无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (11): 1237-1244.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250134 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250134
葛泽生1( ), 刘苗1, 汤哲1, 周岩2(
), 刘苗1, 汤哲1, 周岩2( ), 万舜3, 宗鹏安1(
), 万舜3, 宗鹏安1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-30
修回日期:2025-05-26
出版日期:2025-11-20
网络出版日期:2025-06-03
通讯作者:
宗鹏安, 教授. E-mail: pazong@njtech.edu.cn;作者简介:葛泽生(1998-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: zsge37@njtech.edu.cn
基金资助:
GE Zesheng1( ), LIU Miao1, TANG Zhe1, ZHOU Yan2(
), LIU Miao1, TANG Zhe1, ZHOU Yan2( ), WAN Shun3, ZONG Peng’an1(
), WAN Shun3, ZONG Peng’an1( )
)
Received:2025-03-30
Revised:2025-05-26
Published:2025-11-20
Online:2025-06-03
Contact:
ZONG Peng’an, professor. E-mail: pazong@njtech.edu.cn;About author:GE Zesheng (1998-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: zsge37@njtech.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
碲化铋基材料因具有优异的室温热电性能而得到广泛研究。但碲化铋具有本征脆性, 如何制备柔性高热电性能碲化铋基材料成为热电领域的难点。本研究采用磁控溅射技术在聚酰亚胺(PI)衬底上沉积了Cu0.005Bi0.5Sb1.495Te3, 成功制备了非(00l)层状取向柔性p型热电薄膜, 并研究了磁控溅射工作气压对热电性能的影响。结果表明, 在0.7 Pa磁控溅射工作气压下, 由于晶粒尺寸大、结晶性高, 迁移率提升, 同时载流子浓度得到优化, 达到5.78×1019 cm−3, 室温功率因子(PF)达到1660 μW·m−1·K−2。此外, 该薄膜具有优异的机械柔性, 在弯曲半径为5 mm时, 薄膜电阻率变化小于10%, 在循环弯曲600次后, 薄膜塞贝克系数变化小于5%。基于该柔性薄膜, 设计并集成了由四个p型热电臂(5 mm×25 mm×767 nm)组成的柔性热电器件。当温差为30 K时, 柔性热电器件的输出电压达到18.5 mV, 功率密度达到44.80 μW·cm−2。基于该热电器件的触碰传感语言输出设计有望用于语言辅助与人机交互应用。本研究为高性能柔性碲化铋基热电薄膜的磁控溅射制备与性能优化提供了重要参考。
中图分类号:
葛泽生, 刘苗, 汤哲, 周岩, 万舜, 宗鹏安. 柔性Cu0.005Bi0.5Sb1.495Te3薄膜的磁控溅射制备与热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1237-1244.
GE Zesheng, LIU Miao, TANG Zhe, ZHOU Yan, WAN Shun, ZONG Peng’an. Flexible Cu0.005Bi0.5Sb1.495Te3 Thin Films: Magnetron Sputtering Preparation and Thermoelectric Properties[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1237-1244.
