
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 433-339.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240426
Special Issue: 【信息功能】发光材料与器件(202506)
• RESEARCH LETTER • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Zi1( ), ZHANG Aidi1,2(
), ZHANG Aidi1,2( ), GONG Ke2, LIU Haihua1, YU Gang3, SHAN Qingsong4, LIU Yong2, ZENG Haibo4(
), GONG Ke2, LIU Haihua1, YU Gang3, SHAN Qingsong4, LIU Yong2, ZENG Haibo4( )
)
Received:2024-10-08
Revised:2024-11-15
Published:2025-04-20
Online:2024-12-16
Contact:
ZHANG Aidi, senior engineer. E-mail: zhangaidi@bready.cn;About author:CHEN Zi (1985-), female, PhD. E-mail: chenzi@hyit.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
CHEN Zi, ZHANG Aidi, GONG Ke, LIU Haihua, YU Gang, SHAN Qingsong, LIU Yong, ZENG Haibo. High-brightness and Monodisperse Quaternary CuInZnS@ZnS Quantum Dots with Tunable and Long-lived Emission[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 433-339.
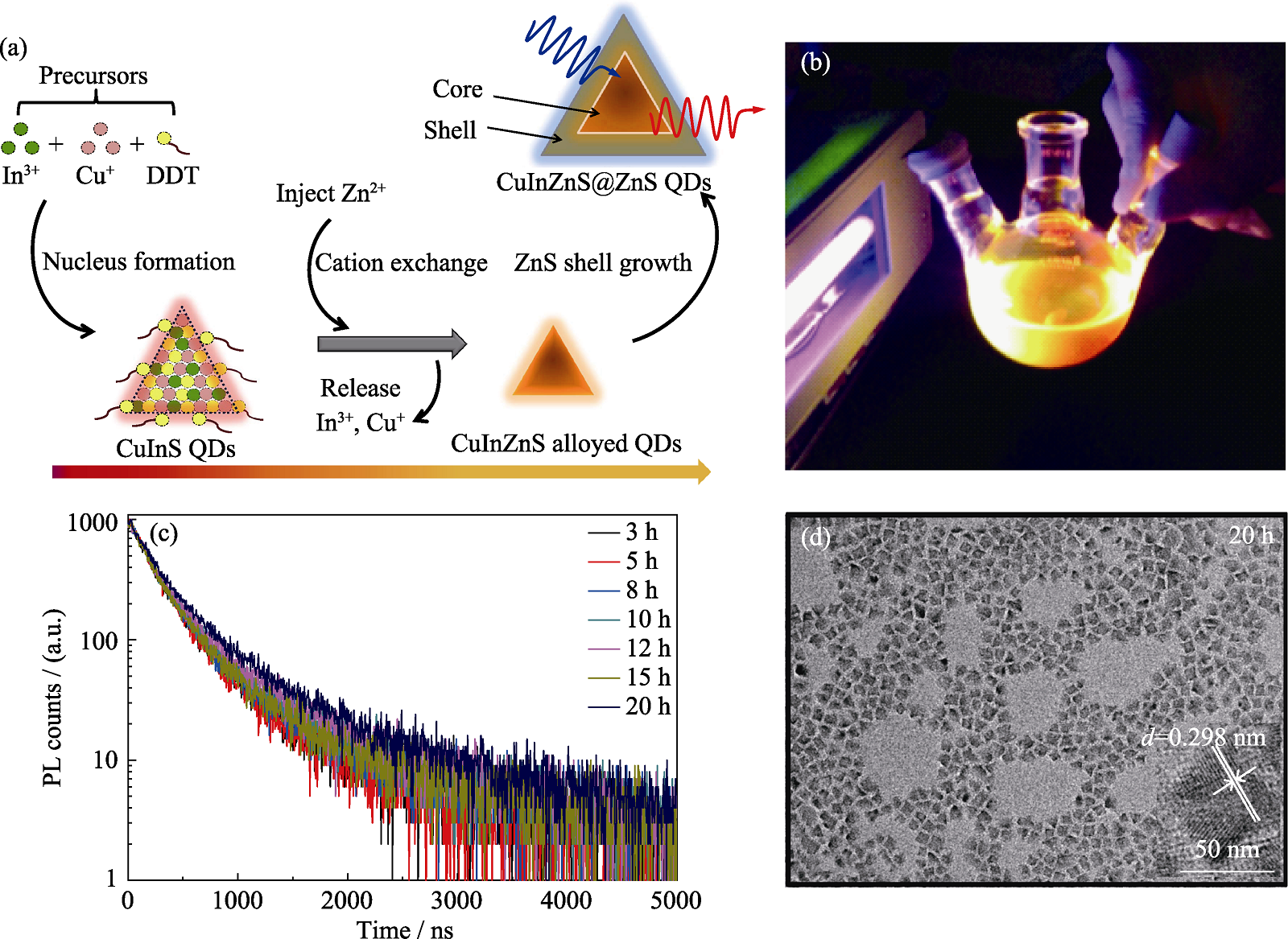
Fig. 1 Optical and morphology characterization of the CuInS-based QDs (a) Synthetic route of the CuInS-based QDs; (b) Photograph of the CuInZnS@ZnS QDs with shell growth of 20 h (Cu : In : Zn is 1 : 2 : 3) under 365 nm showing brilliant luminescence; (c) Transient PL decays of the CuInZnS@ZnS QDs with different shell growth time (Cu : In : Zn is 1 : 2 : 3); (d) TEM images of the CuInZnS/ZnS QDs (Cu : In : Zn is 1 : 2 : 3) with shell growth of 20 h. Colorful figures are available on website
