
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 1-16.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180171
Special Issue: MAX相和MXene材料; 二维材料; 2019~2020年度优秀作者作品欣赏:功能材料
• REVIEW • Next Articles
WANG Ren-Yan, GAN Lin, ZHAI Tian-You
Received:2018-04-19
Revised:2018-06-03
Published:2019-01-21
Online:2018-12-17
About author:WANG Ren-Yan. E-mail: Renyanwang@hust.edu.cn
CLC Number:
WANG Ren-Yan, GAN Lin, ZHAI Tian-You. ReX2 (X=S, Se): A New Opportunity for Development of Two-dimensional Anisotropic Materials[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(1): 1-16.
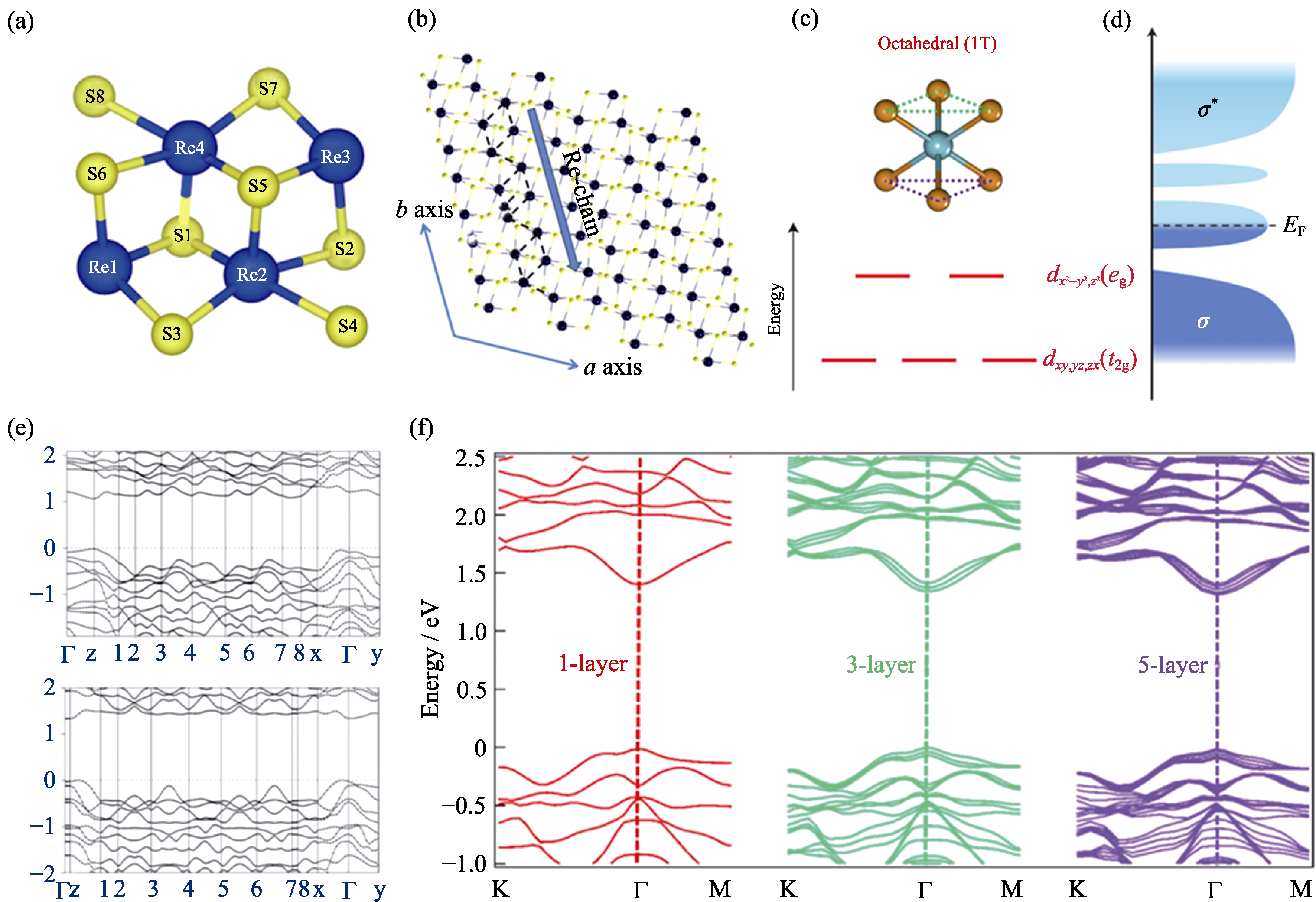
Fig. 1 (a) The model unitcell view of ReS2[33]; (b) Top view of the crystalline structure of distorted-1T phase of monolayer ReX2(Black balls represent Re atoms and yellow balls represent S or Se atoms); (c, d) Schematic images of 1T lattice symmetries and energy levels of d-orbital electrons induced by the crystal field[39,40]; (e) First-principles scalar relativistic projector augmented wave calculations of electronic band structures for bulk (top) and single-layer (down) ReSe2[50]; (f) Band structure of monolayer, trilayer and five-layer ReS2 by ab initio-calculations[51]
| Materials | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | α/(°) | β/(°) | γ/(°) | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ReS2 | 0.6417 | 0.6510 | 0.6461 | 121.10 | 88.38 | 106.47 | 0.21930 |
| ReSe2 | 0.6603 | 0.6717 | 0.6718 | 91.87 | 104.93 | 118.95 | 0.24753 |
Table 1 Original unit-cell lattice parameters of ReS2 and ReSe2[36,37]
| Materials | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | α/(°) | β/(°) | γ/(°) | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ReS2 | 0.6417 | 0.6510 | 0.6461 | 121.10 | 88.38 | 106.47 | 0.21930 |
| ReSe2 | 0.6603 | 0.6717 | 0.6718 | 91.87 | 104.93 | 118.95 | 0.24753 |

Fig. 2 PL spectra of ReS2 flakes with different number of layers; (b) Integrated PL intensity as a function of number of layers (normalized to that of monolayer) in ReS2, MoS2, MoSe2, WS2 and WSe2[50]; Raman spectra recorded on (c) N-layer ReS2 and (d) N-layer ReSe2 in the parallel polarization configuration[58]; (e) Schematic for the process of oriented self assembly of ReS2 nanoscrolls[59]; (f) Schematic for the TIB of a single ReS2 nanowall[60]
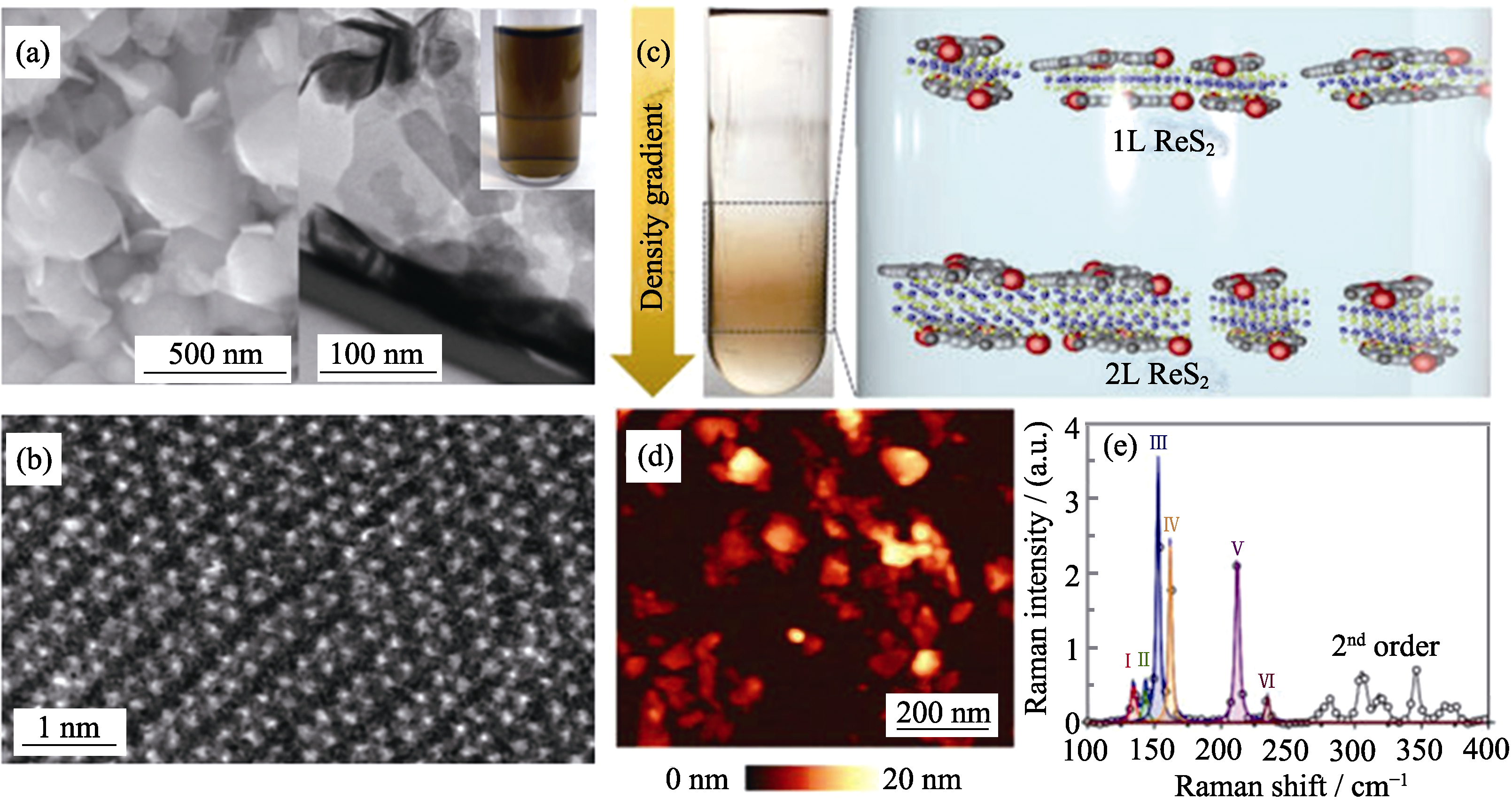
Fig. 3 (a) SEM image of ReS2 powders and TEM image of as-exfoliated ReS2 nanosheets with inset showing photograph of a typical dark-brown exfoliated ReS2 suspension in water; (b) High-resolution STEM image of as-exfoliated ReS2 nanosheets[70]; (c) Schematics for different density gradient ultracentrifugation ReS2 nanosheets through iDGU; (d) Atomic force microscopy image of solution-processed ReS2 following deposition on a Si wafer; (e) Raman spectrum of ReS2 nanosheets[63]

Fig. 4 (a) Schematic diagram of synthesized ReS2 film by PVD; (b) Raman spectrum of ReS2 film ; (c) Optical photograph of grown ReS2 film on the SiO2/Si substrate with inset showing the AFM and TEM images[88]; (d) A picture of bare and as-grown ReS2 bilayer film on sapphire wafer by CVD; (e) Optical microscope image of the ReS2 hexagons[74]
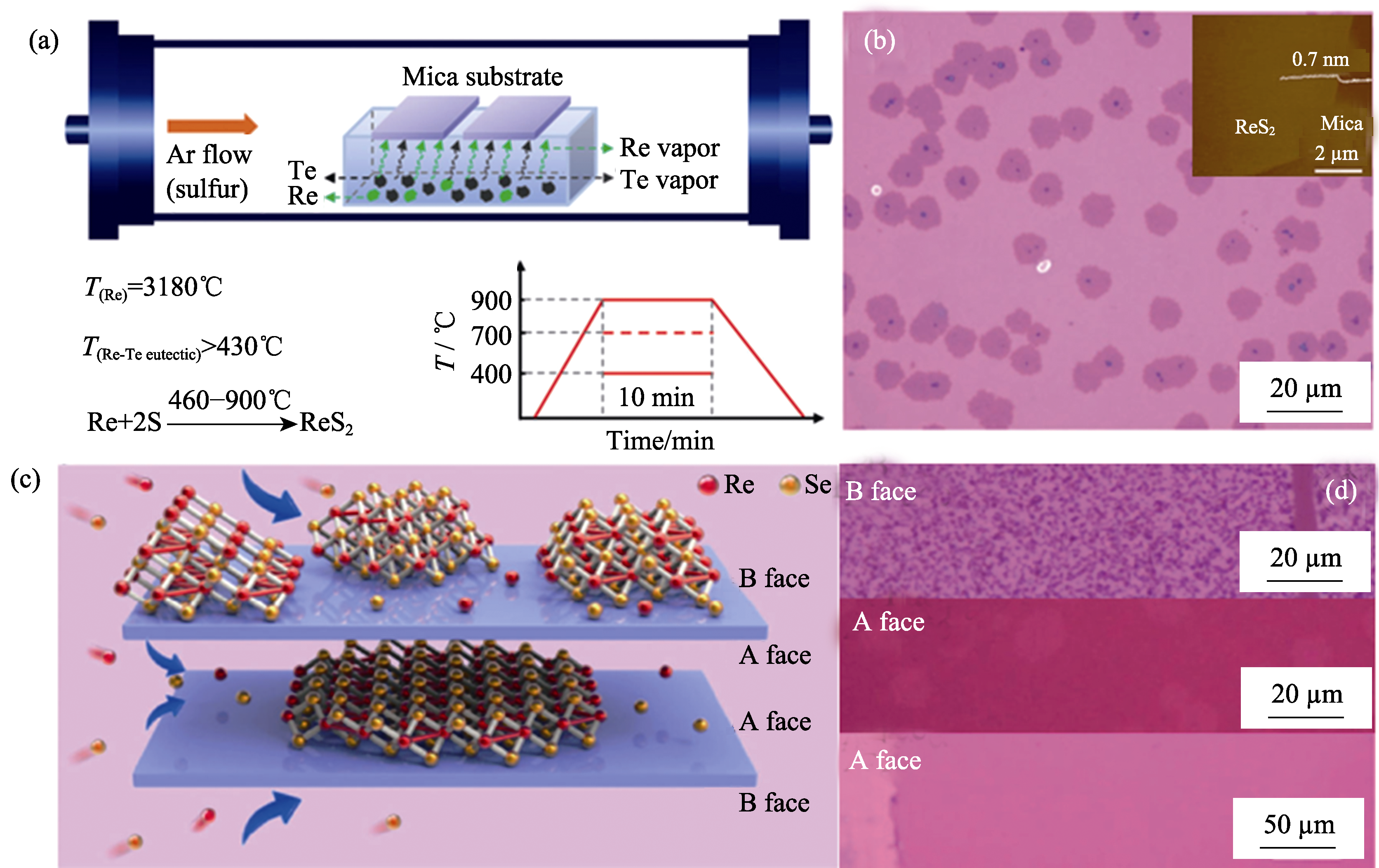
Fig. 5 (a) Schematic for the tellurium-assisted CVD growth approach; (b) Optical image of ReS2 after transferred onto SiO2/Si (300 nm) substrate with inset showing AFM image of ReS2 on mica substrate[77]; (c) Schematic of the CVD growth of ReSe2 in the confined reaction space and the surface reaction during the epitaxial growth of the ReSe2 atomic layer on mica; (d) Optical image of ReSe2 in A and B face[89]
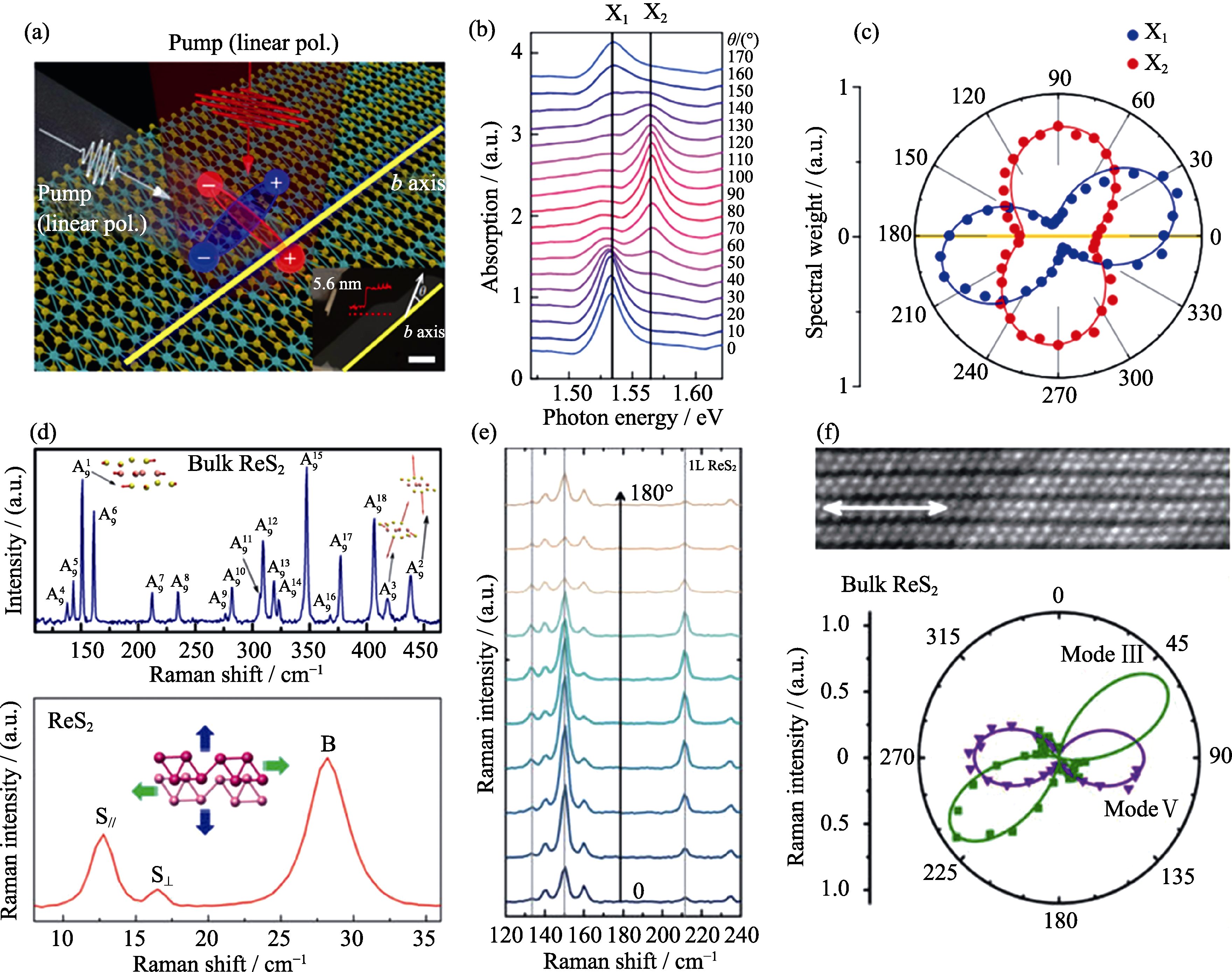
Fig. 6 (a) A schematic illustrating the pump-probe experiment of few-layer ReS2 with inset showing optical image of few-layer ReS2; (b) Polarization-dependent absorption spectra of few-layer ReS2; (c) Corresponding spectral weights of Lorentzian contributions of X1 (blue dots) and X2(red dots). Yellow line represents the b-axis[122]; (d) Raman spectrum for bulk ReS2[128] and Low-frequency Raman spectroscopy of few layer ReS2[131]; (e) Unpolarized Raman spectra as a function of sample orientation angle; (f) High-magnification ADF-STEM image and corresponded polarization-and orientation-resolved Raman spectra[130]
| Symmetry | Bulk/cm-1 | Monolayer/cm-1 | Origin of phonon mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | 140.3 | 139.2 | Out-of-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Ag | 145.9 | 145.3 | Out-of-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 153.1 | 153.6 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 163.6 | 163.6 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 217.2 | 217.7 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 237.1 | 237.7 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Cp | 278.3 | 278.3 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of Re and S atoms |
| Cp | 284.2 | 284.7 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of Re and S atoms |
| Eg | 307.8 | 307.8 | In-plane vibrations of S atoms |
| Eg | 311.0 | 311.0 | In-plane vibrations of S atoms |
