无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (7): 817-825.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250060 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250060
魏志帆( ), 陈国清(
), 陈国清( ), 祖宇飞, 刘渊, 李明浩, 付雪松, 周文龙
), 祖宇飞, 刘渊, 李明浩, 付雪松, 周文龙
收稿日期:2025-02-17
修回日期:2025-03-20
出版日期:2025-07-20
网络出版日期:2025-03-25
通讯作者:
陈国清, 教授. E-mail: gqchen@dlut.edu.cn作者简介:魏志帆(1993-), 男, 博士. E-mail: 424380067@qq.com
基金资助:
WEI Zhifan( ), CHEN Guoqing(
), CHEN Guoqing( ), ZU Yufei, LIU Yuan, LI Minghao, FU Xuesong, ZHOU Wenlong
), ZU Yufei, LIU Yuan, LI Minghao, FU Xuesong, ZHOU Wenlong
Received:2025-02-17
Revised:2025-03-20
Published:2025-07-20
Online:2025-03-25
Contact:
CHEN Guoqing, professor. E-mail: gqchen@dlut.edu.cnAbout author:WEI Zhifan (1993-), male, PhD. E-mail: 424380067@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
近年来, ZrB2作为超高温陶瓷(UHTCs)的代表性材料, 已成为新一代空天飞行器热端部件重要的候选材料体系。然而, 其实际应用受限于材料制备以及复杂构件的加工难题。为此本研究通过引入HfSi2作为烧结助剂, 优化ZrB2基UHTCs的烧结工艺, 重点解决传统ZrB2基陶瓷因较低的扩散系数而导致致密化困难的难题。研究聚焦于核-周结构硼化物的形成机制以及其对ZrB2-HfSi2陶瓷致密化的辅助作用。采用1600 ℃热压烧结制备了ZrB2-HfSi2陶瓷, 结果表明, 在烧结过程中, HfSi2相软化能够有效填充颗粒间隙, 从而实现ZrB2-HfSi2陶瓷的低温烧结。同时, 在保温阶段, Hf与Zr原子通过溶解-再沉淀机制形成具有核-周结构的ZrB2/(Zr,Hf)B2, 促进了烧结粉体之间的物质交换, 从而加速了ZrB2-HfSi2陶瓷的致密化。此外, 该结构主要由核心ZrB2及其周边(Zr,Hf)B2组成, 具有完全共格界面(P6/mmm六方结构), 晶格失配度低(<5%), 界面稳定。ZrB2-HfSi2陶瓷的抗压强度、显微硬度以及断裂韧性分别为(1333±83) MPa、(15.86±0.72) GPa以及(2.01±0.36) MPa·m1/2。该陶瓷主要表现为典型的沿晶断裂形式, 只有少数解理面上出现核-周结构特征。本研究为实现UHTCs低温烧结提供了重要的参考价值。
中图分类号:
魏志帆, 陈国清, 祖宇飞, 刘渊, 李明浩, 付雪松, 周文龙. ZrB2-HfSi2复相陶瓷显微组织及其核-周结构形成机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 817-825.
WEI Zhifan, CHEN Guoqing, ZU Yufei, LIU Yuan, LI Minghao, FU Xuesong, ZHOU Wenlong. ZrB2-HfSi2 Ceramics: Microstructure and Formation Mechanism of Core-rim Structure[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 817-825.
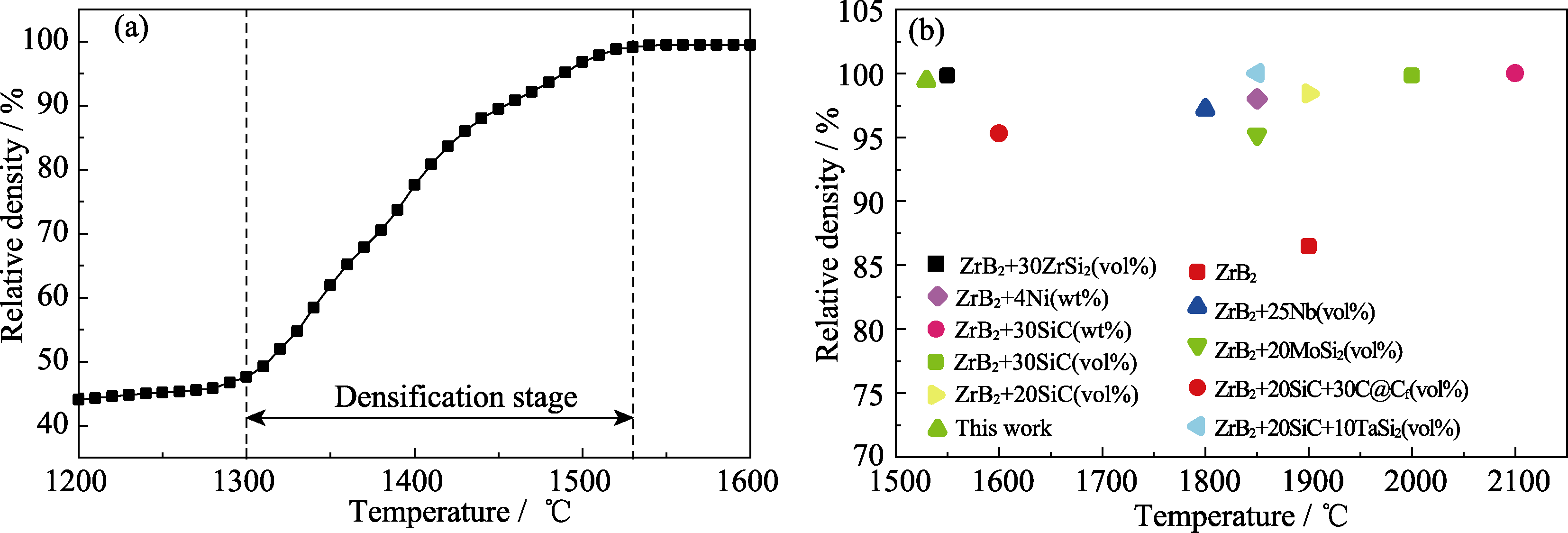
图1 (a) ZrB2-HfSi2陶瓷致密化曲线; (b)其他ZrB2基陶瓷的烧结温度及相对密度[27-34]
Fig. 1 (a) Densification curve of ZrB2-HfSi2 ceramic; (b) Sintering temperature and relative density of other ZrB2 based ceramics[27-34]