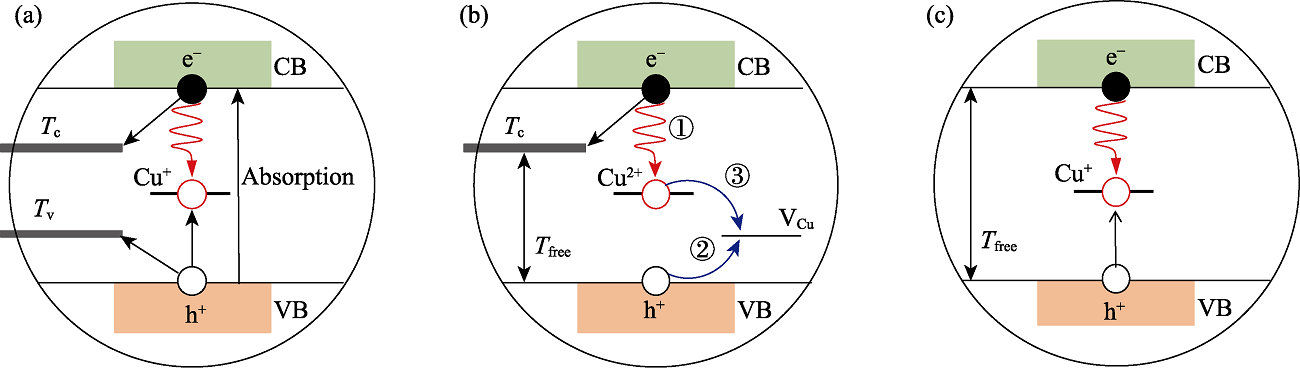
Fig. 2 Schematic depictions of relaxation processes in stoichiometric CuInS QDs (a), Cu-deficient CuInS QDs (b), and Cu-deficient CuInZnS@ZnS core/shell QDs (c) (a) Photon absorption is mainly due to the VB to CB transition. For the CuInS QDs with Cu/In ratio close to stoichiometric, the PL emission was due to radiative recombination of the CB electron with the hole existing in the intragap Cu+ state. (b) For the Cu-deficient CuInS QDs, there are three main processes. Process ①: a hole existing in the ground state forms Cu2+ defect, and it can directly recombine with the CB electron. Process ②: the recombination process was slow with the lifetime lasting hundreds of nanoseconds. To dominate the PL emission, another Cu vacancy trap (noted as VCu) quickly captured the photogenerated hole from the VB state, and formed a charge-compensated pair with the Cu2+ defect. Process ③: the trapped hole at VCu center radiatively recombined with the electron and finished the whole recombination process. (c) For the Cu-deficient core/shell QDs, the diffusion of Zn2+ ions occupied and decreased the VCu intragap states, and