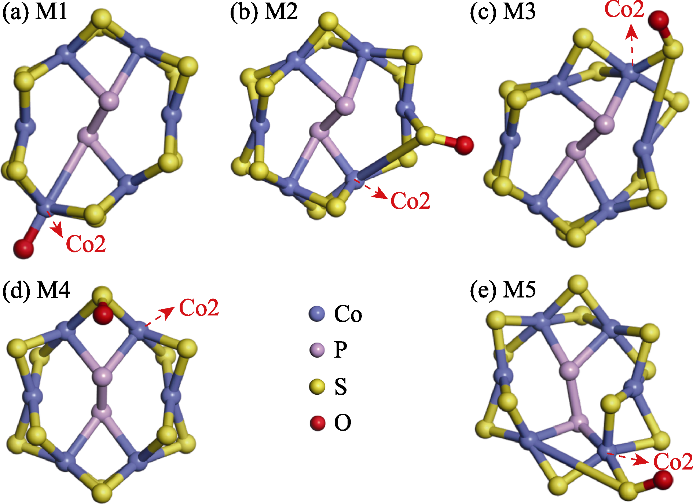
图S4 吸附*OOH、*OH和*O三个氧中间体的M1~M5模型的Co2位点示意图
Fig. S4 Schematic diagrams of the Co2 sites in the M1-M5 models for the adsorption of *OOH, *OH, and *O oxygen intermediates
| [1] |
TEE S Y, WIN K Y, TEO W S, et al. Recent progress in energy- driven water splitting. Advanced Science, 2017, 4(5): 1600337.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
YUE M, LAMBERT H, PAHON E, et al. Hydrogen energy systems: a critical review of technologies, applications, trends and challenges. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 146: 111180.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
SUN H, XU X, KIM H, et al. Electrochemical water splitting: bridging the gaps between fundamental research and industrial applications. Energy & Environmental Materials, 2023, 6(5): e12441.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LI J, HOU C, CHEN C, et al. Collaborative interface optimization strategy guided ultrafine RuCo and MXene heterostructure electrocatalysts for efficient overall water splitting. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(11): 10947.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CHEN R, YANG Y, WU W, et al. Reconstructed β-NiOOH enabling highly efficient and ultrastable oxygen evolution at large current density. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 480: 148100.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LI Y, LIU J, LI S, et al. Codecoration of phosphate and iron for improving oxygen evolution reaction of layered Ni (OH)2/NiOOH. ACS Catalysis, 2024, 14(7): 4807.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
YU M, BUDIYANTO E, TUYSUZ H. Principles of water electrolysis and recent progress in cobalt-, nickel-, and iron-based oxides for the oxygen evolution reaction. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(1): e202103824.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ZHOU B, GAO R, ZOU J, et al. Surface design strategy of catalysts for water electrolysis. Small, 2022, 18(27): 2202336.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HUANG H, KIM H, LEE A, et al. Structure engineering defective and mass transfer enhanced RuO2 nanosheets for proton exchange membrane water electrolyzer. Nano Energy, 2021, 88: 106276.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
ZHANG L, LU C, YE F, et al. Selenic acid etching assisted vacancy engineering for designing highly active electrocatalysts toward the oxygen evolution reaction. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(14): 2007523.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ZHAO S, CHEN Y, LIU Y, et al. Shining light on layered metal phosphosulphide catalysts for efficient water electrolysis: preparation, promotion strategies, and perspectives. Green Chemistry, 2023, 25(16): 6170.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
XUE S, CHEN L, LIU Z, et al. NiPS3 nanosheet-graphene composites as highly efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(6): 5297.
DOI URL |
| [13] | OLIVEIRA F, PASTIK J, MAZÁNEK V, et al. Cobalt phosphorous trisulfide as a high-performance electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(20): 23638. |
| [14] |
KONKENA B, MASA J, BOTZ A, et al. Metallic NiPS3@NiOOH core-shell heterostructures as highly efficient and stable electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(1): 229.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LI W, LI C, DONG H, et al. Expediting oxygen evolution by optimizing cation and anion complexity in electrocatalysts based on metal phosphorous trichalcogenides. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(9): e202214570.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
OLIVEIRA F, PAŠTIKA J, AYAZ I, et al. Alkaline water electrolysis performance of mixed cation metal phosphorous trichalcogenides. Materials Today Energy, 2024, 39: 101468.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SONG B, LI K, YIN Y, et al. Tuning mixed nickel iron phosphosulfide nanosheet electrocatalysts for enhanced hydrogen and oxygen evolution. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7: 8549.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LIU P, PU Y. Construction of two-dimensional CoPS3@defective N-doped carbon composites for enhanced oxygen evolution reaction. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(1): 197.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
HUANG C, LIN H, CHIANG C, et al. Manipulating spin exchange interactions and spin-selected electron transfers of 2D metal phosphorus trisulfide crystals for efficient oxygen evolution reaction. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(43): 2305792.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
YU J, SONG H, LI X, et al. Computational studies on carbon dots electrocatalysis: a review. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(49): 2107196.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
SU H, WANG W, SHI R, et al. Recent advances in quantum dot catalysts for hydrogen evolution: synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic application. Carbon Energy, 2023, 5(9): e280.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
MOHANTY B, MITRA A, JENA B, et al. MoS2 quantum dots as efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction over a wide pH range. Energy & Fuels, 2020, 34(8): 10268.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
YANG M, LIAN Z, SI C, et al. Revealing the intrinsic relation between heteroatom dopants and graphene quantum dots as a bi- functional ORR/OER catalyst. Molecular Catalysis, 2022, 518: 112109.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
XIA C, FENG J, MA C, et al. Exploring the underlying oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalytic activities of pyridinic-N and pyrrolic-N doped graphene quantum dots. Molecular Catalysis, 2023, 535: 112880.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
MOHAMMADI N, ESRAFILI M, SARDROODI J. Defect stabilized Fe atom on porous BN sheet as a potential electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction: a first-principles investigation. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 580: 152271.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
PERDEW J, BURKE K, ERNZERHOF M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77: 3865.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
DELLEY B. Hardness conserving semilocal pseudopotentials. Physical Review B, 2002, 66: 155125.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
HEHRE W. Ab initio molecular orbital theory. Accounts of Chemical Research, 1976, 9: 399.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
NØRSKOV J K, ROSSMEISL J, LOGADOTTIR A, et al. Origin of the overpotential for oxygen reduction at a fuel-cell cathode. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2004, 108(46): 17886.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
NØRSKOV J K, BLIGAARD T, LOGADOTTIR A, et al. Trends in the exchange current for hydrogen evolution. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2005, 152(3): J23.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
MAN I C, SU H, CALLE-VALLEJO F, et al. Universality in oxygen evolution electrocatalysis on oxide surfaces. ChemCatChem, 2011, 3(7): 1159.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
TAN G, ZHAO X, ZHANG Z, et al. First-principles study of the oxygen evolution reaction on Ni3Fe-layered double hydroxides surfaces with varying sulfur coverage. Molecular Catalysis, 2022, 519: 112116.
