
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (12): 1457-1565.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230242
Special Issue: 【生物材料】骨骼与齿类组织修复(202506)
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHANGGUAN Li1,2( ), NIE Xiaoshuang2,3, YE Kuicai2,3, CUI Yuanyuan1(
), NIE Xiaoshuang2,3, YE Kuicai2,3, CUI Yuanyuan1( ), QIAO Yuqin2,4(
), QIAO Yuqin2,4( )
)
Received:2023-05-19
Revised:2023-06-16
Published:2023-06-28
Online:2023-06-28
Contact:
QIAO Yuqin, associate professor. E-mail: qiaoyq@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:SHANGGUAN Li (1997-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 20724695@shu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
SHANGGUAN Li, NIE Xiaoshuang, YE Kuicai, CUI Yuanyuan, QIAO Yuqin. Effects of Surface Wettability of Titanium Oxide Coatings on Osteoimmunomodulatory Properties[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1457-1565.
| Gene | Primer sequence (F: forward; R: Reverse; 5ʹ-3ʹ) |
|---|---|
| Arg1 | F: GCC AGG GAC TGA CTA CCT TAA R: AGT TCT GTC TGC TTT GCT GTG |
| IL4 | F: TCA TCC TGC TCT TCT TTC TCG R: CTT CTC CTG TGA CCT CGT TCA |
| CD206 | F: AGG GAA GAG AAG AAG ATC CAG R: TGG GAG AAG ATG AAG TCA AAC |
| TNF-α | F: TAG CCA GGA GGG AGA ACA GA R: CCA GTG AGT GAA AGG GAC AGA |
| IL6 | F: ACC AAG ACC ATC CAA TTC ATC R: CTG ACC ACA GTG AGG AAT GTC |
