无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 1225-1235.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220040 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20220040
收稿日期:2022-01-21
修回日期:2022-02-18
出版日期:2022-11-20
网络出版日期:2022-03-10
通讯作者:
朱敏, 副教授. E-mail: mzhu@usst.edu.cn;作者简介:舒朝琴(1995-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 1573738940@qq.com
基金资助:
SHU Chaoqin1,2( ), ZHU Min1(
), ZHU Min1( ), ZHU Yufang2(
), ZHU Yufang2( )
)
Received:2022-01-21
Revised:2022-02-18
Published:2022-11-20
Online:2022-03-10
Contact:
ZHU Min, associate professor. E-mail: mzhu@usst.edu.cn;About author:SHU Chaoqin (1995-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 1573738940@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
生物活性陶瓷骨修复材料虽然具有优异的成骨性能, 但缺乏抗氧化应激的能力, 妨碍骨修复进程。本研究以β相磷酸三钙(β-TCP)粉体为原料, 采用LiCl-KCl熔盐体系, 以六水合氯化钴(CoCl2·6H2O)为钴源, 利用熔盐法制备出含钴氯磷灰石(Co-MS-TCP)。通过Co-MS-TCP粉体清除过氧化氢(H2O2)分析了含钴氯磷灰石的抗氧化能力; 通过细胞活性、胞内活性氧(ROS)含量变化评价了材料的细胞相容性和细胞水平抗氧化性能。结果表明, 熔盐处理β-TCP粉体能够制备含钴氯磷灰石, 钴含量随CoCl2·6H2O加入量增加而增大; H2O2清除能力随氯磷灰石中钴含量的增加而增强, 6 h内对H2O2的清除率可达90%以上。