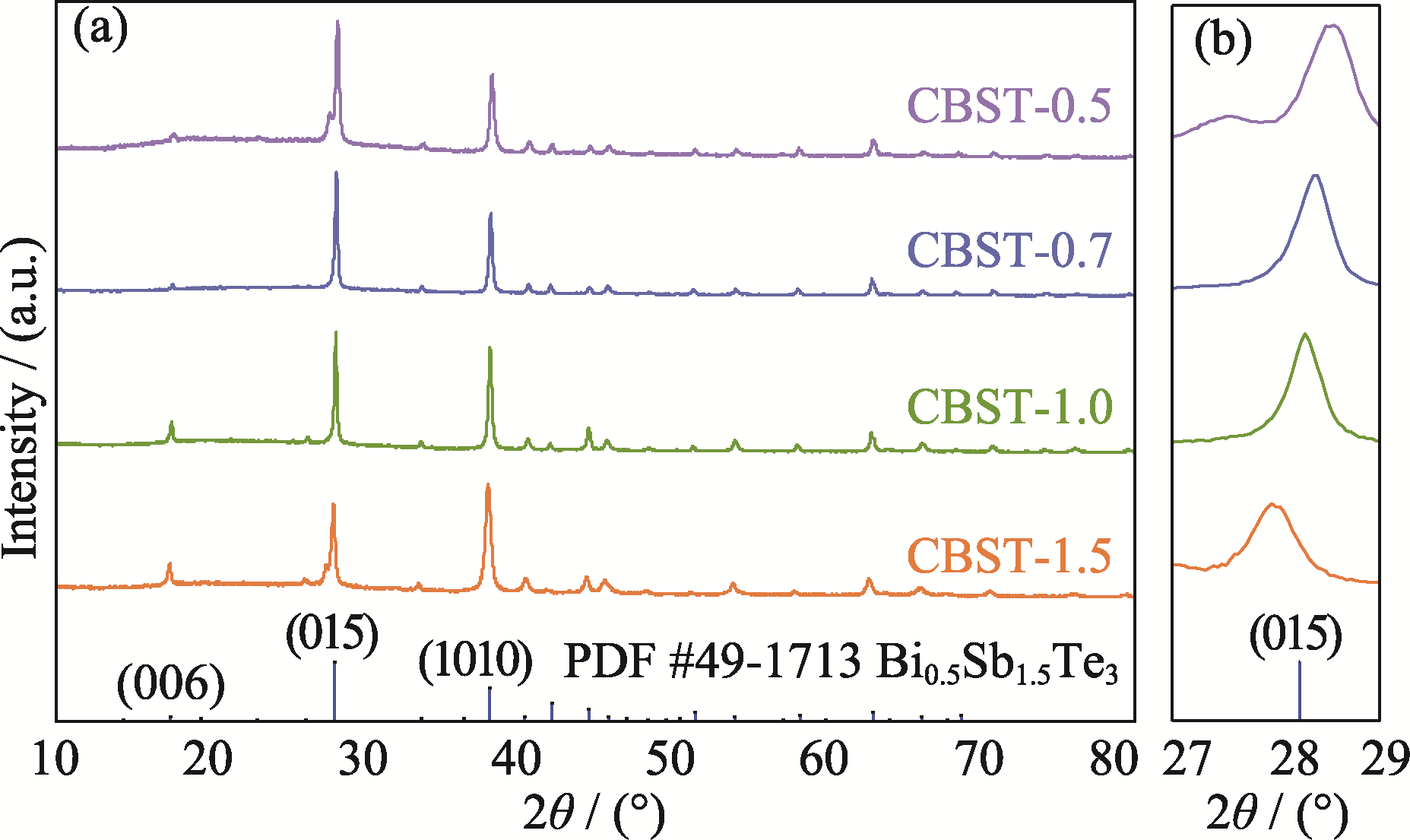
图1 CBST-x(x=0.5, 0.7, 1.0, 1.5)薄膜的XRD图谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of CBST-x (x=0.5, 0.7, 1.0, 1.5) thin films (a) XRD patterns; (b) Localized enlargements of (015) crystal plane diffraction peaks
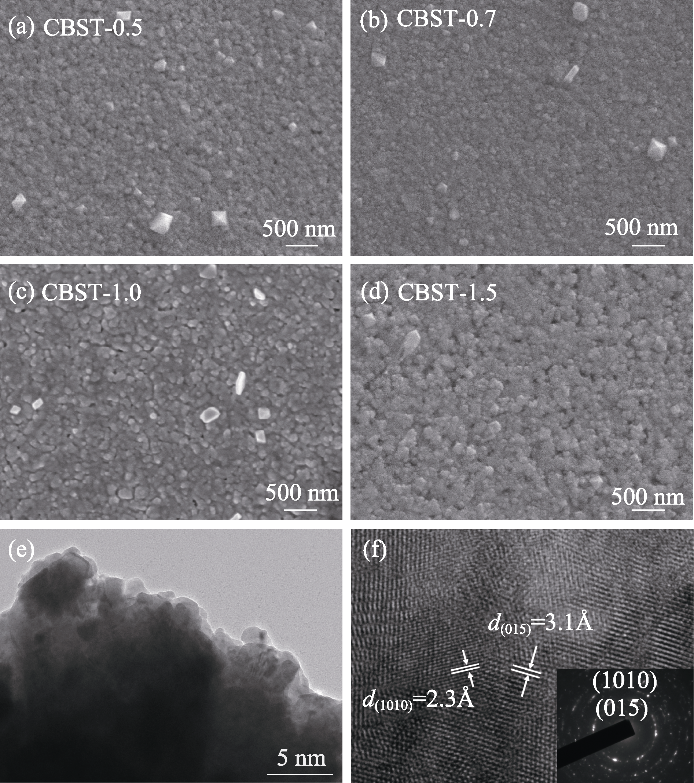
图2 CBST-x(x=0.5, 0.7, 1.0, 1.5)薄膜的表面微观结构
Fig. 2 Surface microstructures of CBST-x (x=0.5, 0.7, 1.0, 1.5) thin films (a-d) Surface SEM images of (a) CBST-0.5, (b) CBST-0.7, (c) CBST-1.0, and (d) CBST-1.5; (e) TEM and (f) HRTEM images with SAED pattern of CBST-0.7
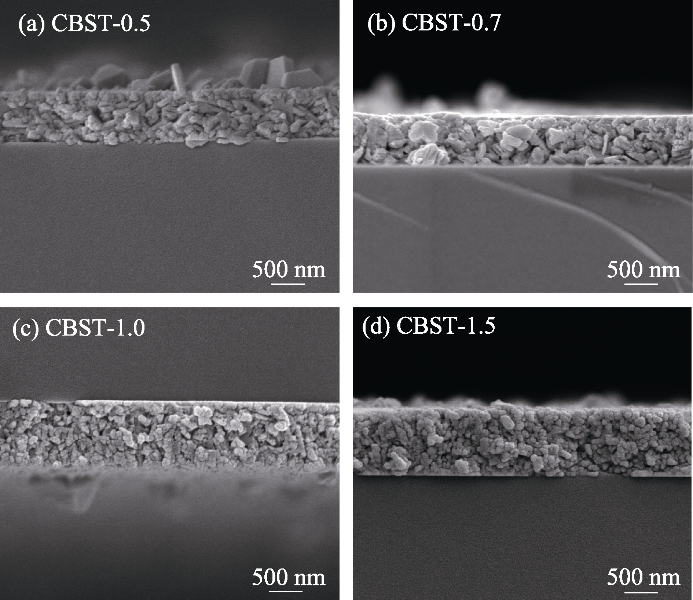
图3 CBST-x(x=0.5, 0.7, 1.0, 1.5)薄膜的截面微观结构
Fig. 3 Cross-sectional microstructures of CBST-x (x=0.5, 0.7, 1.0, 1.5) thin films (a) CBST-0.5; (b) CBST-0.7; (c) CBST-1.0; (d) CBST-1.5
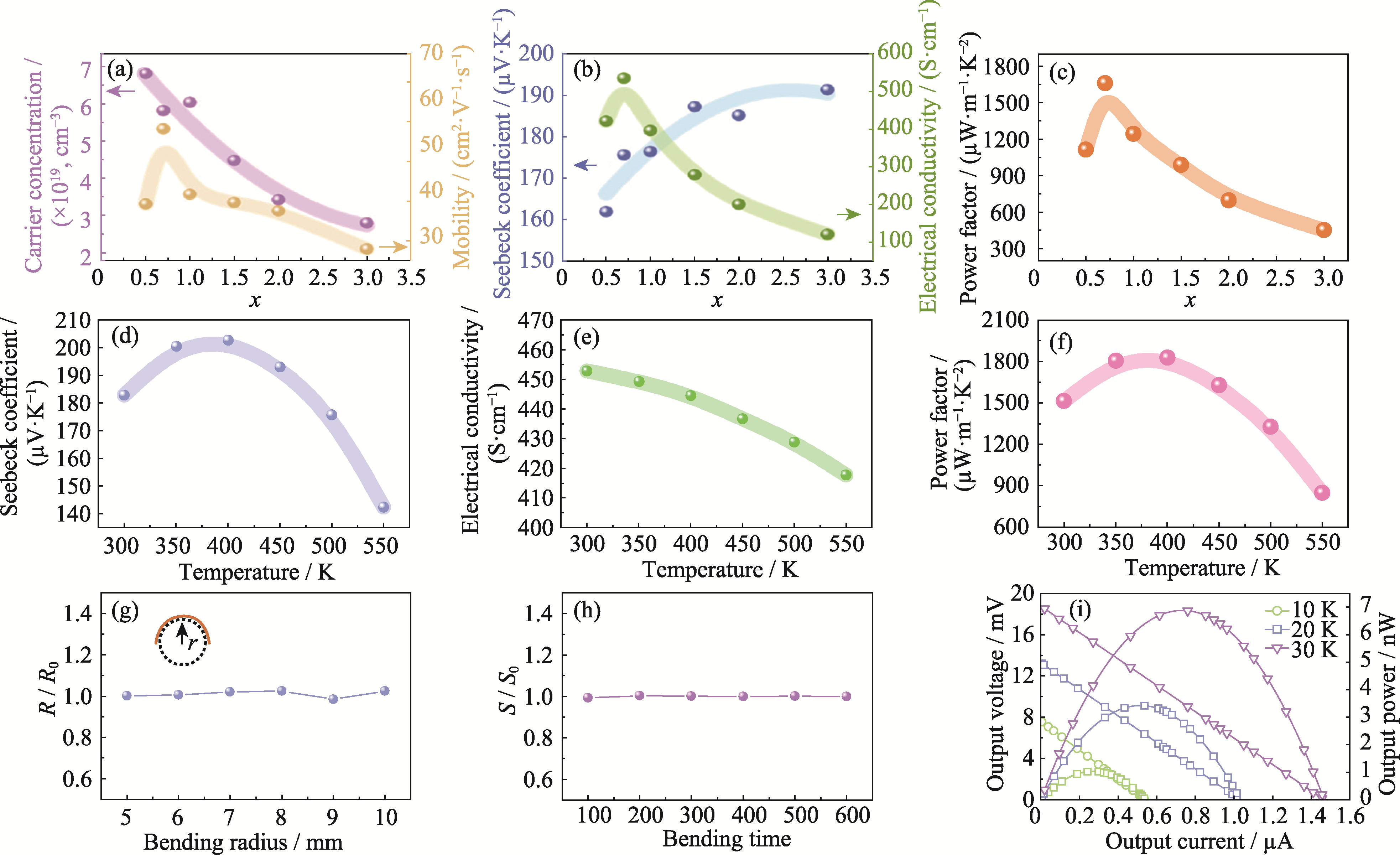
图5 CBST薄膜的热电性能、柔性及集成器件输出性能
Fig. 5 Thermoelectric properties, flexibility and integrated device output properties of CBST thin films (a-c) Variation of (a) n and μ, (b) S and σ, (c) PF of CBST-x (x=0.5, 0.7, 1.0, 1.5) thin films; (d) S, (e) σ, and (f) PF of CBST-0.7 thin film (300-550 K); (g, h) Flexibility characterization of CBST-0.7 thin film: (g) Resistivity change under different bending radii (5-10 mm),(h) Seebeck coefficient changes with bending cycles (100-600 cycles); (i) Relationship between Voc, Poc and current of TEG composed of 4 single p-type thermoelectric legs with optimal performance at different temperatures (10-30 K)
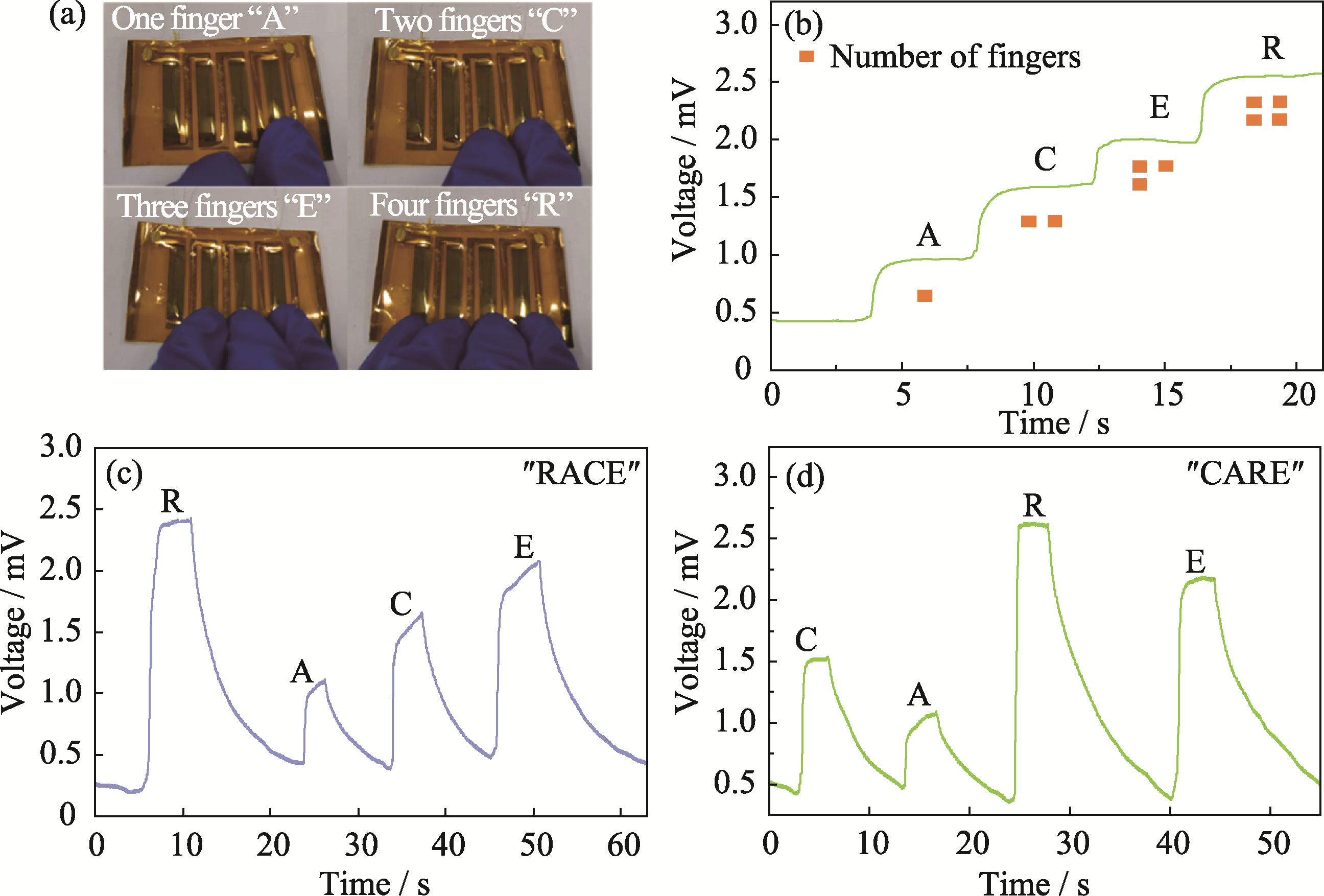
图6 单p型热电器件及触碰传感语言输出设计
