无机材料学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (7): 748-758.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190408 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20190408
所属专题: 结构陶瓷论文精选(2020); 优秀作者论文集锦; 2019~2020年度优秀作者作品欣赏(六)
陈磊1,2,王恺1,2,苏文韬1,2,张文1,2,徐晨光1,2,王玉金1,2( ),周玉1,2
),周玉1,2
收稿日期:2019-08-12
修回日期:2019-10-23
出版日期:2020-07-20
网络出版日期:2019-12-04
作者简介:陈 磊(1983-), 男, 助理研究员. E-mail: chenleihit@hit.edu.cn基金资助:
CHEN Lei1,2,WANG Kai1,2,SU Wentao1,2,ZHANG Wen1,2,XU Chenguang1,2,WANG Yujin1,2( ),ZHOU Yu1,2
),ZHOU Yu1,2
Received:2019-08-12
Revised:2019-10-23
Published:2020-07-20
Online:2019-12-04
Supported by:摘要:
高熵陶瓷是一种新兴的近等摩尔多组元单相固溶体陶瓷材料, 特别是过渡金属碳化物、过渡金属硼化物等过渡金属非氧化物高熵陶瓷体系, 其具有超高硬度、低热导和抗腐蚀等优异的理化性能, 在航空航天、核能和高速切削加工等极端环境有着广阔的应用前景。目前, 高熵陶瓷材料研究尚处于起步阶段, 主要集中在成分设计、制备方法、单相形成能力和力学性能评价等方面, 设计依据和理论方面的研究还相对较少。本文从高熵效应和高熵合金出发, 综述了过渡金属非氧化物高熵陶瓷的制备、表征和理论研究进展, 同时介绍了部分相关的高熵陶瓷涂层研究现状, 总结并展望了非氧化物高熵陶瓷的未来前景和发展方向。
中图分类号:
陈磊,王恺,苏文韬,张文,徐晨光,王玉金,周玉. 过渡金属非氧化物高熵陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(7): 748-758.
CHEN Lei,WANG Kai,SU Wentao,ZHANG Wen,XU Chenguang,WANG Yujin,ZHOU Yu. Research Progress of Transition Metal Non-oxide High-entropy Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 748-758.
| Ranking | HEC | EFA/(eV·atom)-1a | Ranking | HEC | EFA/(eV·atom)-1a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (VNbTaMoW)C | 125 | (23) | (TiZrNbTaW)C | 59 |
| (2) | (TiZrHfNbTa)C | 100 | (29) | (ZrVNbTaW)C | 56 |
| (3) | (TiHfVNbTa)C | 100 | (33) | (TiZrHfNbW)C | 53 |
| (4) | (TiVNbTaMo)C | 100 | (36) | (TiZrHfTaW)C | 50 |
| (5) | (TiZrNbTaV)C | 83 | (44) | (TiZrTaMoW)C | 48 |
| (7) | (TiVNbTaW)C | 77 | (52) | (ZrHfTaMoW)C | 45 |
| (10) | (TiZrNbTaMo)C | 71 | (55) | (TiZrHfMoW)C | 38 |
| (17) | (TiHfNbTaW)C | 67 | (56) | (ZrHfVMoW)C | 37 |
