
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (7): 738-744.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200506
Special Issue: 【虚拟专辑】抗菌材料(2020~2021)
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Endian1,2( ), CHANG Jiang1(
), CHANG Jiang1( )
)
Received:2020-08-31
Revised:2020-10-28
Published:2021-07-20
Online:2020-11-05
Contact:
CHANG Jiang, professor. E-mail:jchang@mail.sic.ac.cn
About author:WANG Endian (1991-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail:wangendian@student.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Endian, CHANG Jiang. Mo Doped Cuprorivaite: Preparation, Antibacterial and Cytocompatibility[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 738-744.
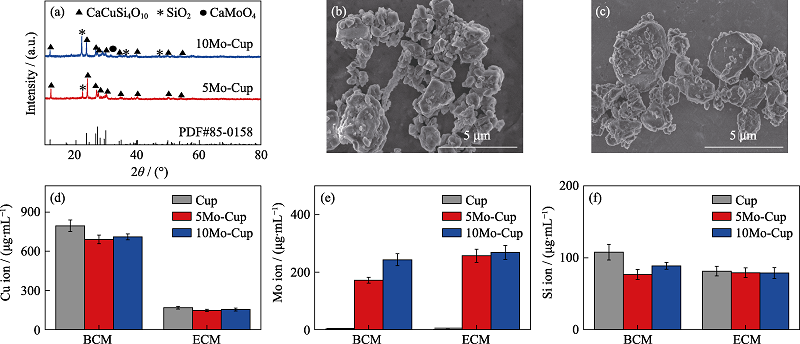
Fig. 1 Properties of Mo doped cuprorivaite (Mo-Cup) (a) XRD patterns, SEM images of (b) 5Mo-Cup and (c) 10Mo-Cup, and content of (d) copper ion, (e) molybdenum ion and (f) silicon ion released from Cup, 5Mo-Cup and 10Mo-Cup in bacterial culture medium (BCM) and cell culture medium (ECM)
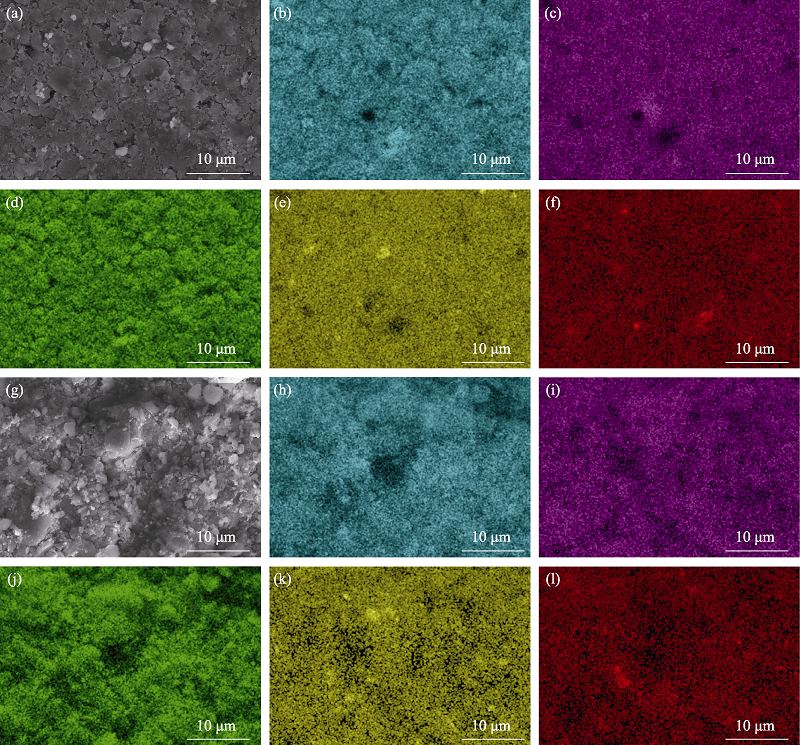
Fig. 2 (a,g) SEM images of (a-f) 5Mo-Cup and (g-l) 10Mo-Cup and (b-f, h-l) corresponding elemental maps (b, h): Si; (c, i): Ca; (d, j): O; (e, k): Cu; (f, l): Mo
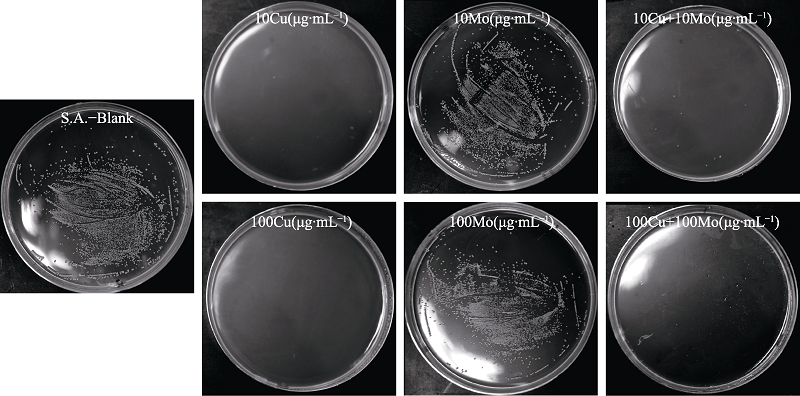
Fig. 3 Effect of different concentrations of copper ion (CuSO4·5H2O) solution and molybdenum ion ((NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O) solution on Staphylococcus aureus
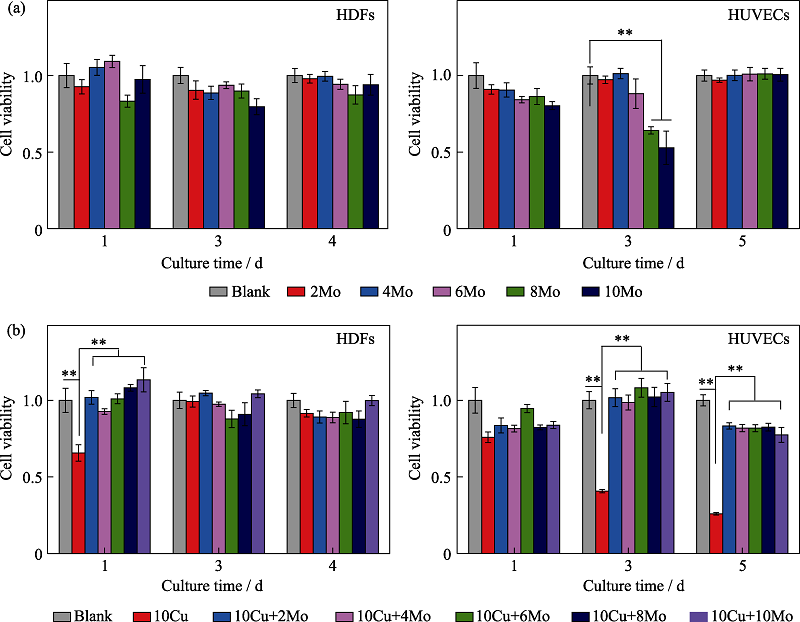
Fig. 4 Effects of culture medium containing 10 μg?mL-1 copper ion, molybdenum ion and copper-molybdenum ions on cell activity assay (a) Effects of molybdenum ions on the proliferation of human dermal fibroblast (HDFs) and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs)(xMo stands for medium containing x μg?mL-1 molybdenum ion; x=2, 4, 6, 8, 10); (b) Effects of copper molybdenum ions combination on the proliferation of HDFs and HUVECs (10Cu+yMo stands for medium containing 10 μg?mL-1 copper ions and y μg?mL-1 molybdenum ions; y=2, 4, 6, 8, 10). **: p<0.01