| Cp | 320.6 | 320.6 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 324.9 | 324.9 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 348.8 | 348.8 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 368.9 | 369.5 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 377.9 | 377.4 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 407.3 | 408.3 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Ag | 418.7 | 419.3 | Out-of-plane vibrations of S atoms |
| Ag | 438.0 | 437.5 | Out-of-plane vibrations of S atoms |
Table 2 The 18 Raman active frequencies in bulk and monolayer ReS2 under 633 nm solid state laser excitation[35]
| Symmetry | Bulk/cm-1 | Monolayer/cm-1 | Origin of phonon mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | 140.3 | 139.2 | Out-of-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Ag | 145.9 | 145.3 | Out-of-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 153.1 | 153.6 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 163.6 | 163.6 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 217.2 | 217.7 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 237.1 | 237.7 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Cp | 278.3 | 278.3 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of Re and S atoms |
| Cp | 284.2 | 284.7 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of Re and S atoms |
| Eg | 307.8 | 307.8 | In-plane vibrations of S atoms |
| Eg | 311.0 | 311.0 | In-plane vibrations of S atoms |
| Cp | 320.6 | 320.6 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 324.9 | 324.9 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 348.8 | 348.8 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 368.9 | 369.5 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 377.9 | 377.4 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 407.3 | 408.3 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Ag | 418.7 | 419.3 | Out-of-plane vibrations of S atoms |
| Ag | 438.0 | 437.5 | Out-of-plane vibrations of S atoms |

Fig. 7 (a) Optical microscope image of ReS2 four probe transistor; (b) The magnified ADF images taken from the sample in (a); (c) The direction-dependent I-V characteristics with inset showing nonlinear I-V behavior indicate the Schottky Au/ReS2 contacts; (d) The direction-dependent transfer characteristics[137]; (e) Transfer curves of anisotropic ReS2 FETs along two sides with top inset showing optical image of the devices (Scale bar, 10 μm) and low inset showing the 4-probe resistance of the same devices. (f) Normalized field-effect mobility of a six-layer device with inset showing the optical image of the device[51]; (g) Angle-dependent transfer curves of ReS1.23Se0.77 alloy device with inset showing optical image of ReS2 device[76]

Fig. 8 (a) The photocurrent of ReS2 change as a function of drain bias under different polarization light illuminations; (b) The change of the photocurrent under different drain biases plotted as a function of polarization angle[112]; (c) Photocurrent response of ReS1.06Se0.94 alloy device under light on and off irradiation, and under light with different polarization direction; (d) Polar plots for the photocurrent with respect to the polarization angle of the incident light[76]; (e) Schematic structure of ReSe2 photodetectors; (f) The SEM image and polarization-dependent photocurrent mapping of the device[15]
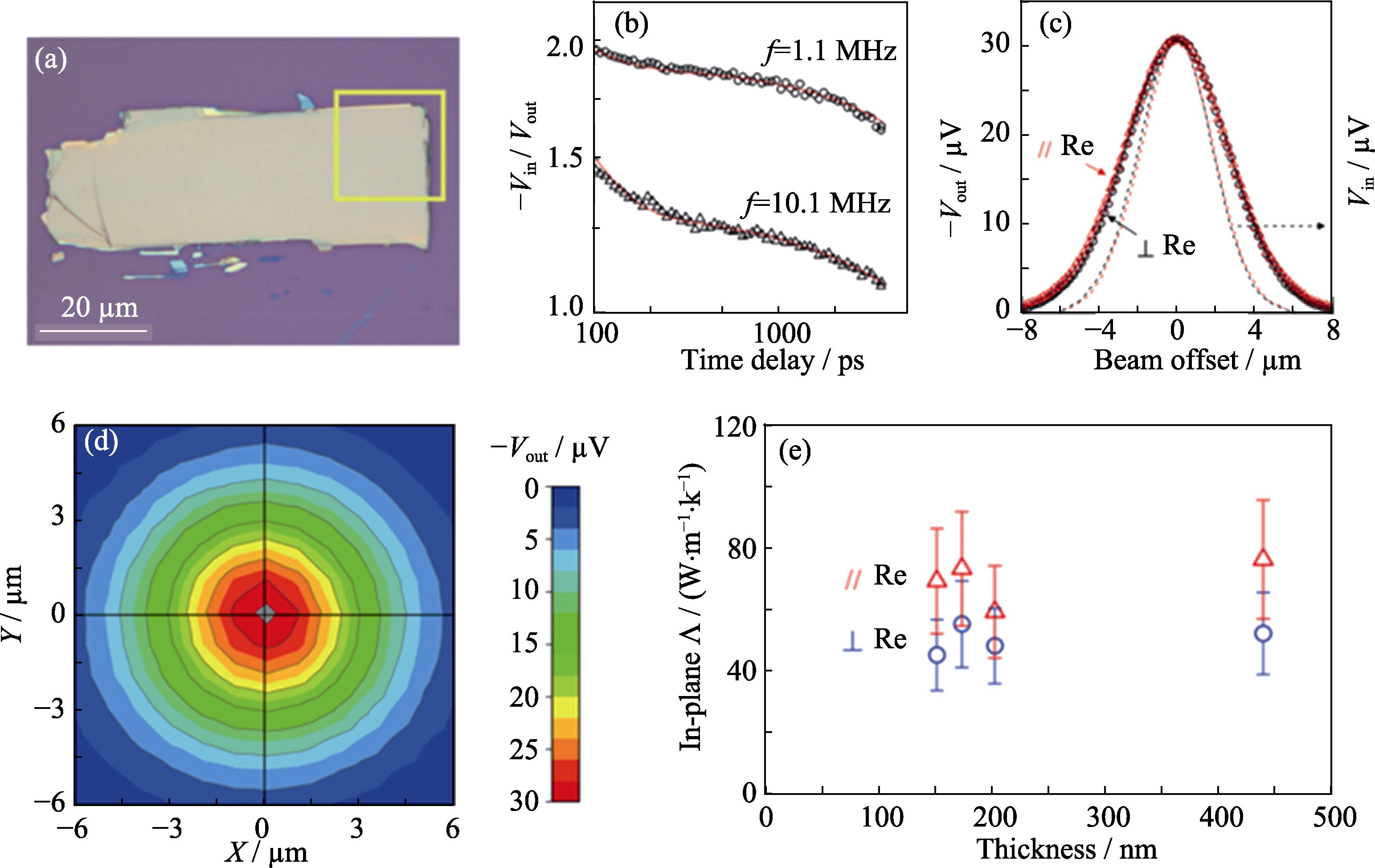
Fig. 9 (a) Optical microscopy image of an exfoliated ReS2 ?ake; (b) Through-plane TDTR data at two modulation frequencies; (c) In-plane TDTR data at f = 1.1 MHz and time delay of -50 ps. The dashed lines are the intensity profile of the laser beam; (d) 2D beam-offset scan of the TDTR signal; (e) In-plane thermal conductivity of exfoliated ReS2 ?akes as a function of thickness[151]
| [1] | GONG C, ZHANG Y, CHEN W, et al. Electronic and optoelectronic applications based on 2D novel anisotropic transition metal dichalcogenides. Adv. Sci., 2017, 4(12): 1700231-1-19. |
| [2] | TIAN H, TICE J, FEI R, et al.Low-symmetry two-dimensional materials for electronic and photonic applications. Nano Today, 2016, 11(6): 763-777. |
| [3] | LIU X, RYDER C R, WELLS S A, et al. Resolving the in-plane anisotropic properties of black phosphorus. Small Methods, 2017, 1(6): 1700143-1-9. |
| [4] | XIA F N, WANG H, JIA Y C, et al. Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics. Nat. Commun., 2014, 5: 4458-1-6. |
| [5] | ZHAO L D, LO S H, ZHANG Y, et al.Ultralow thermal conductivity and high thermoelectric figure of merit in SnSe crystals. Nature, 2014, 508(7496): 373-377. |
| [6] | YANG Y, LIU S C, YANG W, et al.Air-stable in-plane anisotropic GeSe2 for highly polarization-sensitive photodetection in short wave region. [J]. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140(11): 4150-4156. |
| [7] | XU J, CHEN L, DAI Y W, et al. A two-dimensional semiconductor transistor with boosted gate control and sensing ability. Sci.Adv., 2017, 3(5): 1602246-1-8. |
| [8] | SHIM J, OH S, KANG D H, et al. Phosphorene/rhenium disulfide heterojunction-based negative differential resistance device for multi-valued logic. Nat. Commun., 2016, 7: 13413-1-8. |
| [9] | WANG X, HUANG L, PENG Y, et al.Enhanced rectification, transport property and photocurrent generation of multilayer ReSe2/MoS2 p-n heterojunctions. Nano Res., 2016, 9(2): 507-516. |
