无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (10): 1065-1072.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220020 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20220020
陈亚玲1,2( ), 舒松1,2, 王劭鑫1,2, 李建军1,2(
), 舒松1,2, 王劭鑫1,2, 李建军1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-01-13
修回日期:2022-04-14
出版日期:2022-10-20
网络出版日期:2022-04-26
通讯作者:
李建军, 教授. E-mail: jjli@scu.edu.cn作者简介:陈亚玲(1997-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: chenyaling@stu.scu.edu.cn
基金资助:
CHEN Yaling1,2( ), SHU Song1,2, WANG Shaoxin1,2, LI Jianjun1,2(
), SHU Song1,2, WANG Shaoxin1,2, LI Jianjun1,2( )
)
Received:2022-01-13
Revised:2022-04-14
Published:2022-10-20
Online:2022-04-26
Contact:
LI Jianjun, professor. E-mail: jjli@scu.edu.cnAbout author:CHEN Yaling (1997-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: chenyaling@stu.scu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
低温选择性催化还原(SCR)脱硝是工业烟气末端治理的重要技术, 强化催化剂硫抗性是低温SCR领域内亟待解决的问题。本研究以羟基磷灰石(HAP)为载体、Mn为活性组分通过共沉淀法成功合成了Mn-HAP低温(100~200℃)脱硝催化剂, 探究了其脱硝性能及金属硫酸盐和硫酸铵的中毒特性。结果表明: 以HAP作为活性组分Mn的载体能一定程度上提高催化剂的抗硫性。当反应温度为140 ℃时, SCR催化剂脱硝效率达到100%, 金属硫酸盐相较硫酸铵对催化剂低温脱硝活性的影响更显著, 120 ℃时脱硝效率分别降低37.40%和8.83%。不同手段分析表明, 不同表面硫物种均会不同程度地降低催化剂比表面积并改变活性Mn氧化态。金属硫酸盐显著降低Mn4+/Mn比例是造成催化剂失活的主要原因。
中图分类号:
陈亚玲, 舒松, 王劭鑫, 李建军. Mn-HAP基低温SCR催化剂的制备及抗硫中毒性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(10): 1065-1072.
CHEN Yaling, SHU Song, WANG Shaoxin, LI Jianjun. Mn-HAP SCR Catalyst: Preparation and Sulfur Resistance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1065-1072.
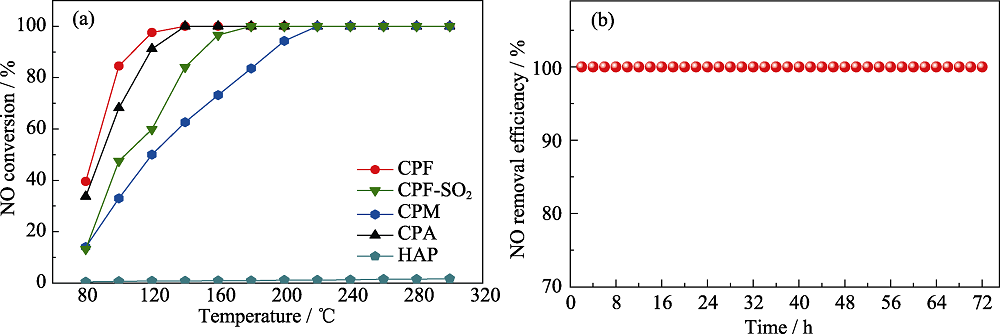
图3 (a)CPF、CPM、CPA和HAP的SCR活性以及CPF的抗硫性测试和(b)CPF稳定性测试图
Fig. 3 (a) SCR activity of CPF, CPM, CPA, and HAP, and sulfur resistance test of CPF and (b) stability test of CPF Colorful figures are available on website
| Catalyst | Preparation method | NO conversion/% | Temperature and condition | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn-HAP | Co-preparation | 62.60 | 140 ℃, 200×10-6 SO2, 2 h | This research |
| NB-C-P | Hydrothermal | 45.00 | 150 ℃, 250×10-6 SO2, 2 h | [ |
| MnO2 | Oxalic acid co-precipitation | 17.65 | 150 ℃, 200×10-6 SO2, 2 h | [ |
| MnCrOx | Hydrothermal redox reaction | 37.46 | 150 ℃, 50×10-6 SO2, 2 h | [ |
表1 不同催化剂活性对比
Table 1 Activity comparison of different catalysts
| Catalyst | Preparation method | NO conversion/% | Temperature and condition | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn-HAP | Co-preparation | 62.60 | 140 ℃, 200×10-6 SO2, 2 h | This research |
| NB-C-P | Hydrothermal | 45.00 | 150 ℃, 250×10-6 SO2, 2 h | [ |
