无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 245-255.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240344 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240344
所属专题: 【制备方法】3D打印(202506)
殷杰1,2( ), 耿佳毅1,2, 王康龙1, 陈忠明1, 刘学建1,2, 黄政仁1,2,3(
), 耿佳毅1,2, 王康龙1, 陈忠明1, 刘学建1,2, 黄政仁1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-19
修回日期:2024-10-05
出版日期:2025-03-20
网络出版日期:2025-03-12
通讯作者:
黄政仁, 研究员. E-mail:zhrhuang@mail.sic.ac.cn作者简介:殷 杰(1986-), 男, 研究员. E-mail:jieyin@mail.sic.ac.cn
基金资助:
YIN Jie1,2( ), GENG Jiayi1,2, WANG Kanglong1, CHEN Zhongming1, LIU Xuejian1,2, HUANG Zhengren1,2,3(
), GENG Jiayi1,2, WANG Kanglong1, CHEN Zhongming1, LIU Xuejian1,2, HUANG Zhengren1,2,3( )
)
Received:2024-07-19
Revised:2024-10-05
Published:2025-03-20
Online:2025-03-12
Contact:
HUANG Zhengren, professor. E-mail: zhrhuang@mail.sic.ac.cnAbout author:YIN Jie (1986-), male, professor. E-mail: jieyin@mail.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
SiC陶瓷具有高强度和良好的热稳定性, 在航空航天、热端部件等领域有着广泛的应用前景。随着对大尺寸和复杂形状SiC陶瓷需求的日益增长, 3D打印技术在制造周期、成本及可靠性等诸多方面明显优于传统减材、等材制造方法, 越来越受到重视。3D打印方法众多, 各具特点: 立体光刻(Stereolithography, SLA)技术可以实现高精度和优良的表面质量, 但实际操作中往往需要设计支撑结构, 再加上残余应力和低固含量等问题, 极大限制了其发展; 激光选区烧结(Selective laser sintering, SLS)技术具有较强的材料普适性, 适用于高分子、金属和陶瓷等多种材料, 可实现大尺寸快速成形, 且制造成本较低, 但其成形素坯表面质量较低, 需进行后续加工; 熔融沉积(Fused deposition modeling, FDM)技术制备的SiC陶瓷材料可借助反应烧结实现致密化, 但成形素坯存在层间结合强度低、表面有较明显条纹等缺陷, 并且成形速度相对较慢, 不适合构建大型零件, 因此在实际生产中受到限制。本文综述了近五年来3D打印SiC陶瓷的最新研究进展, 讨论了成形素坯的后续高温致密化处理方法及其基本物理性能, 并展望了3D打印SiC陶瓷材料的未来前景。新型3D打印技术及其与多种打印方式的融合将在陶瓷宏微观结构的精细化中发挥重要作用, 或将成为未来的重要发展趋势。
中图分类号:
殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255.
YIN Jie, GENG Jiayi, WANG Kanglong, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Recent Advances in 3D Printing and Densification of SiC Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 245-255.
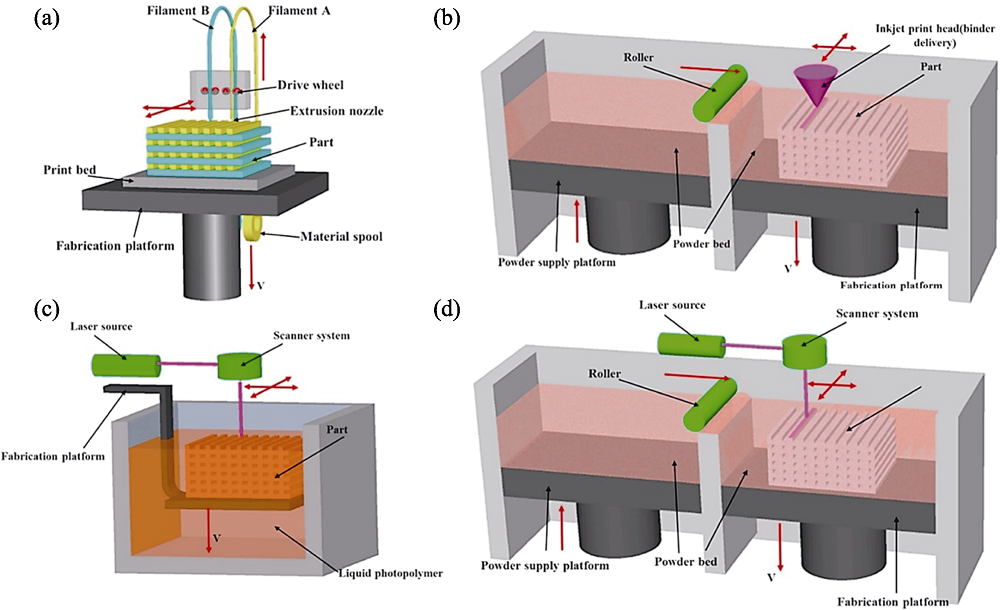
图1 典型陶瓷3D打印成形技术示意图[13]
Fig. 1 Schematic diagrams of typical 3D printing technology for ceramics[13] (a) Fused deposition modeling; (b) Direct ink writing; (c) Stereolithography; (d) Selective laser sintering
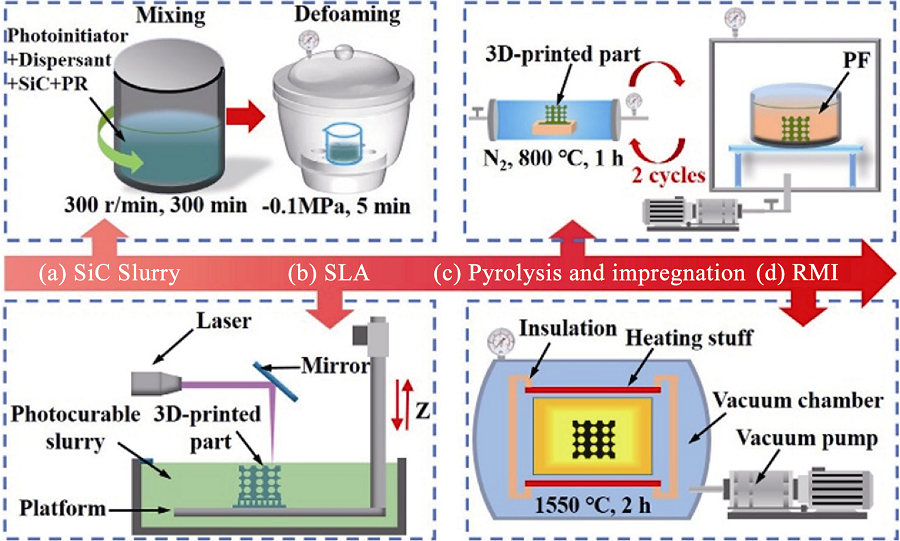
图4 基于SLA和RMI的SiC陶瓷制备工艺[24]
Fig. 4 Fabrication process of SiC ceramic based on SLA and RMI[24] (a) Preparation of SiC slurry; (b) SLA; (c) Pyrolysis and impregnation; (d) RMI
| Sintering method | Sintering temperature/℃ | Mechanical property | Fracture mechanism | Mass transfer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-phase sintering | 2000-2200 | High flexure strength, low fracture toughness, and being sensitive to cracks | Transgranular fracture | Diffusion |
| Liquid-phase sintering | 1850-2000 | High flexure strength and fracture toughness | Intergranular fracture | Viscous flow |
表1 固相烧结和液相烧结SiC陶瓷对比[50]
Table 1 Characteristics of solid-phase sintered and liquid-phase sintered SiC ceramics[50]
| Sintering method | Sintering temperature/℃ | Mechanical property | Fracture mechanism | Mass transfer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-phase sintering | 2000-2200 | High flexure strength, low fracture toughness, and being sensitive to cracks | Transgranular fracture | Diffusion |
| Liquid-phase sintering | 1850-2000 | High flexure strength and fracture toughness | Intergranular fracture | Viscous flow |
| Additive manufacturing process | Mechanical property | Advantage | Challenge | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDM | Bulk density: 3.12 g/cm3 Flexure strength: 465 MPa | Being simple, efficient preparation process and low requirements for equipment | Poor surface roughness, additional support for complex structures, and obvious step effect of layered structure | [60] |
