无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 125-136.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220338 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20220338
所属专题: 【信息功能】纪念殷之文先生诞辰105周年虚拟学术专辑
冯静静1( ), 章游然1,2, 马名生1, 陆毅青1, 刘志甫1,2(
), 章游然1,2, 马名生1, 陆毅青1, 刘志甫1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-17
修回日期:2022-07-29
出版日期:2023-02-20
网络出版日期:2022-09-15
通讯作者:
刘志甫, 研究员. E-mail: liuzf@mail.sic.ac.cn作者简介:冯静静(1989-), 女, 博士. E-mail: fengjingjing@mail.sic.ac.cn
基金资助:
FENG Jingjing1( ), ZHANG Youran1,2, MA Mingsheng1, LU Yiqing1, LIU Zhifu1,2(
), ZHANG Youran1,2, MA Mingsheng1, LU Yiqing1, LIU Zhifu1,2( )
)
Received:2022-06-17
Revised:2022-07-29
Published:2023-02-20
Online:2022-09-15
Contact:
LIU Zhifu, professor. E-mail: liuzf@mail.sic.ac.cnAbout author:FENG Jingjing (1989-), female, PhD. E-mail: fengjingjing@mail.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
采用常规热烧结实现陶瓷粉体的致密化, 烧结温度通常超过1000 ℃, 这不仅需要消耗大量能源, 还会使一些陶瓷材料在物相稳定性、晶界控制以及与金属电极共烧等方面面临挑战。近年来提出的冷烧结技术(Cold Sintering Process, CSP)可将烧结温度降低至400 ℃以下, 利用液相形式的瞬态溶剂和单轴压力, 通过陶瓷颗粒的溶解-沉淀过程实现陶瓷材料的快速致密化。冷烧结技术具有烧结温度低和时间短等特点, 自开发以来受到广泛关注, 目前已应用于近百种陶瓷及陶瓷基复合材料, 涉及电介质材料、半导体材料、压敏材料和固态电解质材料等。本文介绍了冷烧结技术的发展历程、工艺技术及其致密化机理, 对其在陶瓷材料及陶瓷-聚合物复合材料领域的研究现状进行了综述, 其中根据溶解性的差异主要介绍了Li2MoO4陶瓷、ZnO陶瓷和BaTiO3陶瓷的冷烧结现状。针对冷烧结技术工艺压力高的问题及可能的解决途径进行了探讨, 并对冷烧结技术未来的发展趋势进行了展望。
中图分类号:
冯静静, 章游然, 马名生, 陆毅青, 刘志甫. 冷烧结技术的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 125-136.
FENG Jingjing, ZHANG Youran, MA Mingsheng, LU Yiqing, LIU Zhifu. Current Status and Development Trend of Cold Sintering Process[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 125-136.
| Technique | Name (Abbreviation) | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional sintering | Conventional sintering (ConvS) | Thermal sintering at heating rate of 1-10 ℃/min |
| Two step sintering (TSS) | Thermal sintering divided in two steps (heating; cooling and densification) | |
| Fast firing (FF) | Rapid sintering with short soaking times and high heating rates | |
| Sinter forging (SF) | Sintering in presence of uniaxial pressure in die-less configuration | |
| Hot pressing (HP) | Sintering at high temperature and in presence of uniaxial pressure | |
| Hydrothermal hot pressing (HIP) | Sintering at high temperature and in presence of hydrostatic pressure | |
| Liquid phase sintering | Cold sintering process (CSP) | Sintering at T<400 ℃ in presence of solvent and uniaxial pressure |
| Cold hydrostatic consolidation (CHC) | Sintering at room temperature in presence of solvent and hydrostatic pressure | |
| Hydrothermal hot pressing (HHP) | Pressure-assisted sintering in hydrothermal conditions | |
| Hydrothermal reaction sintering (HRS) | Sintering of oxide ceramics in presence of supercritical water | |
| Water vapor-assisted sintering (WVAS) | Conventional sintering in a humid atmosphere | |
| Reactive hydrothermal liquid-phase densification (rHLPD) | Sintering at low temperature assisted by hydrothermal reaction | |
| Flash-like | Flash sintering (FS) | Rapid sintering at low furnace temperature in presence of electric field |
| Thermally insulated flash sintering (TIFS) | Flash sintering where the sample is thermally insulated from the environment | |
| Flash sinterforging (FSF) | Flash sintering in presence of uniaxial pressure in die-less configuration | |
| Sliding electrodes flash sintering (SEFS) | Flash sintering where the electrodes are in relative motion with respect to the sample | |
| Water-assisted flash sintering (WAFS) | Flash sintering in humid atmosphere | |
| Contactless flash sintering (CLFS) | Flash sintering with electrodes in non-contact mode | |