the thick ZnS shell eliminated the electron trap bands associated with the CB. The recombination of hot electron at CB edge and hole located at the intragap state (Cu+) dominated the PL decay process.
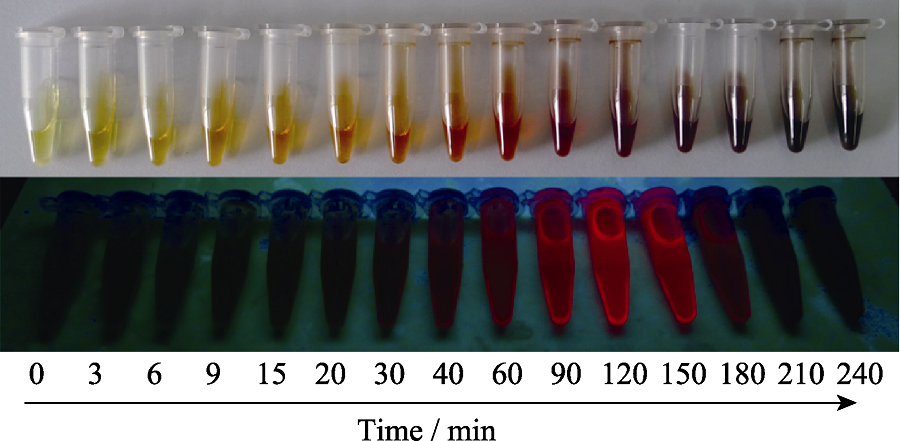
Fig. S2 Digital photographs of CuInS QDs in a typical nucleation growth process under daylight lamp and UV lamp (365 nm) DDT was chosen as the sulfur source, surface ligand, and solvent. The reaction temperature was 200 ℃
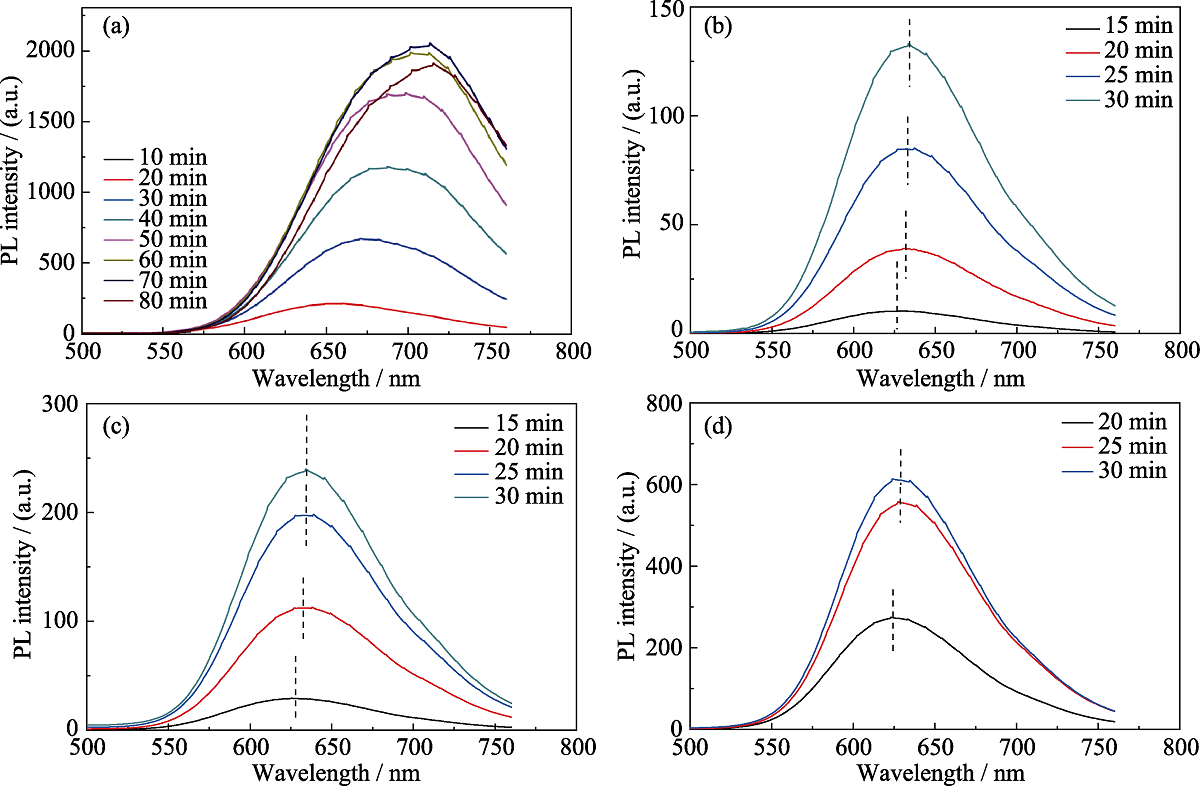
Fig. S4 Temporal evolution of PL emission spectra of CuInS QDs synthesized with different molar stoichiometric ratios of Cu : In precursors (a-d) stand for 1 : 1, 1 : 2, 1 : 4, and 1 : 6. DDT was chosen as the sulfur source. The aliquots of QDs samples for the PL intensity test were fixed. PL spectra were recorded with excitation at 450 nm
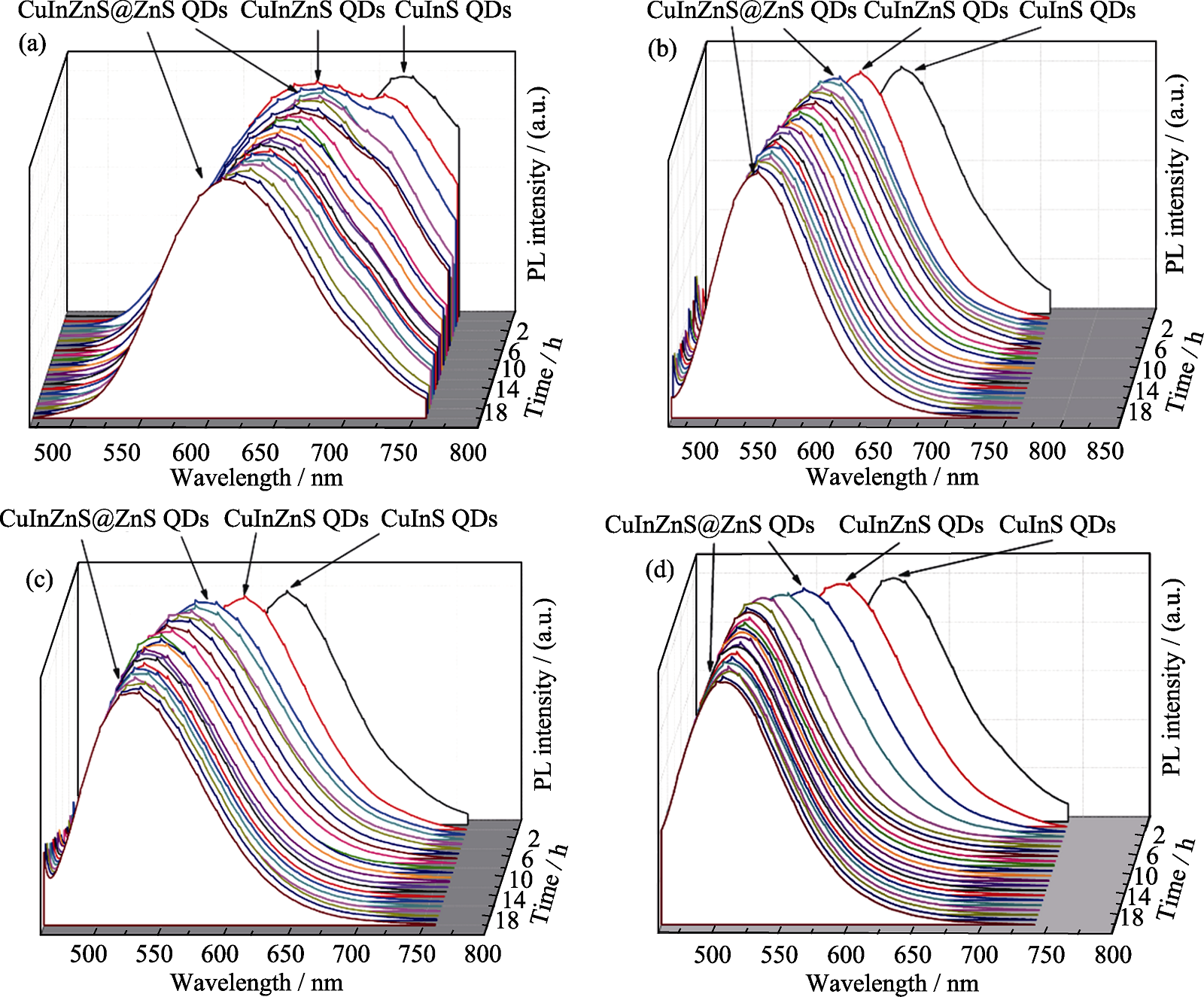
Fig. S5 Temporal evolution of PL spectra of CuInS QDs, CuInZnS QDs, and CuInZnS@ZnS QDs with different growth time (a-d) stand for the stoichiometric ratio of Cu : In at 1 : 1, 1 : 2, 1 : 4, and 1 : 6. PL spectra were recorded with excitation at 450 nm
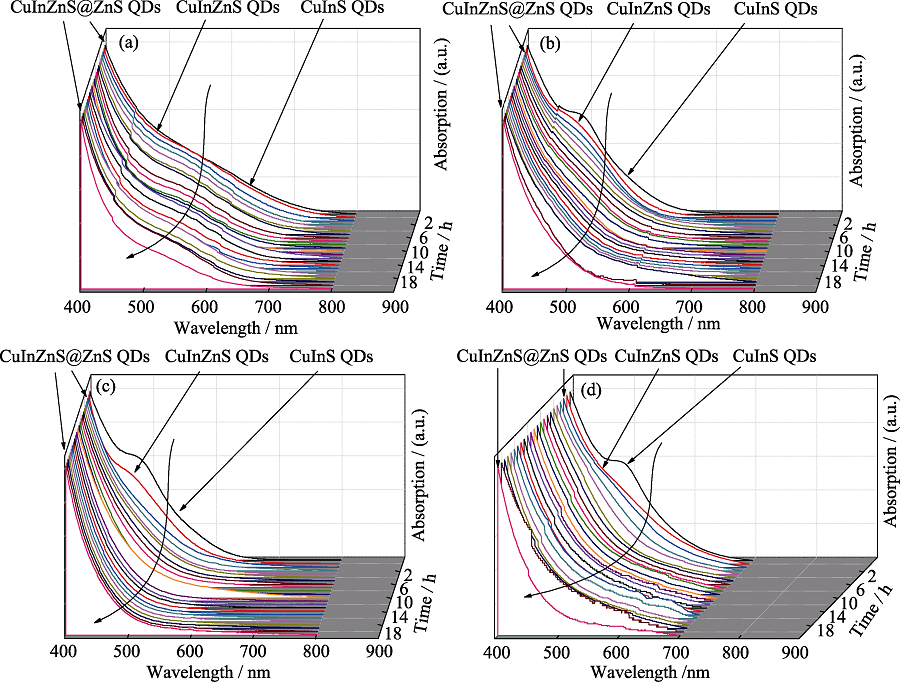