细胞实验证实, 含钴氯磷灰石具有良好的细胞相容性和抗氧化性能, 1.5 mg·mL-1加3% Co盐的MS-TCP (3%Co-MS-TCP)即可保证软骨细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞存活率大于85%, 并且3% Co-MS-TCP可有效清除H2O2, 使得细胞内ROS含量显著降低。因此, 通过熔盐法制备含钴生物活性陶瓷是实现抗氧化应激的一种有效途径, 这也为开发催化活性高、生物相容好的功能化生物活性陶瓷提供了新的策略。
中图分类号:
舒朝琴, 朱敏, 朱钰方. 熔盐法制备含钴氯磷灰石及其抗氧化性能和细胞相容性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1225-1235.
SHU Chaoqin, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Cobalt-incorporated Chlorapatite: Preparation by Molten Salt Method, Anti-oxidation and Cytocompatibility[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1225-1235.
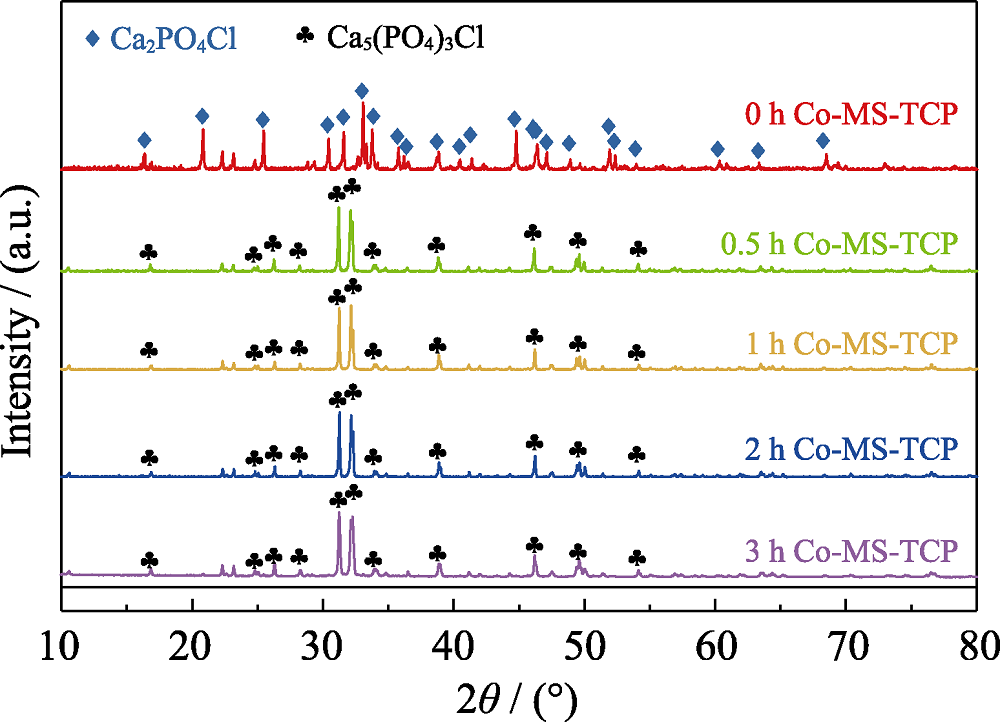
图1 熔盐处理保温不同时间制备的Co-MS-TCP粉体的XRD图谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of Co-MS-TCP powders prepared by molten salt method with different holding time The color figure can be obtained from online edition
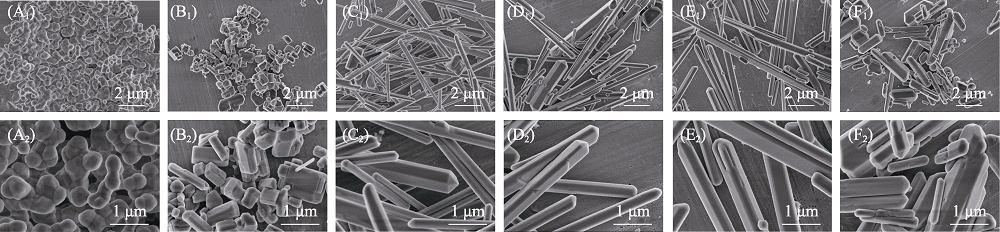
图2 β-TCP粉体经熔盐处理保温不同时间前后样品的微观形貌SEM照片
Fig. 2 SEM images of β-TCP powders before and after molten salt treatment with different holding time (A1-A2) β-TCP; (B1-B2) 0 h Co-MS-TCP; (C1-C2) 0.5 h Co-MS-TCP; (D1-D2) 1 h Co-MS-TCP; (E1-E2) 2 h Co-MS-TCP; (F1-F2) 3 h Co-MS-TCP
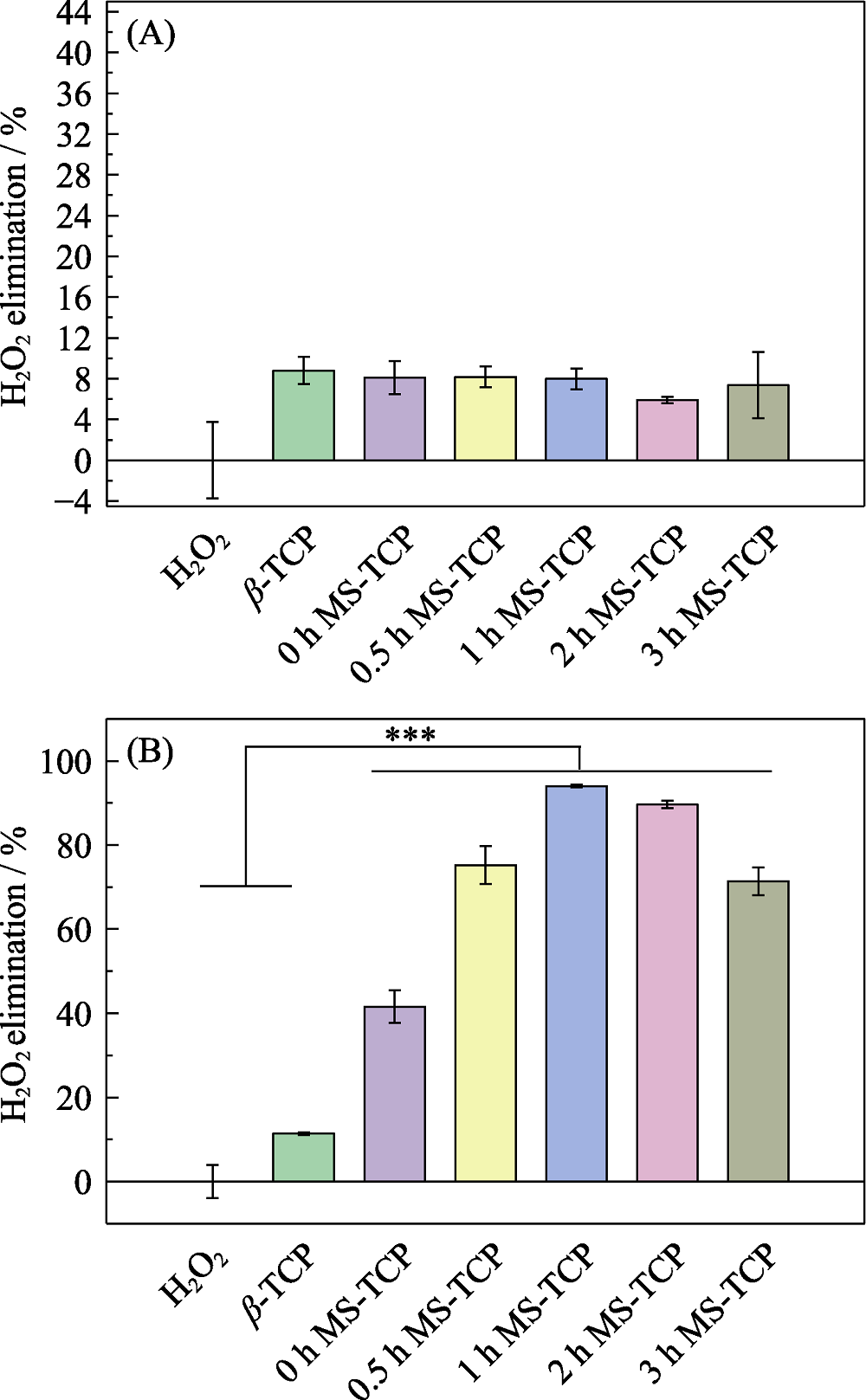
