
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (12): 1441-1448.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230198
Special Issue: 【生物材料】抗菌与肿瘤治疗(202506); 【生物材料】骨骼与齿类组织修复(202506)
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
DU Jiaheng1,2( ), FAN Xinli3,4, XIAO Dongqin2, YIN Yiran1, LI Zhong1, HE Kui1, DUAN Ke1(
), FAN Xinli3,4, XIAO Dongqin2, YIN Yiran1, LI Zhong1, HE Kui1, DUAN Ke1( )
)
Received:2023-04-18
Revised:2023-06-03
Published:2023-10-15
Online:2023-10-15
Contact:
DUAN Ke, professor. E-mail: keduan@swmu.edu.cnAbout author:DU Jiaheng (1997-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: dujiaheng1011@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
DU Jiaheng, FAN Xinli, XIAO Dongqin, YIN Yiran, LI Zhong, HE Kui, DUAN Ke. Electrophoretic Coating of Magnesium Oxide on Microarc-oxidized Titanium and Its Biological Properties[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1441-1448.

Fig. 7 (a) Representative photographs of colonies formed on samples after co-cultured with S. aureus for 24 h, and (b) antibacterial rates Numbers 2, 3 and 4 indicating MAO vs. MAO-MgO30, MAO-MgO45, MAO-MgO60, respectively (p<0.05)

Fig. 8 Micrographs of samples after Live/Dead fluorescent staining on co-cultured S. aureus for 24 h Red pixels: Dead S. aureus cells; Green pixels: Alive S. aureus cells; All scale bars: 100 μm

Fig. 9 SEM micrographs of samples (a) MAO and (b-e) MAO-MgO15 to MAO-MgO60 after co-culture with S. aureus for 24 h; Red arrows pointing to S. aureus cells
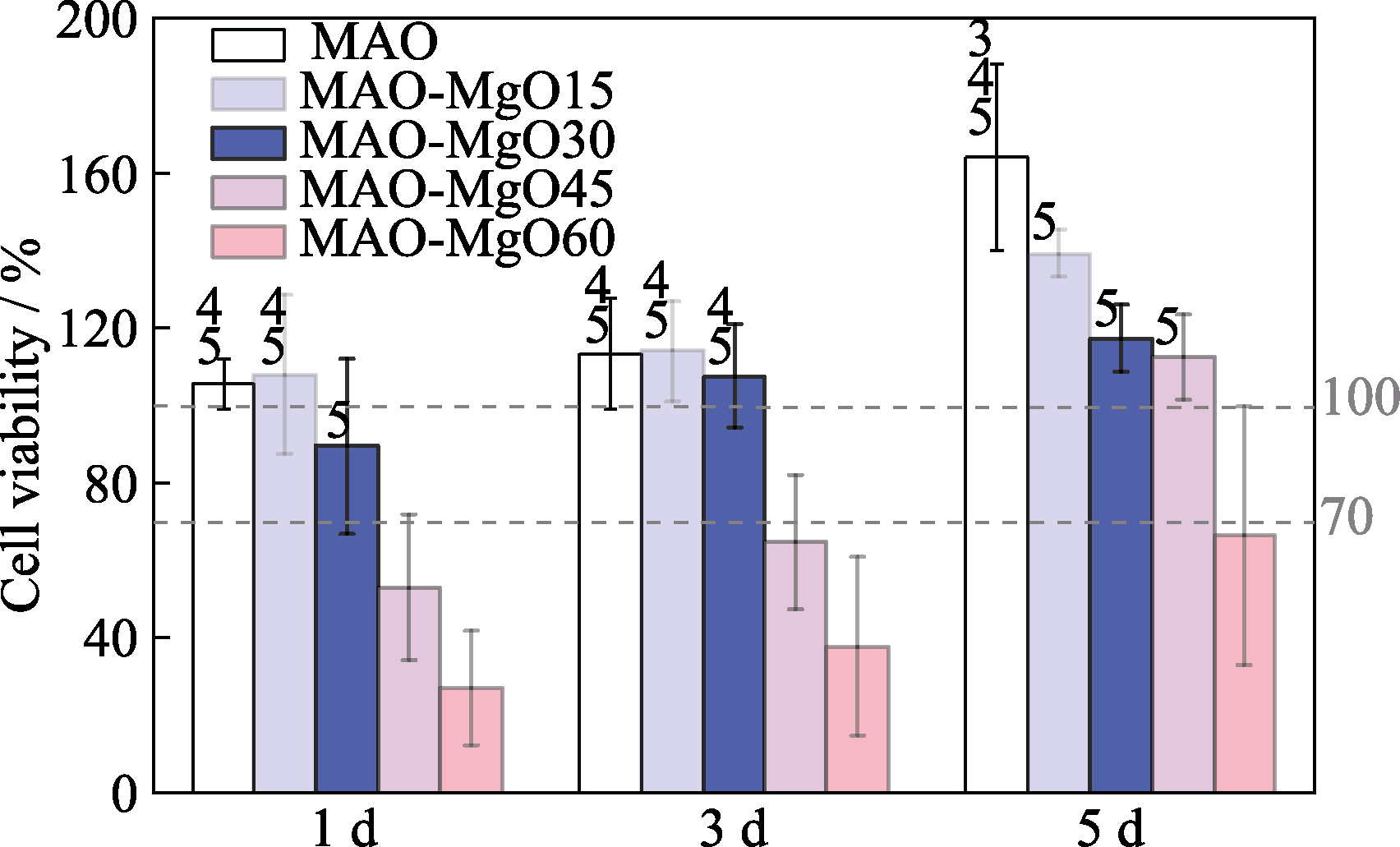
Fig. 10 Viability of rat osteoblasts after co-culture on samples for 1, 3 and 5 d Numbers 3, 4 and 5 indicating MAO vs. MAO-MgO30, MAO-MgO45, MAO-MgO60, respectively (p<0.05)
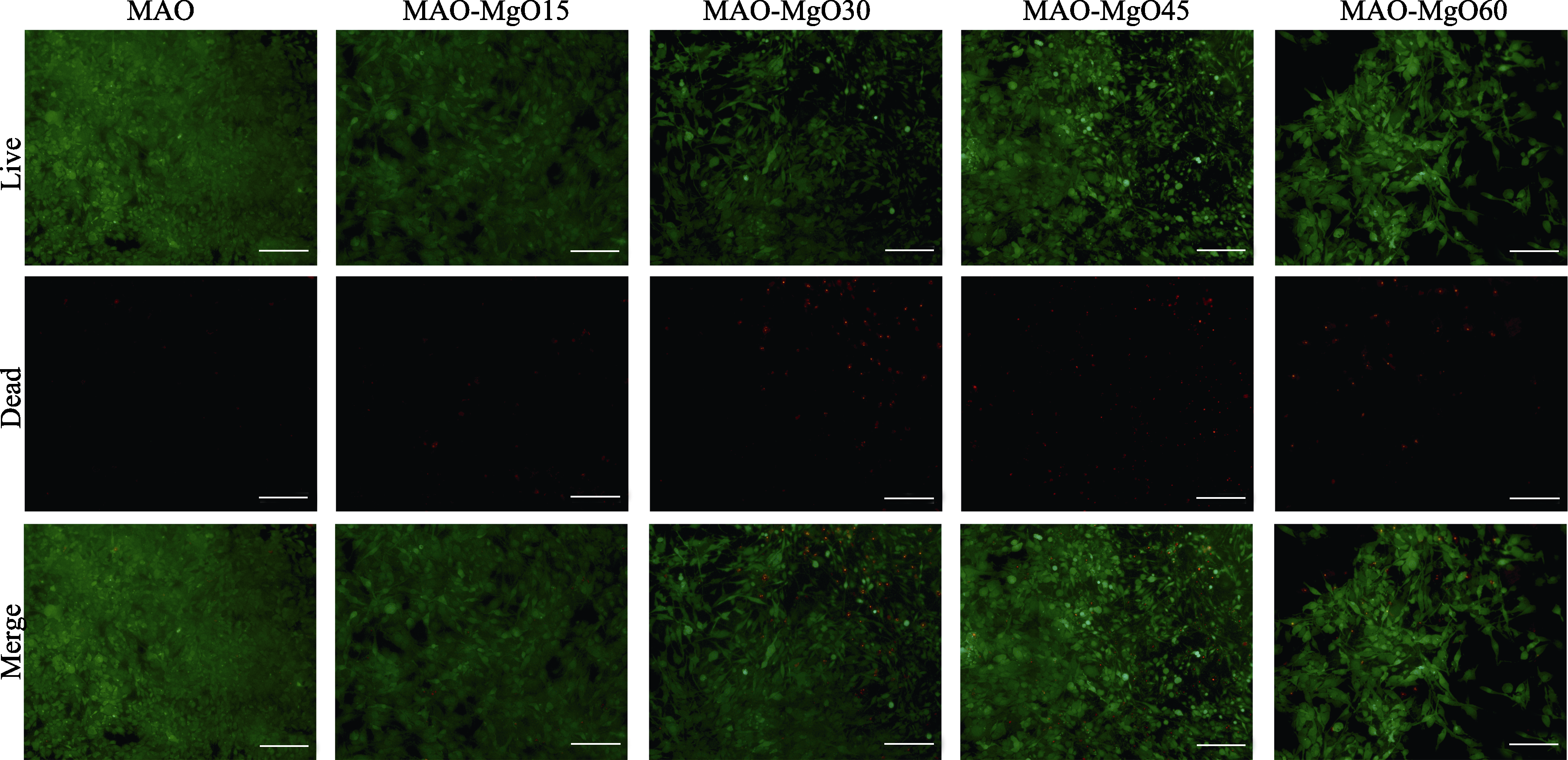
