
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (8): 885-892.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180514
Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Li-Yan1,LI Hong2,HU Li-Li1,WANG Ya-Jie1,3
Received:2018-10-31
Revised:2019-01-07
Published:2019-08-20
Online:2019-05-22
CLC Number:
ZHANG Li-Yan, LI Hong, HU Li-Li, WANG Ya-Jie. Structure Modeling of Genes in Glass: Composition-structure-property Approach[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(8): 885-892.
| Sample | WL /(mg?cm-2) | nd | n2 /(×10-13, esu) | α300 ℃/(×10-6, K-1) | Tg/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | 1.29 | 1.50466 | 1.05 | 12.51 | 493.1 |
| S1 | 0.89 | 1.50574 | 0.99 | 12.75 | 471.9 |
| S2 | 1.07 | 1.50650 | 0.99 | 12.56 | 471.6 |
| S3 | 1.30 | 1.50600 | 0.98 | 12.62 | 482.7 |
| S4 | 1.11 | 1.50554 | 0.99 | 12.27 | 486.1 |
| B1 | 0.65 | 1.50734 | 1.00 | 12.53 | 471.1 |
| B2 | 1.04 | 1.50708 | 0.99 | 12.58 | 472.8 |
| B3 | 0.67 | 1.50841 | 0.99 | 12.48 | 476.8 |
| B4 | 1.11 | 1.50814 | 1.01 | 12.04 | 492.2 |
| L1 | 0.79 | 1.50836 | 0.99 | 12.80 | 466.5 |
| L2 | 0.70 | 1.51001 | 1.03 | 12.48 | 476.8 |
| L3 | 0.65 | 1.51165 | 1.06 | 12.60 | 480.4 |
| L4 | 0.69 | 1.51332 | 1.08 | 12.32 | 484.4 |
Table 1 Number of glass samples and their properties
| Sample | WL /(mg?cm-2) | nd | n2 /(×10-13, esu) | α300 ℃/(×10-6, K-1) | Tg/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | 1.29 | 1.50466 | 1.05 | 12.51 | 493.1 |
| S1 | 0.89 | 1.50574 | 0.99 | 12.75 | 471.9 |
| S2 | 1.07 | 1.50650 | 0.99 | 12.56 | 471.6 |
| S3 | 1.30 | 1.50600 | 0.98 | 12.62 | 482.7 |
| S4 | 1.11 | 1.50554 | 0.99 | 12.27 | 486.1 |
| B1 | 0.65 | 1.50734 | 1.00 | 12.53 | 471.1 |
| B2 | 1.04 | 1.50708 | 0.99 | 12.58 | 472.8 |
| B3 | 0.67 | 1.50841 | 0.99 | 12.48 | 476.8 |
| B4 | 1.11 | 1.50814 | 1.01 | 12.04 | 492.2 |
| L1 | 0.79 | 1.50836 | 0.99 | 12.80 | 466.5 |
| L2 | 0.70 | 1.51001 | 1.03 | 12.48 | 476.8 |
| L3 | 0.65 | 1.51165 | 1.06 | 12.60 | 480.4 |
| L4 | 0.69 | 1.51332 | 1.08 | 12.32 | 484.4 |
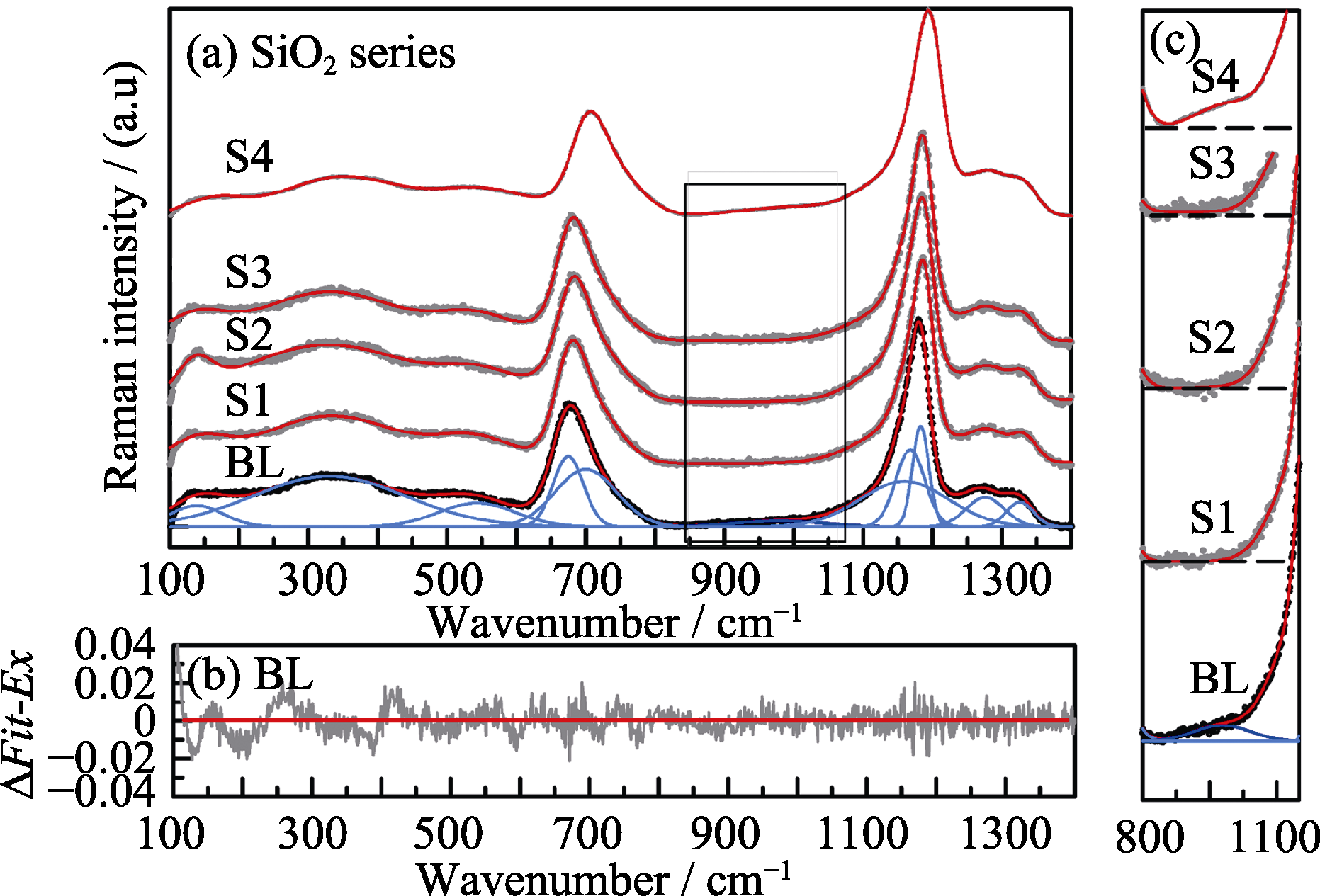
Fig. 1 Raman spectra of BL glass and SiO2 modified glasses, comparing the measured and the simulated spectra (a) along with the corresponding error in detail curve fitting results for BL glass (b), and the fitting detail of gridlines (c) in Fig.1(a)