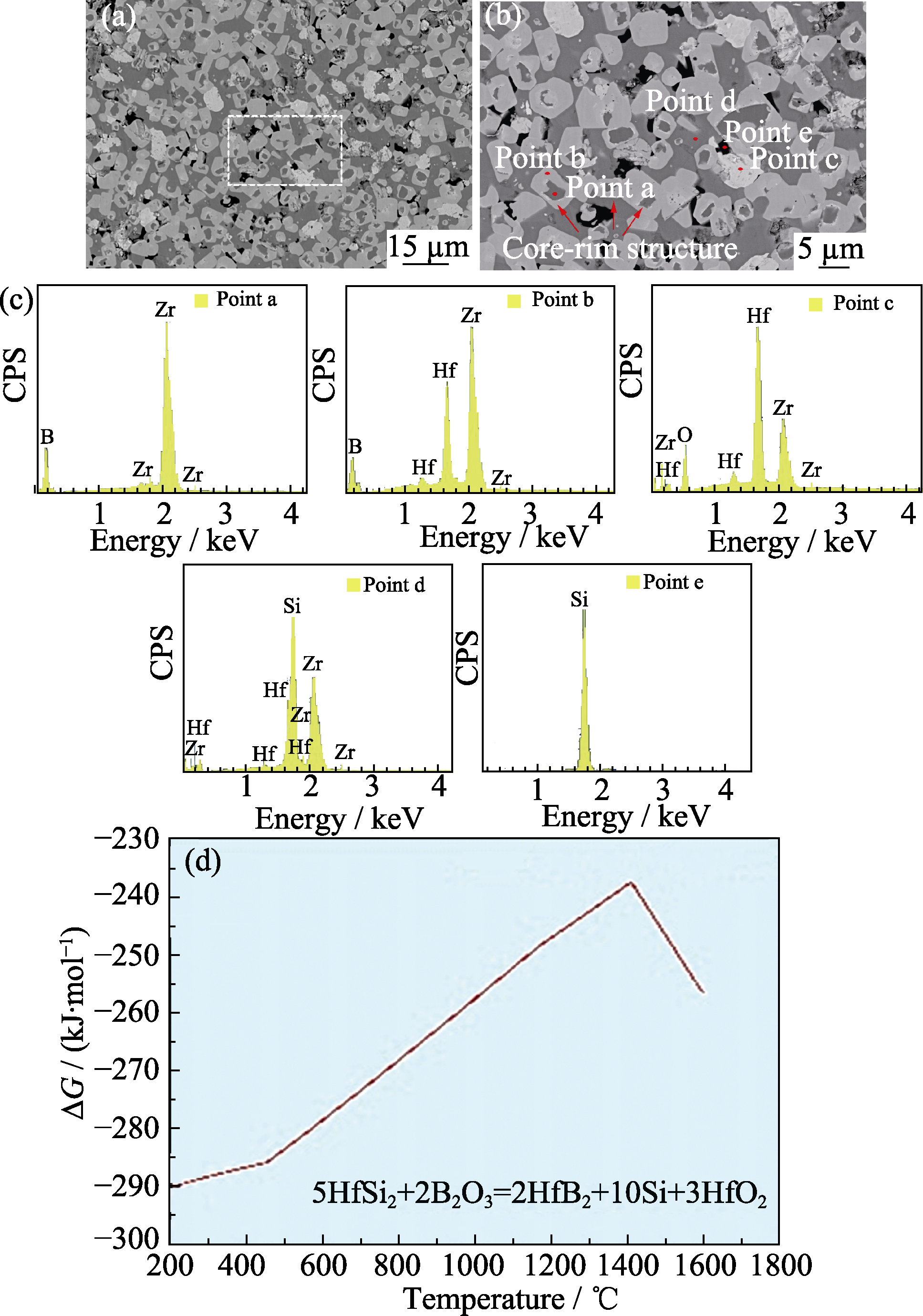
图3 (a, b) ZrB2-HfSi2陶瓷的显微组织(a)及其局部放大图(b); (c) ZrB2-HfSi2陶瓷的EDS结果; (d)反应(6)的吉布斯自由能
Fig. 3 (a) Microstructure and (b) partial enlarged microstructure of ZrB2-HfSi2 ceramic; (c) EDS results of ZrB2-HfSi2 ceramic; (d) Gibbs free energy of the reaction (6)
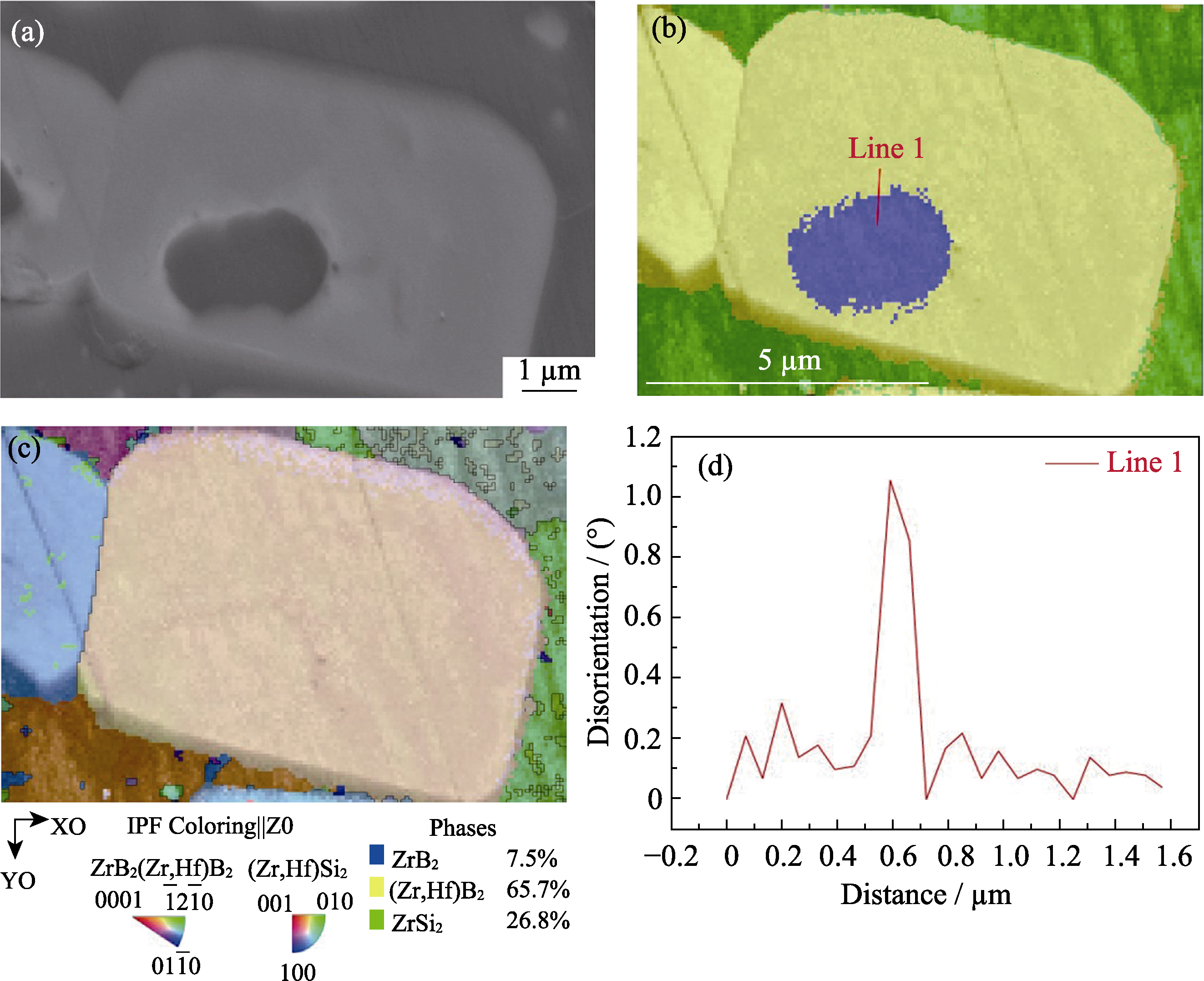
图4 ZrB2-HfSi2陶瓷核-周结构的EBSD分析图
Fig. 4 EBSD analysis diagrams of ZrB2-HfSi2 ceramic with core-rim structure (a) Core-rim structure microstructure; (b) Phase distribution of core-rim structure; (c) IPF of core-rim structure; (d) Orientation angle difference of interface position

图5 (a) ZrB2-HfSi2陶瓷的STEM照片及其元素分布图; (b)核-周结构界面处的显微组织及SAED图案; (c)图5(b)中界面选取位置的HRTEM照片
Fig. 5 (a) STEM image and element distribution of ZrB2-HfSi2 ceramic; (b) Microstructure at the interface of core-rim structure and SAED patterns; (c) HRTEM images of the selected interface position in Fig. 5(b)
| Crystalline plane | Plane spacing measured/ theoretical value | Crystalline plane | Plane spacing measured/ theoretical value | Mismatch ratio measured/theoretical value | Interface |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1¯10¯1)ZrB2 | 0.213/0.216 nm | (1¯10¯1)(Zr,Hf)B2 | 0.216/0.215 nm | 1.4%/0.4% | Common lattice interface |
| (01¯1¯1)ZrB2 | 0.209/0.216 nm | (01¯1¯1)(Zr,Hf)B2 | 0.213/0.215 nm | 1.9%/0.4% | Common lattice interface |
| (01¯11)(Zr,Hf)B2 | 0.214/0.215 nm | (0¯20)(Zr,Hf)Si2 | 0.730/0.734 nm | 228.5%/243.4% | Noncommon lattice interface |
| (¯1102)(Zr,Hf)B2 | 0.146/0.148 nm | (1¯1¯1)(Zr,Hf)Si2 | 0.260/0.258 nm | 78.1%/74.3% | Noncommon lattice interface |
表1 晶面间距及失配度的测量值和理论值
Table 1 Measured and theoretical values of the interplanar spacing and misfit ratio
| Crystalline plane | Plane spacing measured/ theoretical value | Crystalline plane | Plane spacing measured/ theoretical value | Mismatch ratio measured/theoretical value | Interface |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1¯10¯1)ZrB2 | 0.213/0.216 nm | (1¯10¯1)(Zr,Hf)B2 | 0.216/0.215 nm | 1.4%/0.4% | Common lattice interface |