Fig. 11 Images of samples after Live/Dead fluorescent staining on co-cultured rat osteoblasts for 5 d Red pixels: Dead cells; Green pixels: Alive cells; All scale bars: 100 μm
| [1] |
POTAPOVA I. Functional imaging in diagnostic of orthopedic implant-associated infections. Diagnostics, 2013, 3(4): 356.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
MALIZOS K, BLAUTH M, DANITA A, et al. Fast-resorbable antibiotic- loaded hydrogel coating to reduce post-surgical infection after internal osteosynthesis: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, 2017, 18(2): 159.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CAO H, MENG F, LIU X, et al. Antimicrobial activity of tantalum oxide coatings decorated with Ag nanoparticles. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A: Vacuum, Surfaces, and Films, 2016, 34(4): 04C102.
DOI URL |
| [4] | OLSEN I. Biofilm-specific antibiotic tolerance and resistance. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, 2015, 34(5): 877. |
| [5] |
SCHINS R P F, KNAAPEN A M. Genotoxicity of poorly soluble particles. Inhalation Toxicology, 2007, 19(sup1): 189.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
PALACIOS-HERNANDEZ T, DIAZ-DIESTRA DM, NGUYEN A K, et al. Cytotoxicity, cellular uptake and apoptotic responses in human coronary artery endothelial cells exposed to ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 2020, 40(7): 918.
DOI URL |
| [7] | WANG Y, YU H, CHEN C, et al. Review of the biocompatibility of micro-arc oxidation coated titanium alloys. Materials & Design, 2015, 8(5): 640. |
| [8] | XUE T, ATTARILAR S, LIU S, et al. Surface modification techniques of titanium and its alloys to functionally optimize their biomedical properties: thematic review. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2020, 8: 603072. |
| [9] |
AL-AHMAD A, WIEDMANN-AL-AHMAD M, FACKLER A, et al. In vivo study of the initial bacterial adhesion on different implant materials. Archives of Oral Biology, 2013, 58(9): 1139.