| CD86 | F: TCT CCA ACA GCC TCT CTC TTT R: ATC TTC ATT GAC TCC GTT TCC |
| OCN | F: ACC GCC TAC AAA CGC ATC TA R: AGA GGA CAG GGA GGA TCA AGT |
| OPN | F: CTT GAG CAT TCC AAA GAG AGC R: CTT GTG GCT GTG AAA CTT GTG |
| BMP2 | F: TAA GTT CTG TCC CCA GTG ACG R: TTC GGT GCT GGA AAC TAC TGT |
| TGF-β1 | F: AAC CAA GGA GAC GGA ATA CA R: CGT GGA GTT TGT TAT CTT TGC |
| Runx2 | F: GCA GCA CGC TAT TAA ATC CAA R: GCC AAA CAG ACT CAT CCA TTC |
Table 1 Primers for real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
| Gene | Primer sequence (F: forward; R: Reverse; 5ʹ-3ʹ) |
|---|---|
| Arg1 | F: GCC AGG GAC TGA CTA CCT TAA R: AGT TCT GTC TGC TTT GCT GTG |
| IL4 | F: TCA TCC TGC TCT TCT TTC TCG R: CTT CTC CTG TGA CCT CGT TCA |
| CD206 | F: AGG GAA GAG AAG AAG ATC CAG R: TGG GAG AAG ATG AAG TCA AAC |
| TNF-α | F: TAG CCA GGA GGG AGA ACA GA R: CCA GTG AGT GAA AGG GAC AGA |
| IL6 | F: ACC AAG ACC ATC CAA TTC ATC R: CTG ACC ACA GTG AGG AAT GTC |
| CD86 | F: TCT CCA ACA GCC TCT CTC TTT R: ATC TTC ATT GAC TCC GTT TCC |
| OCN | F: ACC GCC TAC AAA CGC ATC TA R: AGA GGA CAG GGA GGA TCA AGT |
| OPN | F: CTT GAG CAT TCC AAA GAG AGC R: CTT GTG GCT GTG AAA CTT GTG |
| BMP2 | F: TAA GTT CTG TCC CCA GTG ACG R: TTC GGT GCT GGA AAC TAC TGT |
| TGF-β1 | F: AAC CAA GGA GAC GGA ATA CA R: CGT GGA GTT TGT TAT CTT TGC |