| (01¯1¯1)ZrB2 | 0.209/0.216 nm | (01¯1¯1)(Zr,Hf)B2 | 0.213/0.215 nm | 1.9%/0.4% | Common lattice interface |
| (01¯11)(Zr,Hf)B2 | 0.214/0.215 nm | (0¯20)(Zr,Hf)Si2 | 0.730/0.734 nm | 228.5%/243.4% | Noncommon lattice interface |
| (¯1102)(Zr,Hf)B2 | 0.146/0.148 nm | (1¯1¯1)(Zr,Hf)Si2 | 0.260/0.258 nm | 78.1%/74.3% | Noncommon lattice interface |
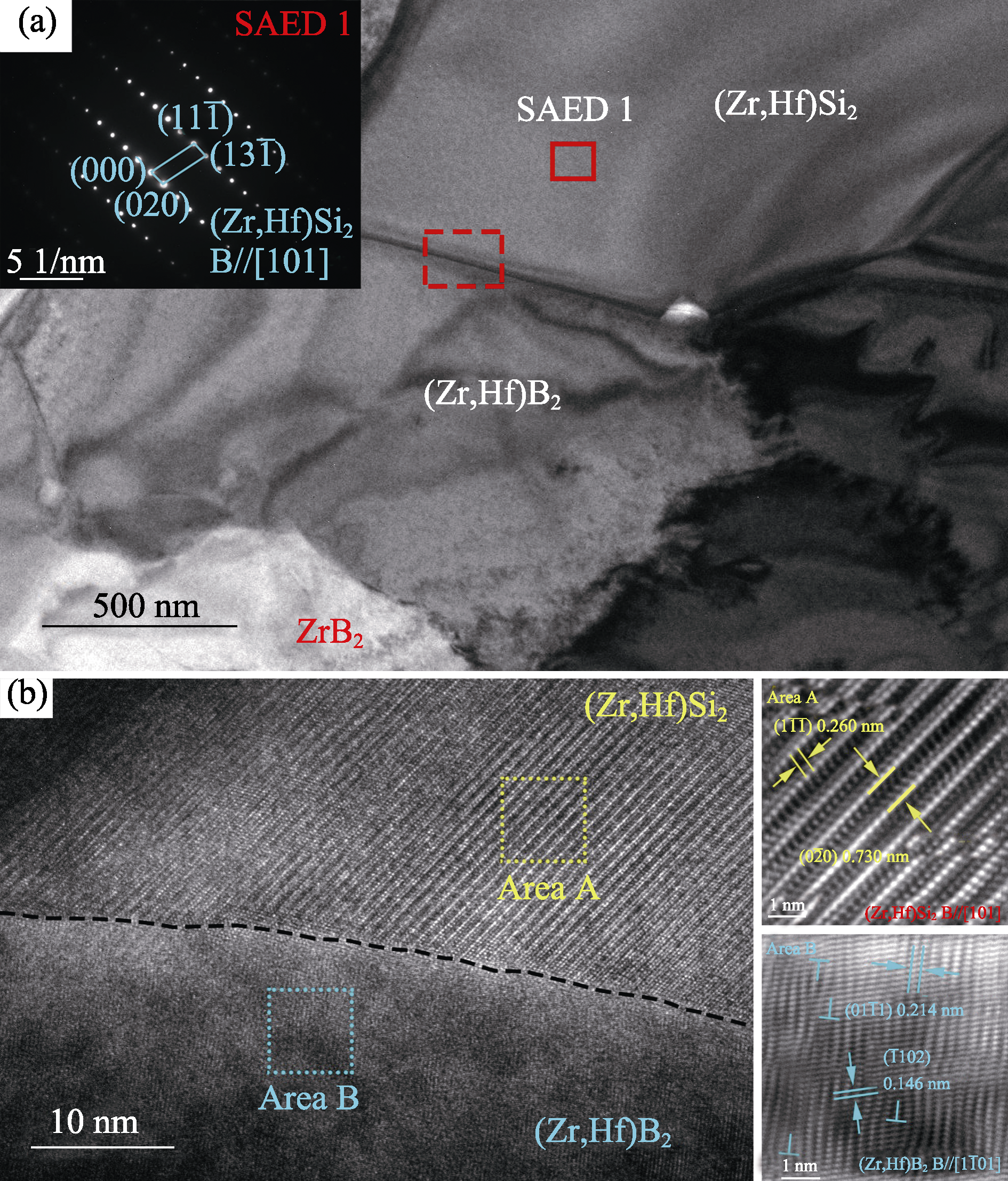
图6 (a)(Zr,Hf)Si2/(Zr,Hf)B2界面处的显微组织及SAED图案; (b)图6(a)中界面选取位置的HRTEM照片
Fig. 6 (a) Microstructure at the interface of (Zr,Hf)Si2/ (Zr,Hf)B2 and SAED patterns; (b) HRTEM images of the selected interface position in Fig. 6(a)
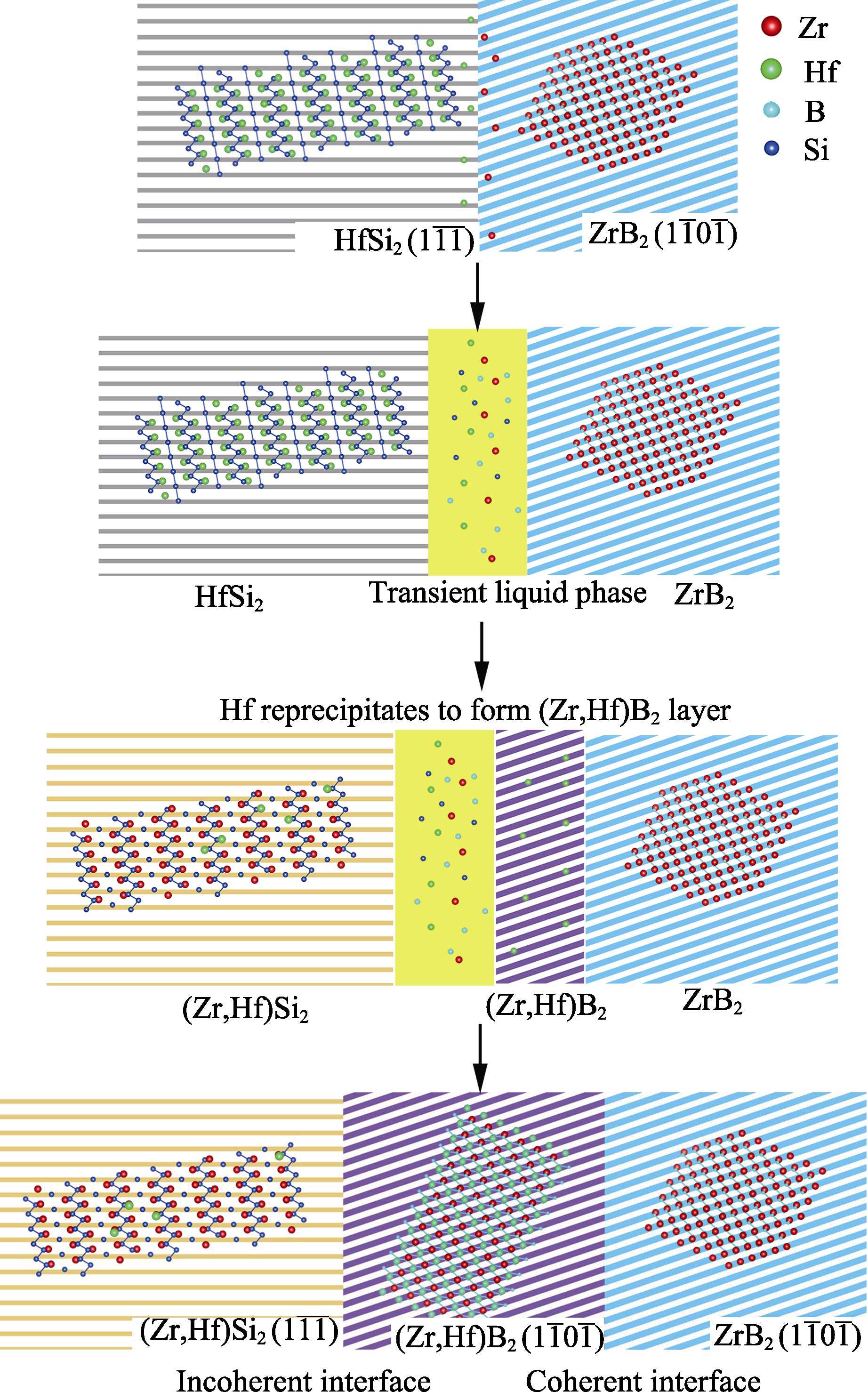
图7 ZrB2-HfSi2核-周结构界面形成机理图
Fig. 7 Formation mechanism diagram of core-rim structure interface in ZrB2-HfSi2 During the initial stage, the surface of ZrB2 melts, and Hf partially dissolves in the transient liquid phase to form a core. During the middle stage, Hf solute diffuses through the transient liquid phase to the surface of the unmelted ZrB2 nucleus, and then precipitates to form a high Hf solubility (Zr,Hf)B2 peripheral layer. During the later stage, the remaining Zr-rich transient liquid phase precipitates to form (Zr,Hf)Si2 phase, and finally forms the hierarchical relationship of ZrB2-(Zr,Hf)B2-(Zr,Hf)Si2.
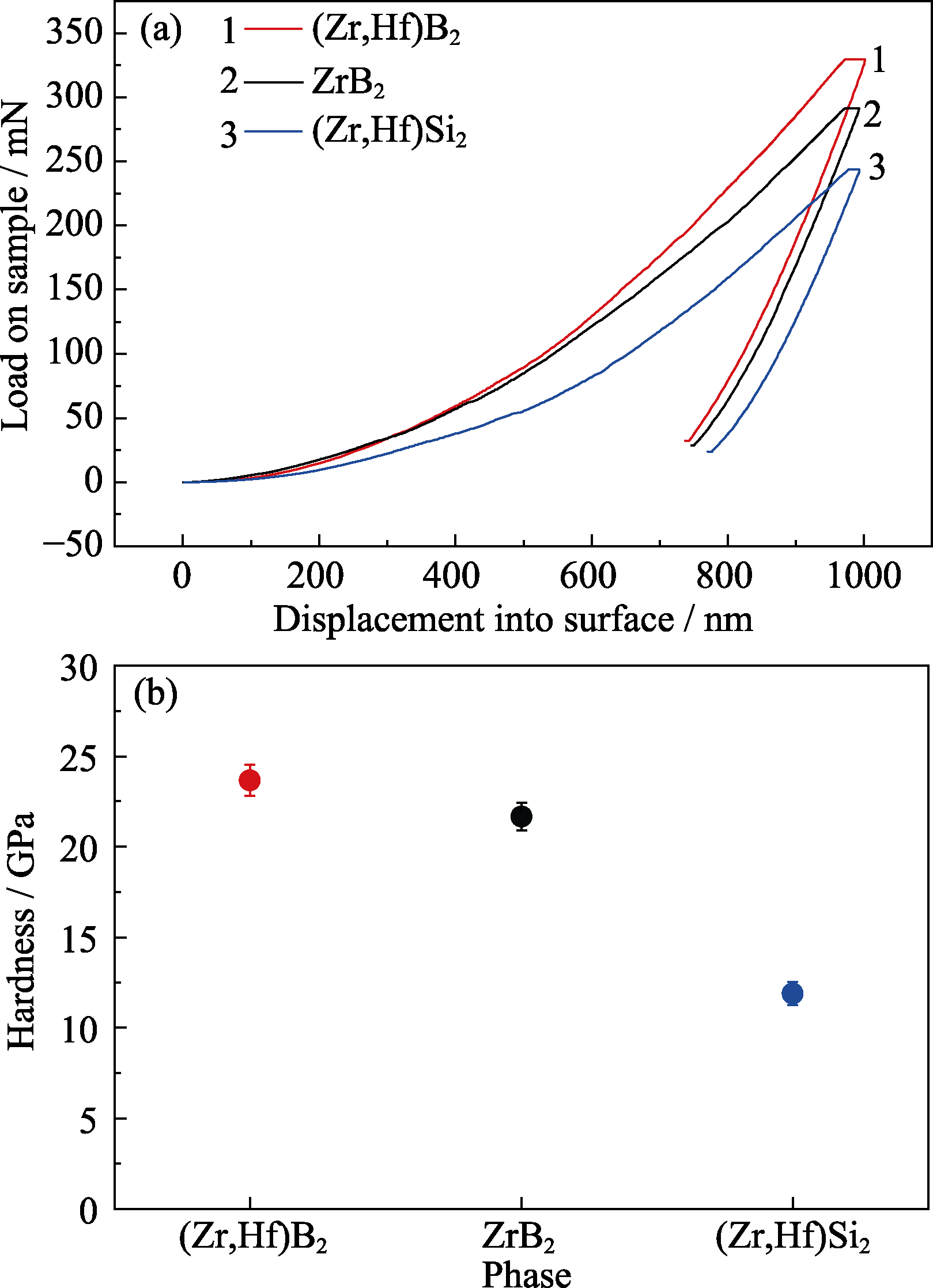
图9 (a) ZrB2、(Zr,Hf)B2和(Zr,Hf)Si2纳米压痕试验的载荷-位移曲线; (b)显微组织中ZrB2、(Zr,Hf)B2和(Zr,Hf)Si2的硬度
Fig. 9 (a) Load-displacement curves of ZrB2, (Zr,Hf)B2 and (Zr,Hf)Si2 in nano indentation experiment; (b) Hardnesses of ZrB2, (Zr,Hf)B2 and (Zr,Hf)Si2 in the microstructures
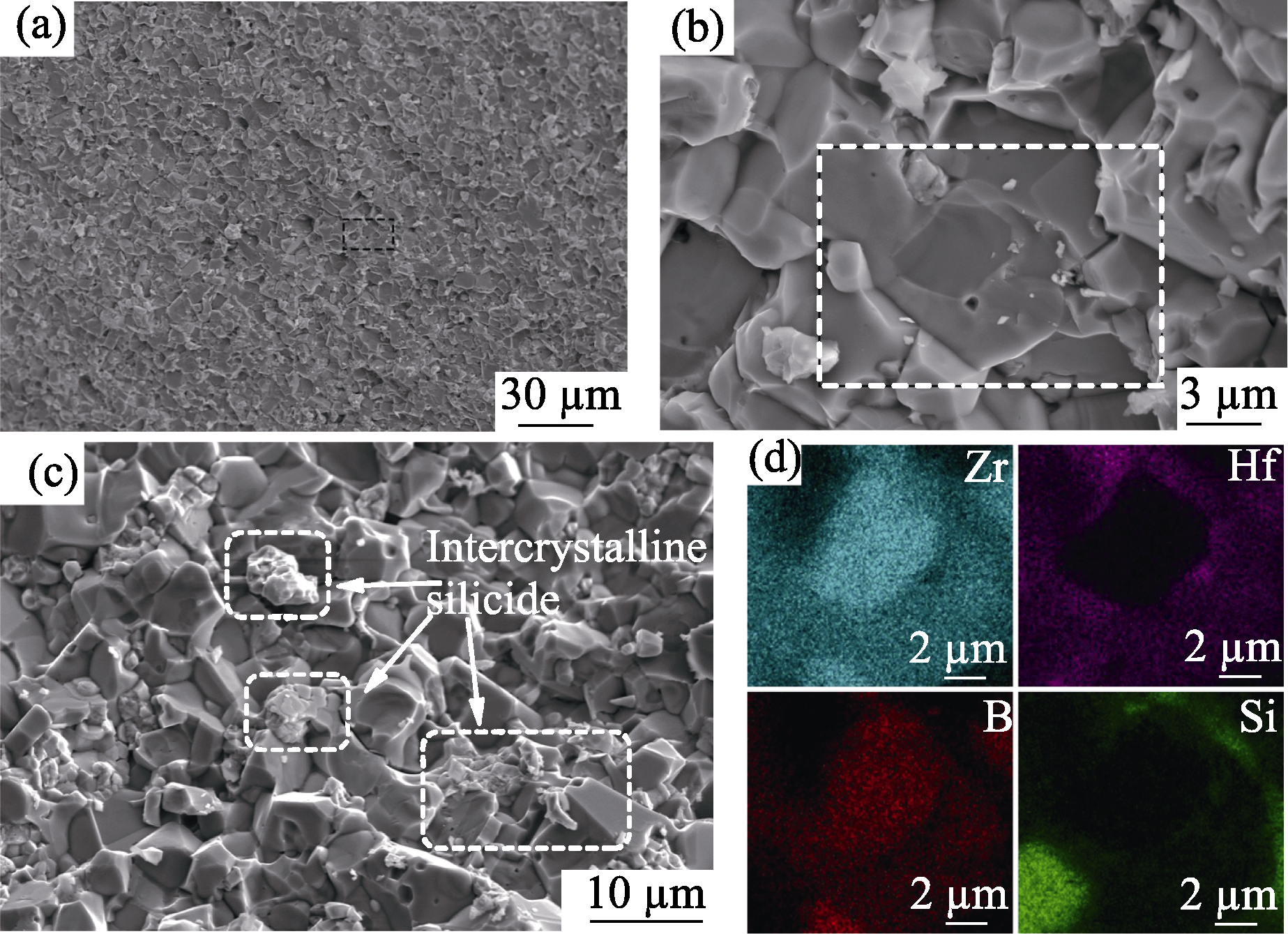
图10 (a) ZrB2-HfSi2陶瓷的断口组织形貌; (b)核-周结构的解理平台; (c)放大的断口组织及其(d) EDS元素分布
Fig. 10 (a) Fracture microstructure of ZrB2-HfSi2 ceramics; (b) Cleavage platform of core-rim structure; (c) Enlarged drawing of fracture and (d) corresponding EDS element distributions
