
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (6): 579-591.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200555
Special Issue: 【虚拟专辑】分离膜,复相陶瓷(2020~2021)
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Ziyi1( ), ZHANG Jiajia1, ZOU Xiaoqin2, ZUO Jiayu1, LI Jun1, LIU Yingshu1(
), ZHANG Jiajia1, ZOU Xiaoqin2, ZUO Jiayu1, LI Jun1, LIU Yingshu1( ), PUI David Youhong3,4
), PUI David Youhong3,4
Received:2020-09-22
Revised:2020-10-27
Published:2021-06-20
Online:2020-12-10
Contact:
LIU Yingshu, professor. E-mail: ysliu@ustb.edu.cn
About author:LI Ziyi(1990-), male, associate professor. E-mail: ziyili@ustb.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
LI Ziyi, ZHANG Jiajia, ZOU Xiaoqin, ZUO Jiayu, LI Jun, LIU Yingshu, PUI David Youhong. Synthesis and Gas Separation of Chabazite Zeolite Membranes[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 579-591.
| Method | Advantage | Disadvantage | Status of use |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-situ synthesis | ① Simple production equipment ② Easy to use | ① Low success rate ② Long synthesis time ③ Difficult to control | Less research, basically used for the synthesis of SAPO-34 membrane |
| Secondary growth | ① Simple production equipment ② High success rate ③ Short synthesis time | ① Tedious steps | More research, conducive to large-scale mass production |
| Microwave heating | ① High success rate ② Short synthesis time | ① Tedious steps ② High equipment cost ③ High energy consumption | New method, still in basic research stage |
Table 1 Comparison of CHA zeolite membrane synthesis methods
| Method | Advantage | Disadvantage | Status of use |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-situ synthesis | ① Simple production equipment ② Easy to use | ① Low success rate ② Long synthesis time ③ Difficult to control | Less research, basically used for the synthesis of SAPO-34 membrane |
| Secondary growth | ① Simple production equipment ② High success rate ③ Short synthesis time | ① Tedious steps | More research, conducive to large-scale mass production |
| Microwave heating | ① High success rate ② Short synthesis time | ① Tedious steps ② High equipment cost ③ High energy consumption | New method, still in basic research stage |
| Influencing factors | SSZ-13 | SAPO-34 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seed conditions | Support | α-Al2O3, mullite | α-Al2O3 |
| Seed crystal | Ball milled nano seeds | Flake nano seeds | |
| Seeding method | Dip coating | Wipe, electrophoretic deposition | |
| Hydrothermal synthesis conditions | Formula (structure directing agent, Si/Al, water content, cationic species) | Non-pure silica: 1SiO2 : (5-100)Al2O3 : (0.1-0.2)NaOH : (0-0.06)KOH(Oriented growth regulation) : (0.05-0.6)TMAdaOH : (0-0.05)TEAOH : (40-120)H2O Pure silica : 1SiO2 : (0.5-1.4)TMAdaOH : (0.5-1.4)HF : (3-6)H2O | 1Al2O3 : (1-2)P2O5 : (0.3-0.6)SiO2 : (1-4)TEAOH : (0-1.6)DPA : (55-400)H2O |
| Temperature | 160-170 ℃ | 180-230 ℃ | |
| Time | 24-72 h | 6-30 h | |
| Calcination conditions | Conventional calcination | 400-550 ℃ (6-12 h), temperature rise and fall rate (0.2-1) ℃/min | 400-480 ℃ (4-10 h), temperature rise and fall rate (0.5- 2) ℃/min |
| Rapid heat treatment | 700-1000 ℃ (0.5-2 min)+conventional calcination | 700 ℃ (1-5 min)+ conventional calcination | |
Table 2 Summary table of preferred conditions for secondary synthesis of SSZ-13 membrane and SAPO-34 membrane
| Influencing factors | SSZ-13 | SAPO-34 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seed conditions | Support | α-Al2O3, mullite | α-Al2O3 |
