无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 553-560.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220513 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20220513
所属专题: 【信息功能】纪念殷之文先生诞辰105周年虚拟学术专辑
收稿日期:2022-09-02
修回日期:2022-10-10
出版日期:2022-12-27
网络出版日期:2022-12-27
通讯作者:
马名生, 副研究员. E-mail: mamingsheng@mail.sic.ac.cn;作者简介:罗淑文(1998-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 1000497469@smail.shnu.edu.cn
基金资助:
LUO Shuwen1,2( ), MA Mingsheng2(
), MA Mingsheng2( ), LIU Feng2, LIU Zhifu2(
), LIU Feng2, LIU Zhifu2( )
)
Received:2022-09-02
Revised:2022-10-10
Published:2022-12-27
Online:2022-12-27
Contact:
MA Mingsheng, associate professor. E-mail: mamingsheng@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:LUO Shuwen (1998-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 1000497469@smail.shnu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
LTCC材料在电镀和化学镀工艺中对酸/碱镀液的耐蚀性是低温共烧陶瓷(Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramics, LTCC)材料在实际应用中需要关注的重要特性。本工作研究了HCl、H2SO4和NaOH溶液(0.01~2.00 mol/L)和浸泡时间(10~300 min)对Ca-B-Si体系LTCC材料腐蚀行为的影响规律。结果表明,LTCC材料在不同的酸溶液中浸泡相同时间, 样品的腐蚀失重量会随着酸溶液浓度增大呈现出先增大后减小的趋势, 而在碱溶液中并未观察到明显的腐蚀现象。当盐酸溶液浓度为1.00 mol/L时, LTCC材料的失重最大为54.96%。当硫酸溶液浓度为0.10 mol/L时, LTCC材料的失重最大为8.80%LTCC材料中的CaB2O4和CaSiO3晶相会与酸溶液发生溶解反应进而造成腐蚀, 并且随着酸溶液浓度增大, 反应后样品表面富Si蚀变层的形成速度更快, 进而使LTCC材料在较高浓度酸溶液中的浸泡失重量减小。LTCC材料在1 mol/L 盐酸溶液和0.1 mol/L硫酸溶液中溶解反应的表观活化能分别为20.38、5.43 kJ/mol, 故盐酸溶液对LTCC材料的腐蚀速率大于硫酸溶液。结合化学腐蚀反应动力学和热力学分析, 揭示了LTCC材料在酸溶液中以离子交换和水解反应占主导的腐蚀机理。
中图分类号:
罗淑文, 马名生, 刘峰, 刘志甫. Ca-B-Si体系LTCC材料腐蚀行为及腐蚀机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 553-560.
LUO Shuwen, MA Mingsheng, LIU Feng, LIU Zhifu. Corrosion Behavior and Mechanism of LTCC Materials in Ca-B-Si System[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 553-560.