| No. | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A6 | A7 | A8 | A9 | A10 | A11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | 3.6 | 29.0 | 6.9 | 8.2 | 13.5 | 1.9 | 15.3 | 8.7 | 6.3 | 4.3 | 2.5 |
| S1 | 4.4 | 27.6 | 8.1 | 9.2 | 13.1 | 0.0 | 14.2 | 9.1 | 7.7 | 4.3 | 2.4 |
| S2 | 3.3 | 36.8 | 6.6 | 6.3 | 14.2 | 0.0 | 12.5 | 9.3 | 5.1 | 4.2 | 1.9 |
| S3 | 4.2 | 28.1 | 7.6 | 7.4 | 14.9 | 0.0 | 13.0 | 10.5 | 7.5 | 4.8 | 2.0 |
| S4 | 3.4 | 19.2 | 10.4 | 6.8 | 13.0 | 3.1 | 18.8 | 8.0 | 9.3 | 5.2 | 2.7 |
| B1 | 3.7 | 27.6 | 7.8 | 7.4 | 13.4 | 2.8 | 12.7 | 10.2 | 5.9 | 7.2 | 1.1 |
| B2 | 3.7 | 29.0 | 6.7 | 8.0 | 13.6 | 1.8 | 15.3 | 8.6 | 6.4 | 4.2 | 2.6 |
| B3 | 3.6 | 29.1 | 10.7 | 4.6 | 16.3 | 2.8 | 15.4 | 10.8 | 5.1 | 6.9 | 0.9 |
| B4 | 3.5 | 28.4 | 8.0 | 3.5 | 16.4 | 2.3 | 17.8 | 7.4 | 5.7 | 5.0 | 1.7 |
| L1 | 3.7 | 27.1 | 7.4 | 8.8 | 12.3 | 2.5 | 13.5 | 11.1 | 5.8 | 5.8 | 1.9 |
| L2 | 3.7 | 27.4 | 7.4 | 8.5 | 12.3 | 2.4 | 12.8 | 11.5 | 5.7 | 6.5 | 1.7 |
| L3 | 3.8 | 27.1 | 7.4 | 9.3 | 11.2 | 2.4 | 16.2 | 10.0 | 6.3 | 4.2 | 2.2 |
| L4 | 5.0 | 23.5 | 9.4 | 9.3 | 11.0 | 2.7 | 13.7 | 11.4 | 6.1 | 6.7 | 1.4 |
Table 2 Integral area of Raman bands derived from the Raman curve fitting (A=Area)
| No. | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A6 | A7 | A8 | A9 | A10 | A11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | 3.6 | 29.0 | 6.9 | 8.2 | 13.5 | 1.9 | 15.3 | 8.7 | 6.3 | 4.3 | 2.5 |
| S1 | 4.4 | 27.6 | 8.1 | 9.2 | 13.1 | 0.0 | 14.2 | 9.1 | 7.7 | 4.3 | 2.4 |
| S2 | 3.3 | 36.8 | 6.6 | 6.3 | 14.2 | 0.0 | 12.5 | 9.3 | 5.1 | 4.2 | 1.9 |
| S3 | 4.2 | 28.1 | 7.6 | 7.4 | 14.9 | 0.0 | 13.0 | 10.5 | 7.5 | 4.8 | 2.0 |
| S4 | 3.4 | 19.2 | 10.4 | 6.8 | 13.0 | 3.1 | 18.8 | 8.0 | 9.3 | 5.2 | 2.7 |
| B1 | 3.7 | 27.6 | 7.8 | 7.4 | 13.4 | 2.8 | 12.7 | 10.2 | 5.9 | 7.2 | 1.1 |
| B2 | 3.7 | 29.0 | 6.7 | 8.0 | 13.6 | 1.8 | 15.3 | 8.6 | 6.4 | 4.2 | 2.6 |
| B3 | 3.6 | 29.1 | 10.7 | 4.6 | 16.3 | 2.8 | 15.4 | 10.8 | 5.1 | 6.9 | 0.9 |
| B4 | 3.5 | 28.4 | 8.0 | 3.5 | 16.4 | 2.3 | 17.8 | 7.4 | 5.7 | 5.0 | 1.7 |
| L1 | 3.7 | 27.1 | 7.4 | 8.8 | 12.3 | 2.5 | 13.5 | 11.1 | 5.8 | 5.8 | 1.9 |
| L2 | 3.7 | 27.4 | 7.4 | 8.5 | 12.3 | 2.4 | 12.8 | 11.5 | 5.7 | 6.5 | 1.7 |
| L3 | 3.8 | 27.1 | 7.4 | 9.3 | 11.2 | 2.4 | 16.2 | 10.0 | 6.3 | 4.2 | 2.2 |
| L4 | 5.0 | 23.5 | 9.4 | 9.3 | 11.0 | 2.7 | 13.7 | 11.4 | 6.1 | 6.7 | 1.4 |