| Runx2 | F: GCA GCA CGC TAT TAA ATC CAA R: GCC AAA CAG ACT CAT CCA TTC |
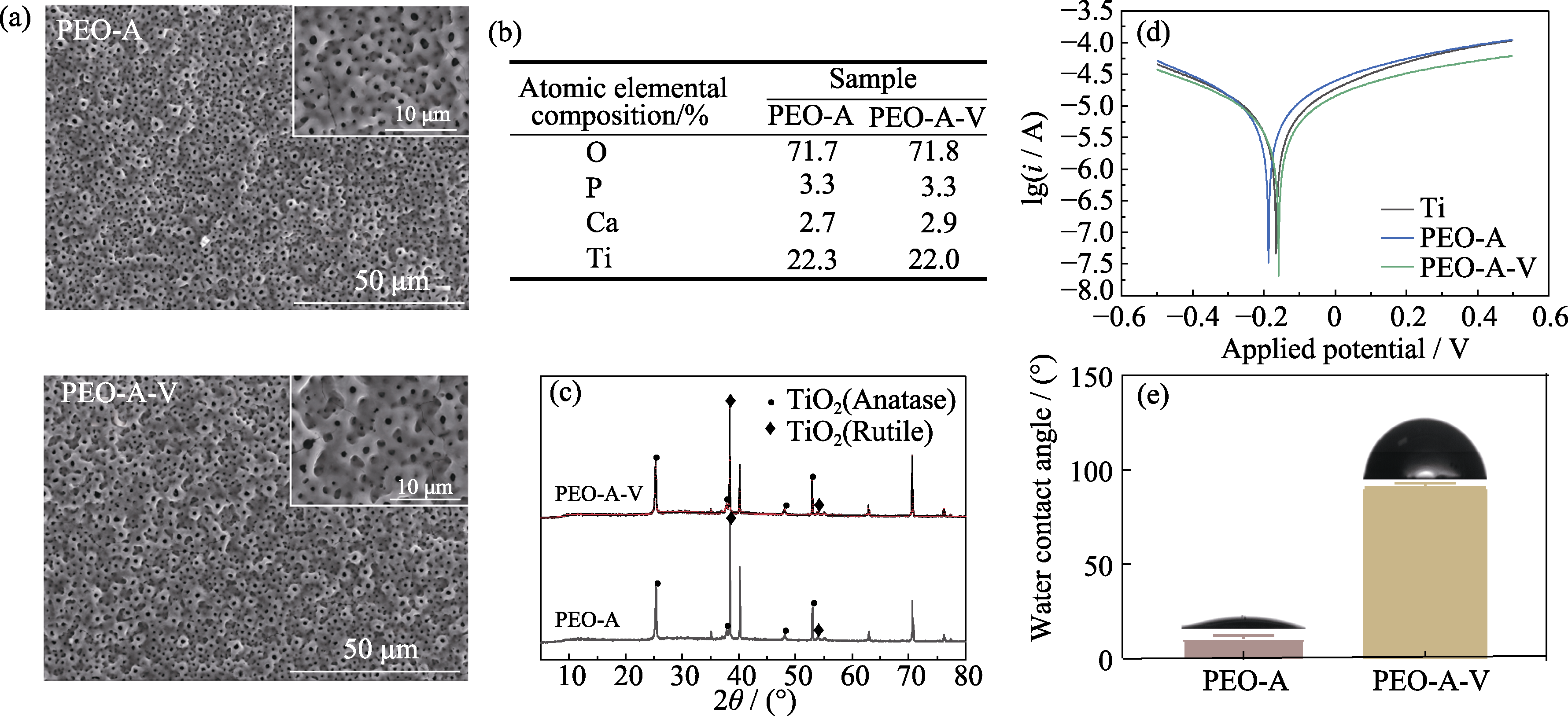
Fig. 1 (a) Surface morphologies, (b) element compositions, (c) phase compositions, (d) electrochemical polarization curves, and (e) water contact angles of the samples Coloful figures are available on website

Fig. 2 Proliferation of Raw264.7 incubated on different samples for 1 and 4 d Data are presented as the mean±SD, n = 3. ****: p < 0.0001 Coloful figures are available on website
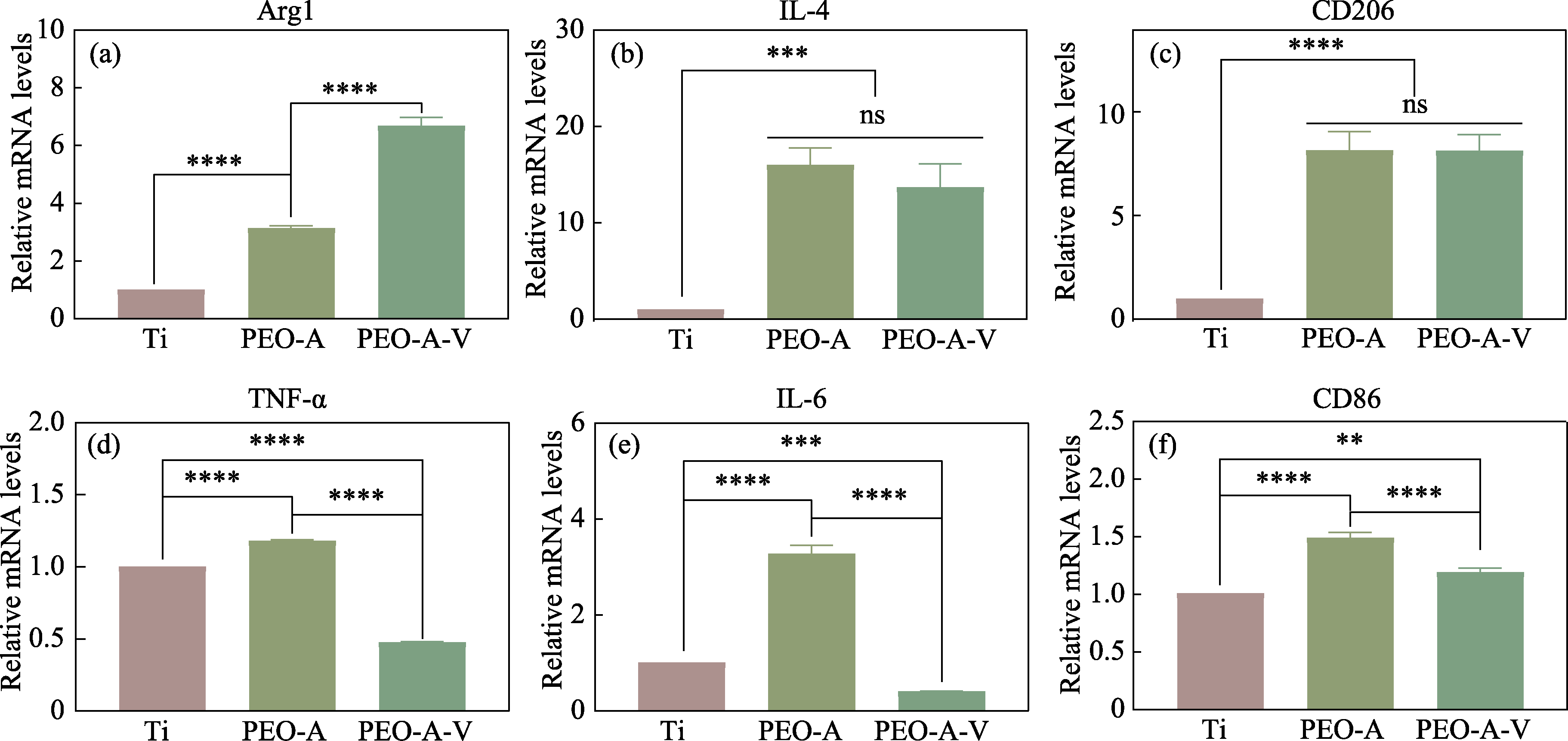
Fig. 4 Relative mRNA levels of inflammatory genes of Raw264.7 incubated on different samples for 4 d (a) Arg-1; (b) IL-4; (c) CD206; (d) TNF-α; (e) IL-6; (f) CD86 Data are presented as the mean±SD, n = 3. ****: p <0.0001; ***: p <0.001; **: 0.05< p <0.01 Coloful figures areavailable on website

Fig. 5 Cell proliferation of mBMSCs incubated on different samples for different time Data are presented as the mean±SD, n = 3. ****: p <0.0001; **: 0.05< p <0.01; *: p<0.05 Coloful figures areavailable on website

Fig. 7 Relative mRNA levels of osteogenic genes of mBMSCs cultured on different samples for 10 d (a) OPN; (b) Runx2; (c) OCN; (d) BMP2 Data are presented as the mean±SD, n = 3. ****: p <0.0001; ***: p <0.001; **: 0.05< p <0.01; *: p <0.05
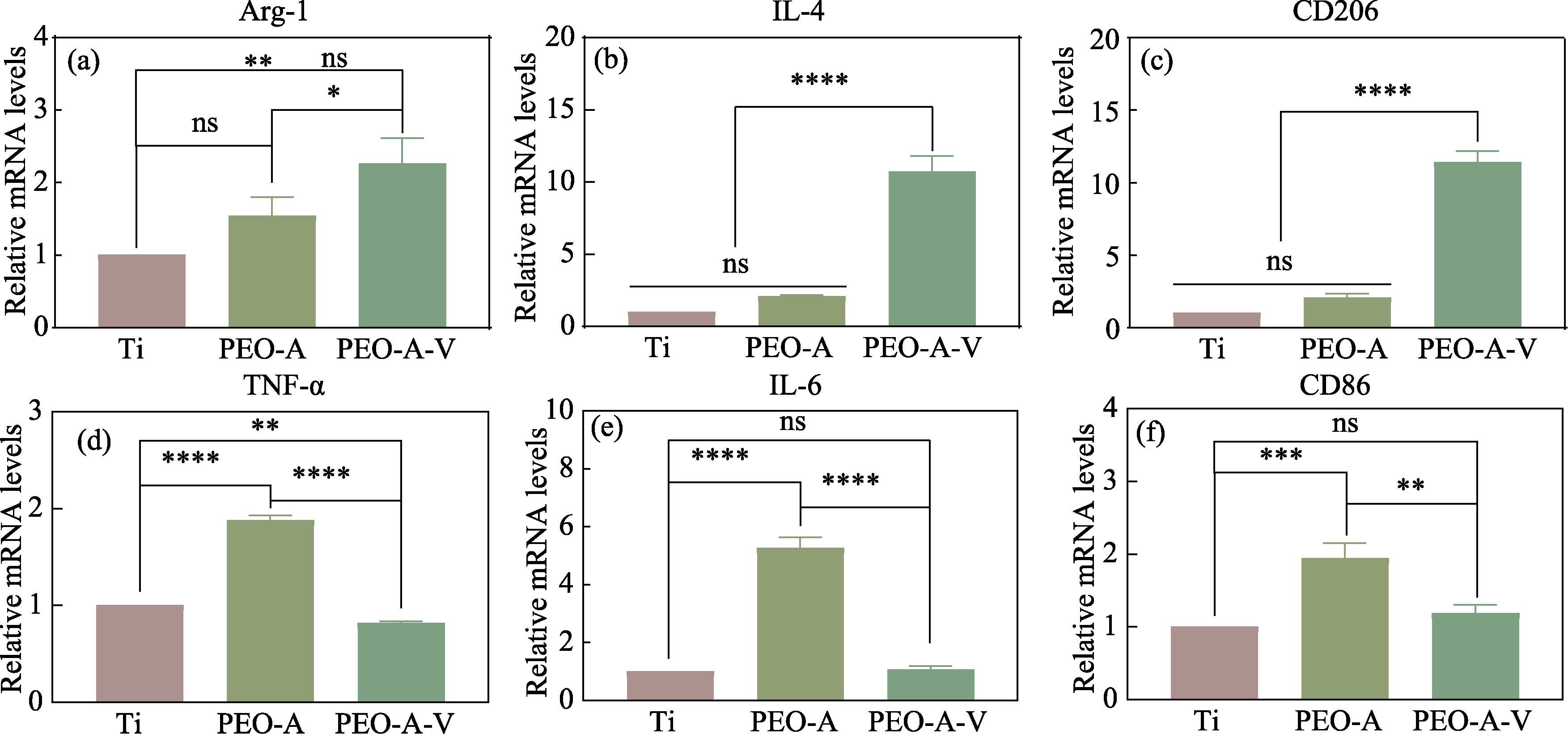