| [10] | DATHBUN A, KIM Y, KIM S, et al.Large-area CVD-grown sub-2 V ReS2 transistors and logic gates. Nano Lett., 2017, 17(5): 2999-3005. |
| [11] | MOHAMMED O B, MOVVA H C P, PRASAD N, et al. ReS2-based interlayer tunnel field effect transistor. J. Appl. Phys., 2017, 122(24): 245701-1-7. |
| [12] | CORBETT C M, MCCLELLAN C, RAI A, et al.Field effect transistors with current saturation and voltage gain in ultrathin ReS2. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(1): 363-370. |
| [13] | CHO A J, NAMGUNG S D, KIM H, et al. Electric and photovoltaic characteristics of a multi-layer ReS2/ReSe2 heterostructure. APL Materials, 2017, 5(7): 076101-1-8. |
| [14] | ZHANG E, JIN Y, YUAN X, et al.ReS2-based field-effect transistors and photodetectors. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2015, 25(26): 4076-4082. |
| [15] | ZHANG E, WANG P, LI Z, et al.Tunable ambipolar polarization- sensitive photodetectors based on high-anisotropy ReSe2 nanosheets. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(8): 8067-8077. |
| [16] | QIN J K, REN D D, SHAO W Z, et al.Photoresponse enhancement in monolayer ReS2 phototransistor decorated with CdSe-CdS-ZnS quantum dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2017, 9(45): 39456-39463. |
| [17] | YANG S, TONGAY S, LI Y, et al.Layer-dependent electrical and optoelectronic responses of ReSe2 nanosheet transistors. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(13): 7226-7231. |
| [18] | CUI Y, LU F, LIU X. Nonlinearsaturable and polarization- induced absorption of rhenium disulfide. Sci. Rep., 2017, 7: 40080-1-9. |
| [19] | ZHANG Q, TAN S, MENDES R G, et al.Extremely weak Van Der Waals coupling in vertical ReS2 nanowalls for high-current- density lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(13): 2616-2623. |
| [20] | QI F, CHEN Y, ZHENG B, et al.Hierarchical architecture of ReS2/rGO composites with enhanced electrochemical properties for lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 413: 123-128. |
| [21] | QI F, HE J, CHEN Y, et al.Few-layered ReS2 nanosheets grown on carbon nanotubes: a highly efficient anode for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 315: 10-17. |
| [22] | QI F, CHEN Y, ZHENG B, et al.3D chrysanthemum-like ReS2 microspheres composed of curly few-layered nanosheets with enhanced electrochemical properties for lithium-ion batteries. [J]. Mater. Sci., 2017, 52(7): 3622-3629. |
| [23] | ESCALONA N, LLAMBIAS F J G, VRINAT M, et al. Highly active ReS2/gamma-Al2O3 catalysts: effect of calcination and activation over thiophene hydrodesulfurization. Catal. Commun., 2007, 8(3): 285-288. |
| [24] | ALIAGA J A, ZEPEDA T N, PAWELEC B N, et al.Microspherical ReS2 as a high-performance hydrodesulfurization catalyst. Catal. Lett., 2017, 147(5): 1243-1251. |
| [25] | SEPULVEDA C, ESCALONA N, GARCIA R, et al.Hydrodeoxygenation and hydrodesulfurization co-processing over ReS2 supported catalysts. Catal. Today, 2012, 195(1): 101-105. |
| [26] | ANTONIO ALIAGA J, ZEPEDA T, FRANCISCO ARAYA J, et al. Low-dimensional ReS2/C composite as effective hydrodesulfurization catalyst. Catalysts, 2017, 7(12): 7120377-1-11. |
| [27] | QI F, WANG X, ZHENG B, et al.Self-assembled chrysanthemum- like microspheres constructed by few-layer ReSe2 nanosheets as a highly efficient and stable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Electrochim. Acta, 2017, 224: 593-599. |
| [28] | HO T C, SHEN Q, MCCONNACHIE J M, et al.Kinetic characterization of unsupported ReS2 as hydroprocessing catalyst. [J]. Catal., 2010, 276(1): 114-122. |
| [29] | GAO J, LI L, TAN J, et al.Vertically oriented arrays of ReS2 nanosheets for electrochemical energy storage and electrocatalysis. Nano Lett., 2016, 16(6): 3780-3787. |
| [30] | RAHMAN M, DAVEY K, QIAO S Z. Advent of 2D rhenium disulfide (ReS2): fundamentals to applications. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27(10): 1606129-1-21. |
| [31] | HAFEEZ M, GAN L, BHATTI A S, et al.Rhenium dichalcogenides (ReX2, X = S or Se): an emerging class of TMDs family. Mater. Chem. Front., 2017, 1(10): 1917-1932. |
| [32] | WILDERVANCK J C, JELLINEK F.The dichalcogenides of technetium and rhenium. Journal of the Less Common Metals, 1971, 24(1): 73-81. |
| [33] | YU Z G, CAI Y, ZHANG Y W. Robust direct bandgap characteristics of one- and two-dimensional ReS2. Sci. Rep., 2015, 5: 13783-1-9. |
| [34] | KEYSHAR K, GONG Y, YE G, et al.Chemical vapor deposition of monolayer rhenium disulfide (ReS2). Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(31): 4640-4648. |
| [35] | FENG Y, ZHOU W, WANG Y, et al. Raman vibrational spectra of bulk to monolayer ReS2 with lower symmetry. Phys. Rev. B, 2015, 92(5): 054110-1-24. |
| [36] | KAO Y C, HUANG T, LIN D Y, et al. Anomalous structural phase transition properties in ReSe2 and Au-doped ReSe2. J. Chem. Phys., 2012, 137(2): 024509-1-7. |
| [37] | TIONG K K, HO C H, HUANG Y S.The electrical transport properties of ReS2 and ReSe2 layered crystals. Solid State. Commun., 1999, 111(11): 635-640. |
| [38] | WANG Q H, KALANTAR-ZADEH K, KIS A, et al.Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2012, 7(11): 699-712. |
| [39] | YANG H, KIM S W, LEE Y H, et al.Structural and quantum- state phase transitions in Van Der Waals layered materials. Nat. Phys., 2017, 13: 931-937. |