| [1] | PARTHASARATHY T A, PETRY M D, CINIBULK M K, et al. Thermal and oxidation response of UHTC leading edge samples exposed to simulated hypersonic flight conditions. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2013, 96(3): 907. |
| [2] | FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E. Ultra-high temperature ceramics: materials for extreme environments. Scripta Materialia, 2017, 129: 94. |
| [3] | FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E, TALMY I G, et al. Refractory diborides of zirconium and hafnium. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2007, 90(5): 1347. |
| [4] | MONTEVERDE F, BELLOSI A, GUICCIARDI S. Processing and properties of zirconium diboride-based composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2002, 22(3): 279. |
| [5] | GOLLA B R, MUKHOPADHYAY A, BASU B, et al. Review on ultra-high temperature boride ceramics. Progress in Materials Science, 2020, 111: 100651. |
| [6] | KHANRA A K, GODKHINDI M M. Effect of Ni additives on pressureless sintering of SHS ZrB2. Advances in Applied Ceramics, 2005, 104(6): 273. |
| [7] | WANG H, CHEN D, WANG C A, et al. Preparation and characterization of high-toughness ZrB2/Mo composites by hot-pressing process. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2009, 27(6): 1024. |
| [8] | GUO S Q. Densification of ZrB2-based composites and their mechanical and physical properties: a review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2009, 29(6): 995. |
| [9] | GUO S. Densification, microstructure, elastic and mechanical properties of reactive hot-pressed ZrB2-ZrC-Zr cermets. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2014, 34(3): 621. |
| [10] | MISHRA S K, PATHAK L C. Effect of carbon and titanium carbide on sintering behaviour of zirconium diboride. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 465(1/2): 547. |