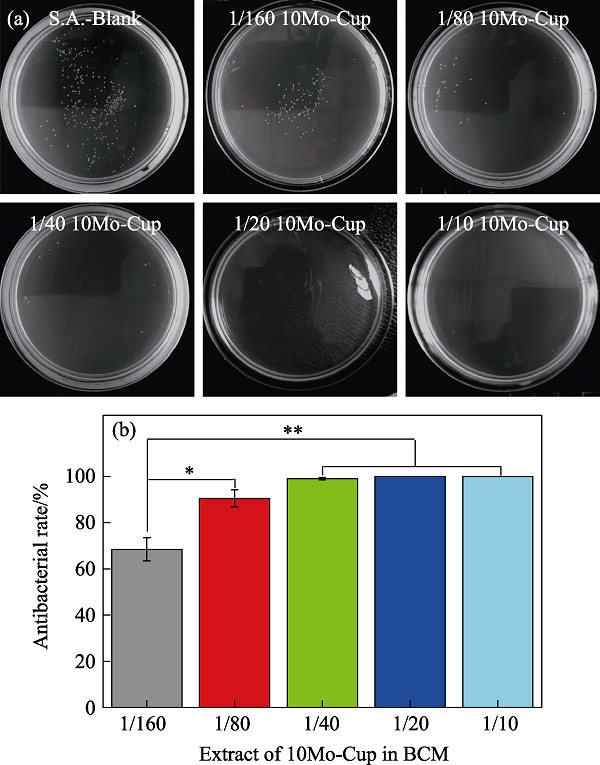
Fig. 5 Inhibition effect of extract from 10Mo-Cup bacterial culture medium on Staphylococcus aureus (a) Number of Staphylococcus aureus after being treated with different dilutions of 10Mo-Cup medium extract; (b) Related antibacterial rate. *: p<0.05; **: p<0.01
| Dilutions of the extract | Cu ion/ (μg∙mL-1) | Si ion/ (μg∙mL-1) | Mo ion/ (μg∙mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 709.86 | 88.71 | 243.10 |
| 1/40 | 17.75 | 2.22 | 6.08 |
| 1/80 | 8.87 | 1.11 | 3.04 |
| 1/160 | 4.44 | 0.55 | 1.52 |
Table 1 Ion contents in the extract with 10Mo-Cup bacterial culture medium after different dilutions
| Dilutions of the extract | Cu ion/ (μg∙mL-1) | Si ion/ (μg∙mL-1) | Mo ion/ (μg∙mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 709.86 | 88.71 | 243.10 |
| 1/40 | 17.75 | 2.22 | 6.08 |
| 1/80 | 8.87 | 1.11 | 3.04 |
| 1/160 | 4.44 | 0.55 | 1.52 |
| Dilution of the extract | Cu ion/ (μg∙mL-1) | Si ion/ (μg∙mL-1) | Mo ion/ (μg∙mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 154.35 | 78.85 | 268.57 |
| 1/4 | 38.59 | 19.71 | 67.14 |
| 1/8 | 19.29 | 9.86 | 33.57 |
| 1/16 | 9.65 | 4.93 | 16.79 |
Table 2 Ion contents in the extract with 10Mo-Cup cell culture medium after different dilutions
| Dilution of the extract | Cu ion/ (μg∙mL-1) | Si ion/ (μg∙mL-1) | Mo ion/ (μg∙mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 154.35 | 78.85 | 268.57 |
| 1/4 | 38.59 | 19.71 | 67.14 |
| 1/8 | 19.29 | 9.86 | 33.57 |
| 1/16 | 9.65 | 4.93 | 16.79 |
| [1] | LI P L, HAN F X, CAO W W, et al. Carbon quantum dots derived from lysine and arginine simultaneously scavenge bacteria and promote tissue repair. Applied Materials Today, 2020,6(19):100601. |