| Seed crystal | Ball milled nano seeds | Flake nano seeds | |
| Seeding method | Dip coating | Wipe, electrophoretic deposition | |
| Hydrothermal synthesis conditions | Formula (structure directing agent, Si/Al, water content, cationic species) | Non-pure silica: 1SiO2 : (5-100)Al2O3 : (0.1-0.2)NaOH : (0-0.06)KOH(Oriented growth regulation) : (0.05-0.6)TMAdaOH : (0-0.05)TEAOH : (40-120)H2O Pure silica : 1SiO2 : (0.5-1.4)TMAdaOH : (0.5-1.4)HF : (3-6)H2O | 1Al2O3 : (1-2)P2O5 : (0.3-0.6)SiO2 : (1-4)TEAOH : (0-1.6)DPA : (55-400)H2O |
| Temperature | 160-170 ℃ | 180-230 ℃ | |
| Time | 24-72 h | 6-30 h | |
| Calcination conditions | Conventional calcination | 400-550 ℃ (6-12 h), temperature rise and fall rate (0.2-1) ℃/min | 400-480 ℃ (4-10 h), temperature rise and fall rate (0.5- 2) ℃/min |
| Rapid heat treatment | 700-1000 ℃ (0.5-2 min)+conventional calcination | 700 ℃ (1-5 min)+ conventional calcination | |
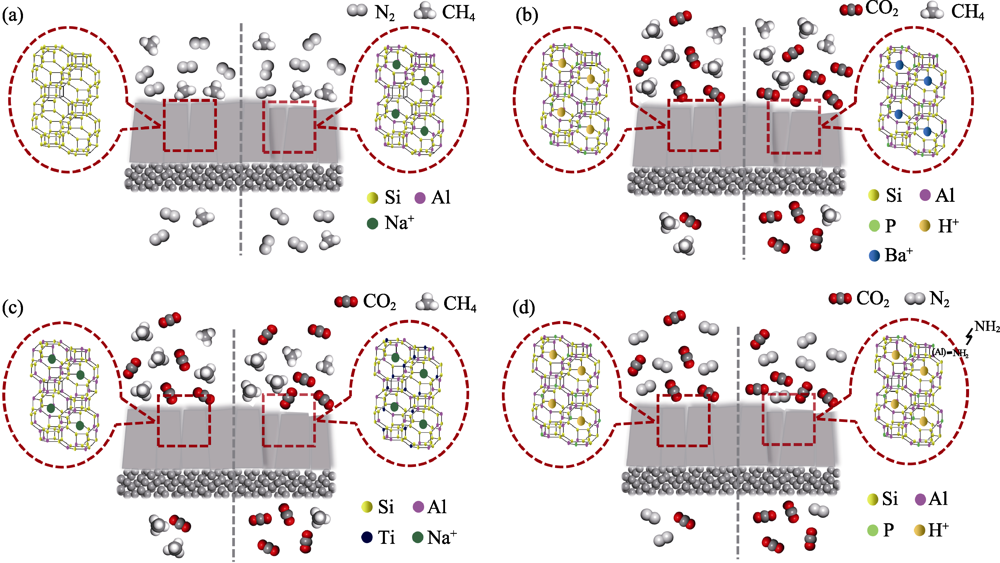
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of gas separation mechanisms on CHA zeolite membrane before (left) and after (right) the modulation of membrane surface chemistry[24,36,49,83,87] (a) Si/Al regulation; (b) Cation exchange; (c) Heteroatom replacement; (d) Amino functionalization
| Serial number | Ref. | Thickness/μm | Temperature/℃ | Pressure/MPa | Gas separation, X/Y | X permeance/ (×10-8, mol·m-2·s-1·Pa-1) | Separation selectivity, X/Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kalipcilar[ | 10-40 | 25 | - | H2/n-C4H10 | 14 | 8.7 |
| 2 | Zheng[ | 10 | 30 | 0.2 | C2H4/C2H6 | 0.29 | 11 |
| 3 | Feng[ | 4.3 | 20 | 0.138 | Kr/Xe | 12 | 35 |
| 4 | Yang[ | 3.7 | 22 | - | H2/C3H8 | 8.4 | 810 |
Table 3 Separation performances of H2, hydrocarbon and noble gases on CHA zeolite membranes
| Serial number | Ref. | Thickness/μm | Temperature/℃ | Pressure/MPa | Gas separation, X/Y | X permeance/ (×10-8, mol·m-2·s-1·Pa-1) | Separation selectivity, X/Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kalipcilar[ | 10-40 | 25 | - | H2/n-C4H10 | 14 | 8.7 |
| 2 | Zheng[ | 10 | 30 | 0.2 | C2H4/C2H6 | 0.29 | 11 |
| 3 | Feng[ | 4.3 | 20 | 0.138 | Kr/Xe | 12 | 35 |
| 4 | Yang[ | 3.7 | 22 | - | H2/C3H8 | 8.4 | 810 |
| Serial number | Ref. | Thickness/μm | Temperature/℃ | Pressure/MPa | Gas separation, X/Y | X permeance/ (×10-7, mol·m-2·s-1·Pa-1) | Separation selectivity, X/Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kosinov[ | 4-6 | 20 | 0.6 | CO2/CH4 | 2.5 | 42 |
| 20 | 0.6 | CO2/N2 | 2.5 | 12 | |||
| 2 | Wu[ | 6-8 | 20 | 0.27 | CO2/CH4 | 2.1 | 178 |
| 20 | 0.27 | N2/CH4 | 0.18 | 9 | |||
| 3 | Song[ | 6 | 25 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 5.6 | 56.5 |
| 25 | 0.2 | N2/CH4 | 0.89 | 10 | |||
| 4 | Li[ | 2 | 25 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 1.16 | 213 |
| 25 | 0.2 | N2/CH4 | 1.07 | 13 | |||
| 5 | Yu[ | 1.5 | -24 | 0.9 | CO2/CH4 | 79 | 76 |
| 6 | Karakiliç[ | 2-4 | 22 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 2.6 | 176 |
| 7 | Qiu[ | 0.44 | 20 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 48 | 153 |
| 8 | Kida[ | - | 40 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 17 | 54 |
| 40 | 0.1 | H2/CH4 | 11 | 34 | |||
| 9 | Tang[ | 10 | 20 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 9.3 | 208 |
| 10 | Kida[ | 5 | 25 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 40 | 130 |
| 11 | Imasaka[ | 3 | 40 | 0.3 | CO2/CH4 | 15 | 115 |
| 12 | Maghsoudi[ | 20 | 30 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 0.34 | 21.6 |