| MnO2 | Oxalic acid co-precipitation | 17.65 | 150 ℃, 200×10-6 SO2, 2 h | [ |
| MnCrOx | Hydrothermal redox reaction | 37.46 | 150 ℃, 50×10-6 SO2, 2 h | [ |
| Sample | Specific area/ (m2·g-1) | Pore volume/ (cm3·g-1) | Average pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPF | 153.6 | 0.5500 | 13.49 |
| CPM | 117.3 | 0.4600 | 14.11 |
| CPA | 133.2 | 0.4300 | 11.57 |
表2 新鲜催化剂与中毒催化剂物理参数
Table 2 Physical parameters of fresh catalysts and toxic catalysts
| Sample | Specific area/ (m2·g-1) | Pore volume/ (cm3·g-1) | Average pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPF | 153.6 | 0.5500 | 13.49 |
| CPM | 117.3 | 0.4600 | 14.11 |
| CPA | 133.2 | 0.4300 | 11.57 |
| Sample | O | Mn | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olatt/O | Oads/O | Oads/Olatt | Mn2+/Mn | Mn3+/Mn | Mn4+/Mn | |
| CPF | 0.9050 | 0.0950 | 0.1050 | 0.06510 | 0.1670 | 0.7300 |
| CPM | 0.9210 | 0.0790 | 0.0860 | 0.10000 | 0.5900 | 0.3100 |
| CPA | 0.8760 | 0.1230 | 0.1410 | 0.13500 | 0.2240 | 0.6410 |
表3 新鲜催化剂与中毒催化剂表面Mn和O的XPS分析结果
Table 3 XPS results of Mn and O on the surface of fresh catalysts and toxic catalysts
| Sample | O | Mn | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olatt/O | Oads/O | Oads/Olatt | Mn2+/Mn | Mn3+/Mn | Mn4+/Mn | |
| CPF | 0.9050 | 0.0950 | 0.1050 | 0.06510 | 0.1670 | 0.7300 |
| CPM | 0.9210 | 0.0790 | 0.0860 | 0.10000 | 0.5900 | 0.3100 |
| CPA | 0.8760 | 0.1230 | 0.1410 | 0.13500 | 0.2240 | 0.6410 |
| [1] | 刘福东, 单文坡, 石晓燕, 等. 用于NH3选择性催化还原NO的非钒基催化剂研究进展. 催化学报, 2011, 32(7): 1113-1128. |
| [2] |
HUANG X B, WANG P, TAO J Z, XI, et al. CeO2 modified Mn-Fe-O composites and their catalytic performance for NH3-SCR of NO. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 573-580.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHEN J, ZHENG Y Y, ZHANG Y B, et al. Preparation of MnO2/MWCNTs catalysts by a redox method and their activity in low-temperature SCR. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(12): 1347-1354.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 谭青, 冯雅晨. 我国烟气脱硝行业现状与前景及SCR脱硝催化剂的研究进展. 化工进展, 2011, 30(S1): 709-713. |
| [5] |
LI J, CHANG H, MA L, et al. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over metal oxide and zeolite catalysts: a review. Catalysis Today, 2011, 175(1): 147-156.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
PUTLURU S S R, SCHILL L, JENSEN A D, et al. Mn/TiO2 and Mn-Fe/TiO2 catalysts synthesized by deposition precipitation- promising for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperatures. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 165: 628-635.