表1 部分碳化物高熵陶瓷的EFA值大小排序[29]
Table 1 Ranking of some high-entropy carbides based on the EFA values[29]
| Ranking | HEC | EFA/(eV·atom)-1a | Ranking | HEC | EFA/(eV·atom)-1a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (VNbTaMoW)C | 125 | (23) | (TiZrNbTaW)C | 59 |
| (2) | (TiZrHfNbTa)C | 100 | (29) | (ZrVNbTaW)C | 56 |
| (3) | (TiHfVNbTa)C | 100 | (33) | (TiZrHfNbW)C | 53 |
| (4) | (TiVNbTaMo)C | 100 | (36) | (TiZrHfTaW)C | 50 |
| (5) | (TiZrNbTaV)C | 83 | (44) | (TiZrTaMoW)C | 48 |
| (7) | (TiVNbTaW)C | 77 | (52) | (ZrHfTaMoW)C | 45 |
| (10) | (TiZrNbTaMo)C | 71 | (55) | (TiZrHfMoW)C | 38 |
| (17) | (TiHfNbTaW)C | 67 | (56) | (ZrHfVMoW)C | 37 |
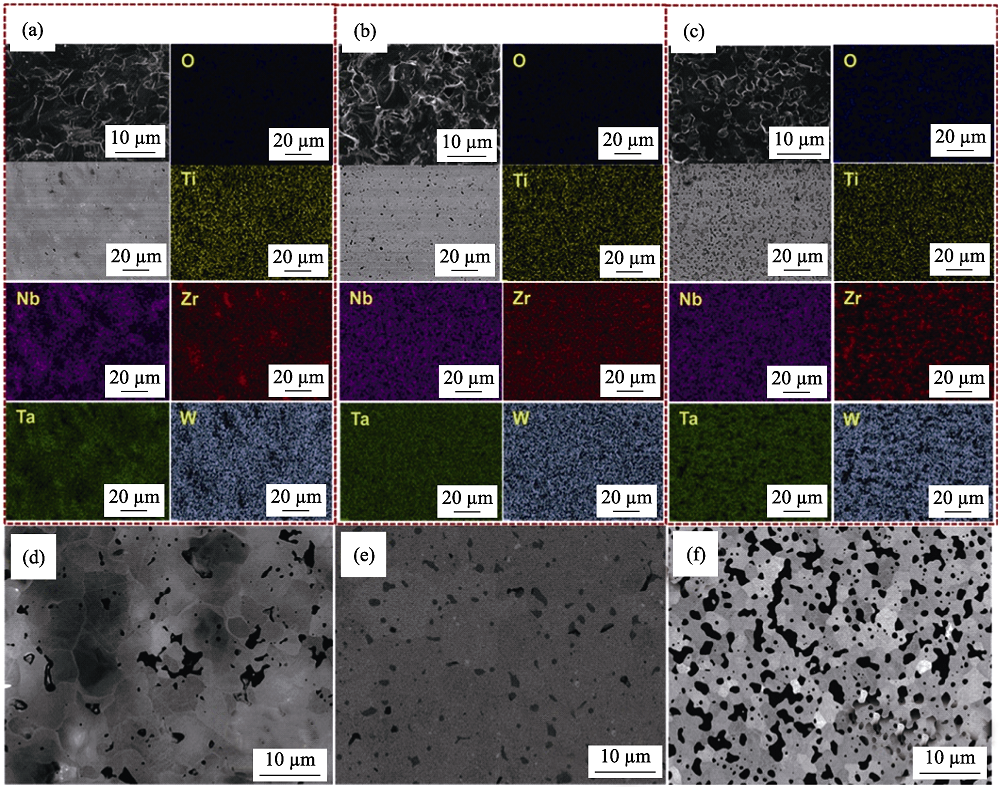
图2 不同原料制备的(TiZrNbTaW)C高熵陶瓷的((a)单质为原料、(b)碳化物为原料和(c)氧化物和碳为原料)断口、表面SEM照片和EDS元素分布, 以(d)单质、(e)碳化物和(f)氧化物和碳为原料制备陶瓷的背散射图像[43]
Fig. 2 SEM images of the fracture surfaces, polished surfaces and their corresponding EDS element mappings of (TiZrNbTaW)C using (a) metallic powders and graphite, (b) metal carbides and (c) metal oxides and graphite as raw materials, as well as the back scattered electron images of (TiZrNbTaW)C using (d) metallic powders and graphite,(e) metal carbides and (f) metal oxides and graphite as raw materials[43]
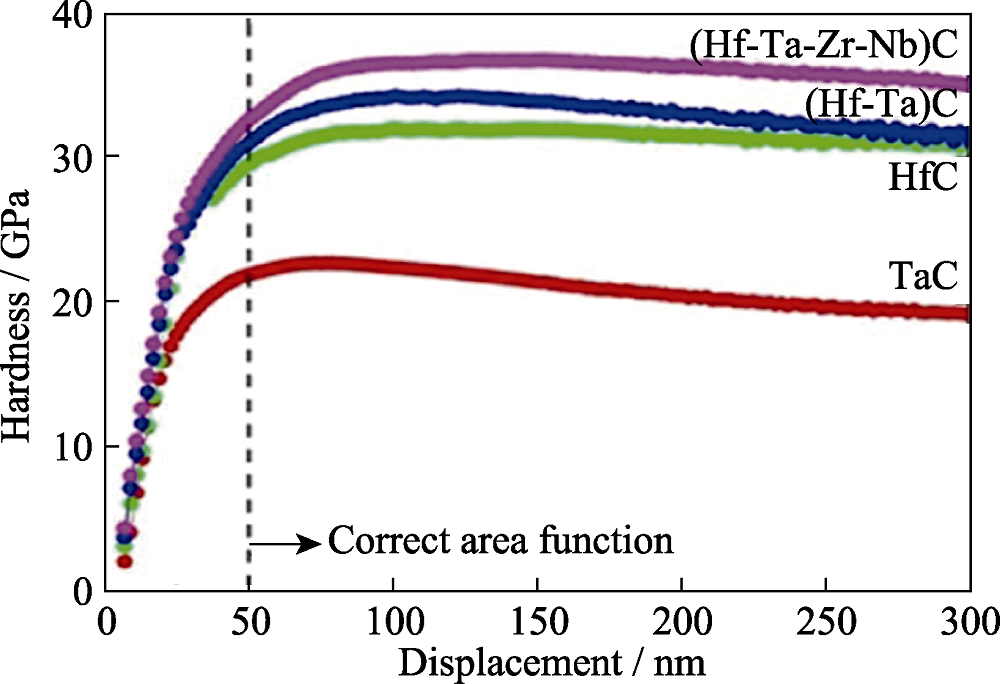
图3 (HfTaZrNb)C高熵陶瓷与一元碳化物、二元碳化物固溶体之间的硬度-深度变化曲线[37]
Fig. 3 Comparison of hardness depth-profiles of the mono, binary and (HfTaZrNb)C high-entropy transition metal carbides[37]
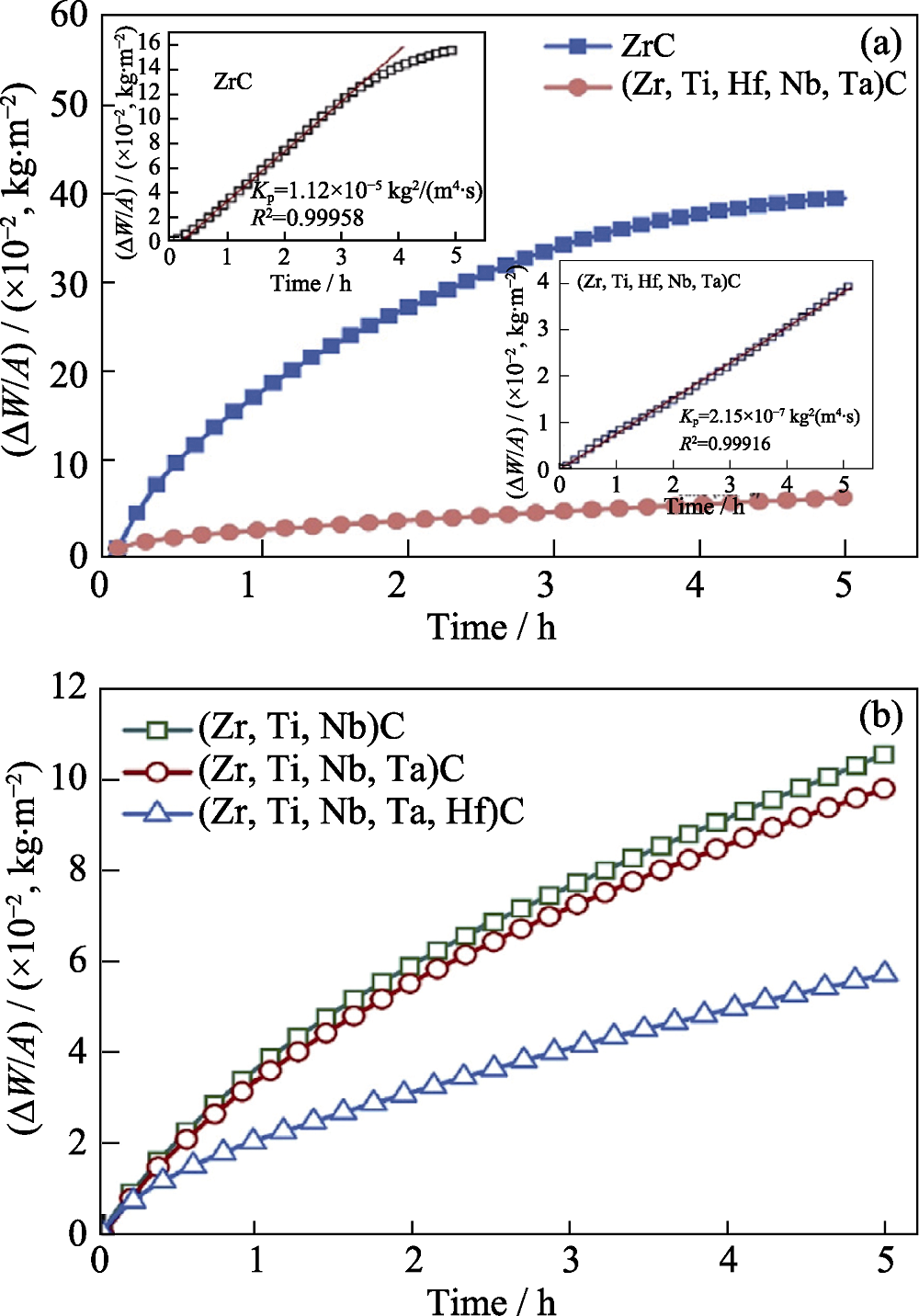
图5 (TiZrHfNbTa)C高熵陶瓷及其相关(TiZrNbTa)C、(TiZrNb)C和ZrC陶瓷材料随时间的增重变化对比[52]
Fig. 5 Comparison of weight gain per unit area as a function of exposure time for (TiZrHfNbTa)C high-entropy ceramic and related (TiZrHNbTa)C, (TiZrNb)C, ZrC ceramic[52]
| [1] |
FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E. Ultra-high temperature ceramics: materials for extreme environments. Scripta Materialia, 2017,129:94-99.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
WEINBERGER C R, THOMPSON G B. Review of phase stability in the group IVB and VB transition-metal carbides. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018,101(10):4401-4424.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
GUO S Q. Densification of ZrB2-based composites and their mechanical and physical properties: a review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2009,29(6):995-1011.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
HUANG P K, YEH J W, SHUN T T, et al. Multi-principal-element alloys with improved oxidation and wear resistance for thermal spray coating. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2004,6(1/2):74-78.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
YEH J W, CHEN S K, LIN S J, et al. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2004,6(5):299-303.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
CHEN T K, SHUN T T, YEH J W, et al. Nanostructured nitride films of multi-element high-entropy alloys by reactive DC sputtering. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2004,188-189:193-200.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
CANTOR B. Multicomponent and high entropy alloys. Entropy, 2014,16(9):4749-4768.
DOI URL |
| [8] | CANTOR B, CHANG I T H, KNIGHT P, et al. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2004,375-377:213-218. |
| [9] |
YEH J W, LIN S J, CHIN T S, et al. Formation of simple crystal structures in Cu-Co-Ni-Cr-Al-Fe-Ti-V alloys with multiprincipal metallic elements. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2004,35(8):2533-2536.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