| 13 | Yu[ | 1.3 | 3 | 0.9 | CO2/CH4 | 84 | 47 |
| 14 | Li[ | 5 | 80 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 2.0 | 270 |
| 15 | Li[ | - | 24 | 0.138 | CO2/CH4 | 1.6 | 67 |
| 16 | Carreon[ | - | 22 | 0.138 | CO2/CH4 | 3.8 | 170 |
| 17 | Venna[ | - | 22 | 0.138 | CO2/CH4 | 5.0 | 245 |
| 22 | 0.138 | CO2/N2 | 2.1 | 39 | |||
| 18 | Huang[ | 2 | 22 | 0.074 | N2/CH4 | 4.93 | 11.3 |
| 19 | Chen[ | 2-3 | 25 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 1.18 | 160 |
| 20 | Chang[ | - | - | 4 | CO2/CH4 | 6.1 | 88 |
| 21 | Liu[ | 3 | 30 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 12 | 95 |
| 22 | Rehman[ | - | 80 | 0.4 | CO2/CH4 | 47.3 | 65 |
| 23 | Liu[ | 7-15 | 25 | 0.1 | CO2/N2 | 18.5 | 29.8 |
| 24 | Li[ | 4-6 | 22 | 7 | CO2/CH4 | 0.4 | 100 |
| 25 | Zhang[ | - | 20 | 4.6 | CO2/CH4 | 8.2 | 55 |
| 26 | Noble[ | - | 22 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 1.2 | 170 |
| 27 | Shi[ | 2-4 | 22 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 23.2 | 186 |
| 28 | Shi[ | 4-5 | 22 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 16.8 | 256 |
| 29 | Li[ | 3 | - | 4 | CO2/CH4 | 13.2 | 62 |
| 30 | Bai[ | 0.8 | - | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 25.3 | 70 |
Table 4 Separation performances of CO2/CH4, CO2/N2, N2/CH4, H2/CH4 on CHA zeolite membranes
| Serial number | Ref. | Thickness/μm | Temperature/℃ | Pressure/MPa | Gas separation, X/Y | X permeance/ (×10-7, mol·m-2·s-1·Pa-1) | Separation selectivity, X/Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kosinov[ | 4-6 | 20 | 0.6 | CO2/CH4 | 2.5 | 42 |
| 20 | 0.6 | CO2/N2 | 2.5 | 12 | |||
| 2 | Wu[ | 6-8 | 20 | 0.27 | CO2/CH4 | 2.1 | 178 |
| 20 | 0.27 | N2/CH4 | 0.18 | 9 | |||
| 3 | Song[ | 6 | 25 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 5.6 | 56.5 |
| 25 | 0.2 | N2/CH4 | 0.89 | 10 | |||
| 4 | Li[ | 2 | 25 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 1.16 | 213 |
| 25 | 0.2 | N2/CH4 | 1.07 | 13 | |||
| 5 | Yu[ | 1.5 | -24 | 0.9 | CO2/CH4 | 79 | 76 |
| 6 | Karakiliç[ | 2-4 | 22 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 2.6 | 176 |
| 7 | Qiu[ | 0.44 | 20 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 48 | 153 |
| 8 | Kida[ | - | 40 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 17 | 54 |
| 40 | 0.1 | H2/CH4 | 11 | 34 | |||
| 9 | Tang[ | 10 | 20 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 9.3 | 208 |
| 10 | Kida[ | 5 | 25 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 40 | 130 |
| 11 | Imasaka[ | 3 | 40 | 0.3 | CO2/CH4 | 15 | 115 |
| 12 | Maghsoudi[ | 20 | 30 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 0.34 | 21.6 |
| 13 | Yu[ | 1.3 | 3 | 0.9 | CO2/CH4 | 84 | 47 |
| 14 | Li[ | 5 | 80 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 2.0 | 270 |
| 15 | Li[ | - | 24 | 0.138 | CO2/CH4 | 1.6 | 67 |
| 16 | Carreon[ | - | 22 | 0.138 | CO2/CH4 | 3.8 | 170 |
| 17 | Venna[ | - | 22 | 0.138 | CO2/CH4 | 5.0 | 245 |
| 22 | 0.138 | CO2/N2 | 2.1 | 39 | |||
| 18 | Huang[ | 2 | 22 | 0.074 | N2/CH4 | 4.93 | 11.3 |
| 19 | Chen[ | 2-3 | 25 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 1.18 | 160 |
| 20 | Chang[ | - | - | 4 | CO2/CH4 | 6.1 | 88 |
| 21 | Liu[ | 3 | 30 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 12 | 95 |
| 22 | Rehman[ | - | 80 | 0.4 | CO2/CH4 | 47.3 | 65 |
| 23 | Liu[ | 7-15 | 25 | 0.1 | CO2/N2 | 18.5 | 29.8 |
| 24 | Li[ | 4-6 | 22 | 7 | CO2/CH4 | 0.4 | 100 |
| 25 | Zhang[ | - | 20 | 4.6 | CO2/CH4 | 8.2 | 55 |
| 26 | Noble[ | - | 22 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 1.2 | 170 |