DOI URL |
| [10] | AL-AHMAD A, WIEDMANN-AL-AHMAD M, FAUST J, et al. Biofilm formation and composition on different implant materials in vivo. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials, 2010, 95(1): 101. |
| [11] | CHEN Y, SHENG W, LIN J, et al. Magnesium oxide nanoparticle coordinated phosphate-functionalized chitosan injectable hydrogel for osteogenesis and angiogenesis in bone regeneration. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(6): 7592. |
| [12] |
CHEN R, CHEN H B, XUE P P, et al. HA/MgO nanocrystal-based hybrid hydrogel with high mechanical strength and osteoinductive potential for bone reconstruction in diabetic rats. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2021, 9(4): 1107.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | LUQUE-AGUDO V, FERNÁNDEZ-CALDERÓN M C, PACHA- OLIVENZA M A, et al. The role of magnesium in biomaterials related infections. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2020, 191: 110996. |
| [14] | NGUYEN N Y T, GRELLING N, WETTELAND C L, et al. Antimicrobial activities and mechanisms of magnesium oxide nanoparticles (nMgO) against pathogenic bacteria, yeasts, and biofilms. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 16260. |
| [15] | COELHO C C, PADRÃO T, COSTA L, et al. The antibacterial and angiogenic effect of magnesium oxide in a hydroxyapatite bone substitute. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 19098. |
| [16] | BOCCACCINI A R, KEIM S, MA R, et al. Electrophoretic deposition of biomaterials. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2010, 7(suppl_5): S581. |
| [17] |
BRUCHIEL-SPANIER N, BETSIS S, NAIM G, et al. Electrochemical and electrophoretic coatings of medical implants by nanomaterials. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2022, 26(9): 1871.