图3 熔盐处理保温不同时间制备的(A)MS-TCP和(B) Co-MS-TCP粉体的清除H2O2情况
Fig. 3 H2O2 scavenging effect of (A) MS-TCP and (B) Co-MS-TCP powders prepared by molten salt method with different holding time *** p<0.001
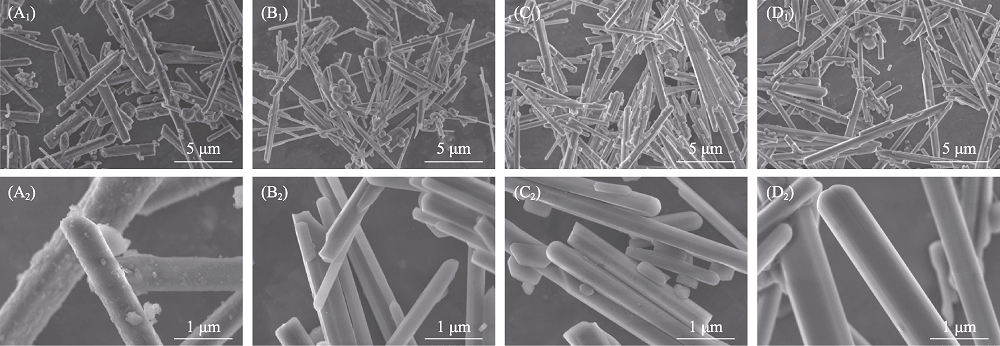
图5 不同钴盐加入量所获熔盐处理制备的Co-MS-TCP粉体的SEM照片
Fig. 5 SEM images of Co-MS-TCP powders prepared by molten salt method with different cobalt salt additions (A1, A2) MS-TCP; (B1, B2) 1% Co-MS-TCP; (C1, C2) 3% Co-MS-TCP; (D1, D2) 5% Co-MS-TCP
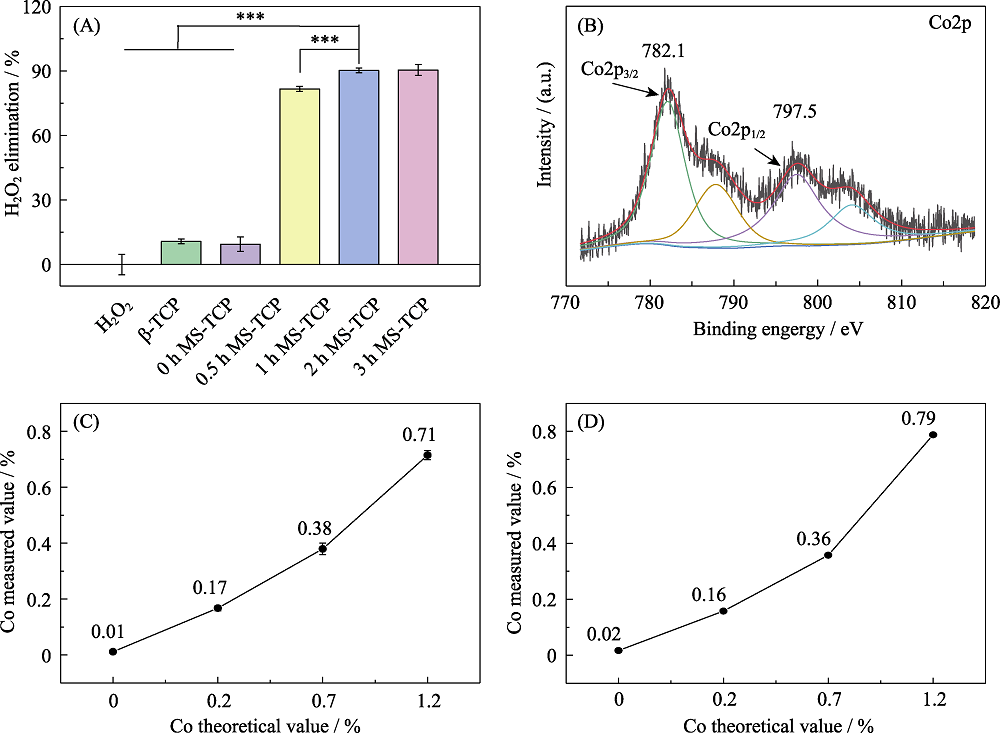
图6 钴含量及其价态在含钴氯磷灰石催化清除H2O2中的作用
Fig. 6 Contents and valence state of cobalt in Co-MS-TCP on H2O2 scavenging ability (A) H2O2 scavenging effect of Co-MS-TCP powders with different cobalt contents; (B) XPS spectra of cobalt in 3% Co-MS-TCP powder; (C, D) Cobalt contents in MS-TCP, 1% Co-MS-TCP, 3% Co-MS-TCP, and 5% Co-MS-TCP powders determined by (C) ICP-AES and (D) XRF methods. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. The color figures can be obtained from online edition
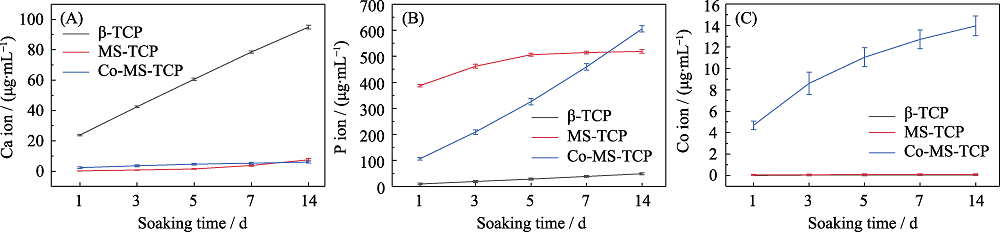
图7 β-TCP、MS-TCP和3%Co-MS-TCP粉体在Tris-HCl缓冲液中(A) Ca、(B) P、(C) Co离子的释放情况