| DIW | Bulk density: 3 g/cm3 Flexure strength: 406.1 MPa | High adaptability of raw materials, simple preparation process, and low manufacturing cost | Dimensional restrictions, and low precision | [16] |
| SLA | Bulk density: 2.85 g/cm3 Flexure strength: 234.8 MPa | High printing accuracy and surface finish, enabling design of macro- and micro-structures | Low green body strength, additional support structures required for complex structures, and toxic photosensitive resins | [23] |
| SLS | Bulk density: 3.1 g/cm3 Flexure strength: 794 MPa | High molding efficiency, and recoverable powder | High thermal stress, and being prone to defects | [39] |
表2 3D打印制备SiC陶瓷的力学性能、优势以及面临的挑战[16,23,39,60]
Table 2 Mechanical properties, advantages and challenges of SiC ceramics by 3D printing techniques[16,23,39,60]
| Additive manufacturing process | Mechanical property | Advantage | Challenge | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDM | Bulk density: 3.12 g/cm3 Flexure strength: 465 MPa | Being simple, efficient preparation process and low requirements for equipment | Poor surface roughness, additional support for complex structures, and obvious step effect of layered structure | [60] |
| DIW | Bulk density: 3 g/cm3 Flexure strength: 406.1 MPa | High adaptability of raw materials, simple preparation process, and low manufacturing cost | Dimensional restrictions, and low precision | [16] |
| SLA | Bulk density: 2.85 g/cm3 Flexure strength: 234.8 MPa | High printing accuracy and surface finish, enabling design of macro- and micro-structures | Low green body strength, additional support structures required for complex structures, and toxic photosensitive resins | [23] |
| SLS | Bulk density: 3.1 g/cm3 Flexure strength: 794 MPa | High molding efficiency, and recoverable powder | High thermal stress, and being prone to defects | [39] |
| [1] | ZOCCA A, COLOMBO P, GOMES C M, et al. Additive manufacturing of ceramics: issues, potentialities, and opportunities. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2015, 98(7): 1983. |
| [2] | BAUX A, JACQUES S, ALLEMAND A, et al. Complex geometry macroporous SiC ceramics obtained by 3D-printing, polymer impregnation and pyrolysis (PIP) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(6): 3274. |
| [3] | SHEN T, XIONG H, LI Z, et al. Fused deposition fabrication of high-quality zirconia ceramics using granular feedstock. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(24): 34352. |
| [4] | CHEN A, SU J, LI Y, et al. 3D/4D printed bio-piezoelectric smart scaffolds for next-generation bone tissue engineering. International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing, 2023, 5(3): 032007. |
| [5] | SHAHZAD A, LAZOGLU I. Direct ink writing (DIW) of structural and functional ceramics: recent achievements and future challenges. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2021, 225: 109249. |
| [6] | JIANG Q, YANG D, YUAN H, et al. Fabrication and properties of Si2N2O-Si3N4 ceramics via direct ink writing and low-temperature sintering. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(1): 32. |
| [7] | HOSSAIN S S, LU K. Recent progress of alumina ceramics by direct ink writing: ink design, printing and post-processing. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(7): 10199. |
| [8] | TANG J, CHANG H, GUO X, et al. Preparation of carbon fiber- reinforced SiC ceramics by stereolithography and secondary silicon infiltration. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(17): 25159. |