| SPS-like | Spark plasma sintering (SPS) | Sintering in presence of a DC electric potential and uniaxial pressure |
| Deformable punch spark plasma sintering (DPSPS) | Spark plasma sintering at very high pressure (1000-2000 MPa) | |
| Flash spark plasma sintering (FSPS) | Hybrid technique of flash sintering and spark plasma sintering | |
| Cool spark plasma sintering (CSPS) | Spark plasma sintering at T<400 ℃ and high pressure (300-600 MPa) | |
| High pressure spark plasma sintering (HPSPS) | Spark plasma sintering at high pressure (102-103 MPa) | |
| Sacrificial material spark plasma sintering (SMPS) | Spark plasma sintering with a sacrificial die to form samples with complex shapes | |
| Others | Ultrafast high-temperature sintering (UHS) | Rapid sintering at heating rate of 103-104 ℃/min |
| Cold sintering (CS) | Sintering of ductile materials at high pressure and low temperature | |
| Microwave sintering (MWS) | Densification assisted by heating with an electromagnetic radiation | |
| Induction sintering (IS) | Densification assisted by heating with an induction system | |
| Capacitor discharge sintering (CDS) | Rapid sintering with electric energy supplied by capacitor discharge |
表1 烧结技术定义表[13-14]
Table 1 Definition table of sintering techniques[13-14]
| Technique | Name (Abbreviation) | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional sintering | Conventional sintering (ConvS) | Thermal sintering at heating rate of 1-10 ℃/min |
| Two step sintering (TSS) | Thermal sintering divided in two steps (heating; cooling and densification) | |
| Fast firing (FF) | Rapid sintering with short soaking times and high heating rates | |
| Sinter forging (SF) | Sintering in presence of uniaxial pressure in die-less configuration | |
| Hot pressing (HP) | Sintering at high temperature and in presence of uniaxial pressure | |
| Hydrothermal hot pressing (HIP) | Sintering at high temperature and in presence of hydrostatic pressure | |
| Liquid phase sintering | Cold sintering process (CSP) | Sintering at T<400 ℃ in presence of solvent and uniaxial pressure |
| Cold hydrostatic consolidation (CHC) | Sintering at room temperature in presence of solvent and hydrostatic pressure | |
| Hydrothermal hot pressing (HHP) | Pressure-assisted sintering in hydrothermal conditions | |
| Hydrothermal reaction sintering (HRS) | Sintering of oxide ceramics in presence of supercritical water | |
| Water vapor-assisted sintering (WVAS) | Conventional sintering in a humid atmosphere | |
| Reactive hydrothermal liquid-phase densification (rHLPD) | Sintering at low temperature assisted by hydrothermal reaction | |
| Flash-like | Flash sintering (FS) | Rapid sintering at low furnace temperature in presence of electric field |
| Thermally insulated flash sintering (TIFS) | Flash sintering where the sample is thermally insulated from the environment | |
| Flash sinterforging (FSF) | Flash sintering in presence of uniaxial pressure in die-less configuration | |
| Sliding electrodes flash sintering (SEFS) | Flash sintering where the electrodes are in relative motion with respect to the sample | |
| Water-assisted flash sintering (WAFS) | Flash sintering in humid atmosphere | |
| Contactless flash sintering (CLFS) | Flash sintering with electrodes in non-contact mode | |
| SPS-like | Spark plasma sintering (SPS) | Sintering in presence of a DC electric potential and uniaxial pressure |
| Deformable punch spark plasma sintering (DPSPS) | Spark plasma sintering at very high pressure (1000-2000 MPa) | |
| Flash spark plasma sintering (FSPS) | Hybrid technique of flash sintering and spark plasma sintering | |
