
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (8): 831-836.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160598
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2016-11-01
Revised:2016-12-14
Published:2017-08-15
Online:2017-07-19
About author:LI Hai-Bin. E-mail: lhb9@sina.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
LI Hai-Bin, WANG De-Ping, WU Ying-Ying, YAO Ai-Hua, YE Song. Effect of Citric Acid Concentration on the Properties of Borate Glass Bone Cement[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(8): 831-836.
| Sample | H3Cit/(g·mL-1) | CS/(g·mL-1) | GP /(g·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.1 | 0.005 | 0.056 |
| S2 | 0.2 | 0.005 | 0.056 |
| S3 | 0.4 | 0.005 | 0.056 |
Table 1 Liquid composition of samples
| Sample | H3Cit/(g·mL-1) | CS/(g·mL-1) | GP /(g·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.1 | 0.005 | 0.056 |
| S2 | 0.2 | 0.005 | 0.056 |
| S3 | 0.4 | 0.005 | 0.056 |
| Sample | Setting time/min | Injectability/% | Injection force/N |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 40±2.0 | 75±7 | 86.5 |
| S2 | 16±0.5 | >95 | 28.1 |
| S3 | 20±1.0 | 35±10 | 17.6 |
Table 2 Setting time and injectability of samples
| Sample | Setting time/min | Injectability/% | Injection force/N |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 40±2.0 | 75±7 | 86.5 |
| S2 | 16±0.5 | >95 | 28.1 |
| S3 | 20±1.0 | 35±10 | 17.6 |
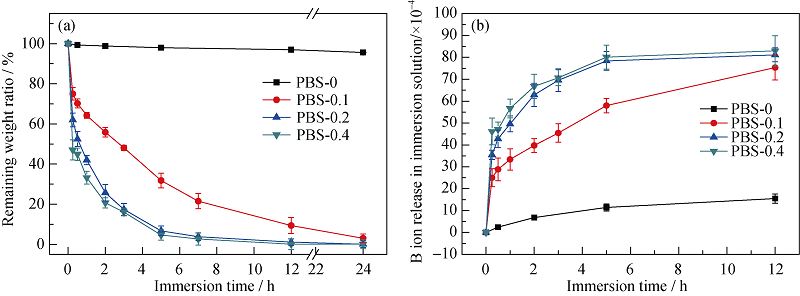
Fig. 6 Degradation curves of borate glass in the PBS-0, PBS-0.1, PBS-0.2 and PBS-0.4 (a) and the B ion release concentration in the immersion solution (b)
| [1] | LAURENCIN C, KHAN Y, El-AMIN S F, Bone graft substitutes.Expert Rev. Med. Devices, 2006, 3(1): 49-57. |
| [2] | KRETLOW J D, KLOUDA L, MIKOS A G.Injectable matrices and scaffolds for drug delivery in tissue engineering.Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59(4/5): 263-273. |
| [3] | DOADRIO J C, ARCOS D, CABANAS M V.Calcium sulphate- based cements containing cephalexin.Biomaterial, 2004, 25(13): 2629-2635. |
| [4] | KUANG G M, YAU W P, LAM W M, et al.An effective approach by a chelate reaction in optimizing the setting process of strontium incorporated calcium phosphate bone cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Re. B, 2012, 100(3): 778-787. |
| [5] | CUI XU, ZHANG YADONG, WANG HUI, et al.An injectable borate bioactive glass cement for bone repair: preparation, bioactivity and setting mechanism.Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2016, 432: 150-157. |
| [6] | CUI XU, ZHAO CUNJU, GU YIFEI, et al.A novel injectable borate bioactive glass cement for local delivery of vancomycin to cure osteomyelitis and regenerate bone. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med., 2014, 25(3): 733-745. |
| [7] | DING HAO, ZHAO CUN JU, CUI XU, et al.A novel injectable borate bioactive glass cement as an antibiotic delivery vehicle for treating osteomyelitis.Plos One, 2014, 9(1): e85472. |
| [8] | ZHANG Y, CUI X, ZHAO S, et al.Evaluation of injectable strontium-containing borate bioactive glass cement with enhanced osteogenic capacity in a critical-sized rabbit femoral condyle defect model.ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7(4): 2393-2403. |
| [9] | HESARAKI SAEED, ZAMANIAN ALI, MOZTARZADEH FATOLLAH.The influence of the acidic component of the gas- foaming porogen used in preparing an injectable porous calcium phosphate cement on its properties: acetic acid versus citric acid.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B, 2008, 86B(1): 208-216. |
| [10] | LIU X, RAHAMAN M N, DAY D E.Conversion of melt-derived microfibrous borate (13-93B3) and silicate (45S5) bioactive glass in a simulated body fluid.J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Med., 2013, 24(3): 583-595. |
| [11] | 赵翠, 任丽莉, 王栋, 等. 煅硼砂的红外光谱分析与评价. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2011, 31(8): 2109-2113. |