| n2/(×10-13, esu) | WL/ (mg?cm-2) | Tg/℃ | CTE /(×10-6, K-1) | SiO2/wt% | B2O3/wt% | La2O3 /wt% | RO*/wt% | R2O*/wt% | Al2O3 /wt% | P2O5/wt% | Obj |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.029 | 0.90 | 486.9 | 12.18 | 2.16 | 2.81 | 0.91 | 13.59 | 10.74 | 11.58 | 59.17 | 0.99 |
| 1.023 | 0.92 | 486.7 | 12.28 | 1.93 | 2.96 | 1.08 | 13.61 | 10.77 | 11.60 | 59.27 | 0.99 |
| 1.027 | 0.88 | 487.0 | 12.26 | 1.89 | 3.04 | 1.27 | 13.59 | 10.74 | 11.58 | 59.15 | 0.98 |
| 1.024 | 0.94 | 488.0 | 12.21 | 2.05 | 2.97 | 0.89 | 13.60 | 10.75 | 11.59 | 59.21 | 0.98 |
| 1.027 | 0.90 | 487.4 | 12.22 | 2.19 | 2.95 | 1.08 | 13.57 | 10.73 | 11.56 | 59.09 | 0.98 |
| 1.027 | 0.93 | 486.0 | 12.28 | 2.03 | 2.78 | 1.21 | 13.62 | 10.77 | 11.60 | 59.30 | 0.98 |
Table 3 Compositions and properties of the glass predicted by C-S-P model
| n2/(×10-13, esu) | WL/ (mg?cm-2) | Tg/℃ | CTE /(×10-6, K-1) | SiO2/wt% | B2O3/wt% | La2O3 /wt% | RO*/wt% | R2O*/wt% | Al2O3 /wt% | P2O5/wt% | Obj |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.029 | 0.90 | 486.9 | 12.18 | 2.16 | 2.81 | 0.91 | 13.59 | 10.74 | 11.58 | 59.17 | 0.99 |
| 1.023 | 0.92 | 486.7 | 12.28 | 1.93 | 2.96 | 1.08 | 13.61 | 10.77 | 11.60 | 59.27 | 0.99 |
| 1.027 | 0.88 | 487.0 | 12.26 | 1.89 | 3.04 | 1.27 | 13.59 | 10.74 | 11.58 | 59.15 | 0.98 |
| 1.024 | 0.94 | 488.0 | 12.21 | 2.05 | 2.97 | 0.89 | 13.60 | 10.75 | 11.59 | 59.21 | 0.98 |
| 1.027 | 0.90 | 487.4 | 12.22 | 2.19 | 2.95 | 1.08 | 13.57 | 10.73 | 11.56 | 59.09 | 0.98 |
| 1.027 | 0.93 | 486.0 | 12.28 | 2.03 | 2.78 | 1.21 | 13.62 | 10.77 | 11.60 | 59.30 | 0.98 |
| Sample | Yb3+ (ICP)/ (×1020, ions?cm-3) | σemi/pm2 | Tg/℃ | Stark splitting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS0 | 2.40 | 0.50 | 477 | 639 |
| PS2 | 2.38 | 0.48 | 441 | 651 |
| PS5 | 2.46 | 0.50 | 462 | 769 |
| PS10 | 2.32 | 0.53 | 503 | 786 |
| PS20 | 2.17 | 0.57 | 509 | 814 |
Table 4 Properties of PS glass
| Sample | Yb3+ (ICP)/ (×1020, ions?cm-3) | σemi/pm2 | Tg/℃ | Stark splitting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS0 | 2.40 | 0.50 | 477 | 639 |
| PS2 | 2.38 | 0.48 | 441 | 651 |
| PS5 | 2.46 | 0.50 | 462 | 769 |
| PS10 | 2.32 | 0.53 | 503 | 786 |
| PS20 | 2.17 | 0.57 | 509 | 814 |
| [1] | ZHAO J C . A perspective on the materials genome initiative. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2014,36(2):89-104. |