| [2] |
ZHANG Y, CHANG M L, BAO F, et al. Multifunctional Zn doped hollow mesoporous silica/polycaprolactone electrospun membranes with enhanced hair follicle regeneration and antibacterial activity for wound healing. Nanoscale, 2019,11(13):6315-6333.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
NING C, WANG X, LI L, et al. Concentration ranges of antibacterial cations for showing the highest antibacterial efficacy but the least cytotoxicity against mammalian cells: implications for a new antibacterial mechanism. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 2015,28(9):1815-1822.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
TAN S X, TAN S Z, LIU Y L, et al. Preparation and antibacterial property of copper-loaded activated carbon microspheres. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010,25(3):299-305.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
WU C T, ZHOU Y H, XU M C, et al. Copper-containing mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds with multifunctional properties of angiogenesis capacity, osteostimulation and antibacterial activity. Biomaterials, 2013,34(2):422-433.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
TIAN T, WU C T, CHANG J. Preparation and in vitro osteogenic, angiogenic and antibacterial properties of cuprorivaite (CaCuSi4O10, Cup) bioceramics. RSC Advances, 2016,6(51):45840-45849.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 孔妮. 掺铜硅酸钙生物陶瓷的制备与表征及其促血管化性能的研究. 上海: 上海交通大学硕士学位论文, 2015. |
| [8] |
KONG N, LIN K L, LI H Y, et al. Synergy effects of copper and silicon ions on stimulation of vascularization by copper-doped calcium silicate. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2014,2(8):1100-1110.
DOI URL |
| [9] | YANG Z J, LONG T, RAN L W, et al. Molybdenum's biological function and roles in animal production. Journal of Henan University of Science and Technology (Agricultrual Science), 2004(2):40-43. |