| [40] | CHHOWALLA M, SHIN H S, EDA G, et al.The chemistry of two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets. Nat. Chem., 2013, 5(4): 263-275. |
| [41] | YIN Z, LI H, JIANG L, et al.Single-layer MoS2 phototransistors. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(1): 74-80. |
| [42] | TONGAY S, FAN W, KANG J, et al.Tuning interlayer coupling in large-area heterostructures with CVD-grown MoS2 and WS2 monolayers. Nano Lett., 2014, 14(6): 3185-3190. |
| [43] | SPLENDIANI A, SUN L, ZHANG Y, et al.Emerging photoluminescence in monolayer MoS2. Nano Lett., 2010, 10(4): 1271-1275. |
| [44] | LI T, GALLI G.Electronic properties of MoS2 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111(44): 16192-16196. |
| [45] | TONNDORF P, SCHMIDT R, BOTTGER P, et al.Photoluminescence emission and Raman response of monolayer MoS2, MoSe2, and WSe2. Opt. Express, 2013, 21(4): 4908-4916. |
| [46] | HART L, DALE S, HOYE S, et al.Rhenium dichalcogenides: layered semiconductors with two vertical orientations. Nano Lett., 2016, 16(2): 1381-1386. |
| [47] | HART L S, WEBB J L, DALE S, et al. Electronic bandstructure and Van Der Waals coupling of ReSe2 revealed by high-resolution angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Sci. Rep., 2017, 7: 5145-1-9. |
| [48] | WEBB J L, HART L S, WOLVERSON D, et al. Electronic band structure of ReS2 by high-resolution angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B, 2017, 96(11): 115205-1-8. |
| [49] | WOLVERSON D, CRAMPIN S, KAZEMI A S, et al.Raman spectra of monolayer, few-layer, and bulk ReSe2: an anisotropic layered semiconductor. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(11): 11154-11164. |
| [50] | TONGAY S, SAHIN H, KO C, et al. Monolayer behaviour in bulk ReS2 due to electronic and vibrational decoupling. Nat.Commun., 2014, 5: 3252-1-6. |
| [51] | LIU E, FU Y, WANG Y, et al. Integrated digital inverters based on two-dimensional anisotropic ReS2 field-effect transistors. Nat. Commun., 2015, 6: 6991-1-7. |
| [52] | EDA G, YAMAGUCHI H, VOIRY D, et al.Photoluminescence from chemically exfoliated MoS2. Nano Lett., 2011, 11(12): 5111-5116. |
| [53] | MAK K F, LEE C, HONE J, et al. Atomically thin MoS2: a new direct-gap semiconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2010, 105(13): 136805-1-4. |
| [54] | ZHAO W, GHORANNEVIS Z, CHU L, et al.Evolution of electronic structure in atomically thin sheets of WS2 and WSe2. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(1): 791-797. |
| [55] | GUTIERREZ H R, PEREA-LOPEZ N, ELIAS A L, et al.Extraordinary room-temperature photoluminescence in triangular WS2 monolayers. Nano Lett., 2013, 13(8): 3447-3454. |
| [56] | ZHAO H, WU J, ZHONG H, et al.Interlayer interactions in anisotropic atomically thin rhenium diselenide. Nano Res., 2015, 8(11): 3651-3661. |
| [57] | TONGAY S, ZHOU J, ATACA C, et al.Thermally driven crossover from indirect toward direct bandgap in 2D semiconductors: MoSe2 versus MoS2. Nano Lett., 2012, 12(11): 5576-5580. |
| [58] | LORCHAT E, FROEHLICHER G, BERCIAUD S.Splitting of interlayer shear modes and photon energy dependent anisotropic raman response in N-layer ReSe2 and ReS2. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(2): 2752-2760. |
| [59] | ZHANG Q, WANG W, KONG X, et al.Edge-to-edge oriented self-assembly of ReS2 nanoflakes. [J]. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(35): 11101-11104. |
| [60] | ZHANG Q, WANG W, ZHANG J, et al. Thermally induced bending of ReS2 nanowalls. Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(3): 1704585-1-7. |
| [61] | JARIWALA B, VOIRY D, JINDAL A, et al.Synthesis and characterization of ReS2 and ReSe2 layered chalcogenide single crystals. Chem. Mater., 2016, 28(10): 3352-3359. |
| [62] | HU D, XU G, XING L, et al.Two-dimensional semiconductors grown by chemical vapor transport. Angew Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(13): 3611-3615. |
| [63] | KANG J, SANGWAN V K, WOOD J D, et al.Layer-by-layer sorting of rhenium disulfide via high-density isopycnic density gradient ultracentrifugation. Nano Lett., 2016, 16(11): 7216-7223. |
| [64] | JAWAID A, NEPAL D, PARK K, et al.Mechanism for liquid phase exfoliation of MoS2. Chem. Mater., 2015, 28(1): 337-348. |
| [65] | ZHENG J, ZHANG H, DONG S, et al. High yield exfoliation of two-dimensional chalcogenides using sodium naphthalenide. Nat. Commun., 2014, 5: 2995-1-7. |
| [66] | COLEMAN J N, LOTYA M, O'NEILL A, et al. Two-dimensional nanosheets produced by liquid exfoliation of layered materials. Science, 2011, 331(6017): 568-571. |
| [67] | NICOLOSI V, CHHOWALLA M, KANATZIDIS M G, et al.Liquid exfoliation of layered materials. Science, 2013, 340(6139): 1226419-1226419. |
| [68] | HUO C, YAN Z, SONG X, et al.2D materials via liquid exfoliation: a review on fabrication and applications. Sci. Bull., 2015, 60(23): 1994-2008. |
| [69] | ZHAO X, MA X, SUN J, et al.Enhanced catalytic activities of surfactant-assisted exfoliated WS2 nanodots for hydrogen evolution. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(2): 2159-2166. |
| [70] | FUJITA T, ITO Y, TAN Y, et al.Chemically exfoliated ReS2 nanosheets. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(21): 12458-12462. |