Fig. 6 Single p-type TEG and touch sensing language output design (a) Touching single-p-type TEG with different numbers of finger; (b) Voc generated by the TEG upon touching by one to four fingers; (c, d) TEG converts the resulting voltage signal into words (c) “RACE” and (d) “CARE”
| Sample | Cu/% | Bi/% | Sb/% | Te/% | (Bi+Sb)/Te | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBST-0.5 | 0.14 | 10.53 | 31.25 | 58.08 | 41.78/58.08 | Cu0.0066Bi0.50Sb1.48Te2.76 |
| CBST-0.7 | 0.12 | 10.52 | 29.90 | 59.46 | 40.43/59.46 | Cu0.0057Bi0.50Sb1.42Te2.83 |
| CBST-1.0 | 0.11 | 9.73 | 29.87 | 60.29 | 39.60/60.29 | Cu0.0056Bi0.50Sb1.53Te3.09 |
| CBST-1.5 | 0.09 | 10.05 | 28.52 | 61.34 | 38.57/61.34 | Cu0.0045Bi0.50Sb1.42Te3.05 |
表S1 不同工作压力(0.5~1.5 Pa)下制备的CBST薄膜的EDS元素原子百分比
Table S1 EDS detected atomic percentages of CBST films prepared at different working pressures (0.5-1.5 Pa)
| Sample | Cu/% | Bi/% | Sb/% | Te/% | (Bi+Sb)/Te | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBST-0.5 | 0.14 | 10.53 | 31.25 | 58.08 | 41.78/58.08 | Cu0.0066Bi0.50Sb1.48Te2.76 |
| CBST-0.7 | 0.12 | 10.52 | 29.90 | 59.46 | 40.43/59.46 | Cu0.0057Bi0.50Sb1.42Te2.83 |
| CBST-1.0 | 0.11 | 9.73 | 29.87 | 60.29 | 39.60/60.29 | Cu0.0056Bi0.50Sb1.53Te3.09 |
| CBST-1.5 | 0.09 | 10.05 | 28.52 | 61.34 | 38.57/61.34 | Cu0.0045Bi0.50Sb1.42Te3.05 |
| Sample | 2θ/(°) | FWHM, β/rad | Grain size, D/nm | Dislocation density, δ/ (×1015, m−2) | Strain, ε/ (×10−3, line−2·m−4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBST-0.5 | 28.26 | 0.00435 | 32.511 | 0.946 | 1.054 |
| CBST-0.7 | 28.18 | 0.00317 | 44.602 | 0.503 | 0.768 |
| CBST-1.0 | 28.14 | 0.00332 | 42.556 | 0.552 | 0.805 |
| CBST-1.5 | 27.98 | 0.00467 | 30.261 | 1.092 | 1.132 |
表S2 不同工作气压下制备的CBST薄膜的XRD分析结果