Fig. S6 Temporal evolution of UV-Vis absorption spectra of CuInS QDs, CuInZnS QDs, CuInZnS@ZnS QDs synthesized with different molar stoichiometric ratios of Cu : In precursors (a-d) stand for the stoichiometric ratio of Cu : In at 1 : 1, 1 : 2, 1 : 4, and 1 : 6. The absorption shoulder/onset is more blue-shifted with less Cu/In ratio
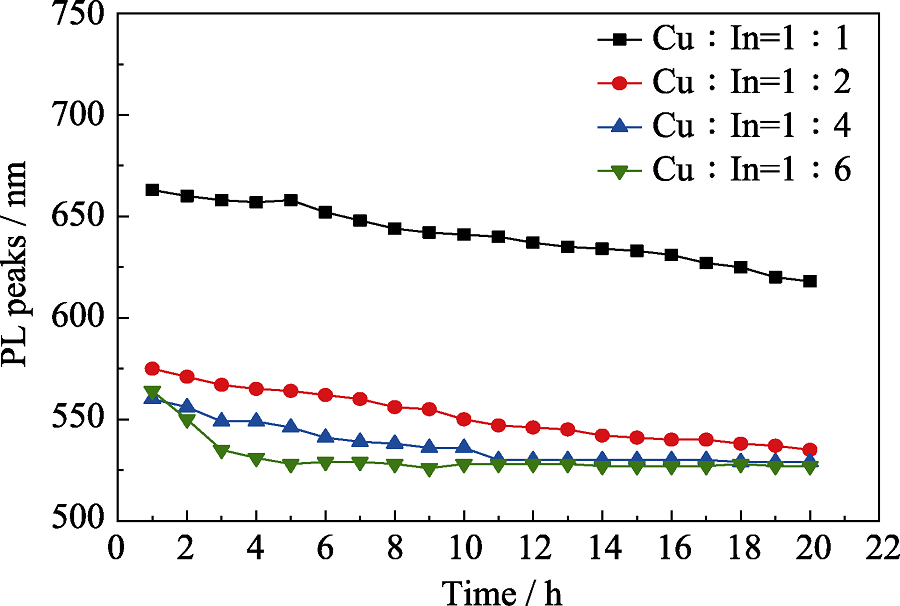
Fig. S7 Temporal evolution of PL central emission peaks for CuInZnS@ZnS QDs with different shell growth time The stoichiometric ratios of Cu : In are 1 : 1, 1 : 2, 1 : 4, and 1 : 6
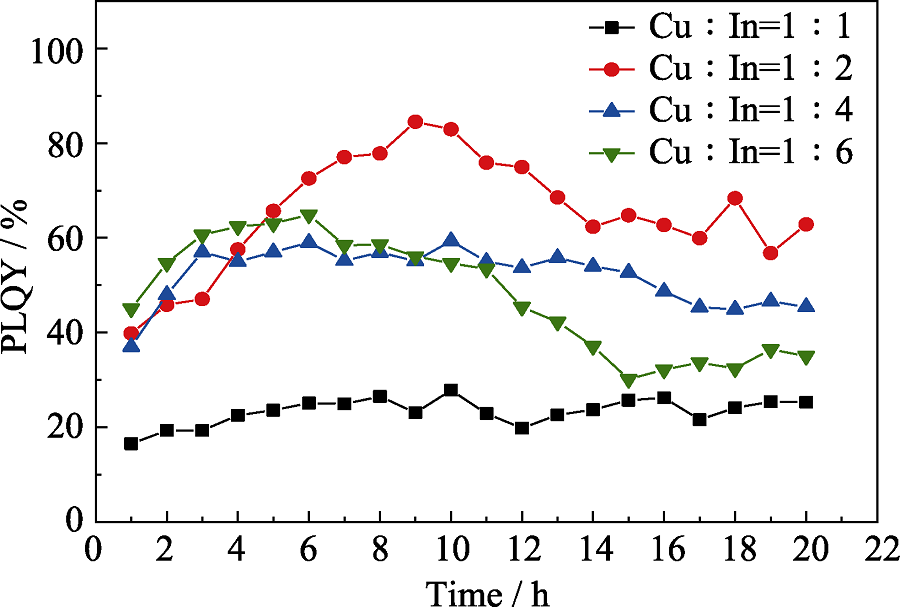
Fig. S8 Temporal evolution of PLQY for CuInZnS@ZnS QDs with different shell growth time The stoichiometric ratios of Cu : In are 1 : 1, 1 : 2, 1 : 4, and 1 : 6
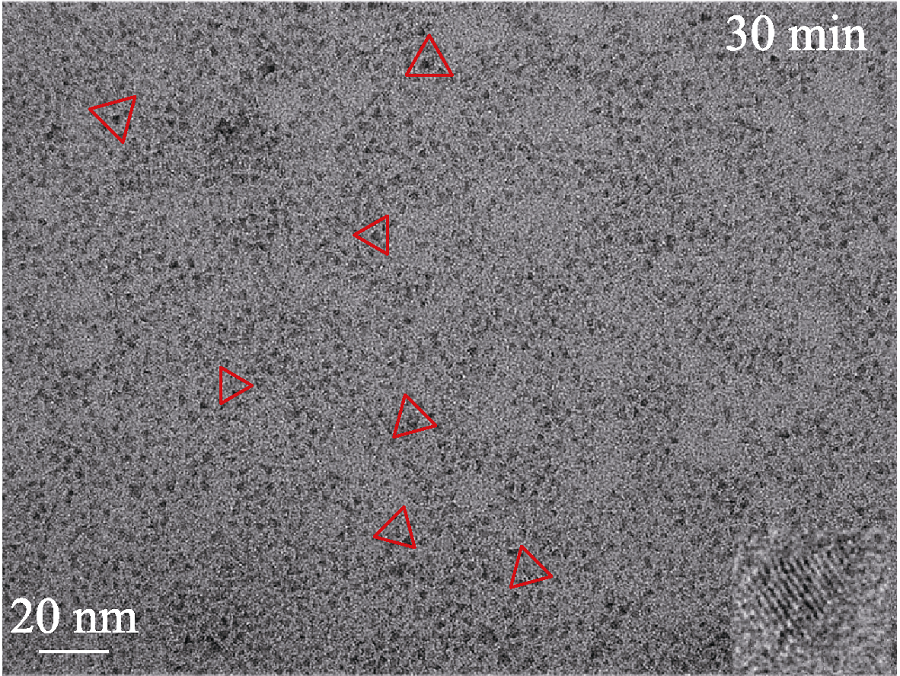
Fig. S11 TEM image of CuInS QDs (the stoichiometric ratio of Cu : In at 1 : 2) with reaction time of 30 min The red triangle frames indicate the shapes of the CuInS QDs
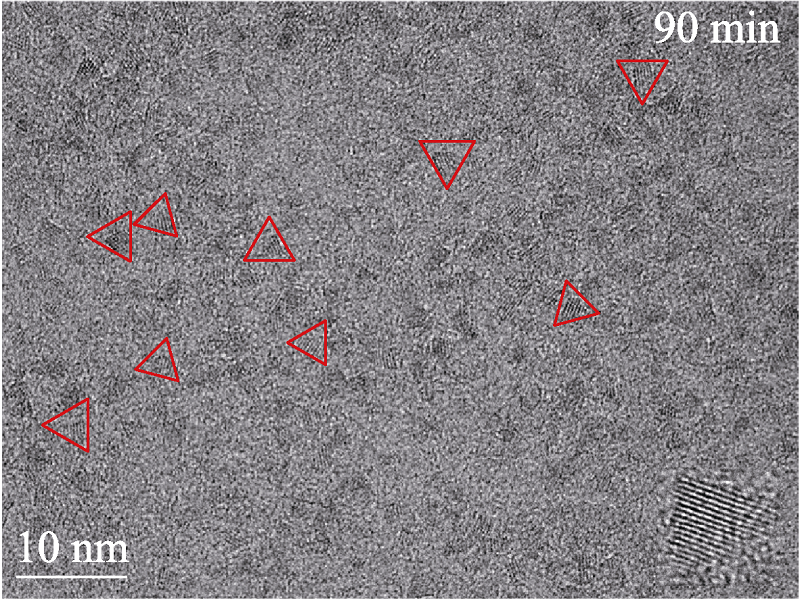
Fig. S12 TEM image of CuInZnS QDs (the stoichiometric ratio of Cu : In : Zn at 1 : 2 : 3) with Zn etching time of 90 min The red triangle frames indicate the shapes of the CuInZnS QDs
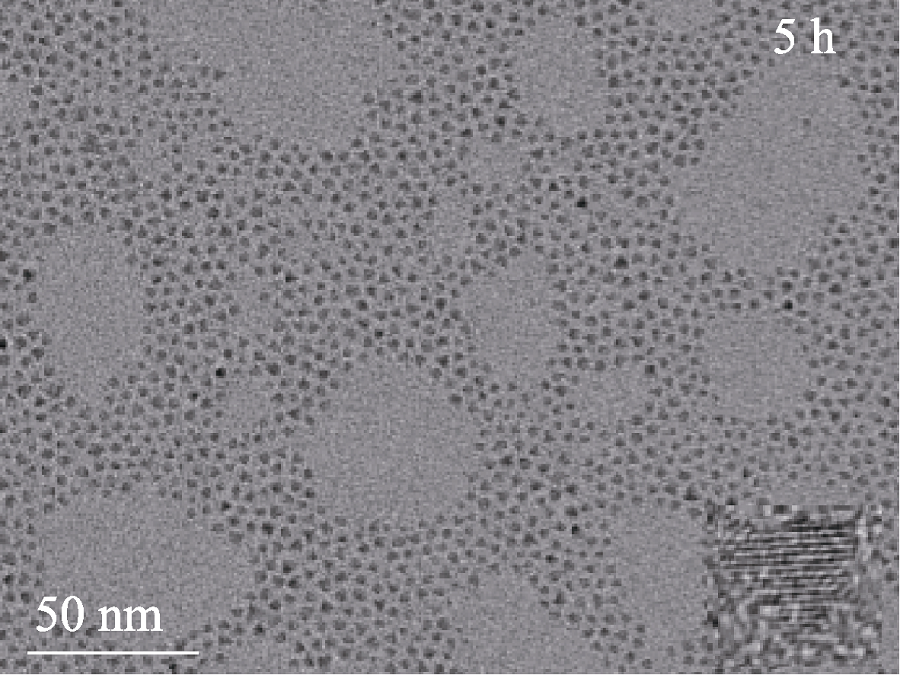
Fig. S13 TEM images of CuInZnS@ZnS QDs (the stoichioetric ratio of Cu : In : Zn at 1 : 2 : 3) with ZnS shell growth time of 5 h The insert showing their representative high- esolution TEM images
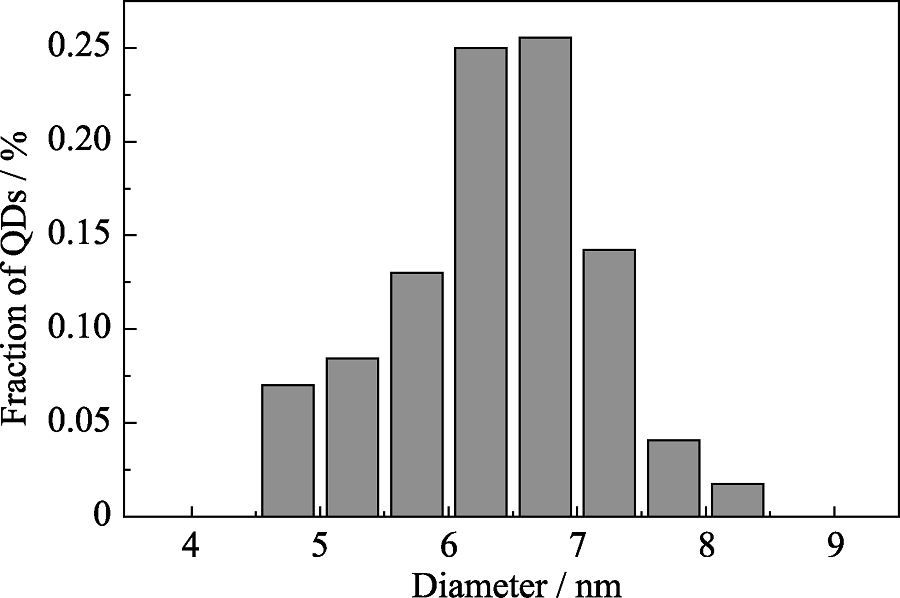