| 27 | Shi[ | 2-4 | 22 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 23.2 | 186 |
| 28 | Shi[ | 4-5 | 22 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 16.8 | 256 |
| 29 | Li[ | 3 | - | 4 | CO2/CH4 | 13.2 | 62 |
| 30 | Bai[ | 0.8 | - | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 25.3 | 70 |
| [1] |
LI S, CARREON M A, ZHANG Y, et al. Scale-up of SAPO-34 membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010,352(1/2):7-13.
DOI URL |
| [2] | NAIR S, LAI Z, NIKOLAKIS V, et al. Separation of close- boiling hydrocarbon mixtures by MFI and FAU membranes made by secondary growth. Microporous & Mesoporous Materials, 2001,48(1):219-228. |
| [3] |
GU X H, DONG J H, NENOFF T M, et al. Synthesis of defect-free FAU-type zeolite membranes and separation for dry and moist CO2/N2 mixtures. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2005,44(4):937-944.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZHU W, GORA L, VAN DEN BERG A W C, et al. Water vapour separation from permanent gases by a zeolite-4A membrane. Journal of Membrane Science, 2005,253(1/2):57-66.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LI S, MARTINEK J G, FALCONER J L, et al. High-pressure CO2/CH4 separation using SAPO-34 membranes. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2005,44(9):3220-3228.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
MA L, CHENG Y, CAVATAIO G, et al. Characterization of commercial Cu-SSZ-13 and Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts with hydrothermal treatment for NH3-SCR of NOx in diesel exhaust. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013,225(3):323-330.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
KALIPCILAR H, BOWEN T C, NOBLE R D, et al. Synthesis and separation performance of SSZ-13 zeolite membranes on tubular supports. Chemistry of Materials, 2002,14(8):3458-3464.
DOI URL |
| [8] | ZHANG L X, JIA M D, MIN E. Synthesis of SAPO-34/ceramic composite membranes. Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, 1997,105(11):2211-2216. |
| [9] |
YAN N, XU H, ZHANG W, et al. Probing locations of organic structure-directing agents (OSDAs) and host-guest interactions in CHA-type SAPO-34/44. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2018,264:55-59.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
YU M, NOBLE R D, FALCONER J L. Zeolite membranes: microstructure characterization and permeation mechanisms. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2011,44(11):1196-1206.
DOI URL |
| [11] | WANG JIN-QU, YANG JIAN-HUA, LI HUA-ZHENG, et al. Research progress of zeolite molecular sieve membrane. Membrane Science and Technology, 2014,34(3):1-7, 42. |
| [12] |
CARO J, NOACK M. Zeolite membranes-recent developments and progress. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2008,115(3):215-233.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
BOWEN T C, NOBLE R D, FALCONER J L. Fundamentals and applications of pervaporation through zeolite membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2004,245(1/2):1-33.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
KOSINOV N, AUFFRET C, GVCVCYENER C, et al. High flux high-silica SSZ-13 membrane for CO2 separation. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014,2(32):13083-13092.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
TOTH A J, SZILAGYI B, HAAZ E, et al. Enhanced separation of maximum boiling azeotropic mixtures with extractive heterogeneous-azeotropic distillation. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2019,147:55-62.
