
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 284-292.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190371
Special Issue: 2020年环境材料论文精选(二)重金属元素去除
Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Li1,GUO Xiaojie2,JIN Yang1,CHEN Chaogui1( ),Abdullah M Asiri3,Hadi M Marwani3,ZHAO Qingzhou4,SHENG Guodong1(
),Abdullah M Asiri3,Hadi M Marwani3,ZHAO Qingzhou4,SHENG Guodong1( )
)
Received:2019-07-22
Revised:2019-09-11
Published:2020-03-20
Online:2020-03-24
About author:LI Li(1995–), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 2740033871@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
LI Li, GUO Xiaojie, JIN Yang, CHEN Chaogui, Abdullah M Asiri, Hadi M Marwani, ZHAO Qingzhou, SHENG Guodong. Distinguished Cd(II) Capture with Rapid and Superior Ability using Porous Hexagonal Boron Nitride: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Aspects[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3): 284-292.
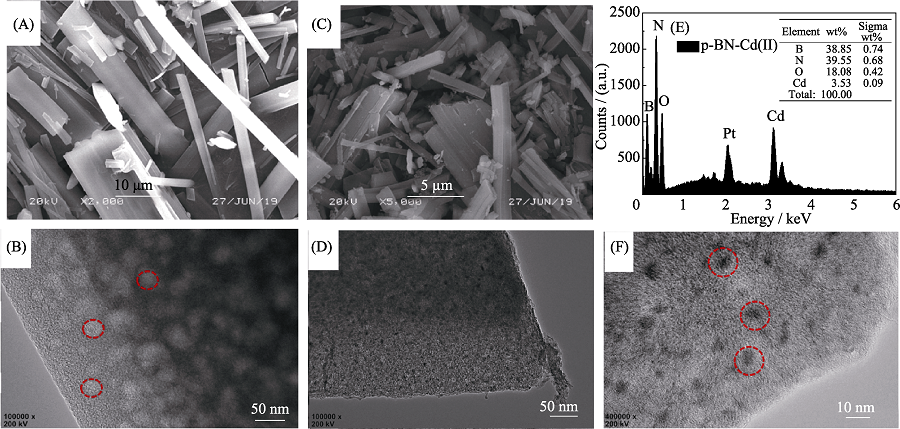
Fig. 1 (A) SEM and (B) HRTEM images of p-BN, (C) SEM and (D) HRTEM images of p-BN after adsorption, (E) EDS analysis and (F) high-magnification HRTEM image of p-BN after adsorption
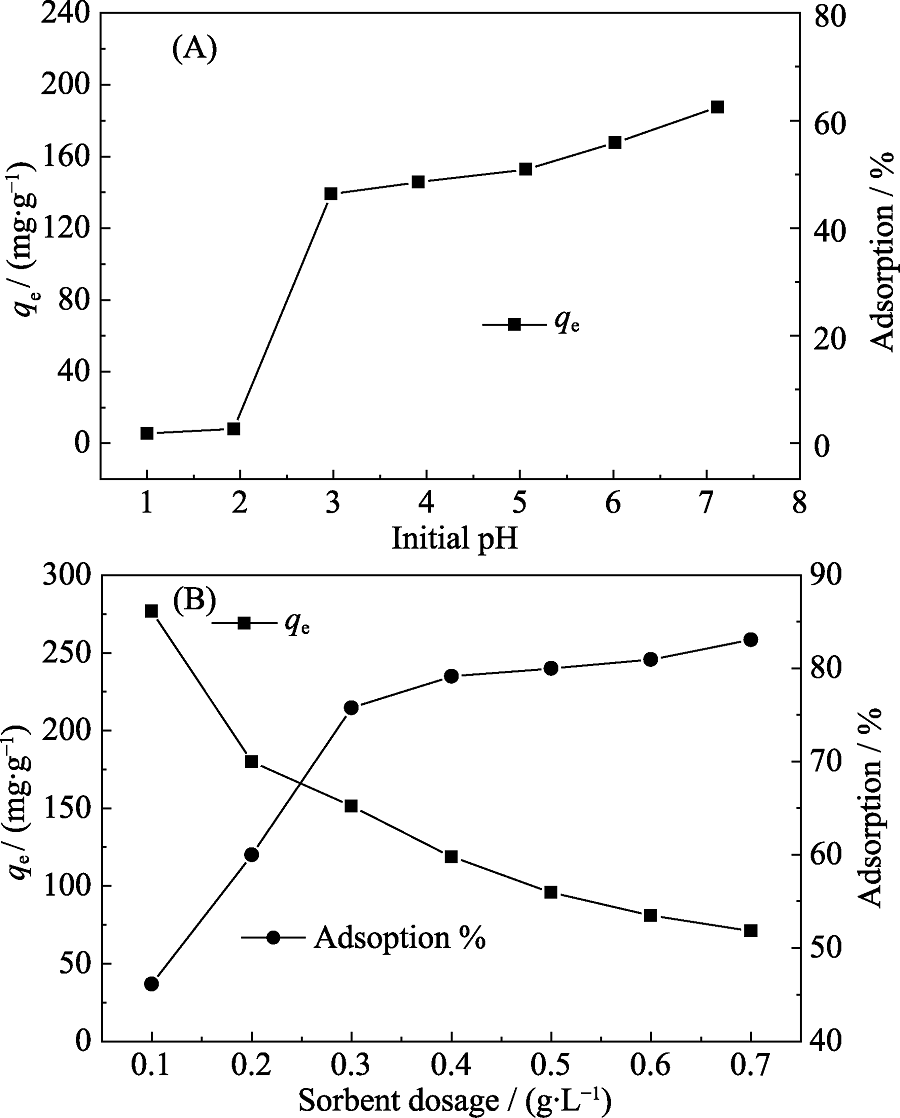
Fig. 3 (A) Effect of initial pH on Cd(II) adsorption capacity (qe) and adsorption percentage at equilibrium, and (B) effect of p-BN dosage on the adsorption capacity (qe) and adsorption percentage of Cd(II)
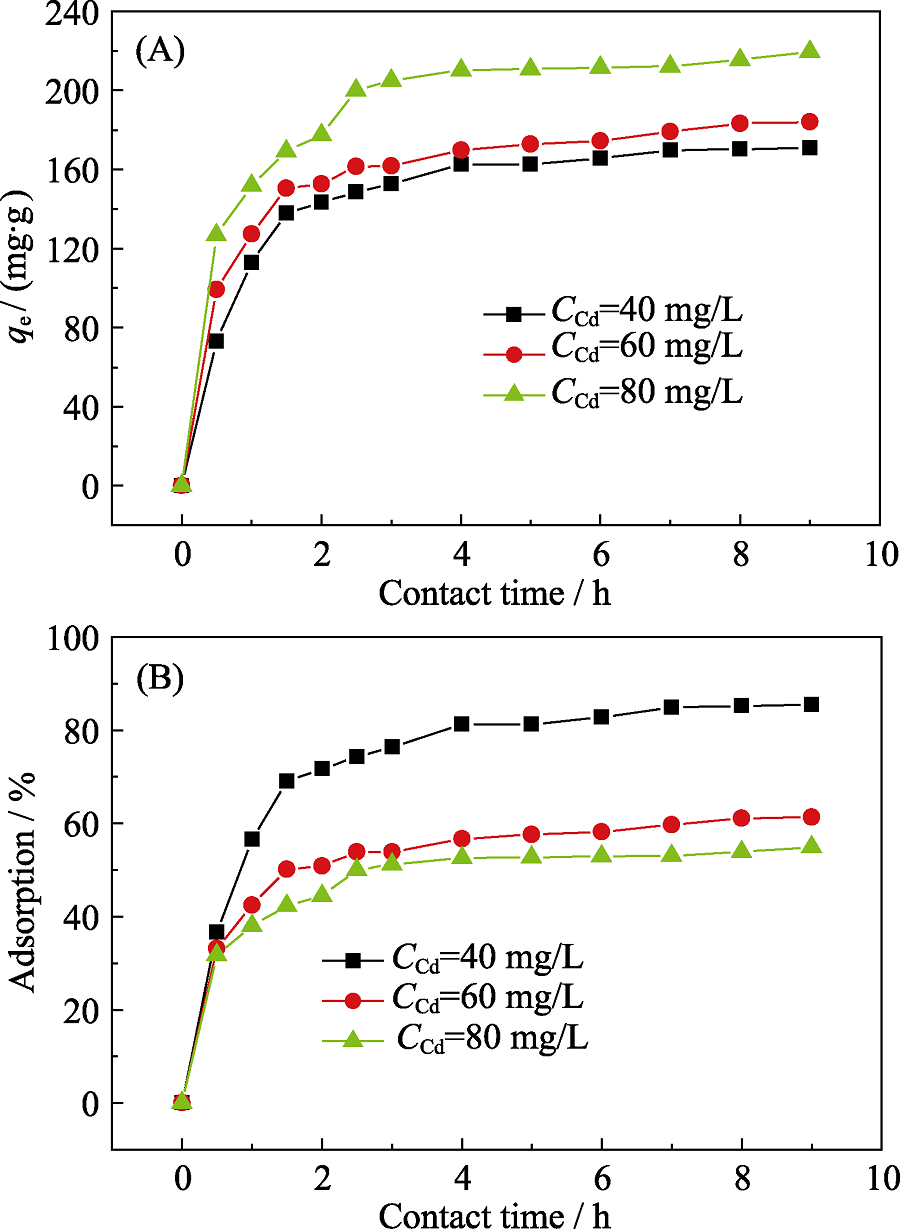
Fig. 4 (A) Adsorption capacities of Cd(II) with various contact times at different initial concentrations of Cd(II), and (B) adsorption percentages of Cd(II) on p-BN with various contact time at different initial concentrations of Cd(II)
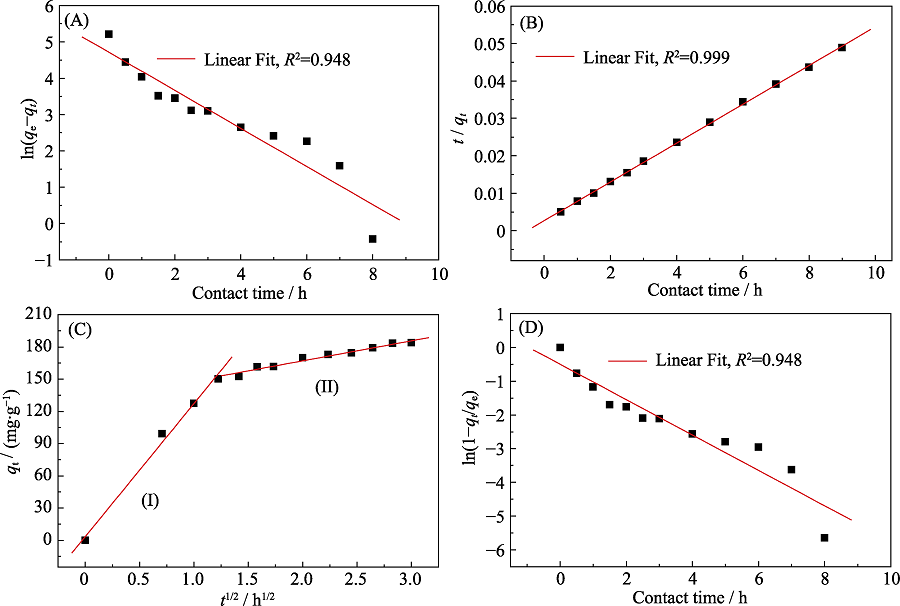
| Cd(II)/p-BN | Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | Pseudo-second-order | Intra-particle diffusion | Liquid-film diffusion | |||||
| Parameters | qe,cal=/(mg·g-1) | 111.7 | qe,cal=/(g·mg-1·h-1) | 193.1 | I | 60.2 | Kf/h-1 | 0.524 |
| K1-1 | 0.524 | K2(g·mg-1·h-1) | 1.00×10-3 | kd/(g·mg-1·h-1/2) | 49.4 | A | -0.499 | |
| R2 | 0.948 | R2 | 0.999 | R2 | 0.872 | R2 | 0.948 | |