Fig. 7 Releases of (A) Ca, (B) P and (C) Co ions from β-TCP, MS-TCP and 3% Co-MS-TCP powders in Tris-HCl buffer The color figures can be obtained from online edition

图8 SBF溶液中浸泡7 d后的β-TCP (A1, A2)、MS-TCP (B1, B2)和3% Co-MS-TCP (C1, C2)粉体的SEM照片和(D)红外光谱图
Fig. 8 SEM images of (A1, A2) β-TCP, (B1, B2) MS-TCP and (C1, C2) 3% Co-MS-TCP after soaking in SBF for 7 d and (D) their corresponding FT-IR spectra The color figure can be obtained from online edition
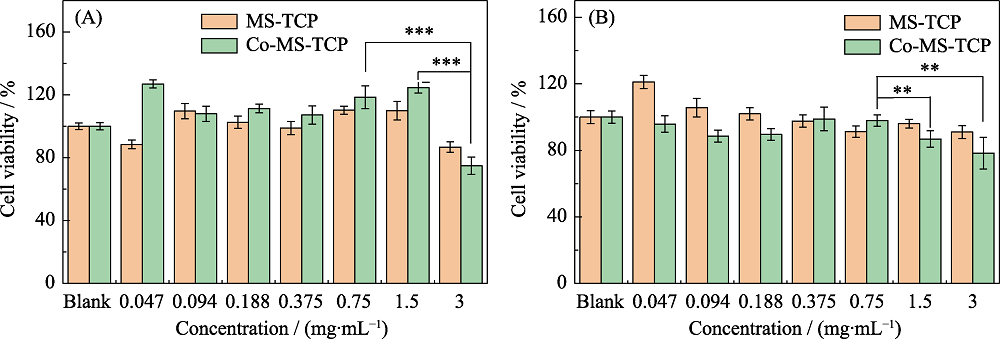
图9 不同浓度MS-TCP和3% Co-MS-TCP 粉体对(A)软骨细胞和(B)骨髓间充质干细胞的细胞毒性评估
Fig. 9 Cell viabilities of MS-TCP and 3% Co-MS-TCP powders with different concentrations on (A) cartilage cells and (B) bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells **p<0.01, *** p<0.001; The color figures can be obtained from online edition
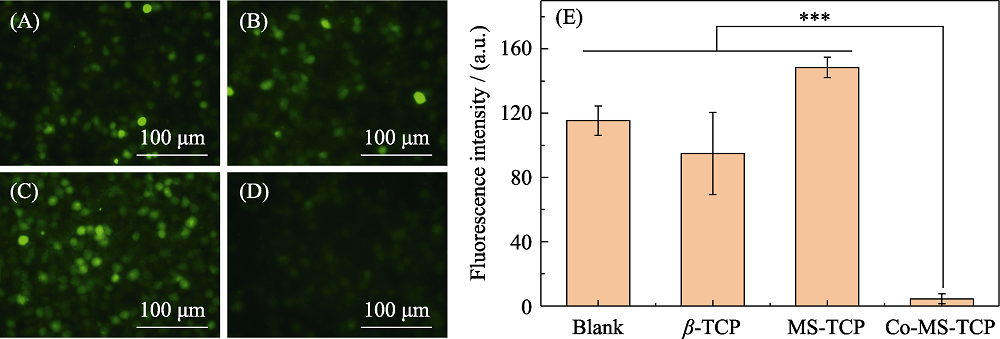
图10 (A)空白组和(B) β-TCP, (C) MS-TCP, (D) 3% Co-MS-TCP粉体处理H2O2刺激的软骨细胞内ROS染色荧光显微镜照片和(E)对应的荧光强度统计
Fig. 10 Images of intracellular ROS staining fluorescence in cartilage cells stimulated by H2O2 treatment with powders (A) Blank, (B) β-TCP, (C) MS-TCP, (D) 3% Co-MS-TCP and (E) corresponding fluorescence intensity statistics ***p<0.001; The color figures can be obtained from online edition