DOI URL |
| [16] | CLET G, GORA L, NISHIYAMA N, et al. An alternative synthesis method for zeolite Y membranes. Chemical Communications, 2001,1:41-42. |
| [17] |
JIANG H, ZHANG B, LIN Y S, et al. Synthesis of zeolite membranes. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004,49(24):2547-2554.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
HONG M, LI S, FUNKE H F, et al. Ion-exchanged SAPO-34 membranes for light gas separations. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2007,106(1/2/3):140-146.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LI S, FALCONER J L, NOBLE R D. SAPO-34 membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2004,241(1):121-135.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
SAPATSIS M, LOVALLO M, OKUBO T, et al. Characterization of zeolite L nanoclusters. Chemistry of Materials, 1995,7(9):1734-1741.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
WU T, DIAZ M C, ZHENG Y, et al. Influence of propane on CO2/CH4 and N2/CH4 separations in CHA zeolite membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015,473:201-209.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
CHISHOLM N O, FUNKE H H, NOBLE R D, et al. Carbon dioxide/alkane separations in a SSZ-13 membrane. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018,568:17-21.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
CARREON M A, LI S, FALCONER J L, et al. SAPO-34 seeds and membranes prepared using multiple structure directing agents. Advanced Materials, 2008,20(4):729-732.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
KOSINOV N, AUFFRET C, BORGHUIS G J, et al. Influence of the Si/Al ratio on the separation properties of SSZ-13 zeolite membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015,484:140-145.
DOI URL |
| [25] | LEE M, HONG S, KIM D, et al. Chabazite-type zeolite membranes for effective CO2 separation: the role of hydrophobicity and defect structure. Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019,11(4):3946-3960. |
| [26] |
HONG S, KIM D, JEONG Y, et al. Healing of microdefects in SSZ-13 membranes via filling with dye molecules and its effect on dry and wet CO2 separations. Chemistry of Materials, 2018,30(10):3346-3358.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ZHENG Y, HU N, WANG H, et al. Preparation of steam-stable high-silica CHA (SSZ-13) membranes for CO2/CH4 and C2H4/C2H6 separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015,475:303-310.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ZHOU R, WANG H, WANG B, et al. Defect-patching of zeolite membranes by surface modification using siloxane polymers for CO2 separation. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015,54(30):7516-7523.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SONG S, GAO F, ZHANG Y, et al. Preparation of SSZ-13 membranes with enhanced fluxes using asymmetric alumina supports for N2/CH4 and CO2/CH4 separations. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019,209:946-954.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
WANG B, ZHENG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Separation of light gas mixtures using zeolite SSZ-13 membranes. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019,275:191-199.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
LI X, WANG Y, WU T, et al. High-performance SSZ-13 membranes prepared using ball-milled nanosized seeds for carbon dioxide and nitrogen separations from methane. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2020,28(5):1285-1292.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
LIANG L, ZHU M, CHEN L, et al. Single gas permeance performance of high silica SSZ-13 zeolite membranes. Membranes, 2018,8(3):43.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
JIANG J, WANG X, ZHANG Y, et al. Fabrication of pure-phase CHA zeolite membranes with ball-milled seeds at low K + concentration. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials , 2015,215:98-108.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
JIANG J, PENG L, WANG X, et al. Effect of Si/Al ratio in the framework on the pervaporation properties of hollow fiber CHA zeolite membranes. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019,273:196-202.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
WU T, LUCERO J, CRAWFORD J M, et al. SAPO-34 membranes for xenon capture from air. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019,573:288-292.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
VENNA S R, CARREON M A. Amino-functionalized SAPO-34 membranes for CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 separation. Langmuir, 2011,27(6):2888-2894.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ZONG Z, CARREON M A. Thin SAPO-34 membranes synthesized in stainless steel autoclaves for N2/CH4 separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017,524:117-123.
DOI URL |
| [38] | FUNKE H H, TOKAY B, ZHOU R, et al. Spatially resolved gas permeation through SAPO-34 membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012,409:212-221. |
| [39] | PING E W, ZHOU R, FUNKE H H, et al. Seeded-gel synthesis of SAPO-34 single channel and monolith membranes, for CO2/CH4 separations. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012,415:770-775. |
| [40] |
HUANG Y, WANG L, SONG Z, et al. Growth of high-quality, thickness-reduced zeolite membranes towards N2/CH4 separation using high-aspect-ratio seeds. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015,54(37):10843-10847.
DOI URL |
| [41] | CHEN Y, ZHANG Y, ZHANG C, et al. Fabrication of high-flux SAPO-34 membrane on α-Al2O3 four-channel hollow fibers for CO2 capture from CH4. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2017,18:30-40. |
| [42] |
WANG M, LI M, CHANG N, et al. Vapor separation of methanol-dimethyl carbonate mixture on SAPO-34 zeolite membrane. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018,565:311-321.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
CHANG N, TANG H, BAI L, et al. Optimized rapid thermal processing for the template removal of SAPO-34 zeolite membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018,552:13-21.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
LIGHTFOOT P, WOODCOCK D A, MAPLE M J, et al. The widespread occurrence of negative thermal expansion in zeolites. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2001,11(1):212-216.