DOI URL |
| [33] | 刘婧, 冷艳丽, 慕红梅, 等. 双金属团簇Cu12Fe吸附CO和H2的理论研究. 原子与分子物理学报, 2023, 40(2): 92. |
| [34] |
JIN Y, JIN Y, LI K, et al. Mixed insulating state for van der Waals CoPS3. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2022, 13(45): 10486.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
LI K, LI N, YAN N, et al. Adsorption of small hydrocarbons on pristine, N-doped and vacancy graphene by DFT study. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 515: 146028.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
LI J. Oxygen evolution reaction in energy conversion and storage: design strategies under and beyond the energy scaling relationship. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 14(1): 112.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
ZHOU G, LI M, LI Y, et al. Regulating the electronic structure of CoP nanosheets by O incorporation for high-efficiency electrochemical overall water splitting. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(7): 1905252.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
LU S, ZHANG Y, LOU F, et al. Non-precious metal activated MoSi2N4 monolayers for high-performance OER and ORR electrocatalysts: a first-principles study. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 579: 152234.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 陈梓, 张爱迪, 龚克, 刘海华, 禹钢, 单青松, 刘勇, 曾海波. 具有可调谐和长寿命荧光发射的高亮度、单分散四元CuInZnS@ZnS量子点[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 433-339. |
| [2] | 吕昕怿, 相恒阳, 曾海波. 长程有序助力钙钛矿QLED高性能化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 111-112. |
| [3] | 李家琪, 李小松, 李煊赫, 朱晓兵, 朱爱民. 暖等离子体合成过渡金属掺杂氧化锰析氧电催化剂[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 835-844. |
| [4] | 岳仔豪, 杨小兔, 张正亮, 邓瑞翔, 张涛, 宋力昕. Pb2+对掺杂硼硅酸盐玻璃中CsPbBr3钙钛矿量子点发光性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 449-456. |
| [5] | 岳全鑫, 郭瑞华, 王瑞芬, 安胜利, 张国芳, 关丽丽. 3D核壳结构NiMoO4@CoFe-LDH纳米棒的高效析氧及全解水性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1254-1264. |
| [6] | 王鹏, 靳遵龙, 陈宁光, 刘勇豪. Mo掺杂α-MnO2电催化析氧反应的理论研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 541-546. |
| [7] | 付永胜, 毕敏, 李春, 孙敬文, 汪信, 朱俊武. 非贵金属/碳氮复合材料电催化析氧反应的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 163-172. |
| [8] | 张枫娟, 韩博宁, 曾海波. 钙钛矿量子点光伏与荧光聚光电池: 现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 117-128. |
| [9] | 田建建, 马霞, 王敏, 姚鹤良, 华子乐, 张玲霞. 锡量子点制备及其电催化还原二氧化碳产甲酸性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1337-1342. |
| [10] | 舒孟洋, 陆嘉琳, 张志洁, 沈涛, 徐家跃. CsPbBr3钙钛矿量子点/C3N4超薄纳米片0D/2D复合材料: 增强的稳定性和光催化活性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1217-1222. |
| [11] | 陈婷, 徐彦乔, 江伟辉, 谢志翔, 王连军, 江莞. 离子液体辅助微波法水相合成Cu-In-Zn-S/ZnS量子点及其在白光LED中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(4): 439-446. |
| [12] | 张盛, 蒋亿, 纪媛媛, 杜莹, 盛振环, 殷竟洲, 李乔琦, 张莉莉. 凹凸棒石/g-C3N4复合材料的制备及其电催化析氧性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(8): 803-810. |
| [13] | 李盛菘, 郑永超, 孟澍临, 吴骊珠, 钟近艺, 赵冲林. 核壳型量子点-纳米金颗粒组装体高效检测神经性毒剂模拟剂[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(8): 893-898. |
| [14] | 刘旸, 于姗, 郑凯文, 陈维维, 董兴安, 董帆, 周莹. N-Bi2O2CO3/CdSe量子点光催化氧化NO及原位红外光谱研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(4): 425-432. |
| [15] | 杨英,潘德群,张政,陈甜,韩晓敏,张力松,郭学益. Ag2Se量子点共敏化固态染料敏化太阳能电池光电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(2): 137-144. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||