Fig. S14 Size distribution histograms for CuInZnS/ZnS QDs (Cu : In : Zn at 1 : 2 : 3) with shell growth of 20 h To build the histograms, over 100 particles were measured
| Cu : In precursor | λem/nm | PLQY/% | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 : 1 | 710 | 3.3 | 264 (65) |
| 1 : 2 | 633 | 8.8 | 270 (71) |
| 1 : 4 | 625 | 18.9 | 293 (86) |
| 1 : 6 | 618 | 21.0 | 299 (95) |
Table S1 Relevant parameters for CuInS QDs synthesized with different molar stoichiometric ratios of Cu : In. λem at the PL central emission peak from the QDs solution when excited at 450 nm. The amounts of DDT (10 mL) and CuI (0.1 mmol) were held fixed
| Cu : In precursor | λem/nm | PLQY/% | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 : 1 | 710 | 3.3 | 264 (65) |
| 1 : 2 | 633 | 8.8 | 270 (71) |
| 1 : 4 | 625 | 18.9 | 293 (86) |
| 1 : 6 | 618 | 21.0 | 299 (95) |
| Cu : In precursor | λem/nm | PLQY/% | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 : 1 | 675 | 14.7 | 277 (102) |
| 1 : 2 | 596 | 16.8 | 284 (101) |
| 1 : 4 | 590 | 24.8 | 284 (110) |
| 1 : 6 | 581 | 36.3 | 282 (112) |
Table S2 Relevant parameters for CuInZnS alloyed QDs synthesized with differnt molar stoichiometric ratios of Cu : In. λem is the PL central emission peak from the QDs solution when excited at 450 nm. The amounts of DDT (10 mL) and CuI (0.1 mmol) were held fixed