| Cd(II)/p-BN | Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | Pseudo-second-order | Intra-particle diffusion | Liquid-film diffusion | |||||
| Parameters | qe,cal=/(mg·g-1) | 111.7 | qe,cal=/(g·mg-1·h-1) | 193.1 | I | 60.2 | Kf/h-1 | 0.524 |
| K1-1 | 0.524 | K2(g·mg-1·h-1) | 1.00×10-3 | kd/(g·mg-1·h-1/2) | 49.4 | A | -0.499 | |
| R2 | 0.948 | R2 | 0.999 | R2 | 0.872 | R2 | 0.948 | |
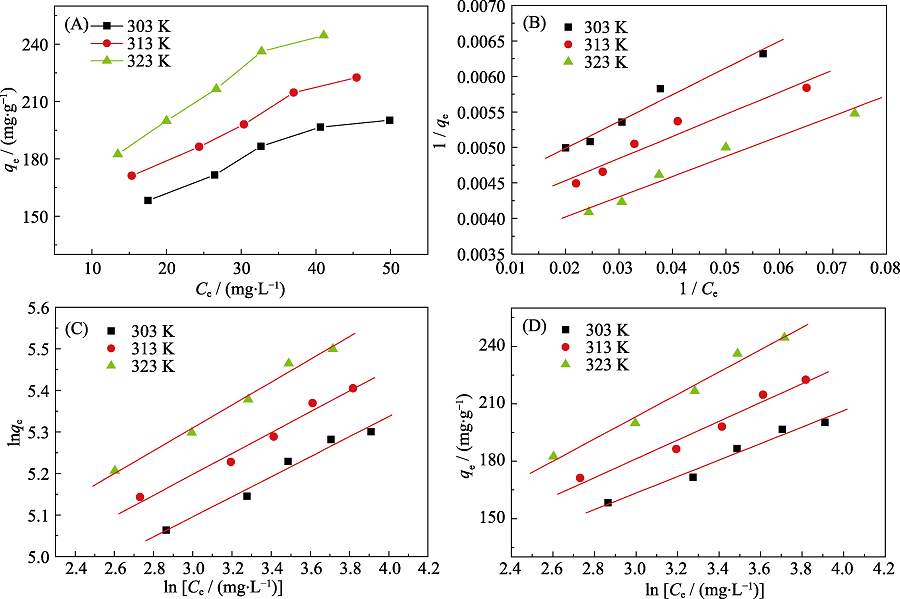
Fig. 5 (A) Adsorption isotherms of Cd(II) on p-BN at T=303, 313 and 323 K, equilibrium adsorption isotherms fitted by (B) Langmuir model, (C) Freundlich model, (D) Tempkin model Experimental conditions: Initial pH at 7.0, C0=60 mg·L-1, m=10.0 mg, V=50 mL
| Model parameter | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | Tempkin model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/(mg·g-1) | KL/(L·mg-1) | R2 | 1/n | KF | R2 | KT/(L·mg-1) | f | R2 | ||
| T/K | 303 | 236 | 0.112 | 0.984 | 0.229 | 1.27 | 0.987 | 43.1 | 2.19 | 0.987 |
| 313 | 256 | 0.126 | 0.968 | 0.225 | 1.29 | 0.989 | 49.1 | 2.00 | 0.984 | |
| 323 | 290 | 0.121 | 0.983 | 0.223 | 1.32 | 0.994 | 58.3 | 1.63 | 0.991 | |
| Model parameter | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | Tempkin model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/(mg·g-1) | KL/(L·mg-1) | R2 | 1/n | KF | R2 | KT/(L·mg-1) | f | R2 | ||
| T/K | 303 | 236 | 0.112 | 0.984 | 0.229 | 1.27 | 0.987 | 43.1 | 2.19 | 0.987 |
| 313 | 256 | 0.126 | 0.968 | 0.225 | 1.29 | 0.989 | 49.1 | 2.00 | 0.984 | |
| 323 | 290 | 0.121 | 0.983 | 0.223 | 1.32 | 0.994 | 58.3 | 1.63 | 0.991 | |
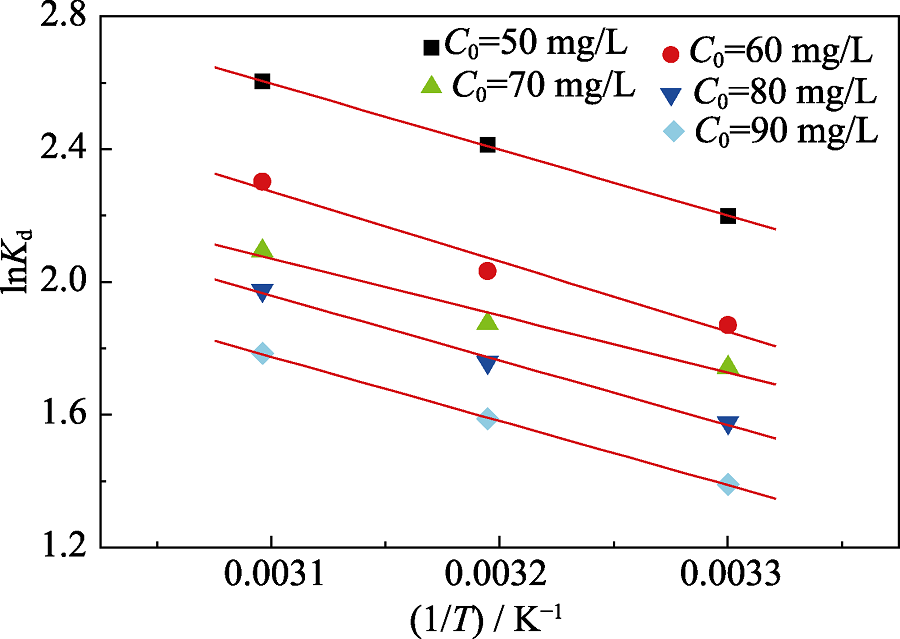
| Adsorbate | C0/(mg·L-1) | ΔHθ/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔSθ/(J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔGθ/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 303 K | 313 K | 323 K | ||||
| Cd(II) | 50 | 16.51 | 72.81 | -5.55 | -6.28 | -7.01 |
| 60 | 17.58 | 73.40 | -4.66 | -5.39 | -6.13 | |
| 70 | 14.25 | 61.39 | -4.35 | -4.97 | -5.58 | |
| 80 | 16.21 | 66.54 | -3.95 | -4.62 | -5.28 | |
| 90 | 16.08 | 64.60 | -3.49 | -4.14 | -4.79 | |