| Cool spark plasma sintering (CSPS) | Spark plasma sintering at T<400 ℃ and high pressure (300-600 MPa) | |
| High pressure spark plasma sintering (HPSPS) | Spark plasma sintering at high pressure (102-103 MPa) | |
| Sacrificial material spark plasma sintering (SMPS) | Spark plasma sintering with a sacrificial die to form samples with complex shapes | |
| Others | Ultrafast high-temperature sintering (UHS) | Rapid sintering at heating rate of 103-104 ℃/min |
| Cold sintering (CS) | Sintering of ductile materials at high pressure and low temperature | |
| Microwave sintering (MWS) | Densification assisted by heating with an electromagnetic radiation | |
| Induction sintering (IS) | Densification assisted by heating with an induction system | |
| Capacitor discharge sintering (CDS) | Rapid sintering with electric energy supplied by capacitor discharge |
| Binary compound | Ternary compound | Quaternary compound | Quinary compound |
|---|---|---|---|
| MoO3 | Li2CO3 | LiFePO4 | LiAl0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 |
| WO3 | CsSO4 | LiCoPO4 | Li0.5xBi1-0.5xMoxV1-xO4 |
| V2O3 | Li2MoO4 | KH2PO4 | (Bi0.95Li0.05)(V0.9Mo0.1)O4 |
| V2O5 | Na2Mo2O7 | Ca5(PO4)3(OH) | Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 |
| ZnO | K2Mo2O7 | (LiBi)0.5MoO4 | - |
| Bi2O3 | ZnMoO4 | CsH2PO4 | - |
| Fe2O3 | K2MoO4 | InGaZnO4 | - |
| SiO2 | Bi2Mo2O9 | K0.5Na0.5NbO3 | - |
| CsBr | Gd2(MoO4)3 | LiFePO4 | - |
| MgO | Li2WO4 | Li2Mg3TiO6 | - |
| PbTe | Na2WO4 | Na0.5Bi0.5MoO4 | - |
| Bi2Te3 | LiVO3 | Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 | - |
| NaCl | BiVO4 | YBa2Cu3O7-x | - |
| ZnTe | AgVO3 | - | - |
| AgI | Na2ZrO3 | - | - |
| CuCl | BaTiO3 | - | - |
| ZrF4 | NaNO2 | - | - |
| ZrO2 | Mg2P2O7 | - | - |
| Al2O3 | BaMoO4 | - | - |
| CeO2 | Cs2WO4 | - | - |
| MnO | NaxCO2O4 | - | - |
| SnO | Ca3Co4O9 | - | - |
| TiO2 | KPO3 | - | - |
| MoS2 | Al2SiO5 | - | - |
| - | Ca3Co4O9 | - | - |
| - | CaCO3 | - | - |
| - | BaFe12O19 | - | - |
| - | ZrW2O8 | - | - |
| - | NaNbO3 | - | - |
| - | SrTiO3 | - | - |
表2 通过冷烧结技术制备的陶瓷材料[29,38,50]
Table 2 Ceramic materials prepared by CSP[29,38,50]
| Binary compound | Ternary compound | Quaternary compound | Quinary compound |
|---|---|---|---|
| MoO3 | Li2CO3 | LiFePO4 | LiAl0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 |
| WO3 | CsSO4 | LiCoPO4 | Li0.5xBi1-0.5xMoxV1-xO4 |
| V2O3 | Li2MoO4 | KH2PO4 | (Bi0.95Li0.05)(V0.9Mo0.1)O4 |
| V2O5 | Na2Mo2O7 | Ca5(PO4)3(OH) | Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 |
| ZnO | K2Mo2O7 | (LiBi)0.5MoO4 | - |
| Bi2O3 | ZnMoO4 | CsH2PO4 | - |
| Fe2O3 | K2MoO4 | InGaZnO4 | - |
| SiO2 | Bi2Mo2O9 | K0.5Na0.5NbO3 | - |
| CsBr | Gd2(MoO4)3 | LiFePO4 | - |
| MgO | Li2WO4 | Li2Mg3TiO6 | - |
| PbTe | Na2WO4 | Na0.5Bi0.5MoO4 | - |
| Bi2Te3 | LiVO3 | Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 | - |
| NaCl | BiVO4 | YBa2Cu3O7-x | - |
| ZnTe | AgVO3 | - | - |
| AgI | Na2ZrO3 | - | - |
| CuCl | BaTiO3 | - | - |
| ZrF4 | NaNO2 | - | - |
| ZrO2 | Mg2P2O7 | - | - |
| Al2O3 | BaMoO4 | - | - |
| CeO2 | Cs2WO4 | - | - |
| MnO | NaxCO2O4 | - | - |
| SnO | Ca3Co4O9 | - | - |
| TiO2 | KPO3 | - | - |
| MoS2 | Al2SiO5 | - | - |
| - | Ca3Co4O9 | - | - |
| - | CaCO3 | - | - |
| - | BaFe12O19 | - | - |
| - | ZrW2O8 | - | - |
| - | NaNbO3 | - | - |
| - | SrTiO3 | - | - |

图4 以不同溶剂冷烧结制备ZnO陶瓷的SEM照片[54]
Fig. 4 SEM images of cold sintered ZnO ceramics with different solvents[54] (a) Water; (b) 0.1 mol/L acetic acid; (c) 1 mol/L acetic acid
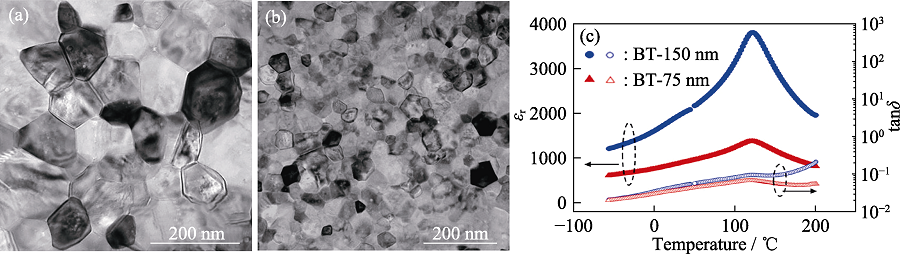
图5 300 ℃保温12 h冷烧结的BaTiO3陶瓷[56]
Fig. 5 Cold sintered BaTiO3 ceramics obtained by holding at 300 ℃ for 12 h[56] TEM images with grain size of 150 nm (a) and 75 nm (b); (c) Dielectric temperature spectra at 1 MHz