Table S2 XRD analysis results of CBST thin films prepared at different working pressures
| Sample | 2θ/(°) | FWHM, β/rad | Grain size, D/nm | Dislocation density, δ/ (×1015, m−2) | Strain, ε/ (×10−3, line−2·m−4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBST-0.5 | 28.26 | 0.00435 | 32.511 | 0.946 | 1.054 |
| CBST-0.7 | 28.18 | 0.00317 | 44.602 | 0.503 | 0.768 |
| CBST-1.0 | 28.14 | 0.00332 | 42.556 | 0.552 | 0.805 |
| CBST-1.5 | 27.98 | 0.00467 | 30.261 | 1.092 | 1.132 |
| Material | Crystal orientation | PF/(μW·m−1·K−2) |
|---|---|---|
| Bi2Te3[ | (00l) | 3000 |
| Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3[ | (00l) | 2000 |
| Bi2Te3[ | (00l) | 1610 |
| Sb2Te3[ | (015) | 1210 |
| Sb2Te3[ | (015) | 1220 |
| W-Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3[ | (015) | 1375 |
| Cu0.005Bi0.5Sb1.495Te3 (This Work) | (015) | 1660 |
表S3 本工作制备的CBST薄膜的室温PF与文献报道数据的对比
Table S3 Comparison of room-temperature PF of the CBST film prepared in this work and literature
| Material | Crystal orientation | PF/(μW·m−1·K−2) |
|---|---|---|
| Bi2Te3[ | (00l) | 3000 |
| Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3[ | (00l) | 2000 |
| Bi2Te3[ | (00l) | 1610 |
| Sb2Te3[ | (015) | 1210 |
| Sb2Te3[ | (015) | 1220 |
| W-Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3[ | (015) | 1375 |
| Cu0.005Bi0.5Sb1.495Te3 (This Work) | (015) | 1660 |
| Material | Device type | N (leg numbers) | ΔT/K | Voc/mV | Pmax/nW | Average Voc/ mV | Pmax density/(μW·cm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi2Te3/CFF (carbon fiber fabric)[ | Single p-type | 5 | 32 | 6.0 | 90.6 | 1.2 | 0.72 |
| Bi2Te3/Ni Foam[ | Single n-type | 5 | 30 | 3.7 | 22.7 | 0.8 | 0.71 |
| Bi2Te3-Sb2Te3[ | π-type | 26 | 24 | 48.9 | 693.5 | 1.9 | − |