| [2] | VOLF M . Mathematical approach to glass. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers, 1988. |
| [3] | LI H, DAVIS M J, URRUTI E H . Eye-safe laser glass development at SCHOTT. Proc. of SPIE, 2010,7686(16):1-12. |
| [4] |
VIENNA J D . Compositional models of glass/melt properties and their use for glass formulation. Procedia Materials Science, 2014,7:148-155.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LI H, CHERYL R, WATSON J . High-performance glass fiber development for composite applications. International Journal of Applied Glass Science, 2014,5(1):65-81.
DOI URL |
| [6] | VIENNA J D, HRMA P R, SCHWEIGER M J , et al . Effect of composition and temperature on the properties of High-Level Waste (HLW) glasses melting above 1200 ℃ (Draft). Office of Scientific & Technical Information Technical Reports, 1996. |
| [7] | YAMASHITA H, YOSHINO H, NAGATA K , et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of alkaline earth phosphosilicate and aluminoborosilicate glasses. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2000,270(1):48-59. |
| [8] |
GREAVES G N . EXAFS and the structure of glass. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 1985,71(1):203-217.
DOI URL |
| [9] | SEN S, RAKHMATULLIN R, GUBAYDULLIN R , et al. A pulsed EPR study of clustering of Yb3+ ions incorporated in GeO2 glass. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids , 2004,333(1):22-27. |
| [10] | ZHANG L Y, LI H, HU L L . Statistical structure analysis of GeO2 modified Yb 3+: phosphate glasses based on Raman and FT-IR study . Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2017,698:103-113. |
| [11] | LI H, ZHANG L Y, HU L L , et al. Statistical Modeling Approach to Glass Research and Development: Composition-Structure- Property Relationships (Invited). 8th International Symposium on Advanced Glass, Shanghai, China, 2018. |
| [12] | CORNELL J A . Experiments with Mixtures: Designs, Models, and the Analysis of Mixture Data, 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 2002. |
| [13] |
DARROCH J N, WALLER J . Additive and interaction in three-component experiments with mixtures. Biometrika, 1985,72:153-163.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
PIEPEL G F, SZYCHOWSKI J M, LOEPPKY J L . Augmenting scheffe linear mixture models with squared and/or crossproduct terms. Journal of Quality Technology, 2002,34(3):297-314.