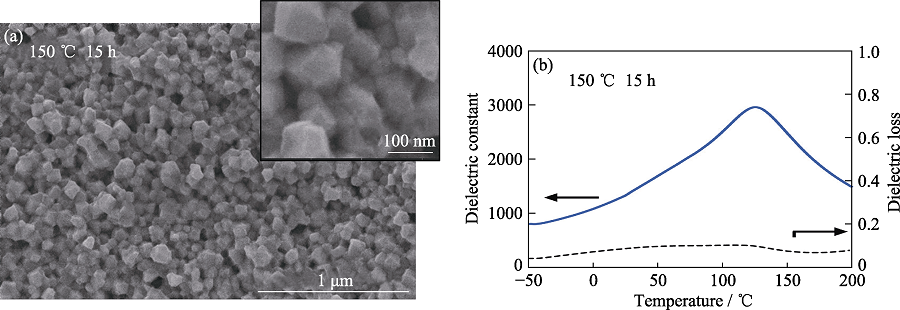
图6 150 ℃下保温15 h冷烧结的BaTiO3陶瓷[57]
Fig. 6 Cold sintered BaTiO3 ceramics obtained by holding at 150 ℃ for 15 h[57] (a) SEM images; (b) Dielectric temperature spectra at 1 MHz
| Ceramic-polymer composite | Solvent | Processing conditions | Relative density | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li2MoO4-PTFE | Deionized (DI) water | 120 ℃, 350 MPa, 15-20 min | 96%-97% | Dielectrics | [19] |
| Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3/PVDF-HFP | DI water | 120 ℃, 400 MPa, 60 min | 80%-86% | Li-ion battery electrolytes | [ |
| V2O5-PEDOT:PSS | DI water | 120 ℃, 350 MPa, 20-30 min | 91%-93% | Negative-temperature-resistance sensors | [ |
| (LiBi)0.5MoO4-PTFE | DI water | 120 ℃, 250-350 MPa, 20 min | >85% | Dielectrics | [ |
| Na2Mo2O7-PEI | DI water | 120 ℃, 175-350 MPa, 20 min | >90% | Dielectrics | [ |
| SiO2-PTFE | TEOS/NaOH | 270 ℃, 430 MPa, 60 min | 90%-99% | Dielectrics | [ |
| BaTiO3-PTFE | Ba(OH)2·8H2O | 225 ℃, 350 MPa, 120 min | >90% | Dielectrics | [ |
| ZnO-PTFE | Acetic acid | 300 ℃, 350 MPa, 30 min | 93%-99% | Varistors | [ |
| LiFePO4-C-PVDF | LiOH | 240 ℃, 30-750 MPa, 30 min | 89% | Li-ion electrodes | [ |
| NaNbO3-PVDF | DI water | 180 ℃, 550 MPa, 10 min | 97% | Dielectrics | [ |
| ZnO-PEEK | Acetic acid | 330 ℃, 300 MPa, 120 min | >98% | Varistors | [ |
| ZnO-PDMS | Acetic acid | 250 ℃, 320 MPa, 60 min | >90% | Varistors | [ |
| ZnO/PVDF-TrFE | Acetic acid | 140 ℃, 300 MPa, 240 min | >95% | Varistors | [ |
| ZnO-PEI-Mn2O3-CoO | Acetic acid | 150 ℃, 27 MPa, 60 min | 88% | Varistors | [ |
| LiFePO4-Li6.95Mg0.15La2.75Sr0.25Zr2O12-PPC-LiClO4 | DMF | 100-140℃, 400 MPa, 90-180 min | >85% | Li-ion battery electrolytes | [ |
表3 通过冷烧结技术制备的复合材料
Table 3 Composites prepared by CSP
| Ceramic-polymer composite | Solvent | Processing conditions | Relative density | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li2MoO4-PTFE | Deionized (DI) water | 120 ℃, 350 MPa, 15-20 min | 96%-97% | Dielectrics | [19] |
| Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3/PVDF-HFP | DI water | 120 ℃, 400 MPa, 60 min | 80%-86% | Li-ion battery electrolytes | [ |
| V2O5-PEDOT:PSS | DI water | 120 ℃, 350 MPa, 20-30 min | 91%-93% | Negative-temperature-resistance sensors | [ |
| (LiBi)0.5MoO4-PTFE | DI water | 120 ℃, 250-350 MPa, 20 min | >85% | Dielectrics | [ |
| Na2Mo2O7-PEI | DI water | 120 ℃, 175-350 MPa, 20 min | >90% | Dielectrics | [ |
| SiO2-PTFE | TEOS/NaOH | 270 ℃, 430 MPa, 60 min | 90%-99% | Dielectrics | [ |
| BaTiO3-PTFE | Ba(OH)2·8H2O | 225 ℃, 350 MPa, 120 min | >90% | Dielectrics | [ |
| ZnO-PTFE | Acetic acid | 300 ℃, 350 MPa, 30 min | 93%-99% | Varistors | [ |
| LiFePO4-C-PVDF | LiOH | 240 ℃, 30-750 MPa, 30 min | 89% | Li-ion electrodes | [ |
| NaNbO3-PVDF | DI water | 180 ℃, 550 MPa, 10 min | 97% | Dielectrics | [ |
| ZnO-PEEK | Acetic acid | 330 ℃, 300 MPa, 120 min | >98% | Varistors | [ |
| ZnO-PDMS | Acetic acid | 250 ℃, 320 MPa, 60 min | >90% | Varistors | [ |
| ZnO/PVDF-TrFE | Acetic acid | 140 ℃, 300 MPa, 240 min | >95% | Varistors | [ |
| ZnO-PEI-Mn2O3-CoO | Acetic acid | 150 ℃, 27 MPa, 60 min | 88% | Varistors | [ |
| LiFePO4-Li6.95Mg0.15La2.75Sr0.25Zr2O12-PPC-LiClO4 | DMF | 100-140℃, 400 MPa, 90-180 min | >85% | Li-ion battery electrolytes | [ |
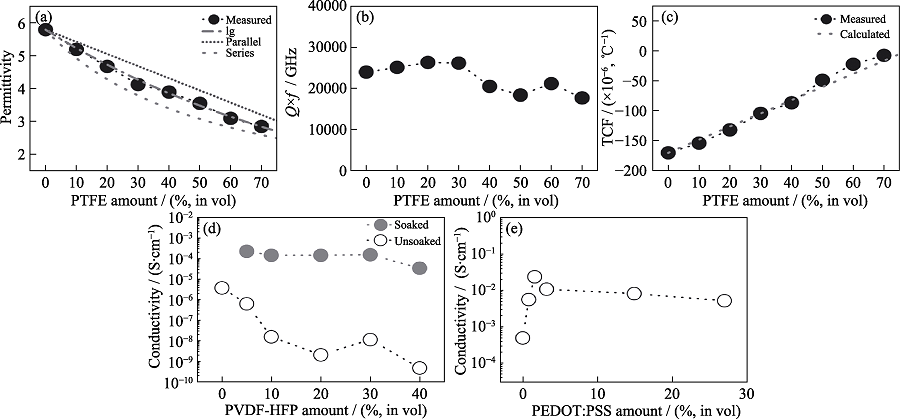
图8 三种冷烧结复合材料的电性能[19]
Fig. 8 Electrical properties of three composites prepared by cold sintering process[19] (a-c) εr, Q×f, TCF of (1-x)Li2MoO4-xPTFE; (d) Conductivity of (1-x)LAGP/xPVDF-HFP; (e) Conductivity of (1-x)V2O5-xPEDOT:PSS