| Adsorbate | C0/(mg·L-1) | ΔHθ/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔSθ/(J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔGθ/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 303 K | 313 K | 323 K | ||||
| Cd(II) | 50 | 16.51 | 72.81 | -5.55 | -6.28 | -7.01 |
| 60 | 17.58 | 73.40 | -4.66 | -5.39 | -6.13 | |
| 70 | 14.25 | 61.39 | -4.35 | -4.97 | -5.58 | |
| 80 | 16.21 | 66.54 | -3.95 | -4.62 | -5.28 | |
| 90 | 16.08 | 64.60 | -3.49 | -4.14 | -4.79 | |
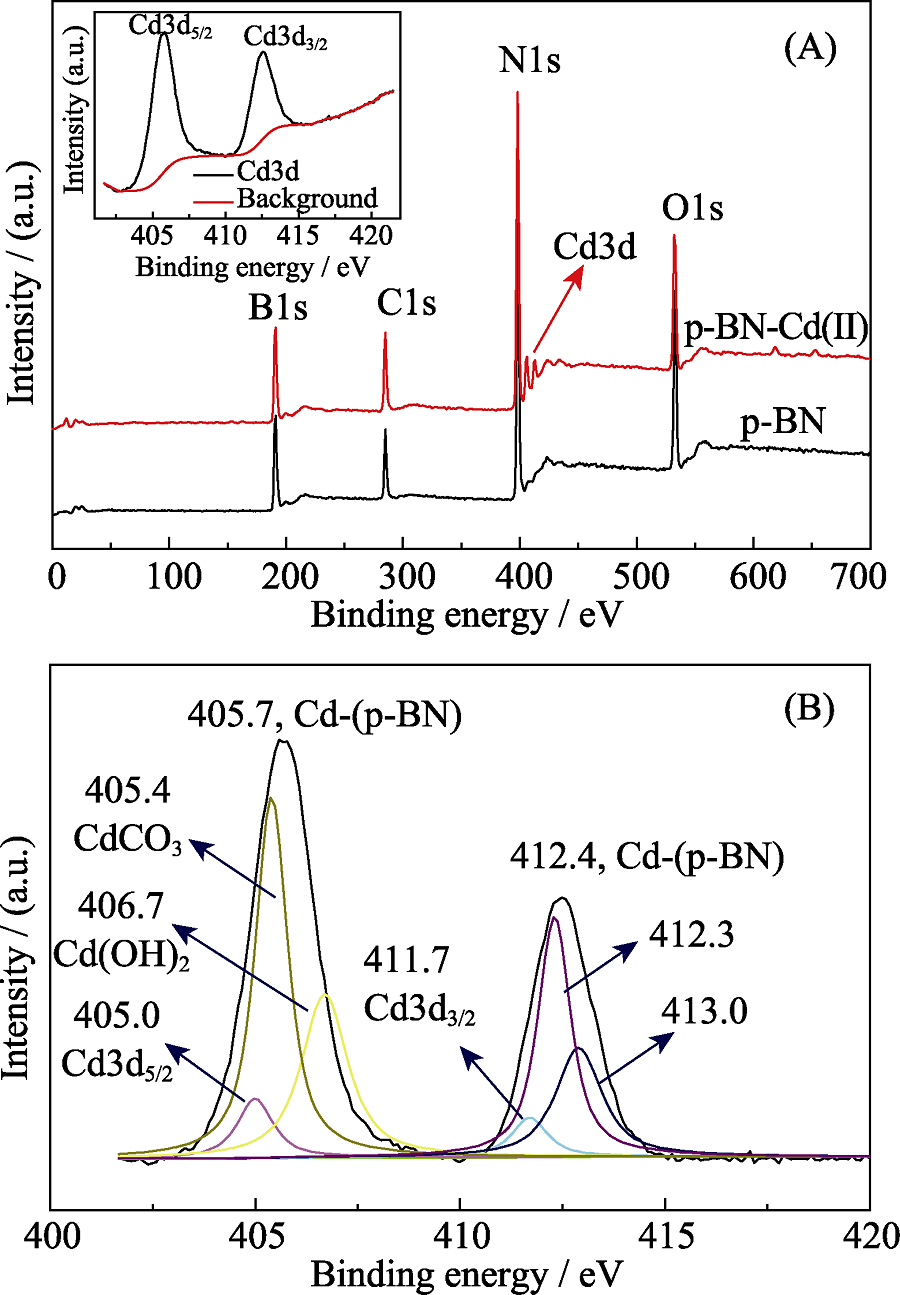
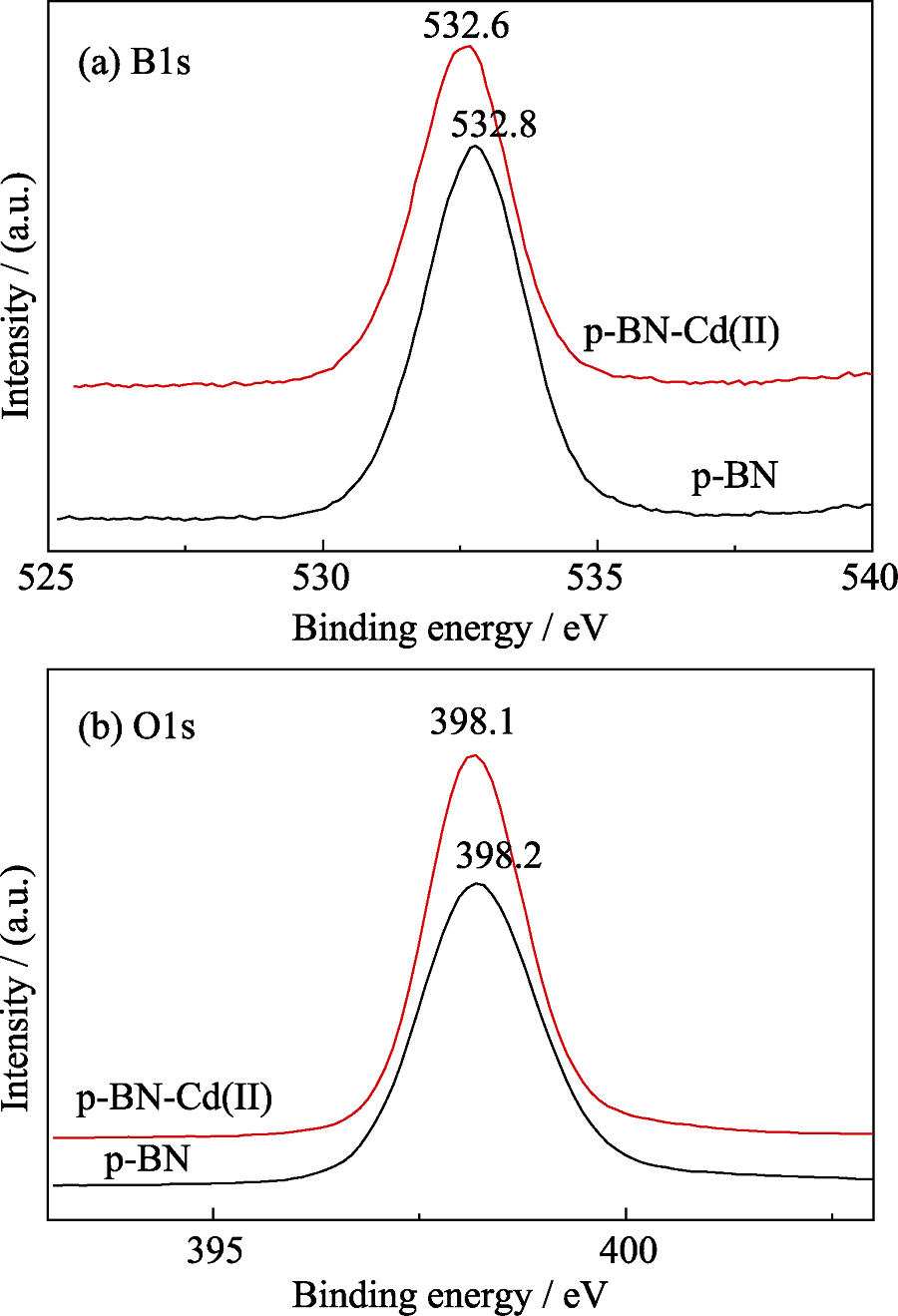
Fig. 6 (A) XPS surveys for p-BN and adsorbed p-BN(inset: high resolution Cd3d XPS spectrum and background); (B) Experimental bonding enerygy peaks of Cd(II) and the comparisons of primary peaks of Cd3d5/2 and Cd3d3/2 for free Cd(II), CdCO3, Cd(OH)2
| [1] | ZOU YI-DONG, WANG XIANG-XUE, KHAN A , et al. Environmental remediation and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites for the removal of heavy metal ions: a review. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016,50(14):7290-7304. |
| [2] | LIAO QING, PAN WANG, ZOU DONG-SHENG , et al. Using of g-C3N4 nanosheets for the highly efficient scavenging of heavy metals at environmental relevant concentrations. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018,261:32-40. |
| [3] | ZIMMERMAN J B, MIHELCIC J R, SMITH J . Global stressors on water quality and quantity. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008,42(12):4247-4254. |
| [4] | ZHAO GUI-XIA, WU XI-LIN, TAN XIAO-LI , et al. Sorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions: a review. The Open Colloid Science Journal, 2011,4:19-31. |
| [5] | ABBAS K, ZNAD H, AWUAL M R . A ligand anchored conjugate adsorbent for effective mercury(II) detection and removal from aqueous media. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018(334):432-443. |
| [6] | ZHANG SHOU-WEI, WANG XIANG-XUE, LI JIA-XING , et al. Efficient removal of a typical dye and Cr(VI) reduction using N-doped magnetic porous carbon. RSC Advances, 2014,4(108):63110-63117. |
| [7] | WANG ZHANG-HONG, SHEN DE-KUI, SHEN FEI , et al. Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium ions (Cd2+ ) removal from aqueous solution using earthworm manure-derived carbon materials. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017,241:612-621. |