| [11] | REZAIE A, FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E. Effect of hot pressing time and temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of ZrB2-SiC. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42(8): 2735. |
| [12] | SHA J J, LI J, WANG S H, et al. Toughening effect of short carbon fibers in the ZrB2-ZrSi2 ceramic composites. Materials and Design, 2015, 75: 160. |
| [13] | ASL M S, NAYEBI B, AHMADI Z, et al. Effects of carbon additives on the properties of ZrB2-based composites: a review. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(7): 7334. |
| [14] | ASL M S, FARAHBAKHSH I, NAYEBI B. Characteristics of multi-walled carbon nanotube toughened ZrB2-SiC ceramic composite prepared by hot pressing. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(1): 1950. |
| [15] | MONTEVERDE F, BELLOSI A. Efficacy of HfN as sintering aid in the manufacture of ultrahigh-temperature metal diborides- matrix ceramics. Journal of Materials Research, 2004, 19(12): 3576. |
| [16] | MONTEVERDE F, BELLOSI A. Effect of the addition of silicon nitride on sintering behaviour and microstructure of zirconium diboride. Scripta Materialia, 2002, 46(3): 223. |
| [17] | MONTEVERDE F, BELLOSI A. Beneficial effects of AlN as sintering aid on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-pressed ZrB2. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2003, 5(7): 508. |
| [18] | SILVESTRONI L, SCITI D. Densification of ZrB2-TaSi2 and HfB2-TaSi2 ultra-high-temperature ceramic composites: densification of ZrB2-TaSi2 and HfB2-TaSi2 ceramic composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2011, 94(6): 1920. |
| [19] | SILVESTRONI L, KLEEBE H J, LAUTERBACH S, et al. Transmission electron microscopy on Zr- and Hf-borides with MoSi2 addition: densification mechanisms. Journal of Materials Research, 2010, 25(5): 828. |
| [20] | SCITI D, SILVESTRONI L, CELOTTI G, et al. Sintering and mechanical properties of ZrB2-TaSi2 and HfB2-TaSi2 ceramic composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(10): 3285. |
