无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 256-270.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240424 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240424
所属专题: 【信息功能】忆阻器材料与器件(202506)
范晓波1( ), 祖梅1(
), 祖梅1( ), 杨向飞2, 宋策1, 陈晨1, 王子3, 罗文华2, 程海峰1(
), 杨向飞2, 宋策1, 陈晨1, 王子3, 罗文华2, 程海峰1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-07
修回日期:2024-11-03
出版日期:2025-03-20
网络出版日期:2025-03-12
通讯作者:
程海峰, 研究员. E-mail: chenghf@nudt.edu.cn;作者简介:范晓波(2000-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: fanxiaobo18@163.com
基金资助:
FAN Xiaobo1( ), ZU Mei1(
), ZU Mei1( ), YANG Xiangfei2, SONG Ce1, CHEN Chen1, WANG Zi3, LUO Wenhua2, CHENG Haifeng1(
), YANG Xiangfei2, SONG Ce1, CHEN Chen1, WANG Zi3, LUO Wenhua2, CHENG Haifeng1( )
)
Received:2024-10-07
Revised:2024-11-03
Published:2025-03-20
Online:2025-03-12
Contact:
CHENG Haifeng, professor. E-mail: chenghf@nudt.edu.cn;About author:FAN Xiaobo (2000-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: fanxiaobo18@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
作为神经网络中数量最庞大的组成部分, 新型人工突触器件的研发成为了硬件实现神经形态计算的关键挑战。基于电化学晶体管的三端突触器件能够有效利用电解质层中的离子来调节通道电导, 也被称为电化学离子突触,该器件通过离子在具有氧化还原活性的沟道材料中的电化学掺杂和恢复过程来模拟生物突触特性。在调制沟道材料电导的离子中, 采用质子(H+)作为掺杂粒子的电化学离子突触具有能耗更低、运行速度更快和循环寿命更长等优势。本文综述了近年来质子调控型电化学离子突触的研究进展, 归纳了用于质子调控型电化学离子突触沟道层和电解质层的材料体系, 分析了质子调控型电化学离子突触面临的挑战, 并展望了其未来的发展。
中图分类号:
范晓波, 祖梅, 杨向飞, 宋策, 陈晨, 王子, 罗文华, 程海峰. 质子调控型电化学离子突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 256-270.
FAN Xiaobo, ZU Mei, YANG Xiangfei, SONG Ce, CHEN Chen, WANG Zi, LUO Wenhua, CHENG Haifeng. Research Progress on Proton-regulated Electrochemical Ionic Synapses[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 256-270.
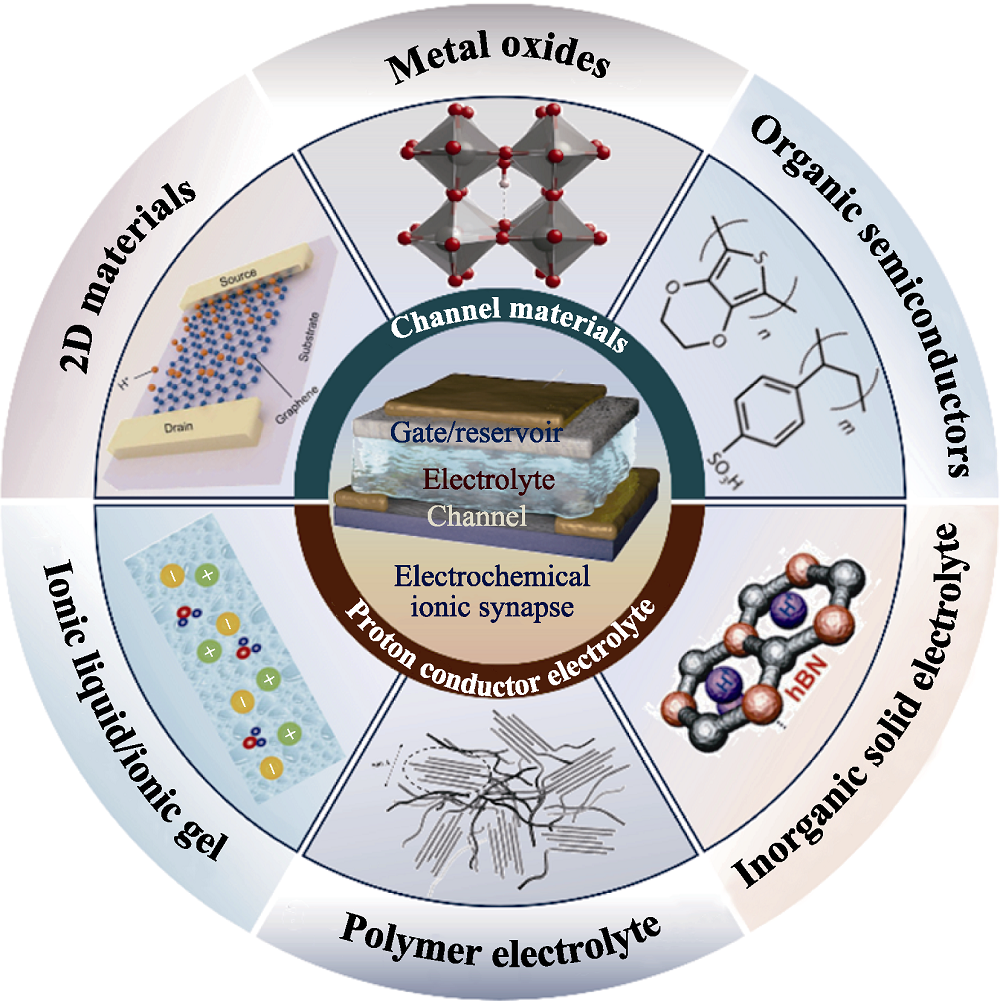
图1 用于质子调控型电化学离子突触的沟道材料及电解质材料的分类
Fig. 1 Classification of channel materials and electrolyte materials for proton-regulated electrochemical ion synapses
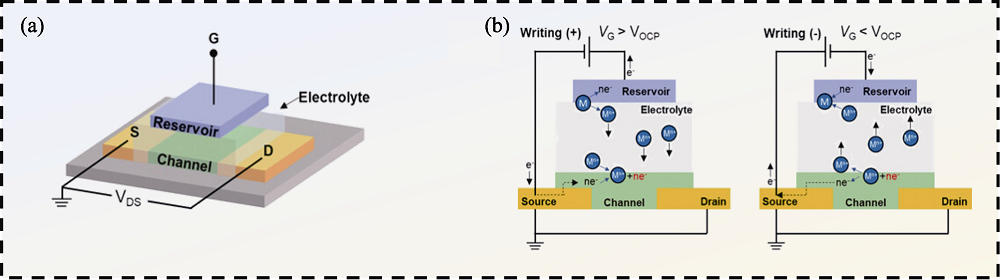
图2 电化学离子突触结构及工作机制示意图[3]
Fig. 2 Device structure and operation principle of an electrochemical ionic synapse[3] (a) Schematic illustration of the device; (b) Schematic illustration of the writing process for an electrochemical ionic synapse based on cation (Mn+) transport and intercalation of M into the channel
| Action ion | Material (channel/electrolyte) | Dynamic range | Operation voltage/current (pulse width) | Energy consumption | Channel dimension | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li+ | Li1-xCoO2/LiPON | 4.5-270 μS | 70 mV (2 s) | <10 aJ per write (projection) | L=2 μm | [4] |
| WO2.7/Li3PO4 | 0.5-3.5 μS | +3 V (1 s)/-2 V (0.5 s) -2.5 V (1 s)/+1 V (0.5 s) | - | W=5 μm L=5 μm | [6] | |
| O2- | TiO2-x/YSZ (work at 160 ℃) | 100-450 nS | ±1.5 V (2 μs) | 8.1 nJ/mm2 | W=250 μm L=8000 μm | [8] |