Fig. 8 Relative mRNA levels of inflammatory genes of Raw264.7 co-cultured with mBMSCs on different samples for 3 d (a) Arg-1; (b) IL-4; (c) CD206; (d) TNF-α; (e) IL-6; (f) CD86 Data are presented as mean±SD, n = 3. ****: p <0.0001; ***: p <0.001; **: 0.05< p <0.01; *: p <0.05

Fig. 9 Relative mRNA levels of osteogenic genes of mBMSCs co-cultured with Raw264.7 on different samples for 3 d (a) OPN; (b) TGF-β1; (c) OCN; (d) BMP2 Data are presented as the mean±SD, n = 3. ****: p <0.0001; ***: p <0.001; **: 0.05< p <0.01; *: p <0.05
| [1] |
HUANG L, NING C, DING D, et al. Wettability and in vitro bioactivity of doped TiO2 nanotubes. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(7): 775.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
HOQUE M E, SHOWVA N-N, AHMED M, et al. Titanium and titanium alloys in dentistry: current trends, recent developments, and future prospects. Heliyon, 2022, 8(11): e11300.
DOI URL |
| [3] | NIE X, ZHANG X, LEI B, et al. Regulation of magnesium matrix composites materials on bone immune microenvironment and osteogenic mechanism. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022, 10: 842706. |
| [4] | DU P, LI K, ZHU B, et al. Development of non-toxic low-cost bioactive porous Ti-Fe-Si bulk metallic glass with bone-like mechanical properties for orthopedic implants. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2022, 17: 1319. |
| [5] |
MI B, CHEN L, XIONG Y, et al. Osteoblast/osteoclast and immune cocktail therapy of an exosome/drug delivery multifunctional hydrogel accelerates fracture repair. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(1): 771.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
GEURTZEN K, LÓPEZ-DELGADO A C, DUSEJA A, et al. Laser-mediated osteoblast ablation triggers a pro-osteogenic inflammatory response regulated by reactive oxygen species and glucocorticoid signaling in zebrafish. Development, 2022, 149(8): dev199803.
DOI URL |
| [7] | LIANG H, JIN C, MA L, et al. Accelerated bone regeneration by gold-nanoparticle-loaded mesoporous silica through stimulating immunomodulation. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(44): 41758. |
| [8] | PAJARINEN J, LIN T, GIBON E, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-macrophage crosstalk and bone healing. Biomaterials, 2019, 196: 80. |
| [9] | SHEN H, SHI J, ZHI Y, et al. Improved BMP2-CPC-stimulated osteogenesis in vitro and in vivo via modulation of macrophage polarization. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2021, 118: 111471. |
| [10] |
HOTCHKISS K M, SOWERS K T, OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R. Novel in vitro comparative model of osteogenic and inflammatory cell response to dental implants. Dental Materials, 2019, 35(1): 176.