| [21] | LAVRENKO V O, PANASYUK A D, GRIGOREV O M, et al. High-temperature (to 1600 ℃) oxidation of ZrB2-MoSi2 ceramics in air. Powder Metallurgy and Metal Ceramics, 2012, 51(1): 102. |
| [22] | MUSA C, LICHERI R, ORRÙ R, et al. Synthesis, sintering, and oxidative behavior of HfB2-HfSi2 ceramics. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(22): 9101. |
| [23] | SAJDAK M, KORNAUS K, ZIENTARA D, et al. Processing, microstructure and mechanical properties of TiB2-MoSi2-C ceramics. Crystals, 2024, 14(3): 212. |
| [24] | GROHSMEYER R J, SILVESTRONI L, HILMAS G E, et al. ZrB2-MoSi2 ceramics: a comprehensive overview of microstructure and properties relationships. Part I: processing and microstructure. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(6): 1939. |
| [25] | NIIHARA K. A fracture mechanics analysis of indentation- induced Palmqvist crack in ceramics. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1983, 2(5): 221. |
| [26] | ZU Y, CHEN G, FU X, et al. Effects of liquid phases on densification of TiO2-doped Al2O3-ZrO2 composite ceramics. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(3): 3989. |
| [27] | MELÉNDEZ-MARTÍNEZ J J, DOMÍNGUEZ-RODRÍGUEZ A, MONTEVERDE F, et al. Characterisation and high temperature mechanical properties of zirconium boride-based materials. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2002, 22(14/15): 2543. |
| [28] | SUN X, HAN W, HU P, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ZrB2-Nb composite. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2010, 28(3): 472. |
| [29] | GUO S Q, KAGAWA Y, NISHIMURA T. Mechanical behavior of two-step hot-pressed ZrB2-based composites with ZrSi2. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2009, 29(4): 787. |
| [30] | ORLOVSKAYA N, STADELMANN R, LUGOVY M, et al. Mechanical properties of ZrB2-SiC ceramic composites: room temperature instantaneous behaviour. Advances in Applied Ceramics, 2013, 112(1): 9. |