| [9] | BAI X, DING G, ZHANG K, et al. Stereolithography additive manufacturing and sintering approaches of SiC ceramics. Open Ceramics, 2021, 5: 100046. |
| [10] | HE R, ZHOU N, ZHANG K, et al. Progress and challenges towards additive manufacturing of SiC ceramic. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(4): 637. |
| [11] | HASSANIN H, ESSA K, ELSHAER A, et al. Micro-fabrication of ceramics: additive manufacturing and conventional technologies. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(1): 1. |
| [12] | CHEN X, YIN J, HUANG L, et al. Microstructural tailoring, mechanical and thermal properties of SiC composites fabricated by selective laser sintering and reactive melt infiltration. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2023, 12(4): 830. |
| [13] | NGO T D, KASHANI A, IMBALZANO G, et al. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): a review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2018, 143: 172. |
| [14] | MEI H, YAN Y, FENG L, et al. First printing of continuous fibers into ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(6): 3244. |
| [15] | LI F F, MA N N, CHEN J, et al. SiC ceramic mirror fabricated by additive manufacturing with material extrusion and laser cladding. Additive Manufacturing, 2022, 58: 102994. |
| [16] | WEN J, ZENG T, PAN X, et al. Effect of solid loading and carbon additive on microstructure and mechanical properties of 3D-printed SiC ceramic. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2022, 19(6): 3007. |
| [17] | XIONG H, CHEN H, ZHAO L, et al. SiCw/SiCp reinforced 3D-SiC ceramics using direct ink writing of polycarbosilane-based solution: microstructure, composition and mechanical properties. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(8): 2648. |
| [18] | XIA Y, LU Z, CAO J, et al. Microstructure and mechanical property of Cf/SiC core/shell composite fabricated by direct ink writing. Scripta Materialia, 2019, 165: 84. |
| [19] | LIU Y, CHENG Y, MA D, et al. Continuous carbon fiber reinforced ZrB2-SiC composites fabricated by direct ink writing combined with low-temperature hot-pressing. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(9): 3699. |
| [20] | LI Z, CHEN Z, LIU J, et al. Additive manufacturing of lightweight and high-strength polymer-derived SiOC ceramics. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 2020, 15(2): 163. |
| [21] | ECKEL Z C, ZHOU C, MARTIN J H, et al. Additive manufacturing of polymer-derived ceramics. Science, 2016, 351(6268): 58. |
| [22] | FU S, ZHU M, ZHU Y. Organosilicon polymer-derived ceramics: an overview. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2019, 8(4): 457. |
| [23] | TANG J, GUO X, CHANG H, et al. The preparation of SiC ceramic photosensitive slurry for rapid stereolithography. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(15): 7516. |
| [24] | LIU T, YANG L, CHEN Z, et al. Effects of SiC content on the microstructure and mechanical performance of stereolithography-based SiC ceramics. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 25: 5184. |
| [25] | FU X, HUCK D, MAKEIN L, et al. Effect of particle shape and size on flow properties of lactose powders. Particuology, 2012, 10(2): 203. |
| [26] | LU H, GUO X, LIU Y, et al. Effect of particle size on flow mode and flow characteristics of pulverized coal. KONA Powder and Particle Journal, 2015, 32: 143. |
| [27] | JULIANO P, MUHUNTHAN B, BARBOSA-CÁNOVAS G V. Flow and shear descriptors of preconsolidated food powders. Journal of Food Engineering, 2006, 72(2): 157. |
| [28] | KRANTZ M, ZHANG H, ZHU J. Characterization of powder flow: static and dynamic testing. Powder Technology, 2009, 194(3): 239. |