| Cu : In precursor | λem/nm | PLQY/% | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 : 1 | 675 | 14.7 | 277 (102) |
| 1 : 2 | 596 | 16.8 | 284 (101) |
| 1 : 4 | 590 | 24.8 | 284 (110) |
| 1 : 6 | 581 | 36.3 | 282 (112) |
| Shell reaction time/h | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|
| 3 | 588 (204) |
| 5 | 647 (208) |
| 8 | 714 (214) |
| 10 | 724 (211) |
| 12 | 729 (219) |
| 15 | 751 (222) |
| 20 | 755 (231) |
Table S3 PL lifetime of CuInZnS@ZnS QDs with the stoichiometric ratio of Cu : In at 1 : 2 after excited at 450 nm.
| Shell reaction time/h | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|
| 3 | 588 (204) |
| 5 | 647 (208) |
| 8 | 714 (214) |
| 10 | 724 (211) |
| 12 | 729 (219) |
| 15 | 751 (222) |
| 20 | 755 (231) |
| Shell reaction time/h | PL emission peak/nm | PLQY/% | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 546 | 57 | 509 (171) |
| 10 | 536 | 50 | 530 (177) |
| 15 | 531 | 53 | 558 (174) |
| 20 | 530 | 58 | 549 (165) |
Table S4 Relevant parameters for CuInZnS@ZnS QDs with the stoichiometric ratio of Cu : In at 1 : 4, synthesized with different ZnS shell growth time. λem is the PL central emission peak from the QDs solution when excited at 450 nm. The amounts of DDT (10 mL) and CuI (0.1 mmol) were held fixed.