TSAI M H, YEH J W. High-entropy alloys: a critical review. Materials Research Letters, 2014,2(3):107-123.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
MIRACLE D B, SENKOV O N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Materialia, 2017,122:448-511.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WANG Y P, LI B S, REN M X, et al. Microstructure and compressive properties of AlCrFeCoNi high entropy alloy. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008,491(1):154-158.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SENKOV O N, WILKS G B, MIRACLE D B, et al. Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics, 2010,18(9):1758-1765.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
SENKOV O N, SCOTT J M, SENKOVA S V, et al. Microstructure and room temperature properties of a high-entropy TaNbHfZrTi alloy. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011,509(20):6043-6048.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
SENKOV O N, SCOTT J M, SENKOVA S V, et al. Microstructure and elevated temperature properties of a refractory TaNbHfZrTi alloy. Journal of Materials Science, 2012,47(9):4062-4074.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
GAO M C, CARNEY C S, DOĞAN Ö N, et al. Design of refractory high-entropy alloys. Journal of the Minerals Metals and Materials Society, 2015,67(11):2653-2669.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LONG Y, LIANG X, SU K, et al. A fine-grained NbMoTaWVCr refractory high-entropy alloy with ultra-high strength: microstructural evolution and mechanical properties. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019,780:607-617.