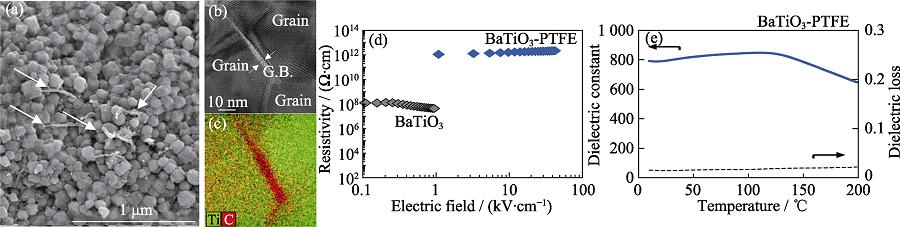
图10 冷烧结BaTiO3-PTFE复合材料[57]
Fig. 10 Cold sintered BaTiO3-PTFE composites[57] (a) SEM image; (b) TEM image; (c) EDS image; (d) Relationship between resistivity and electric field strength comparing with BaTiO3 ceramics; (e) Dielectric temperature spectra
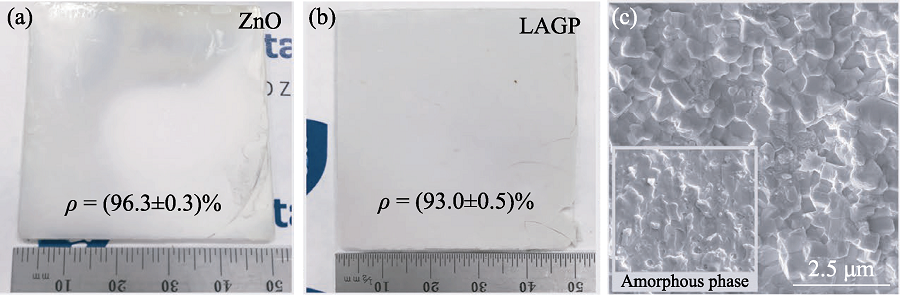
图11 冷烧结ZnO和LAGP陶瓷的大尺寸试样[69]
Fig. 11 Cold sintered ZnO and LAGP ceramic samples with large size[69] (a) Photograph of ZnO; (b) Photograph of LAGP; (c) SEM image of LAGP
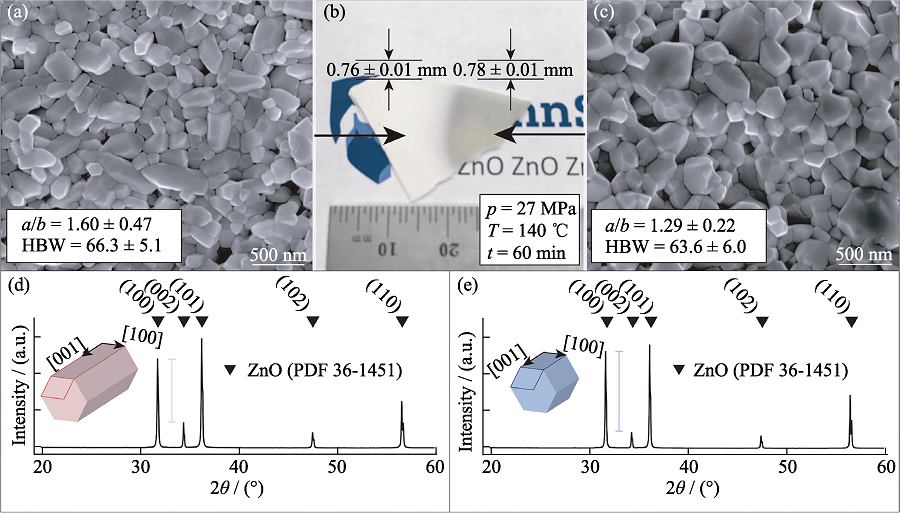
图12 冷烧结ZnO陶瓷的明显不均匀性[69]
Fig. 12 Obvious inhomogeneity of cold sintered ZnO ceramics[69] (a) SEM image of opaque area; (b) Photograph; (c) SEM image of translucent area; (d) XRD pattern of opaque area; (e) XRD pattern of translucent area
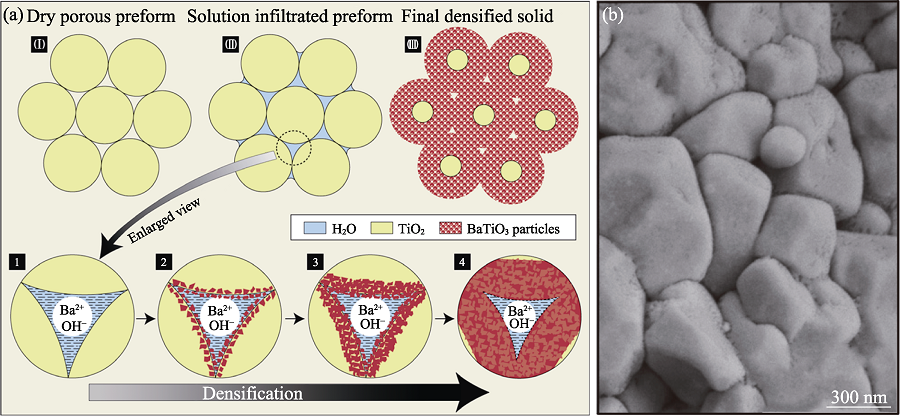
图13 反应水热液相致密化技术[72]
Fig. 13 Reactive hydrothermal liquid phase densification process[72] (a) Schematic of the HLPD process; (b) SEM image of BaTiO3/TiO2 ceramics prepared by rHLPD
| [1] |
VANDIVER P B, SOFFER O, KLIMA B, et al. The origins of ceramic technology at Dolni Věstonice, Czechoslovakia. Science, 1989, 246(4933): 1002.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
GERMAN R M. History of sintering: empirical phase. Powder Metallurgy, 2013, 56(2): 117.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BORDIA R K, KANG S J L, OLEVSKY E A. Current understanding and future research directions at the onset of the next century of sintering science and technology. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(6): 2314.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
NDAYISHIMIYE A, SENGUL M Y, BANG S H, et al. Comparing hydrothermal sintering and cold sintering process: mechanisms, microstructure, kinetics and chemistry. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(4): 1312.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
SMITH B L, SCHÄFFER T E, VIANI M, et al. Molecular mechanistic origin of the toughness of natural adhesives, fibres and composites. Nature, 1999, 399(6738): 761.
DOI URL |
| [6] | RENARD F, BERNARD D, THIBAULT X, et al. Synchrotron 3D microtomography of halite aggregates during experimental pressure solution creep and evolution of the permeability. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31(7): L07607. |
| [7] | FU C L, LI X M, GUO J. Recent progress of dielectric materials prepared via cold sintering process. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(4): 30. |
| [8] | JIANG R Z, LIU J. Research progress of cold sintering technology of ceramics. Journal of Guiyang University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 16(4): 60. |
| [9] |
DURAN C, SATO K, HOTTA Y, et al. Eco-friendly processing and methods for ceramic materials: a review. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 2008, 116(1359): 1175.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
IBN-MOHAMMED T, RANDALL C A, MUSTAPHA K B, et al. Decarbonising ceramic manufacturing: a techno-economic analysis of energy efficient sintering technologies in the functional materials sector. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(16): 5213.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
TODD R I, ZAPATA-SOLVAS E, BONILLA R S, et al. Electrical characteristics of flash sintering: thermal runaway of Joule heating. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2015, 35(6): 1865.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ZHANG Y, JUNG J I, LUO J. Thermal runaway, flash sintering and asymmetrical microstructural development of ZnO and ZnO- Bi2O3 under direct currents. Acta Materialia, 2015, 94: 87.