| WO3/HfO2 | 1.5-3.5 μS | ±4 V (10 μs) | 1 fJ/(nm2×nS) (projection) | W=20 μm L=80 μm | [9] | |
| H+ | P(g2T-TT)/ EMIM:TFSI+PVDF-HFP | 30-75 μS | ±1 V (20 ns) | 80 fJ per write | W=15 μm L=45 μm | [11] |
| WO3/PSG | 87.6-4.28 MΩ | ±10 V (5 ns)/-8.5 V (5 ns) | 10 fJ per write | W=50 nm L=150 nm | [12] | |
| Graphene/Nafion | 1.0-2.8 mS | ±10 μA (1 ms) | 50 aJ/μm2 | W=4 mm L=3-5 mm | [13] | |
| Ti3C2Tx/PVA-H2SO4 | 1.6-2.8 mS | ±1 V (4 μs) | 80 fJ/μm2 | W=1000 μm L=20 μm | [14] |
表1 不同离子调控型电化学离子突触性能比较[4,6,8 -9,11⇓⇓ -14]
Table 1 Comparison of performance of electrochemical ion synapses regulated by different ions[4,6,8 -9,11⇓⇓ -14]
| Action ion | Material (channel/electrolyte) | Dynamic range | Operation voltage/current (pulse width) | Energy consumption | Channel dimension | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li+ | Li1-xCoO2/LiPON | 4.5-270 μS | 70 mV (2 s) | <10 aJ per write (projection) | L=2 μm | [4] |
| WO2.7/Li3PO4 | 0.5-3.5 μS | +3 V (1 s)/-2 V (0.5 s) -2.5 V (1 s)/+1 V (0.5 s) | - | W=5 μm L=5 μm | [6] | |
| O2- | TiO2-x/YSZ (work at 160 ℃) | 100-450 nS | ±1.5 V (2 μs) | 8.1 nJ/mm2 | W=250 μm L=8000 μm | [8] |
| WO3/HfO2 | 1.5-3.5 μS | ±4 V (10 μs) | 1 fJ/(nm2×nS) (projection) | W=20 μm L=80 μm | [9] | |
| H+ | P(g2T-TT)/ EMIM:TFSI+PVDF-HFP | 30-75 μS | ±1 V (20 ns) | 80 fJ per write | W=15 μm L=45 μm | [11] |
| WO3/PSG | 87.6-4.28 MΩ | ±10 V (5 ns)/-8.5 V (5 ns) | 10 fJ per write | W=50 nm L=150 nm | [12] | |
| Graphene/Nafion | 1.0-2.8 mS | ±10 μA (1 ms) | 50 aJ/μm2 | W=4 mm L=3-5 mm | [13] | |
| Ti3C2Tx/PVA-H2SO4 | 1.6-2.8 mS | ±1 V (4 μs) | 80 fJ/μm2 | W=1000 μm L=20 μm | [14] |
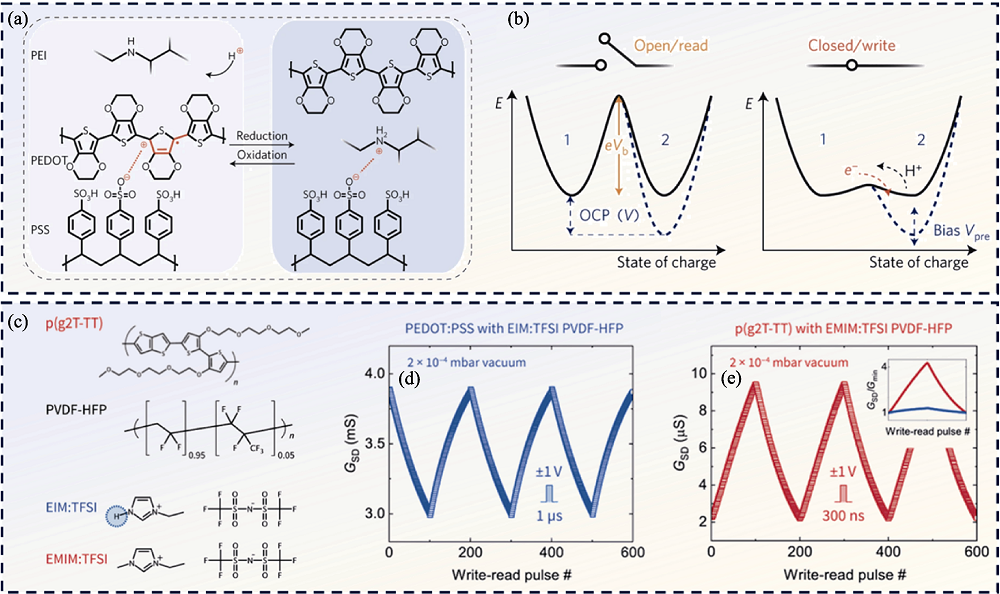
图3 有机半导体沟道材料的研究工作[10-11]
Fig. 3 Researches on organic semiconductor channel materials[10-11] (a) A positive Vpre drives protons into the postsynaptic electrode, which results in the compensation of some PSS by the protonated PEI and the reaction is reversed upon applying a negative Vpre[10]; (b) Schematic explaining the decoupling of the read and write operations[10]; (c) Chemical structures of the channel/gate and electrolyte materials[11]; Cycling of device with PEDOT:PSS (d) and p(g2T-TT) (e) as the channel material[11]. Colorful figures are available on website

图4 基于金属氧化物沟道材料的研究工作[12,22,27,29]
Fig. 4 Researches based on metal oxide channel materials[12,22,27,29] (a) Schematic diagram of synaptic transistor modulation based on VO2 channel material[22]; (b) Calculated electronic structure with protonation in WO3[27]; (c) Electronic conductivity and open circuit voltage changed with hydrogen content in WO3, as well as schematic diagram of the device structure[27]; (d) Ultrafast and energy-efficient modulation characteristics of synaptic transistor (channel, WO3;electrolyte, PSG)[12]; (e) Schematic diagram of device structure and STEM micrograph[29]; (f) Endurance test for 108 write-read pulse cycles[29]. Colorful figures are available on website