| [31] | LI W, ZHANG X, HONG C, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of zirconia-toughened ZrB2-MoSi2 composites prepared by hot-pressing. Scripta Materialia, 2009, 60(2): 100. |
| [32] | ASL M S, KAKROUDI M G, NOORI S. Hardness and toughness of hot pressed ZrB2-SiC composites consolidated under relatively low pressure. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 619: 481. |
| [33] | GUI K, HU P, HONG W, et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties and thermal shock resistance of ZrB2-SiC-Cfcomposite with inhibited degradation of carbon fibers. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 706: 16. |
| [34] | YANG Y, QIAN Y H, XU J J, et al. Effects of TaSi2 addition on room temperature mechanical properties of ZrB2-20SiC composites. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(14): 16150. |
| [35] | MONTEVERDE F. Hot pressing of hafnium diboride aided by different sinter additives. Journal of Materials Science, 2008, 43(3): 1002. |
| [36] | LANG Q, LI N, LIU X, et al. Regulating Mg/Fe interfacial compound formation by in-situ alloying with Gd and Y. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2024, 12(12): 5179. |
| [37] | SONG G, LI T, ZHANG Z, et al. Investigation of unequal thickness Mg/steel butt-welded plate by hybrid laser-tungsten inert gas welding with a Ni interlayer. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2017, 30: 299. |
| [38] | HU D L, GU H, ZOU J, et al. Core-rim structure, bi-solubility and a hierarchical phase relationship in hot-pressed ZrB2-SiC-MC ceramics (M=Nb, Hf, Ta, W). Journal of Materiomics, 2021, 7(1): 69. |
| [39] | ZHU S, LI J, XING J, et al. Cathodoluminescence characteristics of a novel core-rim structure in Bi-doped (Sr,Ba)TiO3 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(6): 8027. |
| [40] | ENGSTRÖM I, LÖNNBERG B. Thermal expansion studies of the group IV-VII transition-metal disilicides. Journal of Applied Physics, 1988, 63(9): 4476. |