| Shell reaction time/h | PL emission peak/nm | PLQY/% | PL decay/ns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 546 | 57 | 509 (171) |
| 10 | 536 | 50 | 530 (177) |
| 15 | 531 | 53 | 558 (174) |
| 20 | 530 | 58 | 549 (165) |
| [1] | JAISWAL J K, MATTOUSSI H, MAURO J M, et al. Long-term multiple color imaging of live cells using quantum dot bioconjugates. Nature Biotechnology, 2002, 21: 47. |
| [2] |
CHAN W C, NIE S. Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science, 1998, 281(5385): 2016.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | ZHANG Y, LV Y, LI L S, et al. Aminophosphate precursors for the synthesis of near-unity emitting InP quantum dots and their application in liver cancer diagnosis. Exploration, 2022, 2(4):20220082. |
| [4] | WU R, WANG T, WU M, et al. Synthesis of highly stable CuInZnS/ZnS//ZnS quantum dots with thick shell and its application to quantitative immunoassay. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 348: 447. |
| [5] | MEINARDI F, COLOMBO A, VELIZHANIN K A, et al. Large- area luminescent solar concentrators based on ‘Stokes-shift- engineered’ nanocrystals in a mass-polymerized PMMA matrix. Nature Photonics, 2014, 8(5):392. |
| [6] | DONG H, RAN C, GAO W, et al. Metal halide perovskite for next-generation optoelectronics: progresses and prospects. eLight, 2023, 3: 3. |
| [7] | YUAN M, LIU M, SARGENT E H. Colloidal quantum dot solids for solution-processed solar cells. Nature Energy, 2016, 1(3):16016. |
| [8] | SARGENT E H. Colloidal quantum dot solar cells. Nature Photonics, 2012, 6(3):133. |
| [9] | CAO W, ZHANG W, DONG L, et al. Progress on quantum dot photocatalysts for biomass valorization. Exploration, 2023, 3(6):20220169. |
| [10] | DAI X, ZHANG Z, JIN Y, et al. Solution-processed, high- performance light-emitting diodes based on quantum dots. Nature, 2014, 515(7525):96. |
| [11] | SUN Q, WANG Y A, LI L S, et al. Bright, multicoloured light- emitting diodes based on quantum dots. Nature Photonics, 2007, 1(12):717. |
| [12] | DONG C, LIU H, ZHANG A, et al. Controllable blinking-to- nonblinking behavior of aqueous CdTeS alloyed quantum dots. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2014, 20(7): 1940. |
| [13] | ZHANG A, DONG C, LIU H, et al. Blinking behavior of CdSe/CdS quantum dots controlled by alkylthiols as surface trap modifiers. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(46):24592. |
| [14] |
MCDONALD S A, KONSTANTATOS G, ZHANG S, et al. Solution-processed PbS quantum dot infrared photodetectors and photovoltaics. Nature Materials, 2005, 4(2):138.
PMID |
| [15] | HUANG P, SUN S, LEI H, et al. Nonlocal interaction enhanced biexciton emission in large CsPbBr3 nanocrystals. eLight, 2023, 3: 10. |
| [16] | LIAN W, TU D, WENG X, et al. Near-Infrared nanophosphors based on CuInSe2 quantum dots with near-unity photoluminescence quantum yield for micro-LEDs applications. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(9):2311011. |
| [17] | DE TRIZIO L, PRATO M, GENOVESE A, et al. Strongly fluorescent quaternary Cu-In-Zn-S nanocrystals prepared from Cu1-xInS2 nanocrystals by partial cation exchange. Chemistry of Materials, 2012, 24(12):2400. |
| [18] | LI L, DAOU T J, TEXIER I, et al. Highly luminescent CuInS2/ ZnS core/shell nanocrystals: cadmium-free quantum dots for in vivo imaging. Chemistry of Materials, 2009, 21(12):2422. |
| [19] | ZHONG H, ZHOU Y, YE M, et al. Controlled synthesis and optical properties of colloidal ternary chalcogenide CuInS2 nanocrystals. Chemistry of Materials, 2008, 20(20):6434. |
| [20] | MCDANIEL H, FUKE N, PIETRYGA J M, et al. Engineered CuInSexS2-x quantum dots for sensitized solar cells. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2013, 4(3):355. |
| [21] |
LI L, PANDEY A, WERDER D J, et al. Efficient synthesis of highly luminescent copper indium sulfide-based core/shell nanocrystals with surprisingly long-lived emission. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(5):1176.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | ZHONG H, LO S S, MIRKOVIC T, et al. Noninjection gram-scale synthesis of monodisperse pyramidal CuInS2 nanocrystals and their size-dependent properties. ACS Nano, 2010, 4(9):5253.<br |
| [23] |
XIE R, RUTHERFORD M, PENG X. Formation of high-quality I-III-VI semiconductor nanocrystals by tuning relative reactivity of cationic precursors. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(15):5691.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | CHUANG P H, LIN C C, LIU R S. Emission-tunable CuInS2/ZnS quantum dots: structure, optical properties, and application in white light-emitting diodes with high color rendering index. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(17):15379. |
| [25] | ZHANG A, DONG C, LI L, et al. Non-blinking (Zn)CuInS/ZnS quantum dots prepared by in situ interfacial alloying approach. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1):15227. |
| [26] | THUY U T D, REISS P, LIEM N Q. Luminescence properties of In(Zn)P alloy core/ZnS shell quantum dots. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 97(19):193104. |
| [27] | KIM Y K, AHN S H, CHUNG K, et al. The photoluminescence of CuInS2 nanocrystals: effect of non-stoichiometry and surface modification. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(4):1516. |
| [28] | PARK J, KIM S W. CuInS2/ZnS core/shell quantum dots by cation exchange and their blue-shifted photoluminescence. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(11):3745. |
| [29] | BOLDT K, KIRKWOOD N, BEANE G A, et al. Synthesis of highly luminescent and photo-stable, graded shell CdSe/CdxZn1-xS nanoparticles by in situ alloying. Chemistry of Materials, 2013, 25(23):4731. |
| [30] |
CHEN Y, LI S, HUANG L, et al. Green and facile synthesis of water-soluble Cu-In-S/ZnS core/shell quantum dots. Inorganic Chemistry, 2013, 52(14):7819.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
MAHLER B, SPINICELLI P, BUIL S, et al. Towards non-blinking colloidal quantum dots. Nature Materials, 2008, 7(8):659.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | SPERANSKAYA E S, BELOGLAZOVA N V, ABE S, et al. Hydrophilic, bright CuInS2 quantum dots as Cd-free fluorescent labels in quantitative immunoassay. Langmuir, 2014, 30(25):7567. |
| [33] | NAM D E, SONG W S, YANG H. Noninjection, one-pot synthesis of Cu-deficient CuInS2/ZnS core/shell quantum dots and their fluorescent properties. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2011, 361(2):491. |
| [34] | CHOI H S, KIM Y, PARK J C, et al. Highly luminescent, off-stoichiometric CuxInyS2/ZnS quantum dots for near-infrared fluorescence bio-imaging. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(54):43449. |
| [35] | PORTNIAGIN A S, NING J, WANG S, et al. Monodisperse CuInS2/CdS and CuInZnS2/CdS core-shell nanorods with a strong near-infrared emission. Advanced Optical Materials, 2022, 10(8):2102590. |
| [36] | LI J J, WANG Y A, GUO W, et al. Large-scale synthesis of nearly monodisperse CdSe/CdS core/shell nanocrystals using air-stable reagents via successive ion layer adsorption and reaction. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(41):12567. |
| [37] |
PENG Z A, PENG X. Formation of high-quality CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals using CdO as precursor. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2001, 123(1):183.