DOI URL |
| [11] | JIANG P, ZHANG Y, HU R, et al. Advanced surface engineering of titanium materials for biomedical applications: from static modification to dynamic responsive regulation. Bioactive Materials, 2023, 27: 15. |
| [12] | ZHENG X, CHEN L, TAN J, et al. Effect of micro/nano-sheet array structures on the osteo-immunomodulation of macrophages. Regenerative Biomaterials, 2022, 9: rbac075. |
| [13] |
LIANG W, GAO M, LOU J, et al. Integrating silicon/zinc dual elements with PLGA microspheres in calcium phosphate cement scaffolds synergistically enhances bone regeneration. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2020, 8(15): 3038.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | MAO L, BAI L, WANG X, et al. Enhanced cell osteogenesis and osteoimmunology regulated by piezoelectric biomaterials with controllable surface potential and charges. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(39): 44111. |
| [15] | HUANG Q, OUYANG Z, TAN Y, et al. Activating macrophages for enhanced osteogenic and bactericidal performance by Cu ion release from micro/nano-topographical coating on a titanium substrate. Acta Biomaterialia, 2019, 100: 415. |
| [16] | HE Y, YAO M, ZHOU J, et al. Mg(OH)2 nanosheets on Ti with immunomodulatory function for orthopedic applications. Regenerative Biomaterials, 2022, 9: rbac027. |
| [17] | LIU J, SHEN X, TANG S, et al. Improvement of rBMSCs responses to poly(propylene carbonate) based biomaterial through incorporation of nanolaponite and surface treatment using sodium hydroxide. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2020, 6(1): 329. |
| [18] |
FERREIRA S A, GAMA F M, VILANOVA M. Polymeric nanogels as vaccine delivery systems. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 2013, 9(2): 159.
DOI URL |
| [19] | XIAN P, CHEN Y, GAO S, et al. Polydopamine (PDA) mediated nanogranular-structured titanium dioxide (TiO2) coating on polyetheretherketone (PEEK) for oral and maxillofacial implants application. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2020, 401: 126282. |
| [20] | LI W, XU F, DAI F, et al. Hydrophilic surface-modified 3D printed flexible scaffolds with high ceramic particle concentrations for immunopolarization-regulation and bone regeneration. Biomaterials Science, 2023, 11: 3976. |
| [21] |
MOYANO D F, GOLDSMITH M, SOLFIELL D J, et al. Nanoparticle hydrophobicity dictates immune response. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(9): 3965.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | BHUSHAN B, JUNG Y C, KOCH K. Micro-, nano- and hierarchical structures for superhydrophobicity, self-cleaning and low adhesion. Philosophical Transactions Series A, Mathematical, Physical, and Engineering Sciences, 2009, 367(1894):1631. |
| [23] | ZHANG C, YI Y, YANG H, et al. Wide spectrum solar energy absorption based on germanium plated ZnO nanorod arrays: energy band regulation, finite element simulation, super hydrophilicity, photothermal conversion. Applied Materials Today, 2022, 28: 101531. |
| [24] |
LV L, XIE Y, LI K, et al. Unveiling the mechanism of surface hydrophilicity-modulated macrophage polarization. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2018, 7(19): 1800675.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WANG H Z, HUANG Z P, CAI Q J, et al. Reversible transformation of hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity of aligned carbon nanotube arrays and buckypapers by dry processes. Carbon, 2010, 48(3): 868.
DOI URL |
| [26] | YUE X, ZHANG T, YANG D, et al. In situ fabrication dynamic carbon fabrics membrane with tunable wettability for selective oil-water separation. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2018, 61: 188. |
| [27] | 翦奉林, 冯军, 李必文, 等. TA2纯钛微弧氧化制备TiO2涂层的性能研究. 材料保护, 2023, 56(1): 64. |
| [28] | AU-ARIA A I, AU-GHARIB M. Dry oxidation and vacuum annealing treatments for tuning the wetting properties of carbon nanotube arrays. JoVE, 2013, ( 74):e50378. |
| [29] |
TIAN T, WANG Z, CHEN L, et al. Photobiomodulation activates undifferentiated macrophages and promotes M1/M2 macrophage polarization via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Lasers in Medical Science, 2023, 38(1): 86.
DOI |
| [30] | ZHAO X N, LI Y N, WANG Y T. Interleukin-4 regulates macrophage polarization via the MAPK signaling pathway to protect against atherosclerosis. Genetics and Molecular Research, 2016, 15(1): 15017348. |
| [31] |
LI K, YAN T, XUE Y, et al. Intrinsically ferromagnetic Fe-doped TiO2 coatings on titanium for accelerating osteoblast response in vitro. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2018, 6(36): 5756.