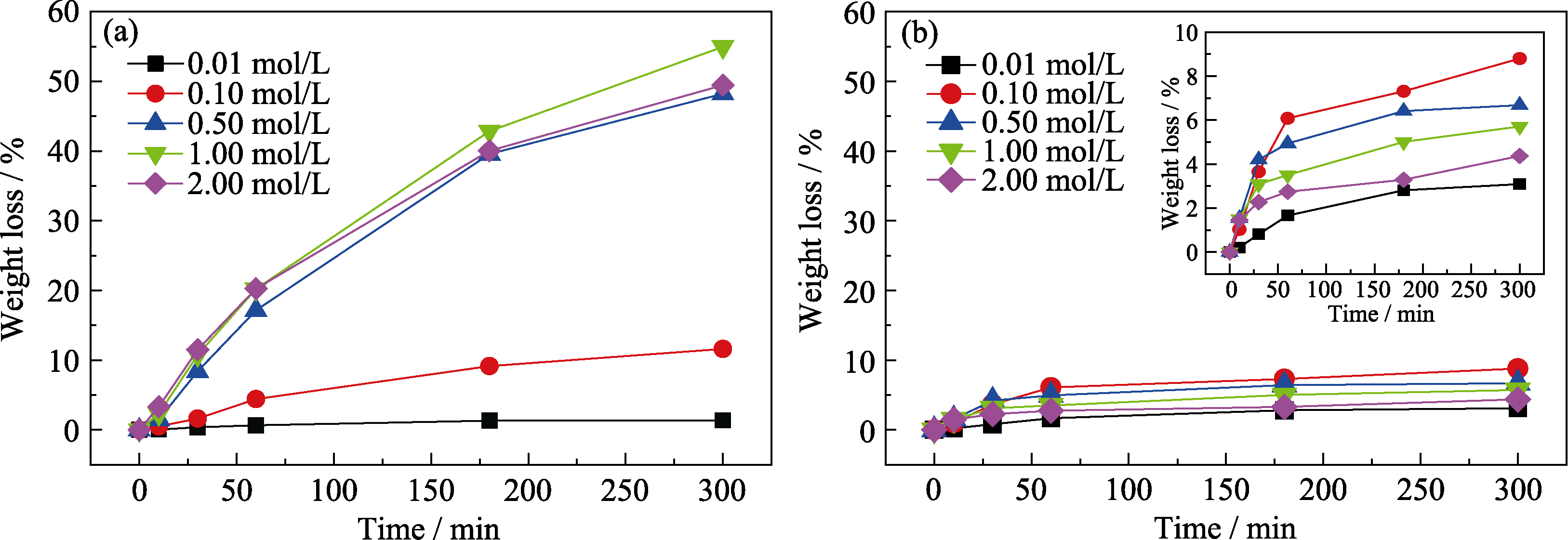
图1 样品在不同浓度酸溶液中失重随腐蚀时间的变化
Fig. 1 Variation of weight loss with corrosion time after corrosion of samples in different concentrations of acid solutions (a) HCl solution; (b) H2SO4 solution
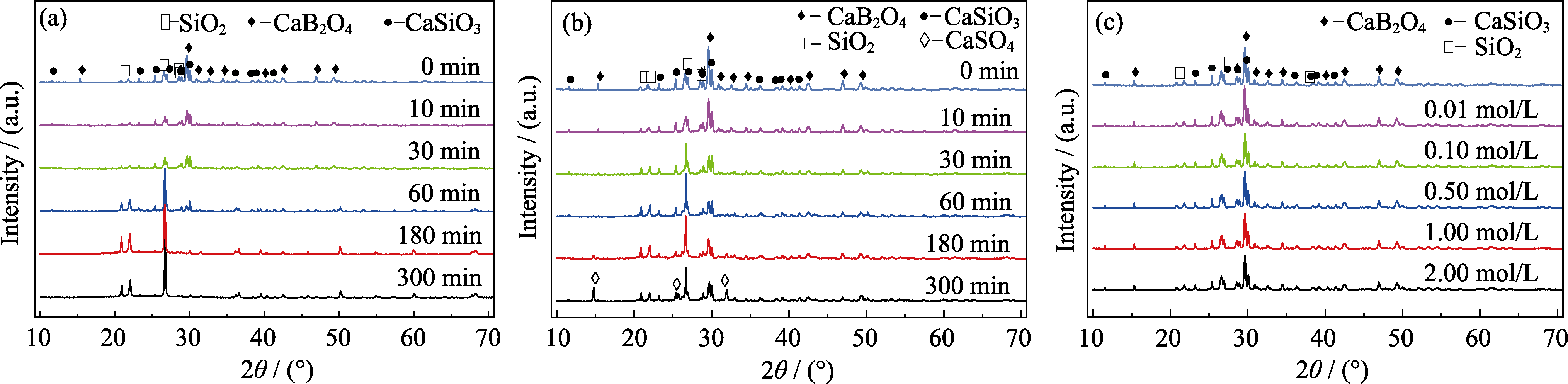
图2 在不同溶液中腐蚀前以及腐蚀不同时间后样品的XRD图谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of samples before and after corrosion for different time in various solutions (a) 1.00 mol/L HCl solution; (b) 0.10 mol/L H2SO4 solution; (c) NaOH solutions at different concentrations

图3 样品在不同浓度盐酸、硫酸和氢氧化钠溶液中腐蚀300 min后进入到溶液中的元素种类及其含量
Fig. 3 Kinds and contents of elements entering the solutions after the samples being corroded in different concentrations of HCl, H2SO4 and NaOH solutions for 300 min Colorful figures are available on website

图4 样品在不同浓度盐酸溶液中腐蚀前以及腐蚀不同时间后的SEM照片
Fig. 4 SEM images of samples in different concentrations of HCl solutions before corrosion and after corrosion for different time (a) 0.50 mol/L HCl solution; (b) 1.00 mol/L HCl solution; (c) 2.00 mol/L HCl solution
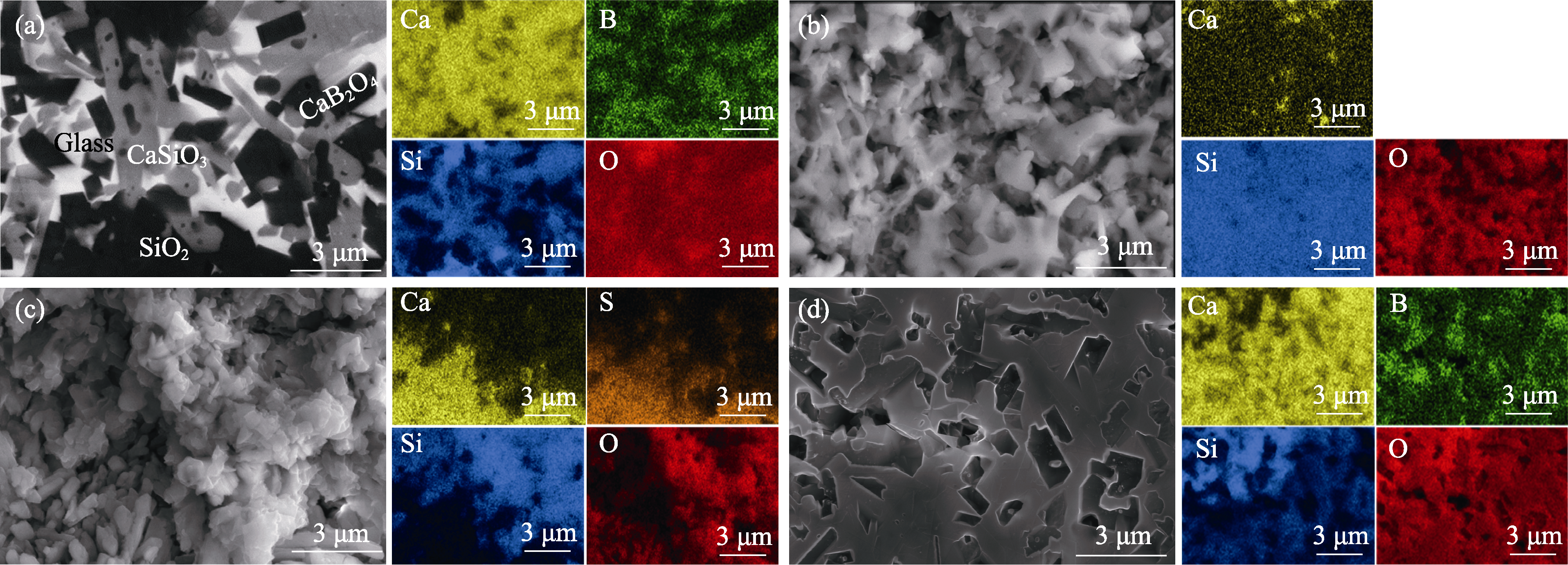
图5 在不同溶液中腐蚀前后样品表面的物相组成及元素分布
Fig. 5 Phase compositions and elemental distributions of sample surfaces before and after corrosion in different solutions (a) No corrosion; (b) Corrosion in 1.00 mol/L HCl solution for 300 min; (c) Corrosion in 0.10 mol/L H2SO4 solution for 300 min; (d) Corrosion in 2.00 mol/L NaOH solution for 300 min

图6 在1.00 mol/L盐酸溶液和0.10 mol/L硫酸溶液中样品损失率随温度变化的阿伦尼乌斯图
Fig. 6 Arrhenius plots of weight loss rate of the sample as a function of temperature in 1.00 mol/L HCl solution and 0.10 mol/L H2SO4 solution

图7 样品在不同酸溶液中腐蚀前以及腐蚀不同时间后的拉曼光谱图
