
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (10): 1237-1244.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230095
Special Issue: 【能源环境】污染物催化去除(202506)
• RESEARCH LETTER • Previous Articles
DAI Jieyan1,2( ), FENG Aihu2(
), FENG Aihu2( ), MI Le2, YU Yang2, CUI Yuanyuan3, YU Yun1,2(
), MI Le2, YU Yang2, CUI Yuanyuan3, YU Yun1,2( )
)
Received:2023-02-25
Revised:2023-03-25
Published:2023-10-20
Online:2023-06-01
Contact:
FENG Aihu, associate professor. E-mail: fengaihu@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:DAI Jieyan (1997-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: daijieyan25@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
DAI Jieyan, FENG Aihu, MI Le, YU Yang, CUI Yuanyuan, YU Yun. Adsorption Mechanism of NaY Zeolite Molecular Adsorber Coating on Typical Space Contaminations[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1237-1244.
| Number | Type | Zeolite | Adsorbate | Pressure/kPa | Temperature/K | Adsorption amount | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Simulation | FAU | Toluene | 0.0022 | 298 | 28 per cell | [36] |
| 2 | Simulation | FAU | Toluene | 100 | 298 | 30 per cell | [20] |
| Simulation | FAU | Toluene | 100 | 350 | 30 per cell | ||
| 3 | Simulation | FAU-NaY | Toluene | 1.5 | 300 | ~2.5 mmol/g (248 mg/g) | [37] |
| 4 | Simulation | FAU-NaY | Toluene | 101 | 298 | ~36 per cell (260 mg/g) | This work |
| Simulation | FAU-NaY | Toluene | 101 | 373 | ~36 per cell | ||
| Experiment | FAU-NaY | Toluene | 3.6 | 298 | 36.3 per cell (262 mg/g) |
Table 1 Comparison of adsorption capacity of different FAU zeolite on toluene
| Number | Type | Zeolite | Adsorbate | Pressure/kPa | Temperature/K | Adsorption amount | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Simulation | FAU | Toluene | 0.0022 | 298 | 28 per cell | [36] |
| 2 | Simulation | FAU | Toluene | 100 | 298 | 30 per cell | [20] |
| Simulation | FAU | Toluene | 100 | 350 | 30 per cell | ||
| 3 | Simulation | FAU-NaY | Toluene | 1.5 | 300 | ~2.5 mmol/g (248 mg/g) | [37] |
| 4 | Simulation | FAU-NaY | Toluene | 101 | 298 | ~36 per cell (260 mg/g) | This work |
| Simulation | FAU-NaY | Toluene | 101 | 373 | ~36 per cell | ||
| Experiment | FAU-NaY | Toluene | 3.6 | 298 | 36.3 per cell (262 mg/g) |
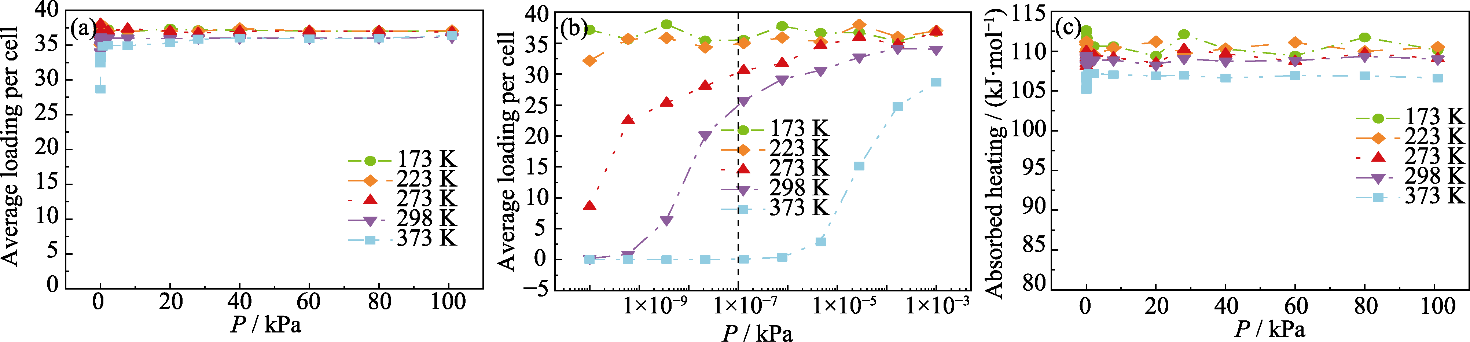
Fig. 5 Simulated toluene adsorption isotherms of NaY zeolite at different pressures (a) 10-3 kPa-101 kPa; (b) 10-10 kPa-10-3 kPa; (c) Adsorption heat of NaY zeolites
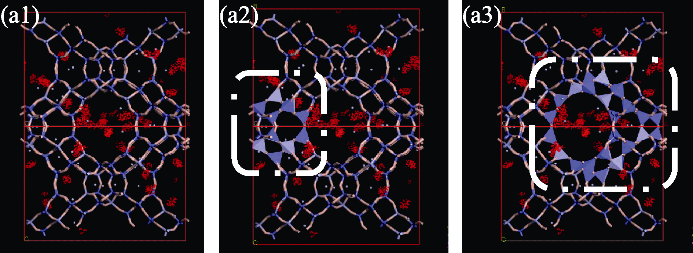
Fig. 7 Density distribution of toluene in NaY zeolite at pressure of 1 Pa (a1) Density distribution image with different visual angle compared with Fig. 6(a3); (a2) Density distribution in β cage; (a3) Density distribution in super-cage

Fig. 10 Density distributions of C10H10O4 (a) and C8H24O4Si4 (b) in NaY zeolite at pressure of 1 Pa (298 K) (a1, b1) Original density distributions; (a2, b2) Density distributions in β cage; (a3, b3) Density distribution in the super-cage
| [1] |
LIMERO T, REESE E, CHENG P, et al. Preparation of a gas chromatograph-differential mobility spectrometer to measure target volatile organic compounds on the international space station. International Journal for Ion Mobility Spectrometry, 2011, 14(2): 81.