| [10] | WU M J. Molybdenum and human health. Studies of Trace Elements and Health, 2006,5(23):66-67. |
| [11] | WANG Q X. Trace element molybdenum and human health. Studies of Trace Elements and Health, 2003,4(20):58-59. |
| [12] | LIU M. The effect of molybdenum on human health. China Molybdenum Industry, 2001,5(25):43-45. |
| [13] | 田瑶. 四硫代钼酸铵抑制顺铂与人铜伴侣蛋白Atoxl的相互作用. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学硕士学位论文, 2018. |
| [14] |
ALVAREZ H M, XUE Y, ROBINSON C D, et al. Tetrathiomolybdate inhibits copper trafficking proteins through metal cluster formation. Science, 2010,327(5963):331-334.
DOI URL |
| [15] | PAN Q, KLEER C G, VAN GOLEN K L, et al. Copper deficiency induced by tetrathiomolybdate suppresses tumor growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Research, 2002,62(17):4854-4859. |
| [16] |
CHAN N, WILLIS A, KORNHAUSER N, et al. Influencing the tumor microenvironment: a phase II study of copper depletion using tetrathiomolybdate in patients with breast cancer at high risk for recurrence and in preclinical models of lung metastases. Clinical Cancer Research, 2017,23(3):666-676.
DOI URL |
| [17] | MIAO Z Z, LI G W, LIU C Z, et al. Study on antibacterial properties of copper-loaded chitosan particles. Journal of Henan Institute of Science and Technology, 2010,38(2):78-80. |
| [18] | XU Q, CHANG M L, ZHANG Y, et al. PDA/Cu bioactive hydrogel with "hot ions effect" for inhibition of drug-resistant bacteria and enhancement of infectious skin wound healing. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020,12(28):31255-31269. |
| [19] |
LI J, ZHAI D, LU F, et al. Preparation of copper-containing bioactive glass/eggshell membrane nanocomposites for improving angiogenesis, antibacterial activity and wound healing. Acta Biomater., 2016,36:254-266.