DOI URL |
| [7] | LEE S, CHOI S, MIN C, et al. Study of variation of internal target volume between 4DCT and slow-ct in respiratory patterns using respiratory motion phantom. Med. Phys., 2014, 41: 180. |
| [8] | 沈伯雄, 郭宾彬, 史展亮, 等. CeO2/ACF的低温SCR烟气脱硝性能研究. 燃料化学学报, 2007(1): 125-128. |
| [9] |
IBRAHIM M, LABAKI M, GIRAUDON J-M, et al. Hydroxyapatite, a multifunctional material for air, water and soil pollution control: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 383: 121139.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
SILVESTER L, LAMONIER J F, VANNIER R N, et al. Structural, textural and acid-base properties of carbonate-containing hydroxyapatites. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(29): 11073-11090.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
KUMAR P A, REDDY M P, JU L K, et al. Novel silver loaded hydroxyapatite catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by propene. Catalysis Letters, 2008, 126(1): 78.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
BOUKHA Z, GONZALEZ-PRIOR J, DE RIVAS B, et al. Synthesis, characterisation and behaviour of Co/hydroxyapatite catalysts in the oxidation of 1,2-dichloroethane. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2016, 190: 125-136.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
FAN Z, SHI J W, GAO C, et al. Gd-modified MnOx for the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3: the promoting effect of Gd on the catalytic performance and sulfur resistance. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 348: 820-830.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ROBLES-AGUILA M J, REYES-AVENDANO J A, MENDOZA M E. Structural analysis of metal-doped (Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) calcium hydroxyapatite synthetized by a Sol-Gel microwave- assisted method. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(15): 12705-12709.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
CAMPISI S, GALLONI M G, BOSSOLA F, et al. Comparative performance of copper and iron functionalized hydroxyapatite catalysts in NH3-SCR. Catalysis Communications, 2019, 123: 79-85.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
GARCIABORDEJE E, PINILLA J, LAZARO M, et al. Role of sulphates on the mechanism of NH3-SCR of NO at low temperatures over presulphated vanadium supported on carbon-coated monoliths: 1. Journal of Catalysis, 2005, 233(1): 166-175.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WANG Y, LI X, ZHAN L, et al. Effect of SO2 on activated carbon honeycomb supported CeO2-MnOx catalyst for NO removal at low-temperature. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(8): 2274-2278.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ZHANG P, CHEN T, ZOU X, et al. V2O5/hematite catalyst for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2014, 35(1): 99-107.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
CHEN H, XIA Y, HUANG H, et al. Highly dispersed surface active species of Mn/Ce/TiW catalysts for high performance at low temperature NH3-SCR. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 330: 1195-1202.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
FANG X, LIU Y, CHEN L, et al. Influence of surface active groups on SO2 resistance of birnessite for low-temperature NH3-SCR. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 399: 125798.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
LI Y, LI Y, WANG P, et al. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over MnFeOx nanorods. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 330: 213-222.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LIU Y, GUO R, DUAN C, et al. A highly effective urchin-like MnCrOxcatalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Fuel, 2020, 271: 117667.
DOI URL |
| [23] | XIAO X, SHENG Z, YANG L, et al. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over a manganese and cerium oxide/graphene composite prepared by a hydrothermal method. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2016, 6(5): 1507-1514. |
| [24] |
GAO F, TANG X, YI H, et al. Promotional mechanisms of activity and SO2 tolerance of Co- or Ni-doped MnOx-CeO2 catalysts for SCR of NOx with NH3 at low temperature. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 317: 20-31.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
HUANG Z, ZHU Z, LIU Z. Combined effect of H2O and SO2 on V2O5/AC catalysts for NO reduction with ammonia at lower temperatures. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2002, 39(4): 361-368.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
FANG X, LIU Y, CEN W, et al. Birnessite as a highly efficient catalyst for low-temperature NH3-SCR: the vital role of surface oxygen vacancies: 33. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(33): 14606-14615.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
WANG J, ZHANG P, LI J, et al. Room-temperature oxidation of formaldehyde by layered manganese oxide: effect of water. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(20): 12372-12379.
DOI URL |
| [28] | PANGILINAN C D C, KURNIAWAN W, HINODE H. Effect of MnOx/TiO2 oxidation state on ozone concentration in a nonthermal plasma-driven catalysis reactor. Ozone: Science & Engineering, 2016, 38(2): 156-162. |
| [29] |
PARK M Y, KIM Y J, CHOI S M, et al. Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite using ammonium hydroxide and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid: synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 2015, 36(7): 1806-1811.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
LEE T, BAI H. Metal sulfate poisoning effects over MnFe/TiO2 for selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 at low-temperature. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(14): 4848-4858.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
FANG N, GUO J, SHU S, et al. Effect of calcination temperature on low-temperature NH3-SCR activity and the resistance of SO2 with or without H2O over Fe-Mn-Zr catalyst. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2018, 93: 277-288.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
GAO F, TANG X, YI H, et al. Novel Co- or Ni-Mn binary oxide catalysts with hydroxyl groups for NH3-SCR of NOx at low temperature. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 443: 103-113.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
JI J, LU X, CHEN C, et al. Potassium-modulated δ-MnO2 as robust catalysts for formaldehyde oxidation at room temperature. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 260: 118210.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
KAPTEIJN F, SINGOREDJO L, ANDREINI A, et al. Activity and selectivity of pure manganese oxides in the selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide with ammonia. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 1994, 3(2): 173-189.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
BONINGARI T, ETTIREDDY P R, SOMOGYVARI A, et al. Influence of elevated surface texture hydrated titania on Ce-doped Mn/TiO2 catalysts for the low-temperature SCR of NOx under oxygen-rich conditions. Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 325: 145-155.
DOI URL |
| [36] | LIU Z M, ZHU J Z, LI J H, et al. Novel Mn-Ce-Ti mixed-oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(16): 14500-14508. |
| [37] |
LIU F. Structure-activity relationship of iron titanate catalysts in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(40): 16929-16936.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
JARRIGE J, VERVISCH P. Plasma-enhanced catalysis of propane and isopropyl alcohol at ambient temperature on a MnO2-based catalyst. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2009, 90(1): 74-82.