| [71] | XU K, DENG H X, WANG Z, et al.Sulfur vacancy activated field effect transistors based on ReS2 nanosheets. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(38): 15757-15762. |
| [72] | KIM Y, KANG B, CHOI Y, et al. Direct synthesis of large-area continuous ReS2 films on a flexible glass at low temperature. 2D Materials, 2017, 4(2): 025057-1-10. |
| [73] | QIN J K, SHAO W Z, XU C Y, et al.Chemical vapor deposition growth of degenerate p-type Mo-doped ReS2 films and their homojunction. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2017, 9(18): 15583-15591. |
| [74] | HAFEEZ M, GAN L, LI H, et al.Large-area bilayer ReS2 film/multilayer ReS2 flakes synthesized by chemical vapor deposition for high performance photodetectors. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26(25): 4551-4560. |
| [75] | CHEN B, WU K, SUSLU A, et al. Controlling structural anisotropy of anisotropic 2D layers in pseudo-1D/2D material heterojunctions. Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(34): 1701201-1-8. |
| [76] | CUI F, FENG Q, HONG J, et al. Synthesis of large-size 1T ' ReS2xSe2(1-x) alloy monolayer with tunable bandgap and carrier type. Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(46): 1705015-1-9. |
| [77] | CUI F, WANG C, LI X, et al.Tellurium-assisted epitaxial growth of large-area, highly crystalline ReS2 atomic layers on mica substrate. Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(25): 5019-5024. |
| [78] | HAFEEZ M, GAN L, LI H, et al.Chemical vapor deposition synthesis of ultrathin hexagonal ReSe2 flakes for anisotropic Raman property and optoelectronic application. Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(37): 8296-8301. |
| [79] | AL-DULAIMI N, LEWIS E A, LEWIS D J, et al.Sequential bottom-up and top-down processing for the synthesis of transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets: the case of rhenium disulfide (ReS2). Chem. Commun., 2016, 52(50): 7878-7881. |
| [80] | YELLA A, THERESE H A, ZINK N, et al.Large scale MOCVD synthesis of hollow ReS2 nanoparticles with nested fullerene-like structure. Chem. Mater., 2008, 20(11): 3587-3593. |
| [81] | KIM S, YU H K, YOON S, et al.Growth of two-dimensional rhenium disulfide (ReS2) nanosheets with a few layers at low temperature. Crystengcomm, 2017, 19(36): 5341-5345. |
| [82] | CHATURVEDI A, SLABON A, HU P, et al.Rapid synthesis of transition metal dichalcogenide few-layer thin crystals by the microwave-induced-plasma assisted method. J. Cryst. Growth, 2016, 450: 140-147. |
| [83] | AL-DULAIMI N, LEWIS D J, ZHONG X L, et al.Chemical vapour deposition of rhenium disulfide and rhenium-doped molybdenum disulfide thin films using single-source precursors. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2016, 4(12): 2312-2318. |
| [84] | AL-DULAIMI N, LEWIS E A, SAVJANI N, et al.The influence of precursor on rhenium incorporation into Re-doped MoS2 (Mo1-xRexS2) thin films by aerosol-assisted chemical vapour deposition (AACVD). J. Mater. Chem. C, 2017, 5(35): 9044-9052. |
| [85] | SIMCHI H, WALTER T N, CHOUDHURY T H, et al.Sulfidation of 2D transition metals (Mo, W, Re, Nb, Ta): thermodynamics, processing, and characterization. J. Mater. Sci., 2017, 52(17): 10127-10139. |
| [86] | BOROWIEC J, GILLIN W P, WILLIS M A C, et al. Room temperature synthesis of ReS2 through aqueous perrhenate sulfidation. J. Phys: Condens. Matter, 2018, 30(5): 055702-1-11. |
| [87] | HU S Y, CHEN Y Z, TIONG K K, et al.Growth and characterization of molybdenum-doped rhenium diselenide. Mater. Chem. Phys., 2007, 104(1): 105-108. |
| [88] | QI F, CHEN Y, ZHENG B, et al.Facile growth of large-area and high-quality few-layer ReS2 by physical vapour deposition. Mater. Lett., 2016, 184: 324-327. |
| [89] | CUI F, LI X, FENG Q, et al.Epitaxial growth of large-area and highly crystalline anisotropic ReSe2 atomic layer. Nano Res., 2017, 10(8): 2732-2742. |
| [90] | LI X, CUI F, FENG Q, et al.Controlled growth of large-area anisotropic ReS2 atomic layer and its photodetector application. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(45): 18956-18962. |
| [91] | ZHANG T, JIANG B, XU Z, et al. Twinned growth behaviour of two-dimensional materials. Nat. Commun., 2016, 7: 13911- 1-7. |
| [92] | CHEN P, WANG J, LU Y, et al.The fabrication of ReS2 flowers at controlled locations by chemical vapor deposition. Physica E, 2017, 89: 115-118. |
| [93] | QIN J K, SHAO W Z, LI Y, et al.Van der Waals epitaxy of large-area continuous ReS2 films on mica substrate. RSC Adv., 2017, 7(39): 24188-24194. |
| [94] | HE X, LIU F, HU P, et al.Chemical vapor deposition of high-quality and atomically layered ReS2. Small, 2015, 11(40): 5423-5429. |
| [95] | YANG S, TONGAY S, YUE Q, et al. High-performance few-layer Mo-doped ReSe2 nanosheet photodetectors. Sci. Rep., 2014, 4: 5442-1-6. |
| [96] | WU K, CHEN B, YANG S, et al.Domain architectures and grain boundaries in chemical vapor deposited highly anisotropic ReS2 monolayer films. Nano Lett., 2016, 16(9): 5888-5894. |
| [97] | CHEN Y, GAN L, LI H, et al. Achieving uniform monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides film on silicon wafer via silanization treatment: a typical study on WS2. Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(7): 160550-1-6. |