DOI URL |
| [2] | ABRAHAM N S, HASEGAWA M M, SECUNDA M S. Application of the molecular adsorber coating technology on the Ionospheric Connection Explorer Program. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9952: 99520D. |
| [3] |
LIMERO T, REESE E, WALLACE W T, et al. Results from the air quality monitor (gas chromatograph-differential mobility spectrometer) experiment on board the international space station. International Journal for Ion Mobility Spectrometry, 2012, 15(3): 189.
DOI URL |
| [4] | SANDERS J T. Molecular contamination of an EUV instrument in geosynchronous orbit. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5526: 44. |
| [5] | CANHAM J S. Revisiting mechanisms of molecular contamination induced laser optic damage. Proceedings of SPIE, 2007, 6720: 67200M. |
| [6] | CHANG C W, KANNENBERG K, CHIDESTER M H. Development of versatile molecular transport model for modeling spacecraft contamination. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7794: 77940O. |
| [7] |
GUO S S, AI W D, FEI J X, et al. Study on the kinetic characteristics of trace harmful gases for a two-person-30-day integrated CELSS test. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(9): 7020.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
SNITKA V, BATIUSKAITE D, BRUZAITE I, et al. Surface- enhanced Raman scattering sensors for biomedical and molecular detection applications in space. CEAS Space Journal, 2021, 13(3): 509.
DOI |
| [9] | SHIMOSAKO N, EGASHIRA T, YOSHINO K, et al. Effects of vacuum on photocatalytic activity of TiO2. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10748: 1074810. |
| [10] | SHIMOSAKO N, YOSHINO K, SHIMAZAKI K, et al. Tolerance to electron beams of TiO2 film photocatalyst. Thin Solid Films, 2019, 686: 137421. |
| [11] | DIBOUNE M, NOUALI H, SOULARD M, et al. Green hybrid zeolite coatings for on-orbit molecular decontamination. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 307: 110478. |
| [12] | SHIMOSAKO N, SAKAMA H. Influence of vacuum environment on photocatalytic degradation of methyl red by TiO2 thin film. Acta Astronaut, 2021, 178: 693. |
| [13] | FENG A H, YU Y, MI L, et al. Synthesis and VOCs adsorption performance of surfactant-templated USY zeolites with controllable mesopores. Chemical Physics Letters, 2022, 798: 139578. |
| [14] | ABRAHAM N S, JALLICE D E. Preliminary testing of NASA's molecular adsorber coating technology for future missions to Mars. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10748: 107480E. |
| [15] | STRAKA S, PETERS W, HASEGAWA M, et al.Development of molecular adsorber coatings. Conference on Optical System Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7794: 77940C. |
| [16] |
CHEN H Y, XI H X, CAI X Y, et al. Experimental and molecular simulation studies of a ZSM-5-MCM-41 micro-mesoporous molecular sieve. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2009, 118(1/2/3): 396.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
MORADI H, AZIZPOUR H, BAHMANYAR H, et al. Effect of Si/Al ratio in the faujasite structure on adsorption of methane and nitrogen: a molecular dynamics study. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2021, 44(7): 1221.
DOI URL |
| [18] | QIAO J, YANG S S, LI J J, et al. Dynamic simulation of deposition processes of spacecraft molecular contamination. Tehnicki Vjesnik- Technical Gazette, 2021, 28(1): 321. |
| [19] | WANG M Y, SHENG Y. Molecular simulation to analyze the influence of ultrafine particles on activated carbon adsorbing low concentration toluene. Building and Environment, 2022, 213: 108875. |
| [20] |
ZHAO F, SUN X S, LU R F, et al. Adsorption of methanol, methanal, toluene, ethylbenzene, and styrene in zeolites: a grand canonical Monte Carlo simulation study. Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 2017, 95(12): 1241.