DOI URL |
| [1] | LIU Song, ZHANG Faqiang, LUO Jin, LIU Zhifu. 0.9BaTiO3-0.1Bi(Mg1/2Ti1/2)O3 Ferroelectric Thin Films: Preparation and Energy Storage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 291-298. |
| [2] | ZHANG Shouchao, CHEN Hongyu, LIU Hongfei, YANG Yu, LI Xin, LIU Defeng. High Temperature Recovery of Neutron Irradiation-induced Swelling and Optical Property of 6H-SiC [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 678-686. |
| [3] | YU Ruixian, WANG Guodong, WANG Shouzhi, HU Xiaobo, XU Xiangang, ZHANG Lei. Effect of High-temperature Annealing on AlN Crystal Grown by PVT Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 343-349. |
| [4] | FU Shi, YANG Zengchao, LI Honghua, WANG Liang, LI Jiangtao. Mechanical Properties and Thermal Conductivity of Si3N4 Ceramics with Composite Sintering Additives [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 947-953. |
| [5] | LIU Dan, ZHAO Yaxin, GUO Rui, LIU Yantao, ZHANG Zhidong, ZHANG Zengxing, XUE Chenyang. Effect of Annealing Conditions on Thermoelectric Properties of Magnetron Sputtered MgO-Ag3Sb-Sb2O4 Flexible Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1302-1310. |
| [6] | WANG Yanxiang, GAO Peiyang, FAN Xueyun, LI Jiake, GUO Pingchun, HUANG Liqun, SUN Jian. Effect of SnO2 Annealing Temperature on the Performance of Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 168-174. |
| [7] | LI Pengpeng, WANG Bing, WANG Yingde. Ultrafast CO Sensor Based on Flame-annealed Porous CeO2 Nanosheets for Environmental Application [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1223-1230. |
| [8] | WANG Jin, TAO Ke, LI Guo-Feng, LIANG Ke, CAI Hong-Kun. Effect of Hydrogen Annealing on the Property of Low-temperature Epitaxial Growth of Sige Thin Films on Si Substrate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(2): 191-196. |
| [9] | REN Nai-Fei, CAO Hai-Di, HUANG Li-Jing, LI Bao-Jia, ZU Wei. Ultrasonic-Vibration-Assisted Laser Annealing on Photoelectric Properties of FTO Thin Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(10): 1083-1088. |
| [10] | HE Shao-Yang, ZENG Jian-Bang, JIANG Fang-Ming. Numerical Reconstruction and Characterization Analysis of Microstructure of Lithium-ion Battery Graphite Anode [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(9): 906-912. |
| [11] |
ZHAO Ran, MA Li-Min, GUO Fu, HU Yang-Duan-Rui, SHU Yu-Tian.
Preparation and Thermoelectric Transport of Polycrystalline In4Se3 with High Figures of Merit [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 249-255. |
| [12] | TIAN Li, ZHANG Xiao-Yong, MAO Qi-Nan, LI Xue-Geng, YU Ping-Rong, WANG Dong. Effect of Vacuum Rapid Annealing Treatment on Performance of CIGS Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(1): 35-40. |
| [13] | QIN Yi, ZHAO Ting, WANG Bo, YANG Jian-Feng. Influence of Deposition and in situ Annealing Time on Composition and Optical Band Gap of h-BN Films Deposited by PECVD [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(7): 729-734. |
| [14] | SHEN Yi-Qiang, SHI Yun, PAN Yu-Bai, FENG Xi-Qi, WU Le-Xiang, KOU Hua-Min, ZHANG Zhi-Ming, WEI Long. Fabrication and 2D-mapping of Pr: Lu3Al5O12 Scintillator Ceramics with High Light Yield and Fast Decay Time [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(5): 534-538. |
| [15] | Li Jian-Ping, QIAN Zheng-Hong, SUN Yu-Cheng, BAI Ru, LIU Jian-Lin, ZHU Jian-Guo. Effect of Magnetic Annealing on IrMn Based Spin Valve Materials with SAF Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(4): 411-416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||