
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2013, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (1): 79-84.DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2013.12107
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZENG Xiao-Bo, HU Hao, XIE Li-Qin, LAN Fang, WU Yao, GU Zhong-Wei
Received:2012-02-23
Revised:2012-04-10
Published:2013-01-10
Online:2012-12-20
About author:ZENG Xiao-Bo. E-mail: zengxiaobo1986@163.com
CLC Number:
ZENG Xiao-Bo, HU Hao, XIE Li-Qin, LAN Fang, WU Yao, GU Zhong-Wei. Preparation and Properties of Supermagnetic Calcium Phosphate Composite Scaffold[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(1): 79-84.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Name of scaffold | Type of SPIO | Mass ratio of SPIO/HA |
|---|---|---|
| HA | — | — |
| MHA0 | SPIO-h | 2:100 |
| MHA1 | SPIO-h | 5:100 |
| MHA2 | SPIO-h | 2:100 |
| MHA3 | SPIO-h | 1:100 |
| MHA4 | SPIO-c | 10:100 |
| MHA5 | SPIO-c | 5:100 |
| MHA6 | SPIO-c | 2:100 |
Table1 Types of magnetic scaffolds of calcium phosphate with SPIO
| Name of scaffold | Type of SPIO | Mass ratio of SPIO/HA |
|---|---|---|
| HA | — | — |
| MHA0 | SPIO-h | 2:100 |
| MHA1 | SPIO-h | 5:100 |
| MHA2 | SPIO-h | 2:100 |
| MHA3 | SPIO-h | 1:100 |
| MHA4 | SPIO-c | 10:100 |
| MHA5 | SPIO-c | 5:100 |
| MHA6 | SPIO-c | 2:100 |
| Name of scaffold | Theoretical content of Fe/% | Actual content of Fe /% | Theoretical Ca/P ratio | Actual Ca/P ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA | Null | 0 | 1.67 | 1.679 |
| MHA0 | 0.85 | 2.87 | 1.67 | 1.658 |
| MHA1 | 2.07 | 2.09 | 1.67 | 1.615 |
| MHA2 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 1.67 | 1.697 |
| MHA3 | 0.43 | 0.51 | 1.67 | 1.673 |
| MHA4 | 6.58 | 6.60 | 1.67 | 1.676 |
| MHA5 | 3.44 | 3.41 | 1.67 | 1.680 |
| MHA6 | 1.42 | 1.44 | 1.67 | 1.684 |
Table 2 Fe content and Ca/P ratio of magnetic scaffolds
| Name of scaffold | Theoretical content of Fe/% | Actual content of Fe /% | Theoretical Ca/P ratio | Actual Ca/P ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA | Null | 0 | 1.67 | 1.679 |
| MHA0 | 0.85 | 2.87 | 1.67 | 1.658 |
| MHA1 | 2.07 | 2.09 | 1.67 | 1.615 |
| MHA2 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 1.67 | 1.697 |
| MHA3 | 0.43 | 0.51 | 1.67 | 1.673 |
| MHA4 | 6.58 | 6.60 | 1.67 | 1.676 |
| MHA5 | 3.44 | 3.41 | 1.67 | 1.680 |
| MHA6 | 1.42 | 1.44 | 1.67 | 1.684 |
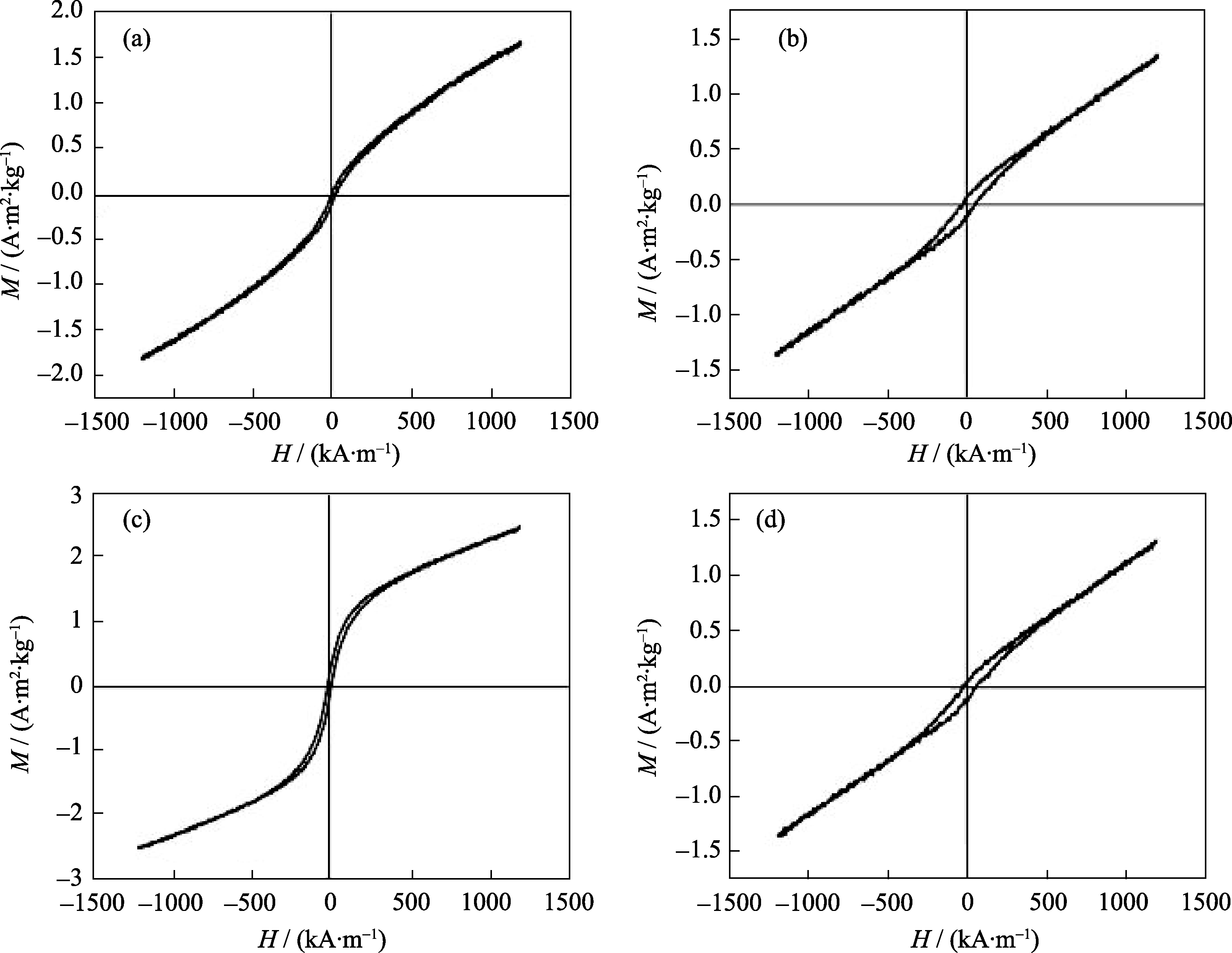
Fig. 4 Magnetization curves of MHA1 after sintered in vacuum (a), MHA1 after sintered in air (b), MHA1 before sintered (c) and HA after sintered in vacuum (d)
| [1] | Bassett C A L, Schink-Ascani M, Lewis S M. Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on steinberg ratings of femoral head osteonecrosis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res., 1989, 185(246): 172-185. |