| Bi2Te3-Sb2Te3[ | π-type | 200 | 40 | 430.0 | 32.0 | 2.2 | 94.81 |
| Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3-Bi2Te2.7Se0.3[ | π-type | 13 | 68 | 70.0 | 11000.0 | 5.4 | 140.00 |
| This work | Single p-type | 4 | 30 | 18.5 | 6.9 | 4.6 | 44.80 |
表S4 本工作的热电器件与其它工作的输出性能对比
Table S4 Comparison of the output performance of the thermoelectric device in this work and literature
| Material | Device type | N (leg numbers) | ΔT/K | Voc/mV | Pmax/nW | Average Voc/ mV | Pmax density/(μW·cm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi2Te3/CFF (carbon fiber fabric)[ | Single p-type | 5 | 32 | 6.0 | 90.6 | 1.2 | 0.72 |
| Bi2Te3/Ni Foam[ | Single n-type | 5 | 30 | 3.7 | 22.7 | 0.8 | 0.71 |
| Bi2Te3-Sb2Te3[ | π-type | 26 | 24 | 48.9 | 693.5 | 1.9 | − |
| Bi2Te3-Sb2Te3[ | π-type | 200 | 40 | 430.0 | 32.0 | 2.2 | 94.81 |
| Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3-Bi2Te2.7Se0.3[ | π-type | 13 | 68 | 70.0 | 11000.0 | 5.4 | 140.00 |
| This work | Single p-type | 4 | 30 | 18.5 | 6.9 | 4.6 | 44.80 |
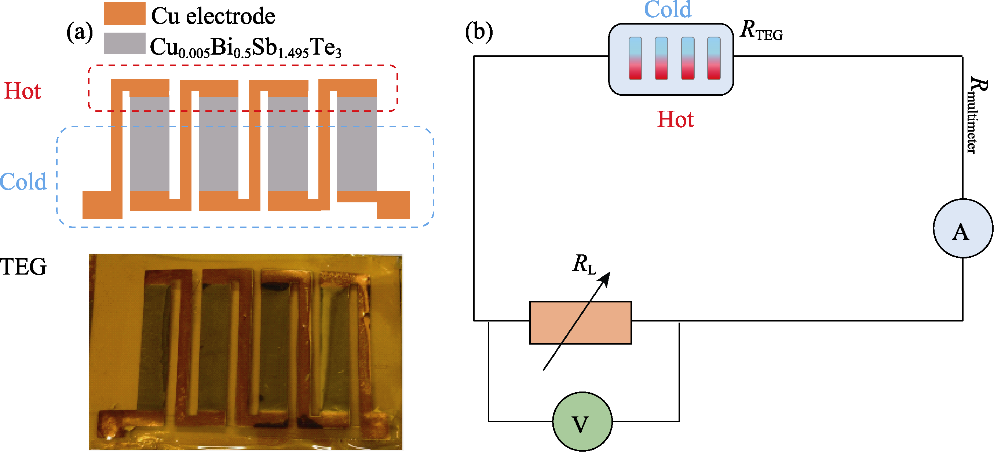
图S4 TEG结构示意、实物图以及发电回路图
Fig. S4 TEG structure diagram, physical diagram and power generation circuit diagram (a) Schematic and photograph of the single-p-type TEG composed of four thin-film legs with optimized performance; (b) Circuit schematic of the TEG integrated with an external load resistor
| [1] | BIAN X L, YANG Z L, ZHANG T, et al. Multifunctional flexible AgNW/MXene/PDMS composite films for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding and strain sensing. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(35): 41906. |
| [2] | FU Y T, ZHANG Q H, HU Z L, et al. Mg3(Bi,Sb)2-based thermoelectric modules for efficient and reliable waste-heat utilization up to 750 K. Energy & Environmental Science, 2022, 15: 3265. |
