
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (12): 1391-1396.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240137
Special Issue: 【信息功能】敏感陶瓷(202506)
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
FENG Xingzhe( ), MA Dongyun(
), MA Dongyun( ), WANG Jinmin(
), WANG Jinmin( )
)
Received:2024-03-21
Revised:2024-05-09
Published:2024-05-31
Online:2024-05-31
Contact:
WANG Jinmin, professor. E-mail: jmwang@usst.edu.cn;About author:FENG Xingzhe (1999-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 212142384@st.usst.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
FENG Xingzhe, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Porous NiMn-LDH Nanosheets Film: Solvothermal Growth and Electrochromic Properties[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1391-1396.
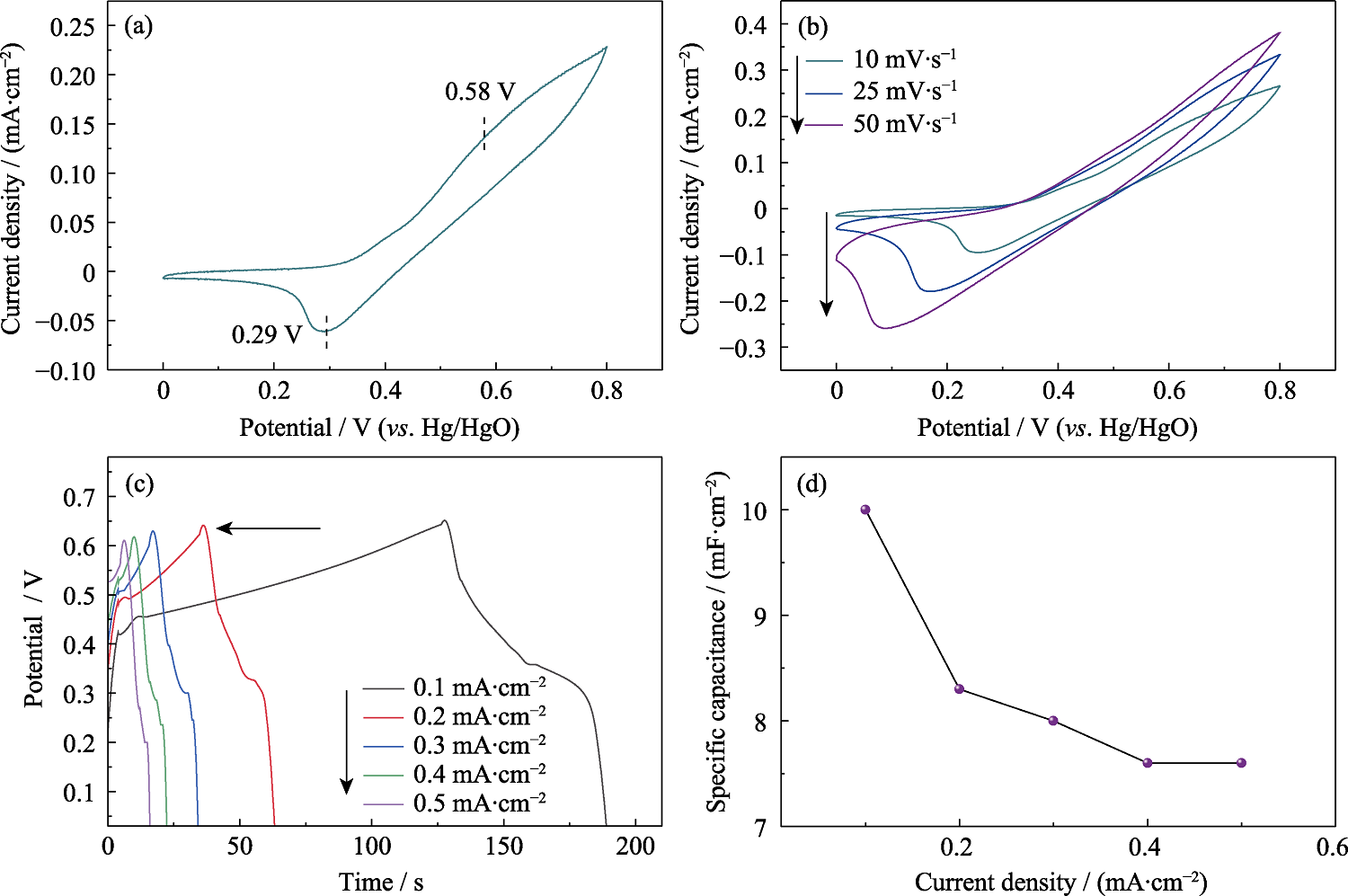
Fig. 3 Electrochemical properties of the NiMn-LDH film (a) CV curve scanned at 5 mV·s-1; (b) CV curves at different scanning rates; (c) GCD curves at different current densities; (d) Specific capacitance variations with respect to the current density