PMID |
| [38] | FUHR A S, YUN H J, MAKAROV N S, et al. Light emission mechanisms in CuInS2 quantum dots evaluated by spectral electrochemistry. ACS Photonics, 2017, 4(10):2425. |
| [39] | GONG K, KELLEY D F. Lattice strain limit for uniform shell deposition in zincblende CdSe/CdS quantum dots. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2015, 6(9):1559. |
| [40] | GONG K, BEANE G, KELLEY D F. Strain release in metastable CdSe/CdS quantum dots. Chemical Physics, 2016, 471: 18. |
| [41] | GONG K, KELLEY D F. A predictive model of shell morphology in CdSe/CdS core/shell quantum dots. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2014, 141(19):194704. |
| [1] | WU Huaxin, ZHANG Qihao, YAN Haixue, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. Optimization of Thermoelectric Transport Properties in Nanocomposite MgAgSb-based Alloys [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 997-1004. |
| [2] | HU Xuemin, ZHANG Xingjian, JIANG Zhihao, HUANG Liwen, DING Kaining, ZHANG Shengli. First-principles Study on Oxygen Evolution Reaction Activity of CoPS3 Quantum Dots Edge States Modified with Oxygen [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1229-1236. |
| [3] | LÜ Xinyi, XIANG Hengyang, ZENG Haibo. Long-range Ordered Films Boost Efficient Perovskite Quantum Dot Light-emitting Devices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 111-112. |
| [4] | YUE Zihao, YANG Xiaotu, ZHANG Zhengliang, DENG Ruixiang, ZHANG Tao, SONG Lixin. Effect of Pb2+ on the Luminescent Performance of Borosilicate Glass Coated CsPbBr3 Perovskite Quantum Dots [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 449-456. |
| [5] | CHEN Hao, FAN Wenhao, AN Decheng, CHEN Shaoping. Improvement of Thermoelectric Performance of SnTe by Energy Band Optimization and Carrier Regulation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 306-312. |
| [6] | ZHANG Fengjuan, HAN Boning, ZENG Haibo. Perovskite Quantum Dot Photovoltaic and Luminescent Concentrator Cells: Current Status and Challenges [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(2): 117-128. |
| [7] | TIAN Jianjian, MA Xia, WANG Min, YAO Heliang, HUA Zile, ZHANG Lingxia. Sn Quantum Dots for Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to HCOOH [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1337-1342. |
| [8] | ZENG Fanxin, LIU Chuang, CAO Yuliang. Sodium Storage Behavior of Nanoporous Sb/MCNT Anode Material with High Cycle Stability by Dealloying Route [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1137-1144. |
| [9] | SHU Mengyang, LU Jialin, ZHANG Zhijie, SHEN Tao, XU Jiayue. CsPbBr3 Perovskite Quantum Dots/Ultrathin C3N4 Nanosheet 0D/2D Composite: Enhanced Stability and Photocatalytic Activity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1217-1222. |
| [10] | CHEN Ting, XU Yanqiao, JIANG Weihui, XIE Zhixiang, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. Ionic Liquid Assisted Microwave Synthesis of Cu-In-Zn-S/ZnS Quantum Dots and Their Application in White LED [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 439-446. |
| [11] | LI Sheng-Song, ZHENG Yong-Chao, MENG Shu-Lin, WU Li-Zhu, ZHONG Jin- Yi, ZHAO Chong-Lin. Core/Shell Quantum Dots and Au Nanoparticles Assembly for Effective Detection of Nerve Agent Mimic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(8): 893-898. |
| [12] | Yang LIU, Shan YU, Kai-Wen ZHENG, Wei-Wei CHEN, Xing-An DONG, Fan DONG, Ying ZHOU. NO Photo-oxidation and In-situ DRIFTS Studies on N-doped Bi2O2CO3/CdSe Quantum Dot Composite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(4): 425-432. |
| [13] | YANG Ying, PAN De-Qun, ZHANG Zheng, CHEN Tian, HAN Xiao-Min, ZHANG Li-Song, GUO Xue-Yi. Photovoltaic Performance of Ag2Se Quantum Dots Co-sensitized Solid-state Dye-sensitized Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(2): 137-144. |
| [14] | GAO Dong, ZHANG Yu-Liang, SUN Jing, FAN Hong-Jun. One-step Synthesis of Specific pH-responsive Carbon Quantum Dots and Their Luminescence Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(12): 1309-1315. |
| [15] | HAN Li, ZHANG Xiao-Min, WU De-Yong. MoS2 Quantum Dots Decorated NH2-MIL-125 Heterojunction: Preparation and Visible Light Photocatalytic Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(11): 1205-1209. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||