| [3] |
LI L, LIU W D, LIU Q F, et al. Multifunctional wearable thermoelectrics for personal thermal management. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(22): 2200548.
DOI URL |
| [4] | GAO M Y, WANG P, JIANG L L, et al. Power generation for wearable systems. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(4): 2114. |
| [5] |
LU Y, ZHOU Y, WANG W, et al. Staggered-layer-boosted flexible Bi2Te3 films with high thermoelectric performance. Nature Nanotechnology, 2023, 18(11): 1281.
DOI |
| [6] |
ZHANG Q H, HUANG X Y, BAI S Q, et al. Thermoelectric devices for power generation: recent progress and future challenges. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2016, 18(2): 194.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HSIEH Y Y, ZHANG Y, ZHANG L, et al. High thermoelectric power-factor composites based on flexible three-dimensional graphene and polyaniline. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(14): 6552.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
TIAN R M, LIU Y Q, KOUMOTO K, et al. Body heat powers future electronic skins. Joule, 2019, 3(6): 1399.
DOI |
| [9] |
ZHU J J, SUN C, FENG W L, et al. Permeable carbon fiber based thermoelectric film with exceptional EMI shielding performance and sensor capabilities. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2024, 13(8): 1119.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
PEREZ-TABORDA J A, VERA L, CABALLERO-CALERO O, et al. Pulsed hybrid reactive magnetron sputtering for high zT Cu2Se thermoelectric films. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2017, 2(7): 1700012.