| [29] | SCHÜSSELE A, BAUER-BRANDL A. Note on the measurement of flowability according to the European Pharmacopoeia. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2003, 257(1/2): 301. |
| [30] | WU S, YANG L, WANG C, et al. Si/SiC ceramic lattices with a triply periodic minimal surface structure prepared by laser powder bed fusion. Additive Manufacturing, 2022, 56: 102910. |
| [31] | CHEN X, YIN J, LIU X, et al. Effect of laser power on mechanical properties of SiC composites rapidly fabricated by selective laser sintering and direct liquid silicon infiltration. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(13): 19123. |
| [32] | POPPER P, DAVIES D G S. The preparation and properties of self-bonded silicon carbide. Powder Metallurgy, 1961, 4(8): 113. |
| [33] | HAYUN S, FRAGE N, DARIEL M P. The morphology of ceramic phases in BxC-SiC-Si infiltrated composites. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2006, 179(9): 2875. |
| [34] | 邓明进.高性能反应烧结碳化硅陶瓷材料制备及其性能研究. 武汉: 武汉理工大学博士学位论文, 2010. |
| [35] | 武七德, 朱齐, 吴小兵, 等. 素坯结构对RBSC材料性能的影响. 武汉理工大学学报, 1996, 18(3): 34. |
| [36] | 李连跃, 孙洪鸣, 田素贵, 等. 炭黑含量对反应烧结碳化硅组织与性能的影响. 中国陶瓷工业, 2017, 24(1): 18. |
| [37] | LI S, ZHANG Y, HAN J, et al. Random chopped fibers in reaction bonded SiC composite: morphology, etching and reinforcing properties. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2012, 551: 104. |
| [38] | 黄清伟, 乔冠军, 高积强, 等. 生坯制备参数对反应烧结碳化硅显微组织与性能的影响. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2001, 30(2): 149. |
| [39] | WU Q, YANG C, ZHANG H, et al. Fabrication and characterization of reaction-bonded silicon carbide with poly(methyl methacrylate) as pore-forming agent. Ceramics International, 2013, 39(5): 5295. |
| [40] | LIU K, WANG J, WU T, et al. Effects of carbon content on microstructure and mechanical properties of SiC ceramics fabricated by SLS/RMI composite process. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(14): 22015. |
| [41] | PELANCONI M, COLOMBO P, ORTONA A. Additive manufacturing of silicon carbide by selective laser sintering of PA12 powders and polymer infiltration and pyrolysis. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(10): 5056. |
| [42] | ZHONG H, WANG Z, ZHOU H, et al. Properties and microstructure evolution of Cf/SiC composites fabricated by polymer impregnation and pyrolysis (PIP) with liquid polycarbosilane. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(10): 7387. |
| [43] | ZOU Y, LI C H, TANG Y, et al. Preform impregnation to optimize the properties and microstructure of RB-SiC prepared with laser sintering and reactive melt infiltration. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(15): 5186. |
| [44] | ZHAO H, LIU W, LV X, et al.β-SiC nano-particles enhanced thermal conductivity of pressureless solid-phase sintering SiC. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(2): 2772. |
| [45] | WANG K, YIN J, CHEN X, et al. Microstructure and properties of liquid phase sintered SiC ceramics fabricated via selective laser printing and precursor impregnation and pyrolysis. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(3): 4315. |
| [46] | XING Y, WU H, LIU X, et al. Grain Composition on solid-state-sintered SiC ceramics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(11): 1167. |
| [47] | SHAFFER P T B. The SiC phase in the system SiC-B4C-C. Materials Research Bulletin, 1969, 4(3): 213. |
| [48] | MADDRELL E R. Pressureless sintering of silicon carbide. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1987, 6(4): 486. |