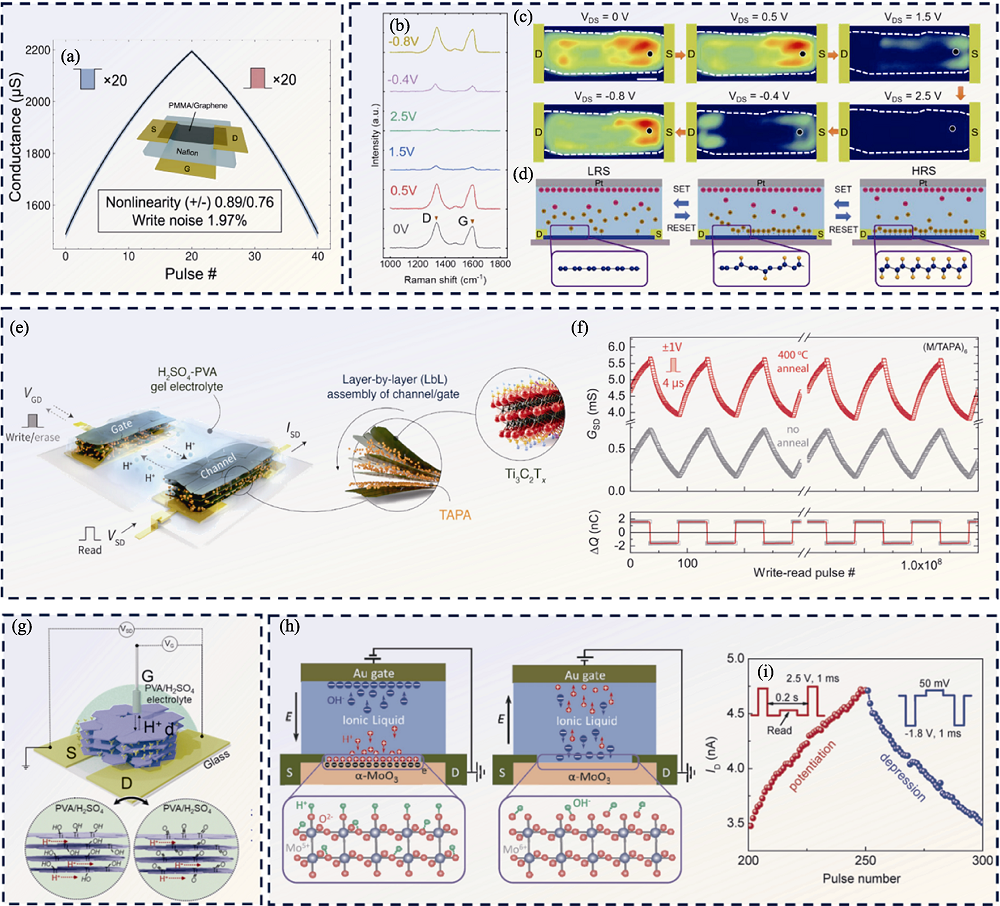
图5 基于二维沟道材料的研究工作[13-14,34,40 -41]
Fig. 5 Researches based on two-dimensional channel materials[13-14,34,40 -41] (a) Schematic diagram of graphene-based artificial synaptic and conductance per pulse number (20 negative and 20 positive pulses)[13]; (b) Raman spectra of hydrogenated graphene at varied VDS in a switching cycle[34]; (c) Raman mappings of the D peak intensity during VDS sweeps from 0 to 2.5 V and a return to -0.8 V[34]; (d) Schematic representation of hydrogenation reactions between graphene lattice and H+ ions[34]; (e) Schematic diagram of synaptic device based on 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene[14]; (f) MXene channel-based synaptic device resilience to high temperature[14]; (g) Schematic diagram of 2D MXene electrochemical transistor[40]; (h) Schematic diagram of the quasi-2D α-MoO3-based three-terminal synaptic device[41]; (i) Gradual channel current modulation under repeated positive and negative gate voltage pulses[41]. Colorful figures are available on website

图6 离子液体、离子凝胶电解质相关研究[28,46,49 -50]
Fig. 6 Related researches on ionic liquid and ion gel electrolytes[28,46,49 -50] (a) Schematic diagram of a synaptic device using the ionic liquid electrolyte[28]; (b) Contaminated water in ionic liquid could dissociate into H+ and OH−, then the small protons can intercalate into WO3 film to form a HxWO3 phase[28]; (c) FT-IR spectra of double-layered pectin/chitosan composite electrolyte film[46]; (d) FT-IR characterization of sodium alginate thin films[49]; (e) Pictures of konjac tuber and solution, and molecular structure of KGM[50]; (f) AFM image of the prepared KGM film[50]. Colorful figures are available on website
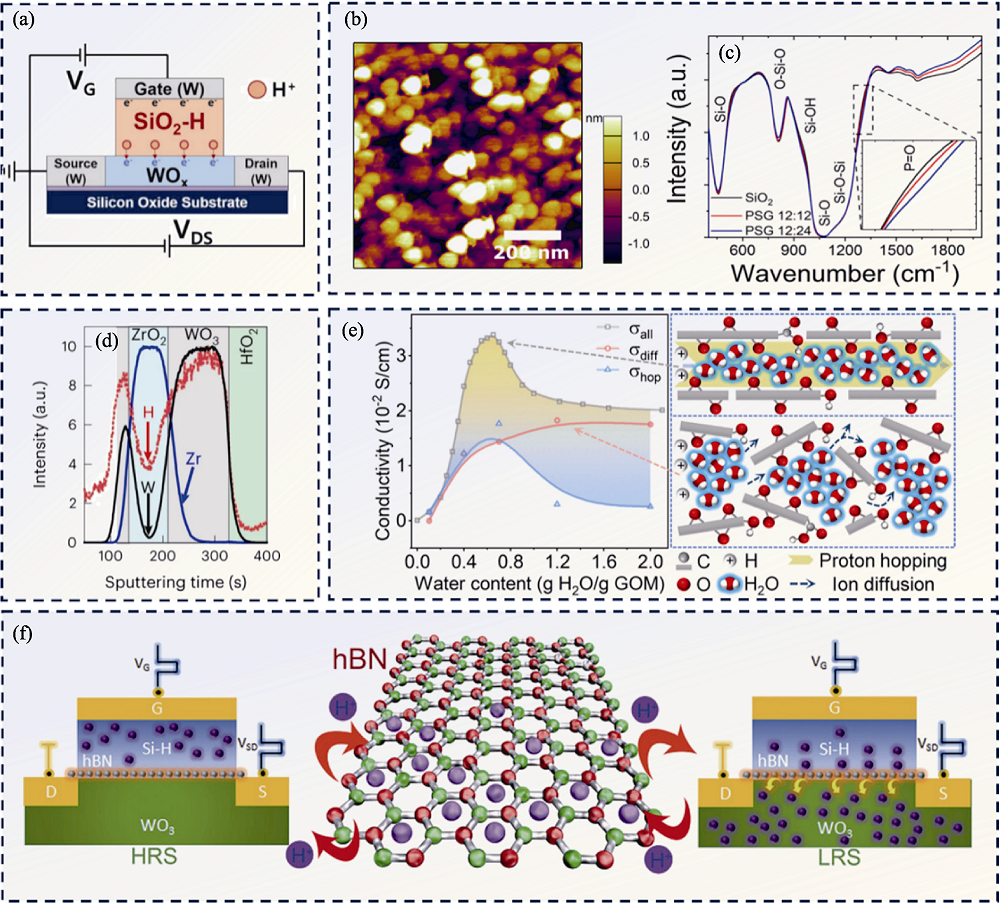
图7 无机固态电解质相关研究[29-30,56⇓ -58]
Fig. 7 Related researches on inorganic solid electrolytes[29-30,56⇓ -58] (a) Schematic diagram of a synaptic device using SiO2 electrolyte[56]; (b) AFM image of PSG thin film surface deposited on Si surface[30]; (c) FT-IR spectra of SiO2 and PSG[30]; (d) SIMS depth profiles for W (black), Zr (blue) and H (red) across device gate stack[29]; (e) Schematic diagram of the change of conductivity of graphene oxide film with water content and its microstructure at a specific water content[57]; (f) Transport of H+ ion through the weak electron cloud of a hexagonal B-N ring of hBN[58]. Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] | ZHU L Q, WAN C J, GUO L Q, et al. Artificial synapse network on inorganic proton conductor for neuromorphic systems. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 3158. |