| [8] | NADERI A, DELAVAR M A, GHORBANI Y , et al.Modification of nano-clays with ionic liquids for the removal of Cd (II) ion from aqueous phase. Appied Clay Science, 2018,158:236-245. |
| [9] | ZHOU GUANG-ZHU, WANG YUE, ZHOU RUN-SHENG , et al. Synthesis of amino-functionalized bentonite/CoFe2O4@MnO2 magnetic recoverable nanoparticles for aqueous Cd2+ removal. Science of the Total Environment, 2019,682:505-513. |
| [10] | AWUAL M R, KHRAISHEH M, ALHARTHI N H , et al. Efficient detection and adsorption of cadmium(II) ions using innovative nano-composite materials. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018,343:118-127. |
| [11] | GUPTA V K, ALI I, SALEH T A , et al. Chemical treatment technologies for waste-water recycling: an overview. RSC Advances, 2012,2(16):6380-6388. |
| [12] | MATURANA H A, PERIC I M, RIVAS B L , et al. Interaction of heavy metal ions with an ion exchange resin obtained from a natural polyelectrolyte. Polymer Bulletin, 2011,67(4):669-676. |
| [13] | MUNGRAY A A, KULKARNI S V, MUNGRAY A K . Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using micellar enhanced ultrafiltration technique: a review. Central European Journal of Chemistry, 2012,10(1):27-46. |
| [14] | KUMAR K S, DAHMS H U, WON E J , et al.Microalgae-a promising tool for heavy metal remediation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2015,113:329-352. |
| [15] | QDAIS H A, MOUSSA H . Removal of heavy metals from wastewater by membrane processes: a comparative study. Desalination, 2004,164:105-110. |
| [16] | INGLEZAKIS V J, LOIZIDOU M D . Ion exchange of some heavy metal ions from polar organic solvents into zeolite. Desalination, 2007,211:238-248. |
| [17] | MATLOCK M M, HOWERTON B S, ATWOOD D A . Chemical precipitation of heavy metals from acid mine drainage. Water Research, 2002,36:4757-4764. |
| [18] | GUPTA V K, SALEH T A . Sorption of pollutants by porous carbon, carbon nanotubes and fullerene-an overview. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2013,20(5):2828-2843. |