DOI URL |
| [45] | SATO K, SUGIMOTO K, SHIMOTSUMA N, et al. Development of practically available up-scaled high-silica CHA-type zeolite membranes for industrial purpose in dehydration of N-methyl pyrrolidone solution. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012,409:82-95. |
| [46] |
BRAUN I, SCHULZ EKLOFF G, WOHRLE D, et al. Synthesis of AlPO4-5 in a microwave-heated, continuous-flow, high- pressure tube reactor. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 1998,23(1/2):79-81.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
HU N, LI Y, ZHONG S, et al. Microwave synthesis of zeolite CHA (chabazite) membranes with high pervaporation performance in absence of organic structure directing agents. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2016,228:22-29.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
LIU X, DU S, ZHANG B. The seeded growth of dense and thin SAPO-34 membranes on porous α-Al2O3 substrates under microwave irradiation. Materials Letters, 2013,91:195-197.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
CHEW T L, AHMAD A L, BHATIA S. Ba-SAPO-34 membrane synthesized from microwave heating and its performance for CO2/CH4 gas separation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011,171(3):1053-1059.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
AKHTAR F, OJUVA A, WIRAWAN S K, et al. Hierarchically porous binder-free silicalite-1 discs: a novel support for all- zeolite membranes. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011,21(24):8822-8828.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
HE Y, CUI X, LIU X, et al. Preparation of self-supporting NaA zeolite membranes using geopolymers. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013,447:66-72.
DOI URL |
| [52] | STOEGER J A, CHOI J, TSAPATSIS M. Rapid thermal processing and separation performance of columnar MFI membranes on porous stainless steel tubes. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011,4(9):3479-3486. |
| [53] |
REHMAN R U, SONG Q, PENG L, et al. Hydrophobic modification of SAPO-34 membranes for improvement of stability under wet condition. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2019,27(10):2397-2406.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
MU Y, CHEN H, XIANG H, et al. Defects-healing of SAPO-34 membrane by post-synthesis modification using organosilica for selective CO2 separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019,575:80-88.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
LIU B, TANG C, LI X, et al. High-performance SAPO-34 membranes for CO2 separations from simulated flue gas. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020,292:109712.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
KOSINOV N, AUFFRET C, SRITAPHI V G P, et al. Influence of support morphology on the detemplation and permeation of ZSM-5 and SSZ-13 zeolite membranes. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2014,197:268-277.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
YU L, HOLMGREN A, HEDLUND J. A novel method for fabrication of high-flux zeolite membranes on supports with arbitrary geometry. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019,7(17):10325-10330.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
CARREON M A, LI S, FALCONER J L, et al. Alumina- supported SAPO-34 membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008,130(16):5412-5413.
DOI URL |
| [59] | LIU J Q, LUO Y B, LI M G, et al. Synthesis of nanosized SSZ-13 zeolite and performance of its mixed matrix membrane for CO2/CH4 separation. China Petroleum Processing & Petrochemical Technology, 2019,21(2):19-26. |
| [60] |
TAKATA T, TSUNOJI N, TAKAMITSU Y, et al. Nanosized CHA zeolites with high thermal and hydrothermal stability derived from the hydrothermal conversion of FAU zeolite. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2016,225:524-533.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
NAJAFI N, ASKARI S, HALLADJ R. Hydrothermal synthesis of nanosized SAPO-34 molecular sieves by different combinations of multi templates. Powder Technology, 2014,254:324-330.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
YANG H, LIU X, LU G, et al. Synthesis of SAPO-34 nanoplates via hydrothermal method. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2016,225:144-153.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
SUN Q, WANG N, GUO G, et al. Ultrafast synthesis of nano- sized zeolite SAPO-34 with excellent MTO catalytic performance. Chemical Communications, 2015,51(91):16397-16400.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
KARAKILIÇ P, WANG X, KAPTEIJN F, et al. Defect-free high-silica CHA zeolite membranes with high selectivity for light gas separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019,586:34-43.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
JABBARI Z, FATEMI S, DAVOODPOUR M. Comparative study of seeding methods; dip-coating, rubbing and EPD, in SAPO-34 thin film fabrication. Advanced Powder Technology, 2014,25(1):321-330.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
HENGE Q, ZHANG Y, KONG L, et al. High performance SSZ-13 membranes prepared at low temperature. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020,603:118023.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
WHITE J C, DUTTA P K, SHQAU K, et al. Synthesis of ultrathin zeolite Y membranes and their application for separation of carbon dioxide and nitrogen gases. Langmuir, 2010,26(12):10287-10293.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
BOHSTRÖM Z, ARSTAD B, LILLERUD K P. Preparation of high silica chabazite with controllable particle size. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2014,195:294-302.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