DOI URL |
| [18] | TUNES M A, VISHNYAKOV V M. Microstructural origins of the high mechanical damage tolerance of NbTaMoW refractory high-entropy alloy thin films. Materials & Design, 2019,170:107692. |
| [19] |
KIM H, NAM S, ROH A, et al. Mechanical and electrical properties of NbMoTaW refractory high-entropy alloy thin films. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2019,80:286-291.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
HOU J, ZHANG M, YANG H, et al. Surface strengthening in Al0.25CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy by boronizing. Materials Letters, 2019,238:258-260.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
HOU L, HUI J, YAO Y, et al. Effects of boron content on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlFeCoNiBx high entropy alloy prepared by vacuum arc melting. Vacuum, 2019,164:212-218.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
BRAIC V, VLADESCU A, BALACEANU M, et al. Nanostructured multi-element (TiZrNbHfTa)N and (TiZrNbHfTa)C hard coatings. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2012,211:117-121.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LEI Z, LIU X, WU Y, et al. Enhanced strength and ductility in a high-entropy alloy via ordered oxygen complexes. Nature, 2018,563(7732):546-550.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] | PIERSON H O. Handbook of Refractory Carbides and Nitrides: Properties, Characteristics, Processing and Applications, William Andrew Publishing, Westwood, NJ, 1996. |
| [25] |
YAN X, CONSTANTIN L, LU Y, et al. (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)C high-entropy ceramics with low thermal conductivity. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018,101(10):4486-4491.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
YANG Y, WANG W, GAN G Y, et al. Structural, mechanical and electronic properties of (TaNbHfTiZr)C high entropy carbide under pressure: ab initio investigation. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2018,550:163-170.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
FENG L, FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E. Low-temperature sintering of single-phase, high-entropy carbide ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019,102(12):7217-7224.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
YE B, WEN T, HUANG K, et al. First‐principles study, fabrication, and characterization of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)C high‐entropy ceramic. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019,102(7):4344-4352.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SARKER P, HARRINGTON T, TOHER C, et al. High-entropy high-hardness metal carbides discovered by entropy descriptors. Nature Communications, 2018,9(1):4980.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] | CHEN H, XIANG H, DAI F Z, et al. High porosity and low thermal conductivity high entropy (Zr0.2Hf0.2Ti0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)C. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2019,35(8):1700-1705. |
| [31] |
HARRINGTON T J, GILD J, SARKER P, et al. Phase stability and mechanical properties of novel high entropy transition metal carbides. Acta Materialia, 2019,166:271-280.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ZHOU J Y, ZHANG J Y, ZHANG F, et al. High-entropy carbide: a novel class of multicomponent ceramics. Ceramics International, 2018,44(17):22014-22018.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
CHICARDI E, GARCíA-GARRIDO C, GOTOR F J. Low temperature synthesis of an equiatomic (TiZrHfVNb)C5 high entropy carbide by a mechanically-induced carbon diffusion route. Ceramics International, 2019,45(17):21858-21863.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
WANG K, CHEN L, XU C, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of (TiZrNbTaMo)C high-entropy ceramic. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2019,39:99-105.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
DEMIRSKYI D, BORODIANSKA H, SUZUKI T S, et al. High-temperature flexural strength performance of ternary high-entropy carbide consolidated via spark plasma sintering of TaC, ZrC and NbC. Scripta Materialia, 2019,164:12-16.