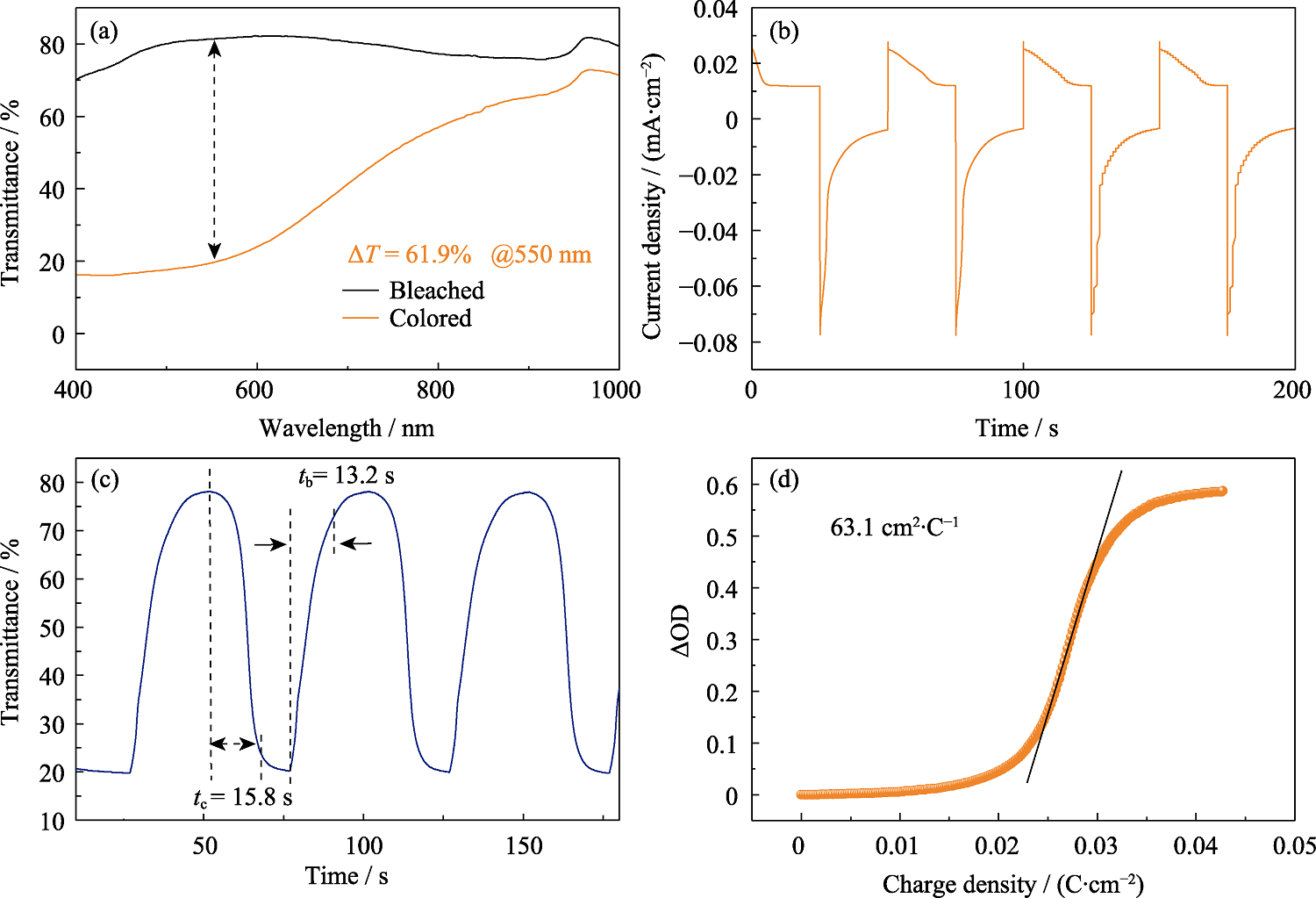
Fig. 5 Electrochromic properties of the NiMn-LDH film (a) Transmittance spectra in the colored and bleached states; (b) Time-current curve measured at -1.2 V for 25 s and 1.0 V for 25 s; (c) Real-time transmittance change; (d) Optical density variations with respect to the charge density at 550 nm
| [1] | WANG J L, SHENG S Z, HE Z, et al. Self-powered flexible electrochromic smart window. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(23):9976. |
| [2] | MA D Y, EH A L S, CAO S, et al. Wide-spectrum modulated electrochromic smart windows based on MnO2/PB films. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2022, 14(1):1443. |
| [3] |
CAI G F, WANG J X, LEE P S. Next-generation multifunctional electrochromic devices. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2016, 49(8):1469.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | ZHOU K L, WANG H, ZHANG Q Q, et al. Dynamic process of ions transport and cyclic stability of WO3electrochromic film. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2):152. |
| [5] |
WANG J M, YU H Y, MA D Y, et al. Progress in the preparation and application of nanostructured manganese dioxide. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(12):1307.
DOI |
| [6] | TUTEL Y, DURUKAN M B, HACIOGLU S O, et al. Cobalt-doped MoO3 thin films and dual-band electrochromic devices with excellent cyclic stability. Applied Materials Today, 2023, 35: 101924. |
| [7] | GAO G, TAO X J, HE Y, et al. Electrochromic composites films composed of MoO3 doped by tungsten atoms with remarkable response speed and color rendering efficiency via electrochemical deposition. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 640(15):158346. |
| [8] | HE Y C, LI T Z, ZHONG X L, et al. Lattice and electronic structure variations in critical lithium doped nickel oxide thin film for superior anode electrochromism. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 316(1):143. |
| [9] |
HU F, YAN B, SUN G, et al. Conductive polymer nanotubes for electrochromic applications. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2019, 2(5):3154.