DOI URL |
| [13] | BIESUZ M, GRASSO S, SGLAVO V M. What’s new in ceramics sintering? A short report on the latest trends and future prospects. Current Opinion in Solid State & Materials Science, 2020, 24(5): 100868. |
| [14] |
GUO J, FLOYD R, LOWUM S, et al. Cold sintering: progress, challenges, and future opportunities. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2019, 49(1): 275.
DOI |
| [15] | COLOGNA M, RASHKOVA B, RAJ R. Flash sintering of nanograin zirconia in <5 s at 850 ℃. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2010, 93(11): 35569. |
| [16] |
BIESUZ M, SGLAVO V M. Flash sintering of ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(2): 115.
DOI |
| [17] |
GUO H Z, BAKER A, GUO J, et al. Protocol for ultralow- temperature ceramic sintering: an integration of nanotechnology and the cold sintering process. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(11): 10606.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
GUO H Z, BAKER A, GUO J, et al. Cold sintering process: a novel technique for low-temperature ceramic processing of ferroelectrics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2016, 99(11): 3489.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
GUO J, BERBANO S S, GUO H Z, et al. Cold sintering process of composites: bridging the processing temperature gap of ceramic and polymer materials. Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(39): 7115.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
GUO J, GUO H Z, BAKER A L, et al. Cold sintering: a paradigm shift for processing and integration of ceramics. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(38): 11457.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
GUO J, BAKER A L, GUO H Z, et al. Cold sintering process: a new era for ceramic packaging and microwave device development. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(2): 669.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
MUNIR Z A, ANSELMI-TAMBURINI U, OHYANAGI M. The effect of electric field and pressure on the synthesis and consolidation of materials: a review of the spark plasma sintering method. Journal of Materials Science, 2006, 41(3): 763.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
GUILLON O, GONZALEZ-JULIAN J, DARGATZ B, et al. Field- assisted sintering technology/spark plasma sintering: mechanisms, materials, and technology developments. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2014, 16(7): 830.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
YANAGISAWA K, KANAHARA S, NISHIOKA M, et al. Immobilization of radioactive wastes in hydrothermal synthetic rock, (II). Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 1984, 21(7): 558.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
YAMASAKI N, YANAGISAWA K, NISHIOKA M, et al. A hydrothermal hot-pressing method: apparatus and application. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1986, 5(3): 355.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
YAMASAKI N, KAI T, NISHIOKA M, et al. Porous hydroxyapatite ceramics prepared by hydrothermal hot-pressing. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1990, 9(10): 1150.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
IOKU K, YAMAMOTO K, YANAGISAWA K, et al. Low temperature sintering of hydroxyapatite by hydrothermal hot-pressing. Phosphorus Research Bulletin, 1994, 4: 65.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
HOSOI K, HASHIDA T, TAKAHASHI H, et al. New processing technique for hydroxyapatite ceramics by the hydrothermal hot-pressing method. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1996, 79(10): 2771.