DOI |
| [18] |
HICKEY D J, MUTHUSAMY D, WEBSTER T J. Electrophoretic deposition of MgO nanoparticles imparts antibacterial properties to poly-L-lactic acid for orthopedic applications. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 2017, 105(11): 3136.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | LIN Y J, LI D Q, WANG G, et al. Preparation and bactericidal property of MgO nanoparticles on gamma-Al2O3. Journal Materials Science: Materials in Medcine, 2005, 16(1): 53. |
| [20] | AL-SHARABI A, SADA'A KSS, AL-OSTA A, et al. Structure, optical properties and antimicrobial activities of MgO-BiCrO nanocomposites prepared via solvent-deficient method. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12: 10647. |
| [21] | LI X, HONG X, YANG Y, et al. Enhanced antibacterial activity of acid treated MgO nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. RSC Advances, 2021, 11(60): 38202. |
| [22] | CHEN Q, GARCIA RP, MUNOZ J, et al. Cellulose nanocrystals-- bioactive glass hybrid coating as bone substitutes by electrophoretic co-deposition: in situ control of mineralization of bioactive glass and enhancement of osteoblastic performance. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(44): 24715. |
| [23] | LIU X, XIE Z, ZHANG C, et al. Bioactive borate glass scaffolds: in vitro and in vivo evaluation for use as a drug delivery system in the treatment of bone infection. Journal Materials Science: Materials in Medcine, 2010, 21(2): 575. |
| [24] |
HOSSEINBABAEI F, RAISSIDEHKORDI B. Electrophoretic deposition of MgO thick films from an acetone suspension. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2000, 20(12): 2165.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 董自艳, 戴翚, 马仕洪, 等.紫外-可见分光光度法快速确定细菌菌液的浓度. 中国药品标准, 2014, 15(2): 120. |
| [26] |
KIM D Y, KIM M, KIM H E, et al. Formation of hydroxyapatite within porous TiO2 layer by micro-arc oxidation coupled with electrophoretic deposition. Acta Biomaterialia, 2009, 5(6): 2196.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
FAN X, FENG B, DI Y, et al. Preparation of bioactive TiO film on porous titanium by micro-arc oxidation. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 258(19): 7584.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
DAGHIGHI S, SJOLLEMA J, VAN DER MEI H C, et al. Infection resistance of degradable versus non-degradable biomaterials: an assessment of the potential mechanisms. Biomaterials, 2013, 34(33): 8013.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
MUÑIZ DIAZ R, CARDOSO-AVILA P E, PÉREZ TAVARES J A, et al. Two-step triethylamine-based synthesis of MgO nanoparticles and their antibacterial effect against pathogenic bacteria. Nanomaterials, 2021, 11(2): 410.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
TAN J, LIU Z, WANG D, et al. A facile and universal strategy to endow implant materials with antibacterial ability via alkalinity disturbing bacterial respiration. Biomaterials Science, 2020, 8(7): 1815.