DOI URL |
| [36] | YE B L, CHU Y H, HUANG K H, et al. Synthesis and characterization of (Zr1/3Nb1/3Ti1/3)C metal carbide solid-solution ceramic. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019,102(3):919-923. |
| [37] |
CASTLE E, CSANADI T, GRASSO S, et al. Processing and properties of high-entropy ultra-high temperature carbides. Sci. Rep., 2018,8(1):8609.
DOI URL PMID |
| [38] |
DUSZA J, ŠVEC P, GIRMAN V, et al. Microstructure of (Hf-Ta-Zr-Nb)C high-entropy carbide at micro and nano/atomic level. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018,38(12):4303-4307.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
YE B, WEN T, NGUYEN M C, et al. First-principles study, fabrication and characterization of (Zr0.25Nb0.25Ti0.25V0.25)C high-entropy ceramics. Acta Materialia, 2019,170:15-23.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
FENG L, FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E, et al. Synthesis of single-phase high-entropy carbide powders. Scripta Materialia, 2019, 162:90-93.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
LI F, LU Y, WANG X G, et al. Liquid precursor-derived high-entropy carbide nanopowders. Ceramics International, 2019,45(17):22437-22441.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
GILD J, KAUFMANN K, VECCHIO K, et al. Reactive flash spark plasma sintering of high-entropy ultrahigh temperature ceramics. Scripta Materialia, 2019,170:106-110.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
WEI X F, LIU J X, LI F, et al. High entropy carbide ceramics from different starting materials. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019,39(10):2989-2994.
DOI URL |
| [44] | ZHANG C. Compressive Creep Properties of (Ta-Hf-Zr-Nb)C HECs Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering. Advanced Research Workshop on Engineering Ceramics, Slovakia, 2019. |
| [45] |
CSANáDI T, CASTLE E, REECE M J, et al. Strength enhancement and slip behaviour of high-entropy carbide grains during micro-compression. Scientific Reports, 2019,9(1):10200.
DOI URL PMID |
| [46] |
BRAIC V, BALACEANU M, BRAIC M, et al. Characterization of multi-principal-element (TiZrNbHfTa)N and (TiZrNbHfTa)C coatings for biomedical applications. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2012,10:197-205.
DOI URL PMID |
| [47] |
JHI S H, IHM J, LOUIE S G, et al. Electronic mechanism of hardness enhancement in transition-metal carbonitrides. Nature, 1999,399(6732):132-134.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
SANGIOVANNI D G, HULTMAN L, CHIRITA V. Supertoughening in B1 transition metal nitride alloys by increased valence electron concentration. Acta Materialia, 2011,59(5):2121-2134.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
GUO S, NG C, LU J, et al. Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011,109(10):103505.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
BALASUBRAMANIAN K, KHARE S V, GALL D. Valence electron concentration as an indicator for mechanical properties in rocksalt structure nitrides, carbides and carbonitrides. Acta Materialia, 2018,152:175-185.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
TAN Y, CHEN C, LI S, et al. Oxidation behaviours of high-entropy transition metal carbides in 1200 ℃ water vapor. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019,816:152523.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
GILD J, ZHANG Y, HARRINGTON T, et al. High-entropy metal diborides: a new class of high-entropy materials and a new type of ultrahigh temperature ceramics. Scientific Reports, 2016,6:37946.
DOI URL PMID |
| [53] |
LIU D, WEN T, YE B, et al. Synthesis of superfine high-entropy metal diboride powders. Scripta Materialia, 2019,167:110-114.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
ZHANG Y, JIANG Z B, SUN S K, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of high-entropy borides derived from boro/ carbothermal reduction. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019,39(13):3920-3924.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
ZHANG Y, GUO W M, JIANG Z B, et al. Dense high-entropy boride ceramics with ultra-high hardness. Scripta Materialia, 2019,164:135-139.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
TALLARITA G, LICHERI R, GARRONI S, et al. Novel processing route for the fabrication of bulk high-entropy metal diborides. Scripta Materialia, 2019,158:100-104.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
GU J F, ZOU J, SUN S K, et al. Dense and pure high-entropy metal diboride ceramics sintered from self-synthesized powders via boro/ carbothermal reduction approach. Science China Materials, 2019,62(12):1898-1909.