| [98] | YAN C, GAN L, ZHOU X, et al. Space-confined chemical vapor deposition synthesis of ultrathin HfS2 flakes for optoelectronic application. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27(39): 1702918- 1-9. |
| [99] | JIN B, HUANG P, ZHANG Q, et al. Self-limited epitaxial growth of ultrathin non-layered CdS flakes for high-performance photodetectors. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28: 1800181- 1-9. |
| [100] | JU M, LIANG X, LIU J, et al.Universal substrate-trapping strategy to grow strictly monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides crystals. Chem. Mater., 2017, 29(14): 6095-6103. |
| [101] | ZHANG Q, XIAO Y, ZHANG T, et al.Iodine-mediated chemical vapor deposition growth of metastable transition metal dichalcogenides. Chem. Mater., 2017, 29(11): 4641-4644. |
| [102] | HUANG W, GAN L, YANG H, et al. Controlled synthesis of ultrathin 2D β-In2S3 with broadband photoresponse by chemical vapor deposition. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27(36): 1702448- 1-9. |
| [103] | GONG Y, LIN Z, YE G, et al.Tellurium-assisted low-temperature synthesis of MoS2 and WS2 monolayers. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(12): 11658-11666. |
| [104] | ZHOU S, GAN L, WANG D, et al. Space-confined vapor deposition synthesis of two dimensional materials. Nano Res., 2017: 12274-1-23. |
| [105] | SONG J G, PARK J, LEE W, et al.Layer-controlled, wafer scale, and conformal synthesis of tungsten disulfide nanosheets using atomic layer deposition. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(12): 11333-11340. |
| [106] | JANG Y, YEO S, LEE H B R, et al. Wafer-scale, conformal and direct growth of MoS2 thin films by atomic layer deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2016, 365: 160-165. |
| [107] | MEMARIAN N, ROZATI S M, CONCINA I, et al. Deposition of nanostructured CdS thin films by thermal evaporation method: effect of substrate temperature. Mater., 2017, 10(7): 773-1-8. |
| [108] | MAZUR M, HOWIND T, GIBSON D, et al.Modification of various properties of HfO2 thin films obtained by changing magnetron sputtering conditions. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2017, 320: 426-431. |
| [109] | ZHAN L, WAN W, ZHU Z, et al. MoS2 materials synthesized on SiO2/Si substrates via MBE. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 2017, 864: 012037-1-5. |
| [110] | HAMALAINEN J, MATTINEN M, MIZOHATA K, et al. Atomic layer deposition of rhenium disulfide. Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(24): 1703622-1-6. |
| [111] | BISWAS D, GANOSE A M, YANO R, et al. Narrow-band anisotropic electronic structure of ReS2. Phys. Rev. B, 2017, 96(8): 085205-1-7. |
| [112] | LIU F, ZHENG S, HE X, et al.Highly sensitive detection of polarized light using anisotropic 2D ReS2. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26(8): 1169-1177. |
| [113] | HUANG C C, KAO C C, LIN D Y, et al. A comprehensive study on the optical properties of thin gold-doped rhenium disulphide layered single crystals. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2013, 52(4): 04CH11-1-6. |
| [114] | HO C H, HSIEH M H, WU C C, et al.Dichroic optical and electrical properties of rhenium dichalcogenides layer compounds. [J]. Alloys Compd., 2007, 442(1/2): 245-248. |
| [115] | CUI Q, HE J, BELLUS M Z, et al.Transient absorption measurements on anisotropic monolayer ReS2. Small, 2015, 11(41): 5565-5571. |
| [116] | ASLAN O B, CHENET D A, VAN DER ZANDE A M, et al. Linearly polarized excitons in single- and few-layer ReS2 crystals. ACS Photonics, 2016, 3(1): 96-101. |
| [117] | ZHENG J Y, LIN D Y, HUANG Y S. Piezoreflectance study of band-edge excitons of ReS2:Au. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2009, 48(5): 052302-1-6. |
| [118] | WU S, SHAN Y, GUO J, et al.Phase-engineering-induced generation and control of highly anisotropic and robust excitons in few-layer ReS2. [J]. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2017, 8(12): 2719-2724. |
| [119] | HO C H, LEE H W, WU C C.Polarization sensitive behaviour of the band-edge transitions in ReS2 and ReSe2 layered semiconductors. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2004, 16(32): 5937-5944. |
| [120] | ARORA A, NOKY J, DRUEPPEL M, et al.Highly anisotropic in-plane excitons in atomically thin and bulklike 1T’-ReSe2. Nano Lett., 2017, 17(5): 3202-3207. |
| [121] | SIM S, LEE D, TRIFONOV A V, et al. Ultrafast quantum beats of anisotropic excitons in atomically thin ReS2. Nat. Commun., 2018, 9(1): 351-1-7. |
| [122] | SIM S, LEE D, NOH M, et al. Selectively tunable optical Stark effect of anisotropic excitons in atomically thin ReS2. Nat. Commun., 2016, 7: 13569-1-6. |
| [123] | CHAVES A, LOW T, AVOURIS P, et al. Anisotropic exciton Stark shift in black phosphorus. Phys. Rev. B, 2015, 91(15): 155311-1-7. |
| [124] | SAITO R, TATSUMI Y, HUANG S, et al. Raman spectroscopy of transition metal dichalcogenides. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2016, 28(35): 353002-1-37. |
| [125] | ZHANG S, MAO N, ZHANG N, et al.Anomalous polarized raman scattering and large circular intensity differential in layered triclinic ReS2. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(10): 10366-10372. |