| [2] | Santini M T, Rainaldi G, Ferrante A, et al. Effects of a 50 Hz sinusoidal magnetic field on cell adhesion molecule expression in two human osteosarcoma cell lines (mg-63 and saos-2). Bioelectromagnetics, 2003, 24(5): 327-338. |
| [3] | McLeod K J, Collazo L. Suppression of a differentiation response in MC-3T3-E1 osteoblast-like cells by sustained, low-level, 30 Hz magnetic-field exposure. Radiation Research, 2000, 153(5): 706-714. |
| [4] | Jansen J, van der Jagt O, Punt B, et al. Stimulation of osteogenic differentiation in human osteoprogenitor cells by pulsed electromagnetic fields: an in vitro study. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 2010, 23(11): 188-1-11. |
| [5] | Fini M, Cadossi R, Cane V, et al. The effect of pulsed electromagnetic fields on the osteointegration of hydroxyapatite implants in cancellous bone: a morphologic and microstructural in vivo study. J. Orthop. Res., 2002, 20(4): 756-763. |
| [6] | Zhang X Y, Xue Y, Zhang Y. Effects of 0.4 T rotating magnetic field exposure on density, strength, calcium and metabolism of rat thigh bones. Bioelectromagnetics, 2006, 27(1): 1-9. |
| [7] | Chang K, Chang W H. Pulsed electromagnetic fields prevent osteoporosis in an ovariectomized female rat model: a prostaglandin E2-associated process. Bioelectromagnetics, 2003, 24(3): 189-198. |
| [8] | Taylor K F, Inoue N, Rafiee B, et al. Effect of pulsed electromagnetic fields on maturation of regenerate bone in a rabbit limb lengthening model. J. Orthop. Res., 2006, 24(1): 2-10. |
| [9] | Wang L, Yang Z, Gao J, et al. A biocompatible method of decorporation: bisphosphonate-modified magnetite nanoparticles to remove uranyl ions from blood. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128(41): 13358-13359. |
| [10] | Kim J, Lee J E, Lee J, et al. Magnetic fluorescent delivery vehicle using uniform mesoporous silica spheres embedded with monodisperse magnetic and semiconductor nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 128(3): 688-689. |
| [11] | Jun Y W, Huh Y M, Choi J S, et al. Nanoscale size effect of magnetic nanocrystals and their utilization for cancer diagnosis via magnetic resonance imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127(16): 5732-5733. |
| [12] | Wei Y, Zhang X H, Song Y, et al. Magnetic biodegradable Fe3O4/ CS/PVA nanofibrous membranes for bone regeneration. Biomedical Materials, 2011, 6(5): 055008. |
| [13] | Meng J, Zhang Y, Qi X, et al. Paramagnetic nanofibrous composite films enhance the osteogenic responses of pre-osteoblast cells. Nanoscale 2010, 2(12): 2565-2569. |