Fig. 7 Raman spectra of samples before and after corrosion in different acid solutions for different time (a) 1.00 mol/L HCl solution; (b) 0.10 mol/L H2SO4 solution
| [1] | IMANAKA Y. Multilayered Low Temperature Cofired Ceramics (LTCC) Technology. New York: Springer Science & Business Media, 2005: 1-17. |
| [2] | WANG Y H, ZHOU J, CUI X M, et al. Development of low temperature cofired ceramic technology in material field. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(2): 267. |
| [3] | WANG Z Y. Reliability analysis of mixed conductor LTCC substrate. Electronic Components & Materials, 2003, 22(2): 7. |
| [4] | CHEN X Y, JIA S X, WANG Y L, et al. Research on the process of LTCC substrates based on ENEPIG. Printed Circuit Information, 2021, 29(6): 52. |
| [5] | BEIKMOHAMADI A, STEWART S, PARISI J, et al. Electroplating and electroless plating process development for DuPont™ GreenTape™ 9K7 LTCC. Additional Papers and Presentations, 2013, 2013(CICMT): 00283. |
| [6] | WANG Y L, LI J. The technology of Enepig of low temperature Co- fired ceramic substitute. Printed Circuit Information, 2020, 28(7): 49. |
| [7] | NAIR K M, SKURSKI M A, VOULTOS J D. Nickel-gold Plateable Thick Film Silver Paste: US8609256B2. 2013-12-17. |
| [8] | THOMAS S, BALAKRISHNAN P, SREEKALA M S. Fundamental Biomaterials:Ceramics. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing, 2018: 223-250. |
| [9] |
LEE S M, LIM W B, CHO Y S. Corrosion behavior of highly- crystallizable BaO-Nd2O3-TiO2-B2O3 glass-based composites. Corrosion Science, 2013, 66: 399.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LIM W B, SHIN D W, MOHANTY B C, et al. Chemical durability of anorthite-based low temperature co-fired ceramics. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 2009, 117(1370): 1138.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
JO Y H, KANG M S, CHUNG K W, et al. Chemical stability and dielectric properties of RO-La2O3-B2O3 (R= Ca, Mg, Zn)-based ceramics. Materials Research Bulletin, 2008, 43(2): 361.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
STEINHÄUßER F, TALAI A, GÖLTL G, et al. Concentration and temperature dependent selectivity of the LTCC porosification process with phosphoric acid. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(1): 714.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
KANG J, WANG J, ZHOU X, et al. Effects of alkali metal oxides on crystallization behavior and acid corrosion resistance of cordierite-based glass-ceramics. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2018, 481: 184.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HAJIAN A, STÖGER-POLLACH M, SCHNEIDER M, et al. Porosification behaviour of LTCC substrates with potassium hydroxide. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(5): 2369.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
SALAMA S N, SALMAN S M. Characterization of glass-ceramic corrosion and durability. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 1994, 13(6): 521.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
GHOSH S, DATTA S. Surface degradation behaviour of MgO- Al2O3-TiO2-SiO2 based glass-ceramics. Transactions of the Indian Ceramic Society, 2014, 73(3): 216.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SEBASTIAN M T, JANTUNEN H. Low loss dielectric materials for LTCC applications: a review. International Materials Reviews, 2008, 53(2): 57.