| [19] | LIAO QING, YAN SHUN-RONG, LINGHU WEN-SHENG , et al. Impact of key geochemical parameters on the highly efficient sequestration of Pb(II) and Cd(II) in water using g-C3N4 nanosheets. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018,258:40-47. |
| [20] | ZHANG HAI-FENG, DANG QI-FENG, LIU CHENG-SHENG , et al. Fabrication of methyl acrylate and tetraethylenepentamine grafted magnetic chitosan microparticles for capture of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019,366:346-357. |
| [21] | CIESIELCZYK F, BARTCZAK P, JESIONOWSKI T . A comprehensive study of Cd(II) ions removal utilizing high-surface-area binary Mg-Si hybrid oxide adsorbent. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2015,12(11):3613-3626. |
| [22] | DIAZ-FLORES P E, LOPEZ-URIAS F, TERRONES M , et al. Simultaneous adsorption of Cd 2+ and phenol on modified N-doped carbon nanotubes: experimental and DFT studies. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2009,334(2):124-131. |
| [23] | HUANG JIE-YING, WU ZHEN-WEI, CHEN LI-WEI , et al. Surface complexation modeling of adsorption of Cd(II) on graphene oxides. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2015,209:753-758. |
| [24] | SHENG GUO-DONG, ALSAEDI A, SHAMMAKH W , et al. Enhanced sequestration of selenite in water by nanoscale zero valent iron immobilization on carbon nanotubes by a combined batch, XPS and XAFS investigation. Carbon, 2016,99:123-130. |
| [25] | BOPARAI H K, JOSEPH M , O’CARROLL D M, et al. Kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium ion removal by adsorption onto nano zerovalent iron particles. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011,186(1):458-465. |
| [26] | MOSTAFA M S, BAKR A A . Adsorptive removal of Cd(II) from contaminated water via hexavalent molybdenum-containing layered double hydroxide: Ni/Mo-LDH. Energy Sources Part A-Recovery Utilization and Environmental Effects, 2019,41(18):2257-2265. |
| [27] | RAHMANIAN O, MALEKI M H, DINARI M . Ultrasonically assisted solvothermal synthesis of novel Ni/Al layered double hydroxide for capturing of Cd(II) from contaminated water. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2017,110:195-201. |