| [126] | TAUBE A, LAPINSKA A, JUDEK J, et al. Temperature dependence of Raman shifts in layered ReSe2 and SnSe2 semiconductor nanosheets. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2015, 107(1): 013105- 1-5. |
| [127] | MIAO P, QIN J K, SHEN Y, et al. Unraveling the Raman enhancement mechanism on 1T'-phase ReS2 nanosheets. Small, 2018: 1704079-1-8. |
| [128] | MCCREARY A, SIMPSON J R, WANG Y, et al.Intricate resonant Raman response in anisotropic ReS2. Nano Lett., 2017, 17(10): 5897-5907. |
| [129] | PRADHAN N R, MCCREARY A, RHODES D, et al.Metal to insulator quantum-phase transition in few-layered ReS2. Nano Lett., 2015, 15(12): 8377-8384. |
| [130] | CHENET D A, ASLAN O B, HUANG P Y, et al.In-plane anisotropy in mono- and few-layer ReS2 probed by Raman spectroscopy and scanning transmission electron microscopy. Nano Lett., 2015, 15(9): 5667-5672. |
| [131] | HE R, YAN J A, YIN Z, et al.Coupling and stacking order of ReS2 atomic layers revealed by ultralow-frequency Raman spectroscopy. Nano Lett., 2016, 16(2): 1404-1409. |
| [132] | WU J, MAO N, XIE L, et al.Identifying the crystalline orientation of black phosphorus using angle-resolved polarized Raman spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 127(8): 2396-2399. |
| [133] | TAO J, SHEN W, WU S, et al.Mechanical and electrical anisotropy of few-layer black phosphorus. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(11): 11362-11370. |
| [134] | XIA F, WANG H, JIA Y. Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics. Nat. Commun., 2014, 5: 4458-1-6. |
| [135] | QIAO J, KONG X, HU Z X, et al. High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus. Nat. Commun., 2014, 5: 4475-1-7. |
| [136] | LI L, GONG P, WANG W, et al.Strong in-plane anisotropies of optical and electrical response in layered dimetal chalcogenide. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(10): 10264-10272. |
| [137] | LIN Y C, KOMSA H P, YEH C H, et al.Single-layer ReS2: two-dimensional semiconductor with tunable in-plane anisotropy. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(11): 11249-11257. |
| [138] | LI L, PI L, LI H, et al.Photodetectors based on two-dimensional semiconductors: progress, opportunity and challenge. Chin. Sci. Bull., 2017, 62(27): 3134-3153. |
| [139] | YAN K, WEI Z, ZHANG T, et al.Near-infrared photoresponse of one-sided abrupt MAPbI3/TiO2 heterojunction through a tunneling process. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26(46): 8545-8554. |
| [140] | ZENG L, TAO L, TANG C, et al. High-responsivity UV-Vis photodetector based on transferable WS2 film deposited by magnetron sputtering. Sci. Rep., 2016, 6: 20343-1-8. |
| [141] | LI L, WANG W, CHAI Y, et al. Few-layered PtS2 phototransistor on h-BN with high gain. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27: 1701011-1-8. |
| [142] | JIANG J W. Thermal conduction in single-layer black phosphorus: highly anisotropic? Nanotechnology, 2015, 26(5): 055701-1-6. |
| [143] | LUO Z, MAASSEN J, DENG Y, et al. Anisotropic in-plane thermal conductivity observed in few-layer black phosphorus. Nat. Commun., 2015, 6: 8572-1-8. |
| [144] | LEE S, YANG F, SUH J, et al. Anisotropic in-plane thermal conductivity of black phosphorus nanoribbons at temperatures higher than 100 K. Nat. Commun., 2015, 6: 8573-1-7. |
| [145] | MA J L, CHEN Y N, HAN Z, et al. Strong anisotropic thermal conductivity of monolayer WTe2. 2D Materials, 2016, 3(4): 045010-1-8. |
| [146] | LIU G, SUN H Y, ZHOU J, et al. First-principles study of lattice thermal conductivity of Td-WTe2. New J. Phys., 2016, 18(3): 033017-1-9. |
| [147] | CARRETE J, MINGO N, CURTAROLO S. Low thermal conductivity and triaxial phononic anisotropy of SnSe. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2014, 105(10): 101907-1-5. |
| [148] | LI Y L, SHI X, REN D D, et al.Investigation of the anisotropic thermoelectric properties of oriented polycrystalline SnSe. Energies, 2015, 8(7): 6275-6285. |
| [149] | GUO R Q, WANG X J, KUANG Y D, et al. First-principles study of anisotropic thermoelectric transport properties of IV-VI semiconductor compounds SnSe and SnS. Phys. Rev. B, 2015, 92(11): 115202-1-13. |
| [150] | SUN B Z, MA Z, HE C, et al.Anisotropic thermoelectric properties of layered compounds in SnX2(X = S, Se): a promising thermoelectric material. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17(44): 29844-29853. |
| [151] | JANG H, RYDER C R, WOOD J D, et al. 3D anisotropic thermal conductivity of exfoliated rhenium disulfide. Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(35): 1700650-1-6. |
| [152] | YU S, ZHU H, ESHUN K, et al. Strain-engineering the anisotropic electrical conductance in ReS2 monolayer. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2016, 108(19): 191901-1-6. |
| [153] | MENG M, SHI C G, LI T, et al.Magnetism induced by cationic defect in monolayer ReSe2 controlled by strain engineering. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 425: 696-701. |
| [154] | MIN Y M, WANG A Q, REN X M, et al.Defect formation and electronic structure regulated by strain engineering in ReS2. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018, 427: 942-948. |