DOI URL |
| [21] | MORADI H, AZIZPOUR H, BAHMANYAR H, et al. Molecular dynamic simulation of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrogen adsorption on Faujasite zeolite. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2022, 43: 70. |
| [22] |
MAURIN G, BELMABKHOUT Y, PIRNGRUBER G, et al. CO2 adsorption in LiY and NaY at high temperature: molecular simulations compared to experiments. Adsorption-Journal of the International Adsorption Society, 2007, 13(5/6): 453.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
PORCHER F, PAILLAUD J L, GABEROVA L, et al. Monitoring by in situ neutron diffraction of simultaneous dehydration and Ni2+ mobility in partially exchanged NaY zeolites. New Journal of Chemistry, 2016, 40(5): 4228.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
AMMOULI T, PAILLAUD J L, NOUALI H, et al. Insights into water adsorption in potassium-exchanged X-type faujasite zeolite: molecular simulation and experiment. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(35): 19405.
DOI URL |
| [25] | XIONG P, HE P, QU Y X, et al. The adsorption properties of NaY zeolite for separation of ethylene glycol and 1, 2-butanediol: experiment and molecular modelling. Green Energy & Environment, 2021, 6(1): 102. |
| [26] | SONG L Q, DU X S, CHEN Y R, et al. Screening of zeolites for H2S adsorption in mixed gases: GCMC and DFT simulations. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2021, 328: 111495. |
| [27] |
VUJIC B, LYUBARTSEV A P. Transferable force-field for modelling of CO2, N2, O2 and Ar in all silica and Na+ exchanged zeolites. Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 2016, 24(4): 045002.
DOI URL |
| [28] | CHEN H Y, WANG W L, DING J, et al. CO2 adsorption capacity of FAU zeolites in presence of H2O: a Monte Carlo simulation study. Energy Procedia, 2017, 105: 4370. |
| [29] | HOU S Y, TANG Y L, ZHU T L, et al. Adsorptive removal of gas phase naphthalene on ordered mesoporous carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 436: 129208. |
| [30] | RAHMATI M, MODARRESS H. Selectivity of new siliceous zeolites for separation of methane and carbon dioxide by Monte Carlo simulation. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2013, 176: 168. |
| [31] | KEYVANLOO Z, POUR A N, MOOSAVI F, et al. Molecular dynamic simulation studies of adsorption and diffusion behaviors of methanol and ethanol through ZSM-5 zeolite. Journal of Molecular Graphics & Modelling, 2022, 110: 108048. |
| [32] | FENG A, YU Y, MI L, et al. Synthesis and characterization of hierarchical Y zeolites using NH4HF2 as dealumination agent. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019, 280: 211. |
| [33] | FENG A, YU Y, MI L, et al. Structural, textural and toluene adsorption properties of NH4HF2 and alkali modified USY zeolite. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019, 290: 109646. |
| [34] |
YOSHIMOTO R, HARA K, OKUMURA K, et al. Analysis of toluene adsorption on Na-form zeolite with a temperature-programmed desorption method. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2007, 111(3): 1474.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
HESSOU E P, BEDE L A, JABRAOUI H, et al. Adsorption of toluene and water over cationic-exchanged Y zeolites: a DFT exploration. Molecules, 2021, 26(18): 5486.
DOI URL |
| [36] | ZHENG H M, ZHAO L, JI J J, et al. Unraveling the adsorption mechanism of mono- and diaromatics in faujasite zeolite. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(19): 10190. |
| [37] |
BRUNCHI C C, SANCHEZ J M C, STANKIEWICZ A I, et al. Adsorption of volatile organic compounds. experimental and theoretical study. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(51): 16697.
DOI URL |
| [1] | WEI Jianwen, ZHANG Lijuan, GENG Linlin, LI Yu, LIAO Lei, WANG Dunqiu. Novel CO2 Adsorbent Prepared with ZSM-5/MCM-48 as Support: High Adsorption Property and Its Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 833-839. |
| [2] | Rong-Hui LI, Yi-Zheng JIA, Nan-Nan HU. 3D Hierarchical Flower Like Alumina Nanomaterials: Preparation and Arsenic Removal Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(5): 553-559. |
| [3] | XU Jian, TANG Zhe-Peng, PENG Yu-Qing, GU Chuan-Qing, KOYO Norinaga, LI Ai-Jun. Numerical Simulation for Influence of Surface Area/Volume Ratio and Inlet Gas Pressure on Pyrolytic Carbon Texture [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(12): 1327-1334. |
| [4] | ZHANG Jun,WANG De-Ping,YAO Ai-Hua,HUANG Wen-Hai. Research on Adsorption Capacity for Ni2+ and Mechanism of Nano-hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(2): 269-274. |
| [5] | LIU Cui-Xia,YANG Yan-Qing,HUANG Bin,ZHANG Rong-Jun,LUO Xian,REN Xiao-Xia. Atomic Scale Simulation of {111}-Oriented SiC Film Growth by Chemical Vapor Deposition Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(5): 933-937. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||