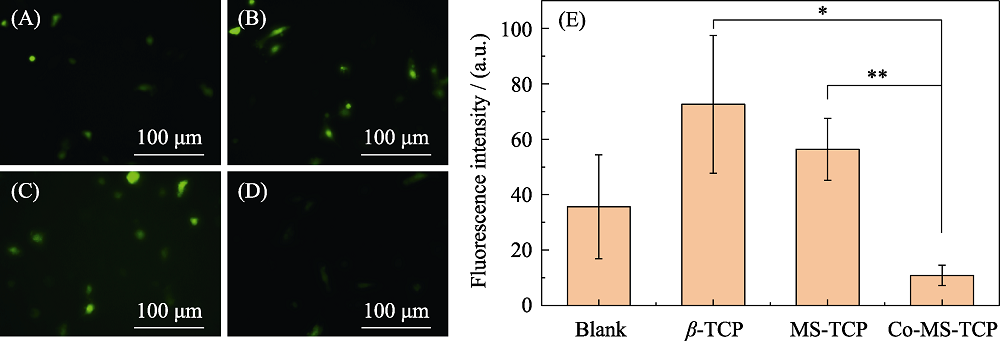
图11 (A)空白组和(B) β-TCP, (C) MS-TCP, (D) 3% Co-MS-TCP粉体处理H2O2刺激的骨髓间充质干细胞后的细胞内ROS染色荧光显微镜照片和(E)对应的荧光强度统计
Fig. 11 Images of intracellular ROS staining fluorescence in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells stimulated by H2O2 treatment with powders (A) Blank, (B) β-TCP, (C) MS-TCP, (D) 3% Co-MS-TCP and (E) Corresponding fluorescence intensity statistics. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01 The color figures can be obtained from online edition
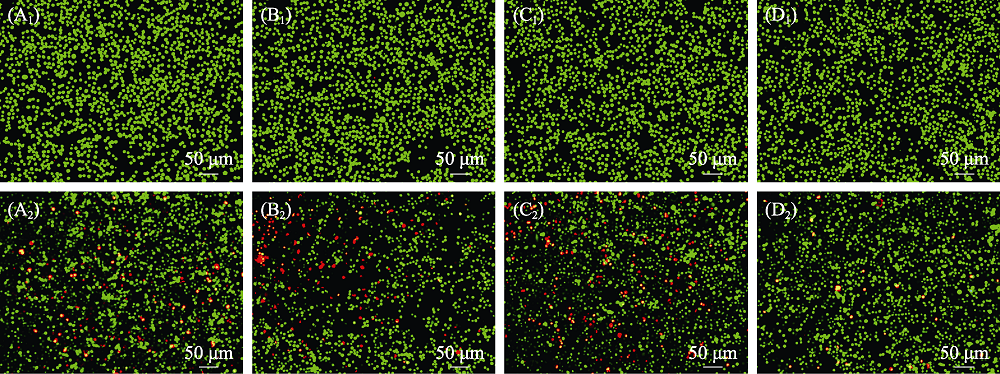
图12 (A)空白组和(B) β-TCP, (C) MS-TCP, (D) 3% Co-MS-TCP粉体处理(A1-D1) 无H2O2刺激与(A2-D2) H2O2刺激的软骨细胞后的细胞活(绿色)/死(红色)Calcein-AM-PI染色荧光显微镜照片
Fig. 12 Calcein AM and PI fluorescence images of cartilage cells treated with different powders((A) Blank; (B) β-TCP; (C) MS-TCP; (D) 3% Co-MS-TCP; (A1-D1) Cells without H2O2 stimulation; (A2-D2) Cells stimulated with H2O2 showing live (green) and death (red) cells) The color figures can be obtained from online edition
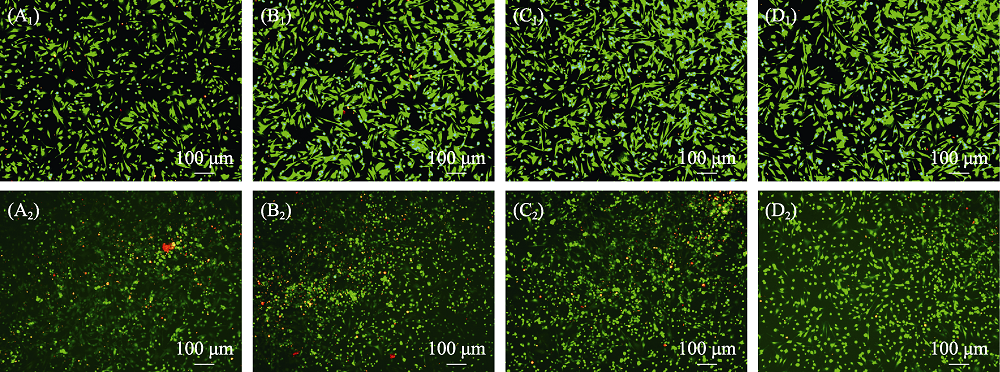