DOI URL |
| [11] | HAO F, QIU P F, TANG Y S, et al. High efficiency Bi2Te3-based materials and devices for thermoelectric power generation between 100 and 300 ℃. Energy & Environmental Science, 2016, 9(10): 3120. |
| [12] |
HAO F, QIU P F, SONG Q F, et al. Roles of Cu in the enhanced thermoelectric properties in Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3. Materials, 2017, 10(3): 251.
DOI URL |
| [13] | TANWAR A, KAUR R, PADMANATHAN N, et al. Electrodeposited CuSbTe thin films with enhanced thermoelectric performance. Sustainable Energy & Fuels, 2023, 7(17): 4160. |
| [14] |
JOO S J, KIM B S, MIN B K, et al. Deposition of n-type Bi2Te3 thin films on polyimide by using RF magnetron co-sputtering method. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2015, 15(10): 8299.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
TAKASHIRI M, TAKANO K, HAMADA J. Use of H2-Ar gas mixtures in radio-frequency magnetron sputtering to produce high-performance nanocrystalline bismuth telluride thin films. Thin Solid Films, 2018, 664: 100.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
DONG G Y, FENG J H, QIU G J, et al. Oriented Bi2Te3-based films enabled high performance planar thermoelectric cooling device for hot spot elimination. Nature Communications, 2024, 15: 9695.
DOI |
| [17] |
ZHU W, DENG Y, WANG Y, et al. Preferential growth transformation of Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 films induced by facile post-annealing process: enhanced thermoelectric performance with layered structure. Thin Solid Films, 2014, 556: 270.
DOI URL |
| [18] | ROKNABADI M R, MOLLAEE M, GARAZHIAN S. Fabrication and thermoelectric properties of nano Sb2Te3, Bi2Te3 thin films using PVD of synthesized nano powder. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2025, 36(3): 218. |
| [19] | LIU Z R, ZHANG Y L, XUE F N, et al. High-performance W-doped Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 flexible thermoelectric films and generators. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(20): 26025. |
| [20] | SHANG H J, LI T G, LUO D, et al. High-performance Ag-modified Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 films for the flexible thermoelectric generator. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(6): 7358. |
| [21] |
MU X, ZHOU H Y, HE D Q, et al. Enhanced electrical properties of stoichiometric Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 film with high-crystallinity via layer-by-layer in situ growth. Nano Energy, 2017, 33: 55.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
SATHYAMOORTHY R, DHEEPA J. Structural characterization of thermally evaporated Bi2Te3 thin films. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2007, 68(1): 111.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
KHUMTONG T, SUKWISUTE P, SAKULKALAVEK A, et al. Microstructure and electrical properties of antimony telluride thin films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering on flexible substrate using different sputtering pressures. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2017, 46(5): 3166.
DOI URL |
| [24] | ANDERS A. Discharge physics of high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2011, 205: S1. |
| [25] |
MCINTYRE N S, COOK M G. X-ray photoelectron studies on some oxides and hydroxides of cobalt, nickel, and copper. Analytical Chemistry, 1975, 47(13): 2208.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
PARMIGIANI F, PACCHIONI G, ILLAS F, et al. Studies of the Cu-O bond in cupric oxide by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and ab initio electronic structure models. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 1992, 59(3): 255.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
SHI T F, CHEN M R, ZHANG C R, et al. Modifying carbon fiber fabric for flexible thermoelectric energy conversion. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 610: 155479.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
AFSIN B, ROBERTS M W. Formation of an oxy-chloride overlayer at a Bi(000l) surface. Spectroscopy Letters, 1994, 27(1): 139.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
MORGAN W E, STEC W J, VAN WAZER J R. Inner-orbital binding-energy shifts of antimony and bismuth compounds. Inorganic Chemistry, 1973, 12(4): 953.
DOI URL |
| [30] | LIU W K, YUEN W T, STRADLING R A. Preparation of InSb substrates for molecular beam epitaxy. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, 1995, 13(4): 1539. |
| [31] | BENVENUTTI E V, GUSHIKEM Y, VASQUEZ A, et al. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and mössbauer spectroscopy study of iron(III) and antimony(V) oxides grafted onto a silica gel surface. Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications, 1991(19): 1325. |
| [32] |
WANG J Q, FENG D M, WU W H, et al. An investigation of the flame retardation mechanism of polypropylene containing a chlorine flame retardant system by XPS(ESCA). Polymer Degradation and Stability, 1991, 31(2): 129.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
TKALICH A K, DEMIN V N, ZLOMANOV V P. Oxidation states of In in Pb1-xInxTe. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1995, 116(1): 33.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
ZHOU Y, ZHOU S, YING P H, et al. Unusual deformation and fracture in gallium telluride multilayers. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2022, 13(17): 3831.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
KONNO H, YAMAMOTO Y. Ylide-metal complexes. XIV. An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study on tellurium complexes of methylenetriphenylphosphorane. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 1988, 61(8): 2990.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
CHOWDARI B V R, KUMARI P P. Thermal, electrical and XPS studies of Ag2O·TeO2·P2O5 glasses. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 1996, 197(1): 31.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
STARÝ Z, HORÁK J, STORDEUR M, et al. Antisite defects in Sb2-xBixTe3 mixed crystals. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 1988, 49(1): 29.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
KAVEI G, KARAMI M A. Formation of anti-site defects and bismuth overstoichiometry in p-type Sb2-xBixTe3thermoelectric crystals. The European Physical Journal Applied Physics, 42(2): 67.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
SUN Y, ZHANG E, JOHNSEN S, et al. Growth of FeSb2 thin films by magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519(16): 5397.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
FAN P, LI R Y, CHEN Y X, et al. High thermoelectric performance achieved in Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 films with high (00l) orientation via magnetron sputtering. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(12): 4016.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
SNYDER G J, TOBERER E S. Complex thermoelectric materials. Nature Materials, 2008, 7: 105.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
NORIMASA O, CHIBA T, HASE M, et al. Improvement of thermoelectric properties of flexible Bi2Te3 thin films in bent states during sputtering deposition and post-thermal annealing. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 898: 162889.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
KIANWIMOL S, SAKDANUPHAB R, CHANLEK N, et al. Effect of annealing temperature on thermoelectric properties of bismuth telluride thick film deposited by DC magnetron sputtering. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2020, 393: 125808.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
JUNLABHUT P, NUTHONGKUM P, SAKDANUPHAB R, et al. Influence of sputtering power density on the thermoelectric and mechanical properties of flexible thermoelectric antimony telluride films deposited by DC magnetron sputtering. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2020, 49(5): 2747.