| [2] | KANEKO Y, NISHITANI Y, UEDA M. Ferroelectric artificial synapses for recognition of a multishaded image. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2014, 61(8): 2827. |
| [3] | HUANG M, SCHWACKE M, ONEN M, et al. Electrochemical ionic synapses: progress and perspectives. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(37): 2205169. |
| [4] | FULLER E J, GABALY F E, LÉONARD F, et al. Li-ion synaptic transistor for low power analog computing. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(4): 1604310. |
| [5] | MILEWSKA A, ŚWIERCZEK K, TOBOLA J, et al. The nature of the nonmetal-metal transition in LixCoO2 oxide. Solid State Ionics, 2014, 263: 110. |
| [6] | LEE J, NIKAM R D, LIM S, et al. Excellent synaptic behavior of lithium-based nano-ionic transistor based on optimal WO2.7 stoichiometry with high ion diffusivity. Nanotechnology, 2020, 31(23): 235203. |
| [7] | YANG C, SHANG D, LIU N, et al. All-solid-state synaptic transistor with ultralow conductance for neuromorphic computing. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(42): 1804170. |
| [8] | LI Y, FULLER E J, SUGAR J D, et al. Filament-free bulk resistive memory enables deterministic analogue switching. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(45): 2003984. |
| [9] | KIM S, TODOROV T, ONEN M, et al. Metal-oxide based, CMOS-compatible ECRAM for deep learning accelerator. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, 2019: 35.7.1-35.7.4. |
| [10] | VAN DE BURGT Y, LUBBERMAN E, FULLER E J, et al. A non-volatile organic electrochemical device as a low-voltage artificial synapse for neuromorphic computing. Nature Materials, 2017, 16(4): 414. |
| [11] | MELIANAS A, QUILL T J, LECROY G, et al. Temperature- resilient solid-state organic artificial synapses for neuromorphic computing. Science Advances, 2020, 6(27): eabb2958. |
| [12] | ONEN M, EMOND N, WANG B, et al. Nanosecond protonic programmable resistors for analog deep learning. Science, 2022, 377(6605): 539. |
| [13] | KIREEV D, LIU S, JIN H, et al. Metaplastic and energy-efficient biocompatible graphene artificial synaptic transistors for enhanced accuracy neuromorphic computing. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 4386. |
| [14] | MELIANAS A, KANG M, VAHIDMOHAMMADI A, et al. High-speed ionic synaptic memory based on 2D titanium carbide MXene. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(12): 2109970. |
| [15] | JONAS F, SCHRADER L. Conductive modifications of polymers with polypyrroles and polythiophenes. Synthetic Metals, 1991, 41(3): 831. |