DOI URL |
| [29] | VAKIFAHMETOGLU C, KARACASULU L. Cold sintering of ceramics and glasses: a review. Current Opinion in Solid State & Materials Science, 2020, 24(1): 100807. |
| [30] |
BOUVILLE F, STUDART A R. Geologically-inspired strong bulk ceramics made with water at room temperature. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 14655.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
INDUJA I J, SEBASTIAN M T. Microwave dielectric properties of mineral sillimanite obtained by conventional and cold sintering process. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(5): 2143.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
INDUJA I J, SEBASTIAN M T. Microwave dielectric properties of cold sintered Al2O3-NaCl composite. Materials Letters, 2018, 211: 55.
DOI URL |
| [33] | WANG D, ZHOU D, ZHANG S, et al. Cold-sintered temperature stable Na0.5Bi0.5MoO4-Li2MoO4 microwave composite ceramics. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(2): 2438. |
| [34] |
GUO J, ZHAO X T, DE BEAUVOIR T H, et al. Recent progress in applications of the cold sintering process for ceramic-polymer composites. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(39): 1801724.
DOI URL |
| [35] | GUO H Z, GUO J, BAKER A, et al. Hydrothermal-assisted cold sintering process: a new guidance for low-temperature ceramic sintering. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(32): 20909. |
| [36] |
HUANG H, TANG J, LIU J. Preparation of Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 ceramics by hydrothermal-assisted cold sintering. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(6): 6753.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
YU T, CHENG J, LI L, et al. Current understanding and applications of the cold sintering process. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2019, 13(4): 654.
DOI |
| [38] | GALOTTA A, SGLAVO V M. The cold sintering process: a review on processing features, densification mechanisms and perspectives. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(16): 1. |
| [39] |
NDAYISHIMIYE A, SENGUL M Y, SADA T, et al. Roadmap for densification in cold sintering: chemical pathways. Open Ceramics, 2020, 2: 100019.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
HONG W B, LI L, CAO M, et al. Plastic deformation and effects of water in room-temperature cold sintering of NaCl microwave dielectric ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018, 101(9): 4038.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
HAUG M, BOUVILLE F, RUIZ-AGUDO C, et al. Cold densification and sintering of nanovaterite by pressing with water. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(3): 893.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
GONZALEZ-JULIAN J, NEUHAUS K, BERNEMANN M, et al. Unveiling the mechanisms of cold sintering of ZnO at 250 ℃ by varying applied stress and characterizing grain boundaries by Kelvin Probe Force Microscopy. Acta Materialia, 2018, 144: 116.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
KANG X, FLOYD R, LOWUM S, et al. Cold sintering with dimethyl sulfoxide solutions for metal oxides. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54(10): 7438.
DOI |
| [44] |
KANG S, GUO H, WANG J, et al. Influence of surface coating on the microstructures and dielectric properties of BaTiO3 ceramic via a cold sintering process. RSC Advances, 2020, 10: 30870.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
FAOURI S S, MOSTAED A, DEAN J S, et al. High quality factor cold sintered Li2MoO4-BaFe12O19 composites for microwave applications. Acta Materialia, 2019, 166: 202.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
ZHOU D, PANG L X, WANG D W, et al. Novel water-assisting low firing MoO3 microwave dielectric ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(7): 2374.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
LIU Y, SUN Q, WANG D, et al. Development of the cold sintering process and its application in solid-state lithium batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 393: 193.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
GUO J, GUO H, HEIDARY D S B, et al. Semiconducting properties of cold sintered V2O5 ceramics and Co-sintered V2O5-PEDOT: PSS composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(4): 1529.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
LIU J A, LI C H, SHAN J J, et al. Preparation of high-density InGaZnO4 target by the assistance of cold sintering. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2018, 84: 17.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
MARIA J P, KANG X Y, FLOYD R D, et al. Cold sintering: current status and prospects. Journal of Materials Research, 2017, 32(17): 3205.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
KÄHÄRI H, TEIRIKANGAS M, JUUTI J, et al. Dielectric properties of lithium molybdate ceramic fabricated at room temperature. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2014, 97(11): 3378.