| [28] | WENG QUN-HONG, WANG XUE-BIN, WANG XI , et al. Functionalized hexagonal boron nitride nanomaterials: emerging properties and applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 2016,45(14):3989-4012. |
| [29] | YU SHU-JUN, WANG XIANG-XUE, PANG H W , et al. Boron nitride-based materials for the removal of pollutants from aqueous solutions: a review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018,333:343-360. |
| [30] | LI JIE, LI JING, XU WUE-WEN , et al. Porous boron nitride with high surface area: hydrogen storge and water treatment. Nanotechnology, 2013,24(15):155603. |
| [31] | XUE YAN-MING, DAI PENG-CHENG, JIANG XIANG-FEN , et al. Template-free synthesis of boron nitride foam-like porous monoliths and their high-end applications in water purification. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016,4(4):1469-1478. |
| [32] | LI JIE, JIN PENG, TANG CHENG-CHUN . Cr(III) adsorption by fluorinated activated boron nitride: a combined experimental and theoretical investigation. RSC Advances, 2014,4(29):14815-14821. |
| [33] | SONG QIAN-QIAN, FANG YI, LIU ZHEN-YA , et al. The performance of porous hexagonal BN in high adsorption capacity towards antibiotics pollutants from aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017,325:71-79. |
| [34] | LI JIE, HUANG YANG, LIU ZHEN-YA , et al. Chemical activation of boron nitride fibers for improved cationic dye removal performance. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2015,3(15):8185-8193. |
| [35] | CHEN MING-MING, WEI DA, CHU WEI , et al. One-pot synthesis of O-doped BN nanosheets as capacitive deionization electrode for efficient removal of heavy metal ions from water. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017,5(32):17029-17039. |
| [36] | LI JIE, XIAO XING, XU XUE-WEN , et al.Activated boron nitride as an effective adsorbent for metal ions and organic pollutants. Scientific Reports, 2013,3:3208. |
| [37] | TANG CHENG-CHUN, BANDO Y, HUANG Y , et al. Synthetic routes and formation mechanisms of spherical boron nitride nanoparticles. Advanced Functional Materials, 2008,18(22):3653-3661. |