图13 (A)空白组和(B) β-TCP, (C) MS-TCP, (D) 3% Co-MS-TCP粉体处理(A1-D1)无H2O2刺激与(A2-D2) H2O2刺激的骨髓间充质干细胞的活/死Calcein-AM-PI染色荧光显微镜照片
Fig. 13 Calcein AM and PI fluorescence images of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells treated with powders (A) Blank; (B) β-TCP; (C) MS-TCP; (D) 3% Co-MS-TCP; (A1-D1) Cells without H2O2 stimulation; (A2-D2) Cells stimulated with H2O2 showing live (green) and death (red) cells The color figures can be obtained from online edition
| [1] | LI X, LI B, SHI Y, et al. Targeting reactive oxygen species in stem cells for bone therapy. Drug Discovery Today, 2021, 5(26): 1226-1244. |
| [2] |
CERQUENI G, SCALZONE A, LICINI C, et al. Insights into oxidative stress in bone tissue and novel challenges for biomaterials. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2021, 130(11): 112433-12.
DOI URL |
| [3] | ADJEI I M, PLUMTON G, SHARMA B. Oxidative stress and biomaterials: the inflammatory link. Oxidative Stress and Biomaterials, 2016: 89-115. |
| [4] |
LI J, DENG C, LIANG W, et al. Mn-containing bioceramics inhibit osteo-clastogenesis and promote osteoporotic bone regeneration via scavenging ROS. Bioactive Materials, 2021, 6(11): 3839-3850.