DOI URL |
| [31] | LEUNG Y H, NG A M C, XU X, et al. Mechanisms of antibacterial activity of MgO: non-ROS mediated toxicity of MgO nanoparticles towards Escherichia coli. Small, 2014, 10(6): 1171. |
| [32] | RICKER A, LIU-SNYDER P, WEBSTER T J. The influence of nano MgO and BaSO4 particle size additives on properties of PMMA bone cement. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2008, 3(1): 125. |
| [33] | DEMIREL M. Mechanical properties and cell viability of MgO- reinforced biografts fabricated for biomedical applications. Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics, 2018, 20(4): 83. |
| [34] |
JANNING C, WILLBOLD E, VOGT C, et al. Magnesium hydroxide temporarily enhancing osteoblast activity and decreasing the osteoclast number in peri-implant bone remodelling. Acta Biomaterialia, 2010, 6(5): 1861.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | AGARWAL S, CURTIN J, DUFFY B, et al. Biodegradable magnesium alloys for orthopaedic applications: a review on corrosion, biocompatibility and surface modifications. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2016, 68: 948. |
| [36] |
ZHU B, WANG L, WU Y, et al. Improving corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of AZ31 magnesium alloy by ultrasonic cold forging and micro-arc oxidation. Journal of Biomaterials Applications, 2022, 36(9): 1664.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
ZHUANG J, JING Y, WANG Y, et al. Degraded and osteogenic properties of coated magnesium alloy AZ31: an experimental study. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, 2016, 11(1): 1.
DOI URL |
| [1] | WANG Yueyue, HUANG Jiahui, KONG Hongxing, LI Huaizhu, YAO Xiaohong. Silver Loaded Radial Mesoporous Silica: Preparation and Application in Dental Resins [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 77-83. |
| [2] | AN Xia, XU Shengrui, TAO Hongchang, SU Huake, YANG He, XU Kang, XIE Lei, JIA Jingyu, ZHANG Jincheng, HAO Yue. High Quality GaN Epitaxy Induced Nucleation by Ar Ion Implantation into Sapphire Substrate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 91-96. |
| [3] | WANG Zhaoyang, QIN Peng, JIANG Yin, FENG Xiaobo, YANG Peizhi, HUANG Fuqiang. Sandwich Structured Ru@TiO2 Composite for Efficient Photocatalytic Tetracycline Degradation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 383-389. |
| [4] | LI Chengyu, DING Ziyou, HAN Yingchao. In vitro Antibacterial and Osteogenic Properties of Manganese Doped Nano Hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 313-320. |
| [5] | ZHANG Zhimin, GE Min, LIN Han, SHI Jianlin. Novel Magnetoelectric Catalytic Nanoparticles: RNS Release and Antibacterial Efficiency [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1114-1124. |
| [6] | ZHANG Shumin, XI Xiaowen, SUN Lei, SUN Ping, WANG Deqiang, WEI Jie. Sonodynamic and Enzyme-like Activities of Niobium-based Coatings: Antimicrobial, Cell Proliferation and Cell Differentiation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1125-1134. |
| [7] | SHANGGUAN Li, NIE Xiaoshuang, YE Kuicai, CUI Yuanyuan, QIAO Yuqin. Effects of Surface Wettability of Titanium Oxide Coatings on Osteoimmunomodulatory Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1457-1565. |
| [8] | XIE Jiaye, LI Liwen, ZHU Qiang. Contrastive Study on in Vitro Antibacterial Property and Biocompatibility of Three Clinical Pulp Capping Agents [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1449-1456. |
| [9] | WU Xuetong, ZHANG Ruofei, YAN Xiyun, FAN Kelong. Nanozyme: a New Approach for Anti-microbial Infections [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 43-54. |
| [10] | SHENG Lili, CHANG Jiang. Photo/Magnetic Thermal Fe2SiO4/Fe3O4 Biphasic Bioceramic and Its Composite Electrospun Membrane: Preparation and Antibacterial [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 983-990. |
| [11] | XUE Hongyun, WANG Congyu, MAHMOOD Asad, YU Jiajun, WANG Yan, XIE Xiaofeng, SUN Jing. Two-dimensional g-C3N4 Compositing with Ag-TiO2 as Deactivation Resistant Photocatalyst for Degradation of Gaseous Acetaldehyde [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 865-872. |
| [12] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [13] | WU Ling, TAN Ji, QIAN Shi, GE Naijian, LIU Xuanyong. Biological Property Investigation of Nitinol Surface Implanted with Tantalum [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1217-1224. |
| [14] | FU Jiajun, SHEN Tao, WU Jia, WANG Chen. Nanozyme: a New Strategy Combating Bacterial [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 257-268. |
| [15] | GUO Xiaowei, LI Yuyan, CHEN Nanchun, WANG Xiuli, XIE Qinglin. Construction of Sustainable Release Antimicrobial Microspheres Loaded with Potassium Diformate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 181-187. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||