| [38] | ZHI CHUN-YI, BANDO Y, TANG CHENG-CHUN , et al. Phonon characteristics and cathodelumininescence of boron nitride nanotubes. Applied Physics Letters, 2015,86(21):213110. |
| [39] | GEORGE S . Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies: Tables and Charts, 3rd Edition . New York: Wiley, 2001: 107-113. |
| [40] | HO YUH-SHAN, MCKAY GORDON . Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemistry, 1999,34(5):451-465. |
| [41] | ZHANG LEI, SONG XIAO-YAN, LIU XUE-YAN , et al. Studies on the removal of tetracycline by multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011,178:26-33. |
| [42] | LI PING, YIN ZHOU-XIN, LIN JIAN-FENG , et al. The immobilization of U(VI) on iron oxyhydroxides under various physicochemical conditions. Environmental Science-Processes& Impacts, 2014,16(10):2278-2287. |
| [43] | Handbook of the Elements and Native Oxides, XPS International, Inc. 1999 |
| [44] | PENG DONG, JINAG WEI, LI FANG-FANG , et al. One-pot synthesis of boron carbon nitride nanosheets for facile and efficient heavy metal ions removal. ACS Sustainable Chemistry&Engineering, 2018,6(9):11685-11694. |
| [1] | WEI Jianwen, ZHANG Lijuan, GENG Linlin, LI Yu, LIAO Lei, WANG Dunqiu. Novel CO2 Adsorbent Prepared with ZSM-5/MCM-48 as Support: High Adsorption Property and Its Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 833-839. |
| [2] | JIANG Zongyu, HUANG Honghua, QING Jiang, WANG Hongning, YAO Chao, CHEN Ruoyu. Aluminum Ion Doped MIL-101(Cr): Preparation and VOCs Adsorption Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 747-753. |
| [3] | HONG Peiping, LIANG Long, WU Lian, MA Yingkang, PANG Hao. Structure Regulation of ZIF-67 and Adsorption Properties for Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 388-396. |
| [4] | WU Guangyu, SHU Song, ZHANG Hongwei, LI Jianjun. Enhanced Styrene Adsorption by Grafted Lactone-based Activated Carbon [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 390-398. |
| [5] | XIE Tian, SONG Erhong. Effect of Elastic Strains on Adsorption Energies of C, H and O on Transition Metal Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1292-1300. |