DOI URL |
| [5] | RAJULA M, PREM B, VENKATASUBBU G, et al. Nano- hydroxyapatite: a driving force for bone tissue engineering. Journal of Pharmacy & Bioallied Sciences, 2021, 13(1): S11-S14. |
| [6] |
SHI H, ZHOU Z Q, LI W D, et al. Hydroxyapatite based materials for bone tissue engineering: a brief and com-prehensive introduction. Crystals, 2021, 11(2): 149-167
DOI URL |
| [7] | XIN Z, SHUN H. Nano-hydroxyapatite and its compound in repairing bone defects. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2012, 16(34): 6403-6406. |
| [8] |
RATNAYAKE J T B, MUCALO M, DIAS G J. Substituted hydroxyapatites for bone regeneration: a review of current trends. Journal Biomedical Materials Research Part B, 2017, 105 B: 1285-1299.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
OVERGAARD S, LIND M, JOSEPHSEN K, et al. Resorption of hydroxyapatite and fluorapatite ceramic coatings on weight-bearing implants: a quantitative and morphological study in dogs. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 2015, 39(1): 141-152.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
DEMNATI I, GROSSIN D, COMBES C, et al. A comparative physicochemical study of chlorapatite and hydroxyapatite: from powders to plasma sprayed thin coatings. Biomedical Materials, 2012, 7(5): 054101-11.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
WARIS A, DIN M, ALI A, et al. Green fabrication of Co and Co3O4 nanoparticles and their biomedical applications: a review. Open Life Sciences, 2021, 16(1): 14-30.
DOI URL |
| [12] | CAO F, ZHANG L, YOU Y, et al. An enzyme-mimicking single-atom catalyst as an efficient multiple reactive oxygen and nitrogen species scavenger for sepsis management. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(13): 5146 -5153. |
| [13] |
LIU G, WANG X, ZHOU X, et al. Modulating the cobalt dose range to manipulate multisystem cooperation in bone environment: a strategy to resolve the controversies about cobalt use for orthopedic applications. Theranostics, 2020, 10(3): 1074-1089.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
LI Y, PAN Q, XU J, et al. Overview of methods for enhancing bone regeneration in distraction osteogenesis: potential roles of biometals. Journal of Orthopaedic Translation, 2021, 27(2): 110-118.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
USANEE P, MARCELA A O, BOCCACCINI A R. Bioactive glasses incorporating less-common ions to improve biological and physical properties. Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Medicine, 2022, 33(1): 3-41.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
SADAT S M, KHORASANI M T, DINPANAH K E, et al. Synthesis methods for nanosized hydroxyapatite with diverse structures. Acta Biomaterialia, 2013, 9(8): 7591-7621.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
TAWALARE P K, BHATKAR V B, OMANWAR S K, et al. Near- infrared emitting Ca5(PO4)3Cl:Eu2+, Nd3+ phosphor for modification of the solar spectrum. Luminescence, 2018, 33(7): 1288-1293.
DOI URL |
| [18] | KULANTHAIVEL S, ROY B, AGARWAL T, et al. Cobalt doped proangiogenic hydroxyapatite for bone tissue engineering application. Materials Science & Engineering, 2016, 58(1): 648-658. |
| [19] |
JAIRTON D, ROBERTO F, SOUZA D, et al. Ionic liquid (molten salt) phase organometallic catalysis. Chemical Reviews, 2002, 102(10): 3667-3692.
PMID |
| [20] |
LIU D, FU Q G, CHU Y H. Molten salt synthesis, formation mechanism, and oxidation behavior of nanocrystalline HfB2 powders. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2020, 9 (1): 35-44.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
SUCHANEK W, YASHIMA M, KAKIHANA M, et al. Hydroxyapatite ceramics with selected sintering additives. Biomaterials, 1997, 18(13): 923-933
PMID |
| [22] |
WANG Y P, YING D W, ZHU N W, et al. Improved removal of phosphorus from incinerated sewage sludge ash by thermo- chemical reduction method with CaCl2 application. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 258(10): 120779-8.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
OISHI S, SUGIURA I. Growth of chlorapatite crystals from a sodium chloride flux. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 1997, 70(10): 2483-2487.
DOI URL |
| [24] | XIE J F, LI J, KANG L Y, et al. Molten-salt-protected pyrolytic approach for fabricating borate-modified cobalt-iron spinel oxide with robust oxygen-evolving performance. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(43): 14596-14704. |
| [25] |
XIAO M, ZHANG L, LUO B, et al. Moten-salt-mediated synthesis of an atomic nickel Co-catalyst on TiO2 for improved photocatalytic H2 evolution. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(18): 7230-7234.