DOI URL |
| [1] | TANG Xinli, DING Ziyou, CHEN Junrui, ZHAO Gang, HAN Yingchao. In vivo Distribution and Metabolism of Calcium Phosphate Nanomaterials Based on Fluorescent Labeling with Rare Earth Europium Ions [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 754-764. |
| [2] | JIANG Zongyu, HUANG Honghua, QING Jiang, WANG Hongning, YAO Chao, CHEN Ruoyu. Aluminum Ion Doped MIL-101(Cr): Preparation and VOCs Adsorption Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 747-753. |
| [3] | SUN Jing, LI Xiang, MAO Xiaojian, ZHANG Jian, WANG Shiwei. Effect of Lauric Acid Modifier on the Hydrolysis Resistance of Aluminum Nitride Powders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 826-832. |
| [4] | ZHANG Jiawei, CHEN Ning, CHENG Yuan, WANG Bo, ZHU Jianguo, JIN Cheng. Electrical Properties of Bismuth Layered Piezoelectric Bi4Ti3O12 Ceramics with A/B-site Doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 690-696. |
| [5] | ZHOU Yangyang, ZHANG Yanyan, YU Ziyi, FU Zhengqian, XU Fangfang, LIANG Ruihong, ZHOU Zhiyong. Enhancement of Piezoelectric Properties in CaBi4Ti4O15-based Ceramics through Bi3+ Self-doping Strategy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 719-728. |
| [6] | YANG Yan, ZHANG Faqiang, MA Mingsheng, WANG Yongzhe, OUYANG Qi, LIU Zhifu. Low Temperature Sintering of ZnAl2O4 Ceramics with CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5 Composite Oxide Sintering Aid [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 711-718. |
| [7] | SUN Yuxuan, WANG Zheng, SHI Xue, SHI Ying, DU Wentong, MAN Zhenyong, ZHENG Liaoying, LI Guorong. Defect Dipole Thermal-stability to the Electro-mechanical Properties of Fe Doped PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 545-551. |
| [8] | AN Ran, LIN Si, GUO Shigang, ZHANG Chong, ZHU Shun, HAN Yingchao. Iron-doped Nano-hydroxyapatite: Preparation and Ultraviolet Absorption Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 457-465. |
| [9] | CHEN Yi, QIU Haipeng, CHEN Mingwei, XU Hao, CUI Heng. SiC/SiC Composite: Matrix Boron Modification and Mechanical Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [10] | PAN Yuzhou, HE Fajian, XU Lulu, DAI Shixun. Broadband 3 μm Mid-infrared Emission in Dy3+/Yb3+ Co-doped Tellurite Glass under 980 nm LD Excitation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 521-528. |
| [11] | YANG Mingkai, HUANG Zeai, ZHOU Yunxiao, LIU Tong, ZHANG Kuikui, TAN Hao, LIU Mengying, ZHAN Junjie, CHEN Guoxing, ZHOU Ying. Co-production of Few-layer Graphene and Hydrogen from Methane Pyrolysis Based on Cu and Metal Oxide-KCl Molten Medium [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 473-480. |
| [12] | QU Jifa, WANG Xu, ZHANG Weixuan, ZHANG Kangzhe, XIONG Yongheng, TAN Wenyi. Enhanced Sulfur-resistance for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Anode via Doping Modification of NaYTiO4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 489-496. |
| [13] | CHEN Xi, YUAN Yuan, TAN Yeqiang, LIU Changsheng. Strategic Study on the Development of Inorganic Non-metallic Biomaterials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 449-456. |
| [14] | LI Jianjun, CHEN Fangming, ZHANG Lili, WANG Lei, ZHANG Liting, CHEN Huiwen, XUE Changguo, XU Liangji. Peroxymonosulfate Activation by CoFe2O4/MgAl-LDH Catalyst for the Boosted Degradation of Antibiotic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 440-448. |
| [15] | LIANG Ruihui, ZHONG Xin, HONG Du, HUANG Liping, NIU Yaran, ZHENG Xuebin. High-temperature Water Vapor Corrosion Behaviors of Environmental Barrier Coatings with Yb2O3-modified Silicon Bond Layer [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 425-432. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||