DOI |
| [45] |
LU Z Q, LIU K K, LI Q, et al. Donor-like effect and thermoelectric performance in p-type Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 alloy. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1331.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
SHI T F, CHEN M R, LIU Z G, et al. A Bi2Te3-filled nickel foam film with exceptional flexibility and thermoelectric performance. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(10): 1693.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
KONG D Y, ZHU W, GUO Z P, et al. High-performance flexible Bi2Te3 films based wearable thermoelectric generator for energy harvesting. Energy, 2019, 175: 292.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
FRANCIOSO L, DE PASCALI C, FARELLA I, et al. Flexible thermoelectric generator for ambient assisted living wearable biometric sensors. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(6): 3239.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
MALLICK M M, FRANKE L, RÖSCH A G, et al. High figure- of-merit telluride-based flexible thermoelectric films through interfacial modification via millisecond photonic-curing for fully printed thermoelectric generators. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(31): 2202411.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 杨光, 张楠, 陈舒锦, 王义, 谢安, 严育杰. 基于多孔ITO电极的WO3薄膜的制备及其电致变色性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 781-789. |
| [2] | 董晨雨, 郑维杰, 马一帆, 郑春艳, 温峥. 压电力显微镜表征Pb(Mg,Nb)O3-PbTiO3超薄膜弛豫特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 675-682. |
| [3] | 陶桂龙, 支国伟, 罗添友, 欧阳佩东, 衣新燕, 李国强. 空腔型薄膜体声波滤波器的关键技术进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| [4] | 赵志翰, 郭鹏, 魏菁, 崔丽, 刘山泽, 张文龙, 陈仁德, 汪爱英. Ti-DLC薄膜压阻性能及载流子输运行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 879-886. |
| [5] | 张慧, 许志鹏, 朱从潭, 郭学益, 杨英. 大面积有机-无机杂化钙钛矿薄膜及其光伏应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 457-466. |
| [6] | 鲍可, 李西军. 化学气相沉积法制备智能窗用热致变色VO2薄膜的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 233-258. |
| [7] | 杨志亮, 杨鏊, 刘鹏, 陈良贤, 安康, 魏俊俊, 刘金龙, 吴立枢, 李成明. 热管理用3英寸硅衬底金刚石薄膜的制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 283-290. |
| [8] | 刘松, 张发强, 罗进, 刘志甫. 0.9BaTiO3-0.1Bi(Mg1/2Ti1/2)O3铁电薄膜制备及储能特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 291-298. |
| [9] | 徐向明, Husam N ALSHAREEF. MXetronics—MXene电子学[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 171-178. |
| [10] | 张波涛, 孙婷婷, 王连军, 江莞. 喷墨打印制备AgCuTe热电薄膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1325-1330. |
| [11] | 刘锁兰, 栾福园, 吴子华, 寿春晖, 谢华清, 杨松旺. 原位生长钙钛矿太阳能电池共形氧化锡薄膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1397-1403. |
| [12] | 任冠源, 李宜冠, 丁冬海, 梁瑞虹, 周志勇. CaBi2Nb2O9铁电薄膜的生长取向调控和性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1228-1234. |
| [13] | 张哲, 孙婷婷, 王连军, 江莞. 不同维度Ag2Se构筑柔性热电薄膜的性能优化与器件集成研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1221-1227. |
| [14] | 戴乐, 刘洋, 高轩, 王书豪, 宋雅婷, 唐明猛, 刘丽莎, 汪尧进. 浓度梯度掺杂实现BiFeO3薄膜自极化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 99-106. |
| [15] | 胡盈, 李自清, 方晓生. 溶液法制备AgBi2I7薄膜及其光电探测性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1055-1061. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||