DOI URL |
| [26] | CHRIS T. Thermodynamics of mixing of liquids in the system Ca3(PO4)2-CaCl2-CaF2-Ca(OH)2. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(12): 2755-2755. |
| [27] |
ZENG K, YANG X, Xie Y, et al. Molten salt pyrolysis of biomass: the evaluation of molten salt. Fuel, 2021, 302(5): 121103-10.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
PRENER J S. The growth and crystallo-graphic properties of calcium fluor- and chlorapatite crystals. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1967, 114(1): 77-84
DOI URL |
| [29] |
KATHLEEN M, JOCHEN L. Synthesis-structure-activity relationships in Co3O4 catalyzed CO oxidation. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2018, 6: 185-197.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
LAN Y P, SOHN H Y, MOHASSAB Y, et al. Nanoceria synthesis in the KCl-LiCl salt system: crystal formation and properties. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100: 1863-1875.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
MO Z Y, YANG W Y, GAO S, et al. Efficient oxygen reduction reaction by a highly porous, nitrogen-doped carbon sphere electrocatalyst through space confinement effect in nanopores. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10 (4): 714-728.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ANDERSON J B, KOSTINER E. The crystal structure of cobalt-substituted calcium chlorapatite. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1987, 66(2): 343-349.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
LIU P, ZHONG D, XU Y, et al. Co/Fe co-doped porous graphite carbon derived from metal organic framework for microelectrolysis- fenton catalytic degradation of Rhodamine B. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(5): 105924-11.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
GAO Y, KONG D R, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Spinel CoMn2O4 hollow nanospheres for very wide linear and sensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 897(15): 163158-9.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
PALUSZKIEWICZ C, LÓSARCZYK A, PIJOCHA D, et al. Synthesis, structural properties and thermal stability of Mn-doped hydroxyapatite. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2010, 976(1/3): 301-309.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
AAIF A, KHALID, CHAUDHRY, et al. Zinc containing calcium phosphates obtained via microwave irradiation of suspensions. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022, 276(15): 124921-11.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
LIU W Y, ZUO R T, ZHU T L, et al. Forsterite-hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds with photothermal antibacterial activity for bone repair. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(5): 1095-1106.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王文婷, 徐敬军, 马科, 李美栓, 李兴超, 李同起. 原位反应/热压合成Ti2AlC-20TiB2复合材料在1000~1300 ℃空气中的高温氧化行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 31-38. |
| [2] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [3] | 刘国昂, 王海龙, 方成, 黄飞龙, 杨欢. B4C含量对(Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C陶瓷力学性能及抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 697-706. |
| [4] | 郑斌, 康凯, 张青, 叶昉, 解静, 贾研, 孙国栋, 成来飞. 前驱体转化陶瓷法制备Ti3SiC2陶瓷及其热稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 733-740. |
| [5] | 张幸红, 王义铭, 程源, 董顺, 胡平. 超高温陶瓷复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 571-590. |
| [6] | 杨博, 吕功煊, 马建泰. 镍铁氢氧化物-磷化钴复合电极电催化分解水研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 374-382. |
| [7] | 周云凯, 刁亚琪, 王明磊, 张宴会, 王利民. 聚苯胺改性Ti3C2(OH)2抗氧化性的第一性原理计算研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1151-1158. |
| [8] | 姚磊, 杨东旺, 鄢永高, 唐新峰. 激光诱导方钴矿自蔓延高温合成过程研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(7): 815-822. |
| [9] | 李光兰, 王天宇, 刘一辰, 路中发. 片状NiFeCo-LDH-Ti6C3.75复合催化剂的制备及电催化析氧性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(7): 823-829. |
| [10] | 胡佳军, 王凯, 侯鑫广, 杨婷, 夏鸿雁. 熔盐法合成高导热磷化硼及其热管理性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 933-940. |
| [11] | 吴爱军, 朱敏, 朱钰方. 含铜硅酸钙纳米棒复合水凝胶用于肿瘤治疗和皮肤伤口愈合性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1203-1216. |
| [12] | 王皓轩, 刘巧沐, 王一光. 高熵过渡金属碳化物陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(4): 355-364. |
| [13] | 夏朝阳, 王慧, 方婧红, 张阳, 汪超越, 贺欢, 倪津崎, 石云, 李勤, 余建定. Co掺杂GaFeO3陶瓷的结构, 导电及磁性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 319-324. |
| [14] | 杨言言, 李永国, 祝小雯, 杜晓, 马旭莉, 郝晓刚. 电活性镍钴双金属氧化物高选择性去除/回收水中磷酸盐离子[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 292-298. |
| [15] | 金高尧, 何海传, 吴杰, 张梦源, 李亚娟, 刘又年. 锂硫电池正极用钴掺杂空心多孔碳载体材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 203-209. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||