DOI URL |
| [39] | 杨超, 刘小青, 黄碧纯, 等. Zr改性MnOx/MWCNTs催化剂的结构特征与低温SCR活性. 物理化学学报, 2014, 30(10): 1895-1902. |
| [40] | 于国峰, 韦彦斐, 金瑞奔, 等. Mn-Ce-Co/TiO2催化剂低温脱硝活性研究. 环境科学学报, 2012, 32(07): 1743-1749. |
| [41] |
WANG X, ZHENG Y, XU Z, et al. Amorphous MnO2 supported on carbon nanotubes as a superior catalyst for low temperature NO reduction with NH3. RSC Advances, 2013, 3(29): 11539-11542.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
WANG L, HUANG B, SU Y, et al. Manganese oxides supported on multi-walled carbon nanotubes for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: catalytic activity and characterization. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 192: 232-241.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
JIN R, LIU Y, WU Z, et al. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over Mn-Ce oxides supported on TiO2 and Al2O3: a comparative study. Chemosphere, 2010, 78(9): 1160-1166.
DOI URL |
| [44] | 王淑勤, 李金梦, 杜志辉. Co共掺TiO2催化剂选择性催化还原脱硝性能研究. 环境污染与防治, 2021, 43(4): 475-480. |
| [45] |
KIJLSTRA W S, BRANDS D S, SMIT H I, et al. Mechanism of the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 over MnOx/Al2O3 reactivity of adsorbed NH3 and NO complexes. Journal of Catalysis, 1997, 171(1): 219-230.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
PEÑA D A, UPHADE B S, SMIRNIOTIS P G. TiO2-supported metal oxide catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: I. evaluation and characterization of first row transition metals. Journal of Catalysis, 2004, 221(2): 421-431.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 安然, 林锶, 郭世刚, 张冲, 祝顺, 韩颖超. 铁掺杂纳米羟基磷灰石的制备及紫外吸收性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 457-465. |
| [2] | 李承瑜, 丁自友, 韩颖超. 锰掺杂纳米羟基磷灰石的体外抗菌-促成骨性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 313-320. |
| [3] | 刘妍, 张宇帆, 王茜蔓, 李婷, 马文婷, 杨富巍, 陈靓, 赵东月, 严小琴. 基于羟基磷灰石材料的风化脆弱骨质文物加固保护研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1345-1354. |
| [4] | 朱雨桐, 谭佩洁, 林海, 朱向东, 张兴栋. 可注射透明质酸/羟基磷灰石复合材料: 制备、理化性能和细胞相容性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 981-990. |
| [5] | 林子扬, 常宇辰, 吴章凡, 包荣, 林文庆, 王德平. 不同模拟体液对硼硅酸盐生物活性玻璃基骨水泥矿化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 745-752. |
| [6] | 吴永豪, 李向锋, 朱向东, 张兴栋. 高强度羟基磷灰石纳米陶瓷的构建及其促成骨细胞活性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 552-560. |
| [7] | 宋可可, 黄浩, 鲁梦婕, 杨安春, 翁杰, 段可. 水热制备锌、硅、镁、铁等元素掺杂羟基磷灰石及其表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1091-1096. |
| [8] | 邵悦婷, 朱英杰, 董丽颖, 蔡安勇. 羟基磷灰石超长纳米线/植物纤维纳米复合“宣纸”及其防霉性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(1): 107-112. |
| [9] | 孙团伟,朱英杰. 一步溶剂热法合成锶掺杂羟基磷灰石超长纳米线[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(6): 724-728. |
| [10] | 刘子阳, 耿振, 李朝阳. 牡蛎壳为原料制备医用CaCO3/HA复合生物材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(5): 601-607. |
| [11] | 代钊,王铭,王双,李静,陈翔,汪大林,祝迎春. 氧化锆基微量元素共掺杂羟基磷灰石增韧涂层研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 179-186. |
| [12] | 付亚康,翁杰,刘耀文,张科宏. 钛网表面含hBMP-2的复合涂层制备及hBMP-2的释放研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 173-178. |
| [13] | 周子航, 王群, 葛翔, 李朝阳. 掺锶羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒的合成、表征及模拟研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(11): 1283-1289. |
| [14] | 肖文谦,张静,李克江,邹新宇,蔡昱东,李波,刘雪,廖晓玲. 荔枝状CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4磁性介孔多级微球的制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 925-932. |
| [15] | 吴金结, 李艳, 魏仁初, 汪建新, 屈树新, 翁杰, 智伟. 微振动应力环境影响羟基磷灰石陶瓷生物活性及力学稳定性的体外评价[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(4): 417-424. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||