| [16] | BOMBILE J H, JANIK M J, MILNER S T. Polaron formation mechanisms in conjugated polymers. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2017, 20(1): 317. |
| [17] | MORIN F J. Oxides which show a metal-to-insulator transition at the neel temperature. Physical Review Letters, 1959, 3(1): 34. |
| [18] | GOODENOUGH J B. The two components of the crystallographic transition in VO2. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1971, 3(4): 490. |
| [19] | LI G, XIE D, ZHONG H, et al. Photo-induced non-volatile VO2 phase transition for neuromorphic ultraviolet sensors. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 1729. |
| [20] | GE C, LI G, ZHOU Q, et al. Gating-induced reversible HxVO2 phase transformations for neuromorphic computing. Nano Energy, 2020, 67: 104268. |
| [21] | PARK J, OH C, SON J. Anisotropic ionic transport-controlled synaptic weight update by protonation in a VO2 transistor. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2021, 9(7): 2521. |
| [22] | DENG X, WANG S, LIU Y, et al. A flexible mott synaptic transistor for nociceptor simulation and neuromorphic computing. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(23): 2101099. |
| [23] | OH C, KIM I, PARK J, et al. Deep proton insertion assisted by oxygen vacancies for long-term memory in VO2 synaptic transistor. Advanced Electronic Materials, 2021, 7(2): 2000802. |
| [24] | WU Z, SHI P, XING R, et al. Flexible mott synaptic transistor on polyimide substrate for physical neural networks. Advanced Electronic Materials, 2022, 8(9): 2200078. |
| [25] | YANG J, MA C, GE C, et al. Effects of line defects on the electronic and optical properties of strain-engineered WO3 thin films. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017, 5(45): 11694. |
| [26] | HJELM A, GRANQVIST C G, WILLS J M. Electronic structure and optical properties of WO3, LiWO3, NaWO3, and HWO3. Physical Review B, 1996, 54(4): 2436. |
| [27] | YAO X, KLYUKIN K, LU W, et al. Protonic solid-state electrochemical synapse for physical neural networks. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3134. |
| [28] | YANG J, GE C, DU J, et al. Artificial synapses emulated by an electrolyte-gated tungsten-oxide transistor. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(34): 1801548. |
| [29] | CUI J, AN F, QIAN J, et al. CMOS-compatible electrochemical synaptic transistor arrays for deep learning accelerators. Nature Electronics, 2023, 6(4): 292. |
| [30] | ONEN M, EMOND N, LI J, et al. CMOS-compatible protonic programmable resistor based on phosphosilicate glass electrolyte for analog deep learning. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(14): 6111. |