DOI |
| [10] | FANG X J, WANG C W, TIAN Q Y, et al. Based on triphenylamine-imidazole skeleton electro-fluorochromic small organic molecules: synthesis and electrofluorochromic properties. Materials Letters, 2023, 333(15):133659. |
| [11] | QIU M J, ZHOU F W, SUN P, et al. Unveiling the electrochromic mechanism of Prussian blue by electronic transition analysis. Nano Energy, 2020, 78: 105148. |
| [12] | MA Q, CHEN J X, ZHANG H, et al. Dual-function self-powered electrochromic batteries with energy storage and display enabled by potential difference. ACS Energy Letters, 2022, 8(1):306. |
| [13] | RAO T K, ZHOU Y L, JIANG J, et al. Low dimensional transition metal oxide towards advanced electrochromic devices. Nano Energy, 2022, 100: 107479. |
| [14] | GUO J J, WANG M, DONG G B, et al. Mechanistic insights into the coloration, evolution, and degradation of NiOx electrochromic anodes. Inorganic Chemistry, 2018, 57(15):8874. |
| [15] | KANDPAL S, BANSAL L, GHANGHASS A, et al. Bifunctional solid state electrochromic device using WO3/WS2 nanoflakes for charge storage and dual-band color modulation. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2023, 11(37):12590. |
| [16] | DONG D M, DJAOUED H, VIENNEAU G, et al. Electrochromic and colorimetric properties of anodic NiO thin films: uncovering electrochromic mechanism of NiO. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 335(1):35648. |
| [17] | YANG H, YU J H, SEO H J, et al. Improved electrochromic properties of nanoporous NiO film by NiO flake with thickness controlled by aluminum. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 461(15):88. |
| [18] | TIAN M H, LIU X Q, DIAO X G, et al. High performance PANI/MnO2 coral-like nanocomposite anode for flexible and robust electrochromic energy storage device. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2023, 253: 112239. |
| [19] | WANG S M, JIN Y H, WANG T, et al. Polyoxometalate-MnO2 film structure with bifunctional electrochromic and energy storage properties. Journal of Materiomics, 2023, 9(2):269. |
| [20] |
HU J, TANG X M, DAI Q, et al. Layered double hydroxide membrane with high hydroxide conductivity and ion selectivity for energy storage device. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1):3409.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | KUMAR J, NEIBER R R, ABBAS Z, et al. Hierarchical NiMn- LDH hollow spheres as a promising pseudocapacitive electrode for supercapacitor application. Micromachines, 2023, 14(2):482. |
| [22] | GUO X L, LIU X Y, HAO X D, et al. Nickel-manganese layered double hydroxide nanosheets supported on nickel foam for high- performance supercapacitor electrode materials. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 194(10):179. |
| [23] | TANG Y Q, SHEN H M, CHENG J Q, et al. Fabrication of oxygen-vacancy abundant NiMn-layered double hydroxides for ultrahigh capacity supercapacitors. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(11):1908223. |
| [24] | BAIG M M, GUL I H, AHMAD R, et al. One-step sonochemical synthesis of NiMn-LDH for supercapacitors and overall water splitting. Journal of Materials Science, 2021, 56(33):18636. |
| [25] | BAIG M M, MEHRAN M T, KHAN R, et al. Direct chemical synthesis of interlaced NiMn-LDH nanosheets on LSTN perovskite decorated Ni foam for high-performance supercapacitors. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2021, 421(15):127455. |
| [26] | ZHANG B, YANG Y, CAI J L, et al. Mg doping of NiMn-LDH with a three-dimensional porous morphology for an efficient supercapacitor. Dalton Transactions, 2023, 52(30):10557. |
| [27] | SUN J W, WAN X Y, YANG T, et al. Preparation and electrochromic properties of Ti2Nb10O29films. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12):1434. |
| [28] | MURUGAN E, GOVINDARAJU S, SANTHOSHKUMAR S. Hydrothermal synthesis, characterization and electrochemical behavior of NiMoO4 nanoflower and NiMoO4/rGO nanocomposite for high-performance supercapacitors. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 392(1):138973. |
| [29] | NIU H B, HUANG J H, LI Q W, et al. Directly hydrothermal growth and electrochromic properties of porous NiMoO4 nanosheet films. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12):1427. |