DOI URL |
| [18] | WANG T, WANG Y, YANG H, et al. Structure, dielectric properties of low-temperature-sintering BaTiO3-based glass-ceramics for energy storage. Journal of Advanced Dielectrics, 2018, 8(6): 1850041. |
| [19] |
ĆURKOVIĆ L, JELAČA M F, KURAJICA S. Corrosion behavior of alumina ceramics in aqueous HCl and H2SO4solutions. Corrosion Science, 2008, 50(3): 872.
DOI URL |
| [20] | CLARK D E, ZOITOS B K. Corrosion of Glass, Ceramics and Ceramic Superconductor: Principles, Testing, Characterization and Applications. New Jersey: Noyes Publications, 1992: 2-28. |
| [21] | SPEIGHT J G. Lange's Handbook of Chemistry. New York: McGraw-hill, 2005: 237-279. |
| [22] |
OSIPOV A A, OSIPOVA L M. Structural studies of Na2O-B2O3 glasses and melts using high-temperature Raman spectroscopy. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2010, 405(23): 4718.
DOI URL |
| [23] | STEFANOVSKY S V, FOX K M, MARRA J C. Infrared and raman spectroscopic study of glasses in the Al2O3-B2O3-Fe2O3- Na2O-SiO2 system. MRS Online Proceedings Library (OPL), 2013, 1518:53. |
| [24] | 王晨. 硅酸盐及含铝硅酸盐矿物的拉曼光谱研究. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2005. |
| [25] | 尤静林. 高温拉曼光谱创新技术、光谱计算和在无机化合物微结构研究中的应用. 上海: 上海大学博士学位论文, 2006. |
| [26] |
YIN C D, OKUNO M, MORIKAWA H, et al. Structural analysis of CaSiO3 glass by X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. Journal of Non-crystalline Solids, 1986, 80(1/2/3): 167.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
WANG Z, SHU Q, CHOU K. Structure of CaO-B2O3-SiO2-TiO2 glasses: a Raman spectral study. ISIJ International, 2011, 51(7): 1021.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
NEUVILLE D R, DE LIGNY D, HENDERSON G S. Advances in Raman spectroscopy applied to earth and material sciences. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2014, 78(1): 509.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
GIN S, ABDELOUAS A, CRISCENTI L J, et al. An international initiative on long-term behavior of high-level nuclear waste glass. Materials Today, 2013, 16(6): 243.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
FRANKEL G S, VIENNA J D, LIAN J, et al. A comparative review of the aqueous corrosion of glasses, crystalline ceramics, and metals. npj Materials Degradation, 2018, 2(1): 15.
DOI |
| [31] |
FRANKEL G S, VIENNA J D, LIAN J, et al. Recent advances in corrosion science applicable to disposal of high-level nuclear waste. Chemical Reviews, 2021, 121(20): 12327.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
RAHIMI R A, SADRNEZHAAD S K, RAISALI G. Chemical durability of lead silicate glass in HNO3, HCl and H2SO4 aqueous acid solutions. Journal of Non-crystalline Solids, 2009, 355(3): 169.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
SALDI G D, KÖHLER S J, MARTY N, et al. Dissolution rates of talc as a function of solution composition, pH and temperature. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(14): 3446.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
WANG J. Thermodynamic equilibrium and kinetic fundamentals of oxide dissolution in aqueous solution. Journal of Materials Research, 2020, 35(8): 898.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
CARTLEDGE G H. Studies on the periodic system. I. The ionic potential as a periodic function. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1928, 50(11): 2855.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
CARTLEDGE G H. Studies on the periodic system. II. The ionic potential and related properties. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1928, 50(11): 2863.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
BUNKER B C. Molecular mechanisms for corrosion of silica and silicate glasses. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 1994, 179: 300.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
COLLIN M, FOURNIER M, FRUGIER P, et al. Structure of international simple glass and properties of passivating layer formed in circumneutral pH conditions. npj Materials Degradation, 2018, 2(1): 4.