| [31] | GOKMEN T, VLASOV Y. Acceleration of deep neural network training with resistive cross-point devices: design considerations. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2016, 10(51): 333. |
| [32] | GUO L Q, HAN H, ZHU L Q, et al. Oxide neuromorphic transistors gated by polyvinyl alcohol solid electrolytes with ultralow power consumption. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(31): 28352. |
| [33] | MOHANTY H N, TSURUOKA T, MOHANTY J R, et al. Proton-gated synaptic transistors, based on an electron-beam patterned Nafion electrolyte. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(15): 19279. |
| [34] | YU C, LI S, PAN Z, et al. Gate-controlled neuromorphic functional transition in an electrochemical graphene transistor. Nano Letters, 2024, 24(5): 1620. |
| [35] | FERRARI A C, BASKO D M. Raman spectroscopy as a versatile tool for studying the properties of graphene. Nature Nanotechnology, 2013, 8(4): 235. |
| [36] | MALARD L M, PIMENTA M A, DRESSELHAUS G, et al. Raman spectroscopy in graphene. Physics Reports, 2009, 473(5): 51. |
| [37] | ELIAS D C, NAIR R R, MOHIUDDIN T M G, et al. Control of graphene’s properties by reversible hydrogenation: evidence for graphane. Science, 2009, 323(5914): 610. |
| [38] | BOUKHVALOV D W, KATSNELSON M I, LICHTENSTEIN A I. Hydrogen on graphene: electronic structure, total energy, structural distortions and magnetism from first-principles calculations. Physical Review B, 2008, 77(3): 035427. |
| [39] | HART J L, HANTANASIRISAKUL K, LANG A C, et al. Control of MXenes’ electronic properties through termination and intercalation. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 522. |
| [40] | SHAKYA J, KANG M A, LI J, et al. 2D MXene electrochemical transistors. Nanoscale, 2024, 16(6): 2883. |
| [41] | YANG C S, SHANG D S, LIU N, et al. A synaptic transistor based on quasi-2D molybdenum oxide. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(27): 1700906. |
| [42] | CHENG H, WEN M, MA X, et al. Hydrogen doped metal oxide semiconductors with exceptional and tunable localized surface plasmon resonances. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(29): 9316. |
| [43] | XIE L, ZHU Q, ZHANG G, et al. Tunable hydrogen doping of metal oxide semiconductors with acid-metal treatment at ambient conditions. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(9): 4136. |
| [44] | KUMAR M N V R. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 2000, 46(1): 1. |
| [45] | REN Z Y, ZHU L Q, YU F, et al. Synaptic metaplasticity of protonic/electronic coupled oxide neuromorphic transistor. Organic Electronics, 2019, 74: 304. |