DOI URL |
| [52] | WU M W, ZHU H F, WANG J F, et al. Review on cold sintering process for preparation of ceramic materials. China Ceramics, 2021, 57(3): 1. |
| [53] | KANG S L, ZHAO X T, ZHANG J X, et al. Recent research progress of cold sintering process and its potential application in electrotechnical fields. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(5): 10984. |
| [54] |
FUNAHASHI S, GUO J, GUO H, et al. Demonstration of the cold sintering process study for the densification and grain growth of ZnO ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(2): 546.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
KANG X, FLOYD R, LOWUM S, et al. Mechanism studies of hydrothermal cold sintering of zinc oxide at near room temperature. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(8): 4459.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
TSUJI K, NDAYISHIMIYE A, LOWUM S, et al. Single step densification of high permittivity BaTiO3 ceramics at 300 ºC. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(4): 1280.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
SADA T, TSUJI K, NDAYISHIMIYE A, et al. High permittivity BaTiO3 and BaTiO3-polymer nanocomposites enabled by cold sintering with a new transient chemistry: Ba(OH)2·8H2O. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(1): 409.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
ZHAO Y Y, BERBANO S S, GAO L S, et al. Cold-sintered V2O5-PEDOT:PSS nanocomposites for negative temperature coefficient materials. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(4): 1257.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
GUO J, PFEIFFENBERGER N, BEESE A, et al. Cold sintering Na2Mo2O7 ceramic with poly(ether imide) (PEI) polymer to realize high-performance composites and integrated multilayer circuits. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2018, 1(8): 3837.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
NDAYISHIMIYE A, TSUJI K, WANG K, et al. Sintering mechanisms and dielectric properties of cold sintered (1-x)SiO2-xPTFE composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(15): 4743.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
SADA T, TSUJI K, NDAYISHIMIYE A, et al. Enhanced high permittivity BaTiO3-polymer nanocomposites from the cold sintering process. Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 128(8): 084103.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
ZHAO X T, GUO J, WANG K, et al. Introducing a ZnO-PTFE (polymer) nanocomposite varistor via the cold sintering process. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2018, 20(7): 1700902.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
SEO J H, GUO J, GUO H Z, et al. Cold sintering of a Li-ion cathode: LiFePO4-composite with high volumetric capacity. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(17): 15370.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
GYAN D S, DWIVEDI A. Structural and electrical characterization of NaNbO3-PVDF nanocomposites fabricated using cold sintering synthesis route. Journal of Applied Physics, 2019, 125(2): 024103.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
SI M M, GUO J, HAO J Y, et al. Cold sintered composites consisting of PEEK and metal oxides with improved electrical properties via the hybrid interfaces. Composites Part B-Engineering, 2021, 226: 109349.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
SI M M, HAO J Y, ZHAO E D, et al. Preparation of zinc oxide/poly-ether-ether-ketone (PEEK) composites via the cold sintering process. Acta Materialia, 2021, 215: 117036.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
NDAYISHIMIYE A, GRADY Z A, TSUJI K, et al. Thermosetting polymers in cold sintering: the fabrication of ZnO-polydimethylsiloxane composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(5): 3039.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
MENA-GARCIA J, DURSUN S, TSUJI K, et al. Integration and characterization of a ferroelectric polymer PVDF-TrFE into the grain boundary structure of ZnO via cold sintering. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(6): 2789.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
BANG S H, TSUJI K, NDAYISHIMIYE A, et al. Toward a size scale-up cold sintering process at reduced uniaxial pressure. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(4): 2322.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
SEO J H, NAKAYA H, TAKEUCHI Y, et al. Broad temperature dependence, high conductivity, and structure-property relations of cold sintering of LLZO-based composite electrolytes. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(15): 6241.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
DE BEAUVOIR T H, TSUJI K, ZHAO X, et al. Cold sintering of ZnO-PTFE: utilizing polymer phase to promote ceramic anisotropic grain growth. Acta Materialia, 2020, 186: 511.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
VAKIFAHMETOGLU C, ANGER J F, ATAKAN V, et al. Reactive hydrothermal liquid-phase densification (rHLPD) of ceramics: a study of the BaTiO3[TiO2] composite system. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2016, 99(12): 3893.
DOI URL |
| [73] | LI Q, GUPTA S, TANG L, et al. A novel strategy for carbon capture and sequestration by rHLPD processing. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2016, 3: 53. |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 余艺平, 肖鹏, 赵长浩, 徐梦迪, 姚立冬, 李伟, 王松. 耐高温层状Ta/Ta0.5Hf0.5C金属陶瓷的高频等离子体风洞烧蚀行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 790-798. |
| [3] | 余乐洋阳, 赵芳霞, 张舒心, 徐以祥, 牛亚然, 张振忠, 郑学斌. 感应等离子球化技术制备喷涂用高熵硼化物粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 808-816. |
| [4] | 魏志帆, 陈国清, 祖宇飞, 刘渊, 李明浩, 付雪松, 周文龙. ZrB2-HfSi2复相陶瓷显微组织及其核-周结构形成机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 817-825. |
| [5] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [6] | 何国强, 张恺恒, 王震涛, 包健, 席兆琛, 方振, 王昌昊, 王威, 王鑫, 姜佳沛, 李祥坤, 周迪. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: 一种被低估的K40微波介质陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 639-646. |
| [7] | 张家维, 陈宁, 程原, 王博, 朱建国, 金城. Bi4Ti3O12铋层状压电陶瓷的A/B位掺杂及其电学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 690-696. |
| [8] | 唐莹, 李洁, 相怀成, 方维双, 林慧兴, 杨俊峰, 方亮. Rattling效应: 一种影响微波介质陶瓷谐振频率温度系数的新机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 656-666. |
| [9] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [10] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [11] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [12] | 周阳阳, 张艳艳, 于子怡, 傅正钱, 许钫钫, 梁瑞虹, 周志勇. 通过Bi3+自掺杂增强CaBi4Ti4O15基陶瓷压电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 719-728. |
| [13] | 杨燕, 张发强, 马名生, 王墉哲, 欧阳琪, 刘志甫. 基于CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5复合氧化物烧结助剂的ZnAl2O4陶瓷低温烧结研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 711-718. |
| [14] | 黄子鹏, 贾文晓, 李玲霞. (Ti0.5W0.5)5+掺杂MgNb2O6陶瓷的晶体结构与太赫兹介电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 647-655. |
| [15] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||