DOI URL |
| [15] | SCHEFFE H . The simplex-centroid design for experiments with mixtures. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 1963,25(2):235-263. |
| [16] | ZHANG L Y, LI H, HU L L . Statistical approach to modeling relationships of composition-structure-property I: Alkaline earth phosphate glasses. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2018,734:163-171. |
| [1] | WANG Xiaobo, ZHU Yuliang, XUE Wenchao, SHI Ruchuan, LUO Bofeng, LUO Chengtao. Effect of PbTiO3 Content Variation on High-power Performance of PMN-PT Single Crystal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 840-846. |
| [2] | SUN Jing, LI Xiang, MAO Xiaojian, ZHANG Jian, WANG Shiwei. Effect of Lauric Acid Modifier on the Hydrolysis Resistance of Aluminum Nitride Powders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 826-832. |
| [3] | TANG Xinli, DING Ziyou, CHEN Junrui, ZHAO Gang, HAN Yingchao. In vivo Distribution and Metabolism of Calcium Phosphate Nanomaterials Based on Fluorescent Labeling with Rare Earth Europium Ions [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 754-764. |
| [4] | YU Leyangyang, ZHAO Fangxia, ZHANG Shuxin, XU Yixiang, NIU Yaran, ZHANG Zhenzhong, ZHENG Xuebin. Preparation of High-entropy Boride Powders for Plasma Spraying by Inductive Plasma Spheroidization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 808-816. |
| [5] | YANG Guang, ZHANG Nan, CHEN Shujin, WANG Yi, XIE An, YAN Yujie. WO3 Films Based on Porous ITO Electrodes: Preparation and Electrochromic Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 781-789. |
| [6] | CHAI Runyu, ZHANG Zhen, WANG Menglong, XIA Changrong. Preparation of Ceria Based Metal-supported Solid Oxide Fuel Cells by Direct Assembly Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 765-771. |
| [7] | WANG Lujie, ZHANG Yuxin, LI Tongyang, YU Yuan, REN Pengwei, WANG Jianzhang, TANG Huaguo, YAO Xiumin, HUANG Yihua, LIU Xuejian, QIAO Zhuhui. Corrosion and Wear Behavior of Silicon Carbide Ceramic in Deep-sea Service Environment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 799-807. |
| [8] | LI Wenyuan, XU Jianan, DENG Han'ao, CHANG Aimin, ZHANG Bo. Effect of V5+ Substitution on Microstructure and Microwave Dielectric Properties of LaTaO4 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 697-703. |
| [9] | DONG Chenyu, ZHENG Weijie, MA Yifan, ZHENG Chunyan, WEN Zheng. Characterizations by Piezoresponse Force Microscopy on Relaxor Properties of Pb(Mg,Nb)O3-PbTiO3 Ultra-thin Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 675-682. |
| [10] | HE Guoqiang, ZHANG Kaiheng, WANG Zhentao, BAO Jian, XI Zhaochen, FANG Zhen, WANG Changhao, WANG Wei, WANG Xin, JIANG Jiapei, LI Xiangkun, ZHOU Di. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: Au Underrated K40 Microwave Dielectric Ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 639-646. |
| [11] | ZHANG Jiawei, CHEN Ning, CHENG Yuan, WANG Bo, ZHU Jianguo, JIN Cheng. Electrical Properties of Bismuth Layered Piezoelectric Bi4Ti3O12 Ceramics with A/B-site Doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 690-696. |
| [12] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [13] | AN Ran, LIN Si, GUO Shigang, ZHANG Chong, ZHU Shun, HAN Yingchao. Iron-doped Nano-hydroxyapatite: Preparation and Ultraviolet Absorption Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 457-465. |
| [14] | CHEN Yi, QIU Haipeng, CHEN Mingwei, XU Hao, CUI Heng. SiC/SiC Composite: Matrix Boron Modification and Mechanical Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [15] | SUN Yuxuan, WANG Zheng, SHI Xue, SHI Ying, DU Wentong, MAN Zhenyong, ZHENG Liaoying, LI Guorong. Defect Dipole Thermal-stability to the Electro-mechanical Properties of Fe Doped PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 545-551. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||