| [46] | LI Y, HUANG Y J, CHEN X L, et al. Multi-terminal pectin/chitosan hybrid electrolyte gated oxide neuromorphic transistor with multi-mode cognitive activities. Frontiers of Physics, 2024, 19(5): 53204. |
| [47] | LI Y, ZHANG C, ZHAO X, et al. Ultrasensitive and degradable ultraflexible synaptic transistors based on natural pectin. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2022, 4(1): 316. |
| [48] | HU W, JIANG J, XIE D, et al. Transient security transistors self- supported on biodegradable natural-polymer membranes for brain- inspired neuromorphic applications. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(31): 14893. |
| [49] | LIU Y, FENG G, ZHU Q, et al. Synaptic devices with sodium alginate ionic gel gating for global regulation. Journal of Applied Physics, 2024, 135(4): 045501. |
| [50] | HUANG K W, ZHU L, YING L Y, et al. Artificial synaptic transistors based on konjac glucomannan for brain-inspired neuromorphic applications. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2024, 6(2): 1521. |
| [51] | KREUER K D. Proton conductivity: materials and applications. Chemistry of Materials, 1996, 8(3): 610. |
| [52] | MAURITZ K A, MOORE R B. State of understanding of Nafion. Chemical Reviews, 2004, 104(10): 4535. |
| [53] | FENG C, HE P F. Moisture and thermal expansion properties and mechanism of interaction between ions of a Nafion-based membrane electrode assembly. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(55): 34556. |
| [54] | LARSSON O, SAID E, BERGGREN M, et al. Insulator polarization mechanisms in polyelectrolyte-gated organic field-effect transistors. Advanced Functional Materials, 2009, 19(20): 3334. |
| [55] | ZHANG W, LI J, CHENG L, et al. Synaptic transistor arrays based on PVA/lignin composite electrolyte films. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2023, 70(6): 3245. |
| [56] | LEE J, LIM S, KWAK M, et al. Understanding of proton induced synaptic behaviors in three-terminal synapse device for neuromorphic systems. Nanotechnology, 2019, 30(25): 255202. |
| [57] | ZHANG L, LIU Z, YANG C, et al. Conduction mechanism in graphene oxide membranes with varied water content: from proton hopping dominant to ion diffusion dominant. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(9): 13771. |
| [58] | NIKAM R D, LEE J, CHOI W, et al. Ionic sieving through one-atom-thick 2D material enables analog nonvolatile memory for neuromorphic computing. Small, 2021, 17(44): 2103543. |
| [59] | WAN C J, ZHU L Q, ZHOU J M, et al. Memory and learning behaviors mimicked in nanogranular SiO2-based proton conductor gated oxide-based synaptic transistors. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(21): 10194. |