| [12] | HUANG W, RAHAMAN M N, DAY D E, et al.Mechanisms for converting bioactive silicate, borate, and borosilicate glasses to hydroxyapatite in dilute phosphate solutions.Phys. Chem. Glasses B, 2006, 47(6): 647-658. |
| [13] | 戈海文, 邓天龙, 姚燕, 等. 硼酸盐晶体及其溶液结构研究现状. 广东微量元素科学, 2011, 18(1): 17-23. |
| [1] | CHEN Xiangjie, LI Ling, LEI Tianfu, WANG Jiajia, WANG Yaojin. Enhanced Piezoelectric Properties of (1-x)(0.8PZT-0.2PZN)-xBZT Ceramics via Phase Boundary and Domain Engineering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 729-734. |
| [2] | LI Wenyuan, XU Jianan, DENG Han'ao, CHANG Aimin, ZHANG Bo. Effect of V5+ Substitution on Microstructure and Microwave Dielectric Properties of LaTaO4 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 697-703. |
| [3] | DONG Chenyu, ZHENG Weijie, MA Yifan, ZHENG Chunyan, WEN Zheng. Characterizations by Piezoresponse Force Microscopy on Relaxor Properties of Pb(Mg,Nb)O3-PbTiO3 Ultra-thin Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 675-682. |
| [4] | HUANG Zipeng, JIA Wenxiao, LI Lingxia. Crystal Structure and Terahertz Dielectric Properties of (Ti0.5W0.5)5+ Doped MgNb2O6 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 647-655. |
| [5] | YIN Changzhi, CHENG Mingfei, LEI Weicheng, CAI Yiyang, SONG Xiaoqiang, FU Ming, LÜ Wenzhong, LEI Wen. Effect of Ga3+ Doping on Crystal Structure Evolution and Microwave Dielectric Properties of SrAl2Si2O8 Ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 704-710. |
| [6] | SUN Yuxuan, WANG Zheng, SHI Xue, SHI Ying, DU Wentong, MAN Zhenyong, ZHENG Liaoying, LI Guorong. Defect Dipole Thermal-stability to the Electro-mechanical Properties of Fe Doped PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 545-551. |
| [7] | CHEN Yi, QIU Haipeng, CHEN Mingwei, XU Hao, CUI Heng. SiC/SiC Composite: Matrix Boron Modification and Mechanical Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [8] | CUI Ning, ZHANG Yuxin, WANG Lujie, LI Tongyang, YU Yuan, TANG Huaguo, QIAO Zhuhui. Single-phase Formation Process and Carbon Vacancy Regulation of (TiVNbMoW)Cx High-entropy Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [9] | XIONG Siyu, MO Chen, ZHU Xiaowei, ZHU Guobin, CHEN Deqin, LIU Laijun, SHI Xiaodong, LI Chunchun. Low-temperature Sintering of LiBxAl1-xSi2O6 Microwave Dielectric Ceramics with Ultra-low Permittivity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 536-544. |
| [10] | LI Ziwei, GONG Weilu, CUI Haifeng, YE Li, HAN Weijian, ZHAO Tong. (Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC Composite Ceramics: Preparation via Precursor Route and Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [11] | GAO Chenguang, SUN Xiaoliang, CHEN Jun, LI Daxin, CHEN Qingqing, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. SiBCN-rGO Ceramic Fibers Based on Wet Spinning Technology: Microstructure, Mechanical and Microwave-absorbing Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [12] | MU Haojie, ZHANG Yuanjiang, YU Bin, FU Xiumei, ZHOU Shibin, LI Xiaodong. Preparation and Properties of ZrO2 Doped Y2O3-MgO Nanocomposite Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 281-289. |
| [13] | GAO Tianyu, LIU Dong, ZHAO Sixue, DENG Wei, ZHANG Boping, ZHU Lifeng. K0.5Na0.5NbO3-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Excellent Temperature Stability and Application in Type 1-3 Transducer [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 297-304. |
| [14] | YE Junhao, ZHOU Zhenzhen, HU Chen, WANG Yanbin, JING Yanqiu, LI Tingsong, CHENG Ziqiu, WU Junlin, IVANOV Maxim, HRENIAK Dariusz, LI Jiang. Yb:Sc2O3 Transparent Ceramics Fabricated from Co-precipitated Nano-powders: Microstructure and Optical Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 215-224. |
| [15] | WANG Yueyue, HUANG Jiahui, KONG Hongxing, LI Huaizhu, YAO Xiaohong. Silver Loaded Radial Mesoporous Silica: Preparation and Application in Dental Resins [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 77-83. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||