| [155] | ZHOU Z H, WEI B C, HE C Y, et al.Anisotropic Raman scattering and mobility in monolayer 1Td-ReS2 controlled by strain engineering. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 404: 276-281. |
| [156] | ZHANG X O, LI Q F. Strain-induced magnetism in ReS2 monolayer with defects. Chin. Phys. B, 2016, 25(11): 117103-1-5. |
| [157] | LI T H, ZHOU Z H, GUO J H, et al. Raman scattering modification in monolayer ReS2 controlled by strain engineering. Chin. Phys. Lett., 2016, 33(4): 046201-1-5. |
| [158] | LI Y L, LI Y, TANG C.Strain engineering and photocatalytic application of single-layer ReS2. Int. [J]. Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(1): 161-167. |
| [159] | KAO Y C, HUANG T, LIN D Y, et al. Anomalous structural phase transition properties in ReSe2 and Au-doped ReSe2. J. Chem. Phys., 2012, 137(2): 024509-1-7. |
| [160] | YAN Y, JIN C, WANG J, et al.Associated lattice and electronic structural evolutions in compressed multilayer ReS2. [J]. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2017, 8(15): 3648-3655. |
| [161] | HOU D, MA Y, DU J, et al.High pressure X-ray diffraction study of ReS2. J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2010, 71(11): 1571-1575. |
| [162] | NAUMOV P G, ELGHAZALI M A, MIRHOSSEINI H, et al. Pressure-induced metallization in layered ReSe2. J. Phys. Condens Matter, 2017, 30(3): 035401-1-6. |
| [163] | YANG S, WANG C, SAHIN H, et al.Tuning the optical, magnetic, and electrical properties of ReSe2 by nanoscale strain engineering. Nano Lett., 2015, 15(3): 1660-1666. |
| [164] | ZHOU D, ZHOU Y, PU C, et al.Pressure-induced metallization and superconducting phase in ReS2. npj Quantum Mater., 2017, 2(19): 1-7. |
| [165] | YAGMURCUKARDES M, BACAKSIZ C, SENGER R T, et al. Hydrogen-induced structural transition in single layer ReS2. 2D Materials, 2017, 4(3): 035013-1-8. |
| [166] | JO S H, PARK H Y, KANG D H, et al.Broad detection range rhenium diselenide photodetector enhanced by (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane and triphenylphosphine treatment. Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(31): 6711-6718. |
| [167] | ALI M H, KANG D H, PARK J H.Rhenium diselenide (ReSe2) infrared photodetector enhanced by (3-aminopropyl) trimethoxysilane (APTMS) treatment. Org. Electron., 2018, 53: 14-19. |
| [168] | ZHANG X, LI Q. Electronic and magnetic properties of nonmetal atoms adsorbed ReS2 monolayers. J. Appl. Phys., 2015, 118(6): 064306-1-7. |
| [169] | LUO M, SHEN Y H, YIN T L.Structural, electronic, and magnetic properties of transition metal doped ReS2 monolayer. JETP Letters, 2017, 105(4): 255-259. |
| [170] | LOH G C, PANDEY R.Robust magnetic domains in fluorinated ReS2 monolayer. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17(28): 18843-18853. |
| [171] | OBODO K O, OUMA C N M, OBODO J T, et al. Influence of transition metal doping on the electronic and optical properties of ReS2 and ReSe2 monolayers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017, 19(29): 19050-19057. |
| [1] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | TIAN Ruizhi, LAN Zhengyi, YIN Jie, HAO Nanjing, CHEN Hangrong, MA Ming. Microfluidic Technology Based Synthesis of Inorganic Nano-biomaterials: Principles and Progress [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [8] | ZHANG Jiguo, WU Tian, ZHAO Xu, YANG Fan, XIA Tian, SUN Shien. Improvement of Cycling Stability of Cathode Materials and Industrialization Process for Sodium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [9] | YIN Jie, GENG Jiayi, WANG Kanglong, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Recent Advances in 3D Printing and Densification of SiC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [10] | CHEN Guangchang, DUAN Xiaoming, ZHU Jinrong, GONG Qing, CAI Delong, LI Yuhang, YANG Donglei, CHEN Biao, LI Xinmin, DENG Xudong, YU Jin, LIU Boya, HE Peigang, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. Advanced Ceramic Materials in Helicopter Special Structures: Research Progress and Application Prospect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [11] | FAN Xiaobo, ZU Mei, YANG Xiangfei, SONG Ce, CHEN Chen, WANG Zi, LUO Wenhua, CHENG Haifeng. Research Progress on Proton-regulated Electrochemical Ionic Synapses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [12] | HAIREGU Tuxun, GUO Le, DING Jiayi, ZHOU Jiaqi, ZHANG Xueliang, NUERNISHA Alifu. Research Progress of Optical Bioimaging Technology Assisted by Upconversion Fluorescence Probes in Tumor Imaging [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [13] | SUN Shujuan, ZHENG Nannan, PAN Haokun, MA Meng, CHEN Jun, HUANG Xiubing. Research Progress on Preparation Methods of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [14] | TAO Guilong, ZHI Guowei, LUO Tianyou, OUYANG Peidong, YI Xinyan, LI Guoqiang. Progress on Key Technologies of Cavity-structured Thin Film Bulk Acoustic Wave Filter [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| [15] | ZHOU Fan, TIAN Zhilin, LI Bin. Research Progress on Carbide Ultra-high Temperature Ceramic Anti-ablation Coatings for Thermal Protection System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 1-16. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||