VAN HEYDEN H, MINTOVA S, BEIN T. Nanosized SAPO-34 synthesized from colloidal solutions. Chemistry of Materials, 2008,20(9):2956-2963.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
MIYAMOTO M, NAKATANI T, FUJIOKA Y, et al. Verified synthesis of pure silica CHA-type zeolite in fluoride media. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2015,206:67-74.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
KIDA K, MAETA Y, YOGO K. Preparation and gas permeation properties on pure silica CHA-type zeolite membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017,522:363-370.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
FENG X, ZONG Z, ELSAIDIl S K, et al. Kr/Xe separation over a chabazite zeolite membrane. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016,138(31):9791-9794.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
CARREON M A. Molecular sieve membranes for N2/CH4 separation. Journal of Materials Research, 2018,33(1):32-43.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
LI S, FALCONER J L, NOBLE R D. SAPO-34 membranes for CO2/CH4 separations: effect of Si/Al ratio. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2008,110(2/3):310-317.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
KIM S J, LIU Y, MOORE J S, et al. Thin hydrogen-selective SAPO-34 zeolite membranes for enhanced conversion and selectivity in propane dehydrogenation membrane reactors. Chemistry of Materials, 2016,28(12):4397-4402.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
RIVERA RAMOS M E, RUIZ MERCADO G J, HERNANDEZ MALDONADO A J. Separation of CO2 from light gas mixtures using ion-exchanged silicoaluminophosphate nanoporous sorbents. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008,47(15):5602-5610.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
AVILA A M, FUNKE H H, ZHANG Y, et al. Concentration polarization in SAPO-34 membranes at high pressures. Journal of Membrane Science, 2009,335(1/2):32-36.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
ZHANG Y, TOKAY B, FUNKE H H, et al. Template removal from SAPO-34 crystals and membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010,363(1/2):29-35.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
PENG C, LIU Z, HOORIMOTO A, et al. Preparation of nanosized SSZ-13 zeolite with enhanced hydrothermal stability by a two-stage synthetic method. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2018,255:192-199.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
KIM J, JANG E, HONG S, et al. Microstructural control of a SSZ-13 zeolite film via rapid thermal processing. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019,591:117342.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
TANG H, BAI L, WANG M, et al. Fast synthesis of thin high silica SSZ-13 zeolite membrane using oil-bath heating. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019,44(41):23107-23119.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
YANG S, KWON Y H, KOH D Y, et al. Highly selective SSZ-13 zeolite hollow fiber membranes by ultraviolet activation at near-ambient temperature. ChemNanoMat, 2019,5(1):61-67.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
KIDA K, MAETA Y, YOGO K. Pure silica CHA-type zeolite membranes for dry and humidified CO2/CH4 mixtures separation. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018,197:116-121.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
LEE M, JEONG Y, HONG S, et al. High performance CO2-perm-selective SSZ-13 membranes: elucidation of the link between membrane material and module properties. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020,611:118390.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
DJIEUGOUE M A, PRAKASH A M, KEVAN L. Catalytic study of methanol-to-olefins conversion in four small-pore silicoaluminophosphate molecular sieves: influence of the structural type, nickel incorporation, nickel location, and nickel concentration. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2000,104(27):6452-6461.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
CHEN X, GUO J, FU Z, et al. Characterization and catalytic behaviors of methylamine modified FAU zeolites. Journal of Porous Materials, 2013,20(5):1271-1281.
DOI URL |
| [87] |
IMASAKA, ISHII H, HAYASHI J, et al. Synthesis of CHA-type titanosilicate zeolites using titanium oxide as Ti source and evaluation of their physicochemical properties. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019,273:243-248.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
ARAKI S, ISHII H, IMASAKA S, et al. Synthesis and gas permeation properties of chabazite-type titanosilicate membranes synthesized using nano-sized seed crystals. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020,292:109798.
DOI URL |
| [89] | SERGEI A ZUBKOV, LEONID M KUSTOV, VADIM B KAZANSKY, et al. Investigation of hydroxyl groups in crystalline silicoaluminophosphate SAPO-34 by diffuse reflectance infrared spectroscopy. Journal of the Chemical Society, 1991,87:897. |
| [90] |
HUANG J, ZOU J, HO W S W. Carbon dioxide capture using a CO-selective facilitated transport membrane. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008,47(4):1261-1267.
DOI URL |
| [91] |
ZOU J, HO W S W. CO2-selective polymeric membranes containing amines in crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol). Journal of Membrane Science, 2006,286(1/2):310-321.
DOI URL |
| [92] | TEE Y H, ZOU J, HO W S W. CO2-selective membranes containing dimethylglycine mobile carriers and polyethylenimine fixed carrier. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2006,37(1):37-47. |
| [93] |
SINGH Z V, COWAN M G, MCDANEL W M, et al. Determination and optimization of factors affecting CO2/CH4 separation performance in poly(ionic liquid)-ionic liquid-zeolite mixed-matrix membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016,509:149-155.