DOI |
| [39] |
OELKERS E H, SCHOTT J. An experimental study of enstatite dissolution rates as a function of pH, temperature, and aqueous Mg and Si concentration, and the mechanism of pyroxene/pyroxenoid dissolution. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(8): 1219.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
GIN S, NEILL L, FOURNIER M, et al. The controversial role of inter-diffusion in glass alteration. Chemical Geology, 2016, 440: 115.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
SCHOTT J, POKROVSKY O S, SPALLA O, et al. Formation, growth and transformation of leached layers during silicate minerals dissolution: the example of wollastonite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 98: 259.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
ZAPOL P, HE H, KWON K D, et al. First-principles study of hydrolysis reaction barriers in a sodium borosilicate glass. International Journal of Applied Glass Science, 2013, 4(4): 395.
DOI URL |
| [43] | BRANTLEY S L. Kinetics of Water-rock Interaction. New York: Springer, 2008: 151-210. |
| [44] |
CAILLETEAU C, ANGELI F, DEVREUX F, et al. Insight into silicate- glass corrosion mechanisms. Nature Materials, 2008, 7(12): 978.
DOI |
| [1] | 尹长志, 成名飞, 雷微程, 蔡弋炀, 宋小强, 付明, 吕文中, 雷文. Ga3+掺杂对SrAl2Si2O8陶瓷晶体结构及微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 704-710. |
| [2] | 杨燕, 张发强, 马名生, 王墉哲, 欧阳琪, 刘志甫. 基于CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5复合氧化物烧结助剂的ZnAl2O4陶瓷低温烧结研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 711-718. |
| [3] | 岳仔豪, 杨小兔, 张正亮, 邓瑞翔, 张涛, 宋力昕. Pb2+对掺杂硼硅酸盐玻璃中CsPbBr3钙钛矿量子点发光性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 449-456. |
| [4] | 范栋, 钟鑫, 王亚文, 张振忠, 牛亚然, 李其连, 张乐, 郑学斌. 富铝CMAS对稀土硅酸盐环境障涂层的腐蚀行为与机制研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 544-552. |
| [5] | 庞力斌, 王德平. 介孔硼硅酸盐玻璃微球药物载体的制备及其性能表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 780-786. |
| [6] | 张晓阳, 彭海波, 刘枫飞, 赵彦, 孙梦利, 管明, 张冰焘, 杜鑫, 袁伟, 王铁山. 多种重离子辐照对硼硅酸盐玻璃机械性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(7): 741-747. |
| [7] | 邱 添, 黄静静, 张 苗, 王先福, 李 辰, 卢晓英, 翁 杰. 不同碳纳米管/羟基磷灰石复合粉末的添加对磷酸钙骨水泥性能和结构的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(1): 91-96. |
| [8] | 俞 佳,肖秀峰, 梁建鹤,刘榕芳, 王春燕,毛 丹. 交替循环浸泡在TiO2纳米管管内填充类骨磷灰石[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(1): 78-84. |
| [9] | 关永军,夏原. 铝合金表面等离子体电解氧化陶瓷涂层在NaCl溶液中的电化学阻抗谱研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(4): 784-788. |
| [10] | 黎慧,周东祥,龚树萍,韩轲. 0.94Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3-0.06BaTiO3无铅压电陶瓷凝胶注模成型[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(3): 631-635. |
| [11] | 王悦辉,周济,崔学民,沈建红. 低温共烧陶瓷{\bf (LTCC)}技术在材料学上的进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2006, 21(2): 267-276. |
| [12] | 陈红兵,朱从善,干福熹. 碘化亚铜微晶掺杂硼硅酸盐玻璃的制备及其电致二阶非线性光学效应[J]. 无机材料学报, 1997, 12(4): 487-493. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||