| [41] | KEIHN F G, KEPLIN E J. High-temperature thermal expansion of certain group IV and group V diborides. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1967, 50(2): 81. |
| [1] | 崔宁, 张玉新, 王鲁杰, 李彤阳, 于源, 汤华国, 乔竹辉. (TiVNbMoW)Cx高熵陶瓷的单相形成过程与碳空位调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [2] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [3] | 何宗倍, 陈放, 刘佃光, 李统业, 曾强. 模拟核芯FCM燃料的振荡烧结行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 501-508. |
| [4] | 杨勇, 郭啸天, 唐杰, 常浩天, 黄政仁, 胡秀兰. 非氧化物陶瓷光固化增材制造研究进展及展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(3): 267-277. |
| [5] | 王椎, 韩建军, 李建强, 李晓禹, 李江涛, 贺刚, 谢俊. 大尺寸La2O3-TiO2-ZrO2非晶塑性烧结行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(4): 433-438. |
| [6] | 聂兰舰, 顾真安, 王玉芬, 向在奎, 张辰阳, 饶传东. SiO2疏松体真空烧结致密化与透明化机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(10): 1060-1066. |
| [7] | 郭胜强, 王皓, 涂兵田, 王斌, 徐鹏宇, 王为民, 傅正义. 细晶MgO·1.44Al2O3透明陶瓷的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(10): 1067-1071. |
| [8] | 袁 钦, 宋永才. Al、O含量对SiAlCO纤维高温转化为Si(Al)C纤维过程的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(4): 393-400. |
| [9] | 袁 钦, 宋永才. SiCxOy相分解方式对SiCO(Al)纤维烧结致密化的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(12): 1320-1326. |
| [10] | 李海涛, 李 谦, 闫焉服, 许荣辉. ZnO掺杂对Ca0.25(Li0.43Sm0.57)0.75TiO3陶瓷烧结性能和微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(4): 369-373. |
| [11] | 杜贤武, 张志晓, 王为民, 傅正义, 王 皓. 粉末粒径对热压烧结碳化硼致密化及力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(10): 1062-1066. |
| [12] | 卢振亚,黄 欢,吴建青. SnO2-Sb2O3基压敏陶瓷致密化及脉冲电流耐受特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(4): 841-844. |
| [13] | 李小雷,马红安,左桂鸿,郑友进,李吉刚,贾晓鹏. AlN陶瓷的高压烧结研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(1): 104-108. |
| [14] | 林 枞,徐 政,彭 虎,孙丹峰. 微波烧结氧化锌压敏电阻的致密化和晶粒生长[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(5): 917-921. |
| [15] | 邹继兆,曾燮榕,熊信柏,谢盛辉,唐汉玲,李 龙. 气体滞留时间对微波热解CVI工艺制备C/C复合材料性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(4): 677-680. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||