| [14] | Banobre-Lopez M, Pineiro-Redondo Y, De-Santis R, et al. Poly(caprolactone) based magnetic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Appl. Phys. , 2011, 109(7): 07B313-1-3. |
| [15] | Bock N, Riminucci A, Dionigi C, et al. A novel route in bone tissue engineering: magnetic biomimetic scaffolds. Acta Biomaterialia, 2010, 6(3): 786-796. |
| [16] | Wu Y, Jiang W, Wen X T, et al. A novel calcium phosphate ceramic-magnetic nanoparticle composite as a potential bone substitute. Biomedical Materials, 2010, 5(1): 015001. |
| [17] | Morrison S Roy. 赵壁英, 刘英俊译. 表面化学物理. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1984: 238-242. |
| [18] | Sun S H, Zeng H. Size-controlled synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124(28): 8204-8205. |
| [19] | Kang Y S, Risbud S, Rabolt J F, et al. Synthesis and characterization of nanometer-size Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3 particles. Chemistry of Materials, 1996, 8(9): 2209-2211. |
| [20] | Lan F, Liu K X, Jiang W, et al. Facile synthesis of monodisperse superparamagnetic Fe3O4/PMMA composite nanospheres with highmagnetization. Nanotechnology, 2011, 22(22): 225604-1-7. |
| [21] | Lan F, Hu H, Jiang W, et al. Synthesis of superparamagnetic Fe3O4/PMMA/SiO2 nanorattles with periodic mesoporous shell for lysozyme adsorption. Nanoscale, 2012, 4(7): 2264-2267. |
| [22] | Jiang W, Wu Y, He B, et al. Effect of sodium oleate as a buffer on the synthesis of superparamagnetic magnetite colloids. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2010, 347(1): 1-7. |
| [23] | Hing K A. Bioceramic bone graft substitutes: influence of porosity and chemistry. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2005, 2(3): 184-199. |
| [24] | 崔国文. 缺陷、扩散与烧结. 北京: 清华大学出版社: 1990: 143-175. |
| [1] | TANG Xinli, DING Ziyou, CHEN Junrui, ZHAO Gang, HAN Yingchao. In vivo Distribution and Metabolism of Calcium Phosphate Nanomaterials Based on Fluorescent Labeling with Rare Earth Europium Ions [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 754-764. |
| [2] | CHEN Xi, YUAN Yuan, TAN Yeqiang, LIU Changsheng. Strategic Study on the Development of Inorganic Non-metallic Biomaterials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 449-456. |
| [3] | LIU Yan, QIN Xianpeng, GAN Lin, ZHOU Guohong, ZHANG Tianjin, WANG Shiwei, CHEN Hetuo. Preparation of Sub-micron Spherical Y2O3 Particles and Transparent Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 691-696. |
| [4] | XIE Jiaye, LI Liwen, ZHU Qiang. Contrastive Study on in Vitro Antibacterial Property and Biocompatibility of Three Clinical Pulp Capping Agents [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1449-1456. |