| [49] | WANG K, YIN J, CHEN X, et al. Effect of particle grading on properties of silicon carbide ceramics by selective laser printing combined with solid phase sintering at atmospheric pressure. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 754. |
| [50] | 陈宇红, 韩凤兰, 吴澜尔. 碳化硅陶瓷的无压烧结技术. 宁夏工程技术, 2002, 1(1): 32. |
| [51] | KINGERY W D. Densification during sintering in the presence of a liquid phase. I. Theory. Journal of Applied Physics, 1959, 30(3): 301. |
| [52] | GERMAN R M, SURI P, PARK S J. Review: liquid phase sintering. Journal of Materials Science, 2009, 44(1): 1. |
| [53] | BISWAS K, RIXECKER G, ALDINGER F. Gas pressure sintering of SiC sintered with rare-earth-(III)-oxides and their mechanical properties. Ceramics International, 2005, 31(5): 703. |
| [54] | PEREVISLOV S N. Mechanism of liquid-phase sintering of silicon carbide and nitride with oxide activating additives. Glass and Ceramics, 2013, 70(7/8): 265. |
| [55] | 孙国帅, 刘荣军, 曹英斌, 等. CVI-GSI工艺制备C/C-SiC复合材料的组成结构与力学性能. 材料工程, 2017, 45(12): 58. |
| [56] | LIU R, WANG F, ZHANG J, et al. Effects of CVI SiC amount and deposition rates on properties of SiCf/SiC composites fabricated by hybrid chemical vapor infiltration (CVI) and precursor infiltration and pyrolysis (PIP) routes. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(19): 26971. |
| [57] | TERRANI K, JOLLY B, TRAMMELL M. 3D printing of high-purity silicon carbide. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(3): 1575. |
| [58] | FU H, ZHU W, XU Z, et al. Effect of silicon addition on the microstructure, mechanical and thermal properties of Cf/SiC composite prepared via selective laser sintering. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 792: 1045. |
| [59] | WANG C, CHEN X, WANG Z, et al. A novel mullite anti-gyroid/SiC gyroid ceramic metastructure based on digital light processing 3D printing with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and mechanical properties. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2024, 13(8): 1212. |
| [60] | LI F, ZHU M, CHEN J, et al. High-strength and low-silicon SiC ceramics prepared by extrusion molding 3D printing. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(2): 617. |
| [1] | 余升阳, 苏海军, 姜浩, 余明辉, 姚佳彤, 杨培鑫. 激光增材制造超高温氧化物陶瓷孔隙缺陷形成及抑制研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [2] | 刘江平, 管鑫, 唐振杰, 朱文杰, 罗永明. 含氮挥发性有机化合物催化氧化的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [3] | 肖晓琳, 王玉祥, 谷佩洋, 朱圳荣, 孙勇. 二维无机材料调控病损皮肤组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [4] | 马景阁, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料用于毛囊和毛发再生的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [5] | 张洪健, 赵梓壹, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料调控神经细胞功能及神经化组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [6] | 艾敏慧, 雷波. 微纳米生物活性玻璃: 功能化设计与血管化皮肤再生[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [7] | 王宇彤, 常江, 徐合, 吴成铁. 硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃促创面修复的研究进展:作用、机制和应用方式[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [8] | 马文平, 韩雅卉, 吴成铁, 吕宏旭. 无机活性材料在类器官研究领域的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [9] | 罗晓民, 乔志龙, 刘颍, 杨晨, 常江. 无机生物活性材料调控心肌再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [10] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [11] | 魏志帆, 陈国清, 祖宇飞, 刘渊, 李明浩, 付雪松, 周文龙. ZrB2-HfSi2复相陶瓷显微组织及其核-周结构形成机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 817-825. |
| [12] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [13] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [14] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [15] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||