| [30] | REN Y, ZHOU X G, ZHANG H, et al. Preparation of a porous NiO array-patterned film and its enhanced electrochromic performance. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018, 6(18):4952. |
| [31] | ZHAO L L, CHEN Z M, PENG Y Q, et al. High-performance complementary electrochromic energy storage device based on tungsten trioxide and manganese dioxide films. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2022, 32: e00445. |
| [32] | ZHOU D, CHE B Y, LU X H. Rapid one-pot electrodeposition of polyaniline/manganese dioxide hybrids: a facile approach to stable high-performance anodic electrochromic materials. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017, 5(7):1758. |
| [33] | CHAVAN H S, HOU B, JO Y, et al. Optimal rule-of-thumb design of nickel-vanadium oxides as an electrochromic electrode with ultrahigh capacity and ultrafast color tunability. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2021, 13(48):57403. |
| [1] | XUN Daoxiang, LUO Xuwei, ZHOU Mingran, HE Jiale, RAN Maojin, HU Zhiyi, LI Yu. ZIF-L Derived Nitrogen-doped Carbon Nanosheets/Carbon Cloth Self-supported Electrode for Lithium-selenium Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1013-1021. |
| [2] | SHI Tong, GAN Qiaowei, LIU Dong, ZHANG Ying, FENG Hao, LI Qiang. Boost Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 to Formate Using a Self-supporting Bi@Cu Nanotree Electrode [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 810-818. |
| [3] | YANG Endong, LI Baole, ZHANG Ke, TAN Lu, LOU Yongbing. ZnCo2O4-ZnO@C@CoS Core-shell Composite: Preparation and Application in Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 485-493. |
| [4] | ZHEN Mingshuo, LIU Xiaoran, FAN Xiangqian, ZHANG Wenping, YAN Dongdong, LIU Lei, LI Chen. Electrochromic Intelligent Visual Humidity Indication System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 432-440. |
| [5] | WANG Xinling, ZHOU Na, TIAN Yawen, ZHOU Mingran, HAN Jingru, SHEN Yuansheng, HU Zhiyi, LI Yu. SnS2/ZIF-8 Derived Two-dimensional Porous Nitrogen-doped Carbon Nanosheets for Lithium-sulfur Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 938-946. |
| [6] | NIU Haibin, HUANG Jiahui, LI Qianwen, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Directly Hydrothermal Growth and Electrochromic Properties of Porous NiMoO4 Nanosheet Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1427-1433. |
| [7] | SUN Jiawei, WAN Xinyi, YANG Ting, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Preparation and Electrochromic Properties of Ti2Nb10O29 Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1434-1440. |
| [8] | CHEN Zhang, ZHAO Ruoyi, HAN Shaojie, WANG Huanran, YANG Qun, GAO Yanfeng. Electrochromic WO3 Thin Films: Preparation by Nanocrystalloid Liquid Phase Coating and Performance Optimization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1355-1363. |
| [9] | WANG Ruyi, XU Guoliang, YANG Lei, DENG Chonghai, CHU Delin, ZHANG Miao, SUN Zhaoqi. p-n Heterostructured BiVO4/g-C3N4 Photoanode: Construction and Its Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 87-96. |
| [10] | HUANG Zhihang, TENG Guanhongwei, TIE Peng, FAN Desong. Electrochromic Property of Perovskite Ceramic Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 611-616. |
| [11] | ZHANG Xiang, LI Wenjie, WANG Lebin, CHEN Xi, ZHAO Jiupeng, LI Yao. Reflective Property of Inorganic Electrochromic Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 451-460. |
| [12] | WANG Tianyue, WANG Mengying, HUANG Qingjiao, YANG Jiaming, WANG Shunhua, DIAO Xungang. Preparation of Lithium Titanate Thin Film for Electrochromic Smart Window by Sol-Gel Spin Coating Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 471-478. |
| [13] | JIA Hanxiang, SHAO Zewei, HUANG Aibin, JIN Pingshi, CAO Xun. Sandwich Structured Electrolyte of High Sputtering Efficiency for All-solid-state Electrochromic Devices by Optical Design [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 479-484. |
| [14] | FANG Huajing, ZHAO Zetian, WU Wenting, WANG Hong. Progress in Flexible Electrochromic Devices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 140-151. |
| [15] | ZHOU Kailing, WANG Hao, ZHANG Qianqian, LIU Jingbing, YAN Hui. Dynamic Process of Ions Transport and Cyclic Stability of WO3 Electrochromic Film [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 152-160. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||