DOI URL |
| [58] | CHEN H, XIANG H, DAI F Z, et al. Porous high entropy (Zr0.2Hf0.2Ti0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)B2: a novel strategy towards making ultrahigh temperature ceramics thermal insulating. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2019,35(10):2404-2408. |
| [59] |
JIN T, SANG X, UNOCIC R R, et al. Mechanochemical-assisted synthesis of high-entropy metal nitride via a soft urea strategy. Advanced Materials, 2018,30(23):1707512.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
YANG Y, MA L, GAN G Y, et al. Investigation of thermodynamic properties of high entropy (TaNbHfTiZr)C and (TaNbHfTiZr)N. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019,788:1076-1083.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
GILD J, BRAUN J, KAUFMANN K, et al. A high-entropy silicide:(Mo0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2Ti0.2W0.2)Si2. Journal of Materiomics, 2019,5(3):337-343.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
QIN Y, LIU J X, LI F, et al. A high entropy silicide by reactive spark plasma sintering. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2019,8(1):148-152.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
ZHANG H, AKHTAR F. Processing and characterization of refractory quaternary and quinary high-entropy carbide composite. Entropy, 2019,21(5):474.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
POGREBNJAK A D, BAGDASARYAN A A, BERESNEV V M, et al. The effects of Cr and Si additions and deposition conditions on the structure and properties of the (Zr-Ti-Nb)N coatings. Ceramics International, 2017,43(1, Part A):771-782.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
POGREBNJAK A D, YAKUSHCHENKO I V, BONDAR O V, et al. Irradiation resistance, microstructure and mechanical properties of nanostructured (TiZrHfVNbTa)N coatings. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016,679:155-163.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
MAYRHOFER P H, KIRNBAUER A, ERTELTHALER P, et al. High-entropy ceramic thin films: a case study on transition metal diborides. Scripta Materialia, 2018,149:93-97.
DOI URL |
| [67] | ZHONG Y, SABAROU H, YAN X, et al. Exploration of high entropy ceramics (HECs) with computational thermodynamics - a case study with LaMnO3±δ. Materials & Design, 2019,182:108060. |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 余乐洋阳, 赵芳霞, 张舒心, 徐以祥, 牛亚然, 张振忠, 郑学斌. 感应等离子球化技术制备喷涂用高熵硼化物粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 808-816. |
| [3] | 陈相杰, 李玲, 雷添福, 王佳佳, 汪尧进. 相界工程和畴工程调控(1-x)(0.8PZT-0.2PZN)-xBZT陶瓷的压电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 729-734. |
| [4] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [5] | 李文元, 徐佳楠, 邓瀚澳, 常爱民, 张博. 钒取代对LaTaO4陶瓷微观结构和微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 697-703. |
| [6] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [7] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [8] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [9] | 黄子鹏, 贾文晓, 李玲霞. (Ti0.5W0.5)5+掺杂MgNb2O6陶瓷的晶体结构与太赫兹介电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 647-655. |
| [10] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [11] | 尹长志, 成名飞, 雷微程, 蔡弋炀, 宋小强, 付明, 吕文中, 雷文. Ga3+掺杂对SrAl2Si2O8陶瓷晶体结构及微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 704-710. |
| [12] | 孙雨萱, 王政, 时雪, 史颖, 杜文通, 满振勇, 郑嘹赢, 李国荣. 缺陷偶极子热稳定性对Fe掺杂PZT陶瓷机电性能影响研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 545-551. |
| [13] | 陈义, 邱海鹏, 陈明伟, 徐昊, 崔恒. SiC/SiC复合材料基体硼改性方法及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [14] | 崔宁, 张玉新, 王鲁杰, 李彤阳, 于源, 汤华国, 乔竹辉. (TiVNbMoW)Cx高熵陶瓷的单相形成过程与碳空位调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [15] | 熊思宇, 莫尘, 朱肖伟, 朱国斌, 陈德钦, 刘来君, 施晓东, 李纯纯. 超低介电常数LiBxAl1-xSi2O6微波介质陶瓷的低温烧结[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 536-544. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||