| [6] | CHAO Shaofei, XUE Yanhui, WU Qiong, WU Fufa, MUHAMMAD Sufyan Javed, ZHANG Wei. Efficient Potassium Storage through Ti-O-H-O Electron Fast Track of MXene Heterojunction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1212-1220. |
| [7] | MA Xiaosen, ZHANG Lichen, LIU Yanchao, WANG Quanhua, ZHENG Jiajun, LI Ruifeng. 13X@SiO2: Synthesis and Toluene Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [8] | GUO Chunxia, CHEN Weidong, YAN Shufang, ZHAO Xueping, YANG Ao, MA Wen. Adsorption of Arsenate in Water by Zirconia-halloysite Nanotube Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 529-536. |
| [9] | WANG Shiyi, FENG Aihu, LI Xiaoyan, YU Yun. Pb (II) Adsorption Process of Fe3O4 Supported Ti3C2Tx [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 521-528. |
| [10] | YU Yefan, XU Ling, NI Zhongbing, SHI Dongjian, CHEN Mingqing. Prussian Blue Modified Biochar: Preparation and Adsorption of Ammonia Nitrogen from Sewage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 205-212. |
| [11] | LING Jie, ZHOU Anning, WANG Wenzhen, JIA Xinyu, MA Mengdan. Effect of Cu/Mg Ratio on CO2 Adsorption Performance of Cu/Mg-MOF-74 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1379-1386. |
| [12] | TANG Ya, SUN Shengrui, FAN Jia, YANG Qingfeng, DONG Manjiang, KOU Jiahui, LIU Yangqiao. PEI Modified Hydrated Calcium Silicate Derived from Fly Ash and Its adsorption for Removal of Cu (II) and Catalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1281-1291. |
| [13] | DAI Jieyan, FENG Aihu, MI Le, YU Yang, CUI Yuanyuan, YU Yun. Adsorption Mechanism of NaY Zeolite Molecular Adsorber Coating on Typical Space Contaminations [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1237-1244. |
| [14] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Mesoporous Organic-inorganic Hybrid Siliceous Hollow Spheres: Synthesis and VOCs Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 991-1000. |
| [15] | LIU Cheng, ZHAO Qian, MOU Zhiwei, LEI Jiehong, DUAN Tao. Adsorption Properties of Novel Bismuth-based SiOCNF Composite Membrane for Radioactive Gaseous Iodine [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1043-1050. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||