| [5] | ZHANG Hang, HAN Kunyuan, DONG Lanlan, LI Xiang. Preparation and Characterization of β-tricalcium Phosphate/Nano Clay Composite Scaffolds via Digital Light Processing Printing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1116-1122. |
| [6] | HUANG Xinyou, LIU Yumin, LIU Yang, LI Xiaoying, FENG Yagang, CHEN Xiaopu, CHEN Penghui, LIU Xin, XIE Tengfei, LI Jiang. Fabrication and Characterizations of Yb:YAG Transparent Ceramics Using Alcohol-water Co-precipitation Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 217-224. |
| [7] | DONG Shaojie,WANG Xudong,SHEN Steve Guofang,WANG Xiaohong,LIN Kaili. Research Progress on Functional Modifications and Applications of Bioceramic Scaffolds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 867-881. |
| [8] | LI Kun-Qiang,QIAO Yu-Qin,LIU Xuan-Yong. Titanium Modified by Copper Ion Implantation: Anti-bacterial and Cellular Behaviors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 158-164. |
| [9] | NIE Lan-Jian, GU Zhen-An, WANG Yu-Fen, XIANG Zai-Kui, ZHANG Chen-Yang, RAO Chuan-Dong. SiO2 Soot Body at Vacuum Sintering Process: Densification and Transparency Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(10): 1060-1066. |
| [10] | CHEN Xi-Liang, CHEN Qing-Hua, ZHUANG Ying, YAN Ting-Ting. KGM/Gelatin/Nano HAP Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering of Intervertebral Disc Annulus Fibrosus [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(1): 60-66. |
| [11] | XIAO Wen, LIU Yu-Mei, REN Kai-Ge, SHI Feng, LI Yan, ZHI Wei, WENG Jie, QU Shu-Xin. Evaluation of Vascularization of Porous Calcium Phosphate by Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane Model ex vivo [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(6): 649-654. |
| [12] | CHEN Xue-Ning, FAN Hong-Song, WANG Hong-Jun. Effect of Phase Composition of Calcium Phosphate (CaP) on Bioactivity of Osteon-like Composite Scaffolds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(1): 107-112. |
| [13] | HUANG Ping, LI Peng, ZHAO Jun-Sheng, QU Shu-Xin, FENG Bo, WENG Jie. Mechanical Activation Reinforced Porous Calcium Phosphate Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(4): 432-438. |
| [14] | ZHAO Jun-Sheng, QU Shu-Xin, HUANG Ping, LIU Zong-Guang, WANG Shi-Wen, WENG Jie. Calcium Phosphate Cement Reinforced by Nanocrystalline Cellulose [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 318-324. |
| [15] | LUO Pin-Feng, ZHI Wei, ZHANG Jing-Wei, SHI Feng, DUAN Ke, WANG Jian-xin, LU Xiong, WENG Jie. Interconnectivity of Bioceramic Scaffolds with Different Porous Structures and Their Fluid Velocity Distribution Analyzed by Micro-CT Computer Modeling [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(1): 71-76. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||