DOI URL |
| [94] |
BARA J E, CAMPER D E, GIN D L, et al. Room-temperature ionic liquids and composite materials: platform technologies for CO2 capture. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2010,43(1):152-159.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
LIU B, ZHOU R, BU N, et al. Room-temperature ionic liquids modified zeolite SSZ-13 membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017,524:12-19.
DOI URL |
| [96] |
CHEN K J, MADDEN D G, PHAM T, et al. Tuning pore size in square-lattice coordination networks for size-selective sieving of CO2. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016,55(35):10268-10272.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
SINGH Z V, COWAN M G, MCDANEL W M, et al. Determination and optimization of factors affecting CO2/CH4 separation performance in poly (ionic liquid)-ionic liquid-zeolite mixed-matrix membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016,509:149-155.
DOI URL |
| [98] |
IMASAKA S, ITAKURA M, YANO K, et al. Rapid preparation of high-silica CHA-type zeolite membranes and their separation properties. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018,199:298-303.
DOI URL |
| [99] |
MAGHSOUDI H, SOLTANIEH M. Simultaneous separation of H2S and CO2 from CH4 by a high silica CHA-type zeolite membrane. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014,470:159-165.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
YU L, HOLMGREN A, ZHOU M, et al. Highly permeable CHA membranes prepared by fluoride synthesis for efficient CO2/CH4 separation. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018,6(16):6847-6853.
DOI URL |
| [101] |
LI S, FALCONER J L, NOBLE R D. Improved SAPO-34 membranes for CO2/CH4 separations. Advanced Materials, 2006,18(19):2601-2603.
DOI URL |
| [102] |
SHI H. Synthesis of SAPO-34 zeolite membranes with the aid of crystal growth inhibitors for CO2-CH4 separation. New Journal of Chemistry, 2014,38(11):5276-5278.
DOI URL |
| [103] |
SHI H. Organic template-free synthesis of SAPO-34 molecular sieve membranes for CO2-CH4 separation. RSC Advances, 2015,5(48):38330-38333.
DOI URL |
| [104] |
LI M, ZHANG J, LIU X, et al. Synthesis of high performance SAPO-34 zeolite membrane by a novel two-step hydrothermal synthesis+dry gel conversion method. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2016,225:261-271.
DOI URL |
| [105] |
BAI L, CHANG N, LI M, et al. Ultrafast synthesis of thin SAPO-34 zeolite membrane by oil-bath heating. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2017,241:392-399.
DOI URL |
| [106] |
KOSINOV N, GASCON J, KAPTEIJN F, et al. Recent developments in zeolite membranes for gas separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016,499:65-79.
DOI URL |
| [1] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | TIAN Ruizhi, LAN Zhengyi, YIN Jie, HAO Nanjing, CHEN Hangrong, MA Ming. Microfluidic Technology Based Synthesis of Inorganic Nano-biomaterials: Principles and Progress [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [8] | ZHANG Jiguo, WU Tian, ZHAO Xu, YANG Fan, XIA Tian, SUN Shien. Improvement of Cycling Stability of Cathode Materials and Industrialization Process for Sodium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [9] | XIN Zhenyu, GUO Ruihua, WUREN Tuoya, WANG Yan, AN Shengli, ZHANG Guofang, GUAN Lili. Pt-Fe/GO Nanocatalysts: Preparation and Electrocatalytic Performance on Ethanol Oxidation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 379-387. |
| [10] | YIN Jie, GENG Jiayi, WANG Kanglong, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Recent Advances in 3D Printing and Densification of SiC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [11] | CHEN Guangchang, DUAN Xiaoming, ZHU Jinrong, GONG Qing, CAI Delong, LI Yuhang, YANG Donglei, CHEN Biao, LI Xinmin, DENG Xudong, YU Jin, LIU Boya, HE Peigang, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. Advanced Ceramic Materials in Helicopter Special Structures: Research Progress and Application Prospect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [12] | FAN Xiaobo, ZU Mei, YANG Xiangfei, SONG Ce, CHEN Chen, WANG Zi, LUO Wenhua, CHENG Haifeng. Research Progress on Proton-regulated Electrochemical Ionic Synapses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [13] | HAIREGU Tuxun, GUO Le, DING Jiayi, ZHOU Jiaqi, ZHANG Xueliang, NUERNISHA Alifu. Research Progress of Optical Bioimaging Technology Assisted by Upconversion Fluorescence Probes in Tumor Imaging [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [14] | SUN Shujuan, ZHENG Nannan, PAN Haokun, MA Meng, CHEN Jun, HUANG Xiubing. Research Progress on Preparation Methods of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [15] | TAO Guilong, ZHI Guowei, LUO Tianyou, OUYANG Peidong, YI Xinyan, LI Guoqiang. Progress on Key Technologies of Cavity-structured Thin Film Bulk Acoustic Wave Filter [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||