| [60] | GUO L Q, WEN J, ZHU L Q, et al. Humidity-dependent synaptic plasticity for proton gated oxide synaptic transistor. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2017, 38(9): 1248. |
| [61] | MENG Y, GAO J, ZHAO Z, et al. Review: recent progress in low-temperature proton-conducting ceramics. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54(13): 9291. |
| [62] | WU Z, SHI P, XING R, et al. Quasi-two-dimensional α-molybdenum oxide thin film prepared by magnetron sputtering for neuromorphic computing. RSC Advances, 2022, 12(28): 17706. |
| [63] | LOZADA-HIDALGO M, HU S, MARSHALL O, et al. Sieving hydrogen isotopes through two-dimensional crystals. Science, 2016, 351(6268): 68. |
| [64] | HU S, GOPINADHAN K, RAKOWSKI A, et al. Transport of hydrogen isotopes through interlayer spacing in van der Waals crystals. Nature Nanotechnology, 2018, 13(6): 468. |
| [65] | WAN C J, ZHU L Q, LIU Y H, et al. Proton-conducting graphene oxide-coupled neuron transistors for brain-inspired cognitive systems. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(18): 3557. |
| [66] | MOGG L, ZHANG S, HAO G P, et al. Perfect proton selectivity in ion transport through two-dimensional crystals. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 4243. |
| [67] | HU S, LOZADA-HIDALGO M, WANG F C, et al. Proton transport through one-atom-thick crystals. Nature, 2014, 516(7530): 227. |
| [1] | 余升阳, 苏海军, 姜浩, 余明辉, 姚佳彤, 杨培鑫. 激光增材制造超高温氧化物陶瓷孔隙缺陷形成及抑制研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [2] | 刘江平, 管鑫, 唐振杰, 朱文杰, 罗永明. 含氮挥发性有机化合物催化氧化的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [3] | 肖晓琳, 王玉祥, 谷佩洋, 朱圳荣, 孙勇. 二维无机材料调控病损皮肤组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [4] | 马景阁, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料用于毛囊和毛发再生的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [5] | 张洪健, 赵梓壹, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料调控神经细胞功能及神经化组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [6] | 艾敏慧, 雷波. 微纳米生物活性玻璃: 功能化设计与血管化皮肤再生[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [7] | 王宇彤, 常江, 徐合, 吴成铁. 硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃促创面修复的研究进展:作用、机制和应用方式[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [8] | 马文平, 韩雅卉, 吴成铁, 吕宏旭. 无机活性材料在类器官研究领域的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [9] | 罗晓民, 乔志龙, 刘颍, 杨晨, 常江. 无机生物活性材料调控心肌再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [10] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [11] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [12] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [13] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [14] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [15] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||